Eighth Grade Students of MTs. Soebono Mantofani Ciputat) “ written by Wini Widyaningsih, student’s registration number : 204014003237, was examined by the committee on 2 September 2010, and was declared to have passed and, therefore, fulfilled one requirements for the academic title of S.Pd. (Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education at the Department of English Education,
Jakarta, 2 September 2010
EXAMINATION COMMITTEE
CHAIRMAN : Drs. Syauki, M.Pd. ( ) NIP. 19641212 199103 1 002
SECRETARY : Neneng Sunengsih S. Pd. ( ) NIP. 19730625 199903 2 001
EXAMINERS : 1. Drs. Sunardi K, Dipl. M.Ed. ( ) NIP. 150022779
2. Drs. Nasifuddin Jalil, M.Pd. ( ) NIP. 19560506 199003 1002
Acknowledged by :
The Dean of Tarbiya and Teachers’ training Faculty
Prof. Dede Rosyada, MA NIP. 19571005 198703 1 003
inappropriate in comprehending the tense will lead us to make a mistake in understanding and producing an English sentence. The very basic tense that is learned and should be understood by the students is Simple Present Tense.
The Simple Present Tense has been learned from the earlier, but it doesn’t make students easy to understand its patterns and use. It is clearly seen from the mistakes that they have made in their tasks.
The inability students in comprehending the Simple Present Tenses -and also other grammar item- is because they regard it as uninteresting and difficult material to be learned. Besides, there are also some students who are not really involved in the learning process in class. For that reason teacher should find ways to overcome the problem. One of the ways is by using a variation of teaching method or technique in teaching the grammar item of simple present tense to students. One of the technique is Cooperative Learning approach with one technique of it that is Students Team Achievement Division (STAD).
Great thanks to Allah for the mercy and blessing that has been given to the writer, so she can accomplish her “skripsi”. Peace and Salutation be upon Muhammad, the beloved Prophet, and his household, companions and his faithful followers.
This “skripsi” is presented to the English Education Department, the Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers Training, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta as a partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of S. Pd. (Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education.
The writer would like to thank her beloved parents for their prayers, encouragement, and understanding, also their support in material and immaterial that helped the writer in finishing this “skripsi”. She also would like to thank to her family.
On this occasion, the writer would like to give her great appreciation, honour and gratitude to Drs. Bahrul Hasibuan, M.Ed., as her advisor, for his time, guidance, corrections, suggestions and patients in the completion of this “skripsi”.
The writer also would like to express her great honour to all people who helped her in completing this “skripsi”, particularly to :
1. All lecturers of English Education Department, for giving motivation, value, knowledge, support, and best experience during her study at Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University, Jakarta.
2. Prof. DR, Dede Rosyada, MA., as the Dean of Tarbiya and Teachers Training Faculty
3. Drs. Syauki, M. Pd. As the Head of English Education Department and Neneng Sunengsih, S. Pd., as the Secretary of English Education Department.
5. The teachers and the staffs of MTs. Soebono Mantofani who have helped the writer in collecting the data.
6. The writer also would like to give her greatest thanks to all her best friends for their support and time in sharing their ideas with the writer in finishing this “skripsi”; Lidya Suanty, Pupung Nurhayati, Erna Satiyah, Siti Imas Maesaroh, Syfaun Najiah and all of the friends in English Department, especially class B 2004. They are the best.
May Allah the Almighty bless them all, Amien.
Jakarta, March 2010
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT...iii
TABLE OF CONTENT...v
LIST OF TABLE...vii
CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION A. The Background of the Study...1
B. The Limitation of the Study...5
C. The Formulation of the Study...5
D. The Significance of the study...5
E. The Method of The Study...6
F. The Organization of the Study...6
CHAPTER II : THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK A. Cooperative Learning 1. The Understanding of Cooperative Learning...8
2. The Elements of Cooperative Learning ...10
3. The Activities in Cooperative Learning...12
4. The Students Team Achievement Division (STAD) as One Technique of Cooperative Learning...13
B. The Simple Present Tense 1. The Understanding of Simple Present Tense ...15
2. The Usage of Simple Present Tense ...16
3. The Form of Simple Present Tense...17
Present Tense ...20
CHAPTER III : THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE RESEARCH A. The Methodology Of The Research 1. The Objective of The Research...22
2. The Place and Time of The Research ...22
3. The Population and Sample of The Research ...22
4. The Technique of Data Collecting ...23
5. The Technique of Data Analysis...23
6. The Procedure of the Research ...25
B. The Findings Of The Research 1. The Description of Data ...26
2. The Analysis of Data...29
3.
The Hypotheses Testing...32CHAPTER IV : CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS A. The Conclusions...35
B. The Suggestions...36
BIBLIOGRAPHY...37
2. Table 3.2. The scores of pre-test and post-test of control class…………...28 3. Table 3.3. The analyse of students’ scores of experimental class………..…..29 4. Table 3.4. The analyse of students’ scores of control class……….…….…..30 5. Improvement points table………...69 6. Table of the personal details of the teachers………...70
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
THE PROFILE OF MTs. SOEBONO MANTOFANI CIPUTAT
A. Brief History Of MTs. Soebono Mantofani
Madrasah Tsanawiyah (MTs.) Soebono Mantofani Ciputat is a non government school in Jombang, Ciputat. It is a kind of Islamic Junior High School, which the students are taught solely on the base of Islamic beliefs. MTs. Soebono Mantofani resides below the Soebono Mantofani foundation. There are four levels of formal education institution that residing below this foundation, they are : Raudathul Athfal (Kindergarten), Madrasah Ibtida’iyah (Elementary School), Madrasah Tsanawiyah (Junior High School) and Madrasah Aliyah (Senior High School) of Soebono Mantofani. All the schools are located in one area on Jl. Sumatera No. 75 Jombang Ciputat, Tangerang Selatan.
MTs. Soebono Mantofani was officially opened in 1995 and now is led by Dra. Hj. S. Abidah Thohayah, M.Ag. There are 16 classes in the school with 525 students and 17 teachers. With the details number of students in each grade are: the seventh grade with 161.students, the eight grade with 170 students, and the ninth grade with 194 students.
B. The Curriculum
Curriculum has important role for the success of an educational institution since it gives guidance for the institution as the basis in carrying out the educational program in order to achieve the institutional goal.
For this time the MTs. Soebono Mantofani uses the School-Level Curriculum the “KTSP”. It has been developed since 2006 and now it is developed into syllabus, lesson plan, and annual program.
C. The Process of Teaching Leaning Activity
As the writer had observed and interviewed, the teacher usually uses the traditional technique in the process of teaching learning activity. She usually presents the material, then gives some exercises to the students, once in a while she governs the class in the group.
English is used in low intensity in class, however the teacher sometimes uses the English expression when she interacts to students. It is intended that the students will become accustomed to English expression and also to raise their interest in English. The teaching learning activity of English is only takes place in class. Besides that, there is an audio-visual room that can be used to support the teaching learning of English.
