Therefore, with the adaptation method, the sink disposal rate according to the cascade is adopted in the rate theory. Since the aim of this dissertation is an improvement of the scientific understanding of the RIDI behavior within the framework of the rate theory, it was attempted to verify the effect of stress and alloying element between SRT and PBM in zircon, and between CDM and PBM in iron.
Research background
First discovery of RIDI
A brief history of development of cladding materials
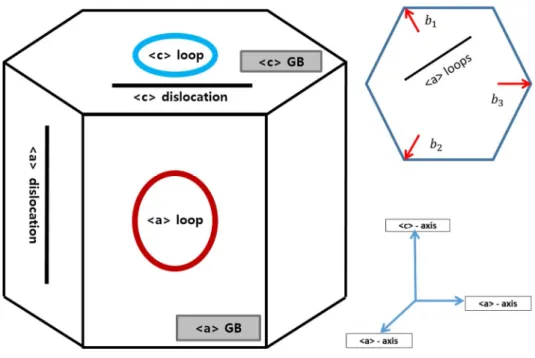
Anisotropy materials: Zirconium alloy
Isotropy materials: Iron-based alloy
History of radiation effect modeling
Particle reaction kinetics
After several years of developing a methodology to reflect the diffusion anisotropy of a non-cubic structure by changing the normal coordinate system. The reaction between an extended sink and mobile defects is one of the special cases in particle reaction kinetics.
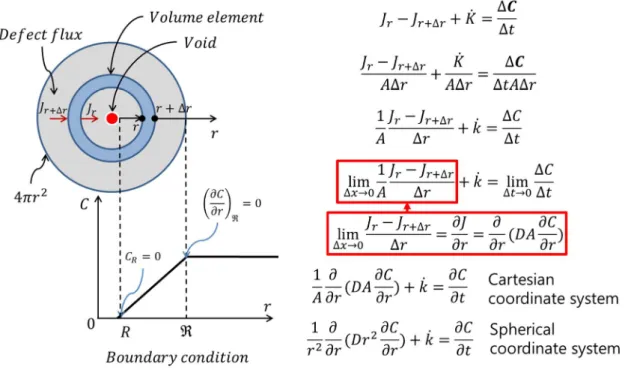
Defect reaction rate theory
Quantification of radiation-induced defect concentration is therefore the essential part of theoretical irradiation growth modeling.
Limitation of radiation damage quantification
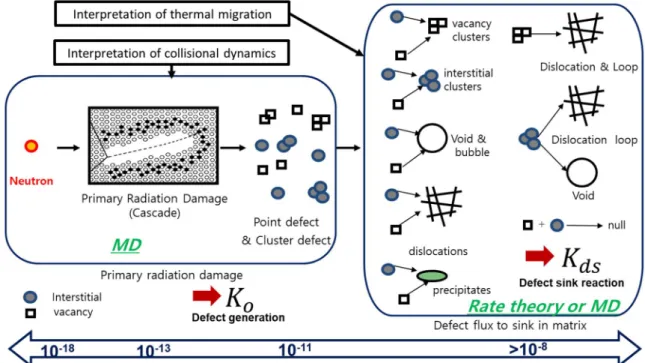
Primary radiation damage
The neutron spectrum could be calculated from the nuclear reactor physics research group. After calculating the average cross-section of the different neutron spectra, the total number of defects could finally be calculated.
Limitation of rate theory
Mean-field approximation
New research trend for limitation of rate theory
Research goal
Cluster dynamic modeling
The physical meaning of the first term on the right-hand side of equation III.2.1 is the rate at which defects are generated. In Equation III.2.2, the first term represents the cluster generation rate and the residual term represents the cluster behavior.
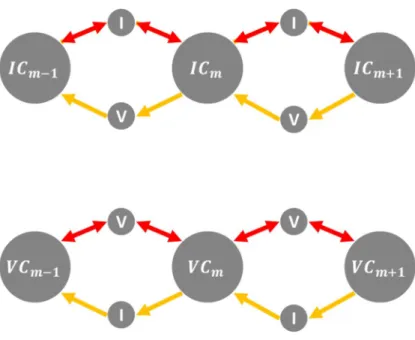
Production bias modeling
The vacancy rate theory follows the same method as that of interstitials in Equation III.2.2 ~ Equation III.2.4. Among these different terms in equation III.2.1, the absorption rate of the sink is the most interesting factor from the point of view of calculating the dimensional instability, because it determines the rate of defect accumulation in the sink.
