PARENTS’ INVOLVEMENT AND ITS INFLUENCE ON STUDENT
ENGLISH ACHIEVEMENT
(A Correlation Study at MTsN Tangerang II Pamulang)
A “Skripsi’
Presented to Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for
the Degree of Strata- 1 (S-1)
By:
Fitriah AB
104014000364
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS’ TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
2009
ABSTRACT
AB, Fitriah, Parents’ Involvement and Its Influence on Student English Achievement, 2009.
Education takes place not only in school but also at home. Parents are the first educators who provide educational milieu for their children. The children also acquire their first language from them. Parent can provide environmental input for gaining their children’s language – first language, second language or foreign language. When the children learn new language, parent can advocate, motivate, show their interest in the language, be model to master it, or join in fun together with their children in learning the language.
The aims of the research are to know the influence of parents’ involvement on student English achievement in Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri Tangerang II Pamulang.
In doing the research, the writer applies the correlation technique to know the influence parent’s involvement on student English achievement. In this quantitative research, data are collected by using questionnaire, documentation, interview and observation.
After doing the research, the writer finds that the influence of parents’ involvement is adequate on second grade students of Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri Tangerang II Pamulang English achievement. It is showed by the result of the research (0,402). It belongs to medium correlation. It means that their parents’ involvement as the motivator, as the advocate in economy, as the monitor, and as the model is sufficient to support the students’ English achievement.
ABSTRAK
AB, Fitriah, Keterlibatan Orang Tua dan Pengaruhnya terhadap Prestasi Belajar Bahasa Inggris Siswa, 2009.
Kata kunci: Prestasi Belajar Bahasa Inggris, Keterlibatan Orang Tua
Pendidikan tidak hanya terjadi di sekolah tetapi juga terjadi di rumah Orang tua sebagai pendidik pertama yang menciptakan lingkungan pendidikan bagi anak mereka. Anak juga mendapatkan bahasa pertama dari orang tua mereka. Orang tua menyediakan input kebahasaan untuk meningkatkan kemampuan berbahasa mereka. Saat seorang anak mempelajari bahasa yang baru, orang tua dapat mendukung, memotivasi, menunjukkan minat mereka terhadap bahasa, menjadi contoh dan teladan, atau bersama-sama dengan anak mereka mempelajari bahasa baru tersebut.
Tujuan penelitian ini adalah untuk mengetahui pengaruh peran orang tua terhadap prestasi belajar bahasa Inggris siswa di Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri Tangerang II Pamulang.
Dalam melakukan penelitian, teknik korelasi digunakan untuk mengetahui pengaruh peran orang tua terhadap prestasi belajar bahasa Inggris siswa. Data yang dikumpulkan untuk penelitian kuantitatif ini diperoleh dengan menggunakan kuesioner, dokumentasi, wawancara, dan observasi.
Pengaruh orang tua terhadap prestasi belajar bahasa Inggris siswa kelas dua Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri Tangerang II Pamulang cukup memadai. Ini ditunjukkan dengan hasil penelitian yaitu 0,402. Hasil ini termasuk dalam tingkat korelasi yang cukup atau sedang. Ini membuktikan bahwa peran orang tua sebagai pemberi motivasi, pendukung secara finansial, pemantau belajar, dan sebagai contoh dalam belajar bahasa Inggris cukup memadai untuk mendukung prestasi belajar bahasa Inggris siswa.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
All praise be to Allah, Lord of the worlds. Because of His blessing, the writer is able to
complete this ‘Skripsi’. Peace and blessing be upon Prophet Muhammad, his family, his relatives, and
his followers.
This ‘Skripsi’ is presented to the English Education Department, the Faculty of Tarbiyah and
Teachers’ Training in State Islamic University Jakarta as a partial fulfillment of the requirements of
the Degree of Strata-1 (S-1).
This skripsi can be finished because of her beloved parents, Abbas Sas and Sa’idah, who have
been getting involved in the writer’s life especially in education, and also her sisters, Nur’aini and
Raudhatul Jannah for their support.
Many people help to do this skripsi. Without their help, it is hard to finish it. In this
opportunity, the writer would like to give her sincere gratitude, especially to Drs. Nasrun Mahmud,
M.Pd., as the advisor who has given his time and guidance for the writer and has forced to finish this
‘Skripsi’, to all her lecturers who have given their knowledge, to Drs. M. Syauki, M.Pd. as the head of
English Department, to Neneng Sunengsih S.Pd. as secretary of English Department. Then, her
gratitude also goes to Prof. Dr. H. Dede Rosyada, M.A., as the Dean of Tarbiyah and Teachers’
Training Faculty, and to MTsN Tangerang II Pamulang, where the research has been done.
The writer would also like to refer her gratitude for all of her classmates (2004), either class A,
B, or C, especially for Tri Wahyuni Martiawati, Dawi Anjani, Asep Mutaqin Abror, Siti Mariam,
Irwan Kurniawan, and Alber Oki, for her roommates, Mia Ma’rifatul Aini, Yayah Kudsiyah, Rahil
Aprilian, Ade Laili Akhiliyah, Rizka Khoerinnisa and Musrifatul Khariyah for the best help that they
have given, for her uncles and aunts who always force and give attention to finish the ‘Skripsi’, and
for the best friend, Humaidi, Mar Zannah and Siti Subaidah for giving more spirit to finish the
‘Skripsi’.
Finally, the writer realizes that ‘Skripsi’ is not perfect yet; it is a pleasure for her to receive
be better. The writer also hopes the ‘Skripsi’ can be useful for the teachers, parents, and people who
are interested in English education.
Jakarta, February 20th 2009
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ABSTRACT ... v
ABSTRAK... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS... ix
LIST OF TABLES ... xi
LIST OF FIGURES ... xii
CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Limitation and Formulation of the Problem ... 5
C. Significance of the Study... 5
D. Organization the Skripsi ... 6
CHAPTER II : THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK... 7
A. English Achievement ... 7
1. Achievement ... 7
2. Achievement Test... 10
3. Factors Affecting the Achievement... 11
B. Parents’ Roles in Students Education... 16
1. Parents’ Involvement in Education ... 17
2. Parents’ Involvement in Teaching and Learning English as Foreign Language 19 C. Conceptual Frame ... 25
D. The Hypothesis ... 26
CHAPTER III : MADRASAH TSANAWIYAH NEGERI II PAMULANG PROFILE 27 A. School Identity ... 27
B. Brief History ... 27
C. Vision, Mission, and Motto ... 29
D. Facilities ... 29
E. Structure of Organization ... 31
F. Teachers, Staff and Students... 32
CHAPTER III : RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND FINDING ... 35
A. Research Methodology... 35
2. Time and Location... 35
3. Method of the Research ... 36
4. Population and Sample ... 36
5. Technique of Collecting the Data... 37
6. Techniques of Data Analysis ... 39
B. Research Finding... 40
1. Data Description... 40
2. Data Analysis ... 45
3. Test of Hypothesis and Interpretation of Data Analysis... 48
CHAPTER IV : CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 51
A. Conclusion ... 51
B. Suggestion... 52
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 53
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1 Facilities in MTsN Tangerang II Pamulang... 30
Table 2 Teachers’ Condition in MTsN Tangerang II Pamulang ... 32
Table 3 Staffs’ Condition in MTsN Tangerang II Pamulang ... 33
Table 4 Students’ Development... 34
Table 5 The Distribution of Students ... 37
Table 6 Indicator of Parents’ Involvement ... 38
Table 7 Score of Questionnaire Answer... 39
Table 8 Questionnaire Result about Parents’ Involvement ... 40
Table 9 Students’ English Achievement ... 43
Table 10 The Correlation between Parents’ Involvement and Students’ English Achievement ... 45
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1 Initial Brainstorming on Motivation... 14
Figure 2 The Socio-educational Model ... 20
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
E.