The teaching learning process in class is begun with socializing, the teacher greets the students, reads attendance list, and then she opens the lesson. She opens the lesson by asking students some question to reviewed the last material and continues by making up some conversation to students as lead in to stimulate them concerning to the new lesson. Then presentation and skill practice are considered as the essence of the process of teaching learning activity.
In the teaching learning activity teacher mostly presents the students with reading material, and then she combines it with teaching other English skills and sub skills.
D. The English Text Book
English textbook which is used by the eighth grade students of MTs. Soebono Mantofani Ciputat is the English textbook published by Mediatama with titled “ English for Junior High School” it is created by Eny Nursanty and Mahmudah Ratna S. there is also students’ work sheet (LKS) that is used as an addition in completing the lesson material.
E. The Profile of The English Teacher
There are three English teachers in MTs. Soebono Mantofani Ciputat. Each teacher teaches each grade level of the class. The following table informs the personal details of the teachers:
The Personal Details Of The Teachers
No Name Age Sex Honorary/Public Servant Civil Teaching Experience Grade/ class Latest Education 1. Tuti Rahayu
43 Female Honorary Since 1995 (15 years)
VII S 1 from “UIN Jakarta” English Education Department 2. Yumaenah 40 Female Public Servant
Civil
Since 1990 (20 years)
VIII S 1 from “UIN Jakarta” English Education Department 3. Dani Setiawan
25 Male Honorary Since 2008 (2 years)
The “Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers’ Training in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements
For the Degree of S.Pd. (Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education
By :
WINI WIDYANINGSIH NIM : 204014003237
THE DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
THE FACULTY OF TARBIYA AND TEACHERS TRAINING
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH
JAKARTA
The “Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers’ Training in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements
For the Degree of S.Pd. (Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education
By :
WINI WIDYANINGSIH NIM : 204014003237
Approved by the Advisor
Drs. H. Bahrul Hasibuan, M. Ed.
THE DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
THE FACULTY OF TARBIYA AND TEACHERS TRAINING
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH
JAKARTA
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
A. The Background of the Study
The receptive and productive skills are skills that are known in learning a language, including English. Receptive skills consist of listening and reading, while productive skills consist of writing and speaking. The four skills need to be developed in order to acquire the communication competency of the language. Besides, in order to acquire of those skills it must be empowered by mastering its’ component.
According to Penny Ur, the components of the target language may be things like spelling or pronunciation or vocabulary – or grammar.1
Among the components of the target language, grammar has great attention related to its necessity in learning a language. Some argue it is not really necessary to learn while other keep it in. In fact, grammar is equally important to be learned since the language itself is constructed by rules.
CM Millward in his book points out that language is a system, or more precisely, series of interrelated systems governed by rules. In other words,
1
Penny Ur, Grammar Practice Activities; A Practical Guide for Teachers, Bell and Bain Ltd, New York, 1992. p : 5
languages are highly structured; they consist of patterns that recur in various combination and rules that apply to produce these patterns.2
The statement above reveals that language is homonymous as a system. Its system consists of elements which are a part of language components, such as; word, sound, and meaning. Each elements in the system has function and relates to each other in order to achieve the goal that is, to yield a meaningful unit of language. For that purpose, those elements need to be constructed by rules. These rules and patterns are arranged in regular way to makes up language easy to learn and enables to use. The first of all patterns and rules in English is what we know as grammar.
Moreover, grammar may be roughly defined as the way a language manipulates and combines words (or bits of words) in order to form longer units of meaning.3
It can be said that grammar has function to combine the succession of words in order to gives meaning to its succession. These words are combined and manipulated to create any number of different sentences. It helps us to convey our meaning and determine others’ accurately. So that it can create an effective communication for us. In another words, grammar will facilitate us in the mastery of the language skills
Structure is the specific instance of grammar. One of its structures is tense. The word tense stands for a verb form or series of verb forms used to express a time relation.4
Since the most basic element of an English sentence is verb, tense become the staple of all grammar structure. It frequently appears both in English utterances and texts. Accordingly tense has fundamental role in the English language, so the inappropriate uses of tenses may obscure the meaning. It can be seen from the following example:
2
CM Millward, A Biography of The English Language, second edition, Thomson Inc., Boston, 1996, p:2
3
Penny Ur, Grammar Practice Activities…, p : 4
4
1. He works in a five star hotel. 2. He worked in a five star hotel.
The two sentences above have a very different meaning, although the differences only in the suffix of the verb ‘work’; s and ed. The first sentence means he works in a five star hotel at this time. The second one has the simple past tense structure, which mean he no longer works in a five star hotel.
The relationship between the tense with the time and the change of the verb form is usually regarded as the difficulty in learning the tense. No exception with the simple present tense, in spite of it is the basic and the first that is introduced to the learners.
The reasons are; not only because the tense doesn’t appear in their native language, but also because some students often consider that the teaching learning activity of grammar item as uninteresting activity in class since there are many patterns and rules to be learned and remembered. Consequently they regard the grammar item as a boring lesson. So that students need a variation of a teaching technique to avoid their boredom and to generate their motivation to learn.
Only a part of students that are really involved in the learning process in class, the rest are busy with their own thinking. They are not interested in the lesson and activity in class. Most of them are lack of self-reliance over their own ability to learn. For that reason, the teacher should foster the sense of believing to students that they all can learn and then find ways that can enable them to be more concern in their learning.
Alfred H. Gorman noted in his book that, teaching is not accomplished by the teachers demonstrating to their students how learned they, the teachers, are. Teaching is accomplished only when learners learn, retain what they learn, and develop both the urge to use their learning in later situations and some methodology for putting learning to work.5
5
Therefore a class should be a place that is provided for students to activate their learning. For that, the teacher should to facilitate the learning process by giving each students opportunity to learn.
Moreover learning particularly in school, as a formal institution of education, is not merely to pass the examination, having a good grade, and also not merely an activity that emphasizes the final goal of the lesson. Rather, the teacher, as the first person in the system who interacts directly to students, should to give experience to students that can be applied in their life when they encounter the real community or workforce.
According to Dewey, education is a social process, and it cannot be separated from the total character and tasks of society. In the school, therefore, should be concentrated all those activities which help and teach the child to share in the process and the fostering of civilization.6
It is clearly seen, the statement above emphasizes that education institution is not only a place to teach the students but also a place to educate them as the social creature. For that reason, teacher should to teach to students a social skill that will be useful for their life. One of the ways that can do by the teacher to include all the needs of the students above is by using a teaching method that is cooperative learning technique in his/her teaching learning activity in class.
