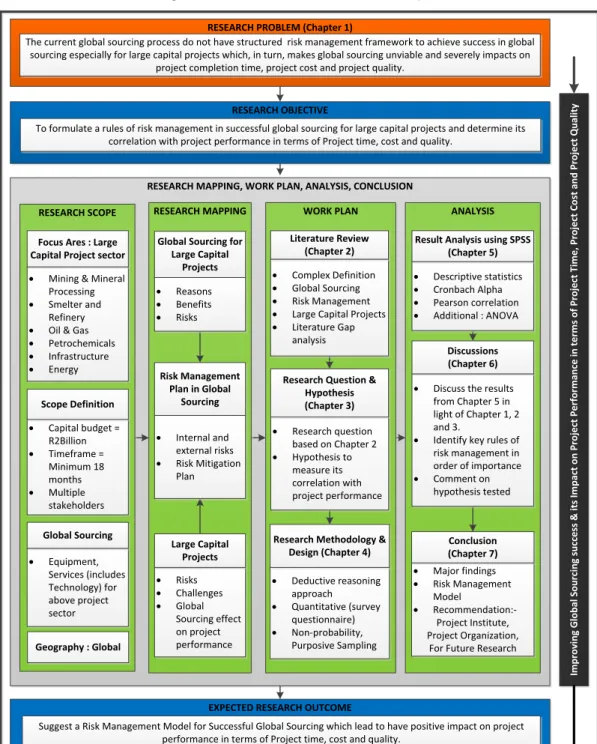
This research study aims to investigate the integrated risk management framework needed to ensure success in global sourcing for large capital projects. It examined the impact of global sourcing on large capital projects and how proactive risk management practices help improve project performance.
INTRODUCTION TO RESEARCH PROBLEM
- Introduction
- The Background of the Problem
- Research Objectives and Motivations
- Structure of this Research Report
Improving global sourcing success and its impact on project performance in terms of project time, project cost and project quality. Design risk management rules for successful global procurement of large capital projects and determine their correlation with project performance in terms of project time, cost and quality.
THEORY AND LITERATURE REVIEW
Introduction
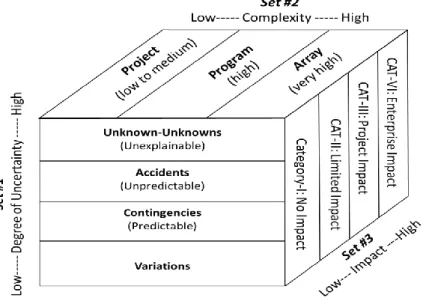
A large amount of academic perspective has been gathered on supply chain risk management practices for the retail sector, but very little has been specifically prepared for global sourcing for large capital projects. Therefore, understanding the risks and their impact framework is essential to the successful delivery of global sourcing for large capital projects.
Complex Definitions of Terms
- Large Capital Projects
- Global Sourcing
- Successful Global Sourcing
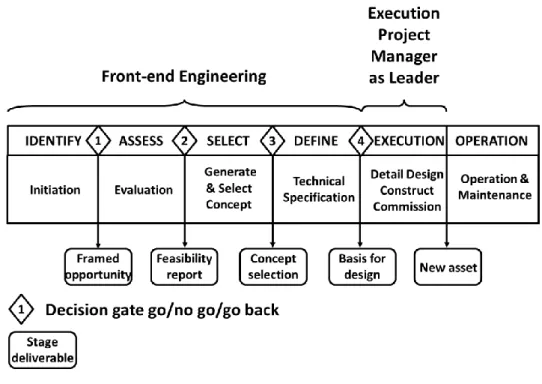
- Front End Loading Process
- Project Risks
- Risk Management in Global Sourcing
Wideman (1986) in Kayis et al., (2007, p. 388) defined project risk as "the possibility that some event will adversely affect project objectives". A definition of risk management in global sourcing adapted by Manuj and Mentzer (2008, p. 205) describes it as "the identification and assessment of risks and consequent losses in the global supply chain and the implementation of appropriate strategies through a coordinated approach among all stakeholders with the objective of improving the performance of the supply chain, reducing the probability rate of events, reducing the rate of subsequent loss, one loss or more events. ve, frequency or exposure".
