It focuses on HR practices and their application in South Africa at the University of KwaZulu-Natal (UKZN), one of Africa's leading higher education institutions as well as one of the top 3% of universities worldwide. The aim of the study was to examine the implications of Human Resource practices on employee engagement at the University of KwaZulu-Natal.
Introduction
Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the implications and influences that a comprehensive set of HR practices can have on organizational commitment in tertiary education institutions. This study seeks to investigate the influence that HR practices can have on the levels of employee engagement at UKZN.
Background of the study
Looking at the history of the UKZN merger, as well as the ongoing growth and changes in student and staff numbers, the need to manage human resources and apply best human resource practices is clear. Moreover, changes in management, in addition to the restructuring of faculties as well as the changes to the University before and after the 2004 merger to date (UKZN, 2015), demand effective human resources.
Problem statement
Therefore, this study will examine HR practices at the UKZN and their effects on employee engagement (organizational commitment). This study can help clarify the impact that HR practices can have on the level of employee engagement at UKZN, at educational institutions in South Africa, as well as at institutions that have undergone restructuring globally.
Purpose of the study
Aim of study
Research objectives
Research questions
Significance and scope of the study
Justification/ rationale of the study
The absence of this study would result in a lack of understanding of how HR practices at UKZN affect organizational commitment. Thus, a gap would remain in contributing knowledge about how and whether HR practices have any impact on organizational commitment in South African higher education institutions.
Limitations of the study
Furthermore, it can benefit employees by making them aware of the various discretionary and transactional HR practices as well as helping them know which HR practices can effectively help them maintain or increase their employee engagement. The study may also increase the knowledge and awareness of employees, HR managers and relevant authorities as to whether HR practices implemented at UKZN have any impacts or implications on the level of organizational or job engagement at UKZN, as well as generally at higher education institutions in the South. Africa and globally.
Ethical considerations
Therefore, extending the study to other schools and faculties in UKZN as well as other HEIs would enable generalization of the findings to other samples as well as provide a comparative analysis of the findings (Gavino et al., 2012).
Overview of the chapters
This section discusses the summary of key findings, linking the study's findings to its objectives and literature. To conclude the study, recommendations for future research and the conclusions of the study are also presented here.
Introduction
History of Human Resource Management
Moreover, Armstrong and Taylor (2014) argue that HRM was conceived in the 1980s and took over human resource management to a significant extent. This is a belief founded by Likert and McGregor in the early 1960s that asserts that people are critical in examining organizational behavior, and that individuals should be treated as both accountable and progressive beings (Armstrong & Taylor, 2014 ).
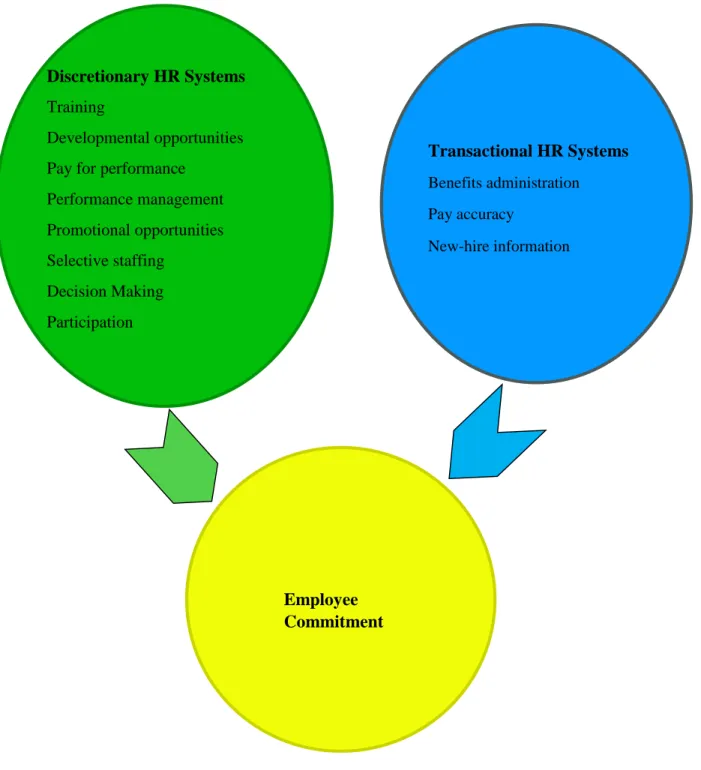
Discretionary and Transactional HR Practices
Types of Discretionary HR systems
Begum and Sarker (2014) claim that there is a positive relationship to work environment, benefits, organizational citizenship behavior (OCB) as well as promotional opportunities. Torka, Schyns, and Looise (2010) pointed out that the relationship between participation quality and commitment has received relatively insufficient consideration in the industrial relations (IR) as well as the HRM literature.
