EVIDENCE FROM THE HOTEL INDUSTRY OF MALAYSIA. behavior control, system quality, information quality and service quality towards co-creation intention. There is a significant relationship between attitude toward co-creative service innovation on social media and co-creation intention.
Attitude towards co-creative service innovation on social media
Attitude toward using new technology is evaluated by perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use (Cham, Low, Lim, Khin, & Raymond, 2018; Porter & Donthu, 2006), both of which guide co-creation intention (Lu, Liu, Yu, & Wang, 2008). Moreover, perceived usefulness means the degree of individual's belief towards their performance and ability that is enhanced and enhanced by the new technology system.
Subjective norms
In the new emerging dynamic of customer empowerment, companies must have a valuable opportunity to use social networking sites to co-create with customers (Kane & Fichman, 2009). Moreover, word of mouth looks at a person sharing their opinion with others and providing reliable information that changes attitudes and behavior on social networking sites (SNS).
Perceived behavioral control
Subjective norms as an antecedent of co-creative service innovation that influence customer intent to co-create. In the hotel context, the subjective norm can be concluded to influence customers' intention to co-create service innovation (Sarmah et al., 2018; Venkatesh et al., 2003).
System quality
A high system quality standard leads to behaviors such as increased website visits (usage) and repeat purchases (user satisfaction). Therefore, system quality can help develop user trust, satisfaction, and intention (Cham, Lim, Cheng, & Lee, 2016; Lai, 2016).
Information quality
According to Kahn et al. 2002), proposed an information quality model (PSP) to measure information quality. This model looks at information quality from two aspects, which are product quality and service quality.
Service quality
Improving service quality (website design) is crucial for co-creation of value (Fyrberg & Jüriado, 2009). In addition, the quality of the e-service and its dimension have an impact on the willingness of the customer to participate in the co-creative process (Sheng & Liu, 2010).
Co-creation intention
SNSs): EVIDENCE FROM THE HOTEL INDUSTRY OF MALAYSIA. SNSs): EVIDENCE FROM THE HOTEL INDUSTRY OF MALAYSIA.
Adoption intention
Review of Relevant Theoretical Models
Theory of planned behavior
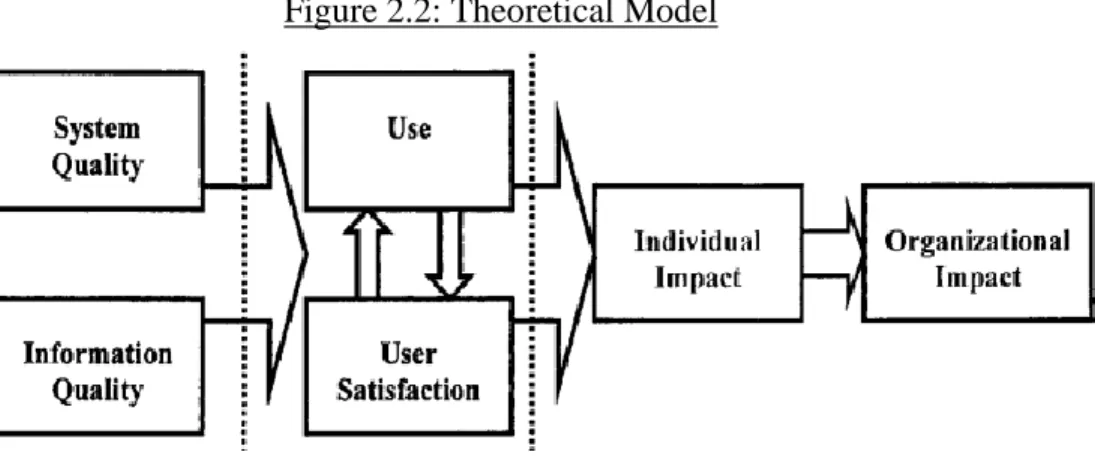
Source: DeLone and McLean Information System model (1992). SNSs): EVIDENCE FROM THE HOTEL INDUSTRY OF MALAYSIA. Furthermore, the dimensions used to examine the technical level, semantic level and influence level (Hellstén & Markova, 2006).