Background of the Study
Language is a means we use to communicate with each other. It helps people to learn about
and share the experiences of others. It is also used as a medium to apply all of the knowledge that
people have gained from one moment to the next. With the aid of language, people are able to learn
culture and then enter the life of the society. Without language they would only in a very limited way
be able to deal with our environment.
Language learning is important for human’s social development. As a language which is used
by more than a half of population in the world, English holds the key as an international language.
English is a tool of communication among peoples of the world to get trade, social-cultural, science,
and technology goals. Moreover, English competence is important in career development. Therefore
students need to understand and use English to improve their confidence to face global competition.
Many factors affect the student’s English achievement. Intelligence is not the only determinant
of academic achievement. The other factors such as motivation, teacher, learning style, environment,
and parents’ involvement can influence the achievement.
Environment is an educational component, which has big influence on instructional process
and instructional product1. It is a place where students live and interact to each other in social life. It
gives environmental input for gaining the students language –first language, second language or
foreign language.
As a unit of society, family is the primary social system for children, because parents are the
children’s first teachers who become most influential teachers. They naturally become teachers for
their children. Lester D. Crow and Alice Crow said2, “The child in the home is the recipient of
whatever constructive or destructive influences may result from the interrelations of his home with the
social order into which he or she has been born”. Many things children learn first from his parent.
Children spontaneously imitate their parents’ language. In this way they acquire their first language.
1
Madyo Ekosusilo and R. B. Kasihadi, Dasar-dasar Pendidikan, (Jakarta: Rineka Cipta,1992) p.51
2
After acquiring the first language, children learn second language and foreign language at
home or outside. In Indonesia, Indonesian language is as second language and English is considered
the first foreign language. They are taught as a timetabled subject in school.
Since Indonesia is as a non-English environment, many people cannot speak English. Children
can speak it outside of school only in limited way. It can limit the students’ input to gain their English
skills and their competences.
In TEFL (Teaching English as Foreign Language) parents can help teacher. Parents can
advocate their children in learning a new language, can be a model for their children for mastering of
the language, can join in the fun and can learn with their children to learn the language, or can show
their interest in their children’s language lessons and their development.
Related to English language proficiency, Sri Astuti 3 explained that it is not enough to preach
to children to like their language lessons at school. Parents have to display their interest in their
children’s language lessons and their development. If their children are learning a new language,
parents can join in the fun and learn with him or her. Parents can also be a model for their children to
be a master of a language. No one would be more ideal for this role of setting the standard for the type
and sophistication level of the learned language than children’s own parents. If parents want their
children to be able to speak English well, parents should speak correct English themselves because a
child can be a very adept imitator of it surroundings. Parents can inspire their children sense of love
and respect toward a language by showing the language plays an important part in their life or
applying it in their environment. They can immerse themselves and their environment with things such
as reading a book and watching a movie that use language at its best. Good books, high quality movies
or TV programs, engaging and relevant conversation, bed-time stories, songs and poetry sung to both
entertain and educate children are some of the things that parents can provide for their children to
develop this love and respect for the role of language. More importantly, parents need to show that
they are fond of these things. 4
When parents do aforementioned things, it serves more than just as an inspiration of love for
language, but also as a stimulus for their children’s language development. In order for children to be
proficient in any language, they have to be immersed with the language as much as possible, from as
early an age as possible. It is necessary for them to be spoken to, sung to, read to, for them to be given
as much interesting, meaningful and relevant input as possible. 5
3
Sri Astuti., “Language Proficiency Starts at Home,” Jakarta Post, 27 Jan. 2008. p.29, col. 1
4
Sri Astuti., “Language Proficiency Starts at Home,”….p.29, col. 1
5
In addition they can support their children in learning new language by giving informal English
language instruction such as English language course, private course, or other institution. Sending
their children to informal English language instruction, parents have expectation that their children get
English skills and competences. Attending informal institution, children can improve their language
skills and can develop their ability. Many informal institutions offer various program to learn new
language for their students from basic to advanced level. However, it is not enough because the
children also need their parents to help their education.
Parents need to be involved in their children’s education not only during early childhood, but
also throughout the school years. Parents are also essential in supporting learning at home, at school,
and in the community. According to Evaries Rosita’s opinion6, “It is important for parents to know
that education takes place not only in school but also at home.”
Educational responsibility is on parents. Nowadays parents have misinterpretation about
education Parent’s responsibility to educate their children is mostly taken by formal and non-formal
educational institution or it may be taken all. It makes parent’s control weaken and schools lessen
parent’s authority on their children. Most of them thought their responsibility has been given to the
school. They do not realize that education takes place at home, in school, and in the community.
Moreover, Evaries Rosita wrote:
Parents’ role in their children academic success cannot be underestimated. Parental help should be seen as a powerful force that can assist children in knowing and then developing their potential. Lamentably, parental involvement in the education of children seems not to be considered a top priority. This is especially true when parents are engaged in their everyday business. Being preoccupied with daily routine, parents often don’t have sufficient time to spend on regularly monitoring their children’s academic achievement.
Based on the above background, the writer is eager to hold a research under the title
“PARENTS’ INVOLVEMENT AND ITS INFLUENCE ON STUDENT ENGLISH ACHIEVEMENT (A Correlation Study at Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri Tangerang II Pamulang)”.
F.
Limitation and Formulation of the Problem
To avoid misunderstanding and to clarify the problems, it is important to set some limitation of
the problems. The research is focused on parents’ involvement in learning English as motivator,
6
advocate in economy, monitor, and model. The writer will also limit this problem of the discussion on
the student English achievement in the odd semester in second grade of Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri
Tangerang II Pamulang.
The formulation of the problem in this writing is “Is (there) the influence of parents’
involvement on student English achievement?”
G.
