(A Correlational Study at the Fifth Semester Students of the Department of
English Education of Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University of Jakarta
in Academic Year 2016/2017)
By:
Hafsyah Maisyarah
1112014000044
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF EDUCATIONAL SCIENCES
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
v
Correlational Study at the Fifth Semester of the Department of English
Education of Syarif Hidayatulla State Islamic University of Jakarta). Skripsi
of English Education at the Faculty of Educational Sciences of Syarif Hidayatulla State Islamic University of Jakarta, 2016.
Advisor I : Neneng Sunengsih, M.Pd.
Advisor II : Yenny Rahmawati, M.Ed.
This study aimed to know and describe the correlatin between students’ verbal – linguistic intelligence and their reading achievement. The population of this study was the fifth semester students of Department of English Education of Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University of Jakarta in academic year 2016/2017. There were 39 students from B and C classes selected as the sample of this study. This study used a quantitative method with the correlational as the reasearch design of study. The instruments used for collecting data were verbal – linguistic intelligence questionnaire and reading achievement test. Both tests were conducted to measure students’ verbal – linguistic intelligence and reading achievement. The data which was collected was calculated by using Pearson Product Moment Correlation to see whether there was any significant correlation between the two variables. Based on the research analysis, the correlation between the two variables was found at the 95% level of confidence (p < 0.05) with the value of rxy was 0.096 which was in the weak or low level. The value was smaller
than the value of rt in the significance of 5% in which 0.096 < 0.316. Moreover,
the significance of t contribution revealed that the result was significant with the value of tcount was 0.590. The value was smaller than the value of ttable at the level
of significance 0.05, in which 0.590 < 2.026. Hence, the alternative hypothesis (Ha) is rejected and null hypothesis (H0) is accepted. In conclusion, there is no significant correlation between students’ verbal-linguistic intelligence and their reading achievements at the fifth semester of the Department of English Education of Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University of Jakarta in Academic Year 2016/2017.
Keywords: Correlational study, Verbal-Linguistic Intelligence, Reading
vi
Hafsyah Maisyarah (1112014000044). The Correlation between Students’
Verbal Linguistic Intelligence and Their Reading Achievement (A Correlational Study at the Fifth Semester of the Department of English
Education of Syarif Hidayatulla State Islamic University of Jakarta). Skripsi
Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2016.
Dosen Pembimbing I : Neneng Sunengsih, M.Pd.
Dosen Pembimbing II : Yenny Rahmawati, M.Ed.
Penelitian ini bertujuan mengetahui dan mendeskripsikan hubungan antara kecerdasan berbahasa dan pencapaian membaca siswa. Populasi pada penelitian ini adalah mahasiswa semester 5 Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta tahun 2016/2017. Sebanyak 39 siswa dari kelas B dan C yang terpilih menjadi sampel penelitian. Penelitian ini menggunakan metode kuantitatif dengan korelasi sebagai desain penelitian. Instrumen penelitian yang digunakan untuk memperoleh data adalah tes pemahaman membaca dan kuesioner kecerdasan berbahasa. Kedua tes tersebut dilakukan untuk mengukur pemahaman membaca dan kecerdasan berbahasa siswa. Data yang diperoleh dihitung menggunakan korelasi Pearson Product Moment untuk mengetahui apakah ada hubungan yang signifikan antara kedua variabel tersebut. Berdasarkan analisa penelitian, hubungan antara kedua variabel ditemukan level signifikansi 95% (p < 0.05) dengan nilai rxy adalah 0.096 yang
berada pada level rendah. Niai tersebut lebih rendah dari pada nilai rt pada tingkat kesalahan 5% yaitu 0.96 < 0.316. Selain itu, signifikan nilai t mengungkapkan bahwa hasil tersebut signifikan dengan nilai dari thitung adalah 0.590. nilai tersebut
lebih rendah dari nilai ttabel pada level signifikansi 0.05 yaitu 0.590 < 2.026. Oleh
karena itu, hipotesis alternatif (Ha) ditolak sedangkan nol hipotesis (H0) diterima.
Dapat disimpulkan bahwa tidak adanya hubungan yang signifikan antara kecerdasan berbahasa dengan pencapaian membaca mahasiswa semester 5 Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
Kata Kunci: Penelitian Korelasi, Kecerdasan Berbahasa, Pencapaian
vii
blessing upon the writer during completing this skripsi as the final assignment in
her study. Peace and salutation may always be upon the Prophet Muhammad, the
savior of the humankind, who has brought the light onto this world and turned it
into a better place.
This Skripsi is a scientific paper that is presented as one of the requirements for the degree “S.Pd.” in English Education. Completing this skripsi is long processes and the writer would not have been able to complete it without help and
support of lecturers, institution, family and friends. Hence, in this occasion, the
writer is pleasure to acknowledge the help and contributions by conveying her
utmost gratitude to them who have helped her in completing this skripsi.
First, the writer would like to express the deepest gratitude to her great
parents; her father Uang Suwandi and her dearest mother Hafni Dewi for their
love, support, and moral encouragement in motivating the writer to finish her
study. Next, the writer would like to express the greatest honor and deepest
gratitude to her advisors, Neneng Sunengsih, M.Pd., and Yenny Rahmwati M.Ed.,
for patiently guiding her and giving her the most valuable help, advice, and
support during completing this skripsi.
Moreover, the writer would like to express her gratitude and appreciation to:
1. Prof. Dr. Ahmad Thib Raya, M.A., as the Dean of Faculty of Tarbiyah
and Teachers’ Training.
2. Dr. Alek, M.Pd., as the Head of Department of English Education.
3. Zaharil Anansy, M.Hum., as the secretary of Department of English
Education.
4. All lecturers in the Department of English Education who always give
motivation and valuable knowledge during her study.
5. All students of the fifth semester of Department of English Education
viii
for members of B class of 2012 for the encouragement, support, and
love.
8. All the people who cannot be mentioned one by one for their
contribution to the writer during completing her skripsi. The words are
not enough to say any appreciations for their help.
Lastly, the writer realizes that this skripsi is still far from being perfect.
Despite the help from the aforementioned people, there are weaknesses and
shortages in this skripsi that remain as the writers’ responsibility. She, therefore,
welcomes all kinds of corrections and suggestions for a better writing.
