David Bourgeois and was originally published in 2014 as part of the Saylor Foundation Open Book Challenge. In keeping with its open textbook roots, many of the updates have come from the community of instructors and practitioners who are passionate about information systems.
Globalization and the Digital Divide
The Ethical and Legal Implications of Information Systems
Trends in Information Systems
In this book, you will be introduced to the concept of information systems, their application in business, and how information systems can be used to gain competitive advantage. This chapter provides an overview of information systems, including the history of how information systems got to where they are today.
WHAT IS AN INFORMATION SYSTEM?
What Is an Information System?
As previously discussed, the first three components of information systems—hardware, software, and data—all fall under the category of technology. Do you agree that we are in a post-PC phase in the evolution of information systems?
Hardware
CPU processing power increases at an astonishing rate (see Moore's Law sidebar). Moore's law has been generalized to the concept that computing power will double every two years for the same price.
Motherboard
Software
The operating system first loads the computer with a startup program, and then manages all programs on the computer, including both programs native to the operating system, such as file and memory management and application software. Companies took the safe route, investing in Microsoft's operating system and Microsoft's software/applications. The most popular spreadsheet package is Microsoft Excel, which saves its files in XLSX format.
Many times a subsequent release of an operating system will include these utility functions as part of the operating system itself. For example, in the terms of the Microsoft Office software license, you will find the following statement: "This software is licensed, not sold. You may not make illegal copies of the software, and you may not use it to do anything illegal.
In the 1990s the need to bring an organization's information back under centralized control became more apparent. All aspects of the organization are affected as legacy systems are replaced by the ERP system. Historically, for software to run on a computer an individual copy of the software had to be installed on the computer.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
For example, if you access your e-mail through your web browser, you are using a form of cloud computing if you use Google Drive's applications. Although these are free versions of cloud computing, there is big business in delivering applications and data storage over the web.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Data and Databases
Each table has a set of fields that define the structure of the data stored in the table. Our solution is to use the student ID as the primary key of the STUDENT table. For example, to track grades, a simple (and wrong) solution might have been to create a Student field in the COURSE table and then simply list the names of all the students there.
Date/Time: a special form of the number data type that can be interpreted as either a number or a time. For example, if we want to perform mathematical operations on one of the fields, we must be sure to tell the database that the field is a numeric data type. When designing a database, a "data dictionary" is created to hold the metadata, defining the fields and structure of the database.
Many times, data visualization is the first step towards a deeper analysis and understanding of the data collected by an organization. The concept of the data warehouse is simple: extract data from one or more databases of the organization and load it into the data warehouse (which is itself another database) for storage and analysis. Once all data is identified as consistent, an organization can generate "one version of the truth."
Networking and Communication
The Internet became commercial in 1994 when technology began to permeate all areas of the organization. It was from ARPA, now called DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency), that the Internet first emerged. As the use of the Internet has grown, the number of IP addresses required has increased to the point where the use of IPv4 addresses will be exhausted.
Much to the surprise of engineers, the early popularity of the Internet was fueled by the use of electronic mail (see next sidebar). The World Wide Web gained even more steam in 1993 with the release of the Mosaic browser which allowed graphics and text to be combined as a way to present information and navigate the Internet. In the 1980s and early 1990s, the Internet was managed by the National Science Foundation (NSF).
Beginning in the early 2000s, major changes occurred in how the Internet was used. The Internet was originally designed as a way for the Department of Defense to manage projects. Services such as e-mail, voice and video, file transfer and the World Wide Web all run over the Internet.
Information Systems Security
Two of the more common ones are: access control list (ACL) and role-based access control (RBAC). The organization should make a complete list of all the information that needs to be backed up and determine the best way to back it up. Physical security is the protection of the actual hardware and network components that store and transmit information resources.
