Directory UMM :Data Elmu:jurnal:J-a:Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology:Vol256.Issue2.Jan2001:
Teks penuh
Gambar

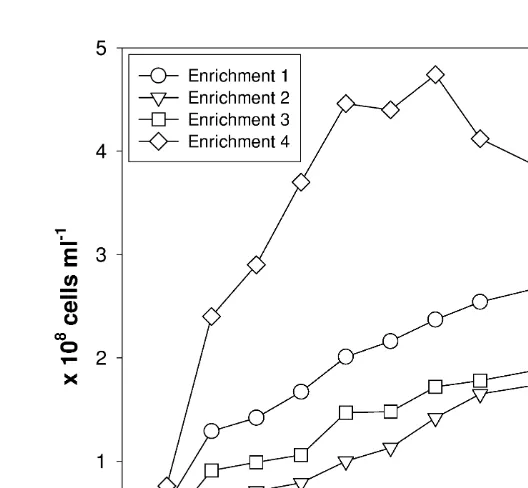
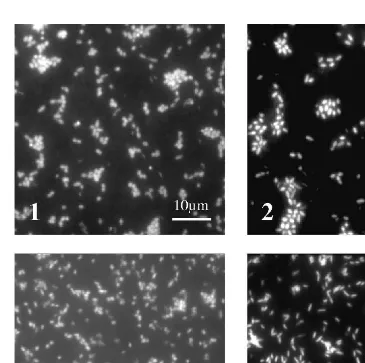
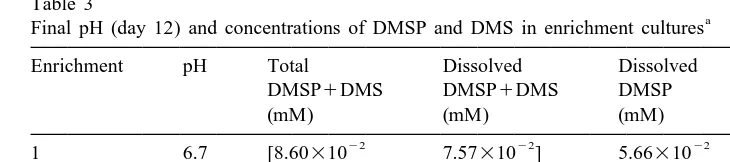
Dokumen terkait
(A) Seasonal course of CH 4 oxidation rates, (B) volumetric soil moisture, (C) soil temperature, and (D) soil NH4 1 -N concentration of the spruce control site (open symbols) and the
Effects of dietary vitamin K on survival, growth, and tissue concentrations of phylloquinone (PK) and menaquinone-4 (MK-4) for juvenile abalone, Haliotis discus. hannai
Further, the maximum specific Na ,K -ATPase activity values registered for both anterior and posterior gills were similar to those reported for gills or other structures involved
Therefore, the objective of this study was to investigate the effect of dietary vitamin K on survival, growth and tissue concentrations of phylloquinone and / or menaquinone-4 in
Recovery percentage (mean 6 S.D.; n 5 4) of the various compounds measured in the controls and the faeces samples compared to the initial tracer (food portion) composition..
Thus the reduced blood osmolality in the organotin groups in this study could be a reflection of the increased osmotic water influx rates caused by stress-induced increase in
In this study, boundary layer characteristics were compared between different size colonies of the corals Dichocoenia stokesii and Stephanocoenia michilini to determine the
Mean number of treated pellets, containing different concentrations (% of natural extract concentration) of extract of Parerythropodium fulvum fulvum embryos and mucus and