I would like to express my deep gratitude to my supervisor, Professor Kim Hwan Seong for his constant help and support during my Master's course in Logistics Engineering. Last but not least, I would like to thank my parents for their constant support and encouragement. The objective of this study is to use the system dynamics methodology to model the supply chain system and then present the optimal control to optimize the supply chain performance by minimizing the quadratic cost function by tracking and keeping the inventory close to the target level. .
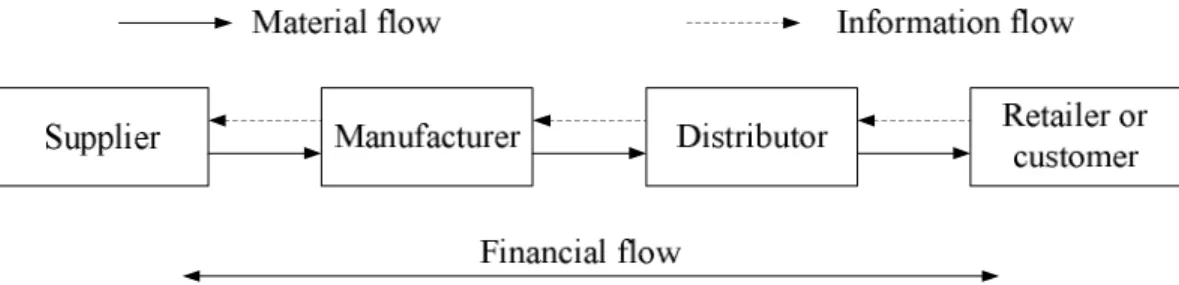
From the perspective of system dynamics, the supply chain was modeled as a time-delayed differential equation modeled as a first-order delay model. On the other hand, using system dynamics allows us to apply different control laws and analyze the dynamic behavior of the system, so that a decision policy can be found to improve the efficiency of the supply chain. In this paper, we use linear quadratic optimal control for such kind of dynamic supply chain system, the goal of the controller is to find the control input as the order quantity to minimize the cost function and maintain high customer satisfaction by tracking the target inventory level.
Introduction
Background
Along with the development trend in logistics, supply chain management still remains the most important theme in a successful business of any organization. Supply chain management involves the planning and management of all activities, including sourcing, purchasing and logistics distribution. The effective and efficient supply chain management (SCM) plays an important role in achieving high profits, lower costs and better customer satisfaction in their business [1].
Due to the mentioned importance of supply chain management, many researchers and managers are drawn to its modeling, analysis and control to search for better policies or managerial methods to improve SCM performance. Among these methodologies, the dynamic system methodology has an outstanding way of investigating supply chain management. In the next subsection, we will present the motivation for using system dynamics to model and control the supply chain.
Motivation of this research
Therefore, it is necessary to apply the systematic policies for planning and controlling the supply chain effectively. To deal with the problems, various alternative approaches to supply chain modeling and control have been proposed. Among these approaches, system dynamics (dynamic system) provides a convenient and compact way to model and analyze the supply chain system.
They apply four different heuristic control laws to evaluate supply chain system performance. On the other hand, only a few of these studies addressed the optimal supply chain solution based on the dynamic system model. Then an optimal control will be presented to find the optimal order quantities while minimizing the cost function of the supply chain system.
Research objectives
All of these works dealt with aggregated product levels or reflected a single product. To find the optimal solution to this problem, Perea used Model Predictive Control (MPC) to manage a multi-product, multi-echelon production and distribution network with lead times, eliminating reorders [13]. They formulated the discrete optimal control problem as a large-scale mixed integer linear programming problem (MILP).
Most previous works do not deal with integrated flow time modeling with dynamic modeling of supply chain entities to build a systematic framework based on state space model methodology. Therefore, this study will propose a systematic supply chain modeling using continuous modeling of supply entities such as factory, distribution, transportation model and flow time. From the perspective of system dynamics, we can apply some control policies as if we applied control laws for dynamic systems, and then the behavior of the system is analyzed and evaluated to improve the efficiency of the supply chain system.