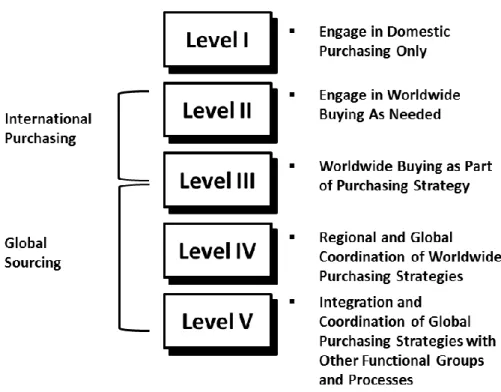
Global Sourcing
- Necessity of Global Sourcing
- Levels of Global Sourcing
- Benefits of Global Sourcing
- Challenges in Global Sourcing
- Global Sourcing Success Factors
- Lessons Learnt from Global Sourcing
Christopher et al. (2011) argued that the benefits of global sourcing go beyond mere cost savings. Rigorous and well-defined processes – explained the importance of having a global procurement process.
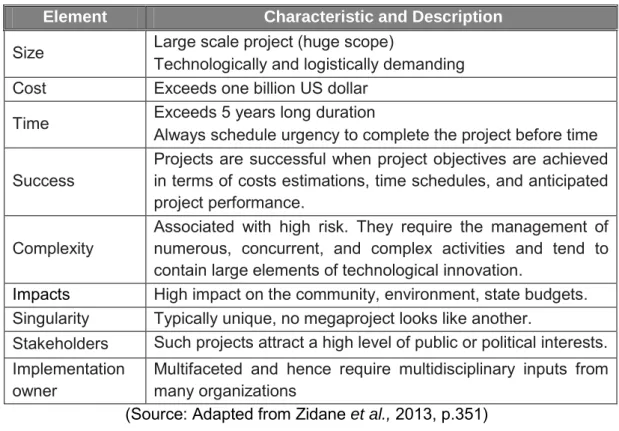
Large Capital Projects
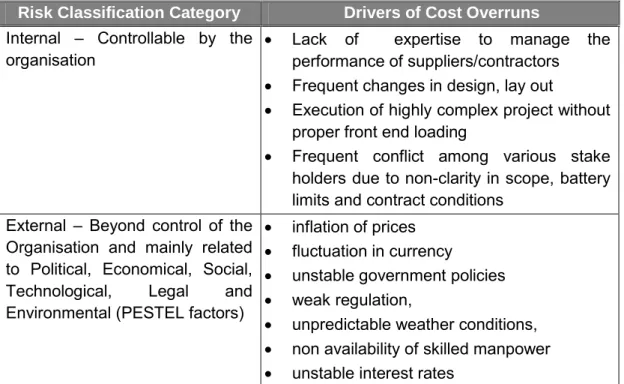
- Characteristics of Large Capital Projects
- Factors Causing Cost Overrun for Large Capital Projects
- Challenges in Large Capital Projects
- Realisation of Project Success
Eweje et al., (2012) argued that the impact of major projects goes far beyond the immediate completion of the project. Eweje et al., (2012) also argued that previous training and the experience level of the project manager, as well as his ability to manage contracts, determined the project success.
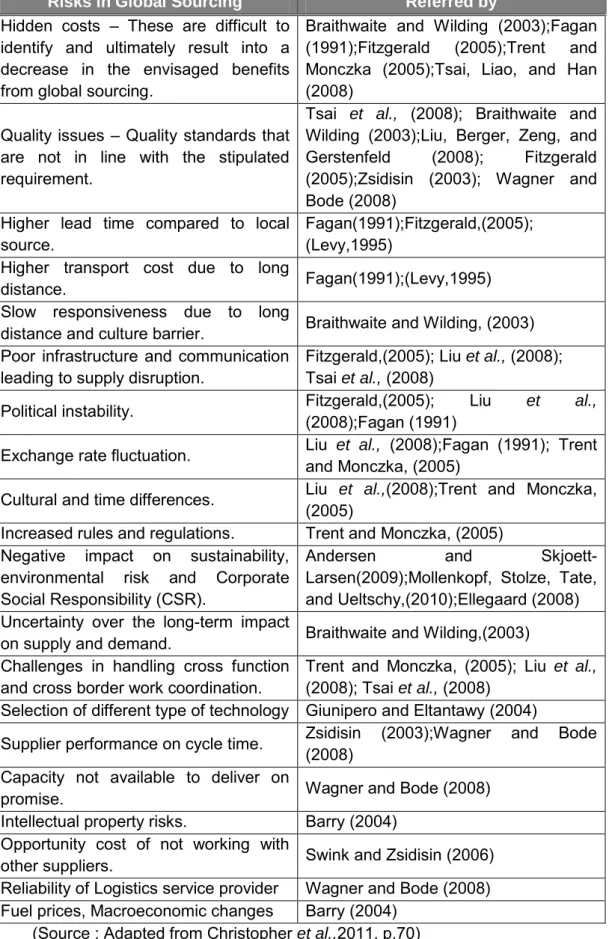
Risk Events in Global Sourcing
- Risks in Global Sourcing
- Dealing with Unknown Risks
Similar risks in global procurement have also been identified by various authors and are compiled here and tabulated in table 4. Risks in global procurement referred by hidden costs - It is difficult to. identify and ultimately lead to a decline in the intended benefits of global sourcing.
