THE TEACHING OF THE SIMPLE PAST TENSE BASED ON
COMMUNICATIVE APPROACH
(A Case Study at the First Year ofSMK Islamiyah Ciputat)
A'Skripsi'
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teacher's Training
in Partial Fulfillment of One of the Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana (S.I)
By:
Sondang Tl"ianasari Reg. nO.l00014018051
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
THE FACULTY OF TARBIYAHAND TEACHER'S TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
THE TEACHING OF THE SIMPLE PAST TENSE BASED ON
COMMUNICATIVE APPROACH
(A Case Study at the First Year of SMK Islamiyah Ciputat)
A "Skripsi"
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teacher's Training
in Partial Fulfillment of One ofthe Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana (S.I)
By:
Sondaog Trianasari Reg. 00.100014018051
Appoved by: Advis
!
D . M.Pd.
NIP. 1502 1 927
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
THE FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHER'S TRAINING SYARIF HlDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
LEGALIZATION OF EXAMINATION COMMITTEE
A skripsi titled "The Teaching of the Simple Past Tense Based on
Communicative Approach (A Case Study at the First year of SMK Islamiyah
Ciputat)" was examined at the examination session ofthe Faculty of Tarbiyah and
Teacher's Training of State Islamic University (UIN) Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta on
l2'h of July 2005. This skripsi has fulfilled the requirement for The Degree ofs。セェ。ョ。
(S.I) at the English Department.
Jakarta, July 2005
Examination Committee
The I-lead of Committee
Examiner I
Drs. Nasrun Mahmud, M. Pd
NIP. 150041 070
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
In the name of Allah, the Beneficent, the Merciful, all praise be to Allah,
Lord of the world, by the whole modest heart, all praise and strength that enable the
writer finish this 'skripsi'. Peace and hlessing he upon the prophct Muhammad, his
ttullily, his companions, and his followers.
This 'skripsi' is presented to the English Department of the Faculty of
Tarbiyah and Teachers' Training Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University (UIN)
Jakmta as a partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree of Strata I (S I) and
alhamdulillah finally the writer gets the title.
It is great honor for the writer
,0
make acknowledgment of indebtedness toexpress her sincere gratitude to her beloved iTlother, Syamsini, her beloved uncle, H.
Suparta, her beloved grandmother, Hj. Sumirah, and her beloved brothers, Pantol11
Sejahtiar, Ricky Nelson, and Muhammad Falen, and her cousin Mbak Nining, who
always encourage her. And last but not least for her beloved father, A. Rusli, thanks
for his prays, the writer knows that he always whishes her luck.
The writer also likes to express her sincere gratitude, particularly to:
I. Dra. Hidayati, M. I'd, as her advisor fur having guided her in writing this skripsi.
2. Prof. DR. Dede Rosyada, MA. the Dean of Tarbiyah Faculty and Teaehns'
Training UIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
3. Drs. Nasrun Mahmud, M. Pd. the I-lead of English Department and Drs. Syauki,
4. The I-lead Master of SMK Islamiyah Cioutat Drs. Hilmudin, who has given the
permission to the writer to do the research and also to the English teachers, Mr.
Indra M, SE and Mrs. Dian R, SE.
5. To all Lectures of English Department who havc taught the writer.
6. Her lovely jj-jends at English Departmelll "angkatan 2000 class B" and IRSAL,
for their goodness and 11'iendship to the wt'iter.
7. All people who have given their contrihltion to tile writer.
May Allah, the Almighty, bless, protect and guided them all. Amin.
Jakarta. July 2005
TABLE OF CONTENTS
EXAMINATION LEGILIZATION
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT i
TABU, OF CONTENTS iii
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION
A. Background or the Study I
B. Statement of the Problem 4
C. Objective of the 'Study 5
D. Significance of the Study 6
E. Scope and Limitati:JI1 of the Study 6
F. Dellnition of Key Terms 7
CHAPTER II: THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. The Simple Past Tense 8
I. Thc Meaning of the Simple past Tense 8
2. The Use of the Simple Past Tense 12
B.
The Communicative Approach 133. The Advantages and Disadvantages of Communicative
Approach 19
C. The Teaching of the Simple Past Tense Based on
Communicative Approach 20
I. I)csGription of' the Problem 20
2. Equipping Learning Materials 22
3. Techniques of' Presentation 22
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Research Design 26
B. Place and Time 27
C. Population and Sample 27
D. Methods of the Study 28
E. Technique of Data Collecting 28
I. Observation 28
2. Interview 28
3. Teaching Learning ?rocess 28
4. Test 31
F. Technique of Data Analysis 31
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
A. Teacher Qualification 36
B. Teaching Preparation 37
C. Instructional Materials , 39
D. Instructional Activities 39
E. Teaching Technique ,.: 40
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIONS
A. Conclusion 41
B. Suggestions 41
BIBLIOGRAPHY
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter contains the background of study, the statement of the problem, the objectivc of the study, the signilicance of the study, the scope and limitation of the study and the definition of key terms.
A. Background of the Study
English plays as an important role in global era as a tool for communication among nation. It is lIsed in many activities such as: commerce,
sport, education, science, and technology. As an international language, most people in the world now speak Englisn. This IS one of the reasons why the
Indonesian government considers English to be taught as the first foreign language starting from elementary school up to the university.