Cooperative has been emerging in the whole life of human history and the technique has been applied in teaching learning activity, which is known as Cooperative Learning. It is a method where students work and learn in-group. Nevertheless, it is not only grouping the students and ask them to accomplish the work. Cooperative learning principles and techniques are tools which teachers use to encourage mutual helpfulness in the groups and the active participation of all members.7
6
Robert Ulrich, History of Educational Thought, American Book Company, New York, 1950. p : 318
7
It means that cooperative learning technique gives an opportunity to students to be an active learner. One techniques of cooperative learning is Student Teams-Achievement Divisions (STAD). The use of STAD will raise students’ level attention to the lesson, because the progress of each member will be counted. Thus, it will push them to learn and to help others team member to do so.
So, by using cooperative learning with Student Teams-Achievement Divisions (STAD) method, students will not only experience the learning process, but also develop their social skills. It will raise their level of attention and motivation to learn. That is why the writer chose The Teaching of Simple Present Tense Through Cooperative Learning (An Experimental Study at Eighth Grade Students of Madrasah Tsanawiyah Soebono Mantofani Ciputat) as the title of this writing.
B. The Limitation of the Study
The writer limits the extend of the study only in the implementation of Cooperative Learning using the method of Student Teams-Achievement Divisions in teaching Simple Present Tense at the eighth grade students of Madrasah Tsanawiyah Soebono Mantofani Ciputat.
C. The Formulation of the Study
Based on the background of study, the writer formulates the problem as; “The writer beliefs that using Student Teams-Achievement Division method as one technique of Cooperative Learning group is better than the Grammar Translation Method in the achievement of the students mastery of the simple present tense”
D. The Significance of the study
It is expected the study will give contribution to English teacher in teaching grammar, in this case Simple Present Tense, particularly to give an alternative way in selecting the method and techniques will be used.
E. The Method of The Study
In doing this research the writer employs experiment method by teaching two different classes using two different techniques. The first class is an experimental class that will be taught by using one technique of Cooperative Learning, which is Student Teams-Achievement Division. The second class is a control class that will be taught by using Grammar Translation Method. This research is begin by administer the pre-test and closed by administer the post-test to the students. Then the results of the two tests are compared using the T-test formula to determine the final calculation of the research.
F. The Organization of the Study
The discussion on this writing encompass of four chapters as follow: Chapter one is the introduction, which explained the background of the study, which is the reason of choosing the topic as the basis of writing. Then it is followed by the limitation of the study, the formulation of the study, the significance of the study, the method of the study and the organization of the study.
Present Tense and the Grammar Translation Method in teaching Simple Present Tense.
Chapter three is the implementation of the research. The chapter is distinct into two divisions that are the methodology of the research and the findings of the research. The methodology of the research consist of the objective of the research, the place and time of the research, the population and sample of the research, the technique of data collecting, the technique of data analysis, and the procedure of the research. While, the findings of the research consist of the description of data, the analysis of data, and the hypotheses testing.
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Cooperative Learning
1. The Understanding of Cooperative Learning
Cooperative learning is a group-centered and student-centered approach to classroom teaching and learning.1 Cooperative learning is used as a variety in teaching learning activity in class that focuses particularly to students. For that purpose the students are put into the groups to achieve the learning goal.
With cooperative learning, students work together in groups where usual size is two to four members.2 Cooperative learning group is a heterogeneous group. Students are put in the group based on the differences in their academic performance, gender, etc.
More clearly Carolyn Kessler points out the definition of cooperative learning as: “… group learning activity organized so that learning is dependent on the socially structured exchange of information between learners in groups and in which each learner is held accountable for his or her own learning and is motivated to increase the learning of others.”3
1
Jack C. Richards and Willy A. Renandya, Methodology in Language Teaching; An Anthology of Current Practice, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2002. p; 52
2
Shlomo Sharan, ed., Handbook of Cooperative Learning Methods, Praeger Publishers, Westport 1994. p: 336
3
According to the statement above cooperative learning group is group learning where all students in the group have equal opportunity to learn. They learn by develop discussion among them to share information or knowledge concerning the material presented.
In cooperative learning group students are individually accountable. For that purpose, to reach the group goal, students not only will take their own responsibility to learn, but also they will encourage and help other group member to do so.
The interaction among students will maintain their interest and motivation, since it provides the space for them to think and discuss the lesson more freely.
2. The Elements of Cooperative Learning
Cooperative learning approach has a wide variety technique that can be adapted in the teaching learning activity of various subject matters. Some of the cooperative learning techniques are; Team Assisted individualization (TAI) that available for teaching of Mathematic; Cooperative Integrated Reading and Composition (CIRC) which suitable to used in teaching reading, writing or language arts; Teams-Games-Tournaments (TGT) and Students Team Achievement Division (STAD) in learning the material that requires factual, right answer information such as language sub skills; jigsaw that work primarily in students’ home groups; discussion group; number head together, etc.
Although cooperative learning group may vary in the technique to regard it as the cooperative learning there are some principal elements require to be applied, and this that make it rather different with the traditional group work. For that purpose David W. Johnson and Roger T Johnson, develop cooperative learning method that emphasizes five elements,4 the five elements are include:
a. Positive interdependence
It promotes a situation in which students work together in small groups to maximize the learning of all members, sharing their resources, providing mutual support, and celebrating their joint success.
Positive interdependence promotes high interaction and a sense of belonging among teammates. Since one’s success means to achieve the group goal, and the group goal only can be achieve if all group member are success. So, it pushes them indirectly to work together and help one another to achieve the group goal.
b. Face-to-face promotive interaction
Accountability to peers, ability to influence each other’s reasoning and conclusions, social modelling, social support, and interpersonal
4
rewards all increase as the face-to-face interaction among group members increases.
Face to face interaction provides the space for group members to discussed material and share their knowledge. Also provides the space to them to give help, influence, and support to each other.
c. Individual accountability
Individual accountability exists when the performance of each student is assessed and the results are given back to the group and the individual.
Individual accountability requires all group members to give a significance contribution to achieve the group goal. It will ensure that all group members take their own responsibility to learn and perhaps have a sense of responsibility for the success of others teammates.
d. Social skills
The success of a cooperative effort requires interpersonal and small-group skills such as, leadership, decision-making, trust-building, communication, and conflict management skills that have to be taught to the students.
Not all students have capability in building their social skill when they put in a group. Teacher needs to assist students when it needed, particularly when the conflict arise, but it doesn’t mean she needs to get intervene deeply. She should give them opportunity to solve the problem firstly. For that purpose teacher need to gives guidance and encouragement to students to evoke their interpersonal and small group skill.
e. Group processing
Group processing exists when group members discuss how well they are achieving their goals and maintaining effective working relationships.
The five elements above are essential to be built in conducting cooperative learning group. Teacher needs to be aware the elements in order to develop a successful cooperative learning group.
3. The Activities in Cooperative Learning
When teacher decided to applied the cooperative learning group in her class, there are some crucial things need to be concerned dealing with the activities should be enrolled by both the teacher and students, here are the summarize of the activities;5
a. Teacher’s activities
In conducting cooperative learning group in class, first of all teacher should learn to recognize and appreciate the students. She also should learn to see groups of students, rather than thinking about them as individuals. She manages the classroom in general and in the process of cooperative learning instruction. In class teacher has to limit her own centrality and domination of the classroom process, instead of, she encourages students to talk to one another and build the classroom system around the learner. Besides, teacher has to assist groups of students to set goals for themselves in order to direct their collective and individual effort.