Effect of Global Sourcing on Large Capital Projects
Tummala and Schoenherr (2011) stated that in today's environment, a global supply chain has become more and more complex with less possibility of achieving the desired performance of a procurement strategy due to risks that are not managed throughout the supply chain. They further emphasized that an organization should plan for disruptions and develop contingency plans based on supply chain interdependencies of potential risk factors and their consequences and severity.
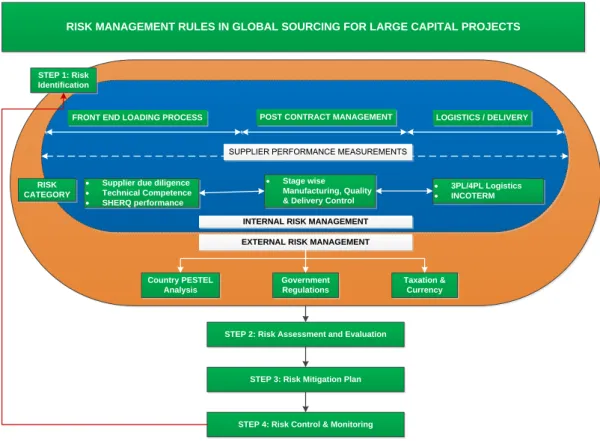
Risk Management Framework for Successful Global Sourcing
- Risk Management Objective
- Approach to Risk Management
- Risk Identification (Step 1)
- Risk Assessment and Evaluation (Step 2)
- Risk Mitigation Plan (Step 3)
- Risk Control and Monitoring (Step 4)
- Supplier Due Diligence
- Supplier Performance Measurement
- Contracting Strategy
- Risk Classification
This changed approach is known as the Rules of Risk Management in Global Sourcing for Large Investment Projects. In the last step of the risk management framework, risk management and monitoring helps to determine possible preventive measures and provide guidelines for further improvement.
Literature Summary
Risks of global sourcing Various authors listed in Table 4. Risk factors identified, but impact on large capital projects not investigated. The impact of the sourcing process on project performance is identified, but global sourcing's impact on project performance is not included. Available risk management frameworks are related to the supply chain in the retail/FMCG sector, but no work has been done on risk management for global sourcing on large capital projects.
No previous research has been conducted to measure the relationship between successful global sourcing and project time, cost and quality.
RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
- Introduction
- Problem Statement
- Objectives of Research
- Research Questions
- Research Question One
- Research Question Two
- Research Question Three
- Research Question Four
- Research Question Five
- Hypothesis
- Hypothesis Background
- Hypothesis One
- Hypothesis Two
- Hypothesis Three
Null hypothesis (1) : H0 : = 0, Risk management rules in global sourcing for large capital projects are NOT effective in shortening project lead time. Alternative hypothesis (1) : H1 : > 0, Risk management rules in global sourcing for large capital projects are effective in shortening the lead time of projects. Null hypothesis (2): H0: = 0, Risk management rules in global sourcing for large capital projects are NOT effective in reducing project costs.
