The three mandatory EPS disclosures - Basic EPS, Diluted EPS and Headline EPS - are discussed to determine their information content and reporting framework. The survey of the attitudes of the preparers of corporate reports on various matters regarding EPS revealed that preparers of annual reports consider Headline EPS to be the most important earnings-based performance measure, and the adopted headline earnings definition as appropriate.
5.14 EPS from continuing operations 79
Background to the research topic
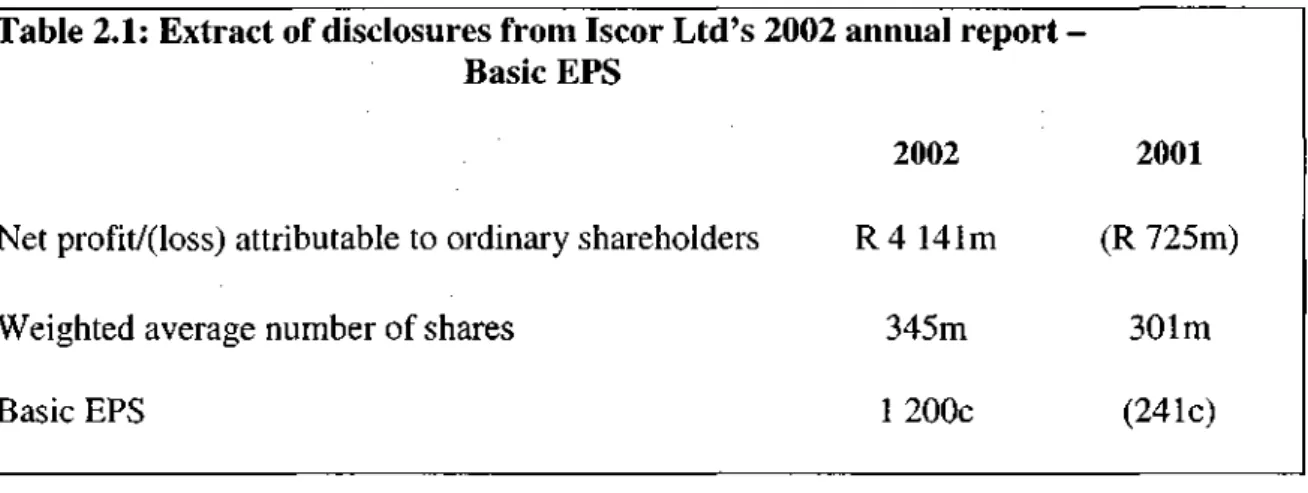
Basic EPS is defined as net profit for the year (after outsider interest, preference dividends and extraordinary items) divided by the weighted average number of ordinary shares issued during the year (South African Institute of Chartered Accountants (SAICA) 1998a: 11 ). If a company has such unusual or irregular items that affect its profit or loss for the period, the Basic EPS number will be misleading as it is not a fair representation of the company's income from ordinary trading activities.
Problem definition
1 - Key Earnings (SAICA 2002), in December 2002, the only accounting statement in EPS The title was an accounting opinion, AC 306 - Key Earnings: Effect of Issuing AC 103 (Revised) on the Calculation and Disclosure of Earnings per Share ( SAICA 1995b). More companies are now disclosing other non-mandatory EPS measures, such as cash flow per share and diluted EPS.
Research objective and approach
The discussion is also intended to provide knowledge for the research conducted in the second part of the study. In discussing Headline EPS, the research shows how Headline earnings have developed in the UK and why this is so necessary in the current reporting climate.
Importance of the research
This provides evidence of whether companies are complying with accounting regulatory bodies' disclosure requirements and whether companies are correctly applying the definition of core earnings. The research also aims to provide the standard setters, both domestic and international, of the regulatory bodies responsible for the statements of Accepted Accounting Practice (GAAP) information about the perceptions of the company's management regarding the definition and disclosure of information. of the main profits.
