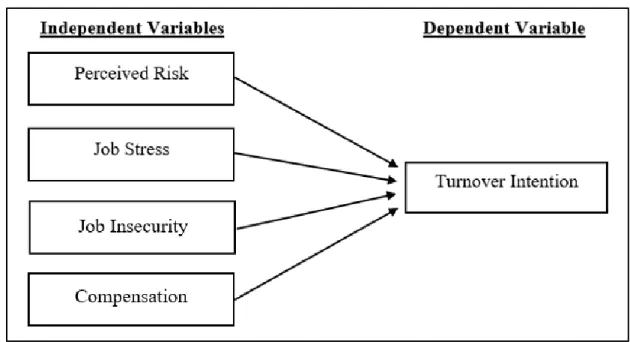
The title of the research project is “Post COVID-19 Era: The Turnover Intention of Employees in Hospitality Industry”. Specifically, this research will shed light on the factors that cause workers in the hospitality industry to leave.
INTRODUCTION
- Introduction
- Research Background
- Problem Statement
- Research Objectives
- General Objective
- Specific Objectives
- Research Questions
- Hypotheses of the Study
- Significance of the Study
- Chapter Layout
- Conclusion
Turnover was a common problem in the hospitality industry before the pandemic and had gotten worse now. Exploring the significant impact of perceived risk on turnover intent among Malaysian hospitality workers in the post-pandemic situation.
LITERATURE REVIEW
- Introduction
- Underlying Theories
- Social Exchange Theory (SET)
- Conservation of Resources Theory (COR)
- Review of Variables
- Dependent Variable - Turnover Intention
- Independent Variable - Perceived Risk
- Independent Variable – Job stress
- Independent Variable – Job Insecurity
- Independent Variable - Compensation
- Review of Relevant Theoretical Models
- Perceived Risk
- Job Stress
- Job Insecurity
- Compensation
- Proposed Conceptual Framework
- Hypothesis Development
- Perceived Risk and Turnover Intention
- Job Stress and Turnover Intention
- Job Insecurity and Turnover Intention
- Compensation and Turnover Intention
- Chapter Summary
It can be used as a guideline for future research on the relationship between perceived risk and turnover intention, how and why it will affect turnover intention. The review of research literature and research results in this research can also be used as a reference for future research studies on turnover intention in post-pandemic situations.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
- Introduction
- Research Design
- Data Collection Methods
- Primary Data
- Sampling Design
- Target Population
- Sampling Frame and Sampling Location
- Sampling Elements
- Sampling Technique
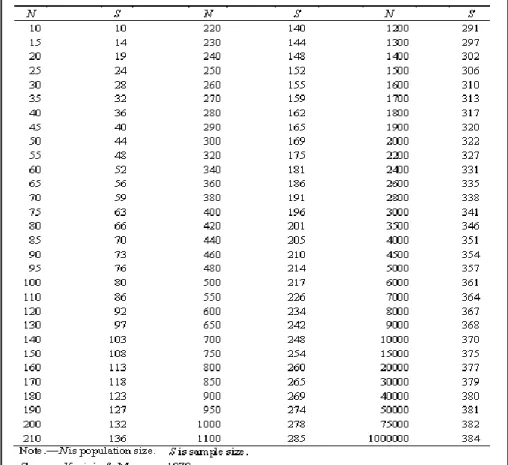
- Sampling Size
- Research Instrument
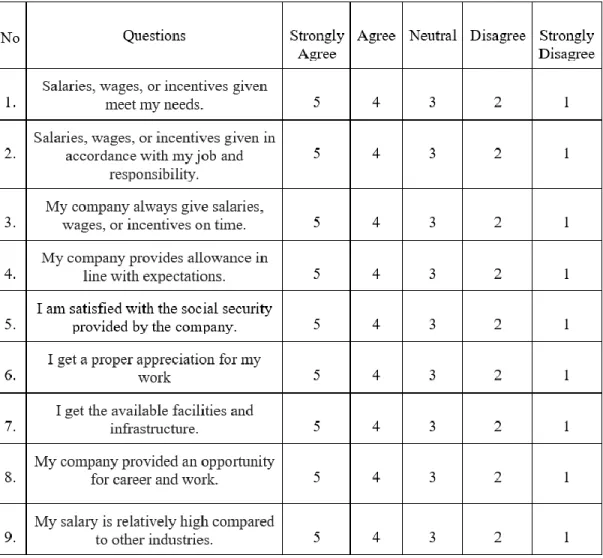
- Questionnaire Design
- Pilot Study
- Construct Measurement
- Origin of Construct Measurement
- Scale of Measurement
- Data Processing
- Data Checking
- Data Editing
- Data Coding
- Data Transcribing
- Data Analysis
- Descriptive Analysis
- Scale Measurement - Reliability Test
- Inferential Analysis
- Chapter Summary
An organization with good productivity that is able to operate in the long term will contribute to employment in the country and will also contribute to the income of the country. In addition, they will discuss and develop the hypothesis, the significance of the study and the layout of the chapter.