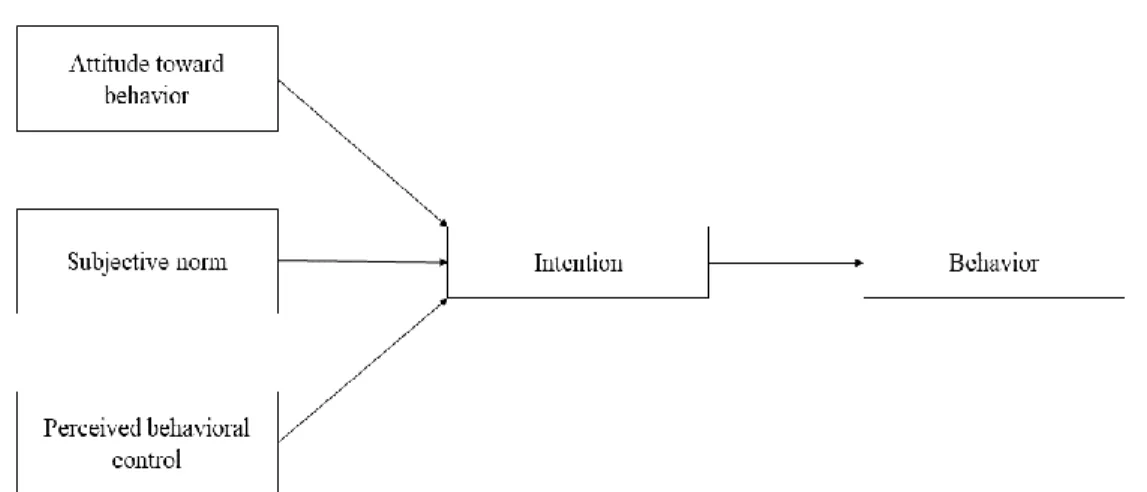
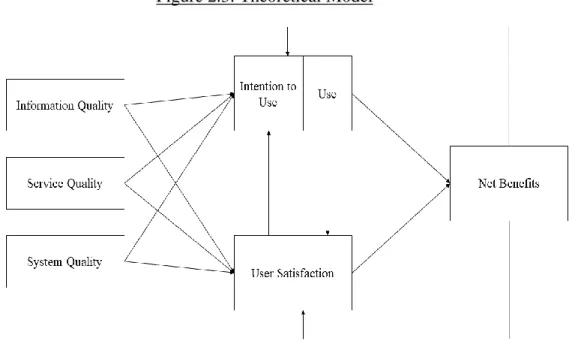
Proposed Conceptual Framework
Hypothesis Development
- The relationship between Customer Innovativeness and Co-creation Intention
- The relationship between Attitude toward co-create service innovation on social media and Co-creation Intention
- The relationship between Subjective Norms and Co- creation Intention
- The relationship between Perceived Behavioral Control and Co-creation Intention
- The relationship between System Quality and Co-creation Intention
- The relationship between Information Quality and Co- creation Intention
- The relationship between Service Quality and Co-creation Intention
- The relationship between Co-creation Intention and Adoption Intention
The relationship between Attitude to co-create service innovation on social media and Co-creation Intention. H2: There is a correlation between attitude towards co-create service innovation on social media and co-creation intention.
Conclusion
The client's desired outcome forces them to co-create to achieve a common goal such as innovation, efficiency and adaptation.
