V.N.KALE Additional Commissioner Mechanization and Technology Division Dept. of Agriculture and Cooperation Ministry of Agriculture Government of India
Farm Mechanization in India:
Total population:1.21 billion (2011)
Population growth rate:1.5% annually
Majority (69%) of people live in rural areas.
Land area: 297.3 million ha (2.4% of world) 17% of population;
Only 4.2% of world water; 1200 mm annual rainfall Agriculture accounts for 80% of water needs; 60%
from ground water.
52% workers in Agriculture: 14% of GDP;
India
3
0 100000 200000 300000 400000 500000 600000 700000
2004-05 2005-06 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 2013-14 247351 296080 352835 346501 342836 393836
545109 607000 590672
696828
Sale of Tractors
Sales of Tractors and Power Tillers in India
0 10,000 20,000 30,000 40,000 50,000 60,000
2004-05 2005-06 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 2013- 14 17,481 22,303 24,791 26,135
35,294 38,794
55,100 60,000
47000
56000
Sale of Power Tillers
Trend of power availability from different sources
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
90%
100%
1971-72 1981-82 1991-92 2001-02 2005-06 2009-10
8.45
18.46
26.14
36.77 38.45 41.67
10.79
15.82
24.84 26.31 25.66 25.13
Electric motors Diesel engines Power Tillers Tractors
Draught Animals Agriculture Workers
Share of agricultural worker
& draught animals came down from 63.5% in 1971- 72 to 13.67% in 2009-10
Comparison of Mechanization with Other Countries
Source: FAO Yearbook 2003
Sl. No. Country Farm Power No. of Tractors per 1000 Ha.
No. of Combine Harvesters per 1000 Ha.
(kW/Ha)
1 India 1.36 15.75 0.026
2 Japan 8.75 461.22 236.98
3 U.K. 2.5 88.34 8.3
4 France 2.65 68.5 4.93
5 Italy 3.01 211.08 4.71
6 Germany 2.35 79.817 11.41
7 Argentina -- 10.74 1.79
8 Brazil -- 13.66 0.915
9 China -- 6.98 2.53
10 Pakistan -- 16.47 0.08
11 Egypt -- 30.7 0.79
United States [2.4%, 95%]
Western Europe [3.9%, 95%]
Former Soviet Union [14.4%, 80%]
Brazil [14.8%, 75%]
Argentina [9.4%, 75%]
India [55%,40%]
China [64.9%, 38%]
Africa [60%, 20%]
Population engaged in Agriculture vis-a-vis level of farm mechanization
Higher share of labour (55%) with lesser contribution to GDP (14%) makes farming in India less remunerative and incidence of farmers’ poverty
Farm Mechanization: Key driver of productivity
Agricultural productivity has positive correlation with level of farm mechanization
0.25 0.31 0.35
0.63
0.92
1.35
1.66
0.522 0.71 0.872
1.023
1.38
1.723
1.92
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4
1951 1961 1971 1981 1991 2001 2010
Foodgrain Yield (T/ha) Farm Power (Kw/Ha)
8
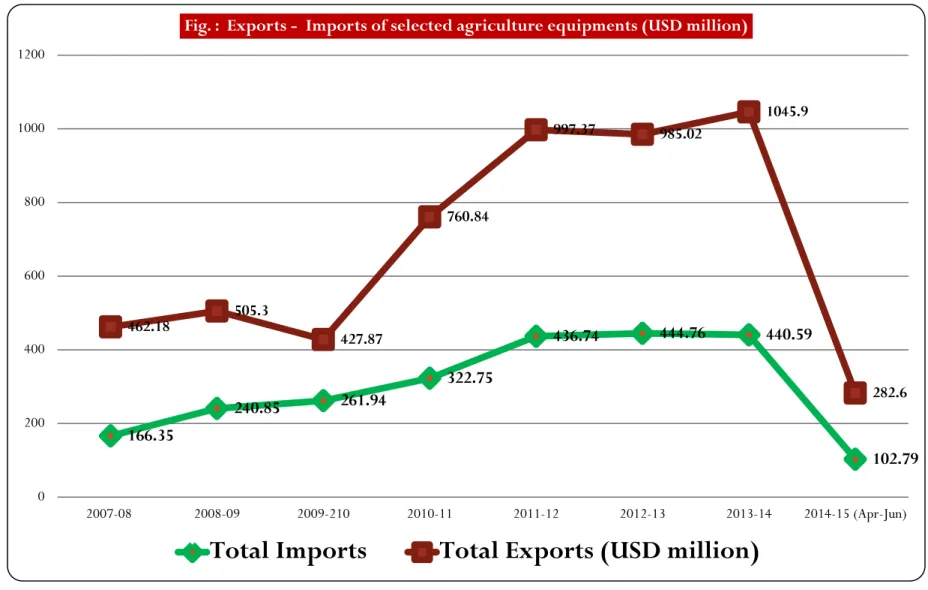
166.35
240.85 261.94
322.75
436.74 444.76 440.59
102.79 462.18 505.3
427.87
760.84
997.37 985.02
1045.9
282.6
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200
2007-08 2008-09 2009-210 2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 2013-14 2014-15 (Apr-Jun)
Fig. : Exports - Imports of selected agriculture equipments (USD million)
Total Imports Total Exports (USD million)
Tillage &
seedbed Preparation
Sowing/
Planting
Fertiliser
Application Irrigation Harvesting Post Harvesting Inter Cultivation
Plant Protection
Level of Farm Mechanization in India
Overall about 40-45%
Large No. of manufacturers
Testing Facility at : 4 FMTTIs , 30 designated centers and BIS labs