MD simulation & First principle
As implied by the name, the first principle has no need of experimental results, because the first principle is the law of existence of all matter in the universe. In the past, thermodynamics were only ways, but nowadays the first principles and MD simulation are the most important issues in the academia of nuclear materials.
Approach and Method
- Definition of the diffusion
- Normal distribution of particle
- Sink strength
- The connection between sink size and RIDI
- Stress effect on RIDI with the traditional method
- Stress effect on RIDI with a recent method
- Alloy effect on RIDI with the traditional method
- Alloy effect on RIDI with a recent method
- Cascade effect on defect generation rate and sink density
Therefore, radiation growth and creep can be calculated from the general strain rate equation. From this equation, the SPIA can be expressed as the equation below by considering the interstitial flux and bulk defect concentration, which reflects the effect of creep stress. In the traditional approach, only the behavior of the point defect can be analyzed, so this information is very valuable information.
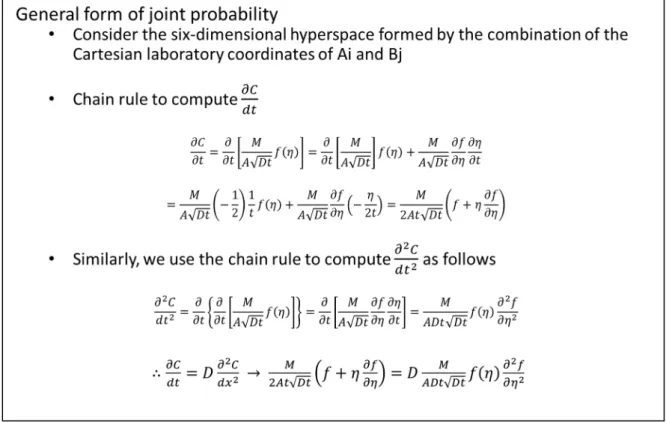
From this information, the Mean Square Displacement (MSD) could be derived to obtain the diffusion tensor.
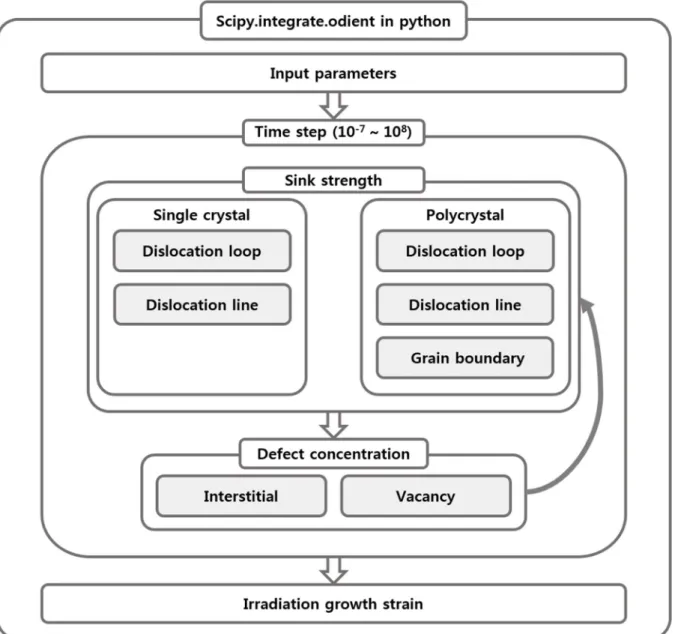
Computer code implementation
The methodology of irradiation growth modeling
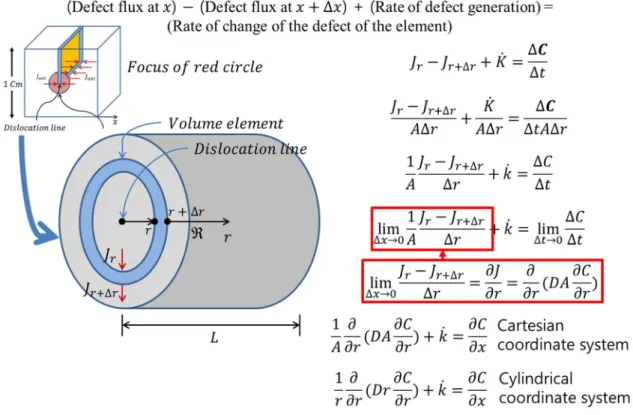
Rate equation of single crystal & polycrystal
The first term on the right-hand side of equation IV.1.1 is the defect generation rate; the second is the rate of recombination; the third is the degree of absorption of the free space of the interstitial loops , which are parallel to the plane of the prism; the fourth is the degree of absorption of vacancies of
However, since the response probability is calculated by SRT using the average value of the fault flux of each sink, the gap rings in the prismatic plane can be neglected without any problem in the situation where the sinks are homogeneously distributed.
