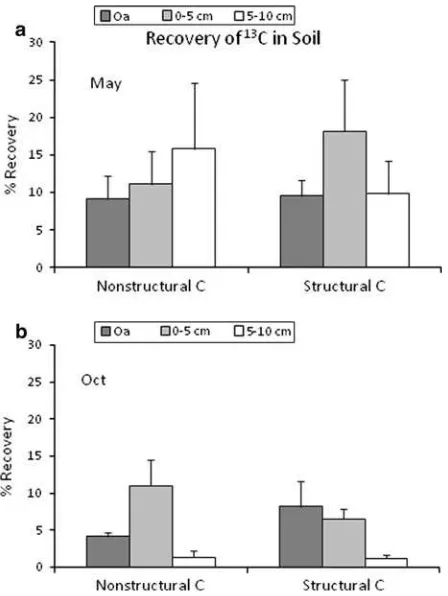
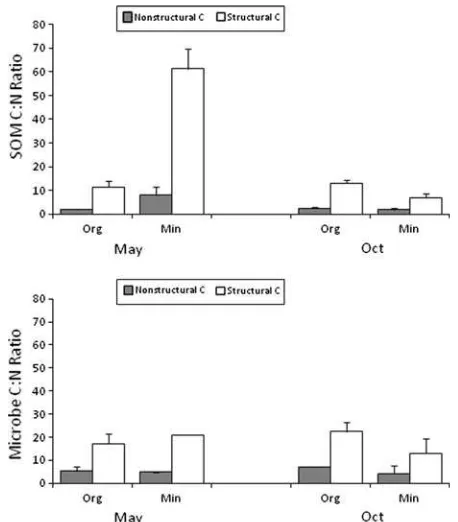
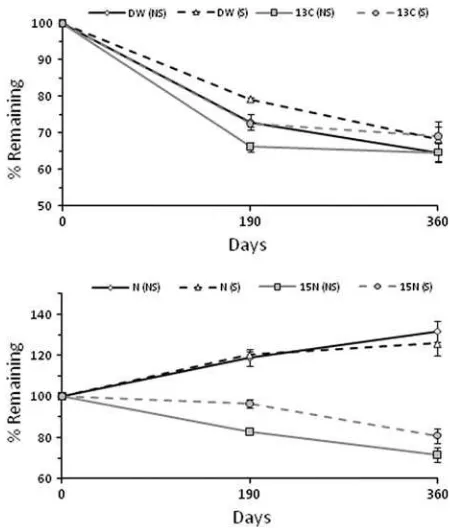
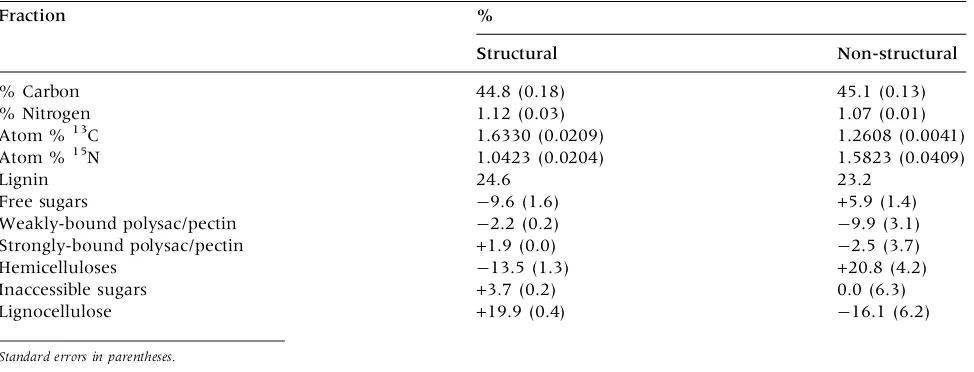
Transport of Carbon and Nitrogen Between (1)
Teks penuh
Gambar
Garis besar
Dokumen terkait
Hence, climate change effects on C- gas flux in taiga forest soils will depend on the relationship between soil temperature and moisture and the concomitant changes in soil
Recent work indicates that P addition in tropical forest can increase soil microbial biomass and alter the composition of soil mi- crobial community (Liu et al. 2012 ), but this
More specifically, we (1) estimate total C stocks by horizon for common soil series on the basis of soil survey data and analyses of data from individual soil profiles;
The objective of this experiment was to determine the influence of long-term (22 and 23 years) conservation tillage and N fertilization on soil carbon storage and CO 2 -C emission
Abstract: Accumulation of soil organic carbon affects soil quality, greenhouse gas mitigation, and overall agricultural ecosystems.. A conceptual model was utilized to explore the
The organic C and total N concentrations and stocks of SOM, FLF, IPOM, and MAOM in the 0–20 cm soil layer were considerably greater than those in the 20–40 and 40–60 cm soil layers for
Soil organic carbon content A and soil carbon storages B in different soil depth under different land use systems PA = protected areas, PC = pine + coffee, PS = pine + crop, MC =
The correlation between some soil properties soil organic-C, soil moisture content, soil pH, soil temperature and yields stalk dry weight, and weight of corn kernels on soil microbial