As a foreign language, English is taught in schools merely as a subject. Itis neither used as a medium of instruction POl' as a means of communication within
the country, in which, students do not have opportunity to practice English outside the classroom. It is essential, the,'efore, that the teacher organizes process, which will not be found outside the cbssroom. The teacher has to learn and
2
The teaching of English in the vocational high school as intended to prepare the students to continue their education at the university level. The aim of teaching is to equip students with woddng knowledge of English in order that they read textbooks and follow lecturers given by foreign lecturers. As a required subject at the vocational school, English functions as a means for the students to develop their knowledge, skills, and atti':udes in the areas of science, technology, and arts. They are expected to participate in the development of the nation. But unfortunately, the result of the teaching of English has not been satisfactory yet.
Due to the 1994 Nationa; Curriculum, the teaching fur Vocational High School students consist of the four fundamental skills that we have to employ in order to comprehend the English language. They are listening, speaking, reading, and writing. They fall into two major skills. The first one is 'productive skills': speaking and writing skills, and the second one is 'receptive skills': reading and listening skills.]
Besides the four language skills, there are several language factors students should master. They are gramm"r, vocabulary, spelling and pronounciation. The four language factors can be tran3terred to the students through the four language skills. The purpose of teaching these language factors as mentioned in GBPP 1994 are to enforce the ability and development of the four language skills in English.
3
The importance of grammar ab:lity, according to the language expClis, has a big role in students' English fluency. However, mastering grammar does not mean mastering the entire language-. Mastering grammar should be integrated with the language skills and the language (actors in order to make the students easier to understand the language during the communication. As Richard said: ... it's not simple a case of more grammar= more proficient; grammar skill interact with other language skills and together determine what learners can do at any given level of proficiency and how well they can?
Proficiency in grammar can give self confidence for students to communicate in the target language.) Knowing they can use the right expression will reduce the scare and embarrassment when they have talk.
The result during some observation while teaching at SMK showed that speaking is the most difficult prol)lem of the other skills; listening, reading, and writing. The students have difficulties in expressing their idea in English, therefore they often make mistakes while trying communicate in English. This problem will not happen if they get not only the grammar and vocabularies of English but also know how to use them in communication. After all, the teaching of English must be about the body of knowledge and the communicative function of it. So, it is important for the teachers to know or to study method of teaching activities by choosing the suitable nlCthod according to the students' need.
2 J.e. Richard, "The Status of Grammar in tlw Language Curriculum," Paper Presented in SEAMD Regional Language Cell tel' (Sing,apNe: RELC, 1985), p. 148
4
Many of the English teachers at SYlK still use the previous methods. One of the methods is Audio Lingual Method, where the language teaching depends on repetitive drill of the mechanical type. For example:
Teacher : there is a book on the tuble Students : there is a book on the table
The writer often hears that teachers who use it always complain about their students' ability. The students cannot n.,ake sentences by using the form correctly or they can produce correct sentenc,"s but they cannot use the forms in appropriate situations.
Based on the explanation above, the writer would like to try to combine the teaching of grammar or structure by applying the communicative approach. This study is intended the teaching of simple past tense based on communicative approach for the first year ofSMK IslUln;yah Ciputat.
B. Statemcnt of thc Problem
6
5, To describe the teaching techniquer. used by the English teachers at the first year of SMK Islamiyah Ciputat in teaching simple past tense,
D. Significance oftheStudy
Hopefully, the study will contribute many advantages to the English teachers in vocational high school and in implementing the teaching of the simple past tense based on the communicative approach at the first year of SMK
lslamiyah Ciputat.
The result of the study hopefully can also assist students in learning the language skills in English in an interesting way, Subsequently, it will assist the students in upgrading their ability to communicate in English,
E. Scopeand Limitatiou of theStudy
7
English teachers at the first year cf SMK lslamiyah Ciputat in teaching simple
past tense.
F. Definition ofKey Terms
To avoid misunderstanding, the following definitions arc given to make
readers have the same understanding or perception for some terms used in this
study. They are also intended to avoid a'nbiguity or misinterpretation. They are
as follows:
1. Teaching refers to the activity where the teacher is giving some explanation
about the lesson to the students
2. Simple past tense refers to the tense in grammatical English. The simple past
tense indicates an activities or situation began and ended at a particular time in
the past.
3. Communicative approach refers to communicative activities to make the
students able to communicate with otht:rs in English.
4. SMK is the acronym of "Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan" or vocational high
school.
5. Islamiyah refers to the name of the scilOol where the writer do the research for
CHAPTERIl
theorセtical I?RAMEWORK
In this chapter we will discuss the meaning of the simple past tense, the use of the simple past tense, the meaning of communicative approach, the characteristics of communicative approach, the advantages and disadvantages of communicative approach and the teaching of the simple past tense based on communicative approach
A, The Simple Past Tense
J, The Meaning of the simple Past tense
Betty Schrampler Azal' stated that the simple past tense indicates an activity or situation bcgan and ended at a particular time in the past4 Another writer, Marcella Frank, stated in her book, that the past tense indicates definite time terminating in the past, whether a time word is given or notS Based on the two definitions above we can conclude that the simple past tense is the form that indicates an activity or situation which is given or not. We can also say that the simple past ',ense is lIsed to describe an action
-1 Betty Schrampfer Azar, Understanding and Using English Grammar (New Jersey, Prentice
Halltne, 1989), P,24,
9
or situation that happen at any time in the past. The simple past tense is
formed by using the simple past form of the verb.
There are two kinds of the verbs here, regular verbs and irregular
verbs. For example:
Regular verbs Irregular verbs
Look looked begin began
Answer answered come came
Play played go went
Agree agreed take took
Borrow borrowed eat ate
Change changed lose lost
Enter entered teach taught
I-Iappen happened choose chose
Study studied understand understood
Work worked wake woke
The simple past tense of regular verbs is form by adding -d or -ed to
the main verb. For example:
- She entered the room
- He traveled to Surabaya last year
- Dina borrowed my bag
Besides the regular wrbs, there are also irregular verbs. For example:
10
- I saw her at the market
- She wrote a letter
The auxiliary verbs do has a past form did. Did and did not
(contracted to didn't) are used with the base form or the past tense. Did and
didn't are also used in short answer. Fc,r example:
Negative statements
- I didn't spend much money
Tina didn't eat breakfast
- They didn't do any mistake
Questions
- Did Feri play football?