Jakarta, 20 November 2016
ix
Surat Pernyataan Karya Sendiri ... iv
ABSTRACT ... v
ABSTRAK ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... ix
LIST OF TABLES ... xii
LIST OF FIGURES ... xiii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xiv
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Identification of the Problem ... 4
C. Limitation of the Problem ... 4
D. Formulation of the Problem ... 4
E. Objective of the Study ... 4
F. Significance of the Study ... 4
CHAPTER II. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ... 6
A. Literature Review ... 6
1. Reading ... 6
a. The Definition of Reading ... 6
b. Types of Reading ... 7
x
c. Types of Multiple Intelligences ... 17
d. The Verbal-Linguistic Intelligence ... 18
e. The Characteristics of Verbal-Linguistic Intelligence ... 19
B. The Relevant Study ... 22
C. Conceptual Framework ... 24
D. Theoretical Hypothesis ... 25
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 26
A. Time and Place of the Study ... 26
B. Method of the Study ... 26
C. Population and Sample ... 26
D. Instruments of the Research ... 27
E. Technique of Data Collection ... 27
F. Technique of Data Analysis ... 31
G. Statistical Hypothesis ... 33
CHAPTER IV. FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION ... 34
A. Research Findings ... 34
B. Discussion ... 52
C. Limitation ... 54
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 55
A. Conclusion ... 55
B. Suggestion ... 55
xii
Table 3.1 The Blue Print of Reading Achievement Test ... 28
Table 3.2 The Blue Print of Verbal-Linguistic Intelligence Questionnaire ... 29
Table 3.3 The Result of Reliability Test of Questionnaire ... 30
Table 3.4 The Range Score of Verbal-Linguistic Intelligence ... 30
Table 3.5 The Interpretation of Pearson Correlation ... 32
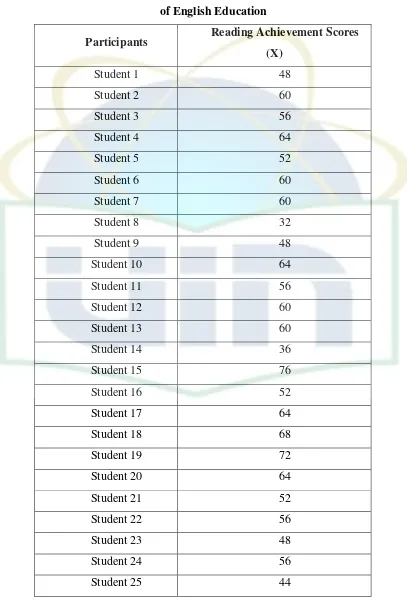
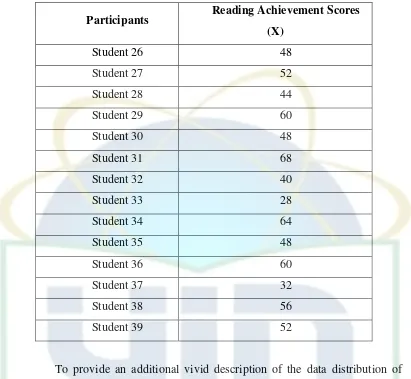
Table 4.1 The Reading Achievement Score of 5th Semester Students of Department of English Education... 35
Table 4.2 The Statistical Score of the Reading Achievement Test ... 38
Table 4.3 The Range Score of Verbal-Linguistic Intelligence Questionnaire ... 39
Table 4.4 The Verbal-Linguistic Intelligence Questionnaire Score ... 40
Table 4.5 The Statictical Score of Verbal-Linguistic Intelligence Questionnaire ... 43
Table 4.6 The Linearity Test Result of the Data ... 44
Table 4.7 The Normality of the Test ... 45
Table 4.8 The Data Analysis of Verbal-Linguistic Intelligence and Reading ... 46
Table 4.9 The Pearson Product Moment Table ... 48
xiii
xiv
Appendix 3 The Reading Achievement Test Scores ... 76
Appendix 4 The Verbal-Linguistic Intelligence Scores... 78
Appendix 5 The Output of Anates ... 81
Appendix 6 The Statistical Score of Reading Achievement ... 94
Appendix 7 The Statistical Score of Verbal-Linguistic Intelligence ... 95
Appendix 8 SPSS Correlation “r” Product Moment of Verbal-Linguistic Intelligence and Reading Achievement ... 97
Appendix 9 Pearson Product Moment Table in Significance Level 5% and 1% 98 Appendix 10 T-Table ... 100
Appendix 11 Surat Permohonan Izin Penelitian ... 102
Appendix 12 Pengesahan Proposal Skripsi... 103
Appendix 13 Surat Bimbingan Skripsi ... 104
Appendix 15 Surat Bimbingan Skripsi ... 105
1
A. Background of the Study
Education is able to help people to become more efficient to achieve their life
goals with increasing facility. The higher people’s education is, the better their
chances of creating good opportunities for themselves. The better people
opportunities are the better people quality of life is. As moslem also has been
obliged to study throughout life because studying could increase their level for
God and human. Indonesia also supports its people to have a higher education.
Education in Indonesia starts from elementary school, junior high school, senior
high school, and college.
One of the ways that can help people to increase their cognitive for better
education is reading. The most of important skill that have to be learnt by the
students is reading, because reading can help them in learning other subjects.
Students who have weakness in reading cannot have a completely normal life1.
These days, technology has improved and people can read everything not only
from books but also from the other resources such as newspaper, website, e-book,
online articles, etc. So, they will become easier to read what they want in order to
improve knowledge for their education, etc.
Besides, in order to increase knowledge, reading makes the students more
successful in the academic field. Researchers have found that most of students
who are good at reading have good achievement in school than who are not good
or less interesting in reading. So, from the findings, researchers conclude that
there is strong relation between reading and their study achievements.2
However, the problem faced by the students in reading activity is some
students have good score in reading and some students have not good score in
reading. Because of this, the writer assumed that there are some problems may
1Arthur E. Traxler, Research in Reading in the United States, The Journal of Educational Research, Vol. 42 (7), 1950, p.481.
influence them in reading. Moreover, the problems that can influence them in
reading achievement involve both internal and external factors. One of the factors
that researcher wants to investigate is their multiple intelligence factor that come
from each individual.3
Ghamati studied about improving reading comprehension and motivation of
young Iranian EFL learners through the application of multiple intelligences (MI).
The results of this study revealed that using reading activities based on the
multiple intelligences theory can increase reading comprehension and it increases
motivation of young EFL learners to read.4 So, it can be concluded that mutiple
intelligences have good contribution in English classroom activity, especially in
reading skill.
There are 7 main multiple intelligences on Howard Gardner’s theory,
linguistic, mathematic, spatial, bodily-kinaesthetic, musical, interpersonal and
intrapersonal. Then, Fasko stated that in 1999, Gardner added an eight,
naturalistic intelligence.5 Howard Gardner’s theory suggests everybody has a
different mind, and no two profiles of intelligences are the same. From the 8
primary intelligences (linguistic, math/logic, visual, art, interpersonal,
intrapersonal, kinaesthetic, natural)6 an individual may excel in one, two or even
three of these, but nobody is good at the all.