Vast network of academic and R&D institutions including 100 centers for research, technology transfer and extension
Equipment manufacturers No. of units
• Agricultural tractors
• Power tillers
• Irrigation pumps
• Plant protection equipment
• Combine Harvester
• Reapers
• Threshers
• Seed Drills and planters
• Diesel oil engines
• Plough, cultivators, harrows
• Chaff cutter
• Rural artisans (hand tools)
13 2 600 300 48 60 6000 2500 200 5000
50
>1 million Source: ICAR 2011
Farm Mechanization: SWOT Analysis Strengths
2.28
2.00
1.84
1.69
1.55
1.41 1.33
1.23 1.16
0.00 0.50 1.00 1.50 2.00 2.50
1970-71 1976-77 1980-81 1985-86 1990-91 1995-96 2000-01 2005-06 2010-11
Average size (in 'ha)
Reference year
Average size of operational holdings
Source: Agriculture Census 2012
.The Core Issues
Small/Medium Farmers : Low credit worthiness
Adverse ‘Economies of Scale’;
Weak financial strength of majority of farmers (SMF);
Lack of access to credit to Rural Entrepreneurs for setting Custom Hiring Centre;
Need for promoting appropriate Farm
Equipment: Low cost, region and crop specific,
indigenous technology
Policy Framework : Addressing Issues
Unbundling Agriculture Services from Farmers;
Facilitate Entrepreneurs to establish Custom Hiring Centre;
• Facilitating rural entrepreneurs
Special incentives to Small and Marginal farmers
Focusing on village level mechanization : low cost, region –crop specific,
indigenous technology
Addressing adverse
‘Economies of Scale’
Access to Credit
Promotion of appropriate
Farm Equipment: Low
cost, region and crop
specific, indigenous
High women workforce in agriculture – both in
production and processing
Ergonomically designed tools and equipment for
Reduced drudgery
Enhanced safety & comfort
Other Key Focus Area : Gender-friendly
tools and equipment
SUB-MISSION ON
AGRICULTURAL MECHANIZATION
Mission Objectives
Increasing the reach of farm mechanization to small and marginal farmers and to the regions where availability of farm power is low;
Promoting ‘Custom Hiring Centres’ to offset the adverse
economies of scale arising due to small landholding and high cost of individual ownership;
Creating hubs for hi-tech& high value farm equipments;
Creating awareness among stakeholders through demonstration and capacity building activities;
Ensuring performance testing and certification at designated
testing centers located all over the country.
Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM) : Key Interventions
1. Promotion and Strengthening of Agricultural Mechanization through Training, Testing and Demonstration
2. Demonstration, Training and Distribution of Post Harvest Technology and Management (PHTM)
3. Financial Assistance for Procurement of Agriculture Machinery and Equipment
4. Establish Farm Machinery Banks for Custom Hiring
5. Establish Hi-Tech, High Productive Equipment Hub for Custom Hiring
6. Promotion of Farm Mechanization in Selected Villages 7. Financial Assistance for Promotion of Mechanized
Operations/hectare Carried out Through Custom Hiring Centres 8. Promotion of Farm Machinery and Equipment in North-Eastern
Region:
Trainees sponsored by the state nodal agencies to the User Level Courses at the FMTTIs will be paid stipend @Rs. 500/- per week per trainee.
Travel expenses to the trainees admitted in these courses will be paid on actual basis by ordinary mode of transport from their place of residence to the training institute and back.