Another activities that should be followed by teacher are, she should prepare the subject-matter resources for the students and pay attention to the quality of the substance student’s study. Most importantly, teacher must constantly observe how groups work, because it will indicate to the teacher the situation when groups’ activity are more or less educative.
b. Students’ activities
Group-centered learning facilitates students to participate in regulating their own activities in the classroom, including the conduct of learning. Students have to sustain their collective learning and professional
5
growth through interaction with their mates by giving and receiving of feedback. Students are directing their personal talents, interest, and knowledge toward the accomplishment of the collective purpose. Students as group member must to identify the problem their experience when they are working together by “processing” the group’s behaviour, so they will find resolution to solve their problem.
4. The Student Teams-Achievement Divisions as One Technique of Cooperative Learning
Students Team Achievement-Division or STAD is one of the cooperative learning method. STAD is a team learning method based on three central concepts; individual accountability, equal opportunities for success, and team rewards, which are essential for basic skill achievement.6 The technique provided in STAD will maintain student’s interest and give opportunity to all students to be success in their learning.
STAD can be used to add variety and interest when the material that students need to learn is factual, “right answer” information.7 Based on the statement, the teaching of English language sub skill such as grammar can use the STAD method. STAD emphasizes five major elements in implement the activities, the five major elements are;8
a. Class presentation
Material in STAD is initially introduced in a class presentation. In this way, students must realize that they must pay careful attention during the class presentation.
In class presentation, teacher present the material clearly so that students can identify and practice the material being presented. In addition to, she also has to explain the activities and rules they are going to
6
Shlomo Sharan, ed., Handbook of Cooperative Learning Methods…, p: 200 7 Lynda A. Baloche, The Cooperative Classroom; empowering Learning, New York, Prentice Hall, 1998. p: 131
8
enrolled, which is the STAD group. So that the learning process will be take place as it plan.
b. Teams
Teams are composed of four to five students who represent a cross-section of the class in terms of academic performance and gender.
Students work and learn together in teams. Before students putting in the group, teacher has to know the students, specifically dealing with their academic performance and their interaction in the class. Teacher has to get the students’ last score or their average score to get information. Teacher can observe students behaviour in class. She can also ask to other teacher of the school.
c. Quizzes
After approximately one to two periods of teacher presentation and team practices, the students then take individual quizzes.
In dong the quiz, students are forbidden to help other students. It is intended that teacher will get the accurate data concerning with students’ improvement score. More importantly, it will ensure that all students will raise their level of attention in learning the material presented.
d. Individual improvement scores
The idea behind the individual improvement scores is to give each student a performance goal that can be attained if he or she works harder and performs better than in the past.
e. Team recognition
Teams may earn certificates or other rewards if their average scores exceed a certain criterion.
The purpose of team recognition is to motivate students achieving their personal and group goal
B The Simple Present Tense
1. The Understanding of Simple Present Tense
The Simple Present Tense is one of English tenses. As it is known, tense is a verb form which shows the time of an action or event.9 The sentence reveals that tense is form of a verb that tells us when is the activity takes place based on the time reference.
Some grammarian divided the time of tense in three difference of time reference such as points out by A. S. Hornby in his book that is; Tenses may indicate whether an action, activity, or state is past, present or future.10 Based on the statement has been presented, the three differences of time reference in tenses are the past time, the present time and the future time.
The Simple Present Tense, as its’ name, based on the differences of time reference is categorized in the present time.
Furthermore, the simple present tense can be described as a tense that expresses events or situations that exist always, usually, habitually, they exist now, have existed in the past, and probably will exist in the future.11
The statement above reveals that Simple Present Tense is the tense used to express an activity that occurs from the past, through the present, and into the future. In other words, it describes a permanent activity or action with indefinite time. Present states, present (complete) events and present habit are
9
Michael Swan, Practical English Usage, Oxford University Press, New York, 1982. p: xxiii
10
A.S Hornby, Guide to Pattern and Usage in English, The English Language Book Society and Oxford University Press, London, 1975. p: 78
11
all referred to by verbs in the simple present tense.12 On the contrary, it doesn’t indicate the temporary action that occurs or in progress at the moment of speaking.
It can be said that simple present tense is a verb form used to describes an event or situation that occur from the past, through the present and into the future. It is usually used to describe a statement of general truth or habitual activity that takes place in present time, and also to express the present statements.
2. The Usage of Simple Present Tense
Based on the description of Simple Present Tense earlier, it can be drawn that the Simple Present Tense is a tense that can be used to tells an activity or action as listed bellow ;
a. Used for general statements of fact, it says that something was true in the past, is true in the present, and will be true in the future,13 the examples are:
- Water consists of hydrogen and oxygen. - The world is round.
b. Express habitual or everyday activity,14 with the use of adverb frequency that tell how often the action is repeated such as; always, usually, often, rarely, seldom, sometimes, never, on Monday, etc.,. The examples are:
- I study for two hours every night. - He often eats a sandwich for lunch.
c. Used to indicate a situation that exists right now, at the moment of speaking.15 It is more concern to a present state, the examples are: - I have only a dollar right now.
- I don’t recognize that man.
12
Edward Woods and Rudy Coppieters, The Communicative Grammar of English Workbook, Pearson Education, London, 2000. p: 46
13
Betty Schrampfer Azar, Understanding and Using English Grammar…, p:11
14
Betty Schrampfer Azar, Understanding and Using English Grammar…, p: 11
15
3. The Form of Simple Present Tense
The forms of all tenses are differed only by the form of its verb form. In simple present tense, as its name it uses a simple verb form, which mean a single verb form for its’ affirmative sentence. Thing that needs little attention in simple present form is, there is a subject and verb agreement for the use of the third singular person in the subject, which is the added of inflectional suffix of s/es to its verb form.
• I, you, we, they go/do not
• He, she, it goes /does not Here the form of simple present tense;
a. Affirmative
Subject + Verb-1 (s/es)/ to be/ do/does + O Example : I am a student
He drinks coffee every night I do the homework by myself b. Negative
Subject + to be/ do/does + not + Verb-1 + O Example : Ahmad isn’t a lazy boy.
I don’t recognize that man. c. Interrogative
To be
To be + subject + O (adjective or adverbial of time) …? Example : Is your father a teacher?
Are they in the library? Auxiliary verb do/does
Do/does + subject + Verb-1 + O…? Example : Does she often read novel?
C. The Teaching of Simple Present Tense
1. The Students Team Achievement Division in Teaching Simple Present Tense
As mentioned earlier the study of this research will use the Students Team Achievement Division (STAD) in conducting the teaching of Simple Present Tense to the students of experimental class. The further explanation of STAD has been discussed earlier in this chapter. This section will only concern about the steps that will be applied by the writer as the teacher in this experiment research in the teaching learning process in class. The steps that should be follow are :
• First of all, the teacher gives the test (pre-test) to students. The result of the test will become the students’ initial base score and also used as the base in governed the students’ group learning.
