DEYELOPMENT
POLICY
FOR
SII,IE'S
AND ENTREPRENE{M.'S
CROSS
CULTURAL
PR.OFILE
a Cross
National
Study on Ilevelopment Policy and CrossCultural
Study on .SIVIE's
Oleh
Dr.Ir.
Eddy
Soeryanto SoegotoYoung
San
Universiry
DEVELOPMENT ROLICT
FOR
S}[E'S
AITI} EHTNEPRET{EUR'S CN(}SS
CT'LTI]RAL
PROFII,E
e
CtGo
N*th*I
Studf
onl}tr@cntFdfuy
md
Crocperhural
Study otrSME'o
This Paper Has Prescuted
rtYourg
SonUniversity
Southl(orco
on Norvembcr1I
2010By
Dr.
Ir.
Eddy
Socryaoto SocgotoApproved by
Prof.
DriJ+DaeSik
DEVELOPMENT
FOLICT
FOR
S}IE'S ANI}
W'S
CR(}SS
CT'LTT'RAL
PROFII,E
a
CrGc
Nrtbnd
Studf
m
D@ptntFoliry
red
CrcerCulturrl
Study oa
SME'o
This Paper Has Preseuted
atYoung
Sar University
South Kornoor
No'vemher 11 2010By
Dr.
Ir. Edry
$oeryaato SocgotoApproved by
Prtf.
DrnJcDaeSik
ABSTRACT
DE\TELOPMENT
POLICY
FOR SME'S AI\ID ENTREPREI\IEUR'S
CROSS
C{ILTURAL PROFILE
a Cross
National Study
onIlevelopment Policy
and CrossCultural
Study
onSME's
By
Dr.Ir.
Eddy
Soeryanto SoegotoCampared
ta
SouthKorea,
the camparative studyof
Small
and MediumEnterprise's
developmentpolicy
informer
timesin
Indonesiadid
not
have anyvision
about theposition of
Small and MediumEnterprise
in
national
economieorganizational structure,
and
if
being
compared
to
Malaysia, there was
nonative's
proprietary
developmentplan
in
national
investmentportion
in Indonesia.Comparative study between Indo*esian m$nsger-en*eperuur (native) and
Tionghoa (non-native)
in
Bandung,Banjarmasin,
and
Palembangin
terms
of
Meaning
of
Workingfound that
there was
no
dffirence
betweentwo
groups especiallyin
Working Centralization, Income Oriented, ond Expressive WorkingAspect,
and
suggeststhct
the opinion
that
there
is
difference
in
working
motivation between
native
enffepeneur
snd
non
native
entrepeneur
isunacceptable.
On the
contrar!, the
low
level
of
Obligatian Oriented
and DependancyOrineted
and the high level
of
Learning
Oriented
of
non-nativegroup can be
referable
toformulate Native
Entrepeneur DevelopmentPalicy
which based on Business Strategt Learning and LearningCukwe
Creation.The condition
af
Small Enterprise
in
Beijing,
Hongzhou-Suzhau andShanghai indicotes
that great condition
of
low
infrastructure
for
investment, excellentplanning
of
urban
area and
husinessarea can
ereate composure inrunning
a
business,
business agresivenessprivacy
in
area,
gre*t
condition
of
police
structure
ondfree of
tmlegal
livies, and
especiallyprivacy
in
businessstrategt
byprofessional
salesmanshipway.
Thehigh
level
of
salesbargaining
practice
has already supportedsmall
and mendiumenteffise
to
be asgood
asbig enterprise.
Homogenity
of tutive group
in
marginal leyel
ard
no*native group
in very high level suggest that the Small and Medium Enterprise DevelopmentPolicy
must havevariation,
hmting lookedat
"gap chsracteristics"
on
each homogengraup.