A good information security policy sets guidelines for employees' use of the company's information resources and provides the company with recourse in the event that an employee violates a policy. For example, if the organization is a university, it must be aware of the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA), which restricts access to student information. One of the first questions an organization should consider is whether mobile devices are allowed in the workplace at all.
Theft of mobile devices (including laptops in this case) is one of the primary methods used by data thieves. One of the oldest methods of encryption was used by Julius Caesar and involved simply shifting the text by a certain number of places in the alphabet. For example, if key = COD, the first letter in the cipher is shifted by 2 characters (because "C" is 2 letters behind the letter "A"), the second letter is shifted by 14 letters (O is 14 letters behind "A"), and the third letter is shifted by 3 letters (D is 3 letters behind "A").
INFORMATION SYSTEMS FOR STRATEGIC
ADVANTAGE
Does IT Matter?
- Mismeasurement of outputs and inputs 2) Lags due to learning and adjustment
In 1991, Erik Brynjolfsson wrote an article, published in Communications of the ACM, entitled "The Productivity Paradox of Information Technology: Review and Assessment". After reviewing studies on the impact of IT investments on productivity, Brynjolfsson concluded that the addition of information technology to the business had not improved productivity at all. Two years later in 2003, Harvard professor Nicholas Carr wrote his article "IT Doesn't Matter" in the Harvard Business Review.
In this article, Carr asserted that as information technology has become ubiquitous, it has also become less differentiated, much like a commodity. According to Carr, all information technology was the same, providing the same value regardless of price or supplier. A year later he was interviewed by CNET on the topic "IT still doesn't matter". Click here to watch video of Carr being interviewed about his book on CNET.
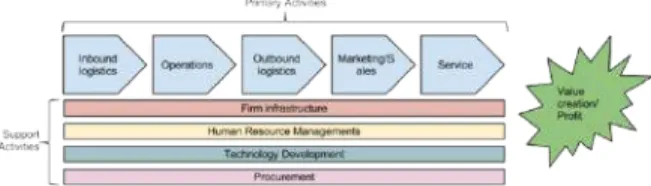
Probably the best thing that came out of the article and the subsequent book were the discussions about the place of IT in business strategy and. In his book Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance, Michael Porter writes that a company is said to have a competitive advantage over its rivals when it is able to sustain profits that exceed the industry average. According to Porter, there are two main methods of gaining competitive advantage: cost advantage and differentiation advantage.
The Value Chain
Business Processes
In the context of information systems, a business process is a set of business activities performed by human actors and/or the information system to achieve a specific result. Diagrams have been used as business process modeling tools in the information systems field. The most commonly used business process diagramming tools are Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN), Data Flow Diagram (DFD), and Unified Modeling Language (UML).
Business process management (BPM) can be thought of as a deliberate effort to plan, document, implement and distribute an organization's business processes with the support of information technology. When an organization implements processes supported by information systems, it can strive to implement best practices for that class of business processes. Business Process Renovation (BPR) does not just mean taking over an existing process and automating it.
However, today many BPR principles are incorporated into companies and are considered part of good business process management. Through business process management, organizations can empower employees and leverage their processes for competitive advantage. What are three examples of business processes from a job you've had or an organization you've observed?
The People in Information Systems
The first group of people to consider plays a role in the design, development and construction of information systems. Almost everyone involved in the creation of information systems has at least a bachelor's degree in computer science or information systems, although this is not necessarily a requirement. In general, the analyst must have a good understanding of the business itself, the purpose of the business, the business processes involved and the ability to document them well.
The analyst identifies the various stakeholders in the system and tries to involve the right people in the analysis process. Before analyzing the problem or care system, the analyst must a) clearly identify the problem, b) get approval for the project, c) identify the stakeholders, and d) develop a plan to monitor the project. It is important to realize what role the users play in the analysis of the system.
Once the requirements are determined, the analyst begins the process of translating these requirements into an information system design. Once the solution is selected, the analyst creates a detailed document describing the new system. This new document requires the analyst to understand how to speak in the technical language of system developers.