PERCEIVED LEVEL OF STRESS AND ANXIETY AMONG CIVIL SERVANTS REMOTE WORKING DURING COVID-19. The thesis entitled: PERCEIVED LEVEL OF STRESS AND ANXIETY AMONG CIVIL SERVANTS WORKING REMOTELY DURING THE PANDEMIC COVID-19 is accepted by the Faculty of Management and. A Conceptual Framework of Perceived Levels of Stress and Anxiety Among Civil Servants in Telecommuting Arrangements in the Time of COVID-19 ..23.
Choi, 2018). However, the majority of government organizations had to close due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The perception of stress and worry among government employees working virtually during the peak of the COVID-19 epidemic, especially during the first six months, is currently unknown. This study focused on the levels of perceived stress and concerns among government employees regarding remote work accommodations during the first six months of the COVID-19 epidemic in the NCR.
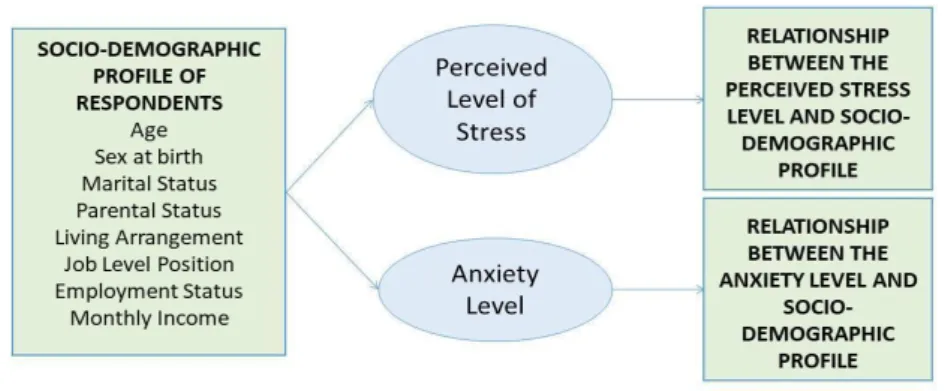
Conceptual framework on perceived level of stress and anxiety among government employees on telework arrangements during COVID-19 pandemic. According to a study of the relevant literature, several government workers claim to have experienced increased levels of stress and anxiety while working virtually during the first six months of the COVID-19 disaster. Some socio-demographic characteristics, including age, sex at birth, marital status, parental status, living arrangement, employment status, job level position and income, appear to be associated with the perceived level of stress and anxiety of government employees on remote work arrangements during the COVID-19 pandemic.
H1: There is a relationship between the perceived level of stress and the socio-demographic profile of the respondents.
METHODOLOGY
Stratified random proportional sampling was the sampling method for the study, where the sample size for each stratum was proportional to the population size of the strata when examined across the population. The memorandum describes the purpose, importance, and potential advantages of the research to the office and its staff. After receiving the request, participants' names were randomly selected along with their email addresses and added to a Google contact list for the purpose of sending survey offers, obtaining electronic informed consent, and providing links. of the survey.
The researcher did not retain personal information such as the identity of the subjects to maintain privacy and security and to comply with the Data Privacy Act. Using Google's cloud services, all research data is stored in an automated version that is password protected. At the end of the survey time, survey forms that were partially completed or incomplete were removed from the study and considered abandoned.
The scholar chose to use "within the first 6 months of the COVID-19 pandemic" instead of "within the past month." Additionally, during ethical approval, the committee recommended that the questionnaires be validated by an expert to determine whether they can be used in Philippine settings. A selection of 12 previous studies was reviewed and evaluated as part of a comprehensive assessment of PSS-10 psychological data. One of the most popular medical self-report measures for determining the intensity of anxiety disorders is the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Assessment (GAD-7).
The researcher pilot tested the surveys with respondents who shared the same characteristics as the real respondents of the study, but who were not part of the sample group, to verify the PSS-10 scale and GAD-7 for use in this study . The aims, purposes, history of the study, and duration of the study were all included in the informed consent. Finally, selecting the accept option on the automated written consent functioned as participants' consent to participate in the study.
Participants were free to leave the study whenever they wanted without any consequences. The researcher did not store any personal information such as identity. Aside from possible mental discomfort that subjects may have felt while responding to delicate or confidential survey questions, there were no known dangers associated with participating in the study. The data and sources will be kept by the scientist for at least ten years after the research. study is finished. Data is completely deleted. The general public will have access to the research report, especially the research results, through online publication and replication in print, electronic or digital formats.
Socio-Demographic Characteristics
One hundred sixty-three respondents (94.2% of the target sample size of 173) completed the online survey, compared to 10 (5.8%) who declined to participate. The presentation of the findings, the analysis and the explanation of the data from the online survey were all covered in this chapter. The results are presented in four sections: findings related to the sociodemographic characteristics of respondents, findings from the PSS-10 Scale, findings from the GAD-7 Assessment Tool, and findings from hypothesis testing and analysis.
A household survey in Spain, which included a range of socio-demographic profiles, was used to determine levels of tension and anxiety during the lockdown period. The results showed that people under 40, particularly those under 25, women reported higher levels of stress (25.6%) and anxiety (19.9%) during confinement and were associated with disruptive biological , social and economic factors (Odriozola-González et al., 2020), while living with two to four people was associated with increased stress and anxiety according to a published scientific journal (Albert, 2015). Socio-demographic profiles of civil servants according to age group, sex at birth, marital status, parental status, living arrangements, employment status, workplace and income range.
Renting an apartment/apartment property with a family 22 13.5 Renting in a student dormitory/pension alone 6 3.68 Renting in a student dormitory/pension with.
Perceived Level of Stress
A similar finding was made in a China-based epidemiological study, with 38.1% of participants reporting moderate to severe stress levels. A survey of stress levels among nearly 10,000 workers from 78 countries, including the European Union, the United States, Cyprus, Spain and Columbia, found that the majority of subjects (55.9%) reported moderate stress levels, while 11% reported severe reported stress levels. . While these studies support increased stress levels, a Malaysian study conducted about two months after COVID-19 was declared a pandemic found that anxiety symptoms increased more than stress indicators.
GENERAL ANXIETY DISORDER ASSESSMENT (GAD-7)
This result is consistent with the scientific report of the World Health Organization that during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, the global prevalence of anxiety (whether mild, moderate or severe) and depression increased dramatically by 25%. In contrast, Wong et al. 2021) assessed the mental health status of Malaysian adults using different time frames spanning from May 2020 to September 2020, with results showing that the prevalence of anxiety increased significantly as the pandemic progressed. In another study conducted by Wang (2021) on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the physical and mental health of Asians, the three countries with the highest anxiety scores were Thailand (mean 18.66, SD 5.98), Pakistan (mean 8.23, SD 9.43) and Malaysia.
Added to this are results from a previous heart rate study conducted in the US, where 41.1% of participants reported experiencing moderate to severe. In Germany and Switzerland, another study was conducted to validate the impact of implementing the COVID-19 lockdown on their populations, especially their workforces. Forty percent (40%) of the 2,118 employees who took part in the research reported that their living conditions had worsened, making them more susceptible to psychological problems such as serious problems.
Hypothesis Testing and Interpretation