• After teacher gets the students score then she governs the class member into small groups. Each group consist of five students that differ in their English academic performance, gender and social interaction.
• Next, the teacher comes to class. At the first meeting she gives explanation about the STAD group to the students, so that they understand about the technique.
• The teacher then put the students into small groups. After that she presents the material of Simple Present Tense. The example of the process of presenting the material in the first meeting are :
∗ First the teacher greets the students then presents the material of Simple Present Tense, once in a while the teacher use the target language in present the material.
∗ The teacher presents the material by building up a communication to the students. Firstly She asks to the students about the activity that they usually do in their daily life. Then she connects the students’ answer with material presented that is Simple Present Tense.
∗ She writes down some students’ answer on the board.
∗ Next, she explains material of simple present tense to students; the form, the rules and the usage.
• After teacher presenting the lesson she gives the task to students by distributed hand out to them. Each student in the group will get form of handout that contain the same material, it is intended that all students in the group will be participate in learning the material.
• Then the students complete the material given. They learn it in group by discussing the material. They share their knowledge with others team-mate until all team member understand the material.
• As the students do the material in the group the teacher observes the group. She observes how does the each group work cooperatively, and sometimes helps them when it needed.
• When the students finish the task, then the teacher gives opportunity to students to discuss the material and gives some feedback to them.
• After the class ended. Teacher immediately checks students’ work and make some notes about the performance of each group. Then she puts each student’s score in students’ individual performance score that will be calculated at the end of the last meeting.
• The last step is the teacher accounts the score of all group members and then chose one group that gain the highest score and perform best in the class as the winner that will be declared in the next meeting.
The group that become the winner mostly in number will become the first winner in the last meeting and will earn a reward from the teacher. The essence of the reward is to motivate students to do better in their study.
2. The Grammar Translation Method in Teaching Simple Present Tense. a. The Concept of Grammar Translation Method
Grammar Translation method is the method use firstly in teaching foreign language particularly classic language which are Latin and Greek. Then it was used to teach a foreign language with a base thought, … that foreign language learning would help students grow intellectually; it was recognize that students would probably never use the target language, but the mental exercise of learning it would be beneficial anyway.16
The statements above points out that the objective of foreign language learning is not to achieve the real communication goal, rather, to raises students’ mental processing. Hence, the reading and writing skills underlying its’ teaching procedure.
b. The Characteristics of Grammar Translation Method
The principal characteristics of Grammar Translation Method were these:17
• The goal of foreign language study is to learn a language in order to read its literature or in order to benefit from the mental discipline and intellectual development.
• Reading and writing are the major focus; little or no systematic attention is paid to speaking or listening
• Vocabulary selection is based solely on the reading texts used, and words are taught through bilingual word lists, dictionary study, and memorization
• The sentence is the basic unit of teaching and language practice
• Accuracy is emphasized. Students are expected to attain high standards in translation.
16
Diane Larsen-Freeman, Techniques and Principles in Language Teaching, Oxford University Press, New York, 1986. p: 4
17
• Grammar is taught deductively – that is, by presentation and study of grammar rules, and then practiced through translation exercises.
• The students’ native language is the medium of instruction.
c. Teaching Simple Present Tense by Using Grammar Translation Method The technique of Grammar Translation Method in teaching Simple Present Tense probably as same as the teaching in Students Team Achievement Division the difference is that the students in STAD class will learn the material in a group while in GTM class the student are set in a whole class setting and they learn the material individually. Besides, the Simple Present Tense is taught deductively, the steps are:
• First teacher greet the students then presented the Simple Present Tense to the students in students’ native language. She writes the formula on the whiteboard, then explain its pattern, rule and usage.
• Teacher gives some examples of Simple Present Tense sentences, next she gives another incomplete sentences and asks students to complete its’ verb form.
• Students answer the teacher’s question loudly.
• Then teacher asks students to practice the pattern, by doing the exercises provided by the teacher.
CHAPTER III
THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE RESEARCH
A. THE METHODOLOGY OF THE RESEARCH 1. The Objective of The Research
The objective of the research is to know the influence of
implementing one technique of Cooperative Learning method namely
Students Team Achievement Division (STAD) in teaching Simple Present
Tense and also to find out whether there is any significant effect in
teaching the Simple Present Tense to the students who are taught using
Students Team Achievement Division (STAD) and Grammar Translation
Method.
2. The Place and Time of The Research
The writer held the research at MTs. Soebono Mantovani Ciputat.
She conducted the research in October 2009. It was begun by observation
and finished by giving an achievement test to the students as the subject of
the research. From 13 October up to 30 October the writer conducted the
field research for seven meeting by giving the pre-test, presenting the
lesson and giving the post-test to students.
3. The Population and Sample of The Research
The population of the research is all students of MTs. Soebono
the school that are divided into five classes. All the classes of the school
are governed based on the level of students’ competency, from the higher
level to the low, from VIII-1 to VIII-5. In this research the writer took only
two classes as the sample of the research that are class VIII-3 and VIII-2
as the class are the students with the middle level of competency. She took
the sample using the purposive cluster sample technique, so she took all
the class member from both classes which are 70 students with 35 in each
classes. These two classes have been treated with two different treatments.
The first class is the experimental class that was taught with one technique
of Cooperative Learning method that is STAD (Students Team
Achievement Division) and the other is control class that was taught by
GTM (Grammar Translation Method).
4. The Technique of Data Collecting
The writer collected the data of the research by giving test to the
students. The tests consist of pre-test and post test. The pre-test was given
before the treatment and the post-test was given after the treatment. From
these data the writer can determine the result of the research.
5. The Technique of Data Analysis
The data that have been collected then would be analysed. In
analysing the data the writer used statistical calculation of the T-test to
determine the final calculation of the research. It is used in order to know
the difference score between the students who were taught simple present
tense using STAD and GTM. In this research the writer used the formula
that compares two small samples that have no relationship each other.