Organisation of the study
This chapter discusses the research design, survey objectives, target groups, data collection techniques and other related matters. This chapter presents the results of a survey of financial statements on companies' compliance with EPS disclosures.
Introduction
AC 104 - Earnings per share
- Background and objective
- Basic EPS
- Objective
- Calculation
- Basic EPS as a measure of performance
- Diluted EPS
- Objective
- Calculation
- Diluted EPS as a measure of performance
- Disclosure requirements for Basic and Diluted EPS
Diluted EPS is calculated by dividing diluted earnings by the potential weighted average number of shares that may be issued in the future. S Basic and diluted EPS must be disclosed on the face of the income statement with equal importance (SAICA 1998a:48).
Headline EPS
- Background
- AC 306 - Headline EPS
- Circular 7/2002
- UKSIP Headline earnings
- Background
- Development of a better measure of performance - Headline earnings
- Sustainable/maintainable earnings
- A factual "Headline earnings" measure
- Headline earnings definition
- Headline EPS illustrative example
- Adoption of Headline EPS in SA
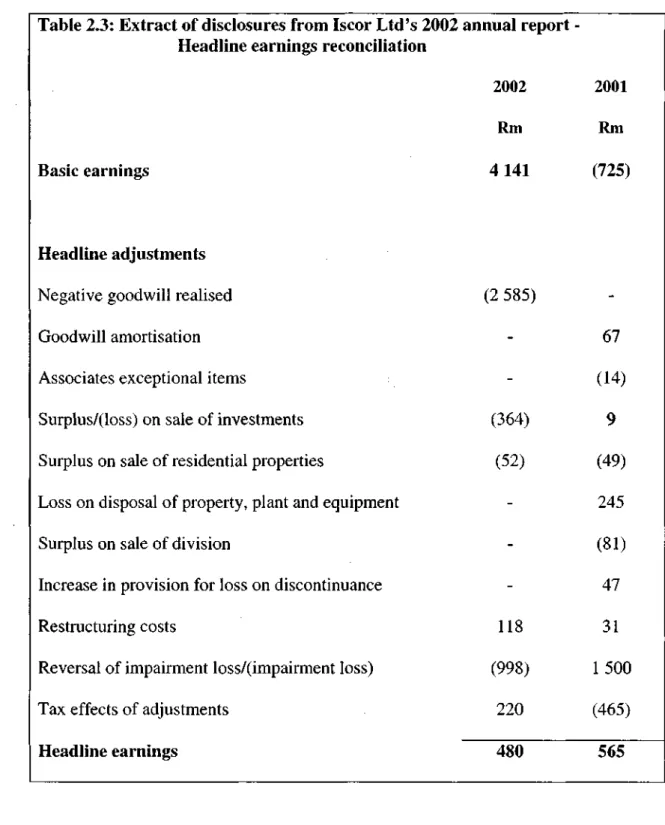
Gains or losses from the discontinuance itself must be excluded (SAICA 1995b:ll{b}, SAICA's Discontinued operations' include operations that will be discontinued in the future SAICA 2002:1). Pension fund costs related to continuing operations must be included in the main profits (SAICA 1995b:ll{h}, SAICA 2002:27).
Voluntary EPS measures
- Cash flow per share
- Diluted Headline EPS
Although Headline EPS was developed in the UK, Headline EPS is not a mandatory disclosure for UK companies (Davies 1998:1343). To overcome this, some companies adjust headline earnings to diluted earnings and report diluted headline earnings per share.
Recent developments
Basic earnings are used as a starting point with adjustments for non-cash items such as deferred tax, depreciation, amortization and gain/loss on disposal of fixed assets. Net cash flow from operating activities, according to the Statement of Cash Flows, is used as a starting point with deductions for taxes, preferential dividends and minority shareholders' interests.