Mix
educational
poth
of
notive
and
non-native
Small ond
Medium Enterprise must be donefor
learning process and integratedpath,
a
least byjoint
Jield
job
visit system.Keywards
:
Indonesian Small
and
fuIedium
Enterprise
Develapment
Plan, BusinessStrategt
Learning Law Infrastructure,
Economic
Area2
L
Introductian
The
issuesSmall
and
Medium Enterprise
development can't
dischargefrom the government policies, education system and the entire ways undertalrer behave. Studyaboard hss
been&ne
with
consideration,give
avision, how
we
ean deal
with
the
other
country
experiencesin
improving Small and Medium Enterprise. What we takc as on entitlement thing, may benot or holf
way
to
makcit perfect.
Whotwe
takeas
afalse
th@,
may
behappens the counter eondition.
In a
researeh case,there\e
so called
error
one
snd
enor
two,we takc.the
entitlement thingas
thefalse
one,and
tke Jblsething
ss
the
entitlement one.For
examplein
employees selection, we reject the competent andpotential
employee (aserror oru),
and we accept the employee who have a loek in Tntentials (asetor
two).The comporative studies enable as to hsve a different
point
ofview,a
dffirent
paradigm, different
assumptions,and we
considerit
as
creative mindsetwhich is really
acquiredin
the enterpriseworld.
The same mindset perhaps create meclwnistic enterprise,but
thelitersl
mindset create anera-changing
enterpriseor
even erestean
enterprisethat
hsveno
similor
with
what had been create before.Planning
wayof small
and medium enterprisewhich rest on internal
or
closed systemwithout
see the experienceand
theother people
world,
and
so
does thepxt
statie
experienceenterprise,
it
doesn't
make
ony
chance
to
think
creattve.
An
approach and
flexible
philosophy
makc it possiblewith
widerplanning.
For
example,if
in
Jakarta there's a stneetcalled
"Mangga DuaStreet"
(means two mangoes)ifwe
visit
and seein
Shenzhen there's aprotocol
streetplanted
by mangoes tree. Whatis
the
philosoplry
beyondthis
de&tctive
experieneeTChina which has
abillion
populations
canplant
the
mango treeson
theprotocol
street,
can Indonesia do the same? What is tlrc meaningof incapability af
Indonesia? Aswe acquainted "The
law don't work
well" a little or a
big
violationfrom
individual ar
groxryean't
befinished by
taws- The spectatars'af
PSSI match disturbances which mastly make damage on people's belongings never solvedby
law-
Thelows
needto
improve effectively- Thelaw
aspectson
business reflectedon
the Shaolin
Temple'seffort
whieh
will
give lsw
actionsto
80L
Introduetion
The
issuesSmall
and
Medium Enterprise
development can't
dischargefrom
the governmentpolicies,
education system and the entire ways undertalrerbehwe. Stufu aboard
has been donewith
consideration,give
avision, how
we
eandeal
with
the othEr
counry
experiencesin
improving Small and Medium Enterprise. What we take as an entitlementth@,
may benot
or
half
way
to
makeit pedect.
Whatwe
takeas
afalse
thing, may
behappens
the
countercondition
In
a
researeh case,there're so called
error
one
and
etror
two,we
tak* the
entitlement thingas
thefalse
ane,and
thelalse
thing as the
entitlement one.For
exmnplein
employees selection, we reject the competent andpatential
emplayee (aserror
one),andwe
accept the employee who hove a laek inpotentials
(as ercor two).The camparative studies ensble us to hsve a
dffirmt
point ofview,
a
differentparadigm, different
assumptions,and we
considerit
as
creative mindsetwhich is
really
acquiredin
the enterpriseworld.
The same mindset perhaps create mechanistic enterprise, but theliteral
mindset create oneilt-changing
enterprisear
etten createafl
entefprisethat
hoveno
similar
with
what had been create before.Planning
way of small and medium enterprisewhich rest an internal
or
elosed systemwithout
see the experienceand
theother people
world,
and
so
does thepast static
experienceenterprise,
it
doesn't
make
any
chance
to
think
creative.
An
approach and
flexible
philosoplry make it possiblewith
widerplanning.