Fundamental parameters
Irradiation growth modeling of single crystal
Average strain value for single crystal
Strain equation for single crystal
Irradiation growth modeling of polycrystal
However, recent studies have reported that the polycrystal growth due to irradiation cannot be easily calculated by a simple anisotropy factor because the difference in the orientation of each grain caused the grain interaction.
Results of irradiation growth modeling
Single crystal
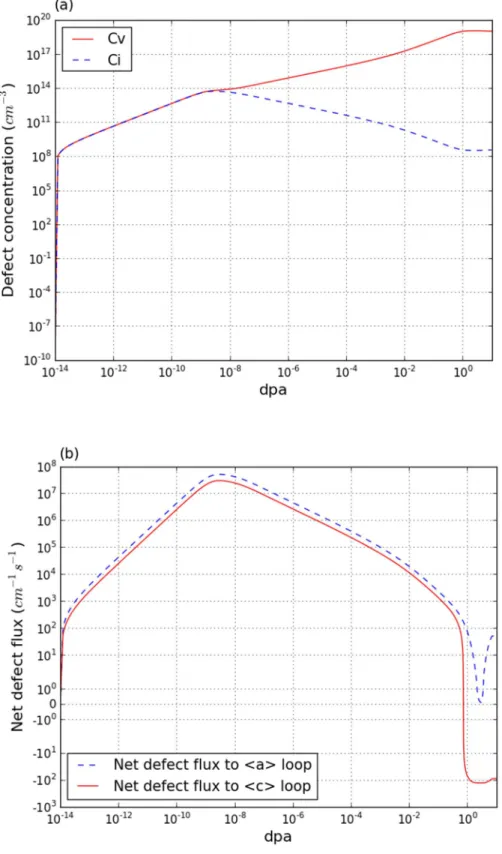
Radiation-induced (a) point defect concentration and (b) net defect flux on dislocation loops in single crystal zirconia at 553 K. The number density and radius of dislocation loops are used to calculate the dislocation density. However, there is no general information about the number density
Nevertheless, those researchers did not verify the number density of dislocation loops with experimental results.