Supply chain management and performance measurements
- Supply chain management
- Structure of supply chain management
- Performance measurement of supply chain management
- Process in supply chain management
Recently, according to the Council of Supply Chain Management Professionals (CSCMP), supply chain management includes the planning and management of all activities involved in sourcing, purchasing, conversion and logistics management [15]. Inventory management is a key factor in supply chain management and the important metric to measure supply chain performance. The key success of supply chain management is the speed with which all activities/functional processes can be implemented and how well customer requirements and customer satisfaction are achieved.
Strategic decisions deal with company policies and must look at the overall supply chain structure. Account management software, product configurations, enterprise resource planning systems and global communications are key components of an effective supply chain management strategy. But performance metrics change over time according to the complexity of the supply chain, the development trend of the logistics supply chain.
After introducing performance measurement and its importance in supply chain management, we need to classify performance measures into some categories. Traditionally, supply chain management separately managed their processes, such as ordering process, replenishment process, manufacturing process and purchasing process. The last process in the supply chain is the purchasing process, which takes place at the manufacturers/suppliers.
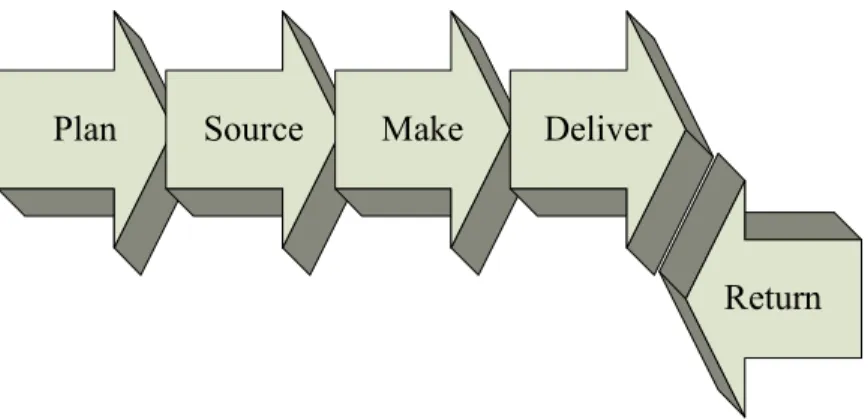
Therefore, a successful supply chain management must integrate all individual activities/functions into general management processes in SCM. Supply chain management process integration involves collaborative work between buyers and suppliers, joint product development, common systems and shared information. According to the Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR) model [14], there are five key process integrations for supply chain management shown in figure 2-3: plan, source, make, deliver and return.
The planning will cover supply chain performance, data collection, inventory, capital assets and transportation, etc. Although there are five key processes in SCOR model, according to [18], eight processes shown in figure 2-4 must be managed and integrated for successful supply chain management. The demand management process aims to balance the customers' requirements with the capabilities of the supply chain.
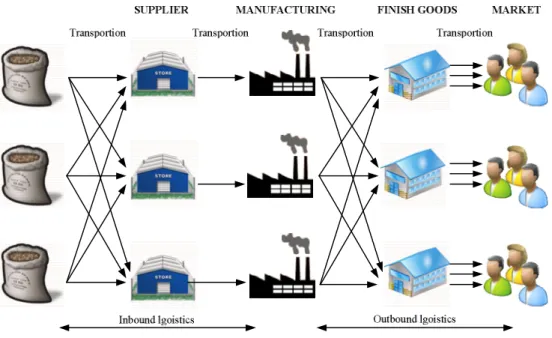
Dynamic modeling of supply chain
- Production model
- Transportation model
- Distribution model
- State-space of supply chain model
- Costs function of supply chain
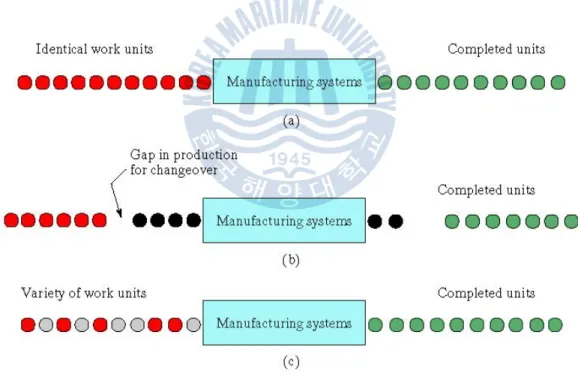
Production activities in the process industries and the discrete product industries can be divided into continuous production and batch production. Continuous production means that the process is performed on a continuous stream of material, without interruptions in the output stream, as indicated in Figure 3-2a. However, within the framework of this work, we mention about the classification of production systems based on the second factor and fifth factor, and also the serial or parallel characteristics of the systems are taken into account.