For
example,if
in Jakarta there's a streetcalled
"Mangga DuaStreet"
(means twa mangoes)if
wevisit
and seein
Sheruhen there's aprotocol
streetplanted
by mangoes tree. Whatis
the philosophy
beyondthis
de&rctive
experience?China which has
abillion
populatio.ns canplant
the
mango treeson
theprotocal
street,
can Indonesia do the some? What is the meaningof incapability
af Indonesia? Aswe acquainted "The
law don't work
well" a little or a
big
violationfrom
individual or grsup
can't
befinished by
taws. Thespectatars'o/PSSl
rnatch disturbances which mostly makc damage on people's belongings never solvedby
law.
Thelows
ncedto
improve effeetively. Thelow
aspectson
business refiectedon
ihe Shaalin
Temple'seffort
whieh
will
give law
actionsto
80a
J
Shaolin
nameusers' countries
is
a
hugeactians
an
creative
basedon
thecertainty
of low
(see thejournal of visiting
China).
Theuncertainty
of
law
whichffiicts
the copy entitlement in Indonesia becauseit
makes theartist
or
art
creatorfrustrated.
Howfar
the entrepreneur and the citizenprotect their
copyentitlement in Indonesia and abroad?Batikfor
example.Enterprise
developmentrelated
to
a
conducive business climate (see thejournal af
visiting
China) which can createIS(N
new business each dayor
55A.000Wr
year
with
investment about3 billion
Yuan(3,
6 billion
Rupiah).
Wbat &bout lfidanes.ia?Informatienfrom
Keaenteriaa
Kaperasi&
UKM
&
BPS informsthat
basiness enterprisegrowth
in
Indonesiafrom
39,93 million
to
41, 36 million
ar
increaseI,
43 million.
It
meonsthat
the developmentof
businessin
Indonesia
is
better thon
Chinc.
This
condition makescleor
theposition of
Indonesia, andgives
o
legitimoting Small
and Me dium Ent erpr i s e pol icy.II.
Research
and
Obsemation
Small and Medium Enterprise
DevelopmentPolicy Abroad: Malaysia, Japan, South Korea, Philippine,
Indonesia,Suirs,
andChina
2.l.Results
of Small andllledium
Enterprise
Obsemationin China
With
a
backgroundof
"muchpopulation" problem and
"the wideregion"
problem
and
"problem
of
communistculture
which turn
intofree
tradeculture".
Thisfollowing
data shows the economic and entrepreneurship in China:l)
Flight Annual World
Wealth Report whichpublished
by
Capgemini andMerril
Lynch
say that
in
the end
of
2005in
Mainland China
existed236.000
billionoire,
increasing
12percent than last yeor
(2004).
This country has turnedinto
the second countryafier
Japanwhich
in
quantityof
billionaire.
The
report
also
srys
that
approximately
7,
7 million
of
billionaire
rytreadall
wer
theworld
in
the endaf
2AA5, wh:ich increasing7, 5 percent than last year.
2)
According to Head
afAll-
China Federationof
In&xtry
and
Cammerce, each dayI5A0
newprivate
enterprise establishedin Mainland
Chinawith
4
amount
of
capital which
registeredin aII
that
companies about3 billion
Yuan (JS$361,45
million). Now China
hove
32 million self
employed businessmanwhich
reJlected
2, 5
percent
of
its
population
(total
population of China is 1, 28billion)
In
thelastfive
years,there're
99 China's omtversity students who graduate Masterfrom
BusinessAdministration
ofHarvard
Business School, and 2a university studentswill
settletheir
MBAfrom
Harvard
Business School in1991, one
o{them
is studsnt froat Sftcttg&ai.Accarding
ta
Dep$y
af .China
Cammerce
Ministry
entrepreneurfrom
Taiwon had investedin
Mainland
Chinafor
62.00a cornpanieswith
total
actual
investment US$37,
I
billion.
TheGwernment of Mainland
Chinawill
not
changethe
"fovorablepolicy"
af
investarfrom
Taiwan andtheir
"entitlements
af
law"
will
be seeured
In
other side, China
Center Government had declared that theywill
not let entrepreneursfrom
Tatwangain
a
prafit
in
China
Mainland
f
alt
the
entrepreneurssupporting
afreedom of Taiwan.