Significance of the Study
The result of this research is expected to be an input for parents and teachers in gaining
parents’ involvement on student English achievement. Parents and teachers should know that there are
some factors affecting the achievement. One of the factors is environment condition. Parents can
provide a learning condition to support their children’s in learning English. The writer hopes this will
be useful for them who are interested in parents’ involvement and the research also will enrich and
improve their knowledge and skill.
H.
Organization the Skripsi
This skripsi consists of five chapters and each chapter has some sub-chapters, as follows:
The first chapter is introduction, which consists of four parts: background of the study,
limitation and formulation of the problem, significance of the study, and organization of the ‘skripsi’.
The second chapter will be focused on the discussion of theoretical framework. It is divided
into four parts: English achievement, parents’ role on students education, conceptual frame and
hypothesis.
The third chapter is encompassed about Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri Tangerang II Pamulang
profile.
The fourth chapter is research methodology and research finding. Research methodology
discusses objective of the research, time and location, method of the research, population and sample,
technique of collecting the data and technique of data analysis. Research finding explains about data
description, data analysis, and test of hypothesis and interpretation of data analysis.
The last chapter consists of two parts: conclusion and suggestion. The conclusion here is taken
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
E.
English Achievement
4. AchievementIn general, achievement means all things that people obtain from his/her effort. But in
education, achievement means the result of tests designed to determine a student’s mastery of a
given academic area.7
Achievement is what a person has already learned. It means achievement is the child’s
past learning – that is, his accumulated knowledge in a particular field.8
In dictionary of education9, achievement is defined as accomplishment or proficiency
of performance in a given skill or body of knowledge, while academic achievement is
knowledge attained or skills developed in the school subject, usually designated by test scores
or by marks assigned by teachers, or by both.
The other definition of learning achievement is the extent to which a person has
achieved something acquired certain information or mastered certain skills, usually as a result
of specific instruction.10
Another idea about learning achievement is expressed by Jum C. Nunnally. Learning
achievement is how much students a count of lessons that students have learned up to a
particular point in time.11 It means that achievement is an amount of lessons that the students
have got through an instructional process in the particular class for several times.
Achievement, in Theodore Huebener’s opinion, is the amount that has been learned.
The achievement is also defined as the pupil’s degree of mastery of a given section of a
textbook.12
7
Julian C. Stanley, Measurement in Today’s Schools, (New Jersey: Practice Hall, 1964), p. 2
8
Louis J. Karmel, Testing in Our Schools, (New York: The Macmillan, 1966), p.38
9
Carter Victor Good and Winifred R. Merkel (ed), Dictionary of Education, (New York: McGraw-Hill Book, 1973), p.7
10
M. Chabib Thoha, Teknik Evaluasi Pendidikan, (Jakarta: Raja Grafindo Persada, 1994), p. 44
11
Jum C. Nunnally, Educational Measurement and Evaluation, (New York: McGraw-Hill, 1964), p. 172
12
Related to achievement, Asep Jihad and Abdul Haris have quoted the definitions of the
achievement from experts’ opinion13, and then they conclude that learning achievement is
“pencapaian bentuk perubahan perilaku yang cenderung menetap dari ranah kognitif, afektif,
dan psikomotoris dari proses belajar yang dilakukan dalam waktu tertentu yang sesuai dengan
tujuan pengajaran (the change of the attitude in cognitive, affective, and psychomotoric after
instructional process that the students have done in particular time and it based the objective of
teaching and learning activities).
In addition to definition of learning achievement, some experts express his idea, as
follows14:
1) J. Romizowski says that learning achievement is outputs from an input process system.
2) Nana Sudjana: Learning achievement is one’s ability that he has after he got learning
experience.
Furthermore Myra Pollack Sadker and David Miller Sadker express learning
achievement is student’s actions that they have disciplined minds and adhere to traditional
morals and behavior. They demonstrate their competency in academic subjects or traditional
skills through tests and writings.15
Based on the concepts above, they can be concluded that learning achievement is the
result of student’s past learning after instructional process in harmony with the instructional
objective in particular period of time.
After explanation of definition of the achievements above, it can be stated that English
achievement is learners’ ability to use the target language (English).16 It means the students
have achieved the skill and knowledge in using target language- English.
According to Scott Thornburry, English achievement is what learners have learned
about target language – English, over a week, month, term or entire course. 17
13
Asep Jihad and Abdul Haris, Evaluasi Pembelajaran, (Yogyakarta: Multi Pressindo, 2008), p. 14 – 15
14
Asep Jihad and Abdul Haris, Evaluasi Pembelajaran, …, p. 14
15
Myra Pollack Sadker and David Miller Sadker, Teachers, Schools, and Society, (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2005), p. 330
16
Moreover, English achievement is how much of a foreign language (English) a student
knows.18 Students have to struggle through a course or a learning experience of some sort to
achieve a certain amount of control of the language.
Besides those definitions, Theodore Huebener says that English achievement is the
skills and the knowledge the pupils have acquired in each of the various phases of the language
learning.19
Some definitions about the English achievement, the writer takes a conclusion that
English achievement is the student’s ability, skill, and knowledge in English which they have
acquired or learned in particular time.
In education, achievement is signed by scores, which may be taken from the average of
daily scores and from final tests. Test is used to measure the achievement. Such test is usually
called achievement test.
5. Achievement Test
To measure how much of a foreign language a student knows, the test which is used is
called achievement test. The test makes reference to the fact that students have to struggle
through a course or a learning experience of some sort to achieve a certain amount of control of
the language.20
The main uses of achievement testing are21:
a. Progress tests – to see how students are getting on in a course;
b. End of course tests – to see how well students have learnt what the course set out to teach
them;
c. Course evaluation – to see where the course is more or less successful.
17
Scott Thornburry, An A-Z of ELT: A Dictionary of Terms and Concepts Used in English Language Teaching, (Oxford: Macmillan, 2006), p. 3
18
Robert Lado, Language Testing: The Construction and Use of Foreign Language Tests, 9th ed., (London: Longman, 1977), p. 369
19
Theodore Huebener, How to Teach Foreign Languages Effectively, …, p.212
20
Robert Lado, Language Testing: The Construction and Use of Foreign Language Tests,…, p. 369
Therefore Jum C. Nunnally stated that the purpose of achievement test is to measure
progress in school up to a particular point in time22.
In teaching English, the test indicates overall language gains. In order to determine the
extent to which the learner has attained particular course objectives, various other forms of
continuous assessment may be used, including observation, verbal feedback from the teacher
or others, teacher constructed tests, self-rating scales, learner self reports, teacher or learner
diaries, and videotaped or audiotaped samples of learners’ work.23
6. Factors Affecting the Achievement
There are a lot of factors that influence the achievement of student. Some factors that
influence the student’s achievement are24:
1) Intelligence degree: this factor is dominant in affecting the result of students’
achievement.
2) Motivation: this factor also has huge influence in affecting students’ achievement.