DATA ANALYSIS
Introduction
Descriptive Analysis
- Respondent Demographic Profile
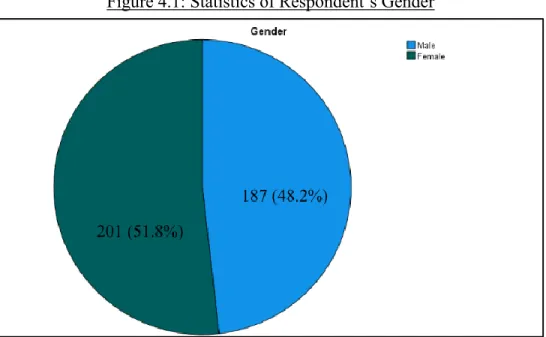
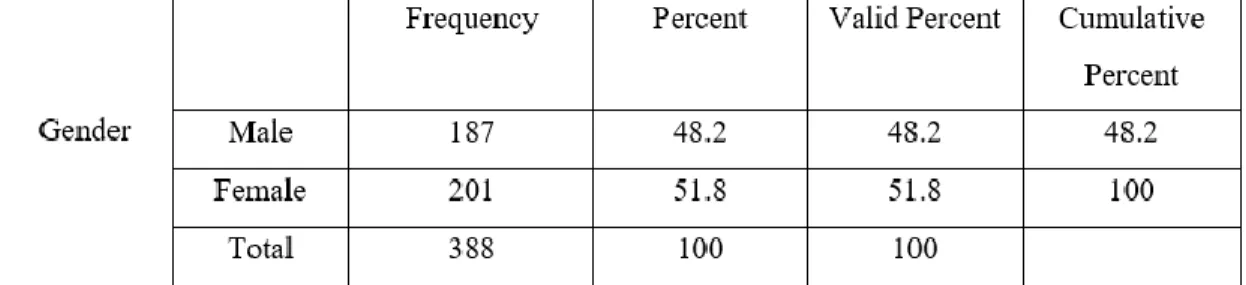
- Gender
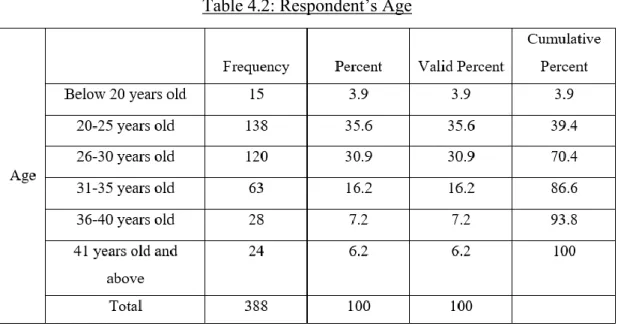
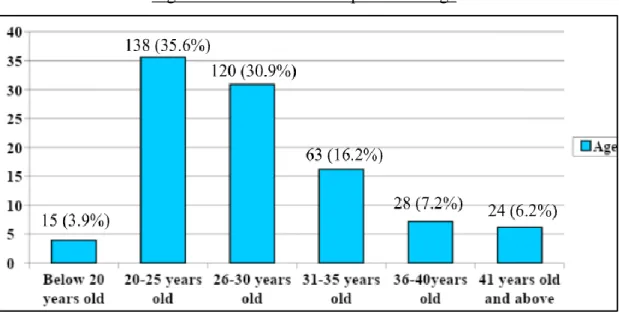
- Age
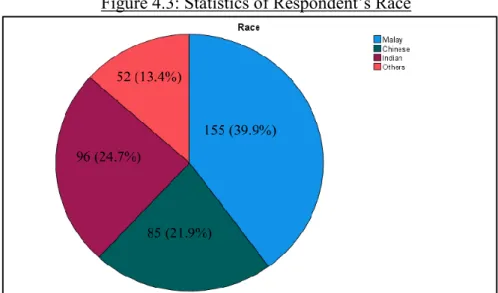
- Race
- Marital Status
- State
- Salary
- Working Experience
- Type of Accommodation Sector
- Central Tendencies Measurement of Construct
- Turnover Intention
- Perceived Risk
- Job Stress
- Job Insecurity
- Compensation
In the fourth chapter, descriptive analysis, scaling and inferential analysis are examined and justified. Based on Table 4.4 and Figure 4.4, we know that 57.7% of the survey respondents are single, representing the majority of the 224 respondents. Based on the results, there is a range of work experience of less than 1 year, which are the 65 respondents (16.8%).