Shaolin Temple
in
Henan ts readyfor
hard battle to sqve shootin Kungfu. This Shaolin Temple had spread theapplication
to 80 countries to register theshaolin Kungfu Trademark
They have inventorying processall
overthe world and there're
lI7
trademarkswhich use "Shaolin"
nsme or
"Shaolin Temple", most
of
themfound
in
Australian and Japan.
In
Mainland
ofchina
alsofound
a hundred companies and about 54 kindsof
product
which have a netme"Slnolin" from
car even to beer- Every oneof
them is out of lmowledgably of ShaolinTemple.
More
thanhalf
internet cafd rental have incame tessthan
j000
yuan(JS$
361,
45)per
month.
This matterreported,
it
because theseinternet
caJdrentals have to
paid
olot
offeesfor
much kind af government institutes.2.2.Resul*
af
surr,ll addMediua
E*erprire
ohservatlon
in
sourhKore*
l)
1961
is
thefirst
year
of
Small and
Medium Enterprise
DevelopmentPlanning-in
SouthKorea.
Thepolicy
is that technologt
saphisticotionof
Small and Medium Enterprise.3)
4)
5)
6)
5
In
1973 the poticy
of
developing cooperation enterprise
established. Cooperation enterprise aimed at :a.
A
business which needs a collaborating ofall
the business man.b.
A
traditional
business which generally done by handicrart maker.Established
special
bank
for
smull
ond
medium enterprise
beyondGovernment General
Bank
2.3.
Obsem&ion Worh
Orbntatlon
af
Smatl
and
Middk
Entrepreneurc
Culture
Crcssin
W*t
Jwa
(Bandung, Sukabumi,
Tasikmalaya), South Sumatra(Palemhand,
Sodh
Borneo(Bsniarruosin, Baniarharu).
Work CentralitY
Abrosd
among them.
low centrality of
Britannia
(2- 4) about t3o/o. German's centrality high 35% and thelow
oneis
1495.Holland's centrality high
i5ok
and thelow
one
is
10%o-Belgian's centrality
high
j9%
and the
low
ane
isI0%.
(JS'scentratity high
4t%
ond the
low
one
is
1094.Israel's
centrality high 43% and the
low
oneis *ok.
Yugoslavia'scentrality
high 54% and the
low
oneis
6"k.And Japan's centrality high
59% and the low one is 6Yu (MOWInternationolTeam
1997:
8i:84)
chemical engineers group,
followed by
teacher,turtile
worker, tool
and
die
mokcrs,
unemployed,affice
worker, pensioner,
university student, and the lowestoru
ispafi-
timer-
(MOWInternational
Team1997
:
85)2,3.1.
Four
Pffierns
theMeoning
of
Work:Abroad
Coantry Sanaplcentitlemint
-
law abligation) 3)6
and abligation)
(MOW
International
WorkTeam1997:
187)2.3.2.
Four Patterns the Meaningaf
Wark (Abroad Cauntry) Background: Competency and Work Understanding Problemo
Reported on past that Indonesian wark orientationim't
like the westerner. Thework eentrality is
low
says Boeke (1993) and cansidered not supportor
not
matchwith
developmentpragram
(Ka*ioranfutgrat,
2AAl).
On
adiscussion
of
dualistic
econonry
theory
Boeke
(199i)
explain
the characteristie of Indonesimt peopleare:
"...there
is almost no oriented onprofit
for
the East People (Indonesia). Speculativeprafrt
attracting
them,but these
profits
haye noregatarity
and eontimtity elementwhich
identify of income concept. East industryide*ifiedwith
"doesn't likecapital"
ond"the lingering
hatred when invest afund
beeausethe
risk always behindit";
just
a
little
desire
on
a
finishing and occuraq/, lack
of
businessquality,
evenfailed
on granting
stondard and samples,lack
of
elasticitysupplying,
lack
of
organizatio4
and
indiscipline
and
lack
of
the entitlement local specialization. (Baeke, I 99i)
o
They dedicatedfor
following
"bypcss
culfitre" as
a
work habit
whtchdisobey
stiptlation
and
broke the lav,procedure
in
effort
to
accomplish instrumental w ork goals.o
According
to
opinion that
Indonesia
isn't
suit
to
support
the
eeonomy development,the
goyernment suggestedto wkely not
on
speculative by hangit
onaathority
capacityof
ethniegroup in
Indanesic. (Boeke,]993;
Higgins,
1999).Previotts Research
o
Almostin all
studiesterminologt
of
"Indonesianpeople" cnd
"Indonesia Manager"
meeffLt Indonesia* Etlmie(Kwt$araningrat,
2AA1;
Dananiaya,2006;
Geertz,
1999;Hadisumarta,
1998; Hoefstede, 1982) and IndonesiaEthnic Manager @ananjrya ZAAfi-
Indanesian
Ethnie
entrepreneur'
contrastedfrom
hrdonesian
non-ethnic
enlrepreneur,
that
ls
ethnic7
entrepreneur
and
non
ethnic
entrepreneur
(Iionghao
or
China Entrepreneur)In
several culture cross study, terminologt
of
Indonesia
use only
for
Indonesian ethnic as an
appealfrom
other nation. (Hofstede, 1982; Redding&
Casey,
1996).
