This is to certify that I am responsible for the work presented in this project, that the original work is my own, except as specified in the references and acknowledgments, and that the original work herein was not undertaken or done by unspecified sources or persons. Thank you for the advice, tips, motivations you have given me during this project. The guidance and support received from all members who contributed and are contributing to this project was vital to the success of the project.
This project introduces storytelling as a mechanism to capture tacit knowledge believed to be experiential knowledge. This project provides a bridge and a platform that will allow the capture of tacit knowledge in a structured method. The objective of this project is to develop a knowledge management system that captures tacit knowledge using storytelling.
Throughout this project we will attempt to capture, store, retrieve and transfer and/or share knowledge within an entity.
INTRODUCTION
- Chapter Overview
- Background of Study
- Problem Statement
- Objectives of Study
- Scope of Study
Tacit knowledge also known as experiential knowledge is knowledge that has been gained through years of experience. But as for tacit knowledge, some systems can provide the facility to share tacit knowledge. Staff often try to capture tacit knowledge through chats or emails, but this does not allow for proper knowledge capture.
Another problem that can be faced when trying to capture tacit knowledge is that not many experts are willing to share this knowledge without interaction with the requester. What changes can be made to project management methods to ensure that tacit knowledge is properly shared in an organization. What system can be built to allow the proper capture and proper sharing of tacit knowledge.
This system will serve as a platform and a means to facilitate the capture and sharing of tacit knowledge.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Chapter Overview
Knowledge
Knowledge Capture
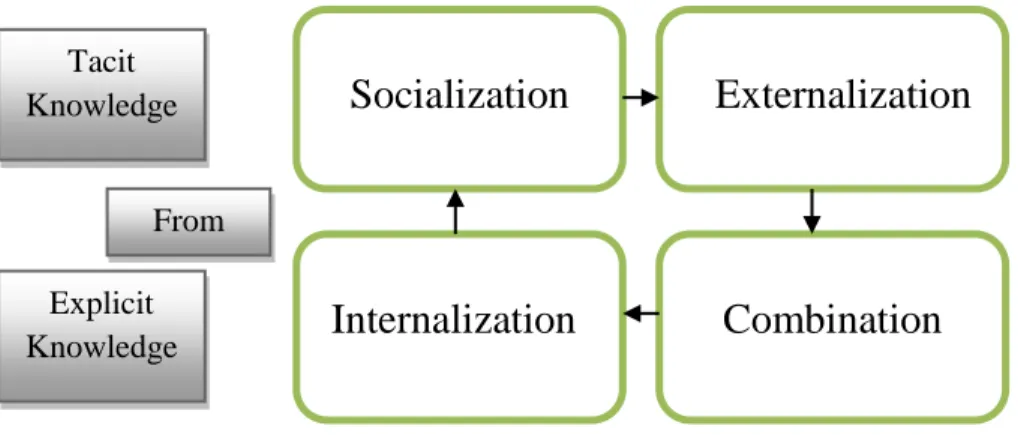
There are four types of interaction: Socialization (tacit to tacit), Explication (tacit to explicit), Combination (explicit to explicit) and Internalization (explicit to tacit). The knowledge conversion occurs through the spiral of organizational knowledge creation that includes different organizational levels. It is known that the way things are formally organized in most companies (their processes) is not the same as the way things are actually done.
Knowledge is not always easy to grasp even in the case of clear knowledge; knowledge will be even more difficult if it is knowledge based on experience, tacit knowledge (Brown and Duguid, 2001). Capturing tacit knowledge is difficult because such knowledge actually resides inside an expert's head. What makes the process even more difficult is that the expert from whom one is trying to derive it may not even be aware of it or even consider it current knowledge (Tagger, 2005).
There are many platforms that were introduced as means to capture tacit knowledge, one of these platforms is storytelling.
Storytelling
The content of the story may vary from person to person, but the purpose is still the same. In the last several millennia, the ancient Greeks began to think seriously about things they thought they knew and understood, they discovered to their surprise that they actually did not understand some of the seemingly simplest and most obvious things (Denning, 2000) . One of those seemingly obvious things that, even in modern times, is not as straightforward as it seems at first glance, is a story.
Telling a story is simple and can be done by anyone, anywhere, anytime. It may be true or false, it may be from one's imagination, nevertheless it is still a story. Over the past years, information technology has proven how useful it can be when it comes to knowledge sharing.
Although it is true that the creation of the actual knowledge and integration process are human-based actions, this points to the importance of human knowledge in an organization / entity.