3) Physical conditions
4) Environment condition
a. Intelligence
Individual characteristics of learners may be directly or indirectly related to
achievement in foreign language learning. According to Steven H. McDonough25, one of
the characteristics is intelligence. Intelligence manifests itself in terms of how an individual
behaves in his society26.
The term ‘intelligence’ has traditionally been used to refer to performance on certain
kinds of tests27. Intelligence, especially as measured by verbal IQ tests, may be a strong
22
Jum C. Nunnally, Educational Measurement and Evaluation, …, p. 169
23
Geoff Brindley, Language Testing in the 1990s: the Communicative Laegacy,…, p. 154
24
Syaiful Bahri Djamarah, Psikologi Belajar, (Jakarta: Rineka Cipta, 2008), p. 175-205 25
Steven H. McDonough, Psychology in Foreign Language Teaching, (London: George Allen and Unwin,1981), p.125
26
James M. Sawrey and Charles W. Telford, Educational Psychology, 4th ed., (Boston: Allyn and Bacon, 1973), p. 607
27
factor when it comes to learning which involves language analysis and rule learning,
intelligence may play a less important role in classrooms where the instruction focuses
more on communication and interaction28.
Intelligence is regarded as a potential capacity. This potential capacity is probably a function of heredity, congenital development, and growth. The growth of intelligence toward the potential capacity may be impeded by environmental stresses and strains or may be accelerated by proper stimulation. 29
It is important to keep in mind that intelligence is complex and that individuals have
many kinds of abilities and strengths, not all of which are measured by traditional IQ tests.
Many students whose academic performance has been weak have experienced considerable
success in second or foreign language learning.30
b. Motivation
Motivation is one of the most important variables in learning. A high degree of
motivation engenders an active and aggressive attitude with regard to educational goals.31
Motivation is actually a cluster of factors that energize behaviour and give it direction32.
Motivation involves the learner’s reasons for attempting to acquire the second
language, but precisely what creates motivation is the crux of the matter.33
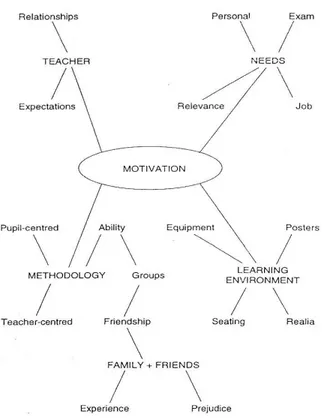
Related to motivation in learning, Gary Chambers has described as a figure follows:
28
Patsy M. Lightbown and Nina Spada, English Language Teaching in Its Social Context, …, p. 31
29
James M. Sawrey and Charles W. Telford, Educational Psychology, … , p. 608 30
Patsy M. Lightbown and Nina Spada, English Language Teaching in Its Social Context, …, p. 31
31
James M. Sawrey and Charles W. Telford, Educational Psychology, … , p. 517-518
32
Jane Arnold (ed), Affect in Language Learning, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1999), p.13
Figure 1. Initial brainstorming on ‘motivation’34
The figure above shows that motivation may be enhanced by various conditions. It can
be from methodology, teacher, needs, and learning environment.
One factor which often affects motivation is the social dynamic or power relationship
between the languages.35 Positive attitudes and motivation are related to success in second
and foreign language learning. Motivation in second or foreign language learning is a
complex phenomenon which can be defined on terms of two factors: learners’
communicative needs and their attitudes towards the second or foreign language
community.36
c. Physical conditions
Physical conditions are part of all learning. Healthy five senses will support teaching
learning process. Student’s health affects their sensory-motor functioning37. Sometimes
students with sight problem, hearing problem, malnutrition, etc can influence the student’s
34
Gary N. Chambers, Motivating Language Learners, (Clevedon: Multilingual Matters, 1999), p. 14
35
Patsy M. Lightbown and Nina Spada, English Language Teaching in Its Social Context, …, p.34
36
Patsy M. Lightbown and Nina Spada, English Language Teaching in Its Social Context, …, p.33
37
achievement. A student has headache, fever, stomachache, or some injury needs immediate
consideration because it can disturb the instructional process.
d. Environment condition
Environment is one of the important components of instructional process because it can
influence the students. A learner lives in a complex learning situation that may be divided
into three parts: the social environment, the physical environment, and the cultural
environment. Parts of the social world, the physical world, and the cultural world are
selected to become stimuli to the learner38.
Educational environment is defined as the emotional, physical, and intellectual climate
that is set up by the teacher and students to contribute to wholesome learning situation39. It
has to support the instructional process. Educational milieus comprise of family (parent and
sibling), school and community.
As one of tripartite education40, family is primary community for the children. Family
is the first and primary educational environment for the child. It becomes the first
educational environment because the child got his education and counseling for the first
time. The family is also as primary educational environment because the child spends most
of his time in a family.41 Additionally, the parents and siblings can focus attention on one
child and so opportunity for interested, motivated, natural help is available covering
considerable amounts of time.42
Bad environment may cause stress for students. In many cases students with bad
environment may have worst achievement than students with good environment.
38
David Ray Stone and Elwin C. Nielsen, Educatonal Psychology: The Development of Teaching Skills, ( New York: Harper & Row, 1982), p. 15
39
Carter Victor Good and Winifred R. Merkel (ed), Dictionary of Education,…, p.214
40
This term is used by Ki Hadjar Dewantara to deal with three educational institutions (“Tripusat Pendidikan”). They are family, school, and community.
41
M. Alisuf Sabri, Pengantar Ilmu Pendidikan, (Jakarta: UIN Jakarta Press, 200), p. 23
42
F.
Parents’ Role in Students Education
The child is born into a family – his first socializing group and the most basic agency of
socialization in all societies. The family not only is the first group to which he is exposed, but also is
in many ways the most influential.43 One reason for importance of the family is that it has the main
responsibility for socializing children in the crucial early years of life. The family is where children
establish their first close emotional ties, learn/ acquire language, and begin to internalize cultural
norms and values.44
As the unit of the society, the home sets the pattern for social development and adjustment to
form the attitudes and behaviour habits. A child’s physical, mental, and emotional potentialities reflect
the physical, mental, and emotional characteristics of his parent. They are formed by the interaction
between the child and the parent45.
1. Parents’ Involvement in Education
The term “parents’ involvement” is used broadly in this writing. It includes several
different forms of participation in education and with the schools. Parents get involved in
their children’s education because one of their functions is giving education for their
children.
The children’s education is primarily a concern of the family, not the society. Based
on Republic of Indonesia law 23 of the year 2002 on Child Protection article 26:
Parents obligate and assume responsibility for:
1) nurturing, taking care, giving education, and protecting the child,
2) developing their child’s ability, talent, and interest.