Summary
Introduction
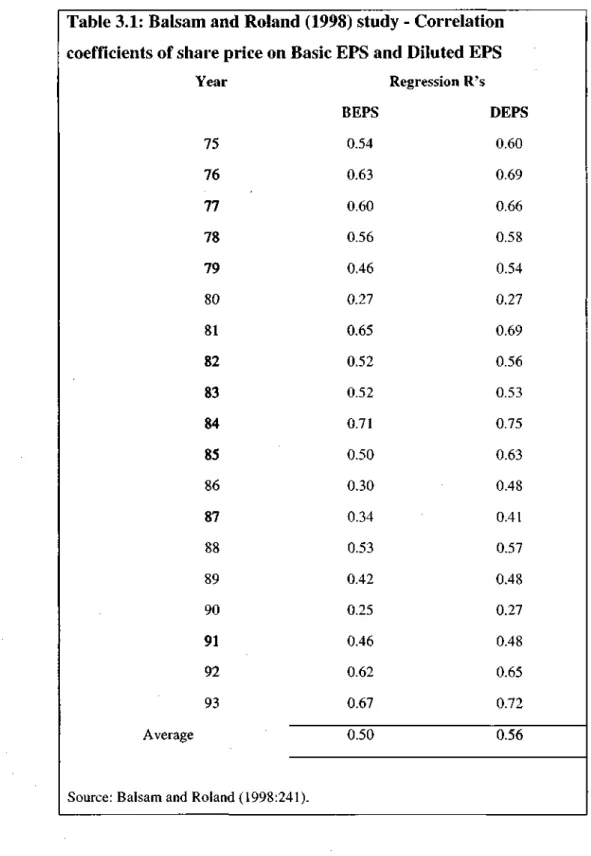
Correlation between EPS and share prices
- Hemus and Mildenhall - 1994
- Demsetz -1995
- Balsam and Roland - 1998
- De Villiers et al - 2003
De Villiers et al found that both core EPS and cash flow per share had an effect on stock prices. However, the study found that underlying EPS had a higher correlation with stock prices than cash flow per share.
Use of EPS in financial analysis
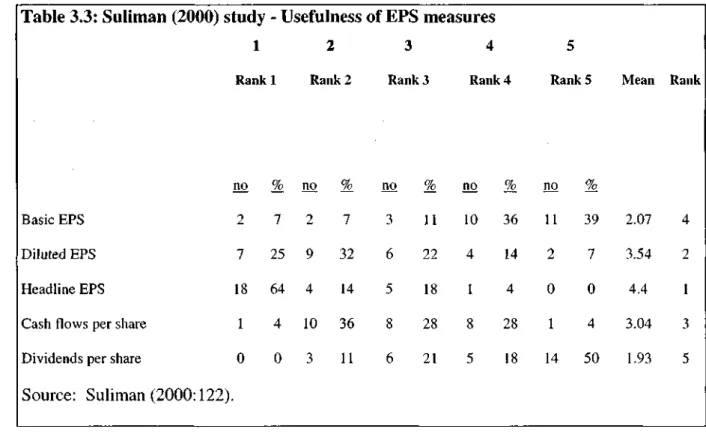
The denominator used for Cash Flow per share was the same as for Basic EPS. Diluted EPS is considered more useful than Basic EPS and Cash Flow per share.
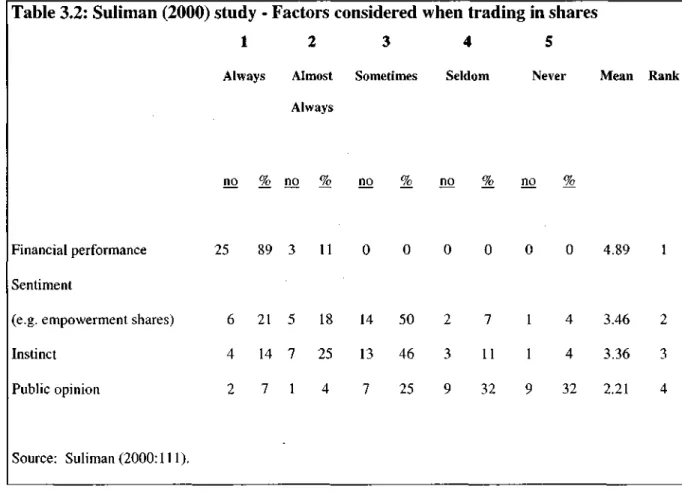
Susceptibility of earnings to manipulation
SAIGR also believes that companies attempt to manipulate earnings as they state that companies work around accounting standards to achieve desired results (SAICA 2003b).