One of the intelligence that has strong relation to the reading skill is
verbal-linguistic intelligence. Verbal-verbal-linguistic intelligence is defined by Gardner as
sensitivity to the spoken and written language to achieve goals.7 Furthermore,
there are many characteristics of verbal-linguistic intelligence such as good with
languages, loves reading, writing, listening and speaking, notices grammatical
3RatnaWulan, Peranan Inteligensi, Penguasaan Kosakata, Sikap, dan Minat Terhadap
Kemampuan Membaca Anak,Jurnal Penelitian dan Evaluasi Pendidikan, 2010, p.169.
4NargesMoheb, Mohammad S. Bahgeri, Relationship between Multiple Intelligences and
Writing Strategies, Journal of Language Teaching and Research, 2013, 4(4), p. 778.
5 Anna SvavaSòlmundardòttir, The Multiple Intelligence Theory in English Language Teaching, (Kennarahàskòli Islands: Kennarabraut, grunnskòlakennarafræði, 2008), p.3
6 Adi W. Gunawan, Genius Learning Strategy, (Jakarta: PT GramediaPustakaUtama, 2007)
pp. 231-241
7KarimHajhashemi, KouroshAkef, Neil Anderson, The Relationship between Multiple
mistakes, enjoys with foreign language, etc. Amir Reza N.T and FoadAmjadi
studied about the relationship between linguistic intelligence and reading
comprehension. The result of this study was there is significant relationship
between those two variables. In fact, from this study revealed that academic
achievement of Iranian EFL learners was not associated with IQ, but it showed a
strong correlation between reading achievement and verbal intelligence, a
subsection of IQ.8 Teele identified that student who has verbal-linguistic
intelligence shows high auditory ability and likes reading, writing, and playing
words.9
The characteristics of verbal-linguistic intelligence are suitable to be owned
by English education students because they learn and study about language and words. However, based on the data score of students’ reading 4 in Department of English Education in UIN Jakarta in academic year 2013 – 2014 revealed that
most of students in reading 4 got low score. From that observation, the writer
found the score from 73 students in reading class they got A: 1 student, B: 13
students, C: 44 students, D: 8 students and E: 7 students for their achievements in
reading 4. The data score revealed that more than 50% of students got low scores
for their final reading achievement. So, to be successful in educating all of
students, especially in reading, teachers need to be aware of this students’
problem.
Since reading is very important to be mastered by students, teachers have to
know and upgrade their background knowledge of students. Teacher knowledge
about how to organize classroom and to understand every student conditions
makes teaching and learning process more effective and this can help to improve
good achievement for students.
In this case, the writer would like to conduct a research with the title: The
correlation between students’ verbal-linguistic intelligence and their’ reading
8 Amir Reza NematTabrizi and FoadAmjadi, The Relationship Among Linguistic
Intelligence, Ethnic Identity, and Bilingual Iranian EFL Learners’ Reading Comprehension,
Modern Journal of Language Teaching Methods, 2015, 5(2), p.55.
achievement (a correlational study in 5th semester of Department of English
Education in UIN Jakarta).
B. Identification of Problems
The problem in this study can be identified as follows:
1. The problems influence reading achievement both from internal and external
factors.
2. Intelligence is one of internal factors influences reading achievement.
3. Most of 4th semester students in academic year 2013-2014 got low score in
reading.
C. Limitation of the Problems
The writer concerns and limits the problem in this research on the correlation between students’ verbal-linguistic intelligence and students’ reading achievement.
D. Formulation of the Study
The formulation of the problem is "Is there a correlation between students’
verbal-linguistic intelligence and students’ achievement in reading?”
E. Objective of the Study
The objectives of the study is to find out whether there is a correlation between students’ verbal-linguistic intelligence and students’ reading achievement in 5th semester of Department of English Education.
F. Significance of the Study
This study hoped can provide useful information for students, lecturer, and
1. The students
The result of this research hopefully can help the students to acknowledge
their intelligences so they can find the way for themselves in reading.
2. The lecturer
The result of this research is expected to be useful for reading lecturers in
improving their teaching capacity to improve students’ reading achievement.
3. The Institution
The result of this research is also expected to be useful input for headmaster
to support teaching and learning activity by improving and developing the quality
of education in the college, in order that students are motivated and interested in
6
A. Literature Review
1. Reading
a. The Definition of Reading
Reading is a mental process. It is called mental process because it
involves brain to receive the message or information from print text while the
eyes are sending the information to the brain. Related to this, Gough, Hoover
and Peterson stated there are two parts of mental process: word recognition
and comprehension.1 It can be concluded that reading engage a cognitive process because it need the reader’s comprehension to get the meaning of text.
In addition, reading is not just a basic skill. Many people think that
reading is a basic skill that was taught in the first year of school. Most of
teachers teach their students reading based on their level and the vocabularies
based on the content. “Reading is a simple process: readers decode (figure out
how to pronounce) each word in a text and then automatically comprehend the
meaning of the words, as they do with their everyday spoken language. This is not our understanding of reading”, said Ruth Schoenbach, Cynthia Greenleaf, Christine Cziko, and Lori Hurwitz.2
Reading is a process for the reader and the text. When the reader read a
text, the reader not only has to find the information, but also the reader has to
work together with the text. Working together with the text means that the
reader has to engage the meaning of the text and what the author want to say
in the text with the reader background knowledge. Hunt said that reading is a process that is formed by text, reader’s background, and the situation that
1 David Colins, Ann Colins, Advancing Reading Achievement Becoming Effective Teachers of Reading through Collective Study, South Florida: HTRA, 1998, p.8.
occurs in.3 Related to the previous statements, Urquhart and Weir said that reading use the reader’s cognitive ability so that both the reader and the text can interact well.4
In defining reading, it is important to pay attention in the reader external and internal factors, both factors related to how the reading’s readability and understanding. There are some factors involved both external and internal such as reader’s intelligence, experience, and background knowledge, words, phrases, sentences, and grammatical cues.5 So, like the previous statements,
reading is a process that involves all of reader attention to read the reading.
When the reader read the text, it will be better if the reader has good attention
especially to both factors.
So, the writer concludes that reading is all about the process such as
mental process, brain process, and the process how the reader can work with
the text. In reading, the reader who has background knowledge related to the
text is better than the reader who has lack background knowledge. This
because of the reader can easily read the text. Moreover, because of reading is
a mental process that involves brain to work with, the reader has to have
ability to work with the written text in order to get the meaning and main idea
easily.
b. Types of Reading
In the reading activity, there are two types of reading which are usually
done by the students. They usually read a short text for getting detail
information. In addition, they usually read a longer text for getting the overall
meaning of the passage. The kinds of reading are intensive and extensive
reading.