Alternative hypothesis (2) : H1 : > 0, Risk management rules in global resources for large capital projects are effective in reducing project cost.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Research Design
Population, Sample and Sampling Method
Assumptions
The Research Instrument
- Survey Questionnaire Design
- Survey Tool and Pre-Testing
- Survey Questionnaire - Accuracy, Reliability and Validity
Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Data Collection (Step 1)
- Data Reduction (Step 2)
- Data Display (Step 3)
- Conclusion Drawing / Verification (Step 4)
Limitations of the Study
RESULTS
Introduction
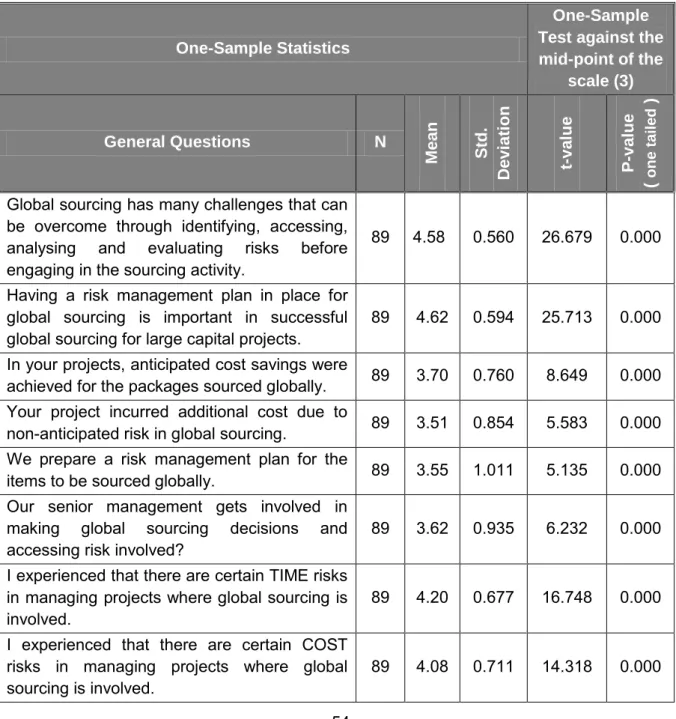
The objective of this research section is to present an overview and summary of the main findings of the survey in relation to the research questions and hypotheses that were stated in chapter 3 and to see if the researcher's expectations regarding the characteristics and quality of the data have been met. Analysis of survey data included descriptive statistics, internal consistency test, a one-sample t-test for comparison of sample means performed according to significance. Hypotheses were tested based on measuring correlations between risk management rules for successful global sourcing in large capital projects and its correlation with project time, cost and quality.
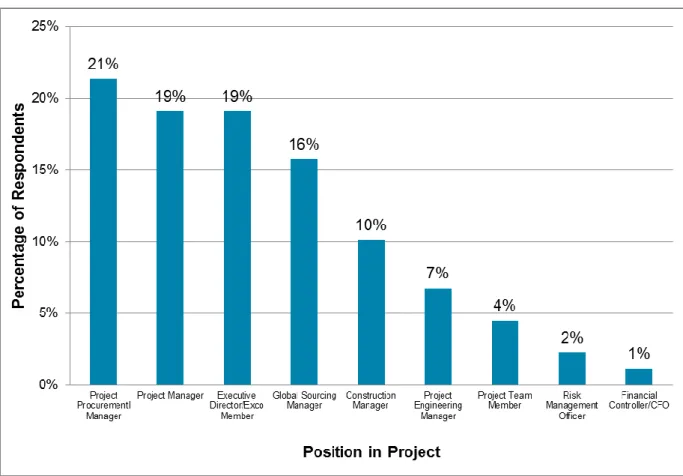
This chapter discusses a comparison of opinions between key positions responsible for the success of large capital projects.