For
example,
it's
identffing
thot
IndonesianManager
whowork
onmultinational
companyfound
that they having leadership stylelower
than other nation. (Redding&
Casey, 1996).In
several studies
about
economicof
lrdonesia wrote
byforeign
writer,
terminologt fraft
*
etlmic
Indanesia
almast alwrys
mecrnby
Chiruse
or
Tionghaa whalive in
Indonesia.(Suryadartna,
1996,;Wong,
1998; Gungwu,tees).
For
guarantee the succeedof
develapmentprogram
where thediffirences
of
ethnicsnd
non ethnic
regardedas
a
sourceof
the
dffirences
perfarmance and theability of
these groups, then the government often takea'position
to entrustrealizing
of economy developmentprogramfor
theabilities
of this non ethnic group. (Moh.Sadli,
1999).There are government
attentiow
toftx
the waywe behwe and
ethnic group orientedof
businesswith a
torget: "to
educate Indonesians dealingwith
real
competitivemarket"
(Moh Sadli,
1999)2. 4. Purpose
of
Researchingo
Studying: howfar
index the meaning ofwork
(work centrality, work norm,work
output) manager/ ethnic
entrepreneur
differ
than
non
ethnic entrepreneur?o
Studying:
haw
far
the matngerial
job
- fit
of
the
monoger/
ethnic entrepreneurdffir
than non ethnic entrepreneur?Managerial
Fit
between emplayee
qaalification witk
requbements of managerial work
(Yan
der
Yen andDruin).
Relatedwith
situationfactar of
business'
rtrategt, and
attached
with
the other
business aspects, imbalance8
score
can be
mt
important
measurementsof
managerial
job
fit
(Leontiades, 1993)stratification
measurementfrom
eoch managerial worker
group. (Wanous, 1974;Lawler,
1987). Imbalance score on a general studies, the meaning ofwork
measuredin
T-
Scorefrom
Index. The meaningof
work which
eotmtedfrom
employee'shope
and their
contexl
of
work.
It
expectedthe
ratio of
one mattagerialgroup
with
the
other could reveal eaehprafiIesfrom
grot*p, theffirences
and thesimilar
between two groups.
il[.