- Did you go to scholl by bus?
- Did Nany like cats?
Short answer
- Did mother buy some eggs?
Yes, she did
No, she didn't
- When did you go to Bandung?
Last week (I went to Bandung last week)
- Where did you eat dilmer?
II
The next one is the simple past tense form of be. Was and were are
the past tense form of be. For example:
- Didi is at work today
Didi was at work yesterday
- She is happy now
She was happy last week
- There are many people now
There were many people yesterday
In the question form, the verb be and the subject are reversed. For
example:
- He was late this morning
Was he late this morning?
- Gina was sick last month
Was Gina sick last month?
- Sari was born in 1982
Was Sari born in 1982?
- Mrs. Ida was angry last night
Was Mrs. Ida angry last night
Certain past time expression l:sually occur with verbs in the simple
past. If the time expressions do not cccur, it is because they are understood.
13
When I was young, I swam every week. c. duration of an event completed in the past
In the Colombus' day, peopic believed that the earth was flat
She lived in Bogor for ten years and she decided to return to Jakarta
B. Commuuicativc Approach
I. The Meaning of Communicative Approach
Jeremy Harmer states a definition about the communicative approach that is the focus on communicPctive activities and the concentration on language as a mean of c0l11111uniration6This is because as one of the approaches in the teaching of English with its basic aim to make the students able to communicate with others ii, English.
Janice Yalden, who is als0 interested 111 communicative approach
says as follows:
In this approach, language is viewed not only as a body of knowledge about sound, vocabulary and grammar, but also very much as an instrument for interpersonal communication for a whole range of purposes as a wide variety of situation.7
6Jeremy Harmer, 7Yle Practice of E'nglish Language Teaching (London: LonglllClll Group UK
Ltd, 1991),p.48
7 Janice Vaiden, COl11lJlunicatior Language Teaching(Ontario: The Ontario Institute for Studies
14
From the description above, it scems that Janice Yalden thought that
the teaching of English must be about the body of knowledge and the
communicative functions of it. Those are the materials of English teaching
according to the communicative approach.
Since the communicati'le capacity becomes the starting point of
communicative approach, it needs a teacher's creativity to elaborate the
situation that can mal<e the students really feel interested and get involved to
the class environment, so that the students expand their ideas accordingly.
Longman dictionary of langl.:age teaching and applied linguistics
defines the communicative appwach or communicative language teaching
(eLT) as an approach to foreign or second language teaching which
emphasize that the goal of language learning is communicative
competence.8This approach has been developed by British applied linguistics
as reaction away from grammar-based approaches.
Communicative Competence
As stated before that the goal of language teaching based on
communicative approach is to develop communicative competence, it is
necessary to understand the concept of communicative competence.
15
The communicative compet(';nce was' first coined by Dell Hymes
(1972) as a reaction against the concept of language competence proposed
by Noam Chomsky in 1965. The term communicative competence has
received various interpretations, mostly based on sociolinguistics studies.
Communicative competence is the competence which enables us to
transmit and interpret messages and give meaning in the interaction between
individuals in a specific contexl.9 Communicative competence involves
being able to use the language appropriate to a given social context, to do
this learners need knowledGe of the linguistic forms, meanings and
functions. They must be [,ble to choose from among these the most
appropriate form, given the social context and the roles of the interlocutor.
They must also be able to manage the process of negotiating meaning with
their intern.
The concept proposed by Dell Hymes was subsequently developed
by other linguists. One development often cited in references is the model
developed by Michael Canale. According to him, communicative
competence consists of four domains of knowledge and skill, i.e.
grammatical, sociolinguistic, discourse and strategic competence.
16
a. Grammatical competence
This component is identical with linguistics competence. It involves the mastery of language codes both verbal and non-verbal, such as vocabulary, sentence formation, pronounciation, spelling, and semantics. This competence is required for the understanding and expressing literal mean ing of an utterance.
b. Sociolinguistics competence
Sociolinguistics competence relates to the extent an utterance expressed and understood correctly in different sociolinguistic context, which is turn depend on certain factors such as speaker-listener status, the objective of the interaction, and the rules and norms of the interaction. The appropriateness involves form as well as meaning.
c. discourse competence
18
According to Morrow, activities that are truly communicative have
three characteristics, those are: information gap, choice, and feedback.
a. Information gap.
In
the eourse of doing the activity, one participantshould be in a position to tell one or more other people something that
the others do not yet know.
b. Choice. The speaker must !'ave some role in deciding exactly what he
say and how he will say;\. This also means that there should be somc
unccliainty in the mind ofthc listener about the speaker will say next.
c. Feed back. What the speake;' say to the person he is communicating with
depend not only on what the other person say, but also what the speaker
wants to accomplish via the conversation.I I
Finocchiaro and Brumfit s'lid some characteristic of communicative
approach. The characteristics are:
a. Meaning is paramount
b. Dialogues, if used, cemer around communicative functions and are not
normally memorized
c. Contextualization is a basic prem ise
d. Language learning is learnirlg to communicate
e. Effective communication is sought
f. Attempt to communicate may be encouraged from the very beginning
1I Keith Morrow and Keith Johnson in Diane Larsen Freeman, Techniques and Principles in
19
g. Drilling may occur, but peripherally
h. Translation may be useG where students need or benefit from it
I. Reading and writing can stmt from first day, if desired
J. The target linguistic system will be learned best through the process of struggling to communicatc
k. Communicative competence is the desired goal (i.e. the ability to use the linguistic system effectively and appropriately)
I. Linguistic variation is a centml concept in materials and methodology m. Teacher help learners in any way that motivates them to work with the
language
n. Students are expected to interact with people, either in the flesh, through pair and group work, or in their wrings.
o. Intrinsic motivation will spring from an interest in what is being communicated by the lallguage.12
3. The Advantages and Disadvantages ufComl11unicative Approach
There are some advantages and disadvantages of communicative approach in learning-teaching process.
