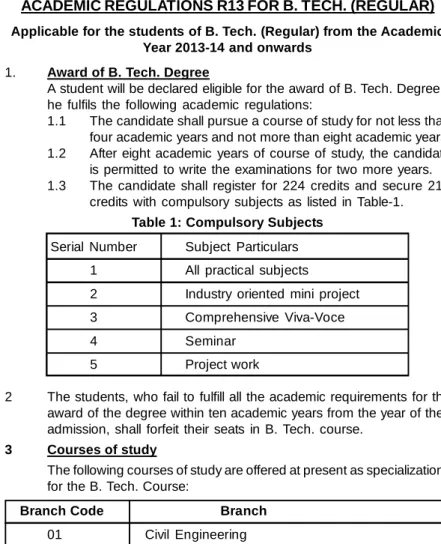
The end-of-semester examination of the project work is carried out by the same committee that was set up for the industry-oriented mini-project. The evaluation of the project work is carried out at the end of the IV year.
TECH. CHEMICAL ENGINEERING I YEAR
Chapter titled 'Risk Management' from "Skills Annex - Functional English for Success" Published by Orient Black Swan, Hyderabad. Chapter titled 'Sports and Health' from "Skills Annex - Functional English for Success" Published by Orient Black Swan, Hyderabad.
UNIT II
In the future, global problems and issues will require an in-depth understanding of chemistry to have a global solution. This syllabus aims to bridge concepts and theory of chemistry with examples from practical areas of application, thus strengthening the connection between natural sciences and engineering.
UNIT III
Computer Assisted Language Learning (CALL) Lab
Interactive Communication Skills (ICS) Lab
The Internet & World Wide Web module presents various ways of connecting a computer to the Internet from home and at work, as well as efficient use of the Internet. Week 5 - Task 5: Hardware Troubleshooting: Students are given a computer that won't boot due to improper assembly or faulty peripherals. Week 6 - Task 6: Software Troubleshooting: Students should be given a non-working processor due to problems with the system software.
If there is no Internet connection, instructors must prepare to simulate the WWW on the LAN. Week 10 - Task 4: Cyber Hygiene: Students would be exposed to the various threats on the internet and would be asked to configure their computer to be secure on the internet. Importance of LaTeX and MS office 2007/equivalent (FOSS) tool Word as a word processor Details of the three tasks and functions that will be covered in each, using LaTeX and Word – Access, overview of toolbars, saving files , Use of help and resources, rulers, format templates.
Week 15 - Excel Orientation: The mentor must tell the importance of MS office 2007/equivalent (FOSS) tool Excel as a spreadsheet tool, give the details of the two tasks and functions that will be covered in each. Week 16 - Task 2: Calculation of GPA - .Functions to be covered:- Cell reference, formulas in excel – average, std. Students are given a model power point presentation to replicate (exactly how it is asked).
TRADES FOR DEMONSTRATION & EXPOSURE
The goal is to find the relationship between the variables x and y from the given data (x,y). This unit also aims to find relationships that pass exactly through the data or approximately satisfy the data under the least sum of squares of error condition. This topic covers methods for finding roots of an equation and solving a differential equation.
Results: From the given discrete data, it will be possible to predict the value of the data at an intermediate point and, by fitting the curve, find the most appropriate formula for the predicted relationship of the data variables. After studying this unit, one will be able to find the root of the given equation and will be able to find the numerical solution for the given differential equation. It will be possible to find the expansion of a given function with the Fourier series and the Fourier transform of the function.
Differential equation for an unknown function with many independent variables and finding their solution. Therefore, it is very important to understand the nature of the equation and find a suitable solution. It is an essential requirement for an engineer to understand the behavior of the physical system.
UNIT II
This course introduces the concepts of DC and AC electrical circuits, basic laws of electricity, instruments for measuring electrical quantities, various methods for solving electrical networks, operational features of construction of power conversion equipment ie.
UNIT III
Moment generating functions of the above three distributions, and thereby finding the mean and variance. This course allows the studies for the selection and design of the internal parts of the column such as packing, baking efficiency, calculation of transfer units, etc. Objective: To provide the students with knowledge about the ways of heat transfer and the design of evaporators for heat transfer equipment, etc., .
Heat transfer by conduction in solids: Fourier's law, thermal conductivity, stable conduction in plane walls and composite walls, composite resistors in series, heat flow through a cylinder, conduction in spheres. Principles of heat flow in fluids: typical heat exchange apparatus, countercurrent and parallel current flows, energy balances, rate of heat transfer, total heat transfer coefficient, electrical analogy, critical insulation radius, logarithmic average temperature difference, variable general coefficient, multi-pass exchangers, individual heat transfer coefficients, resistance form of the total coefficient , pollution factors, classification of individual heat transfer coefficients, magnitudes of heat transfer coefficients, effective coefficients of heat transfer in an unstable state. Heat transfer to liquids without phase change: regimes of heat transfer in liquids, thermal boundary layer, heat transfer by forced convection in laminar flow, heat transfer by forced convection in turbulent flow, the transfer of heat through turbulent eddies and analogy between transfer of momentum and heat, heat transfer to liquid metals, heating and cooling of liquids in forced convection outside tubes.