METHODOLOGY
- Introduction
- Research Design
- Data Collection Methods
- Sampling Design
- Target Population
- Sampling Frame and Sampling Location
- Sampling Elements
- Sampling Technique
- Sample Size
- Research Instrument
- Questionnaire Design
- Pilot Test
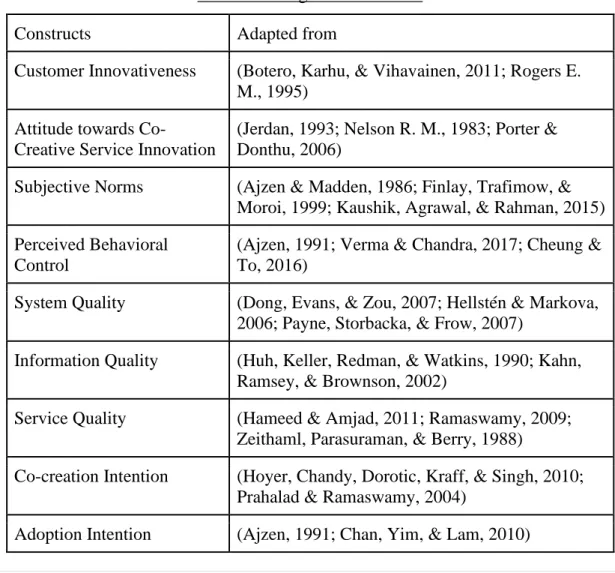
- Construct Measurement
- Data Analysis Tool
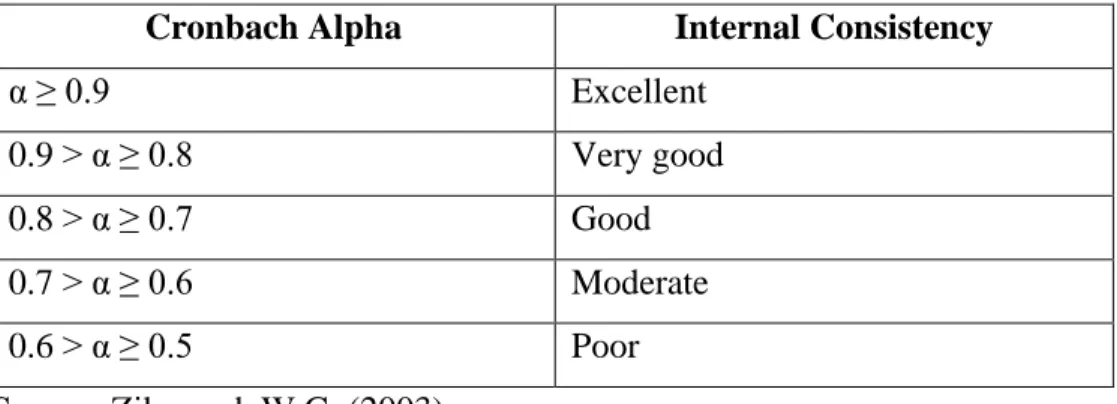
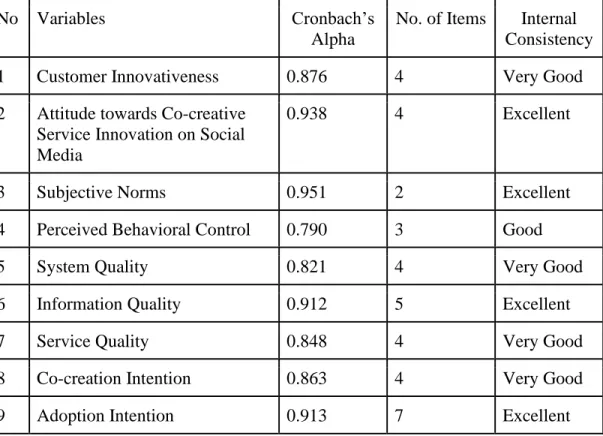
- Reliability Test
- Descriptive Analysis
- Inferential Analysis
- Conclusion
The judgment sampling method, one of the non-probability sampling techniques, will be used to conduct this research. Judgmental sampling was used to access respondents who are suitable for the research requirements. It refers to a technique used to collect data that invites each response to the same questionnaire for a specific purpose (Saunders, Lewis, & Thornhill, 2009).
The pilot test is essential to practice to ensure the reliability and accuracy of the result. Additionally, the reliability test was used to assess whether all variables are reliable or highly correlated. Moreover, it was used to evaluate the acceptance of the hypothesis, as well as to reject or accept it.
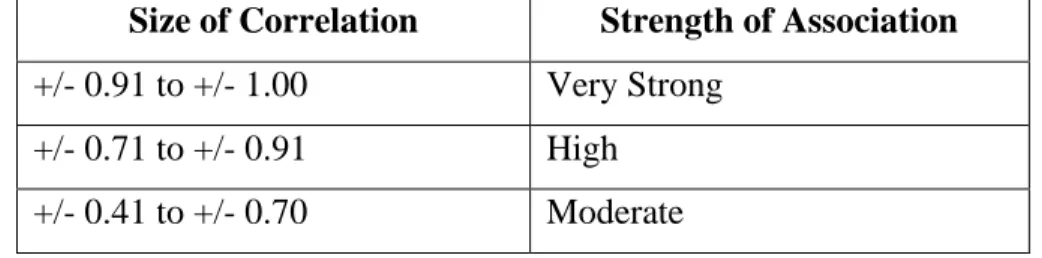
Is a method used to analyze data produced by Karl Pearson in 1896 called as correlation coefficient or as r. The equation formed as below can be used to evaluate the relationship between those variables. The data analysis tool used to produce the findings of the study as well as descriptive analysis, simple linear regression and multiple linear regression.