11 Mary Finocchiaro and Christopht;r J. Brumfit. The Flmctional National Approach; From
20
a. The Advantages
I) The students can use the language that it is learned as an instrument to communicate.
2) Psychologically studems are more active in asking question based on their communication nceds.
3) The relationship between the teacher and students are more familiar. 4) It is more humanistic, because it concerns with the students'
activities in real situations and has meaning in content or function in language.
b. The Disadvantages
1) It takes more time for the tel:cher to make preparation. 2) It needs teachers' creativity to make the class alive.
3) The teacher should master the materials in shorts of real situation in class activities.
4) Discouraging shy students to express their ideas (to produce sentences) because they are shy in other people in front ofthe class.
C. The Teaching of Simple Past Tense Based on Communicative Approach 1. Description of the Problem
21
functional as well as structural aspects of language, combining those into a
j. II . . . IJ
more TI y communicative View.
From the description above, it can be seen the two aspects of language, that are functional a'ld structural, combined are taught in order to makc the students able to cClr.municple with others in English.
The description of the teaching of the simple past tense Il1
communicative approach will be clearer and easier to be understood by the English teachers with the two terms. that areusage and use./4
The first term is usnge, refers to the manifestation of language system. It can be said that someone, who learns English, master the usage of English ifhe can produce sentences in English like the following:
The cat sat on the chair The farmer killed the duckI:ng
The dialogue is an example of usage of English: Teacher
Students Teacher Students
: Book
: There was book in my bag : Rain
: Itwas rain yesterday
lJ William Littlewood, Communicative Language Teaching (London: Cambridge University
Press, 1981J.p.94
14 H. G. Widdowson, Teaching Langage as Communication (London: Oxford Universily
22
The second term is the use ofthe longuage. Itcan be described as the knowledge of how usage is applied for normal communicative purposes. The students must be master both usage and use of language if they want to be able to communicate with others in the language they learn, for example if the students have mastered t:1e simple past tense in a conversation bellow: Dini . Did you go to the beach last holiday?
Agus : Yes, I did
Dini : What's on there'!
Agus : TlIltles.Itwere the big turtles.
The main goal of English te"ching based on communicative appro2ch
IS to enable the students to cor,1lTIunicate with others appropriately in
English.
2. Equipping Learning Materials
Before entering the class and giving the materials to the students, a teacher should note sever,11 preparation to make teaching and learning process successful and to meet theセエオ、・ョエGウ need.
a. selecting and preparing materials and class room activities b. integrating form meaning and content in syllabus design
23
d. preparing appropriate exercises and activities for rule presentation or error correction
e. consulting a variety of grammar rderence books in order to establish how a structure is formed, when it is used and whether there are any particular
I . " 15
ru es or exceptIons governmg Its usage.
• 3. Techniques of Presentation
There are some techniques or materials associated with the communicative approach which can be applied in the teaching learning process such as authentic materials, scrambled sentences, language games, picture strip story, and role-play. 16
a. Authentic Materials
This is used to overcome the typical problem that students cannot transfer what they learn in the classroom to the outside world and to expose students to natural language in a variety of situations. 1n this lesson the teacher uses foto copy of a genuine newspaper article. Healso assigns the students homework, requiring they listen to a live radio or television broadcast.
15 Marianne Celce Murcia and Sharon Hilles, Techniques and Resources In Teaching
Grammar(Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1988),p.7-8
24
b. Scrambled Sentences
The students are given a passage (a text) in which the sentences are in a
scramble order. In キイゥエエセョ passages, students might also be asked to
unscramble the lines of a mixed-up dialogue.
c. Language Games
games are used frequently in the communicative approach. The students
find them enjoyable, and if they arc properly designed, they give the
students value able communicative practice. Games also have the three
features of communication: in form "tion gap, choice, and feedback.
d. Picture Strip Story
In this activity, one student in a small group is given a strip story. I-Ie
shows the first picture of the story to the other members of his group and
asks them to predict what the second picture would look like. An
infOlmation gap existed, the students in the groups do not know what the
picture contained. They have a choice as to what their prediction would
be and how they would word it. They receive feedback, not on the content
of prediction, by being able to view the picture and compare it with their
prediction.
e. Role-Play
Role-play are very important in the communicative approach because
they give students an opportunity to practice communicating in different
25
that they are very structvre (for example, the teacher tells the students
who they are and what they would say) or in a less structured way (for
example, the teacher tells the students who they are, what the situation is,
and what they are talking about, but the students determine what they will
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter presents the description of the research method used in the study. It includcs thc research design, place and lime, population and samplc, method of sllldy, technique of data collecting,エ・」ィョゥアオセ of data analysis, and data analysis.
A. Research Design
This study is descriptive-evaluative in nature. It is called descriptive because this study tries to describe the objective condition about teaching the simple past tense based on communicative approach at the first year of SMK Islamiyah Ciputat. Since this study only focuses on specific school namely SMK lslamiyah Ciputat at first year, it is also considered as a case study.