3 Julian Hermida, The Importance of Teaching Academic Reading Skills in First-Year
University Courses, The International Journal of Research and Review, Vol.3, 2009, p.23.
4 Feng Liu, Reading Abilities and Strategies: A Short Introduction, International Education Studies, Vol.3, 2010, p.153.
5Seyyede Zahra Naghibi and Mahmud PourhassanMoghaddam, The Effect of Intensive Vs.
1) Intensive Reading
Intensive Reading is different from extensive reading. Intensive reading
involves the reader reads in detail and need specific aim and task. Brown explains “intensive reading calls attention to grammatical forms, discourse markers, and other surface structure details for the understanding literal meaning, implication, rhetorical relationship, and the like.”6 In this type of
reading they need to be more focus on the text because this type of reading involves reader’s attention to read the text for getting information. Intensive reading allowed the reader to read the text that the reader likes in order to
motivate in reading and the text also based on the reader ability.
Hafiz and Tudor said that in intensive reading students given a short
text to get specific aspects of lexical, syntactic, or to provide the basis for
targeted reading strategy practice.7 So, to improve student achievement, they
need to pay attention of accuracy of reading regarding to the reading text,
vocabulary, and organization. The purpose of intensive reading is to help
students to get the detail meaning of the text, to develop their reading skill
such as identifying main ideas, recognizing text connectors, and the
knowledge of grammar.8 So, it can be concluded that intensive reading is kind of reading short text that needs reader’attention to the spesific detail, have some aims to read and do more attention to the structure of the text or
language rules.
2) Extensive Reading
According to Carrell and Carson extensive reading is reading rapidly of
large material or reading long text for general comprehending and focus on
6Maija MacLeod, Types of Reading, 2016, p.1,
http://fis.ucalgary.ca/Brian/611/readingtype.html#intensivereading
7Hesham Suleiman Alyousef, Teaching Reading Comprehension to ESL/EFL Learners, Journal of Language and Learning, Vol.5 (1), 2006, p.66.
the meaning of the text than the language itself.9 Extensive reading occurs when the reader read very easy enjoy the reading in order to build the reader’s reading speed or in order to help them become better in that skill rather than
reading to study about language itself
On the other hand, Davis defines that extensive reading is reading
activity which the reader is given the time and the materials to read pleasurably in the reader’s level as many book as the reader can, without the pressures of testing.10 So, in extensive reading the reader can read so many
books at the time which was given without any worries for testing, this kind
of reading shows a fun reading activity. Moreover, there are some reasons
why extensive reading is good for language skills development:
a) Allows the reader learn about language in context naturally.
b) Extensive reading helps the reader to build new vocabularies.
When the reader read a lot and enjoy it, the reader will find new
vocabularies that can help him/her to find out what the vocabularies
mean are then grammar may come next.
c) Help the reader to improve reading speed and reading fluency.
d) Build confidence, enjoyment, and motivation to learn about
language.
e) Extensive reading makes the reader read and listen a lot, so that
they can develop good reading and listening habits.
f) Help the reader to get a sense of how grammatical patterns work in
context.11
Extensive reading means that the reader can read as much as possible for the reader’s own pleasure but this type of reading can help the reader to improve his/her speed in reading. Nuttall said that an extensive reading
activity is the important way to improve both vocabulary and reading skill in
9 Willy A. Renandya, The Power of Extensive Reading, SEAMEO Regional Language Centre, Vol.38(2), 2007, p.134.
10Ibid., p.134.
11ERFoundation, Extensive Reading Foundation, 2016, P.1,
general.12 Nuttall statements supports that extensive reading is good for who
wants to improve his/her reading without any cognition about linguistic
structure. So that the writer concluded that extensive reading is reading longer
text than in intensive reading, but the reader reading the text pleasurably
without any kinds of reading tasks.
c. Purpose of Reading
In this era, students can read everything what they want in every time
and everywhere. But, each student has different purpose of reading. Based on
Grabe and Stoller there are some purposes in reading, such as:13
a) Reading to search for simple informationIn this purpose of reading,
usually the reader does scanning to get specific word or
information.
b) Reading to skim quickly. The reader does skimming for the text in
a short time to find out the general information of the text.
c) Reading to learn from text. In this purpose, the reader learns the
important information from the text and relates the information to the reader’s background knowledge.
d) Reading to integrate information. This purpose allows the reader to
read and decide what information they are going to pick.
e) Reading to write. Like reading to integrate information, this
purpose of reading requires the reader to read the text and get some
information or sources in order to develop writing.
f) Reading to critique text. In this purpose of reading, the readers
need to select, critique and compose the information of the text.
g) Reading for general information. Reading for general information
is a complex reading allows the reader to read words rapidly and
12 Thomas N. Robb, Bernard Susser, Extensive Reading vs Skills Building in EFL context, Reading in Foreign Language, Vol.5 (2), 1989, p.1.
13 William Grabe, and Fredrica L. Stoller, Teaching and Researching Reading, (London:
build strong skills in forming general meaning in representing of
mind ideas which is doing in short time.
On the other hand, Megan stated there are two main purposes of
reading, they are:14
a) Reading for literary experience. The reader becomes involved in
imagined events, settings, actions, consequences, characters,
atmosphere, feelings, and ideas; he or she brings an appreciation of
language and knowledge of literary forms to the text. This is often
accomplished through reading fiction.
b) Reading to acquire and use information. The reader engages with
types of texts where she or he can understand how the world is and
has been, and why things work as they do. Texts take many forms,
but one major distinction is between those organised
chronologically and those organised non-chronologically. This area
is often associated with information articles and instructional texts.
Furthermore, reading can have three main purposes, such as:15
a) Reading for survival is how to be aware to the environment, to find
an information like street signs, advertising, or timetables.
b) Reading for learning is reading purpose that occurs in the
classroom activity and requires some goals.
c) Reading for pleasure is something does not have to be done.
d. Definition of Reading Achievement
Reading achievement is a result from reading comprehension. So,
reading achievement has similar meaning to reading comprehension.
Therefore, reading comprehension effects reading achievement because reader’s comprehension to the text will increase or decrease reader’s
14 Megan Chamberlain, An Overview of National Findings from the Second Cycle of the Progress in International Reading Literacy Study, (New Zealand: Ministry of Education, 2005-2006), p.39.
achievement in reading. Reading comprehension is when reader develops
understanding while interacts with the text.16 According to Kintsch reading
comprehension is the result of process that produce while reading to make a
mental production of the situation made by the text, reffered to as a situation
model.17
Moreover, reading comprehension is a process of concluding or
produce meaning from the text. The main goal of reading comprehension is to
get whole information from the text rather than to get meaning only from
words or sentences.18 So, it can be concluded that reading comprehension is
the main focus on reading activity to interact or to build up understanding
with the text. Without understanding in reading, the reader will get nothing
from the text.