KM Storytelling
Storytelling allows you to get a clear idea from one point of definition to another; it provides a clear line for tacit knowledge. They also claim ownership of the story as they are the ones telling it and they are also the ones who decide to tell the story and in the way they choose to tell it. A winner of the Nobel Prize for Literature (Gabriel García Márquez, 2004) has expressed his pleasure in telling stories.
He says, "To me, stories are like toys, and making them up is, in one way or another, like a game." In this statement, he was not referring to the Internet revolution. In its relatively short history, the Internet has displaced the economic foundations of traditional media, but it has also created for society, in general, and journalists, in particular, new possibilities for how their stories can be told. It has broken the paradigm of one-way communication in which "we talk, you listen", and to do so it has required journalists to develop new storytelling skills.
Related Work
- Narrative and Social Tacit Knowledge . 13
Chapter Overview
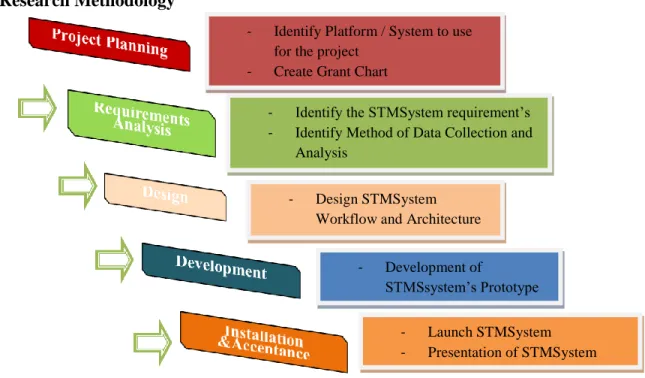
Research Methodology
- Project Planning
- Requirements Analysis
- STMS Design
- STMS Development
- Installation and Acceptance
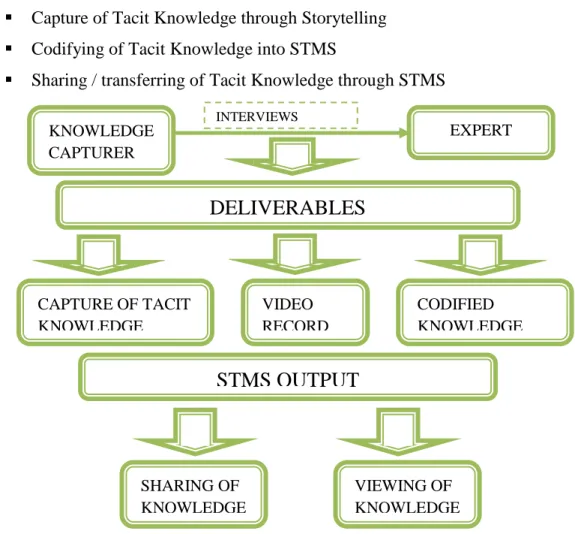
The Storytelling Management System will allow a company's staff (users) to view insights that have been captured during an interview with a company expert. The purpose of data collection is to give us an idea of what the company is doing, its objectives and the difficulties faced by the staff of this company. The first stage is to gather knowledge from the oil and gas company and the second stage is to develop the project.
But first a study of the company was done to identify the most suitable method for gathering knowledge and experts who should be the source of knowledge. Assessment of the challenges and opportunities related to knowledge, then identification and analysis (i.e. confidentiality, process, organization, personnel or technology) Preliminary Recommendation Based on the findings, preliminary. It is essential to understand and perform a current knowledge management assessment on the current situation in order to provide better understanding of the knowledge management practices in the organization.
In order to collect data for this project, it has been decided to conduct an interview, through which we will try to collect information about the company's staff. For this interview, the method followed is a series of questions that will depend on the answers given by the interview participants, thus making the interview a semi-structured interview. The purpose of analyzing the data is to understand the outcome of the interview that was conducted and provide evidence for STMS as an effective mechanism for capturing tacit knowledge in the oil and gas company.
Next, for the process data analysis, common themes were identified within the participants' responses, and then the number of times a common response occurred was assigned. The development of the StoryTelling Management System took place in the second phase of the project. It was expected that the development of STMS would take approximately three months, during which a platform for development was chosen, following the design of the interface and the launch of the website, as testing was required to verify the effectiveness of the StoryTelling Management System.
Installation and acceptance is the final stage during which the prototype of the StoryTelling management system will be launched. This stage requires the prototype of the system and it involves the presentation of the system as the last part of this study.