Besides this study is also called evaluative because it tries to evaluate objectively about teaching tile simple past tense based on communicative approach at the first year ofセmk Islamiyah Ciputat. The evaluations conducted by way analyzing the teaching of simple past tense based on communicative approach. 17
27
B. Place and Time
The writer did the research at th(; first year of SMK Islamiyah Ciputat located in Jl. Kihajar Dewantara No. 23 Ciputat. The research has been started since Mei 23rd,2005 until June 04th,2005.
C. Populatiou and Sample
Population of the research is students at the first year of SMK Islamiyah Ciputat. This level consists of 3 classes with 42 students in each class and the total number of students are 146 students.
Here the writer did not take total of population as sample. But for observation the sample are only 40 studen:s.
D. Method of Study
In completing data, the writer conducts Library study and Field research. In the library study, the writer reads some books dealing with the topic as listed in the bibliography to support this article and the books are found from three libraries in Jakarta: library of UIN Jakarta, library of UNJ Jakarta, and library of AMINEF.
28
tense based on communicative approach. The list of questions can be seen in the instrument of research.
Eo Technique of Data Collecting
In completing the data, the writer uses some techniques of data collecting such as observation, teaching learni'1g process, interview, and test.
I. Observation
Before doing research, the writer first of all observes the location and population where the researcb is carry out. The observation was done on Monday, Mei 23'd2005.
The writer observed about the application of communicative approach
111 teaching the simple pm,! tense at SMK Islamiyah Ciputat. Therefore, this
technique can be categorized as non-participant observation. 2. Interview
interview was hold witl, the English teacher at the first year of SMK Islamiyah Ciputat. The inerview was done on Wednesday, Mei 25th 2005. It is meant to know the real condition in applying the communicative approach and how far the students' interest and their ability in learning English grammar especially simple past tense.
3. Teaching Learning Process
29
teaching Icarning process are devided into three parts, namely motivating strategies, prescntation, skill and practicc. This activities were hold on Saturday, Mei 28th2005 and Wednesday, June 01st2005.
First, the writer did thセ motivating strategies by making communicative activities with asking some students, such as: "what did you do this morning?", and many serltences are given by the students, such as: "1
watch telenovela","Iwent to the market", "Iread a story book", etc.
Second, the writer explained about the pattern of simple past tense like the following:
Subject
+
Past Verb+
ComplementBesides the pattern of simple past tense above, the writer explained to about the regular & irregula" verbs, the past tense form of be (was & were), the past form of auxiliary verb do (did & didn't) and the time expressions.
In
every explaining, the writer gr.ve separated sentences as the examples, such as:
I went to East Java last month He played badminton yesterday Mother was at home this morning My brother didn't go to school yesterday
The writer repeated this セ」エゥカゥエゥ・ウ two times 111 order to make the
30
writer asked if the students had question related to the explanation of simple past tense forms.
Third, the writer did skill practice. The writer asked to some of the students to made the sentence of simple past tense. When the students made wrong sentences, the writer corrected it. For example:
The wrong sentences: Teacher
Student 1 Teacher Student 2 Student 3 Student 4 Student 5
: What did you do yesterday? : IgQto Ira's house yesterday : When was you born? : I am born in 1989
: 1 visit my grandmother last year : I stud.): English this morning
: I doing my home work last night
The writer gave the correct of wrong sentences above, such as: I went to the Ira's house yesterc1ay
I was born in 1989
I visited my grand mother last year I studic:d English this morning I did my home work last night
31
4. Test
The test is given to the students to know the students' ability after
learning simple past tense based on communicative approach. The writer gave
the test on Saturday, June 04th 2005 and it consisted of 20 questions to the
students. The student must did the test individually. The writer counted that
the students were able to do the test in 20 minutes. The results of the test is
listed in the technique of analysis and data analysis.
F. Technique of Data Analysis
The technique analysis used in this research is descriptive analysis
technique (percentage) which is described in the table percentage using formula:
P :
f
x
100 %N
P : Persentage
F : Frequency
N : Number / amount
After having the percentage and frequency, the average mark will be
taken by using formula:
Mean
If.
xi32
G. Data Analysis
As stated 111 method of "tudy, the writer conducted the field research
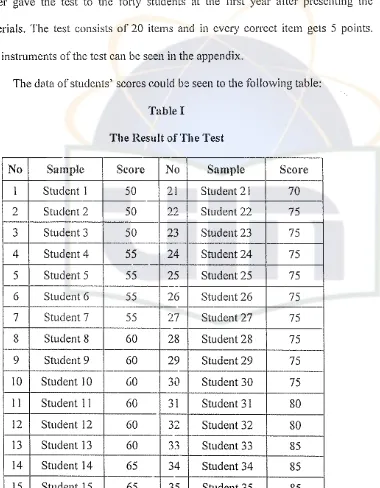
method and she collected the data from application test of simple past tense. The writer gave the test to the torty students at the first year after presenting the materials. The test consists of 20 items and in every correct item gets 5 points. The instruments ofthe test can be seen in the appendix.