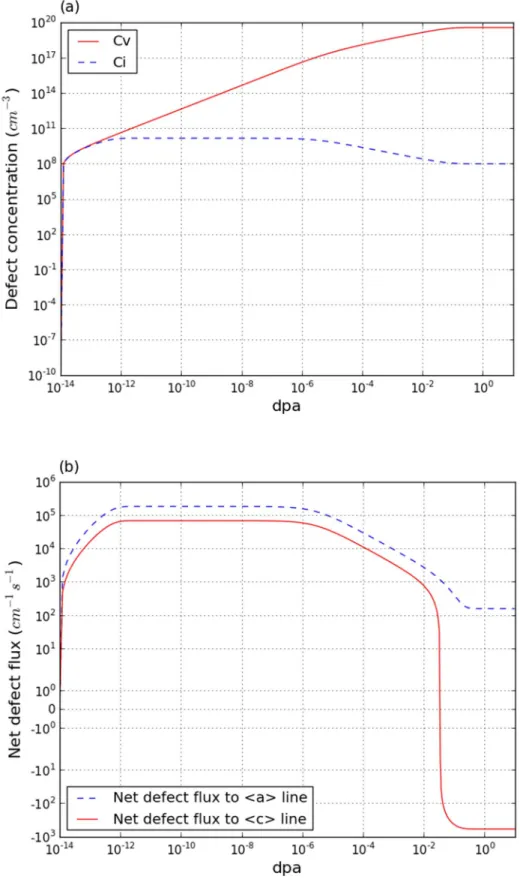
Cold worked polycrystal
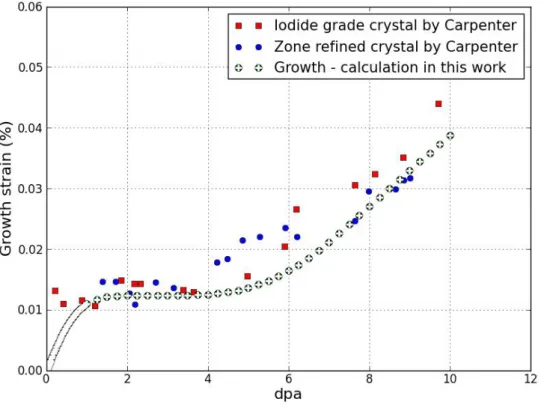
Because the largest sinks in cold-worked polycrystalline zirconium are dislocation lines and grain boundaries, three types of sinks are investigated. The irradiation growth strain of cold-worked polycrystal zirconium is also quite similar to experimental results. The results for cold-worked polycrystalline zirconium were compared with experimental data for cold-worked zircaloy due to an absence of data for cold-worked polycrystalline zirconium.
In cold-worked polycrystalline zircon, dislocation lines are the most powerful factor in modeling radiation growth.
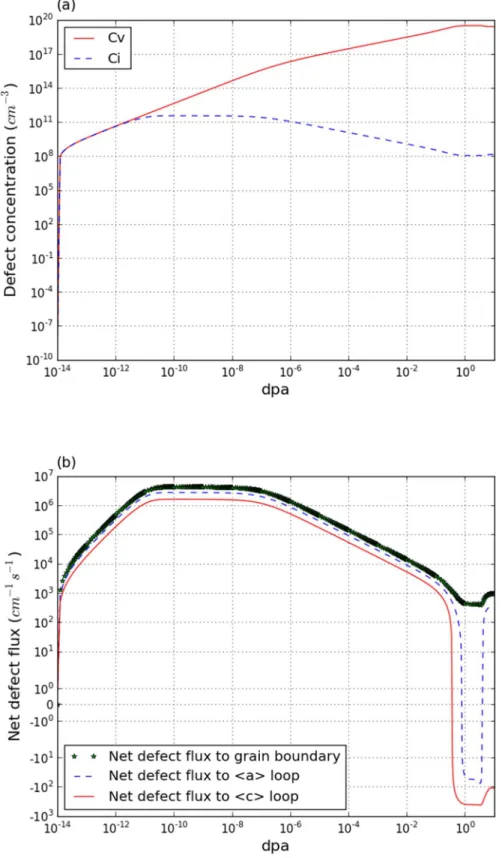
Annealed polycrystal
In annealed polycrystalline zirconia, the main sinks and
The dislocation loop density has the shape of a semicircle before 4 dpa, after which the dislocation rings are saturated.
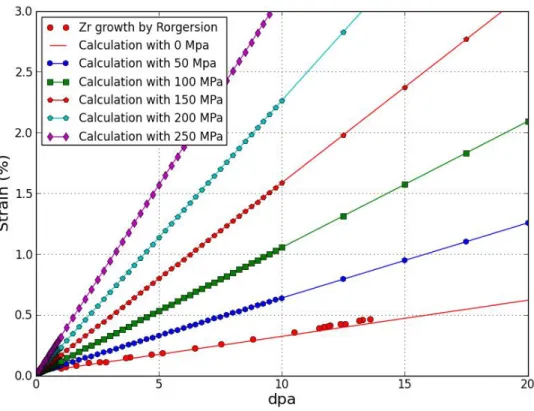
Stress effect on zirconium
In the case of cold-worked zirconium alloy, it was assumed that the dislocation density is already saturated. However, in the case of stainless steel, the behavior of the sink should be analyzed because stainless steel is more ductile than zirconium.