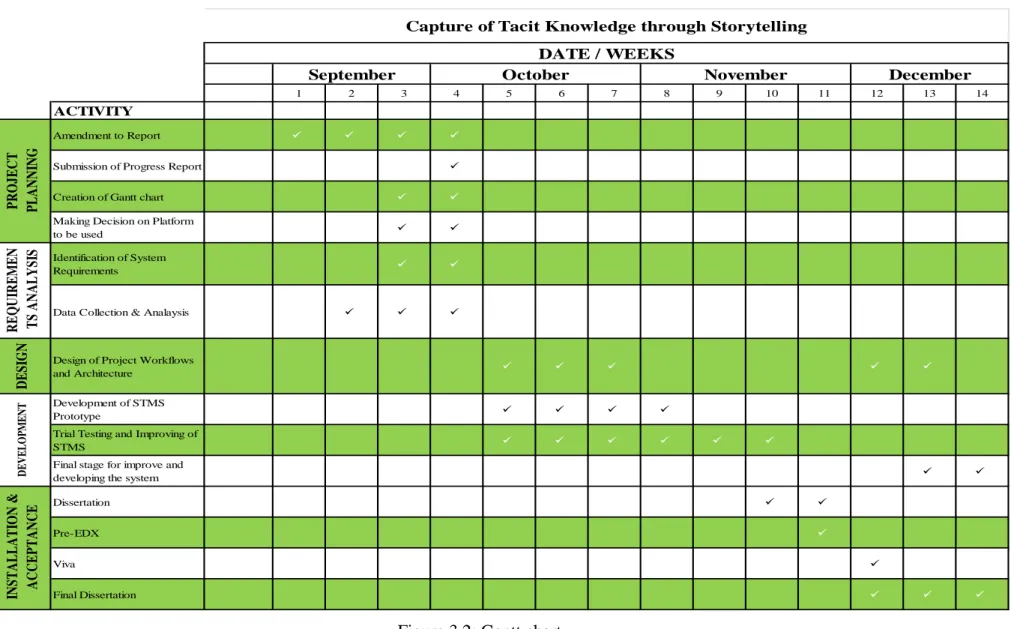
Gantt Chart
This chapter will give a conclusion to the main objective of the interview that took place. Although this makes the introduction of STMS more complicated, it shows that there is no system in the company that is used only to capture the experience-based knowledge of the staff. This question allows the recognition of the effectiveness of the current systems implemented in the organization in capturing tacit knowledge from the users' perspective.
When this question came in, the participants did not show much enthusiasm regarding the introduction of STMS. Although the implementation of the system was approved by the management, there were difficulties during the collection of data.”. This shows that the participants believe that the StoryTelling Management System can prove useful if they are the user of the system, as it will allow them to capture the tacit knowledge of their colleagues at all times.
As a conclusion of the collected results from the interview, we can say that the StoryTelling Management System could prove to be useful for the company's employees if. The results collected can under no circumstances be considered a representation of the entire company. This step is taken to ensure that the essence of the knowledge was captured.