[image:37.521.67.447.205.693.2]The data of students' scores could be seen to the following table: Table I
The Result of The Test
No Sample Score No Sample Scorc
1 Student 1 50 21 Student 21 70
2 Student 2 50 22 Student 22 75
0
Student 3 50 23 Student 23 75
.J
-4 Student 4 55 24 Student 24 75
5 Student 5 55 25 Student 25 75
6 Student 6 55 26 Student 26 75
7 Student 7 55 27 Student 27 75
8 Student 8 60 28 Student 28 75
9 Student 9 60 29 Student 29 75
10 Student 10
GO
30 Student 30 75II Student 11 60 31 Student 31 80
12 Student 12 60 32 Student 32 80
-13 Student 13 60 33 Student 33 85
14 Student 14 65 34 Student 34 85
16 Student 16 65 36 Student 36 85
-17 Student 17 65 37 Student 37 85
_.-18 Student 18 70 38 Student 38 90
-19 Student 19 70 39 Student 39 90
20 Student 20 70 40 Student 40 90
_._-
--To find out number of class and interval of data students' scores using: Number of Class (C)
C = 1+(3,3) Log n
= 1
+
(3,3) Log 40 = 1 + (3,3) (1,6021) = 6, 28693= 6 classes
Ratio (R) is the highest mark (H) minus the lowest mark ( L )
R =I-l-L+ I
=90-50+ 1
= 41 Interval ( I )= R
C
= 41 6 =6,83 =7
34
The following table presents the frequency and percentage ofthe test result: Table II
Frequency and Percentage of The Test Result Frequeuey Percentage Mid Poiut
FXi Iuterval
(F)
(P)
(Xi)- - - -セ セM セMM M M M セ --- - - -
-90 -97 0
1,5 93,5 280,5
j
-
---82 -89 5 12,5 85,5 427,5
-
-74- 81 11 27,5 77,5 852,5
66-73 4 10,0 69,5 278
58 -, 65 10 25,0 61,5 615
50 - 57 7 17,5 53,5 374,5
-Total 40 100
2828
The formula used to find out mean: Mean = I: Fxi
N 2828
40
= 70,7
Iuterpretation
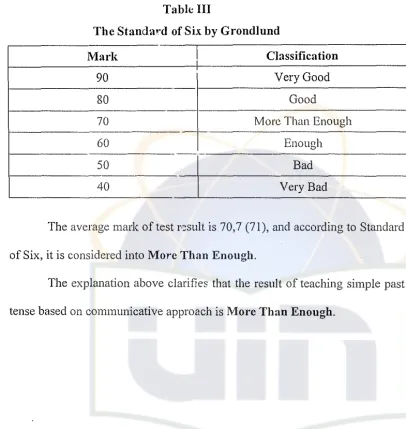
Before interpreting and discussing the data, the standard of mark that is made by Norman E. Grondlund. mark that is called of six of following:
writer will quote
18
The standard of
35
Table III
The Standm·d of Six by Grondlund
Mark
I
ClassificationI
90
Very Good80
Good70
More Than Enough- -
f-60
Enough
-50
Bad40
Very BadThe average mark of test p;sult is
70,7
(71), and according to Standardof Six, it is considered intoMore Than Enough.
The explanation above clarifi.c8 that the result of teaching simple past
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents and discusses the findings of the research based on the data gathered during the investigation. According to the research problems, it presents and discusses the research findings as follows: teacher qualification, teaching preparation, instructional materials llsed at the first year SMK Islamiyah Ciputat, instructional activities, and the teac'ling technique used by the English teacher at the first year of SMK Islamiyah Ciputat.
The findings are analyzed on the ba3is of the gathered data and the discussion
IS derived from the analysis of findings and theoretical framework discussed in
chapter II.
A. Teacher Qualificatiou
At first year of selling department of SMK Islamiyah Ciputat there is one teacher who teaches English subject, namely . the table bellow will shows the personal details of the teacher:
Table IV
TC}lcher Qualification
Dian Rostikawati,sャセ
1999, En lish course fl'Om
11<!110rHl')' ..
S I from S'1'JEI, Faculty of Economy
Female 25
ndnl M,SE
glish course from
' L - .
STIE Ahmad
acuity of Economy
No Descrintion M.I
1 Age 3:
2 Sex Male
) j"lonorary/Public ServantHセゥセゥNANNNM ⦅ャAセ
4 Latest Education Sj from
37
lEe L1A
.._--_.
---_._---Iyear, since2004/2005
Experiences I ケセ。イL since 2004/200;
CipllLat aClllit'lllit..: vcar
--Experiences
-
-( lslamiyah
-6 English Teaching aL SMK Islami ail 7 English Teaching
Beside at SMI Ciputat
Based on the data shown in the bble, the writer conclude that the English teacher at first year of SMK Islamiyah Ciputat are not qualified to teach based on 2004 curriculum because they are not graduated from English department.
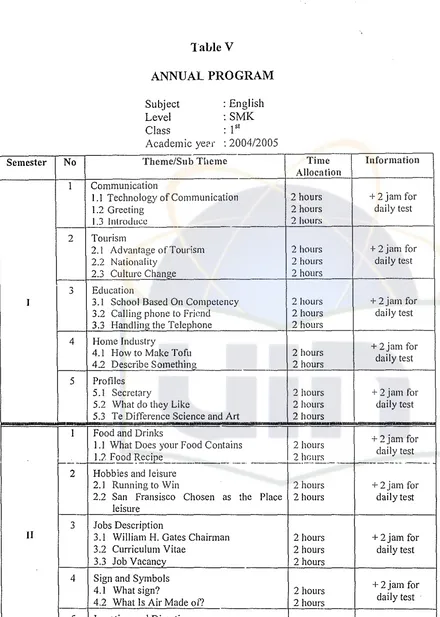
B. Tcaching Preparation
Table V
ANNUAL PROGRAM
38 Subject Level Class Academic yep!" : English :SMK : 1sl:2004/2005
Semester No Theme/Sub TllCll1e Time Information
Allocation 1 Communication
l.l Technology of Communication 2 hours +2jam for
1.2 Greeting 2 hours daily test
1.3 Introduce 2 hours
2 Tourism
2.1 Advantageof TOllrlsm 2 hours +2jamfor
2.2 Nationality 2 hours daily test
2.3 Culture Change 2 hours
3 Education
1 3.1 School Based On Competency 2 hours +2jam for
3.2 Calling phone to Friend 2 hours daily test
3.3 Handlin" the Teleohone 2 hours 4 Home Industry
+2jam for
4.1 How to Make Tofu 2 hours
4.2 Describe Something 2 hours daily test
5 Profiles
5.1 Secretary 2 hours +2jam for
5.2 What do they Like 2 hours daily test
5.3 Te Difference Science and Art 2 hours
I Food and Drinks
+2jam for
1.1 What Does your Food Contains 2 hours
1.7 Food R.."cipe____.____ .._____ 2 heurs daily test
I- t-=-:-.. - ..- ..- 1---._---_..._.-.