Response Rate
Demographics
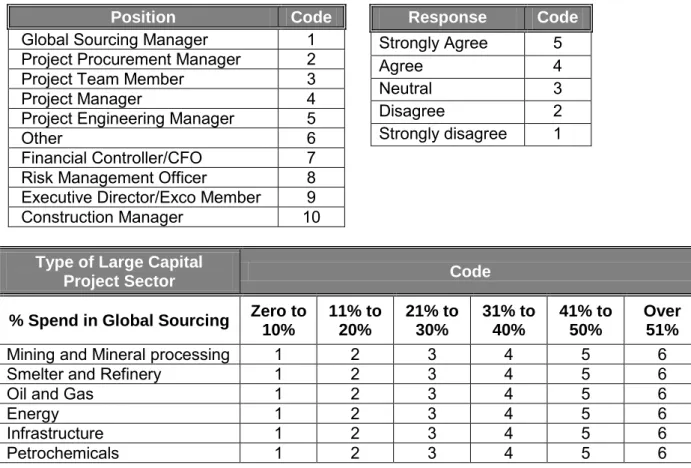
- Position of Respondent in Large Capital Projects
- Respondent’s Geographical Experience in Large Capital Projects
- Respondent’s Years of Experience
- Global Sourcing Spend in Large Capital Project Sector
Total years of experience and related experience in major capital projects was a factor that was used to determine respondents' average years of total experience, particularly in major capital projects. The majority of respondents had over twenty-five years of experience in total (39%), of which 16% of respondents had more than twenty-five years of experience in executing large capital projects. This was required to track the amount spent globally on major capital projects and to observe the difference in global resource spending between different project sectors.
In summary, more than 80% of respondents believed their global sourcing spend in major capital projects ranged from 11% to more than 50%.
Internal Consistency (Reliability) Test
One Sample T-Test
- General Questions
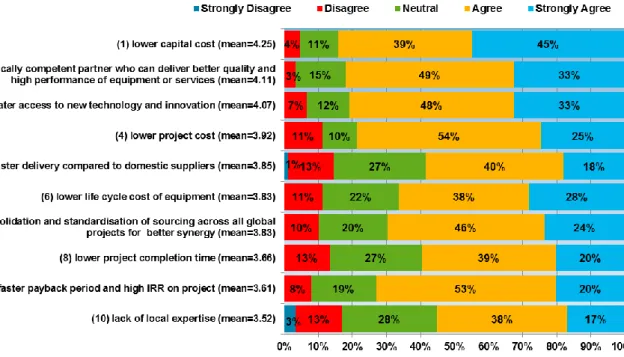
- Reasons for Global Sourcing in Large Capital Projects
- Indicators for successful Global Sourcing in Large Capital Projects
- Risk Management in Global Sourcing for Large Capital Projects
- Reasons for Failure of Global Sourcing in Large Capital Projects
The reasons for global resources in large capital projects based on the highest average value are tabulated in descending order in Table 15. The highest indicator for identifying risks in global resources for large capital projects are tabulated in descending order based on their average value and are presented in Table 17. The most important reason for the failure of degraded global aids in large capital projects.
There was agreement on the claims of risk management in global sourcing for major capital projects.
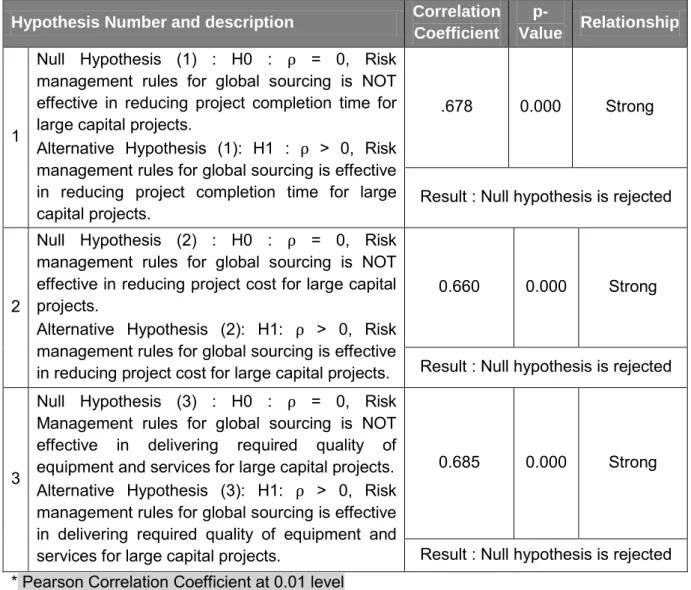
Correlation Coefficient and Hypothesis testing
- Hypothesis One
- Hypothesis Two
- Hypothesis Three
Null hypothesis (2): H0: = 0, Risk management rules for global sourcing are NOT effective in reducing project costs for large capital projects. Alternative hypothesis (2) : H1 : > 0, Global sourcing risk management rules are effective in reducing project costs for large capital projects. Section B.5 : The reasons for global sourcing failure in major investment projects are due to.