In addition, Gray divided reading understanding or comprehension in 3 kinds. First, reading “the lines” is understanding of the text structure. Second, reading “between the lines” is understanding about the text meaning. The last, reading “beyond the lines” is understanding about how the reader critiques the text19. Reading is important skill taught in schools. Readers,
especialy students, need to comprehand the reading to achive good
achievement. Comprehension requires the reader put the meanings of words in reader’s memory until the reader’s can think or interpret about the collective meaning.20
So that from those statements, the writer concluded that reading comprehension is the reader’s way to understand how the text, structure, or meaning then, the reader also can conclude the reading with his/her own
statement or opinion. In summary, reading comprehension is how the reader
16Paula J. Clarke. et al., Developing Reading Comprehension, (UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd,
2014), p.2.
17Kristi L. Santi and Deborah K. Reed (ed.), Improving Reading Comprehension, Literacy Studies, Vol. 10, 2015, p.2.
18 Gary Woolley, Reading Comprhension; Assisting Children with Learning Difficulties,
(New York: Springer Science+Business Media, 2011), p.15.
19 J. Charles Alderson, Assessing Reading, (Edinburgh: Cambridge University Press, 2001),
p.8.
understand and interpret the meaning of the reading text. There are some
steps how compehension works21:
a) Word recognition allows the reader to accsess the meaning or
multiple meaning of words in a sentence.
b) As more word meanings are accumulated in the reader’s short-term
memory, the reader is able to sort through multiple meanings and
select the appropriate one.
c) As the number of meanings held in short-term memoy increases,
the reader begins to form an expectation of the complete meaning
of the sentence. This occurs as the reader assembles those
meanings and come acts them to prior knowledge.
d) Only when all of the meanings have been assembled can the reader
finally determine the meaning of the sentence.
So, improving reading achievement through reading comprehension can
be improved by mastering a lot of vocabularies and syntactic rules. On the
other hand, there are some ways to improve reading comprehension22:
a) Develop a broad background
Develop knowledge can by reading newspaper, magazines, or
intrest in world events.
b) Know the structure of paragraph
This kind of grammar rules, so the reader can know where the
beginning, midde, or end of the paragraph, part of speech, etc.
c) Identify the type of reasoning
Does the author use cause and effect reasoning, hypothesis, models
building, induction or deduction, system thinking?
d) Anticipate and predict
The smart reader can anticipate or predict what is the main idea or
topic of the text.
21Collins, op. cit., p.16.
22Donald Martin, How To Be a Successful Student, ( United States of America: Martin Press,
e) Look for the method of organization
Is the material organized chronologically, serially, logically,
functionally, spatially, or hiererchical?
f) Create motivation and interest
To create reader motivation and interest, the reader can preview the reading and discuss with other readers. The stronger reader’s otivation, the greater reader’s comprehension.
g) Pay attention to supporting cues
Identify the pictures, graphs, and headings. Read the first and last
chapter or sentence.
h) Highlight, summarize, and review
To develop deep understanding, the reader have to highlight,
summarize and review important ideas.
i) Build a good vocabulary
Build good vocabulary can by reading or use dictionary regurally.
j) Use a systematic reading technique
Develop a systematic reading style, like the SQ3R method and
make adjusments to it, depending on priorities and purpose.
k) Monitor effectiveness
Good readers monitor their attention, concentration, and
effectiveness. They quickly recognize if they have missed an idea
and backup to reread it.
2. Intelligence
a. The Definition of Intelligence
Thousands years ago, intelligence has been defined differently.
Intelligence was difficult to define and cause confusions between researchers.
The most important definition is how people solve their problems.
Intelligence also has been defined as ability to understand, communicate,
researchers have been identified about relationship between human’s intelligence, behavior, and development of each person.23
The term of intelligence commonly be taken to mean how a person
understand and learn, but different people have their own meaning of
intelligence and this also can caused by their background knowledge both
from historical or cultural factors. According to Howard Gardner (1983) “intelligence comprises a set of separate intelligences, each of which is specialized for acquiring knowledge and solving problem in different areas of
cognitive activity”.24
Snyderman and Rothman defined that intelligence is the ability that a
person has to deal with something that she/he can get and learn from
phenomenon and/or events and how to solve and learn the problem.25 From
those statements, the writer concludes that intelligences of each person are
not the same. Those intelligences can be changed and/ or improved. The
combination of the most prominent intelligences can help people to learn and
to solve the problem.
Bainbridge said that intelligences is always be defined as general mental
ability to learn and apply the knowledge in manipulating environment, as well
as the ability to think abstractly.26 On the other hand, Binet sees that
intelligence is based on three primary components, first is the ability to direct
thought and action, second is the ability to change direction of thought and
action, and third is the ability to criticize own thoughts and actions.27 So, it
can be concluded that intelligence defines as people ability to adapt with
environment, knowledge, and the ways of thinking that can be developed by
themselves.
23 Sam Goldstein, Dana Priciotta, Jack A. Naglieri (eds), Handbook of Intelligence, (New
York: Springer Science+Business Media New York, 2015), p.3.
24 Kerri – Lee Krause. et al., Educational Psychology for Learning & Teaching, (South
Melbourne: Cengage Learning Australia, 2010), p. 294.
25 Robert E. Slavin, Educational Psychology Theory and Practice, (New Jersey: Pearson
Education, Inc., 2012), p.103.
26 Muhammad Yaumi and Nurdin Ibrahim, PembelajaranBerbasisKecerdasanJamak (Multiple Intelligences), (Indonesia: KencanaPrenadanedia Group, 2013), p.9.
Intelligence can be developed by three main factors:
a) Biological endowment – generic factors and how brain works
before, during and after birth.
b) Personal life history – this factors involves experience with
parents, teachers, peers, friends, and others who developed the
intelligences
c) Cultural and historical background – time and place in which the
people were born and raised. Then, the nature and state of cultural
or historical developments in different areas.28
b. The Definition of Multiple Intelligences
The theory of multiple intelligences was first introduced by Howard
Gardner in the late 1970 and early 1980. Before Gardner introduced Multiple
Intelligence theory, intelligences was measured by logic and language. Then,
Gardner argues that brain has others types of intelligences. According to
Gardner, all people have these intelligences but people differ in the strengths
and combination of intelligences. Refers to multiple intelligences theory,
Gardner believes that every people can change or increase the intelligences
through training and practice.29
Since Gardner introduced the Multiple Intelligence theory, many
researchers have tried to identify the theory of Multiple Intelligence. Gardner
theory’s identified eights intelligences such as, verbal-linguistic, musical,
logical-mathematical, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, intrapersonal, interpersonal
and naturalist. However, in 2006 Moran, Kornhaber, and Gardner added one
intelligence and became nine multiple intelligences, linguistic,
logical/mathematical, musical, spatial, bodily/kinesthetic, naturalistic,
interpersonal, intrapersonal, and existential.30
28 Thomas Armstrong, Multiple Intelligences in the Classroom, (Virginia: ASCD, 2009),
p.27.