2 Hobbies and leisure
2.1 Running to Win 2 hours + 2jam for
2.2 San Fransisco Chosen as the Place 2 hours daily test leisure
3 Jobs Description
11 3.1 William H. Gates Chairman 2 hours +2jam for
3.2 Curriculum Vitae 2 hours daily test
3.3 Job Vacancy 2 hours
4 Sign and Symbols
+ 2jam for
4.1 What sign? 2 hours
4.2 What Is Air Madeof? 2 hours daily test
5 Location and Direction
5.1 Showing the Bank 2 hours +2jamfor
5.2 Expression for Feeling 2 hours daily test
[image:43.531.16.456.61.678.2]--39
C. The Instructional Materials Used
The English text book used at SMK Islamiyah Ciputat consist of two books, namely; (1) English text book and (2) book of students' spread sheet. Both of the books published by Yudisti'·a.
Pursuant to curriculum used at the lirst year of SMK Islamiyah Ciputal is 2004 curriculum. The Objectives of Fnglish Lesson based on 2004 Curriculum are:
1. Communication in English
2. Understanding English as a system 3. Understanding culture
4. Knowledge
D. The Instructionl Activities
Teaching activities of teachi"g simple past tense from the research, it Islam found that the activities of te1ching s;mple past tense at the first year of SMK Is[amiyah Ciputat as shown as follows:
I. Greeting
2. Checking the attendance list 3. Giving students' Motivation
40
7. Giving exercise 8. Discussing exercise 9. Giving homework
K The Teaching Teehniqnes Used
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION ANDsugc[eセ[tioャ|イs
A. Conclusion
Based on the prevIous datel analysis, the writer make conclusion the effectiveness of teaching of simple past tense based on communication approach is more than enough. That is can be seen the average score of the test. The average score is 70,7 (71). According te the standard of six made by Norman E. Grondlund, that score meansmore than enough.
B. Suggestions
There are some suggestion that can be given in relation to the writers' conclusion. The suggestion are as foliows:
I. The English teacher should use communicative approach in English teaching learning process.
2. Itis necessary for English teacher to :mprove their knowledge of English language anclmethods of language teaching.
3. The English teacher should be creaCve in developing the teaching learning activities in classroom to make the class alive.
4. The English teacher ought to give the students oppoltunities to be active in teaching learning process.
lHBUOGRAPHY
Alexander,Longman English Grammar,London: Longman Groove UK Ltd, 1988. Azar, Betty Schrampfer, Undentanding Using English Grammar, New Jersey:
Prentice Hall Inc., 1972.
Brown, D. H., Principles of Language Le_7ming and Teaching, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 1937.
Canale, Michael, From Communicative Competence Language Pedadogy, In Richards J. C. and R. W. Schmidt, Language and Communication, London:
Longman Group Limited, 1983.
Diane Larsen Freeman, Techniques aud Principles in Language Teaching, Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1986.
Frank, Marcelle, Modern English: A Praclical Reference Guide, New Jersey:Prentice Hall Inc., 1972.
Harmcr, Jercmy, 7'l7e Practice of English Language Teaching, London: Longman Group UK Ltd, 1991.
Littlewood, William, Communicative Language Teaching, London: Cambridge University Press, 1981.
Murcia, Marianne Celce, and I-Iillcs, Sharon, Techniques and resources in Teaching Grammar,Oxford University Pre3s, 1988.
Richard, J. C., The Status o/Grammar in the Language Curriculum, Paper Presented in SEAMD Regional Language Cenkr, Singapore: RELC, 1985.
Widdowson, H. G., Teaching Language as Communication, London: Oxford University Press, 1984.
Appendix 1
Insrument of R",search
The interview with the English teacher:
I. What is the book llsed as teaching material?
2. What is the method llscd in teaching Engli"h in the class?
3. What is the most emphasized in teaching English (speaking. reading, writing or
listening)?
4. Is there any media used beside the book?
5. How is the conception and attention from the students 111 teaching English
especially in grammar?
6. According to you, what should the teachers do to obtain satisfactory in teaching
Appendix 2
RESEARCH INSTRUMENT
Name
Class
Fill the blank with the correct answer! 1. I to the mall yesterday
Subject: Dllte a.go b.gone e. went d.goed
2.