The training institutions will claim Rs 4000/- per person per week for the conduct of these courses. This includes:
stipend of Rs. 500/- per trainee per week
Actual to and fro travel expenses by ordinary mode of transport in ordinary class, upto maximum of Rs. 500/- per trainee
boarding and Lodging Charges @ Rs. 1500/- per trainee per week
Institutional charges (including stationary, training material, honorarium) @ Rs. 1500/-per trainee per week
Financial Assistance:
Training
Northern Region Farm Machinery Training and Testing Institute
Hissar, 1963
Central Farm
Machinery Training and Testing Institute Budni 1956
North-Eastern Region Farm Machinery Training and Testing Institute,
Biswanath-Chariali 1990
Southern Region Farm Machinery Training and Testing Institute, Garladinne, Anantpur 1983
Capacity Building Location of FMTTI’S
Demonstration
Field demonstrations of package of machines/equipments will be conducted on cropping systems based approach in the districts identified for AAP.
Power operated/self- propelled equipment
Rs. 4000/- per hectare For hilly areas, cost per demonstration will be 1.5 times of said cost.
Animal drawn equipment Rs. 2000/-per hectare
Manually operated equipment
Rs. 1500/-per hectare
Financial Assistance: Demonstrations will be organized by ICAR, PSUs of GOI and State Government’s organizations. Government of India will provide 100%
assistance for contingency expenditure per demonstration, as per following norms:
Establishment of post harvest technology
The units utilizing the available post harvest technologies and management, value addition, scientific storage, packaging technologies and technologies for bi-product management .
Technical guidance on the available post harvest technologies will be provided by CIPHET Ludhiana and also by other ICAR/CSIR/SAU centers.
Financial assistance: PHT units shall be established in the production
catchments with 50% assistance from the Government of India limited to Rs.
1.25 lakhs per machine/technology. (Additional 10 % assistance limited to Rs.
1.50 lakhs will be available for SC, ST, small & marginal farmers, women, and NE States beneficiary). Remaining cost will be borne by beneficiary.
Financial Assistance for Procurement of Agriculture Machinery and Equipment
Ranges 25% to 50% subsidy per machine
10% more subsidy to SC/ST/Women/Small & Marginal
farmers/ NER states beneficiery
Farm Machinery Banks for Custom Hiring
S.N ITEM MAXIMUM
PERMISSIBLE PROJECT COST
PATTERN OF ASSISTANCE
A Procurement subsidy for establishment of Custom Hiring Centre upto 10 lakh
Project based Rs. 4.0 lakh
40%
B Procurement subsidy for establishment of Custom Hiring Centre upto 25 lakh
Project based Rs. 10.0 lakh
40%
C Procurement subsidy for establishment of Custom Hiring Centre upto 40 lakh
Project based Rs. 16.0 lakh
40%
D Procurement subsidy for establishment of Custom Hiring Centre upto 60 lakh
Project based Rs. 24.0 lakh
40%
Hi-Tech, High Productive Equipment Hub for Custom Hiring:
Financial Assistance
S.N ITEM MAXIMUM
PERMISSIBLE PROJECT COST
PATTERN OF ASSISTANCE
A Procurement subsidy for establishment of Custom Hiring Centre upto 100 lakh
Project based Rs. 40.0 lakh
40%
B Procurement subsidy for establishment of Custom Hiring Centre upto 150 lakh
Project based Rs. 60.0 lakh
40%
C Procurement subsidy for establishment of Custom Hiring Centre upto 200 lakh
Project based Rs. 80.0 lakh
40%
D Procurement subsidy for establishment of Custom Hiring Centre upto 250 lakh
Project based Rs. 100.0 lakh
40%
Promotion of farm mechanisation
in
selected villages
Objectives:
To establish farm machinery banks by the Cooperative Societies of farmers, Self Help Group of Farmers etc. in the selected
villages of low mechanized states so as to encourage members to take up appropriate mechanized operations
To conduct demonstrations through Custom Hiring Centres in large areas with the assistance of Custom Hiring Centres set up under component (4).
Financial Assistance: Each village will be eligible for setting up of farm machinery banks upto a maximum project cost of Rs.
10 lakhs. Financial assistance @ 80% of the project cost will be
provided for such machinery banks.
Assistance for Mechanized operations.