Cash flow per share
Belamant and De Klerk (2002) also believe that Cash flow per share is a better measure than the earnings-based measures. Since cash flows cannot be manipulated by different accounting treatments, they believe that cash flows per share is better than EPS.
Headline EPS
Headline EPS therefore meets the requirements of both authors and users of annual reports. However, Damant argues that the value of a firm depends on the excess wealth created, including profits and losses on trading activities and capital assets (Damant 2002:3).
Presentation and disclosure
- Holgate and Kirby - 1994 .1 Motivation for the survey
- Hattingh - 1999a .1 Motivation for the survey
Since Headline EPS is a measure of trading performance, it cannot in itself be a measure of value. Although UKSIP 1 called for the publication of Headline EPS, most companies in the UK had chosen not to publish Headline EPS.
Summary
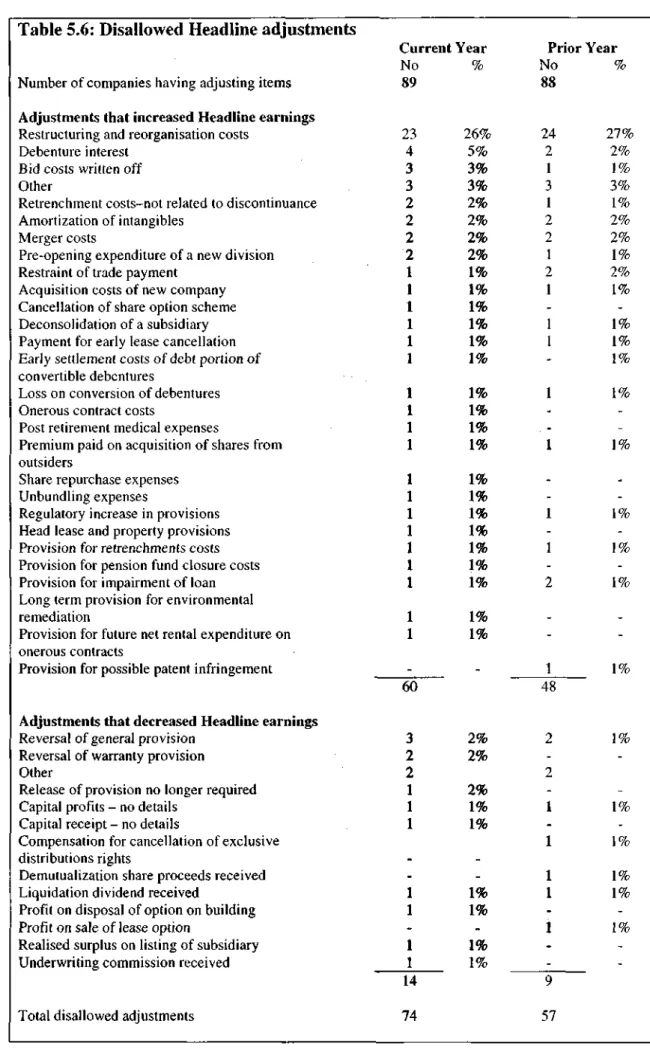
With regard to "restructuring costs", Hattingh states that AC 306 para, {fjallows the reversal of a "provision" for restructuring costs. The study also found that the majority (75%) of companies disclosing Headline EPS had violated the Headline earnings definition.
Introduction
Research design
As this study seeks to obtain data on/from a large number of companies and draw inferences based on sample findings, the statistical study method is most appropriate for purposes of this study.