Statement 'Are you often thinking about another job that will suit your personal needs?' (P1) which is the highest average value of 3.95, the majority of respondents agree with this statement. As we can see from the table, Q9 (I think that COVID-19 is more serious than other respiratory diseases.) has the highest mean value of 3.68, which indicates that it is strongly agreed by the majority of respondents. The lowest mean of perceived risk falls under "I lack control to protect myself and my loved ones against the Coronavirus". (T6), with a value of 2.67.
In addition, the statement "I'm afraid the coronavirus will only get worse with the passage of time." (Q3) received the highest standard deviation value of 1.279. The lowest value of the standard deviation of the perceived risk falls under "I have no control over myself and my loved ones against the coronavirus." (Q6), with the value of 1.044. 34;I feel more short-tempered at work." (Q7) has the highest average of 3.44, indicating that most respondents agree with this statement.
Scale Measurement
- Reliability Analysis
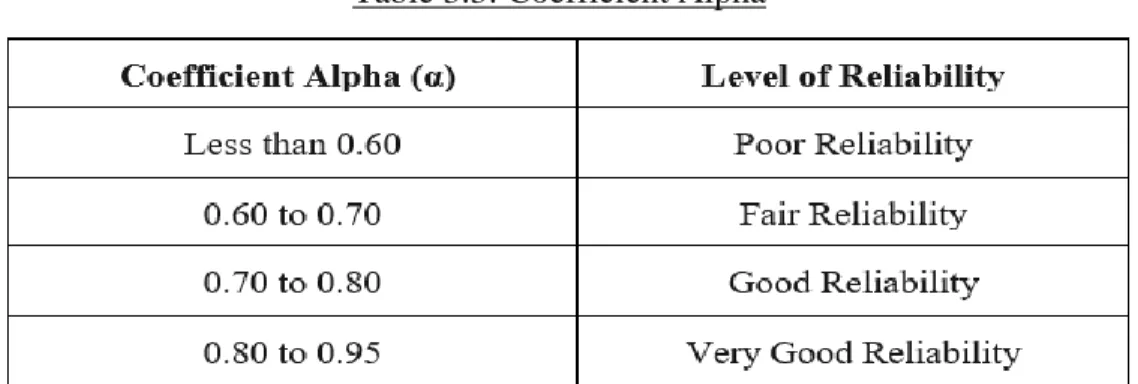
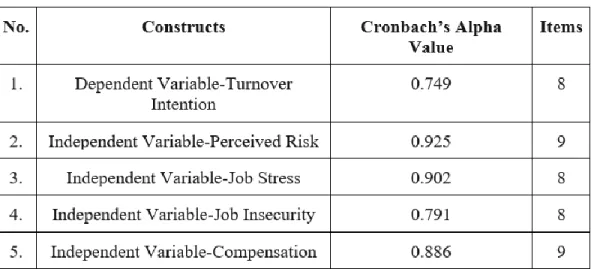
Cronbach's alpha for this variable is 0.801, which falls within the range of 0.80 to 0.95, indicating that the 8 items measuring turnover intention are highly reliable. Since Cronbach's alpha in this case is 0.806, which falls within the range of 0.80 to 0.95, the 9 items measuring perceived risk have very good reliability. Since the Cronbach's alpha value in this case falls within the range of 0.70 to 0.80, the 8 items measuring workplace stress have good reliability.
A Cronbach's Alpha of 0.649 is considered to be in the range of 0.60 to 0.70, indicating that the 8 items measuring job insecurity are reasonably reliable. Based on Cronbach's Alpha value of 0.894, which falls within the range of 0.80 to 0.95, the 9 items measuring compensation are highly reliable.