29Jack C. Richards and Theodore S. Rodgers, Approaches and Methods in Language Teaching a Description and Analysis, (United States of America: Cambridge University Press, 2001), p.115.
Moreover Gardner claims that people can develop their multiple
intelligence, one, some of the intelligences or all of them. The intelligences is
changing. The multiple intelligences is something that can be developed or nurtured. “There are seven autonomous brain systems that work out together in complex ways; no intelligence exists by itself,” said Gardner.31 On the other hand, in educational field, Chrristison said that the theory of multiple
intelligence can help teachers to find out learning style and others ways to
know about what have been taught in classroom activities.32
c. Types of Multiple Intelligences
Gardner identified there are nine intelligences, there are:
1) Verbal-linguistic Intelligence is an ability to perceive or generate
spoken and written language.
2) Musical Intelligence is sensitivity to pitch, rhythm, and timbre; the
ability to create, communicate and understand meaning in sound; the
ability to discern sound patterns.
3) Logical-mathematical Intelligence is an ability to use and appreciate
of numerical, causal, abstract or logical relations.
4) Spatial Intelligence is an ability to perceive visual and spatial
information, and to transform or modify this information and re-create
visual images.
5) Bodily-kinesthetic Intelligence is an ability to control of all or parts of one’s body and to solve problems or create products.
6) Intrapersonal Intelligence is a capacity to form a mental model of
one-self and use the model to make informed decisions about possible
actions
31Heather M. Prescott, Helping Students Say How They Know What They Know, The Clearing House, Vol. 74 (6), 2001, p.328.
32Akram Hashemi, The Relationship Between Multiple Intelligence and Reading
7) Interpersonal Intelligence is a capacity to recognize, distinguish between and/or influence in desired ways others’ feelings, belifes, and intentions.
8) Naturalist Intelligence is an ability to understand and work effectively
in the natural word.33
9) Existential Intelligence it is involves an individual’s ability to use
collective values and intuition to understand others and the world
around them.34
d. The Verbal Linguistic Intelligence
In fact that verbal – linguistic intelligence has been identified many
years before the appearance of others intelligences. Verbal – linguistic
intelligence and logical – mathematical intelligence was used as measurement
of IQ. Both intelligences have become standardized test in some academic
such as National Assessment of Educational Program (NAEP), Iowa Test of
Basic Skill (ITBS), etc.,35
In addition, more than century ago, Alfred Binet made an IQ test to
measure elementary children in France. Later on, the U. S Armed Forces
began using the test in World War I. Basically, the Binet Test only measured
two intelligences: verbal – linguistic intelligence and logic – mathematical
intelligence36. So, it can be concluded that those intelligences were used as
the main focuses of the intelligences from years ago.
So, what is Verbal – Linguistic Intelligence? Verbal – Linguistic
Intelligence is an ability to use words in spoken or written language
effectively. This intelligence involves the ability to manage the language
form, the phonology or sounds of language, the semantics or meanings of
33 Kerri – Lee Krause. Et al., op. cit., p. 295.
34Melissa Kelly, Profile of Existential Intelligence, 2016, p.1,
(http://712educators.about.com/od/multipleint/p/existential-Intelligence.htm)
35 Fred C. Lunenburg and Melody R. Lunenburg, Applying Multiple Intelligences in the
Classroom: A Fresh Look at Teaching Writing, International Journal of Scholarly Academic Intellectual Diversity, Vol. 16 (1), 2014, p.1.
language, and the pragmatic dimensions or practical uses of language. Some
of these uses include rhetoric (using language to convince others to take a
specific course of action), mnemonics (using language to remember
information), explanation (using language to inform), and metalanguage
(using language to talk about itself).37
The Verbal – Linguistic Intelligence is the intelligence of language and
communication. Language ability that involves speaking, articulating, expressing, and delivering one’s thoughts and feelings to others with one or more languages. The intelligence can be at spoken or written language.38
Gardner, Chapman, and Freeman state that people who have good ability in
Verbal – Linguistic Intelligence usually good at memorizing vocabularies
which lead deliver them to read books and to be engaged in the books and
have good appearance in English classes.39
The Verbal – Linguistic Intelligence involves high sensitivity to words
and language function. People with high Verbal – Linguistic Intelligence love
reading, writing, and good at expressing themselves. According to the
intelligence, it involves the ability to recognize language use, good at
remember things, enjoy joking, likes to explain or teach, know how to
persuade people, understands about language rules.40 So, it can be concluded
that people who have good verbal – linguistic intelligence have good ability
to know about language whether in oral or written language.
e. The Characteristics of Verbal – Linguistic Intelligence
There are some characteristics of Verbal – Linguistic Intelligence41:
1) Love to read, write, talk, and listen
2) Often speak what they have read
37 Armstrong, op. cit., p.6.
38 International Montessori Schools and Child Development Centre (World School:
Brussels-Belgium), p.3.
39KarimHajhashemi, KouroshAkef, Neil Anderson, The Relationship between Multiple
Intelligences and Reading Proficiency of Iranian EFL Students, World Applied Science Journal, 2012, 19 (10), p.1476.
40Prescott, op.cit., p.329.
3) Good at spelling patterns
4) Applying grammar rules
5) Likes playing word games such as, puzzle, poems, etc,.
6) Maintaining book collection
7) Have good memory for general knowledge
8) They can remember quotes and famous sayings easily
9) Orderly and systematic
10) Good at reasoning
11) Can speak what their viewpoint clear, beautiful, and refined manner
12) Can explain abstract content clearly
13) Good public speaker
14) Likes to debate
15) Likes to use “fancy” words
16) Have good knowledge about language use, such as persuasion,
information, etc,.