ANALYSIS OF DATA
- Introduction
- Demographic Analysis
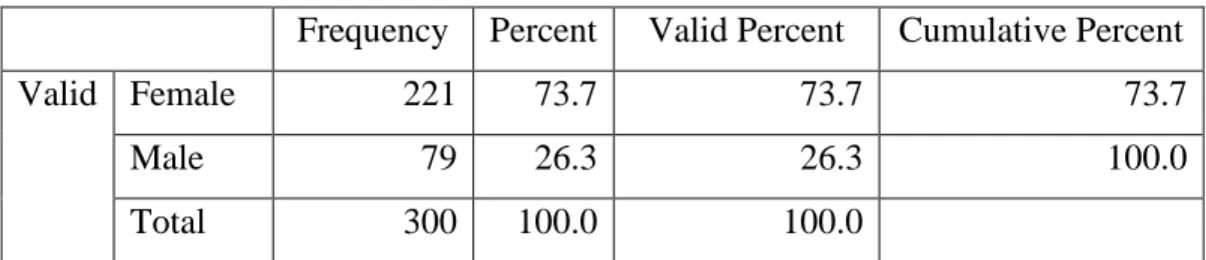
- Gender
- Age Group
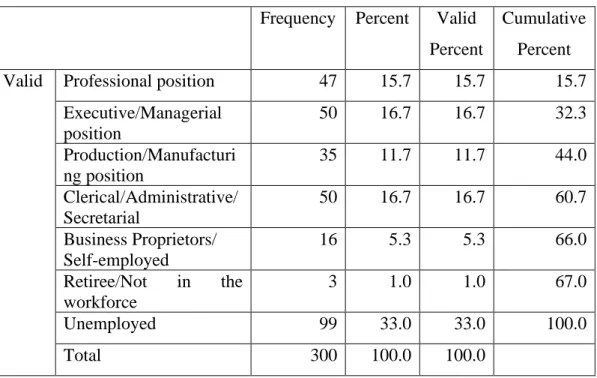
- Employment
- Education Level
- Income Level
- Do you have any hotel experience?
- Number of hotel visits per year
- Hotel reservation method
- Do you know about co-creative service innovation
- How frequent you co-create with hotels via social media
- Central Tendencies Measurement of Constructs
- Inferential Analysis
- Multiple Linear Regression Analysis
- Simple Linear Regression Analysis
- Conclusion
Among the 300 respondents, everyone knows about co-creative service innovation on social networking sites. Predictors: (Constant), Customer Innovation, Attitude towards co-creative service innovation on social media, Subjective Norms, Perceived Behavioral Control, System Quality, Information Quality, Service Quality. Based on the result, R-squared value is 0.277 which means that the 27.2% of the variances in co-creation intention were influenced by the predictors.
The main variable that influenced respondents' co-creation intent is the attitude towards co-creative service innovation on social media, which scores the beta score of 0.333. The second significant variable that influenced co-creation intent is subjective norms, which scores the beta of 0.232. The third significant variable that influenced co-creation intent is information quality, which scores the beta score of 0.228.
The table above shows a model summary of simple linear regression between co-create intent and adoption intent. The significant value is 0.000, which is lower than the p-value of 0.05, meaning that co-create intent is a significant predictor of variations in adoption intent. The results showed that there is a positive relationship between these seven predictors of co-creation intention.
CONCLUSION
Introduction
Summary of Statistical Analysis
- Descriptive Analysis
- Inferential Analysis
- Multiple Linear Regression
- Simple Linear Regression
The result generated from multiple linear regression between the predictors (customer innovativeness, attitude towards co-creative service innovation on social media, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control, system quality, information quality, service quality) and dependent variable (co-creation intent) has an R-squared value of 0.277, indicating that 27.7% of the variances in co-creation intent can be explained by customer innovativeness, attitude towards against co-creative service innovation on social media, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control, system quality, information quality, and service quality. Meanwhile, the result shows that attitude towards co-creative service innovation on social media (B = 0.333) has the strongest impact on customer co-creation intention, while system quality (B = 0.041) has the weakest impact. The result of simple linear regression between co-create intent and adoption intent has an R-squared value of 0.536.