The data that have been collected from the pre-test and post-test then were
analysed by the following steps:
a. Finding out gained score of students’ scores by comparing students’
determining the variable of the data, the gained scores of experimental
class is variable X and the gained scores of control class is variable Y.
b. Determining mean of experiment class with formula
MX = ∑ X N
c. Determining mean of control class with formula
d. Determining deviation score of variable X with formula
Note : Sum of
χ
or
∑χ
equal to null. Then she square theχ
to gained ∑χ
²MY = ∑ Y N
χ
= X - MXe. Determining deviation score of variable Y with formula
γ
= Y - MYNote : Sum of
γ
or
∑γ
equal to null. Then she square theγ
to gained ∑γ
²f. Finding out the standard deviation of variable X
SDx = ∑f (X-MX) ² n
√
g. Finding out the standard deviation of variable Y
SDy = ∑f (Y-MY) ² n
√
h. Finding out the standard error of the mean variable X
SEMx = SDx
n-1
√
i. Finding out the standard error of the mean variable Y
SEMy = SDy
n-1
√
j. Finding out the standard error. The comparison of mean variable X
and Y
k. Finding out the to with formula :
t o = MX - MY
SEMx-y
l. Giving interpretation
6. The Procedure of the Research
In conducting the research, the writer did some procedures in order
to gain the result of the research. The procedure consists of some steps as
the following:
a. The writer began the research by observing the condition and
population of MTs. Soebono Mantovani, she also took some
supporting data for the research.
b. Then the writer took the sample from the population of the eight grade
students of the school. The samples are class VIII-3 and VIII-2, with
35 students in each class. The first class is experiment class and the
other is control class.
c. The writer then administered the same instrument of pre-test to both
classes. In experiment class, the students’ pre-test scores are used as
the basic score in govern the groups learning of Students Team
Achievement Division (STAD).
d. The next step was the treatment. In this treatment the writer conducted
the teaching learning process in class by herself. She presents the same
material which is Simple Present Tense to the two classes, but treated
them with two different methods. The experiment class was taught by
using STAD method where student are put into small groups, each
group consist of five students, and the control class was taught by
using Grammar Translation Method where students are put into the
whole class setting.
e. After the treatment that consists of five meeting finish, then the writer
f. Finally the data that have been collected from the pre-test and post-test
were calculated using statistical calculation of T test to figure out the
result or conclusion of the research.
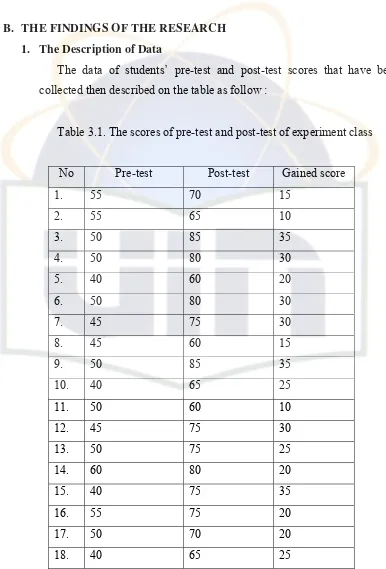
B. THE FINDINGS OF THE RESEARCH 1. The Description of Data
The data of students’ pre-test and post-test scores that have been
[image:40.595.110.496.175.744.2]collected then described on the table as follow :
Table 3.1. The scores of pre-test and post-test of experiment class
No Pre-test Post-test Gained score
1. 55 70 15
2. 55 65 10
3. 50 85 35
4. 50 80 30
5. 40 60 20
6. 50 80 30
7. 45 75 30
8. 45 60 15
9. 50 85 35
10. 40 65 25
11. 50 60 10
12. 45 75 30
13. 50 75 25
14. 60 80 20
15. 40 75 35
16. 55 75 20
17. 50 70 20
19. 35 50 15
20. 50 75 25
21. 45 70 25
22. 55 60 5
23. 40 60 20
24. 45 65 20
25. 55 75 20
26. 30 40 10
27. 45 60 15
28. 55 70 15
29. 45 50 5
30. 40 65 25
31. 50 75 25
32. 45 60 15
33. 55 75 20
34. 35 45 10
35. 55 65 20
∑
χ
1 = 1650
M
χ
1 = 47.14
∑
χ
2 = 2360
M
χ
2 = 67.43
∑10
X = 720
M
X = 20.57
The writer determines mean of experiment class scores using the
formula
MX = ∑ X = 720 = 20.57 N 35
The range score of pre-test is gained between 30 and 60, and the
mean score is 47.14. The range score of pre-test is gained between 40
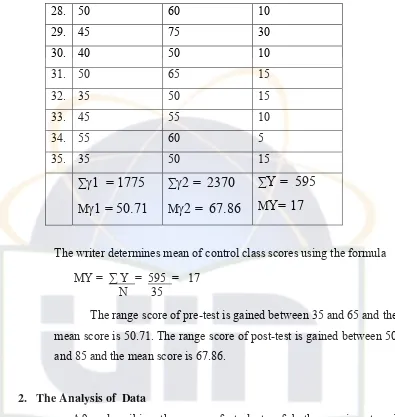
Table 3.2. The scores of pre-test and post-test of control class
No Pre-test Post-test Gained score
1. 55 65 10
2. 40 60 20
3. 45 65 20
4. 50 70 20
5. 55 85 30
6. 65 80 15
7. 60 85 25
8. 50 80 30
9. 55 75 20
10. 60 85 25
11. 55 65 10
12. 65 75 10
13. 45 60 15
14. 55 75 20
15. 50 75 25
16. 45 65 20
17. 55 65 10
18. 60 75 15
19. 50 65 15
20. 55 70 15
21. 45 75 30
22. 40 50 10
23. 55 55 0
24. 55 70 15
25. 60 75 15
26. 45 65 20
28. 50 60 10
29. 45 75 30
30. 40 50 10
31. 50 65 15
32. 35 50 15
33. 45 55 10
34. 55 60 5
35. 35 50 15
∑
γ
1 = 1775
M
γ
1 = 50.71
∑
γ
2 = 2370
M
γ
2 = 67.86
∑
Y = 595
M
Y= 17
The writer determines mean of control class scores using the formula
MY = ∑ Y = 595 = 17 N 35
The range score of pre-test is gained between 35 and 65 and the
mean score is 50.71. The range score of post-test is gained between 50
and 85 and the mean score is 67.86.
2. The Analysis of Data
After describing the score of students of both experiment and
control class, the writer then calculates the deviation and square deviation
[image:43.595.113.508.110.527.2]of two classes on the table three (3) and four (4) as follow.