Data collection techniques
Financial Statement survey
- Survey objective
- Population definition
- Annual reports
- Disclosure checklist
- Testing of the checklist
- Data analysis
The company reports from 2002 have been selected for inspection because this was the last reporting year at the time the annual accounts audit was conducted. Because the essence of this research was on companies' compliance with relevant disclosure requirements, the disclosure requirements from the relevant statements were used as a basis for drawing up the checklist.
Survey of company managements' EPS perceptions
- Survey objective
- Data collection method
- Population definition
- Questionnaire design
- Testing of questionnaires
- Mailing
- Response rate
- Data analysis
The covering letter was printed on University of Natal stationery, which implied university approval of the study. The cover letter and final questionnaire were sent to each of the selected companies in March 2001.
Summary
Introduction
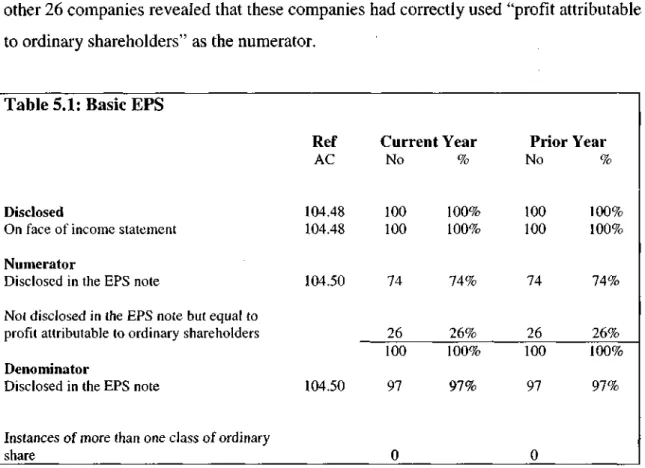
Basic EPS
- Basic EPS survey results
- Summary on Basic EPS disclosures
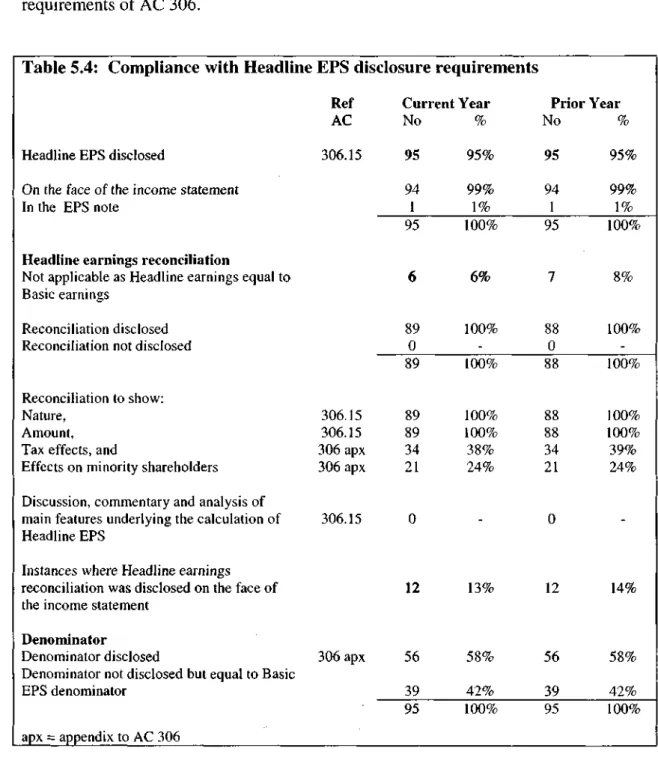
Other EPS disclosures (Diluted and Headline) that make up the EPS note for the three companies that did not disclose the denominator were examined to see if the Basic EPS denominator could be determined from them. One company disclosed the number of shares used in the calculation of core EPS and a recalculation of Basic EPS for this company confirmed that this was the denominator used for Basic EPS.