Inferential Analysis
- Multiple Linear Regression Analysis
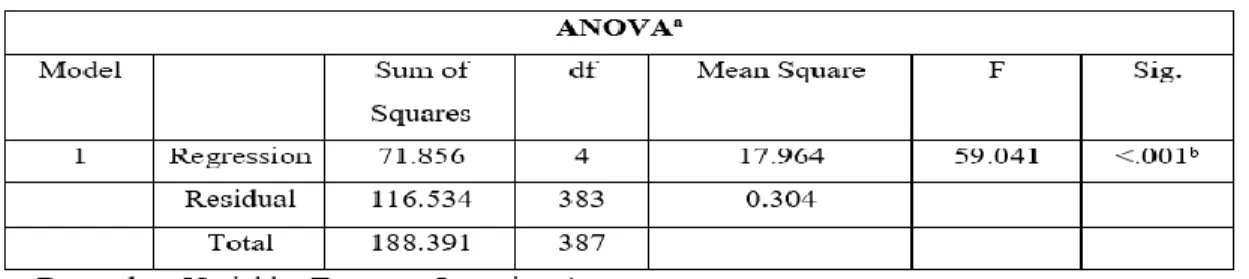
As a result, the independent variables (perceived risk and job stress) are significant in explaining the variation in turnover intention among Malaysian hospitality employees. Based on the result, perceived risk is significant to predict employee turnover intention because p value <0.001 is less than alpha value 0.05. Based on the result, job stress is significant to predict employee turnover intention because p value <0.001 is less than alpha value 0.05.
Based on the result, job insecurity is not significant to predict employee turnover intention because p-value 0.397 is greater than alpha value 0.05. Based on the result, compensation is not significant to predict employee turnover intention because p-value 0.745 is greater than alpha value 0.05. Work stress contributes the most to the change in turnover intention, because the beta value which is 0.534 for this independent variable is the highest compared to other independent variables.
This means that job stress makes the strongest contribution to explaining the variance in dependent variable, when the variance explained by all other predictor variables in the model is controlled. This suggests that job insecurity makes the third strongest unique contribution to explaining the variation in turnover intention. Out of all the independent variables in the model, job insecurity accounts for the third highest percentage impact on turnover intention.
Conclusion
71 . second strongest contribution when taking into account the variance described by all other independent variables in the model. Compared to the other 3 independent variables, job insecurity has the third largest beta value at 0.035. Compared to all other independent variables, compensation contributes the least to the variation in revenue intent, as the beta value of 0.014 is the smallest.
This shows that compensation makes the least contribution to explaining the variation in the dependent variables when controlling for the variance explained by all other predictor variables in the model.
DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
Introduction
Summary of Statistical Analysis
- Descriptive Analysis
- Summary of Central Tendencies Measurement
- Scale Measurement
- Summary of Inferential Analyses
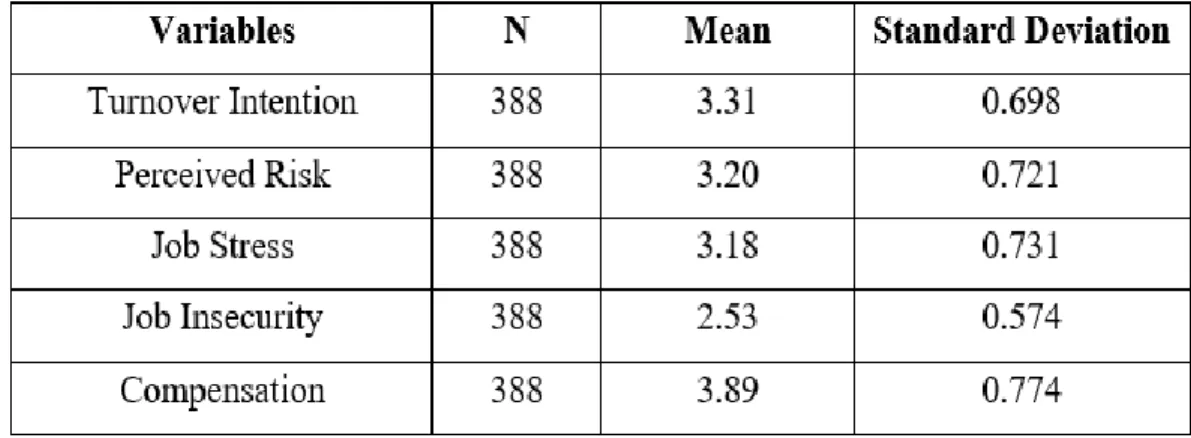
Based on the result shown above, compensation has the highest average score (mean) which is 3.89 with a standard deviation of 0.774. The variable with the second highest mean value is turnover intention (3.31) with a standard deviation of 0.698, followed by perceived risk (3.20) with a standard deviation of 0.721. Job stress has the fourth highest mean value of 3.18 with a standard deviation of 0.731 and the variable with the lowest mean value among these variables is job insecurity which is 2.53 with a standard deviation of 0.574.