Methadologt
distributed adequately between
Chins's
Manager and Indonesia, theywork
in
business environment
in
three
big
cities,
Bandung,Banjarmasin,
and
Palembang. They
ore
disordcred
cltutery from
businesslist
in
Industry and
CommereeDepartment. Indexes
the meaningof
works
countedfor
gaining work
centrality
point
(WC),normative entitlement
(EW,
normative obligation
for
public
advantage, economy
functions,
(PAY)intrinsic
and
expressivework
result (IR), and a chance to trainedandput
towork
(OPp)standard,
with total
cverage counted onscale
50. To evoluating the score extent three elarifications madq which are :o
High
:
T- score>
54o
Medium:
T-
score:
46-
54o
Low:T-score<46
Y
Analyzingfactor mesfr to
clwify vuiables
todominsntfactors
which construct dominant managerial work point.tinguish
scnnplegroup and classification group
basedon
analyze9
result, discriminate
usefor
comparing
the
level
of
discriminate analyze validity.for
examine managerialjob-frtfor
both group.IV
Research Ro,ult:
Ethnb
Group
a*d
Non
Ethaic
Group
iu
SrxInd*es
MOW (fncon*,
Centrality
of
Worh,
Intrinsic,
Contact, ObligatianNonn,
undOpportunity)
Table
l:
IncameMeon
'
Std deviation F-value Sign level (a) Indonesianethnics
50.47 4.52 0.0310 0.8606
Non-ethnic (Chinese)
s4.59 4.99
'able 2 Work
(Cll
Mean Std
deviation
F-v*lue
Sign levelh)
Indonesian ethnics 49.80 4.54 1.768
0.019**
Non-ethnic (Chinese) 54.11
4.9i
Table 3:
Intrinsic
WarkIv{ean Std
deviation
F-value Sign level (a)
Indonesian ethnics 49.62 6.72 0.219 0.640
Non-ethnic (Chinese) 50.98 8.02
Table 4: Contact
Mean Srd
deviation
F-value Sign level
h)
Indonesian ethnics 50.02 5.16 0.215 0.643
Non-ethnic (Chinese) 49.68 5.19
a.016**
'able 6
:
Oooartzmitv/ EntitlementsMean
std
deviation
F-value Sign level
h)
Indonesian ethnics 50.61 6.94 3.245
0.073**
Non-ethnic (Chinese) 48.3s 6.49
[image:14.612.137.571.268.746.2]Research
resuh: the
Dffircnces
hetweenManagerial
Fit
Ethnic
Manager
Group andNon
Ethnic
Table 7:
Ratiojob
-
fit
of
ethnicand non ethnic
in vmiation,
learning,promotion,
i*terest, snd mentaleffirt.
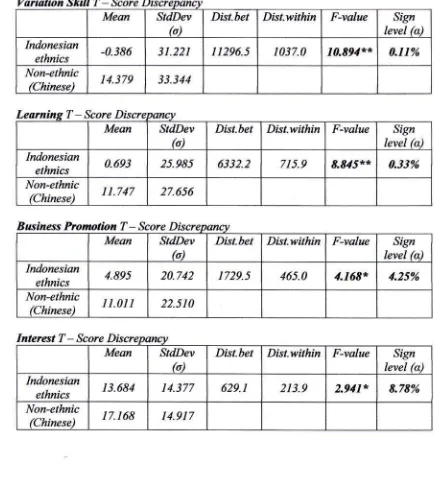
Variation
Skill
T-
Score ,.I''LMean StdDev
tu)
Dist.bet Dist.within F-value Sign level fu) Indonesian
ethnics
-0-i86
i
1.221 11296.51$7.4
10.894** 0.11% Non-ethnic(Chinese) 14.379
i3.344
-
Score DisereoancMesn StdDev
b)
Dist-bet
Dist-within
F-value Sign level fu) Indonesianethnics 0.693 25.985 6332.2 715.9
E.815**
0.33%Non-ethnic
(Chinese) 11 747 27.656
Business
Prumotion
T-
Score DiscrepancMean StdDev
b)
Dist.betDist.within F-value Sign level fu) Indonesian
ethnics 4.895 20.742 1729.5 465.0
4.168*
4.25%Non-ethntc
(Chinese) 11.01I 22.s 10
nterest
7'-
Score ,qrwMean StdDev
b)
Dist.bet Dist.within F-vslue level SiSn(a) Indonesianethnics 13.684 14.377 629.1
21i,9
2.911*
8.78%Non-ethnie
(Chinese) 17.168 14.917
l1
The Indonesia Managers
for
Indonesia
Managbr
(etlmic)
found thot
work
aspect
DecisionMaking
unbalance
very worth
(p<0.0000)
(I-Yolue
:
16.894) between hope andreality.