17) Good at interpretingn others
18) Learn foreign language easily and enjoy it
19) Flexibility in extraxcting meaning when speaking several languages
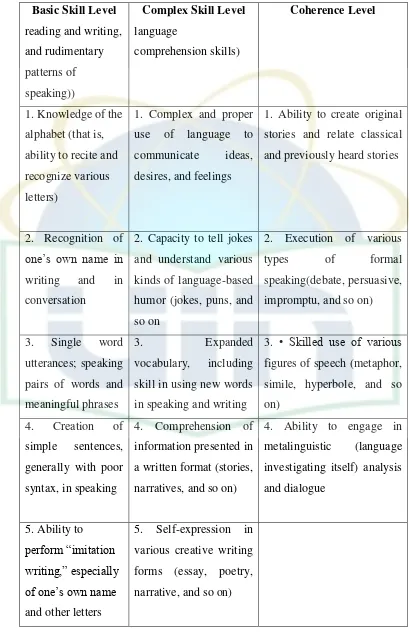
[image:34.595.108.513.114.737.2]Table 2.1
Verbal – Linguistic Capacities Developmental Journey42
Basic Skill Level (involves
acquisition and
basic development of “building block” language arts
capacities,
including simple
Complex Skill Level (involves understanding
various aspects of
language as a system,
for example, grammar,
syntax, phonetics, and
praxis, and the
development of
Coherence Level (involves development of
the creative and
self-expressive dimensions of
linguistic communication
and expanded
comprehension and
interpretive capacities)
Basic Skill Level reading and writing,
and rudimentary
patterns of
speaking))
Complex Skill Level language
comprehension skills)
Coherence Level
1. Knowledge of the
alphabet (that is,
ability to recite and
recognize various
letters)
1. Complex and proper
use of language to
communicate ideas,
desires, and feelings
1. Ability to create original
stories and relate classical
and previously heard stories
2. Recognition of one’s own name in writing and in
conversation
2. Capacity to tell jokes
and understand various
kinds of language-based
humor (jokes, puns, and
so on
2. Execution of various
types of formal
speaking(debate, persuasive,
impromptu, and so on)
3. Single word
utterances; speaking
pairs of words and
meaningful phrases
3. Expanded
vocabulary, including
skill in using new words
in speaking and writing
[image:35.595.108.517.111.746.2]3. • Skilled use of various
figures of speech (metaphor,
simile, hyperbole, and so
on)
4. Creation of
simple sentences,
generally with poor
syntax, in speaking
4. Comprehension of
information presented in
a written format (stories,
narratives, and so on)
4. Ability to engage in
metalinguistic (language
investigating itself) analysis
and dialogue
5. Ability to perform “imitation writing,” especially of one’s own name and other letters
5. Self-expression in
various creative writing
forms (essay, poetry,
B. The Relevant Study
There are some relevant studies about verbal – linguistic intelligence and
reading. The first study was conducted by Hashemi, his research is about
investigating whether there is any relationship between multiple intelligence and
reading ability. The participants were 122 Iranian undergraduate EFL (English as
Foreign Language) students were selected from Islamic Azad University,
Raudehen Branch. The research used IELTS and multiple intelligence
questionnaire as the instruments of the research. The IELTS test was used as a
main instrument for the testing reading ability and the McKenzie’s questionnaire used to identify students’ intelligences profiles. The result from correlational design revealed that verbal – linguistic intelligence and kinesthetic intelligence
made the greatest contribution toward predicting reading ability scores.43
The second study was conducted by Narges Moheb and Mohammad S.
Bagheri. Their research is about finding the relationship between multiple
intelligences and writing strategies among Iranian EFL learners. The participants
in this study were 120 adult males and females studying at high and advanced
level of Iran Language Institute. The researchers used questionnaires to measure
the variables. The first questionnaire was about multiple intelligences and the
second was about writing skill and strategies questionnaire for checking the students’ use of general, before, during, and after writing. According to the result, verbal – linguistic intelligence was correlated with general writing strategies44.
The third research was invastigated by Rahimi and Sadighi. This research was
examined about the impact of linguistic intelligence and emotional intelligence on
the reading comprehension ability of the Iranian EFL learners. The participants
were 135 senior English major (both male and female). But, only 90 students at an
intermediate level of proficiency were analyzed for the study. The data gathered
through two questionnaires and a reading test and analyzed through two-way
ANOVA and Multiple Regression. The result indicated that the linguistic
43Hashemi, op.cit., p.100.
44Narges Moheb and Mohammad S. Bagheri, Relationship between Multiple Intelligence and
intelligence is a relatively strong predictor of reading performance, accounting for more than 40% of the variance observed in the students’ performance on the reading comprehension test.45
The last research was conducted by Eva Stranovska, et.al. This research was
conducted to find the measure of influence of cognitive-individual variables (Need
for structure, Ability to Achieve Cognitive Structure, Self-Esteem, Cognitive Style
Category With), linguistic variables (Verbal Intelligence, Morphology Score), and
demographic variables (Study-year, Grade, Living abroad) on syntactic abilities
of students studying English language and culture at the Constantine the
Philosopher University in Nitra. The participants was 114 students (31 men, 83
women), students of first, second, and third year of English Language and Cultue
studies (full-time study). This research used PNS Scale – Personal Need for
Structure by Thomson Naccarato and Parker (12 items), AACS Scale (24 items)
studied abot how students react in uncertain situation, Estimation Scale C-W
(Category Width) (20 statement items): C-W scale measures rthe Cognitive Style ‘Category Width’ and real estimation, RSES to measure the level of self-esteem scale, Intelligence Structure Test I-S-T, Verbal Intelligence Sub-tets (consists of
three sub-tests), and Test of Syntactic Abilities (80 items divided into four
areas)measured the ability to create syntactic structures. The result of the study
shows that a positive correlation between syntactic ability and Verbal Intelligence
and a negative correlation between Verbal Inteligence and Need for Structure46.
There has been some studies invastigated that showed verbal-linguistic
intelligence related to language proficiency, especially in reading. However, not
many studies have investigated verbal-linguistic intelligence correlates to a
specific language skill, reading. Moreover, since there has been investigations that
showed verbal-linguistic intelligence correlates to language proficiency for EFL
45M. Rahimi, F. Sadighi and Z. Heosseiny Fard, The Impact of Linguistic and Emotional
Intelligence on the Reading Performance of Iranian EFL Learners, The Journal of Teaching Language Skills (JTLS), Vol.3 (1), 2011, p.151.
46Eva Stranovska, et al., Cognitive-Individual, Linguistic and Demographic Variables, and
learners in others country, so this study will examined the correlation between
verbal-linguistic intelligence and reading in Indonesia.
C. Conceptual Framework
Based on the theories above, it can be concluded that reading is one of the
most important material to be learnt. In reading, the reader can get information
through the written text. Especially in language learning, reading is one of the
most important skills that can help the language learner to improve their
knowledge about the foreign language. As mentioned in the theories about
reading, reading is a mental process that involves the reader and the reader’s brain
is getting together with the text to get the meaning of the text. While the eyes
read the text, the brin try to get the meaning of it. So, reading also called as a cognitive process because when the reader reads, the reader’s not only reads the words by words but also need reader’s comprehension in understanding the text. Without comprehension, the reader just reads the words without getting the
message of the text.