Table 3.3. The analyse of students’ score of experiment class
No X f fX X-MX (X-MX) ² f(X-MX) ²
1. 35 3 70 14.43 208.22 624.66
2. 30 4 150 9.43 88.92 355.68
3. 25 7 175 4.43 19.62 31.01
4. 20 9 180 -0.57 0.32 2.88
6. 10 4 40 -10.43 111.72 446.88
7. 5 2 10 -15.57 242.42 484.84
8. 0 0 0 -20.57 423.12 0.0
N=35 ∑fX=720 ∑f(X-MX)²
= 2238.4
From the data on the table above then the writer found out the MX,
SD, SEM using the formula as follows:
MX = ∑fX = 720 = 20.57
N 35
SDx = ∑f (X-MX) ² = 2238.4 = 63.95 = 7.99 = 8
√
n 35√
√
SEMx = SD = 8 = 8 = 1.37
n-1 34 5.83
√
√
Table 3.4. The analyse of students’ score of control class
No. Y f fY Y-MY (Y-MY) ² f(Y-MY) ²
1. 35 0 0 18 324 0
2. 30 4 120 13 169 676
3. 25 4 100 8 64 256
4. 20 7 140 3 9 63
5. 15 10 150 -2 4 40
6. 10 8 80 -7 49 392
7. 5 1 5 -12 144 144
8. 0 1 0 -17 289 289
N=35 ∑fY=
595
From the data on the table above then the writer found out the MX,
SD, SEM using the formula as follows:
MY = ∑fY = 595 = 17
N 35
SDy = ∑f (Y-MY) ² = 1860 = 53.14 = 7.29 n 35
√
√
√
SEMy = SD = 7.29 = 7.29 = 1.25
n-1 34 5.83
√
√
Having gained MX, SDx, SEMx, MY, SDy, SEMy then the writer
calculated the data to find out the SEDx-y and t o
a. SEDx-y = (SEMx) ² + (SEMy) ²
√
= (1.37 ) ² + (1.25) ²
√
= 1.88 + 1.56 = 3.44 = 1.85
√
√
t o = MX - MY SEDx-y
= 20.57 –17
1.85
= 3.57 = 1.93
1.85
b. Then, the writer found out the degree of freedom (df) to complete
the result of this research as follow :
df = N1 + N2 –2
c. There is no degree of freedom from 68, so the writer uses the closer
df that is 70. From the t table (t t), df=70 the writer took degree of
significance 5% to interpret the t o that have been gained, that is : y In degree of significance 5% t t = 2.00
d. The t o=1.93, so the result of t t : to in degree of significance 5% is,
t o : t t = 1.93 < 2.00 = to < t t
It means that t o is lower than t t in degree of significance 5%
3. The Hypotheses Testing
The purpose of the test of hypothesis is used to find out the answer
of the question in this research that is, whether there is any significant
difference in result between the students who have been taught of Simple
Present Tense using one technique of cooperative learning that is STAD
and Grammar Translation Method.
For that purpose the writer proposed the alternative Hypothesis
(Ha) and null Hypothesis (Ho) as below:
Ha = “There is a significant difference in result between the students who
have been taught of Simple Present Tense using Cooperative
Learning and Grammar Translation Method”.
Ho = “There is no significant difference in result between the students who
have been taught of Simple Present Tense using Cooperative
Learning and Grammar Translation Method”.
With note that: If t o>t t, it means that there is a difference and Ha is
accepted; if to<t t, it means that there is no difference and means that Ha is
rejected and Ho is accepted.
Based on the result in the calculation of to it is known that the to =
1.93 and df = 70 (there is no df=68). Since it is a social research, so the
writer took only the degree of significance in level 5% to give
interpretation of the result of this research. With df = 70 the degree of
Then the writer compare the t o with the value of t t, the result is
t o : t t = 1.93 < 2.00. The comparison between to and t t indicates that t o
is lower than t t in the degree significance of 5%.
As it is known t o is lower than t t in degree of significance 5% it
means that Ho is accepted in degree of significance 5%. In another words
it means that Ha is rejected. It can be concluded that there is no significant
difference in result between students of MTs.Soebono Mantofani grade
VIII who have been taught of Simple Present Tense using one technique of
Cooperative Learning that is STAD and Grammar Translation Method,
although there is a difference but the difference doesn’t indicate a
significant difference.
The analysis above points out that the teaching of Simple Present
Tense using Students Team Achievement Division as one technique of
Cooperative Learning to the students of MTs.Soebono Mantofani grade
VIII does not give a significant effect to the students. It is happen because
some factors which affect it.
From the observation of the teaching learning process in class the
writer have found some factors that influence the result of the research.
Some of them are: students are lack in their English competency especially
in vocabulary, it is seen when they were doing the task or the test most of
the time they try to found its’ meaning on the dictionary or asked the
teacher. In spite of the teacher always remind them to be more focus to the
sentence pattern than its’ vocabulary they still do that. Students also
sometimes still get confused in the use of subject verb agreement of the
simple present tense pattern, particularly in the negative and interrogative
sentences.
Another factors are students sometimes get difficulty when they
learn and work together in a group since they rarely have this experience.
They don’t feel confidence both with their and other team-mates’ ability
they rather like to ask to the teacher than to their team-mates to solve the
the writer as the teacher in this research must always remind them
considering these things.
Nevertheless from the observation the writer also found some
positive aspect that can be gained from the implementing of cooperative
learning in class. In cooperative learning group students are not only can
learn the material that presented by the teacher but also they are facilitated
to learn other experience. The students can learn how to work and study
together as a team, they learn how to negotiate with others, they learn how
to conveying their ideas and thought, they learn how to respect other, and
learn to take responsibility over their task. Students can also learn as a
teacher and a leader when they taught and manage other team-mates.
Besides that students also learn how to believe with their ability and feel
confidence when they try to solve their problem alone.
Furthermore, the writer found that students in cooperative learning
class are more motivated to learn than students of the other class. This
motivation is the thing that should always build up by the teacher when
she came to class. However, it doesn’t mean that teacher should always
implement the cooperative learning all the time in class but it means that
cooperative learning can be used as a variation in teaching learning
activity in class in order to hinder students’ boredom, so it can motivate
CHAPTER IV
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
A. The Conclusions
From the data that have been described earlier, the writer has found out that there is no significant effect between the eighth grade students of MTs. Soebono Mantofani Ciputat who have been taught Simple Present Tense using one technique of Cooperative Learning that is Students Team Achievement Division with the Grammar Translation Method.
It can be concluded that the use of Students Team Achievement Division and Grammar Translation Method has the same effect to the students of the school in comprehending the grammar item of Simple Present Tense. The Cooperative Learning can’t work effectively since the technique is sometimes is not easy to implement particularly to the students who rarely have this experience. Nevertheless, there is a benefit that can be gained from the technique that are, the students can learn how to be focus to their learning in class. Besides that, they also can learn other aspect which is the social aspect of life such as; learn how to work together as a team, learn how to respect other, learn to negotiate with other and learn how to convey their idea to other. It is hopefully all those experiences will be useful for students’ life in the future.
B. The Suggestions
Based on the result of research above, the writer would like to give more suggestion as the following :
1. The teacher should always read a lot in order to gain information and add their knowledge, particularly related to the way of organising and managing of the class. So she/he can implement any number of different teaching method and technique that suitable to the condition of students in class. It is intended to give variation to students in order to hinder their boredom from the routine activity in class.
2. When the teacher teach the students in class, she should give them not only a knowledge but also give them other experience of learning such as the use of cooperative learning method that will give many experience to students such as : learn how to work together as a team, learn how to respect other, learn to negotiate with other and learn how to convey their idea to other. It is hopefully the skill will be useful for students’ life in the future.
3. When the teacher teach the students, she should always find ways to make students get interest and get involved in the learning process in class. By giving encouragement, trust and motivation that they all can learn and have opportunity to learn and become success in their learning.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Arikunto, Suharsimi, Prosedur Penelitian, Jakarta : Rineka Cipta, 2006.