Financial Assistance: Financial assistance will be available to the beneficiaries upto a maximum of 1 ha area as per following norms:
For tractor/power operated operations – 50% of the cost of operation /ha limited to Rs. 2000/ha per farmer per year
For animal drawn mechanized operations- 50% of the cost of operation /ha limited to Rs. 1000/ha per farmer per year
For manual operations –50% of the cost of operation /ha limited to Rs. 750/ha per farmer per year
Promotion of farm machinery and equipment in North-Eastern States
Financial Assistance
ITEM MAXIMUM
PERMISSIBLE PROJECT COST
PATTERN OF ASSISTANCE
(a) Financial assistance for procurement of machinery/
implements
Upto Rs.1.25 lakhs per beneficiary
100% of cost of machinery/implement
/equipment
(b) Financial assistance for Farm Machinery Banks for group of farmers
Upto Rs.10 lakhs per Farm Machinery Bank
95% of cost of Farm Machinery Banks
Distribution of Agricultural Machinery and Tools-(2014-15)
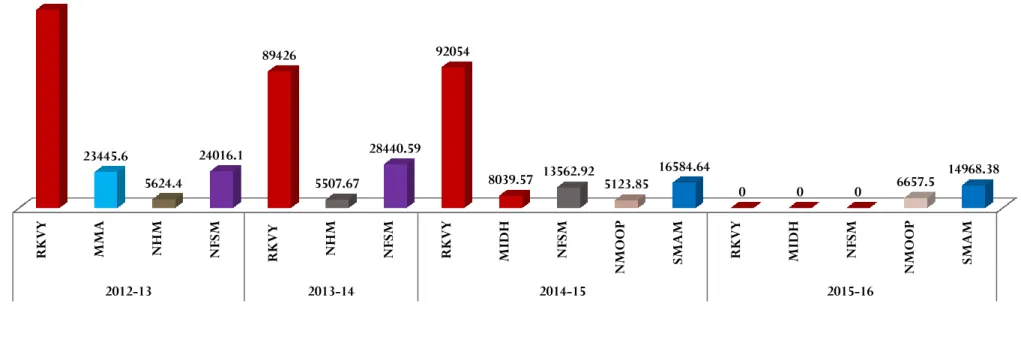
28
1515 20108 19755
186594
92852
275972
59266
23380
679442
0 100000 200000 300000 400000 500000 600000 700000 800000
29
RKVY MMA NHM NFSM RKVY NHM NFSM RKVY MIDH NFSM NMOOP SMAM RKVY MIDH NFSM NMOOP SMAM
2012-13 2013-14 2014-15 2015-16
129914
23445.6
5624.4
24016.1
89426
5507.67
28440.59 92054
8039.57 13562.92 5123.85 16584.64
0 0 0 6657.5 14968.38
Fig : Details of fund released to the state Governmnet during the last three years and the current years for Farm Mechanisation (Rs in Lakhs)
RKVY- Rastriya krishi Vikas yojna MMA-Micro management in Agriculture NHM National horticulture Mission NMOOP- National Mission on oil seed and oil palm NFSM- National food security Mission SMAM- Sub mission on Agricultural mechanisation
30
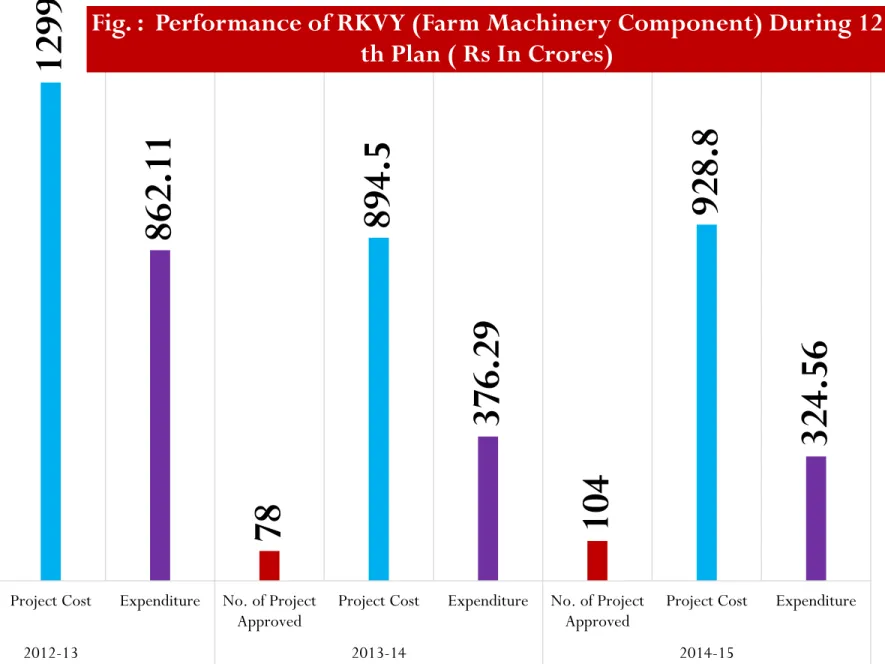
104 1299.2 862.11 78 894.5 376.29 104 928.8 324.56
No. of Project
Approved Project Cost Expenditure No. of Project
Approved Project Cost Expenditure No. of Project
Approved Project Cost Expenditure
2012-13 2013-14 2014-15
Fig. : Performance of RKVY (Farm Machinery Component) During 12 th Plan ( Rs In Crores)
31