0, Risk management rules in global procurement for large capital projects are NOT effective in reducing project completion time.
Additional Analysis
- Comparison of Opinion through ANOVA Test
- Comparison of Opinion One : Successful Global Sourcing
- Comparison of Opinion Two : Project Cost
- Comparison of Opinion Three : Project Time
- Comparison of Opinion Four : Project Quality
Summary of Hypotheses Tested
Null Hypothesis (1): H0 : = 0, Risk management rules for global sourcing are NOT effective in reducing project completion time for large capital projects. Alternative hypothesis (1): H1 : > 0, Risk management rules for global sourcing are effective in reducing project completion time for large capital projects. Null Hypothesis (3): H0 : = 0, Risk Management rules for global sourcing are NOT effective in providing the required quality of equipment and services for large capital projects.
Alternative hypothesis (3): H1: > 0, Risk management rules for global procurement are effective in providing the required quality of equipment and services for large capital projects.
DISCUSSION OF RESULTS
Introduction
Discussion of Results
- Research Question One
- Research Question Two
- Research Question Three
- Research Question Four
- Research Question Five
- Hypothesis One
- Hypothesis Two
- Hypothesis Three
Only 8% felt that the list of reasons mentioned was not as important for global sourcing in large investment projects. The front-end loading process for global sourcing of large investment projects has a direct relationship with project performance. The attitude profile of the project team is also very important in achieving global success in large investment projects.
What happens to project performance (in terms of project time, project cost, project quality) when an organization develops a risk management plan before engaging in global sourcing for large capital projects.
Conclusion
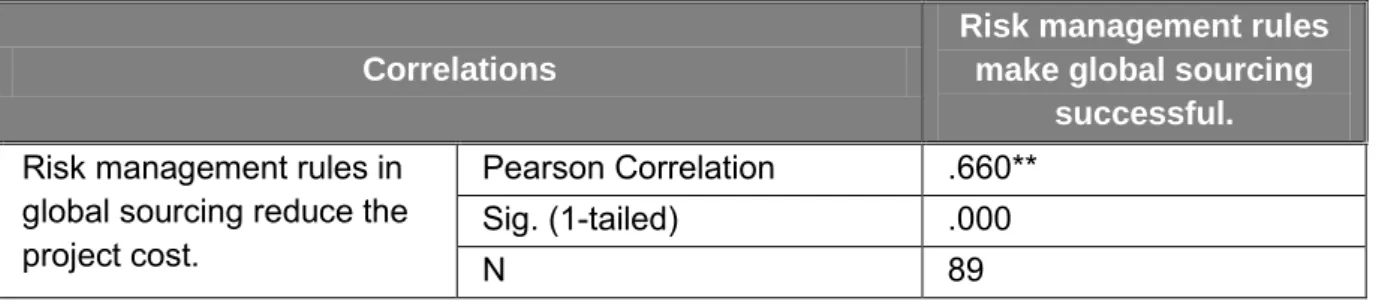
The results in Table 29 show a positive correlation between a risk management plan for successful global procurement and delivering the right project quality (r = 0.685) for large capital projects. The literature indicates that poorly managed risks in front loading and global sourcing can lead to quality problems (Cousins et al., 2004). It was clear that if a global procurement process is not closely monitored, the likelihood of an undesirable outcome is high.
There was sufficient evidence in favor of the alternative hypothesis and with strong correlations, it can be concluded that the establishment of risk management rules for global procurement in large capital projects will be effective in delivering real project quality in terms of required quality of equipment and services.