Types of Transactional HR systems
According to Gallagher and Sias (2009), employee socialization research conceptualizes new hires as people who face uncertainty and seek information to reduce ambiguity. Therefore, new employees are conceptualized as a source of ambiguity and old employees as those who face uncertainty and pursue information to reduce uncertainty (Gallagher & Sias, 2009).
Organisational Commitment
Therefore, it is argued that there are three different forms of organizational commitment (Allen & Meyer, 1990) known as “Affective commitment, which represents workers who have a high degree of emotional attachment and feel integrated into and identify with the organization; Normative commitment, where employees show their moral, ethical commitment to the organization, where their emotional attachment is motivated by the employers' regular payment of wages; as well as Continuance commitment, which is driven by the motivation to avoid imminent costs associated with a possible change of employer and where the employees' commitment increases as they increasingly see the costs of such a change, e.g. salary loss, relocation, etc. " (Kanning & Hill, 2013, p.1-2). In addition to what other researchers and pioneers in the field of organizational commitment has stated, Meyer and Herscovitch (2001) conceptualized commitment as a force that binds a person to an action relevant to a specific goal.

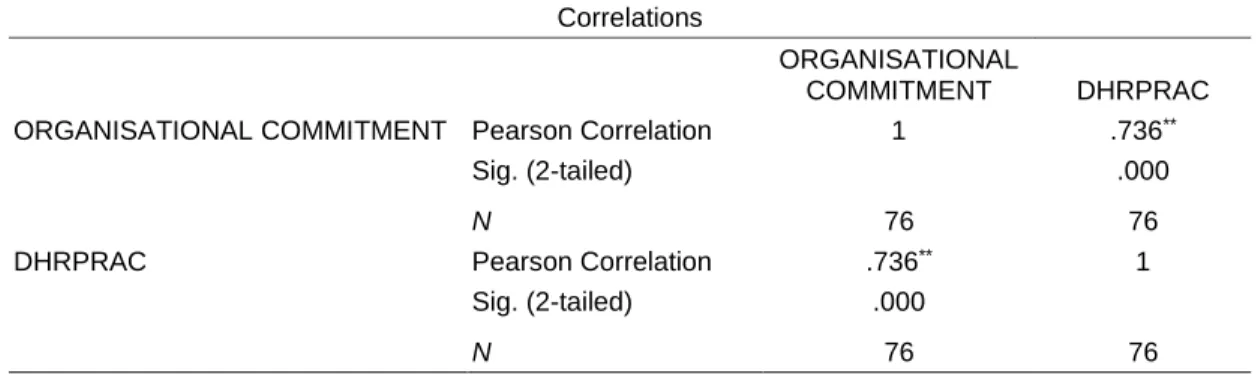
HR Practices and Organisational Commitment
Developmental HR practices (practices concerned with progress, growth and performance to help employees achieve greater levels of work, for example training and internal promotion) are advocated for promotion (Kooij et al., 2010). Moreover, it provides an understanding of how HR practices relate to the performance of the organization as well as to the commitment of employees.
Theoretical Framework
Social Exchange Theory (SET)
Moreover, the social exchange theory also suggests that employees' interpretations of human resource practices especially affect their affective commitment as well as job satisfaction (Kooij et al., 2010). Hence, as the current study is a relational study as well as a behavioral study, as it looks at the implications of HR practices on employee commitment.
Conceptual Framework
Discretionary and Transactional HR Practices Model
This model also posits that an awareness of human resource systems that are more significantly related to employee behavior, such as commitment and motivation, would help workplace decision makers motivate their workers by increasing their commitment to vital human resource systems. when they communicate and interact with workers (Gavino et al., 2012). The study will use discretionary and transactional HR systems to show how different HR systems can affect employee engagement in organizations.