Then, in Republic of Indonesia law 20 of the year 2003 on National Education
System article 7:
Parents’ Authority and Obligation
43
Cole S. Brembeck, Social Foundations of Education : A Cross-Cultural Approach, (New York: John Wiley and Sons Inc., 1967), p. 121
44
Ian Robertson, Sociology, (New York: Worth Publishers, Inc., 1978), p.108
45
Lester D. Crow and Alice Crow, Introduction to Education (Fundamental Principles and Modern Practices), (New York: American Book Company, 1960) p.453
1) Parents have authority in choosing school and get information about their children
development.
2) Parents who have learning-aged children obligate to give basis education to their
children.
Talking about parents involvement, it can be defined as a process that the parents
use all their ability to develop their children’s potency.46 Parents obligate as positive habit
former for strong foundation in informal education. With the habits, the children will adapt
and will adopt their parents.47 Then parents have important role in developing children
potency.
Parents can support their children’s schooling by attending school functions and
responding to school obligations, for example: parents-teacher conferences. They can
become more involved in helping in their children improve their schoolwork by providing
encouragement, arranging for appropriate study time and space, modelling desired
behaviour such as reading for pleasure, monitoring homework, and actively tutoring their
children at home.48
Outside the home, parents can serve as advocates for the school. They can volunteer
to help out with school activities or work in the classroom. Or they can take an active role
in the governance and decision making necessary for planning, developing, and providing
an education for the community’s children.
In this respect, parents play a crucial role as a tutor, counselor, facilitator, and
character builder at home, an advocate in school and supporter in academic competition.
These mixed roles exert considerable influence in shaping not only children’s intellectual
talents or potential, but also their psychological, social and emotional maturity.49
The kinds of parents involvement are parents-teacher conferences, homework
assistance/ tutoring, establishing a daily family routine, and home educational enrichment.
46
Soemiarti Patmonodewo, Pendidikan Anak Prasekolah, (Jakarta: Rineka Cipta, 2003), p. 124
47
Ary H. Gunawan, Sosiologi Pendidikan: Suatu Analisis Sosiologi Tentang Pelbagai Problem Pendidikan, (Jakarta: Rineka Cipta, 2000), p.49
48
http://www.nwrel.org/scpd/sirs/3/cu6/html
49
While Soemiarti Patmonodewo, who has quoted from Morrison, said that parents’
involvements in education are50:
Task oriented – parents help their children do homework
Process oriented – parents choose proper textbook for their children
Development oriented – parents develop their children’s potency
2. Parents’ Involvement in Teaching and Learning English as Foreign Language
Children acquire a large percentage of their language from their parents. The home
environment is the dominant factor in shaping early language development for most
children and then for fulfilling this role the home provides a natural setting51. The type of
language a child is exposed to in the home domain is a critical factor in determining that
child’s proficiency in the language.
According to Milner’s opinion which has been quoted by Gary N. Chambers52, there
is a model of attitudinal influence to which three processes contribute:
a) Direct tuition from parents
b) Indirect tuition, i.e. the attitudes of the parents are implicit in their behaviour
c) Role-learning, i.e. the behaviour of the children reflects the behaviour of those around
them.
Moreover, Milner 53stated that:
Within the context of foreign language learning, the success of these three processes may depend largely on: (1) positive attitudes of parents to learning in general and language learning in particular; (2) the level of parent’s foreign language competence; and (3) their willingness to demonstrate this competence not only when helping with homework but also when in the company of native speakers of the target language.
50
Soemiarti Patmonodewo, Pendidikan Anak Prasekolah, ..., p. 125
51
Rolland J. Van Hattum, Developmental Language Programming for the Retarded, …, p. 51
52
Gary N. Chambers, Motivating Language Learners, …, p. 82
53
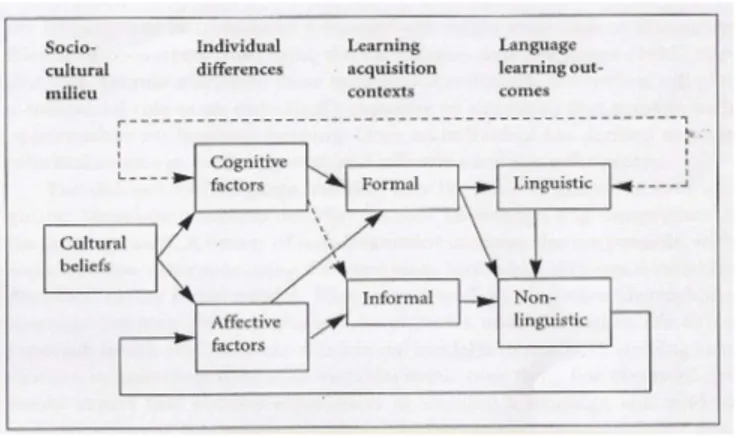
Figure 2. The socio-educational model54
Four major parts of the model are shown: the socio-cultural milieu, individual
differences, language acquisition contexts, and language learning outcomes. According to
Gardner and MacIntyre, the socio-cultural milieu plays a role in influencing both cognitive
(intelligence, language aptitude, and language learning strategies) and affective (attitudes,
motivation, language anxiety, and self-confidence) individual differences among language
learners. 55
The attraction of this model is the central role played by motivation and the social
dimension. The language learners, their families, and friends may have a view of the target
language community based on considerable experience of living with or close to that
community.
The potential influence a parent’s view may have on the attitude which the pupil
brings to the foreign language lesson. Parents’ roles on teaching and learning English as
foreign language56:
a. as motivator
Family, ethnic, religious, cultural, and sub-cultural motivational influences are all
intertwined. Prevailing climates of opinion and the levels of expectancy displayed in the
home can do much to nurture and sustain high educational achievement.57
54
Peter D. MacIntyre, Individual Differences and Instructed Language Learning, ed. Peter Robinson, (Amsterdam: John Benjamins, 2002), p.47
55
Peter D. MacIntyre, Individual Differences and Instructed Language Learning, …,p. 47
56
Sri Astuti., “Language proficiency starts at home,” Jakarta Post, 27 Jan. 2008. p.29, col. 1
57
The family is the primary and most important social source of motivation in the
students58. They largely reflected the attitudes and beliefs of their parents. It is within the
family that the basic foundations of the social motivational systems are laid down.59
Parental attitude towards foreign language learning and indeed learning in general
may be influenced by educational, socio-economic, socio-cultural, ethnic and linguistic
background. Learners with the most positive motivation towards learning foreign language
tend to be integratively-orientated and to come from homes where parents have a basic
integrative orientation in combination with pro-English attitudes.60
It is important to encourage the children. There is much that parents can do. They can
actively demonstrate the value for learning. Parents also can congratulate the children for
their success. Then, while they do not perform well in academic, parents should support
them. This will help them to see how important to keep trying.
b. as advocate in economy
One factor can influence instructional process is economy. Parent’s economy
condition will affect the education and every economy status has different ways to educate
the children.