Because reading is also called as cognitive process, many people in education
believe that intelligence is one of the factors whether the student potential level up
or not. In many schools, reading and intelligence test are becoming a standard for
understanding students self-background. In addition, intelligence is often
considered to be a major factor causing high and low reading achievement. Based on Howard Gardner’s theory, there are 9 types of multiple intelligence.
One of them is verbal – linguistic intelligence which one of its characteristics
is loves to read. As theories above, verbal linguistic intelligence is an ability to
understand written and oral language. This intelligence involves how a person can
understand and enjoy easily with language skills. As writer mentioned, reading is
one of the ability that can easily mastered by the person who have dominant
verbal – linguistic intelligence in themselves. However, most people does not
realize what their dominant intelligence are. Since intelligence is something that
can be changed and/or improved, so people can changed or improve the
Thus, based on the explanation above, it can be identified that verbal –
linguistic intelligence has a great deal with reading. it can be supposed that the
more students getting aware about their verbal – linguistic intelligence and having
a better knowledge about what their dominant initelligence are, they will easily
get comprehension with the text and also they can help themselves in learning
process based on their learning styles which developed by intelligences.
D. Theoretical Hypothesis
26
X Y
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A.
Time and Place of Research
This study was conducted for four months, from July to October 2016. The
study was conducted for verbal-linguistic intelligence and reading
achievementtest. The place of the study is at “SyarifHidayatullah” State Islamic
University of Jakarta which is located at Jl. Ir. Juanda No.95, Ciputat, Tangerang
Selatan. The consideration of conducting the study at this site was because of the
accessibility and familiarity of the situation and the participants.
B.
Method of Study
The method of this study was quantitative method. Meanwhile, the research
design of this study was correlational study. For the real design of the study is
[image:40.595.111.517.199.536.2]represented as follows:
Figure 3.1 Research Design
From the figure above, this study investigated the correlation between two
variables. The variables were independent and dependent variables. The independent variable is “reading achievement” which was known as X variable. Dependent variable is “verbal – linguistic intelligence” which was known as Y variable.
C.
Population and Sample
students, 5B: 20 students, and 5C 19 students. The total numbers of 3 classes are
54 students. The target population of this study was chosen because they have
already given all of reading materials. According to Cohen, taking the larger
sample is better to give greater reliability and facilitate more sophisticated
statistics to be used.1 Therefore, the study was considered to take sample for
collecting data consisted of 39 students which selected using random sampling
technique. The samples derived from 5B and 5C classes. Meanwhile, the other 15
students which were from 5A were involved to be participants in testing validity
and reliability of the instrument of this study.
D.
Instrument of the Research
In collecting the data, two instruments were used in this study. The first
instrumentwas the reading achievement test scores which given to the 5th semester
based on Reading 4 syllabus. Then, the second instrument was questionnaire
Likert type scale of questionnaire about Verbal-Linguistic Intelligence taken from
Multiple Intelligence Questionnaire by Walter McKenzie, International
Montessori Schools and Child Development Centres Brussels, Belgium, and
Multiple Intelligence in the Classroom by Thomas Armstrong were used to measure students’ Verbal-Linguistic Intelligence.
E.
Technique of Data Collection
The instrument of this study was reading achievemetn test as variable X and
Verbal – Linguistic Intelligence Questionnaire score as Y variable.
1. Reading Achievement Test
In this study, reading achievement test was adopted from Longman Complete
Course for the TOEFL Test Preparation for the Computer and Paper Test, Step by
Step to Reading Skills 4, and E-book of The Official Guide to the TOEFL Test 4th
Edition by ETS. The reason why those books were chosen is because those consist
of test of the TOEFL paper-based which requires the materials from Reading 4
1 Louise Cohen, et al., Research Method in Education (6th Ed.), (New York: Routledge,
syllabus. In other words, the tests were suitable for the participants of this study
because they have learned about all the materials in Reading 4. The main aspect of
this test was comprehending English passage. The test consisted of 25 questions
in multiple choice test. The participants had 25 minutes for answering the test.
The writer analyzed the score by using ANATES program version 4.0. So, the
reading test score will be correlated with the verbal – linguistic intelligence
[image:42.595.108.523.212.619.2]questionnaire score in order to find its significant relationship.
Table 3.1
The Blue Print of Reading Achievement Test
Indicator Item Number Total
Item
1. Main Idea and Topic 2, 7, 25 3
2. The organization of
Ideas
21, 22 2
3. Thinking in English 10, 11 2
4. Vocabulary Question 4, 14, 17 3
5. Stated Detail Question 12, 23, 24, 9 4
6. Unstated Detail
Question
1, 8, 13 3
7. Pronoun Referent 6, 16 2
8. Previewing, Predicting,
and Transition
18, 19, 20 3
9. Inferences 3, 5, 15 3
2. Verbal – Linguistic Intelligence Questionnaire
The writer conducted Verbal – Linguistic Intelligence Questionnaire was a
(1999)2, International Montessori Schools and Child Development Centres
Brussels, Belgium3, and Multiple Intelligence in the Classroom by Thomas
Armstrong4 as the research instrument. It was a self-report questionnaire using a
Likert-type scale. The structure of the Verbal – Linguistic Intelligence
Questionnaire consists of general characteristics of Verbal – Linguistic
Intelligence.
The Verbal – Linguistic Intelligence comprised of 26 items categorized
under eight components in self-direction in learning. The components of Verbal – Linguistic Intelligence Questionnaire present in Table 3.2 included language skills and creativity in language. In the questionnaire section, the participants
were required to choose form one of five scales (1 = Strongly Disagree, 2 =
Disagree, 3 = Undecided, 4 = Agree, and 5 = Strongly Agree).
[image:43.595.106.520.112.548.2]Table 3.2
The Blue Print of Verbal – Linguistic Intelligence Questionnaire
Indicator Item Number Total
Item
Language skills 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 11, 13, 15,
16, 17, 20, 21, 23, 24, 25,
18
Creativity in language 6, 8, 12, 14, 18, 19, 22, 26 8
a. Validity Instrument
Validation of the instrument was conducted to know whether the
instrument capable to collect data or not. The writer got the standard
coefficient validity minimum for this instrument with N = 15 and coefficient
significance level 5%. The coefficient validity is 0,514. To see the validity
2YaminaBoudraf, “The Relationship between English Language Students’ Multiple
Intelligences and Reading Comprehension,” Dissertation in Mohamed Khider University, Biskra, 2012, p. 71, published.
3International Montessori Schools and Child Development Centre (World School:
Brussels-Belgium), p.3.
4 Thomas Armstrong, Multiple Intelligenc