SENTRIFUGASI
1
Sentrifugasi
Proses pemisahan solid dari liquid dengan prinsip grafitasi.
Densitas solid harus lebih besar dari densitas liquid
07/10/2014 Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
Peran gaya sentrifugal:
1. Mendorong partikel kecil agar mengendap 2. Menahan brownian motion
3. Mencegah arah free convection fluida
4. Mengurangi penumpukan “cake” pada screen (untuk
centrifugal filtration)
General principle
07/10/2014 Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
3
Klasifikasi centrifuge
Kapasitas
Labratory centrifuge
Preparative centrifuge
Kegunaan
Sedimenting centrifuge
Filtering centrifuge Ultracentrifugation
Tubular bowl
Basket
Disk stack
Scroll decanter
Basket
Pusher
Baffle
Inverting bag
Cone screen
Tubular bowl centrifuge
1000-15000rpm
Klasifikasi centrifuge
Labratory centrifuge
Tubular bowl centrifuge
500-2000 rpm
07/10/2014 Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
5
Better performance
than turbular flow
Preparative centrifuge
Steve, 2007
Klasifikasi centrifuge
Sedimenting centrifuge
07/10/2014 Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014 Steve, 2007
Klasifikasi centrifuge
Filtering centrifuge
centrifugal filtration
1
centrifugal settling
2
07/10/2014 Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
9
Gas-solid cyclone separator
3
horizontal axis scroll decanter centrifuge
4
07/10/2014 Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
11
Peeler centrifuge
Pusher
centrifuge
Ultracentrifugation
1000-15000 rpm
Digunakan untuk pemisahan atau analisa campuran makromolekul
(AUC). Ex: protein
Rpm tinggi
menimbulkan
panas sehingga
memerlukan
cooling
13
07/10/2014 Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
Applications of centrifuges in food processing
Persamaan pada sentrifugasi
07/10/2014 Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
20
Persamaan pada centrifuge settling
• Settling: acceleration from gravity (F g )
• Centrifuge:
– acceleration from centrifugal force (F c )
– circular motion and acceleration occurred from centrifugal force
a c = acceleration from centrifugal force (m/s 2 ) r = radial distance (m)
2
r a c
Persamaan pada centrifuge settling
Centrifugal force (F c )
Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
21
• The centrifugal force, F c acting on an object of mass m, rotating in a circular path of radius R, at an
angular velocity of ω is :
(1) and
(2)
where N = rotational speed (rpm) ω= an angular velocity (rad s -1 )
2
mR F c
30 60
2 N N
Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
23
g force (gravities or g’s)
• The steady-state velocity of particles moving in a streamline flow under the action of an
accelerating force
Where v t =terminal velocity of particle; ρ s and ρ l = density of solid and liquid ; r = distance of the
particle from center of rotation; µ = viscosity of liquid.
18
) ( s l s 2
t
D v g
from
18
)
( 2
2
s l
s t
D
v r
Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
23
Centrifugation time
• Time taken by the particle to move though the liquid layer is called residence time (t r ).