Conclusion
This model will help identify the extent to which each HR system affects or has implications for organizational behavior such as workplace engagement, focusing on the implications of HR systems in higher education institutions.
Introduction
Research design and Sampling strategies
Research approach/ paradigms
Research setting/ Study site
Target population
Sample size
Therefore, the ideal sample size depends on the parameters of the phenomenon being studied, such as the rarity of the event or the projected size of differences in outcome between the intervention and control groups (Marshall, 1996). Consequently, the sample size was adequate as it adequately answered the research questions and established the trends and relationships, which are crucial for quantitative studies.
Sample
Data collection and Data instruments/ Measurements
Data collection
The study had zero to very little estimated risk and/or discomfort as the subject of the study did not delve into deeply personal or disturbing events. Therefore, the study can inform HR departments, the College and School at which the study was conducted, in addition to government and higher education institutions, in creating and implementing HR practices and policies that are effective for productivity, reduced employee turnover, and as well as increasing substantial overall organizational commitment among employees.
Measurements
The scale includes fifteen items that measure "(1) the extent to which an individual identifies himself/herself as being involved in a specific organization; (2) a willingness to exert considerable effort on behalf of the organization; and (3) a strong desire to continue membership in the organization". Therefore, the Likert/summary scale was used in the questionnaires, since according to Welman and Kruger (2002, p.150), "the Likert scale can be used for many-.
Conclusion
Introduction
Thus, the better the perception of the Discretionary HR practices, the greater the employee's commitment to the organization. Section C of the questionnaire was based on the Discretionary HR practices and aimed to achieve the second objective of the study.
Recoding of variables
Statistics tests
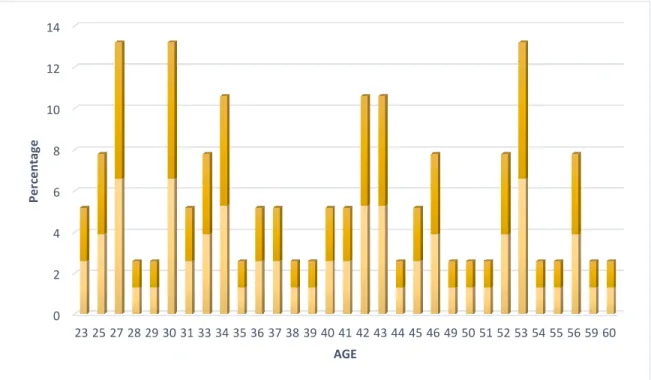
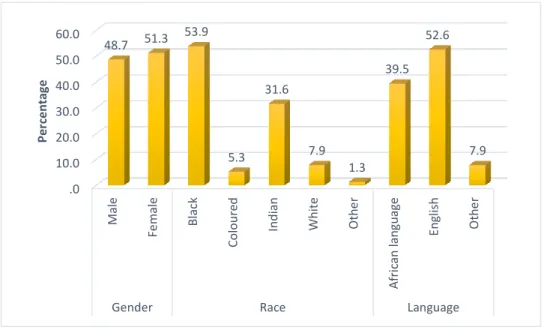
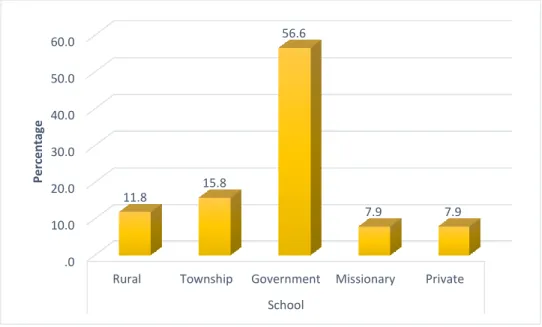
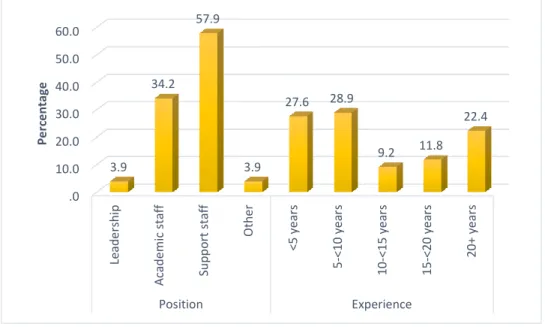
Section A: Demographic sample
Descriptive Statistics
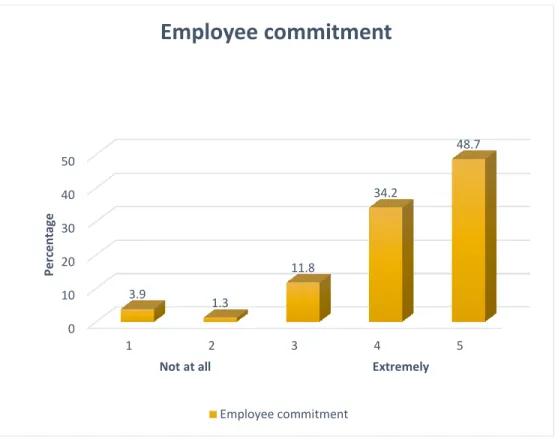
Section B: Employee Commitment
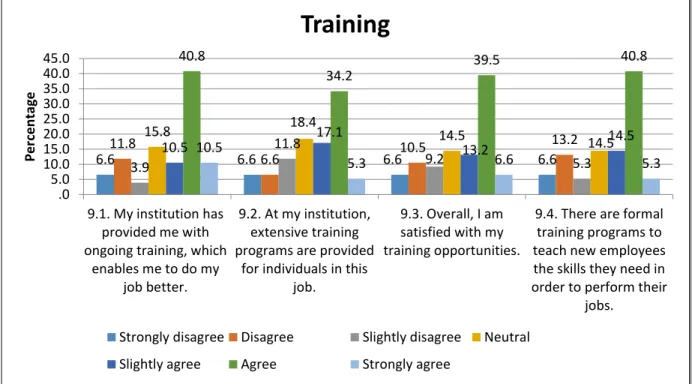
Section C: Discretionary HR Practices and Organisational Commitment
Section D: Transactional HR Practices and Employee Commitment
Section E: Occupational Commitment Questionnaire (OCQ)
Section F: Objective Four: Demographics and Employee Commitment