Alloy effect on zirconium
Limitation of SRT frame and PBM approach as a possible breakthrough
Methodology of iron-based alloy modeling
Rate equation of pure iron
Fundamental parameters
Irradiation swelling modeling
Results of irradiation swelling modeling
Pure iron
Both sink radii were increased by 10-6 dpa because the number density is too low, and up to 10-4 dpa both radii were decreased. In the case of the void, the absorption rate is much higher than the emission rate, hence the jet growth at a given number density.
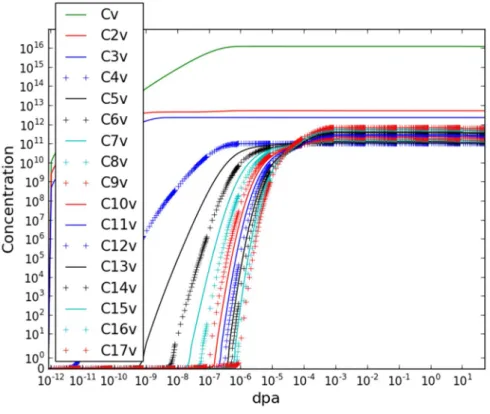
Stress effect on iron
This is the most common measure of the spatial extent of random motion and can be thought of as the measurement of the portion of the system that is "explored" by the random walker, this is called the MSD. From the extracted trajectories of the single interstitial diffusivity, the OVITO is used for visualization of the dimensionality of the diffusivity. The migration energies represent difference of total energy between the initial SIAs configuration and the SIAs at saddle.
The MD approach does not preselect the migration paths, so the value of n was determined from the extracted defect diffusion trajectories for the 1 ns simulation using the OVITO code, and the migration energies are obtained from the temperature dependence equation.
Alloy effect on iron
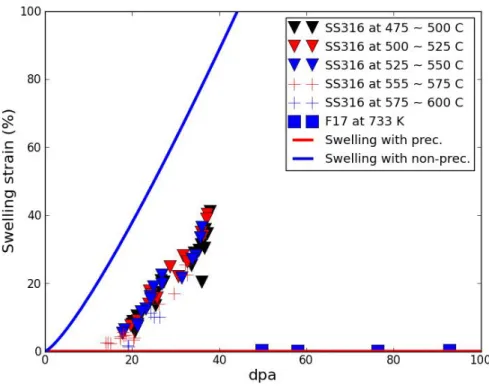
In the case of precipitation, the total concentration is lower than that of the case without precipitation. When compared with the experimental results, the swelling rate of no precipitation has the same slope as that of SS316 steel.
Cascade effect on iron
Limitation of CDM frame and PBM approach as a possible breakthrough
Recently, there have been many MD and ab-initio studies on the influence of stress and alloys on failure behavior. Therefore, it is natural to think that the effect of stress on SIA in PBM could provide a clue to explain this change in framing. Therefore, verifying the effect of external stress on PBM can be an indirect proof of Barashev's proposal [26].
As expected, the irradiation swelling is saturated with the steady-state defect concentration, as shown in Fig. V.8.1.