My brother ... a bear an hour agoa. seen
b. saw
3.Alex did not last weekend a. work b. worked c. sees d. seed e. working d. worker
4 Mike visit his grandmother last holiday? a. did
b. are
e. does
d. was
5... Judy and LiJis at last months' ュ・・エゥョァセG
a. did
b.
aree.
wasd. were
6. We ... not happy after the sad ending
a. was b. were
c.da
7. ... you see
J
ani's new cat yet?a. did c. do
b. are d. was
8. Sorry, I hear you at the door
a. wasn't c. am ョッセ
b. didn't d. don't
9. I English for two years
a. study e. studied
b. studying d. studies
10. What ... you eat for luneh yesterday?
a.do
b. did
II. Did tara phone you 1st night?
a. no, she do
b. no, she does
12. I ... in Medan for two years
a. live
b. life
C. was
Q. wert'
c. yes, she was
d. yes, she did
c.lived
d. leaves
13 you watch foot ball champion last week?
a. do c. did
14. We didn't the telephone
a. hear
b. heard
c. hears
d. her
15. Did you tennis three days ago
a. plays c. pl'Wed
b. play
16. We not late for the train
a. are
b. were
17. It cold yesterday
a. are
b. were
18. He didn't ... the movic
a. like
b. likes
19. She the door
a.open
d. playing
c. \vas
d. did
c. \Vas
d. did
d. liking
c. opened
b. opens d. opening
20. Dery and Mary at home this morning
a. are c. do
Appendix 3
!<:EYANSWER
I.e
11. D2. B 12.
e
3. A 13.
e
4. A 14. A
5. D 15. B
6. B 16. B
7. A 17.
e
8. B 18. A
9.
e
19.e
NomoI' Lamp Hal
:Istimewa
: I (satu) lcmbar
: Pengajuan judul Skripsl
Ciputat, 14 Juli 2004
Kepada Yth,
Ketua Jurusan
Tadris Bahasa Inggris Di,
Tempat
Assalalllu' alaikulll Wr. Wb.
Semoga kesejahteraaan tercmahkan kepacla Bapak elan sclalu sukses menjalankan aktifitas sehari-hari, Amin.
Mengingat akan berakhirnya m:lsa stueli saya eli tingkat strata 1 (S I), maIm saya yang bertanda tangan eli bawah ini:
Nama : Sondang trianasari
NIM : 100014018051
Fakultas : Tarbiyah
Jurusan : Tadris Bahasa 1nggrls Bermaksuel mengajukan skripsi mengenai:
THE TEACHING OF SIMPLE PAST TENSI, BASIW ON
COMMUNICATIVE APPROACH (A Case Study at First Year Of SMK Islamiyah Ciputat)
Sebagai bahan pertimbangan bagi Bapilk, bersama ini saya lampirkan: 1. abstraksi
2. Outline
Mengetahui,
k・エオ。Lセ urusan
( '
[セiゥスG
'j11.L /
Drs, Nasrllil
Mahl1111cl rv1.pclPemohon
Sondang Trianasari
DEPARTEMEN AGAMA
UNIVERSITAS ISLAM NEGERI
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH JAKARTA
FAKUL'l'AS ILMU TARBIYAH DAN KEGURUAN
ndn Nomor 95, Cipula! 15412, Indonesia
T,lr. :(62-21) 7443328, 7401925.Fax.(62-21) 7402982
Email: [email protected] .
_ _ twew
M_ _
er'M W_UIlIIliI!!I'?PU'IWIlTWlWV'?''''1fJWJ> M
NomoI' Lamp. Hal
:
ETITL.02.2/VI/2005
:'Instrumen Riset
:RISET IWAWANCARA
Kepada Yth.
Kepala SMEA Islamiyah Ciplltat
di-Tempat
Jakarta, 20 Mei 2005
Assalamu'alaikum WI'. ·wb.
Dengan hormat kami sampaikan bahwa : N a m a : Sondang Trianasari
adalah benar mahasiswa Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah& Keguruan UIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta: NIM Jurllsan Semester Program : 100014018051
: Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris : X (sepuluh)
: S-1
Sehubllngan dengan tugas penyclcsaitln skripsi yang bcrilldlll:
"The Teaching of Simple Past Tense Based on Comrmmicative Approach (A Case Study at First Year of SMK Islamiyah C'iputat)"
Kami mohon kesediaan SauJara untuk menerima dan membantu mahasiswa/i tersebut. Atas perhatian dan bantuan Saudara, kami ucapkan terima kasih.
Wassalamu'alaikum WI'. wb.
Tembusan:
I. Dekan FITK 2, Ketua Jurusan ybs.
3. MahasiswaValW hersmwtmtRn
a.n. Dekan
Pembantu Dekan Bidang Akademik,
f\a
356r-[PUTAT
YAYASAN ISLAMIYAH CIPUTAT
Akta
NomoI'16, TanggaI 11 Agustus 1978 Bank: BRI danBI'D Rek. 21201
SEKOLAH MENr.-NGAH KEJURUAN ISLAMIYAH
(STATUS: DlSAMAKAN)
NO. 79jC.C7jKEPji'PjZOOOAlamat:)1. Kihajar Dewantara No. 23 Ciputat. Telp. 7409814
SURAl'
keteiゥFセGQNomoI' : 425/D.3/SMK-ilC/VV2005
Assalaamu'alaikum WI'. Wb.
Yang bCl'tandatangan di bawlIh ini, Kepala 8MI< Islamiyah Cipulat menerangkan bahwa : Nama
NIM JUl'Usan Fakultas Universitas
: Sondang Trianasari
: 100014018051
:PBI
: Tarhiyah dan Hmu Keguman : DIN SyarifHidayatulIah Jakarta
Te1ah me1aksanakan Penelitian eli sekolah Kami pada tanggal : 23 Mei 2005 s.d. 4 Juni 2005, denganjudul :
"TIle Teaching of Simple Pasi Tense Based On Communicative Approach (A Case Study at First Year ofsャセik Islamiyall Ciputat)"
Demikianlah surat keterangan ini kami buat. Atas perhatiannya kami mengucapkan tcrima kasill.