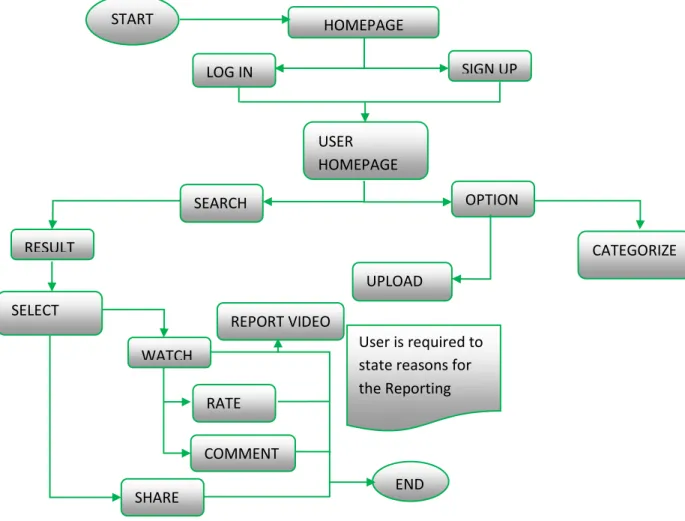
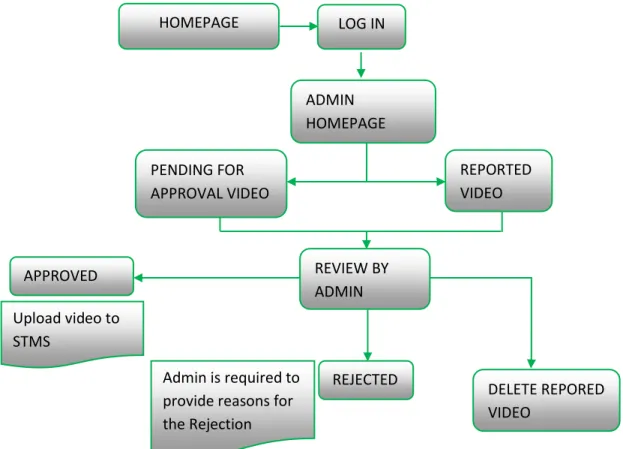
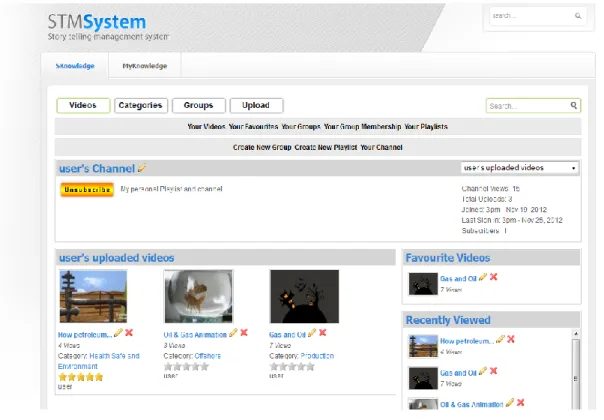
Tagging, categorization and description of the video will be done by the system administrator. Because the knowledge video has been uploaded to STMS and is enabled for users to view. On the next page is a presentation of the work flow of the project, which first showed that the process used to capture the tacit knowledge of the expert is the interview.
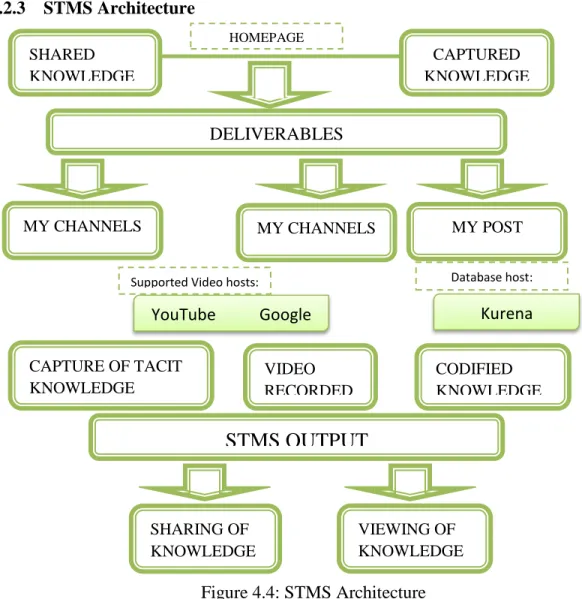
For the workflow of the administrator, it explains the roles of the administrator as the person responsible for the system. This architecture also shows the results of the system and the functions of that system. Public users can watch the video to capture the knowledge as this is a sharing system, but public users cannot use any specific feature of the system.
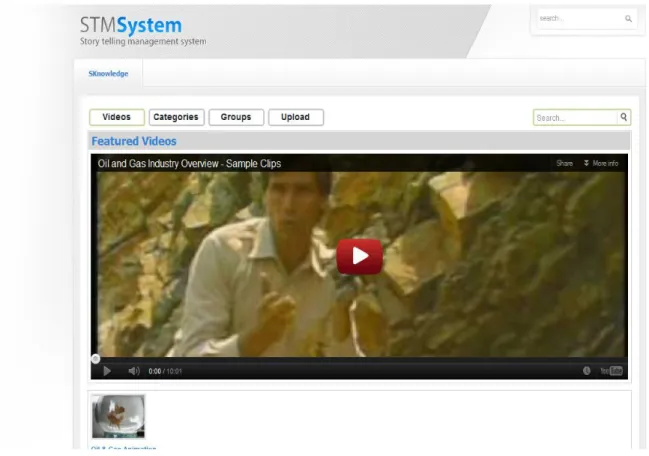
Under this menu is all the knowledge that is shared by all users of the Storytelling Management System. This site provides the user with the required knowledge as well as the functionality to allow the user to provide a video review by rating and/or commenting. The second phase which is the development of the STMS system has been completed by providing a prototype.