Azar, Betty Schrampfer, Understanding and Using English Grammar, 2nd ed. New Jersey : Prentice Hall Regents, 1989.
Baloche, Lynda A., The Cooperative Classroom; empowering Learning, New York: Prentice Hall, 1998.
Bany, Mary A. and Lois V. Johnson, Classroom Group Behavior ; Group Dynamics in Education, New York : The Macmilan Company, 1967.
Dwijatmiko, BB., Communicative Grammar Practice ; For First Year English Department University Students, Yogyakarta : Kanisius, 1990
Fraenkel, Jack R. and Norman E. Wallen, How to Design and Evaluate Research in Education, 5th ed., New York : Mc. Graw Hill, 2003.
Gorman, Alfred H., Teachers and Learners the Interactive Process of Education, Boston : Allyn & Bacon Inc, 1969.
Hornby, AS., Guide to Patterns and Usage in English, London: The English Language Book Society and Oxford University Press, 1975.
Kessler, Carolyn., Cooperative Language Learning; A Teacher’s Resource Book.New Jersey : Prentice Hall Regents Inc., 1992.
Larsen-Freeman, Diane., Techniques and Principles in Language Teaching, New York : Oxford University Press, 1986.
Martin, Jerome and Dorothy Carnahan Olson, Patterns of Language-Level G, New York : Litton Educational Publishing Inc., 1977
Millward, CM. A Biography of The English Language. 2nd ed. Boston : Thomson Inc, 1996.
Raimes, Ann. How English Work; A Grammar Handbook with Readings, 2nd ed. New York: Cambridge University Press, 1998.
Richards, Jack C. and Willy A. Renandy. Methodology in Language Teaching; An Anthology of Current Practice. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press, 2002.
Schunk, Dale H. et.al., Motivation in Education; Theory, Research, and Applications, 3rd ed., New Jersey : Pearson Education Inc., 2002
Sharan, Shlomo. ed., Handbook of Cooperative Learning Methods. Westport: Praeger Publishers, 1994.
Slavin , Robert E. Cooperative learning Theory; research and Practice, 2nd ed. Boston : Allyn and Bacon, 1995.
Sudijono, Anas, Pengantar Statistik Pendidikan, Jakarta, PT Raja Grafindo Persada, 1987.
Swan, Michael. Practical English Usage, New York: Oxford University Press, 1982.
Ulrich, Robert. History of Educational Thought. New York: American Book Company, 1950.
Ur, Penny. Grammar Practice Activities; A Practical Guide for Teachers. New York : Bell and Bain Ltd, 1992.
Wernej, Patricia K. et.al., Interactions 2 Grammar, 4th ed., New York : Mc Graw Hill, 2002.
Wishon, George E. and Julia M. Burks. Let’s Write English, revised ed. New York: American Book Company, 1980.
RENCANA PELAKSANAAN PEMBELAJARAN (Experimental Class)
Satuan Pendidikan : MTs. Soebono Mantofani Ciputat Mata Pelajaran : Bahasa Inggris
Kelas / Semester : VIII / 1
Alokasi waktu : 2 x 40 menit (Pertemuan ke-1) Tema : Simple Present Tense
I Tujuan Pembelajaran
•Siswa dapat memahami penggunaan kalimat berpola simple present tense dalam kehidupan sehari-hari.
•Siswa dapat membedakan penggunaan bentuk verb; to be, auxiliary verb do/does dan simple verb (+ e/es) untuk masing-masing kata ganti orang pada subjek kalimat berpola simple present tense.
II. Materi Pokok dan uraian materi * Simple present tense
* To be : *Auxiliary verb do and does dan simple verb (+ s/es) Subject Verb: Auxiliary Verb: Simple
do/does verb (+ s/es)
I
We do work/go You
They She
He does works/goes It
Subject Verb : To be I am
We
You are They
She
He is It
III. Media Pembelajaran : whiteboard, marker, handout IV. Sumber Pelajaran
a. The Bridge English Competence text book for SMP Grade VIII b. LKS Pasti Bahasa Inggris untuk SMP/Mts.
c. Interaction 2 Grammar
V. Strategi, Model, Pendekatan, Metode
Strategi : Two ways communication Model : Group work
Metode : STAD group work VI. Langkah pembelajaran
No Kegiatan Alokasi waktu
6.1 Kegiatan awal
6.1.1. Salam dan tegur sapa 6.1.2. Guru mengabsen siswa 6.1.3. Guru memotivasi siswa
10 menit
6.2. Kegiatan inti
6.2.1. Guru menjelaskan technique cooperative learning metode Students Team Achievement Division (STAD) kepada siswa.
6.2.2. Guru membagi siswa ke dalam kelompok cooperative learning, setiap kelompok terdiri dari lima orang siswa
6.2.3. Guru menjelaskan materi simple present tense mengenai penggunaan bentuk to be, auxiliary verb do/does dan simple verb (+ s/es) untuk masing-masing kata ganti orang pada subjek kalimat simple present tense
6.2.4. Siswa mengerjakan tugas (handout) yang diberikan guru dan mempelajarinya secara berkelompok
6.2.5. Guru bersama siswa membahas hasil kerja siswa
60 menit
6.3. Kegiatan Akhir
6.3.1. Guru menyimpulkan materi yang diajarkan
6.3.2. Guru memberikan kesempatan kepada siswa untuk mengungkapkan hambatan-hambatan yang dialami siswa selama proses pembelajaran
10 menit
∗ Instrumen penilaian (handout) terlampir
Ciputat, Oktober 2009 Mengetahui,
Guru Bidang Studi Guru Praktikan
RENCANA PELAKSANAAN PEMBELAJARAN (Eksperimental Class)
Satuan Pendidikan : MTs. Soebono Mantofani Ciputat Mata Pelajaran : Bahasa Inggris
Kelas / Semester : VIII / 1
Alokasi waktu : 2 x 40 menit (Pertemuan ke-2) Tema : Simple Present Tense
I. Tujuan Pembelajaran
• Siswa dapat memahami penggunaan kalimat berpola simple present tense dalam kehidupan sehari-hari.
• Siswa dapat membedakan penggunaan bentuk verb; to be, auxiliary verb do/does dan simple verb (+ e/es) untuk masing-masing kata ganti orang pada subjek kalimat berpola simple present tense.
• Siswa dapat memahami bentuk affirmative dan negative pola kalimat simple present tense.
II. Materi Pokok dan uraian materi * Simple present tense
a. The pattern of affirmative statements : S + Verb (s/es) + O
b. The pattern of negative statements
To be : S + is / are + not + adjective / adverbial of place Auxiliary do/does : S + do / does + not + O…
III. Media Pembelajaran : whiteboard, marker, handout IV. Sumber Pelajaran
a. The Bridge English Competence text book for SMP Grade VIII b. LKS Pasti Bahasa Inggris untuk SMP/Mts.
c. LKS Wajar Bahasa Inggris SMP kelas VIII V. Strategi, Model, Pendekatan, Metode