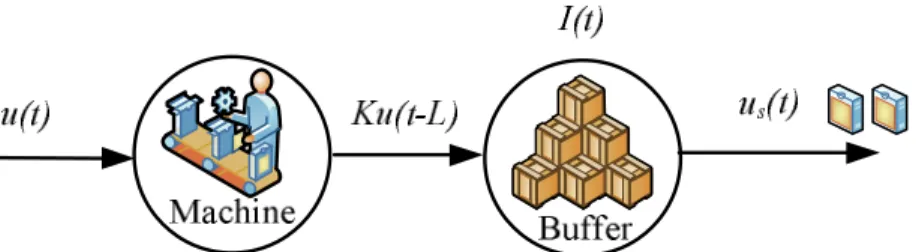
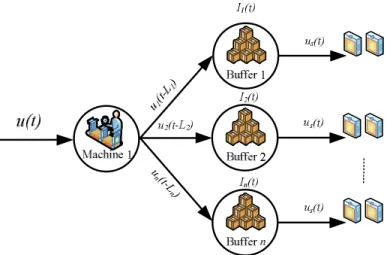
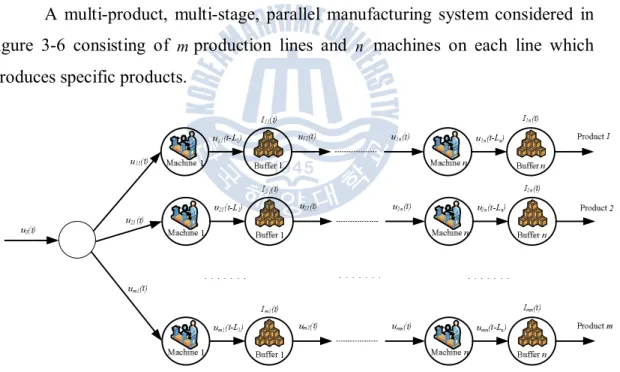
Consider a serial system with one product and multiple phases in Figure 3.4. The production system consists of n machines and In(t) is the number of products produced by the production system at time t. A multi-product, single-state production system as described in Figure 3.5. In this system the machine can produce different products, for example product A,B,C,…,N. A multi-product, multi-stage, parallel production system as shown in Figure 3-6, consisting of mproduction lines and n machines on each line that produce specific products.
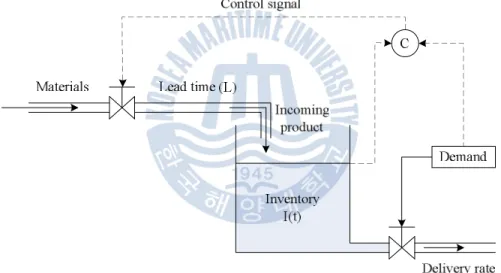
In this section, we apply the fluid analogy methodology to model the dynamics of manufacturing system [20]. The fluid analogy representation of factory model is shown in figure 3-7, the inventory and work-in-progress (WIP) are considered as materials stored in "tank" and in the pipe respectively.. tank" is replenished products from the factory to the production lead timeL Figure 3-7: Fluid analogy of factory model The choice of transportation methods must balance between the quality of service offered and the cost of that service.