Natural Convection: Natural Convection to Air from Vertical Forms and Horizontal Planes, Effect of Natural Convection in Laminar-Flow Heat Transfer. Heat transfer to liquids with phase change: Heat transfer from condensing vapors, heat transfer to boiling liquids. Radiation: Introduction, properties and definitions, black body radiation, real surfaces and the gray body, absorption of radiation by opaque solids, radiation between surfaces, radiation shielding, radiation to semi-transparent materials, combined heat transfer by conduction, convection and radiation.
Heat Exchange Equipment: General Design of Heat Exchange Equipment, Heat Exchangers, Condensers, Boilers and Calenders, Expanded Surface Equipment, Stirring Vessel Heat Transfer, Scraped Surface Heat Exchangers, Packed Bed Heat Transfer, Heat Exchanger Efficiency (NTU Method ). Result: The student will be able to apply the principles of heat transfer in the selection and design of a heat exchanger, evaporator, etc.
Unit III
Activities on Fundamentals of Inter-personal Communication and Building Vocabulary - Starting a conversation – responding
Activities on Writing Skills – Structure and presentation of different types of writing – letter writing/Resume writing/ e-correspondence/
Activities on Presentation Skills – Oral presentations (individual and group) through JAM sessions/seminars/PPTs and written
Activities on Group Discussion and Interview Skills – Dynamics of group discussion, intervention, summarizing, modulation of voice,
English Language Communication: A Reader cum Lab Manual Dr A Ramakrishna Rao, Dr G Natanam & Prof SA Sankaranarayanan, Anuradha Publications, Chennai 2008. The practical examinations for the ACS Laboratory practice will be conducted according to the University norms that are prescribed for the nuclear engineering practice. sessions. For the English Language laboratory sessions there will be continuous evaluation during the year for 25 session marks and 50 final exam marks.
Of the 25 points, 15 points are awarded for daily work and 10 points for carrying out internal laboratory test(s). The Final Exam is administered by the relevant teacher, by inviting the External Examiner from outside. If the external examiner is not available, another teacher from the same department can act as external examiner.
A Report on the same has to be prepared and presented
Study the temperature distribution along the length of a pin fin under natural and forced convection conditions. The student will be able to understand the thermal conductivity measurement, heat transfer coefficient, calculation in natural and forced convection and some of the radiation aspects. Mathematical formulation of the Physical Problems: (i) Application of the law of conservation of mass-salt accumulation in a stirred tank, equilibrium still-solvent extraction in two phases, Diffusion with chemical reaction. ii) Application of the law of conservation of energy - Radial heat transfer through a cylindrical conductor, Heating of a closed Kettle-Flow of heat from a fin.(iii).
Implications of the above holistic understanding of harmony on professional ethics: the natural acceptance of human values. Determination of reaction order using batch reactor and data analysis by (a) differential method (b) integral method. Equations of change for isothermal systems: (i) Equations of continuity, motion and mechanical energy in rectangular and curvilinear coordinates, (ii) Use of equations of change to set up steady flow problems (iii) Dimensional analysis of equations of change.
Mass transport: the equations of change for multi-component systems: i) The equations of continuity for a binary mixture (ii) The equations of continuity of A in curvilinear coordinates and (iii) Dimensional analysis of the equations of change for a binary isothermal fluid mixture. Concentration distributions in turbulent flow: (i) Concentration fluctuations and the time-smoothed concentration (ii) Time-smoothing of the continuity equation of A. Interphase transport in multi-component systems: (i) Definition of binary mass transfer coefficients in one phase, (ii) Correlations of binary mass transfer coefficients in one phase at low mass transfer rates (iii) Definition of binary mass transfer coefficients in two phases at low mass transfer rates, and (iv) Definition of the transfer coefficients for high mass transfer rates.
UNIT IV
UNIT V
Outcome: This course will help students understand and apply the principles of biochemical engineering to the analysis and design of industrial biochemical processes.
Unit II
Unit III
Result: The student will be able to gain knowledge about different types of polymers and polymerization processes. Result: The student will be able to optimize the problems related to design, planning and operations in a chemical industry. Outcome: The student will be able to gain knowledge about different types of pollution caused by industries, solid and hazardous waste management.
Objective: To teach the student about the basic principles of fluidization and its application in the chemical industry. Outcome: The student will be able to learn the importance and applications of fluidization in chemical and related industries. Objective: To acquaint the student with the preparation and testing of pharmaceutical and fine chemicals and their industrial production.
Objective: To teach the student about different unit operations involved in the food processing industry. Outcome: The student will be able to learn microwave heating and preservation methods and strategies in food technology. Outcome: The student will be equipped with the knowledge that ensures thorough safety in the organization.