Conclusion
This chapter presented the demographic and descriptive statistical interpretations and analyzes of data collected at UKZN, School of Management, Information Technology and Governance (Westville Campus). Furthermore, according to the researcher, the clarification and analysis of the data collected during the study showed and proved the effectiveness of the research design and the instruments used as a design, along with the instruments helped to answer the research questions and fulfill the goals and objectives. of the study.
Introduction
Overview of the study
The fourth chapter discussed the data analysis, the various tests used in the data analysis and the findings of the study according to the objective of the study to ensure a clear and systematic presentation of the research findings. Here the conclusions about the study were drawn and the objectives of the study were discussed and achieved.
Discussion
On the other hand, 5 - < 10 years of work experience at UKZN accounted for 40.2% of the variance in commitment. Our findings show that age accounted for 31.2% of the variance in the relationship between selective staffing and engagement.
Recommendations
Practices such as decision-making and training influence how employees behave and contribute extra-role behaviors when employees feel that the organization is a good place to work (Gavino et al., 2012). Therefore, it is recommended that organizations should concentrate more on HR practices that provide more benefits and investments to employees.
Conclusion
Training, development opportunities and decision-making, as well as benefits enrollment, information provided by the HR department and salary accuracy are the highest discretionary and transactional HR practices at the University of Kwazulu-Natal, School of Management, IT & Governance, College of Law and Management Studies respectively , (Westville Campus). Therefore, HR practices have significant consequences for employee behavior, such as employee engagement in higher education institutions.
Frequency and percentage tables
It would take very little change in my current circumstances for me to leave this institution. Often, I find it difficult to agree with this institution's policies on important issues concerning its employees.
Gatekeeper letter
Ethical clearance letter
Informed consent form
Your participation in the study is voluntary and by participating you give the researcher permission to use your answers. You can refuse to participate or withdraw from the study at any time without negative consequences.
Questionnaire
In the positions I have held at my institution, I have often been given additional challenges. I would accept almost any kind of job to continue working at this institution.