Referring to the table above, turnover intention from the dependent variables has a very good reliability with an alpha value greater than 0.80. Based on the result above, the R-squared value obtained indicates that the turnover intention and the independent variables are positive and have moderate correlations as the R-squared value is 0.381. In contrast, 61.9% is unexplained, suggesting that other important variables are likely to contribute to turnover intention, which have not been adequately investigated.
From the results of multiple regression analysis, job stress has the largest standard coefficient beta value of 0.534, which means that this variable provides the most input to turnover intention. The second largest stand coefficient beta value is from perceived risk with 0.230, then followed by job insecurity with 0.035 and the smallest standard coefficient beta value of 0.014 for the variation of turnover intention is from compensation. Apart from that, perceived risk and job stress have a significant influence on Malaysian hospitality workers' turnover intention in post-pandemic situations, but job insecurity and compensation have no significant influence on it.
Discussion of Major Findings
- Perceived Risk
- Job Stress
- Job Insecurity
- Compensation
This clearly shows that the perceived risk of employees has a major influence on turnover intention in the hospitality industry. H2: Work stress has a significant impact on hospitality workers in Malaysia. revenue intent in the post-pandemic situations. Based on the results, job stress has a significant impact on the turnover intent of hospitality workers in Malaysia, as the p-value of <0.001 is less than the alpha value of 0.05.
The findings of Aguiar-Quintana et al. 2021) found that most employees have experienced significant work stress while working in the hospitality industry. The results also show that there are many employees in the hospitality industry who experience work stress at work, especially in the post-pandemic. Thus, in this context, work stress is most likely to influence employee turnover intention in the hospitality industry.
According to the results of this study, job insecurity does not significantly influence the turnover intent of hospitality workers in Malaysia, as the p-value of 0.397 is greater than the alpha value of 0.05. H4: Compensation significantly impacts revenue intent of Malaysian hospitality workers in the post-pandemic situations. The outcome of this study showed that compensation does not significantly affect the revenue intent of hospitality workers in Malaysia, as the p-value of 0.745 is greater than the alpha value of 0.05.
Implications of the Study
- Theoretical Implication
- Managerial Implication
Limitation of the Study
- Response Rate
- Language Proficiency Issues
- Limited Sampling Location
Most employees in the hotel industry have a low level of education because there are different departments within it and some focus more on skills than education. Because of this, they will not be able to understand the questionnaire, which is written in English. When we distributed questionnaires to the respondents, we found that when they answered the questionnaire, some of them would type the words on translation websites to understand what the questionnaire means.
In addition, some respondents have difficulty answering the questionnaires due to their limited English skills, which has made them bored when answering the questionnaires. In this research, questionnaires were only distributed in four states (Perak, Pahang, Johor and Selangor) due to time constraints and resource constraints. Thus, it is possible that the data obtained are insufficient to represent employee turnover intentions in the Malaysian hospitality industry.
Recommendations for Future Research
Conclusion
Does turnover intention mediate the effects of job insecurity and coworker support on social loss?. The impact of job insecurity and distributive injustice after COVID-19 on social stripping behavior among hotel workers: The mediating role of turnover intention. Stress and turnover intention among healthcare workers in Saudi Arabia during the time of COVID-19: Can social support play a role.
The impact of work environment, compensation and job satisfaction on turnover intention in public service agency. Identifying patterns of turnover intention among alabama frontline nurses in hospital settings during the covid-19 pandemic. Effect of job insecurity on job satisfaction and turnover intention of employees at Agro Tourism.
The impact of job stress and state anger on turnover intention among nurses during COVID-19: The mediating role of emotional exhaustion. Qualitative job security and turnover intention: The mediating role of basic psychological needs in the public and private sectors. The effect of compensation and career development on employee turnover intention in the culinary sector.
Questionnaire
Reliability Test for Pilot Study
Reliability Test for Actual Study
Multiple Linear Regression Analysis