CONCLUSION
Introduction
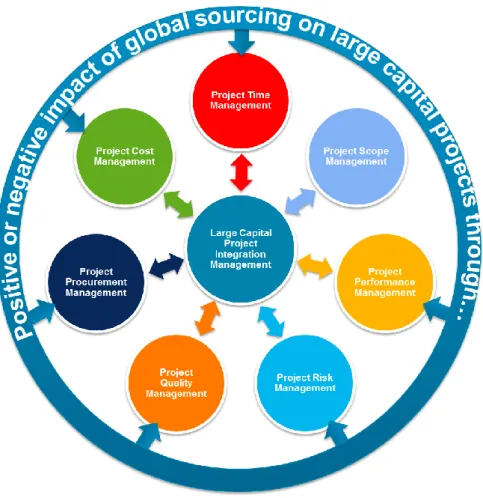
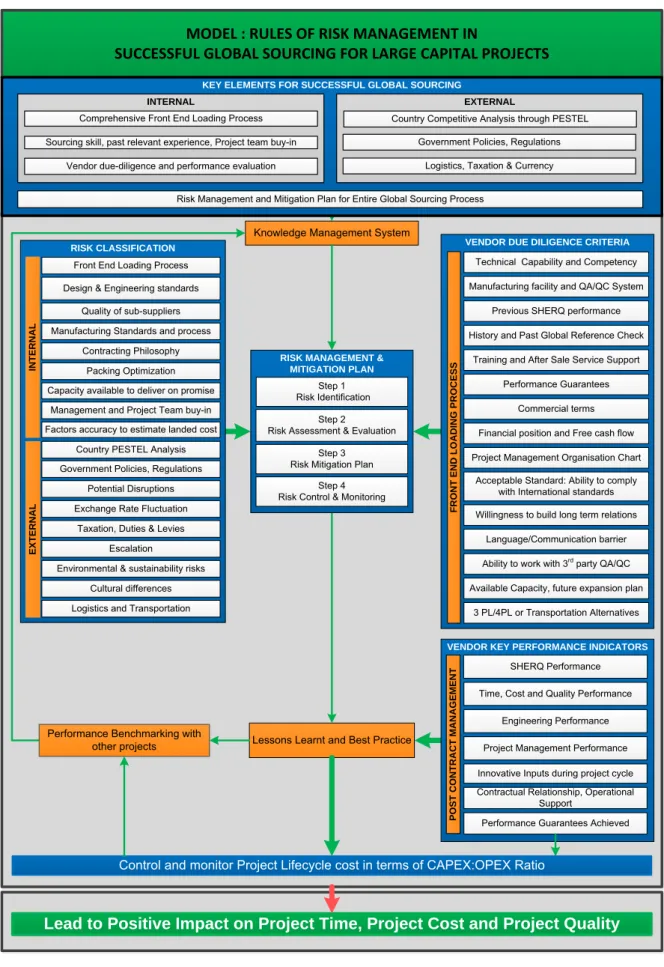
Major Findings
Based on the empirical findings of the study, key elements for global procurement success were identified, namely supplier due diligence, supplier performance measurement, risk classification and lessons learned. The top block of the model shows three internal and three external elements for successful global procurement that must be evaluated through risk management and mitigation planning. The left column in the middle of the model shows the internal and external risk classifications that are important to evaluate before deciding on global procurement solutions in major capital projects.
Risk management and mitigation plan for the entire global procurement process Contractor due diligence and performance evaluation.
Benefits of the Model
Applicability of this Model
Considerations and Limitations
It is reasonable to assume that there may be some organizations that already exercise some level of risk management discipline in global sourcing. If organizations involved in the implementation of large capital projects could be identified and persuaded to share some of their risk management practices, this would greatly contribute to a more measured assessment of the accuracy of the proposed model, further substantiating the accumulated technical knowledge of project management. The model proposed here describes the risk management rules for successful global sourcing of large capital projects and can be used to increase global sourcing success by positively impacting project time, cost, and quality.
This model can also be used by organizations involved in the execution of large capital projects, engineering and project management consultants, Project Management Institutions and various project management elements and stakeholders within an organization.
Recommendations for Project Management Institutes
It is essential to note that the model developed here cannot be generalized to all projects at the international level. It is therefore necessary to take a contextual view of the risk management plan for the specific project to improve project performance. Project leadership should also plan to have brainstorming sessions with interdisciplinary project teams to solicit input and thereby ensure buy-in of their collective experience beforehand and, to further strengthen the global sourcing process through the preparation of detailed risk mitigation plans.
Recommendations for Future Research
Conclusion
This section consists of a series of statements indicative of the performance of global procurement in major capital projects. Section B.3: The success of global sourcing in large capital projects depends on ..( Note: This text applies to all questions in this section. Section B.4: Large capital projects must manage risk in global sourcing by identifying ..( Note: This text applies to all questions in this section.
Research question three: How should risk be managed in global sourcing for large investment projects.