dt
V t dr
18
)
( 2
2 D r
v t s s
18
)
2 (
2
D s r s dt
dr
Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
23
) (
ln 18
18
) ln (
18
) 1 (
2 2
1 2 2
2
1 2
0 2
2 2
1
r
r s
s
t s
s r
r
D
r r t
D t r
r
D dt
r dr
Calculation of flow rate for continuous centrifuge
• flow rate (Q)
1 2
2 2 2
1 2
2
1 2 2
2
2 2
1 2
ln 18
) (
) (
ln 18
) (
) (
ln 18
r r D b
r r
r r D
Q V
D
r r V t
Q V
s s
s s
s s
r
Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
23
• r 1 = inside radius (m)
• r 2 = outside radius (m)
• b = height of centrifuge(m)
• µ = viscosity (Pa.s)
• ω = an angular velocity (rad s -1 )
• ρ s = density of solid (kg/m 3 )
• ρ = density of liquid (kg/m 3 )
• D s = diameter of particle(m)
• V(m 3 )=operating
Example 1
Find centrifugation time t r of a particle d=1mm. In a centrifuge
Given
. 25 . 0
. 20 . 0
/ 1000
/ 1100
. 10
1 . 8
995
3 3 4
m R
m R
m kg
m kg
s Pa RPM N
o i
f P
R
iR
oNur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
23
s rad
N
/ 20
. 104
60
995 2
60 2
Find ω
sec 10
25 . 3
1000 1100
20 . 104 001
. 0
) 20 . 0 / 25 . 0 ln(
10 1
. 8 18
) /
ln(
18
3
2 2
4 2
2
r r
f p
i o
r
t t
d
r t r
Find time
t r of particle d=1mm. in centrifuge≥3.25x10 -3 sec
Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
23
Example 2
Beer with a specific gravity of 1.042 and a viscosity of
1.04x10 -3 N s/m 2 contains 1.5% solids which have a
density of 1160kg/m 3 . It is clarified at a rate of 240 l/h
in a bowl centrifuge which has and operating volume
of 0.09 m 3 and a speed of 10000 rev/min. The bowl
has a diameter of 5.5 cm and is fitted with a 4 cm
outlet. Calculate the effect on feed rate of an increase
in bowl speed to 15000 rev/min and the minimum
particle size that can be removed at the higher speed.
• Solution
Initial flow rate
new flow rate
) /
ln(
18
) 60 /
2
( 1 2 2
1
i o
f p
r r
D N
Q V
) /
ln(
18
) 60 /
2
( 2 2 2
2
i o
f p
r r
D N
Q V
Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
23
As all conditions except the bowl speed remain the same,
Therefore,
Q = 0.15 l/s
2 2 2
2 1
2 2
1 2
) 60 / 10000 142
. 3 2
(
) 60 / 15000 142
. 3 2
( )
3600 /
240 (
) 60 / 2
(
) 60 / 2
(
Q
N N Q
Q
To find the minimum particle size
m D
V N
r r
D Q
f p
i o
8 . 10 6
62 .
2
10 20
. 1
09 .
0 ) 1042 1160
( ) 60 /
15000 142
. 3 2
(
)]
02 .
0 / 0275 .
0 ln(
10 40
. 1 18
[ 15 . 0
) (
) 60 /
2 (
)]
/ ln(
18 [
7 3
2 3
2 2
2 2
Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
23
1
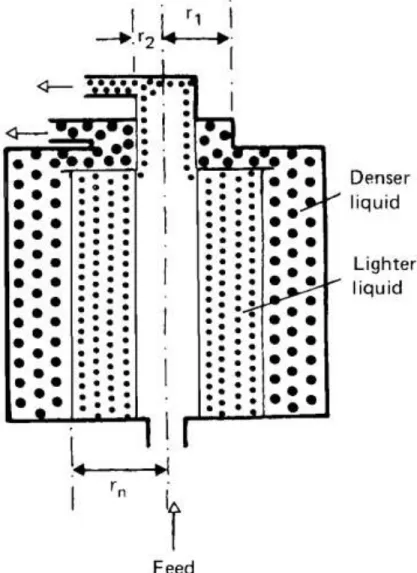
# A and B are dense and light liquid,
rA, rB =outlet radius
r
n=radius of neutral zone.
Fig 6.1. Separation of immiscible liquids Ω = angular velocity,
Q = volumetric flowrate,
V = operating volume of the centrifuge, D = diameter of the particle,
r
2= radius of light phase outlet, r
1= radius of dense phase outlet, N =speed of rotation
2
3
Separation of liquids
Example3
• A bowl centrifuge is used to break an oil-in- water emulsion. Determine the radius of the neutral zone in order to position the feed pipe correctly. (Assume that the density of the continuous phase is 1000 kg/m 3 and the density of the oil is 870 kg/m 3 . the outlet radius from the centrifuge are 3 cm and 4.5 cm).
Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014
23
• Solution
m r
r r
n n n
098 .
0
130
783 .
0 025
. 2
870 1000
) 03 .
0 ( 870 )
045 .
0 (
1000 2 2
2
THANKS FOR YOUR ATTENTION
The best person is one give something useful always
07/10/2014 Nur Istianah-KPP-Sentrifugasi-2014