Discussions of Major Findings
The result of a simple linear regression between intention to co-create and intention to adopt has an R-squared value of 0.536. of the variation in adoption intention can be explained by co-creation intention. H2: There is a relationship between attitude towards innovation of social media co-creation services and intention to co-create. Based on the results, it is recommended that all variables best fit the proposed model, which has an overall good rating with the data.
In short, all the variables supported in the research except customer innovativeness and system quality. From the results of past studies, it has been investigated that customer innovativeness has a significant impact on customers' intentions in co-creation, as customers are ready to introduce and get involved in the service development process (Morosan, 2015; Sarmah, 2018). SNSs): EVIDENCE FROM MALAYSIA'S HOTEL INDUSTRY. A likely reason is the inability to differentiate and recognize the use of co-creation (Witell et al., 2011).
Once the company has failed to identify customer preference or behavior, it leads to no response and no response from the customer (Füller et al., 2006). According to Dumond (2000), system quality was found to have a significant influence on co-creation intent, as the system is able to capture customer value. Customers refused to respond when they felt they had nothing to do, and there's no plan for the company to get in touch.
Implications of the Study
- Managerial Implications
According to Lusch et al. 2007), stated that the right communication process is essential to resonate with customer response. The content from the company's online system is a lack of activities and thus generates the weak connection and creation towards the respondent (Kohler, 2011). Furthermore, service providers are needed to ensure that the service system is within the customer's control, as they can expect what the next steps will be when using the company's system.
For example, the hotel industry should design the system well in ease of use, ease of access, simple navigation, data accuracy, etc. The successful service system that is able to meet the customer's desire for control and personal preference, they can perform better than the service providers' expectations (Andrew, Peever, & Pryor, 2009).
Limitations of the Study
A successful service system that can fulfill the customer's desire for personal control and preferences can perform better than service providers' expectations (Andrew, Peever, & Pryor, 2009). SNSs): EVIDENCE FROM MALAYSIA'S HOTEL INDUSTRY. The result of this survey may only represent persons aged 25 and under and not from the perspective of the labor force respondents. The result is therefore a lack of precision for the presentation of all respondents from the perspective of co-creating service innovation.
Recommendation for Future Study
Conclusion
EVIDENCE FROM THE MALAYSIAN HOTEL INDUSTRY. the employment of the target respondents may have different perspectives as well as preference, knowledge, attitude and behavior towards the co-creative goal. Vine Journal of Information and Knowledge Management Systems SNSs): EVIDENCE FROM THE MALAYSIAN HOTEL INDUSTRY. Data Collection, Primary vs Secondary, 1. Retrieved from http://www.joophox.net/publist/ESM_DCOL05.pdf.
Customer co-creation in hotel service innovation: An interpretive structural modeling and MICMAC analysis approach. Research Methods for Business Students (6th Edition). SNSs): EVIDENCE FROM MALAYSIA'S HOTEL INDUSTRY. Value co-creation and purchase intent on social networking sites: the role of electronic word-of-mouth and trust - a theoretical analysis.
An empirical study of the effect of e-service quality on online customer satisfaction and loyalty.
UNIVERSITI TUNKU ABDUL RAHMAN Faculty of Accounting and Management
BACHELOR OF INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS FINAL YEAR PROJECT
TITLE OF TOPIC: Antecedents of co-creative service innovation in Social Network Sites (SNSs): Evidence from
Survey Questionnaire
I think using co-creative service innovation on social media sites is a pleasant idea. I think users who are important to me will think that I should co-create services on social media sites. I think users who influence my behavior will think that I should co-create services on social media sites.
I have the resources, knowledge and ability to co-create services on social media sites. I think that during my trip, I will go to social media sites to buy products/services to consume. I think during my trip, I will go on social media sites to do an online review of my current trip.
I think during my trip, I will take to social media sites to provide updates about my current trip.