Since freight transport costs absorb between one-third and two-thirds of total logistics costs, an efficient transportation system plays an important role in the logistics system. Creating more competition is the first contribution of an efficient and cheap transport system in terms of helping to expand the market by reducing land costs for products so that they can compete with other products sold in the same markets. From a dynamic modeling perspective, the transportation system can be modeled as a first-order delay model, as shown in Figure 3-8.
The supply chain cost structure is shown in Figure 3-11. This includes inventory costs, reorder costs, production costs and transport costs. Inventory costs are defined as the costs the system incurs to store products (or materials) in the distribution warehouse or factory warehouse. The fixed setup costs are independent of the production quantity and are only incurred for starting production of a product.
Controller design
State-space model
Linear Quadratic Regular control design
This problem can be solved by various approaches, for example, the transition matrix method, Riccati equation approach and dynamic programming. Now we will consider the case where the final state is free and its value can be varied during the optimization process. By using the Riccati equation approach (sweep method), the solution of the two-point boundary value problem can be solved as
Optimal tracking controller
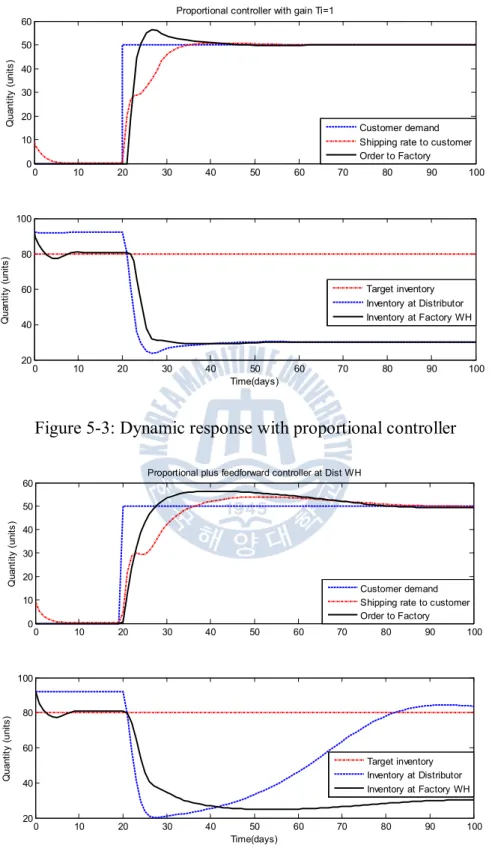
Simulation results
Demand and control parameters
Simulation results and analysis
In this section, we will measure the average cost of the supply chain, then we will compare the average inventory level for each echelon as well as average cost between dynamic model and traditional inventory model such as EOQ. It is clear that the economic order quantity associated with fixed setup (ordering) costs Table 5-1 shows the results with different ordering costs.
Conclusion
Dynamic modeling and control of supply chain systems: a review”, Journal of Computers and Operations Research, Vol. M Beamon, (1998) “Supply chain design and analysis: models and methods”, International Journal of Production Economics, Vol.55, pp.281-294. Tahmassebi, (2000) “Dynamic modeling and classical control theory for supply chain management”, International Journal of Computers and Chemical Engineering, Vol.
Lin, (2004) "Applications of control theory to the production-inventory problem", International Journal of Production and Research, Vol. 1982) “Dynamic analysis of an inventory and order based production control system”, International Journal of Production and Research, Vol.20, pp.671-687.
![Figure 2-4: Eight processes of successful supply chain management [18]](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dokinfo/10540454.0/26.774.98.675.231.652/figure-2-processes-successful-supply-chain-management-18.webp)
![Figure 3-1: The production system [19]](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dokinfo/10540454.0/28.774.80.680.273.911/figure-3-1-the-production-system-19.webp)