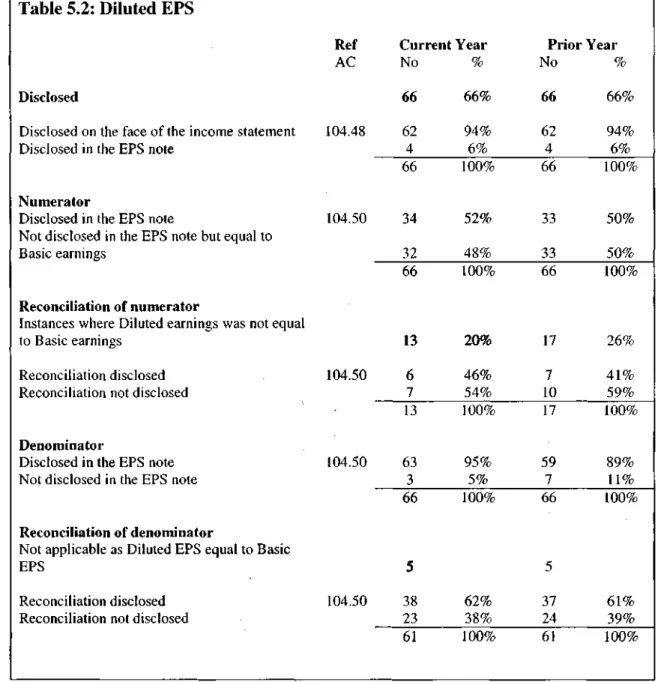
Diluted EPS
- Diluted EPS survey results
- Summary on Diluted EPS disclosures
Regarding the diluted EPS denominator, although most companies (current year 95%; previous year 89%) disclosed this, some companies (current year 5%; previous year 11%) did not disclose the denominator as required by the AC 104.50. As mentioned, five companies disclosed diluted EPS even though it was equal to basic EPS for both years presented.
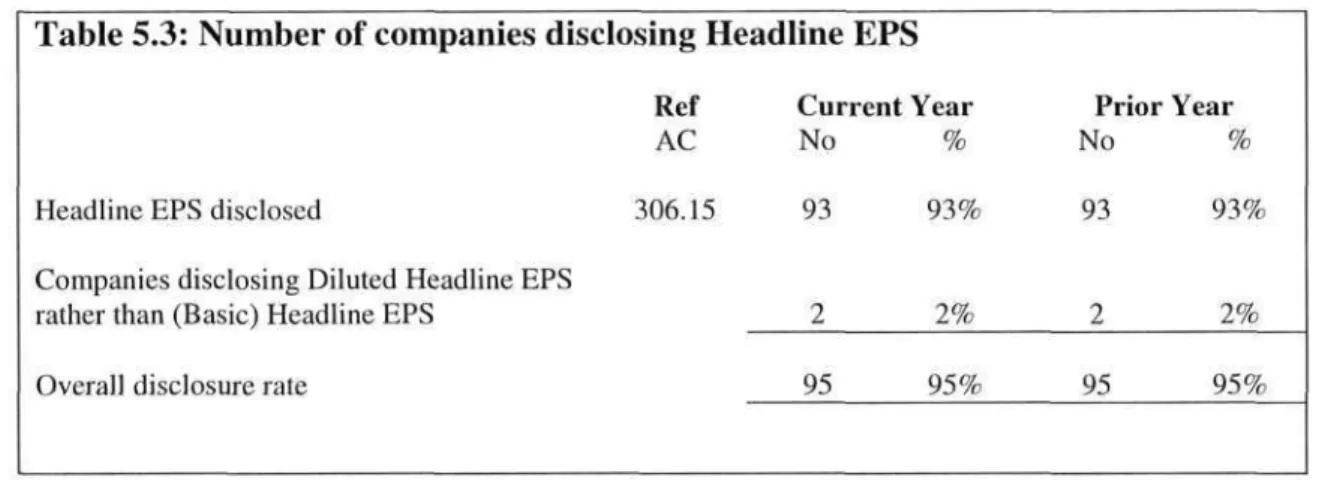
Headline EPS
- Headline EPS disclosures
- Number of companies disclosing Headline EPS
- Company compliance with AC 306 disclosure requirements
- Summary on Headline EPS disclosures
- Headline EPS adjustments
- Allowed Headline adjustments
- Disallowed Headline EPS adjustments
- Summary on Headline EPS adjustments
Hattingh found that the 75% of companies that had reported Headline EPS had violated the definition of Headline earnings (Hattingh 1999a:25). About half (current year 49%, previous year 42%) of the affected companies violated the definition of overall earnings.