To some, socioeconomic level is the major familial influence after heredity on
intellectual functioning61. Children coming from homes of higher socioeconomic status are
apt not only to have come from more brilliant parents initially but also to have had
provided for them better opportunities for development intellectually, physically, and
emotionally. Not only favorable heredity but also a stimulating environment continues to
favor intellectual growth.62
The higher socioeconomic family will be easier to support the educational facilities at
home. The facilities can help to develop the students’ English achievement.
c. as monitor
58
James M. Sawrey and Charles W. Telford, Educational Psychology, … , p. 519
59
James M. Sawrey and Charles W. Telford, Educational Psychology, … , p. 493
60
Gary N. Chambers, Motivating Language Learners, … , p. 83
61
Lita Linzer Schwartz, Educational Psychology: Focus on the Learner, (Boston: Holbrook Press, 1972), p. 107
62
Parents can monitor their child’s academic achievement by giving attention on their
student’s learning. They also should monitor homework given by teacher, out-of-school
activities for example setting limits on television watching, and arranging for after school
activities.
Gary N. Chambers stated that63:
If pupils equate parental encouragement with the willingness and ability of their parent to offer and provide them with help to do their homework, it may be interesting to ascertain how many pupils perceive their parents as being in a position to provide assistance with foreign language homework.
If the parents monitor and give assistance their children, the children will have more
awareness to get better English achievement.
d. as model
As the home is the first classroom, the family members are the first teachers. The
mother is the most important figure in this process but all family members contribute. If
family members can understand that the child is receiving stimuli from his environment
even though reactions may not be noted to signal this, they will be more effective
teachers.64 Some insight may be gleaned nevertheless from pupils’ thoughts on the
encouragement they think their parents give.65
In foreign language learning, input is an essential component for learning in that it
provides the crucial evidence from which learners can from linguistic hypotheses.66
After getting input by hearing the surroundings, the children try to interact with the
other people. Interaction facilitates the process of acquiring a second language and foreign
language as it provides learners with opportunities to receive modified input and to receive
feedback, both explicitly and implicitly, which in turn may draw learners’ attention to
problematic aspects of their interlanguage and push them to produce modified output67.
63
Gary N. Chambers, Motivating Language Learners, …, p. 87
64
Rolland J. Van Hattum, Developmental Language Programming for the Retarded, …, p. 55
65
Gary N. Chambers, Motivating Language Learners, …, p. 84
66
Susan M. Gass and Alison Mackey, Theories in Second Language Acquisition, ed. Bill VanPatten and Jessica Williams, (New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 2007), p. 177
67
Interactions are important because it is in this context that learners receive information
about the correctness and, more important, about the incorrectness of their utterances68.
In theory, pupils who hear their parents and friends at home interacting in a foreign
language with guests at home may have more appreciation of the usefulness of the target
language than those who do not have this opportunity.
The hypothesis of the research which has been done by Gary N. Chambers is pupils
who hear the target language spoken at home and who claim to know people, who speak
the target language as their mother-tongue, may be more aware of the usefulness of the
target language.69
G.
Conceptual Frame
Learning achievement can be influenced by many factors, such as motivation, teachers,
method, educational system, or educational milieu. All of the factors are allied to affect the
achievement. The factors can support each other.
As educational components, parents take place as educator and they also provide the
educational milieu for their children. So, parents should involve in their children’s education. They
can do many things to get involved in their children’s academic by providing encouragement,
arranging for appropriate study time and space, monitoring homework and out of school activities,
modelling desired behaviour such as reading for pleasure, and actively tutoring their children at
home.
Students whose parents get involved in their education will have encouragement to learn
English. In other words, if their home environment and their parents’ involvement in their
education are good, they will do best to achieve better English.
So, it can be concluded that the students whose parents involve in their education will get
better score in English subject. In other words, there is a correlation between parents’ involvement
and student English achievement.
H.
The Hypothesis
68
Susan M. Gass and Alison Mackey, Theories in Second Language Acquisition,…, p. 178
Based on the theoretical and conceptual framework above, the writer formulated the hypothesis
of this research: there is a correlation between parents’ involvement and student English
achievement.
The statistical hypothesis is formulated as follows:
1. Alternative Hypothesis (Ha): there is significant correlation between English achievement and
parent involvement.
2. Null Hypothesis (Ho): there is no significant correlation between English achievement and
CHAPTER III
MADRASAH TSANAWIYAH TANGERANG II PAMULANG PROFILE
A.
School Identity
Name of school : Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri Tangerang II
Postal address : Jl. Pajajaran No. 31 Pamulang Tangerang Banten 15417
Telephone number : 021-741 5023
Website : madsane2007.blogspot.com
E-mail : [email protected]
B.
Brief History
Madrasah Tsanawiyah Tangerang II was built in 1981 at Cimanggis, Ciputat at first and
Drs. Syamsuddin P., M.Pd. became the headmaster. Because of his spirit to develop the madrasah,
MTsN Tangerang II was moved to Pamulang in 1987. It is located about 50 m from the main
street.
In new area the headmaster tried to develop this school when the people who lived around
the school still underestimated ‘madrasah’ because they thought that madrasah had religion
subjects only.
The people also has opinion that madrasah has unprofessional management. It makes the
headmaster, school staff, and teachers organize the school carefully and hard. Because of high
spirit of Drs. Syamsuddin, Edy Djunaedy, and Drs. Nasharudin Sarbini to organize the school,
MTsN Tangerang II Pamulang can be well-known by the people. After that, more people trusted
their children to study in this ‘Madrasah’. They also realize that they have to support and
participate in financial problem of the madrasah. It was started in 1990 until now. The results of
their participation such as buildings and facilities can be seen.
The madrasah increase the buildings and facilities in quantity and quality slowly. Madrasah
has changed from the unpretentious buildings into the luxurious buildings. Not only buildings but
also the facilities in this madrasah have gained in quantity and quality. Then, the people become
proud with the satisfactory buildings and complete facilities on leadership of Dra. Iis Aisyah, Drs.
People’s perception on madrasah is changed. They think that it has over plus than other
school because in madrasah their children are taught both religious subjects and lessons such as
science, social, math etc.
With the people’s belief on the madrasah, the headmaster, staff and all of the teachers
innovated in academic, curriculum, management, and administration. They use modern technology
for management. In academic and administration they manage many programs such as special
quality class, talent development, leadership and character builder.
C.
Vision, Mission and Motto
1. VisionMadrasah with national achievement
2. Mission
Based on the vision, the missions of MTsN Tangerang II Pamulang are:
a. Create optimal education and preceptors who have optimal competences.
b. Form intelligent, creative and Islamic students.
c. Organize management of Madrasah which emphasize in primal service.
d. Provide complete educational facilities.
e. Create clean, comfortable, safe, beautiful, Islamic milieu in madrasah.
f. Give Islamic values and national spirit to the students.
3. Motto
Islamic and National Achievement
D.