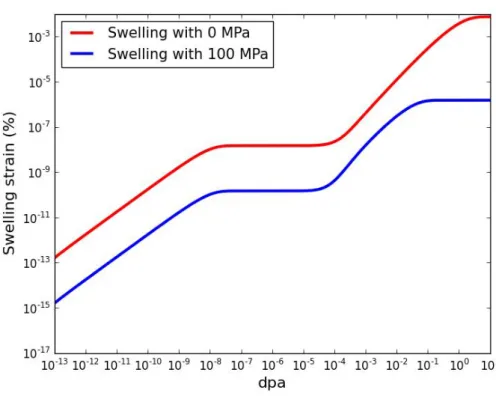
Parametric study
Defect generation rate
Diffusivity
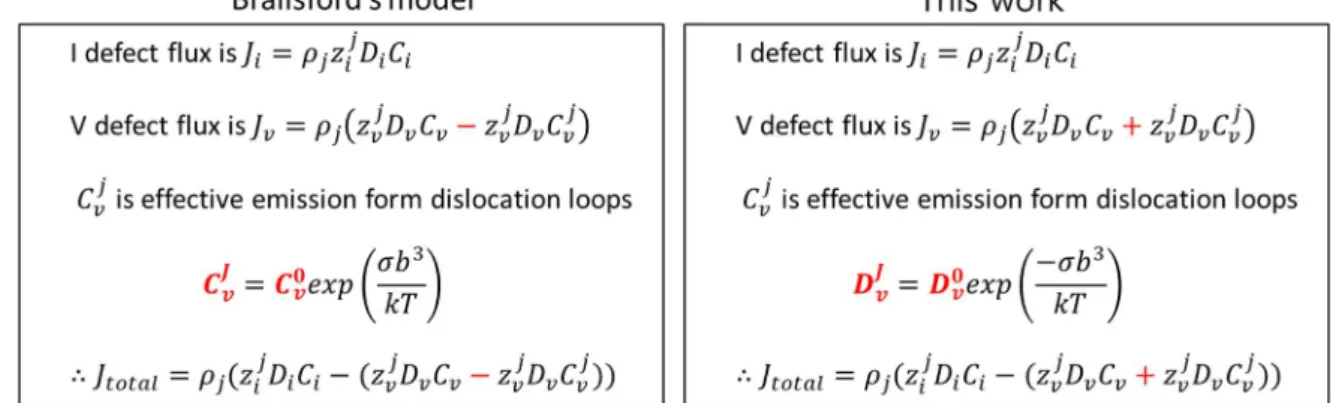
In detail, since the only appropriate value of diffusivity is applied to predict the radiation growth of zircon, the dislocation radius should be compared between calculation and experimental results. In this study, the effect of stress was considered in both ways; Conventionally, the modified Brailsford method is applied to zircon; Recent MD simulation results were adopted in the iron-based alloy. Since the precipitates are treated as a neutral bias sink, the vacancy defect flux should be a negative value at the initial stage as shown in Figure VI.1.3.
Nevertheless, the vacancy absorption rate must be changed at the initial stage because the precipitation effect is so strong.
Bias factor
In MD simulation, the correlation between defect and solution state of the alloy element was considered. Nevertheless, there was no recognition about cascade extinction of the basin, it was successfully assumed in rate theory. Assuming that all defects are destroyed in a cascade zone, the quantitative analysis may be possible.
To derive the total area size of the cascade, depending on the neutron spectrum, the NRT method or MD simulation must be applied with the entire energy set.
Path forward
- Reaction kinetics of defects
- Frame of rate theory (SRT vs CDM vs PBM)
- Cluster number density
- He effects on iron-based alloy
- Stochastical fluctuation
- Residual stress
Due to the complexity of the CDM and PBM approach, classical velocity theory based on stochastic fluctuations may be more suitable for anisotropy materials. In this paper, residual stress effects on the anisotropy factor were neglected in annealed polycyrstal. Unfortunately, no residual stress data are available for the specimen used in this paper.
In this study, stress, alloy and cascade extinction effects were considered with conventional and recent method to improve the fundamental understanding of the RIDI.
Zirconium and its alloys
In this study, alloy effect on RIDI was considered in the other way, which has never been considered in rate theory for RIDI, i.e. Christensen [35] calculates in detail the interstitial diffusivity within 0.5 % of Nb and 2.5 % Sn and in zirconium matrix. Adding 0.5 % Nb in cold-worked zirconia yields 0.2 % strain, while cold-worked pure zirconium shows almost 0.3 % strain at 10 dpa.
Since there was no experiment on radiation growth of Zr-0.5% Nb and Zr-2.5Nb, experimental results were compared and simulation results show good agreement.
Iron-based alloy
Bullough, "조사된 금속의 공극 성장으로 인한 팽창 속도 이론", Journal of Nuclear Materials, vol. Barbu, "지르코늄 단결정의 조사 성장에 대한 클러스터 역학 모델링," Journal of Nuclear Materials, vol. Second, I would 지도교수이신 김지현 교수님께 감사의 말씀을 전합니다.
우리는 Dr. Dr에게도 감사를 표하고 싶습니다. 권준현 박사님과 한국원자력연구원 이경근입니다.