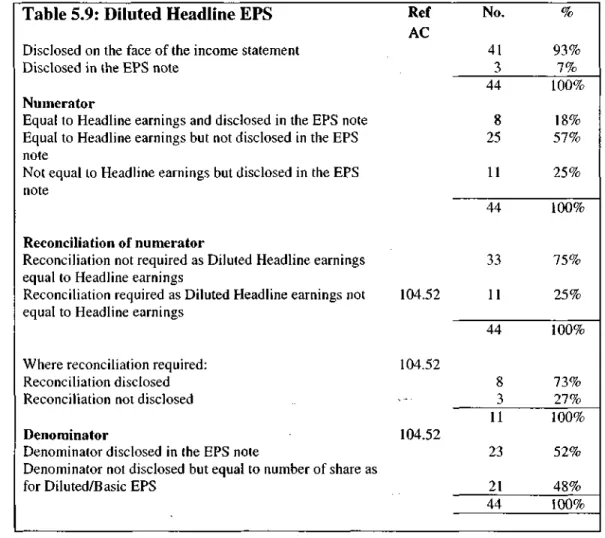
Voluntary EPS disclosures
- Diluted Headline EPS
- Cash flow measures
- Cash equivalent EPS
- Attributable cash flow per share
- Company motivation for disclosing cash flow EPS measures
- Summary on cash flow EPS measures
- Headline EPS from continuing operations
- EPS before exceptional items
- Comparison between other EPS measures and Basic and Headline EPS As with the cash flow measures, it was decided to investigate whether the companies
- Summary on voluntary EPS measures
Cash equivalent EPS compared to Basic and Principal EPS The results of this investigation are presented in table 5.12. As with Cash Equivalent EPS, a relationship cannot be established between Attributable cash flow per share and Material EPS.
Overall survey summary
This cannot be said for "core earnings per share from continuing operations" and "earnings per share before extraordinary items", as companies were found to disclose these measures primarily to stabilize their core earnings per share disclosures, rather than to improved its trading performance. In terms of compliance with disclosure requirements, AC 104 is not very clear in setting out the disclosure requirements for voluntary EPS measures.
Introduction
Respondent profile
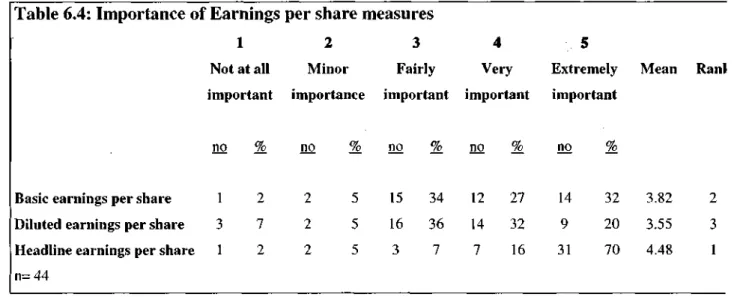
Importance of accounting measures of performance
Importance of other financial measures and EPS measures
- Importance of financial measures of performance
- Importance of EPS measures
Since cash flow per share is ranked 3rd, it can be concluded that both management and investors consider earnings based on per share. It can also be concluded that EPS measures are more important/useful than Cash Flow per Share measures.