Facilities
Many facilities were provided to support teaching learning activities. Facilities in Madrasah
Table 1
Facilities in Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri Tangerang II Pamulang
No Nama Jumlah Baik R.Ring R.Brt
1 Ruang Kelas 30 30 - -
2 Ruang Kamad u. 4x7 M2 1 1 - -
3 Ruang Wakamad 3x3 M2 1 1 - -
4 Ruang Guru 7x18 M2 1 1 - -
5 Ruang TU 1 1 - -
6 Ruang Lab. IPA 1 1 - -
7 Ruang Lab. Bahasa 1 1 - -
8 Ruang Audio Visual 1 1 - -
9 Studio Musik u. 2,5x7 M2 1 1 - -
10 Ruang OSIS 2,5x7 M2 1 1 - -
11 Ruang Lab. Komputer 7x9 M2 1 1 - -
12 Raung UKS u. 3x2,5 M2 1 1 - -
13 Ruang BP u. 3x2,3 M2 1 1 - -
14 Mushala u. 7x9 M2 1 1 - -
15 WC Siswa (dihitung pintu) 18 18 - -
16 WC Guru (dihitung pintu) 4 4 - -
17 WC Kamad 1 1 - -
18 WC Umum (guru dan TU) 1 1 - -
19 Meja murid dan kursi (pasangan) 624 300 324 -
20 Meja guru 30 30 - -
21 Komputer 20 20 - -
22 Lapangan Footsal u. 30x60 M2 1 1 - -
23 Alat musik sederhana 1 set 1 set - -
24 Alat musik marawis sederhana 1 set 1 set - -
25 Drumband sederhana 1 set 1 set - -
26 Ruang Bangdik u. 3x2,5 M2 1 1 - -
27 Ruang Komite u. 2x2 M2 1 1 - -
28 Ruang Simad u. 2x2 M2 1 1 - -
E.
Structure of Organization
To make good relationship between headmaster, teachers, staff, and students, it is needed to
Figure 3
Structure of Organization
Keterangan:
= garis komando
= garis
F.
Teachers, Staff and Students
1. Teachers and StaffBoth teacher and staff are components of the madrasah. They have to cooperate together in
order to this madrasah can develop. Quality of the teachers and staff is considered.
Teachers in Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri Tangerang II Pamulang have different
educational background and level. It is shown in table as follows:
Table 2
Lab. dan Sarana
Perpustakaan Pembina
OSIS
Pembina K + M Kepala
Madrasah Kelompok Kerja
Madarasah
Komite Madrasah
Kepala TU Wakil
Kamad
Koordinator Bid. Kurikulum Tenaga
Kependidikan
Koordinator Bid. Kesiswaan
Teacher’s Condition in Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri Tangerang II Pamulang
Pendidikan Status Golongan
No Bidang Studi Jumlah
S1 S2 PNS HNR III IV
1 Agama
a. Aqidah Akhlak 3 3 - 1 2 - 1
b. Fiqh 3 3 - 2 1 2 -
c. Qur’an Hadits 3 3 - 2 1 2 -
d. S K I 3 3 - 2 1 2 -
2 PPKn 3 2 1 3 - 3 -
3 Matematika 7 6 1 6 1 6 -
4 Bahasa Indonesia 8 4 4 8 - 7 1
5 Bahasa Inggris 6 6 - 5 1 4 1
6 Bahasa Arab 4 4 - 3 1 2 1
7 IPA 6 5 1 5 1 5 -
8 IPS 6 5 1 5 1 5 -
9 TIK 3 3 - - 3 - -
10 Penjaskes 3 3 - 2 1 1 1
11 Kesenian/KTK 3 3 - 2 1 2 -
12 Mulok 1 1 - - 1 - -
13 BP 3 3 - 3 - 2 1
Jumlah 65 57 8 49 16 43 6
To organize the school administration, staffs are needed. They also have different
educational background and status. It is described as the table below:
Table 3
Pendidikan Status Golongan
SMP SMA D3 S1 PN HN II III
3 8 2 5 9 9 2 7
18 18 9
2. Students
Students have gained in number every year. The development is shown as follows:
Table 4
Student’s Development
Year Grade VII Grade VIII Grade IX Total
2003 326 416 418 1160
2004 334 328 405 1067
2005 419 329 337 1085
2006 402 410 337 1147
2007 424 400 400 1224
2008 302 402 393 1097
Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri II Pamulang has thirty classes with total 1097 students in
acamdeic year 2008/2009. They are divided into 5 class types; regular class, Bina Prestasi
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND FINDING
C.
Research Methodology
1. Objective of the ResearchThis study has aims, as follows:
a) To find out the relationship of parents’ involvement and student achievement especially in
English
b) To know the influence of parents’ involvement on student English achievement
c) To expand and improve the writer’s knowledge about parents’ involvement on student
English achievement
2. Time and Location
The research has been done in Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri Tangerang II Pamulang at
Jl. Pajajaran No. 31 Pamulang Tangerang Banten. While the time of research is for one month,
namely from January 20, 2009 until February 20, 2009 and the questionnaire was given in
February 11, 2009 until February 17, 2009.
3. Method of the Research
In doing the research, the writer uses quantitative method. Then, the correlation
technique is applied to know the influence parents’ involvement on student English
achievement.
The independent variable of this research is parents’ involvement (variable X) and the
dependent variable is student’s English achievement (variable Y). In this case, it can be
assumed that parents’ involvement in teaching and learning English (variable X) is considered
as a factor that influence student’s English learning achievement (variable Y). Finally both
variables can be tried to be correlated.
Notes:
X = Parents’ involvement
Y = Students English achievement
= Correlation
4. Population and Sample
The population of the research consists of eleven classes with total 402 students from
second grade of MTsN 2 Pamulang. They are divided into 5 class types; regular class, Bina
Prestasi class, Sains class, bilingual English class, and bilingual Arabic class.
Table 5
The Distribution of Students
No Class Students
1 8.1 38
2 8.2 38
3 8.3 39
4 8.4 37
5 8.5 37
6 8.6 36
7 8.7 38
8 8.8 (Sains) 38
9 8.9 (Bilingual Arabic) 38
10 8.10 (Bilingual English) 38
11 8.11 (Bina Prestasi) 25
Because the population is heterogeneous, the writer took the sample about 10% from
402 students randomly. So the total of the students that are taken as the sample are 40 students.
5. Technique of Collecting the Data
When the writer did the research, different instruments were applied to obtain the data:
a. Documentary Study
To know the students’ English learning achievement, the writer took the report book
score of second grade students of Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri Tangerang II Pamulang for
first semester in academic year of 2008/2009 in English learning achievement semester
because from report book the learning outcome that has been reached, can be measured.