Income statement classification
- Abnormal items and exceptional items excluded from extra-ordinary items Question 4 asked respondents whether or not they agreed with the AC 103's 1993
- Extra-ordinary items included in Basic earnings
Since investors are concerned about potential dilutions in their investment, they view Diluted EPS as more useful than the preparers do. Twelve respondents (27%) disagreed with the revised definition and fourteen (32%) respondents agreed with the revised definition.

Diluted EPS
- Continued disclosure of Diluted EPS
Diluted EPS is usually not materially different from basic EPS, 6.6.2 Diluted EPS as a measure of future earnings. The most popular response (41%) was that diluted EPS is not a strong indicator of future earnings.

Headline EPS
- Headline earnings as a measure of sustainable earnings
- The Headline earnings definition
Unlike Circular 7/2002 AC 306 did not comment on whether or not headline earnings per share is a measure of sustainable profit. Ninety-one percent of respondents indicated that headline earnings per share were perceived (by investors, press, etc.) as a measure of sustainable profitability.

LIBRARY
Manipulation of Headline EPS
Although 15 respondents/companies stated that companies manipulate the EPS of the Title, their companies did not dispute the definition of the EPS of the Title for the inspected years. Seven (70%) of the 10 respondents/companies that stated that headline EPS is not being manipulated met the definition of core earnings.
Continued disclosure of Headline EPS
Given the revised definition of extraordinary items, the Headline EPS is more meaningful than the Basic EPS. Affected respondents believe that if companies manipulate Headline EPS, Headline EPS is unreliable as a performance measure.

Need for better guidance on Headline EPS
However, Circular 7/2002 is not a statement of GAAP, as the majority of respondents wanted. However, Damant (2002) indicated that the concept of Main Line EPS will be brought to the attention of the IASB, which may lead to an international position on Main EPS.
Other recommended disclosures
Therefore, the respondents were partially granted their claim as Circular 7/2002 provides better guidance than AC 306. Whether or not companies will comply better with Circular 7/2002 than with AC 306 is uncertain at this stage .
Summary
The survey found that the majority (73%) of respondents believe that Headline EPS is a measure of sustainable earnings. However, because they believe that Headline EPS is a "fundamentally logical concept", the majority (75%) support continued disclosure of Headline EPS.
Summary and conclusions
Main research findings
- Financial Statement survey
- Basic EPS
- Diluted EPS
- Headline EPS
- Voluntary EPS disclosures
- Financial Manager questionnaire survey
- Importance of measures of performance
- Diluted EPS
- Headline EPS
Of basic earnings per share, diluted earnings per share, total earnings per share, and cash flow per share, diluted earnings per share is the least important metric per share. The research revealed that Headline EPS is considered the most important/useful metric per share for management.
Recommendations
- Use of another voluntary EPS measure
- JSE listing requirements should be amended
- Headline EPS monitoring committee
The regulatory authorities should consider establishing an overall EPS monitoring committee to monitor the company's compliance with the definition of overall earnings. A Headline EPS monitoring committee would certainly prevent or help prevent corporate abuse of the definition of Headline earnings, thereby increasing confidence in this crucial measure of corporate performance.
Areas for further research
Numerator not disclosed in notes, but = earnings attributable 1.1.3 Denominator (weighted average number of shares) disclosed. Numerator not disclosed in notes, but = attributable earnings 1.2.3 Denominator (weighted average number of shares) disclosed.
LZZI
Denominator not disclosed but same as for basic/diluted EPS 4.1.3 Numerator equal to earnings of title and disclosed in note. Numerator equal to title earnings and not disclosed in note Numerator not equal to title earnings and disclosed in note.
SURVEY OF ATTITUDES TOWARDS EARNINGS PER SHARE DISCLOSURES
Item (check only one box) A Very important B Very important C Important D Not very important E Not important at all . 6) Do you think Headline EPS is a measure of sustainable profits? Item (check the appropriate box)... 8) AC 306, Headline EPS, lists several items that require adjustment in calculating Headline EPS.