2. Distribution of Questionnaire
The research instrument is used in collecting the data is a questionnaire which
formulated and designed based on the indicators of the variables of parents’ involvement in
learning English. The questionnaire about the parents’ involvement of students is given to
the students consisting of 20 items. In this case, it concerns about parents involvement in
student English achievement.
Table 6
Indicator of Parents’ Involvement Total
No Indicator
Positive Negative
Item number
1 As motivator 5 0 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
2 As advocate in economy 4 0 6, 7, 8, 9
3 As monitor 4 1 10, 11, 12, 13, 14
4 As model 6 0 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20
In composing questionnaire, the writer applied Likert’s scale form:
1) Always (selalu)
3) Sometimes (kadang-kadang)
4) Never (tidak pernah)
Table 7
Score of Questionnaire Answer Score Alternative Answer
Positive Negative
Always Often Sometimes Never 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 3. Interview
Interview was also applied to support data about school profile and to know parents’
engagement in school.
4. Observation
The writer makes an observation to the school in order to get better understanding of
intended object.
6. Technique of Data Analysis
In analyzing the data and testing the hypothesis, the correlation technique was used, by
using Pearson’s product moment correlation as follows:
rxy =
(
)(
)
(
)
][(
)
][N X2 X 2 N Y2 Y 2
Y X XY N − − −
rxy = Coefficient Correlation
N = Number of Respondents
X = Total Score of X (parents’ involvement)
Y = Total Score of Y (students’ English achievement)
D.
Research Finding
1. Data DescriptionHaving field research about parents’ involvement and the students’ English achievement in
Madrasah Tsanawiyah Negeri Tangerang II Pamulang, the writer took the scores of 40 students
sampling and analyzed those score in order to find out whether there is any correlation between
English achievement and parents’ involvement by Pearson’s product moment.
The data of students’ score of questionnaire and report book can be seen on the following
tables:
Table 8
Questionnaire Result about Parents’ Involvement
Respondent Score
1 30
2 32
3 35
4 43
5 43
6 41
7 36
8 31
9 51
10 54
12 27
13 56
14 47
15 49
16 27
17 40
18 41
19 45
20 31
21 41
22 43
23 55
24 49
25 43
26 50
27 53
28 36
29 47
30 41
31 55
32 46
33 29
34 36
35 42
36 57
37 36
39 39
40 40
The table above shows that the total score from 40 respondents is 1659. After
calculating statistically, the writer got minimum score is 24, the maximum is 57, the
median is 41, the mode is 43 and the mean is 42.
Table 9
Student’s English Achievement
Respondent Score
1 60
2 71
3 69
4 66
5 69
6 65
7 69
8 71
9 71
10 83
11 70
12 78
13 71
14 70
16 71
17 66
18 71
19 66
20 66
21 68
22 69
23 91
24 79
25 74
26 80
27 80
28 69
29 75
30 76
31 79
32 91
33 67
34 71
35 80
36 80
37 77
38 80
39 78
From the student’s report books about their English achievement as shown on the table
above, it can be found that the total score from 40 respondents is 2935. In statistical
calculation, it showed the minimum score is 60, the maximum is 91, the median is 71, the
mode is 71, and the mean is 73.
2. Data Analysis
In order to know the correlation between parents’ involvement and students’ English
achievement, Pearson’s product moment formula is applied. The data are described on the
following table:
Table 10
The Correlation between Parents’ Involvement and Students’ English Achievement
No X Y XY X2 Y2
1 30 60 1800 900 3600
2 32 71 2272 1024 5041
3 35 69 2415 1225 4761
4 43 66 2838 1849 4356
5 43 69 2967 1849 4761
6 41 65 2665 1681 4225
7 36 69 2484 1296 4761
8 31 71 2201 961 5041
9 51 71 3621 2601 5041
10 54 83 4482 2916 6889
11 38 70 2660 1444 4900
12 27 78 2106 729 6084
13 56 71 3976 3136 5041
14 47 70 3290 2209 4900
16 27 71 1917 729 5041
17 40 66 2640 1600 4356
18 41 71 2911 1681 5041
19 45 66 2970 2025 4356
20 31 66 2046 961 4356
21 41 68 2788 1681 4624
22 43 69 2967 1849 4761
23 55 91 5005 3025 8281
24 49 79 3871 2401 6241
25 43 74 3182 1849 5476
26 50 80 4000 2500 6400
27 53 80 4240 2809 6400
28 36 69 2484 1296 4761
29 47 75 3525 2209 5625
30 41 76 3116 1681 5776
31 55 79 4345 3025 6241
32 46 91 4186 2116 8281
33 29 67 1943 841 4489
34 36 71 2556 1296 5041
35 42 80 3360 1764 6400
36 57 80 4560 3249 6400
37 36 77 2772 1296 5929
38 24 80 1920 576 6400
39 39 78 3042 1521 6084
40 40 79 3160 1600 6241
From the calculation of statistic, it can be showed that:
X = 1659
Y = 2935
XY = 122664
X2 = 71801
Y2 = 217163
rxy =
(
)(
)
(
)
][(
)
][N X2 X 2 N Y2 Y 2
Y X XY N − − −
rxy =
(
)(
)
(
1659)
][40 217163(
2935)
] 71801 40 [ 2935 1659 122664 40 2 2 − − − x x xrxy =
] 8614225 8686520 ][ 2752281 2872040 [ 4869165 4906560 − − −
rxy =
] 72295 ][ 119759 [ 37395
rxy =
8657976905 37395
rxy =
25041 , 93048
37395
rxy = 0,401888265 rxy = 0,402
From this calculation the result is 0.402
3. Test of Hypothesis and Interpretation of Data Analysis
After counting the formula, the writer has found out the result of the correlation. The
From the correlation above, it appears that the correlation index between X variable and
Y variable is positive. It means between both variables, there is positive correlation. To give
simple interpretation toward the correlation index ‘r’ product moment (rxy), it can be seen in
the following table.70
Table 11
Interpretation of Product Moment Value “r” value of Product moment Interpretation
0,00 – 0,20 Considered as no correlation
0,20 – 0,40 Low correlation
0,40 – 0,60 Medium correlation
0,60 – 0,80 Strong correlation
0,80 – 1,00 Very strong/ perfect correlation
After the calculation, the next step is to test the hypothesis. From the calculation result,
it is obtained that the values of rxy is 0.402. Based on the table above, it can be seen that the
correlation index (rxy= 0.402) is in the interval of 0.40 – 0.60, this means that the correlation
belongs to “medium correlation”. In the other words, there is a correlation between variable X
(parents’ involvement) and variable Y (student English achievement).
In table of Pearson product moment about degree of freedom71, it stated that the degree
of freedom (df) is N – 2 = 40 – 2 = 38 and the significance of 1% is 0.393 and the significance
5 % is 0,304. After comparing the value of rxy = 0.402 and tt 0.393 and 0.304, the writer
eventually made the assumption as follow:
1
Anas Sudjiono, P