Thisis
indicated that there are perceptionsfor
their
needsin
for
their
businessreconstruction
which want
to realize and thereality couldn't sry
the same.learning
opportunity
from
worfr personal
contoctfrom
job,
work
conditions, work safety,flextime,
mentaleffirt,
variatian skill,
income, autonoflry, responsibility and intrinsicwarkpoint, found
that there areno
imbslanceswhieh
worth
enougfuThis
discovery concludesthat
what do matter are hopes andreality
lrorte asimilwity
in thisgroup-The
Nan-eth*ic
(Chinesc)Indonaian
MoaagellsTest
Tfor
imbalance
of
work situotion and work
preferences among Chinese ethnic managerialgroqp
in
managetluir
businessin
Bandung, Banj armasin, and Palembang show thisfollowing
statement :they perceive
workyoriation
morethanwhat
they could expect.could expected
than they could expected
Mental
-
Scare t{ratLMeon StdDev
b)
Dist.bet Dist.within F-value Sign level
h)
Indonesianethnics 41.202 27.433 1729.5 608.5
2.812*
9.330/6 Non-ethnic(Chinese) 46.979 2A.8
t2
The opportunity to
tafu
a self decisionfound assufieient,
means thereare
imbolances(p<0.0Aq which are
their preferencesis higher
than the reality.Opportunity
for
promotion through work which is now
thereality
is very signtfy (lr<O.A0q more opportunities that they eould expected.Managerial
Fif
Ethnie Menager
Group andNon
Ethnic
hope
for
wark
basedwery
Trcrceptionfram w*nager.
Ratio team upfor
managerialfit
between two groups nrcasure byF-
Testinvariation
analyze
from
T- Score differenees betweenwork reality
and hopefor
work in that
group
(1%o) some dimensions of
managerialfitfound
dffirent.
group,
verysignificant
in skill variation
0r<A.0AIl),
very
signiJicantin
opportunity
of
lewaing
(p<0.0033), signiJicont enough
inpromotion
@<0.0425),rather significant
in
mentaleffort
b<0.093),
which
meon
the
Indonesian ethnie
is
under China's
group
in
managerialfit-Conclusion
and Recommendationfor
Improving
Corupelivenessof
Small
andMiddlc
BusinessSeminar
Comparative study
gives
an
illustration more
completeabout
thesuccess
andfailure
of
policy.
Comparative
stu$t
amongcounry
refer
to
hugeproblems can
be a referencefor
regtonpotiqt
or
wider.Comparative study
found d
strong
tendencyin
central variables
the meaningof work
betweenmorugeriol group
of
China ond Indonesia cangive ilbstration
for
strategic
of
develaping entrepreneurshipin
Indonesia.Enterprise creativity sppeors
and
need the protection
from
law
splendidly.Tlnugh
theereativity
c{m rytrear in
*ery
condition,
butthe certainty
af la*,
whichproteet
the
rights and obligations
is
the most important thing so thefreedom of enterprise maregucranteedfor
internal even external.Reference
Boeke, J.H., Ecanornics ond Economic Policy
af Ducl
Societies,NewYorlg
1993.Danandjay4 Andreas
A.,
Sistem
Nilai
Manajer
Indonesia
(Yalue
Systemof
Indonesiun
Marugers),
Jakarta: Pustaka Binaman Pressindon, 2006.Geertz,
Hilfred,
Aneks Budflyo dan Komunitasdi
Indonesia, YayasanIlmu-ilmu
Sosial
&
FIS-UI,
1981,
translated
from
"Indonesian Cultures
and Communities". In Ruth T.McVey
(ed.) Indonesia,HRAF
Press, 1963. Higgins,Benjamin,
Economie Developmenr, Revised EditiorUNew York:
Norton,1998.
Higgins,
Benjamin, "Jan Boeke and theDoctrine
of
theLittle
Push",Bulletin
of
Indanesian Economic Studies,1994
Vol
)OL
3, 55-69.Koentj
araningrat
Ri ntangon-r int ongan Merrtol
dalun
P e mbongunan Eka nomidi
Indonesia.
(Mental
Obstaclesin
Economic
Developmentin
Indonesia),LIPI,
Jakda:
Bhaal
1989.Lawler,
EE and Porter, L5rman W-,ollhe Effect of
Perforrnanceon
Satisfaction",Industrial
Relations, I 997 (October), 7,p.23.
Mow-International
Research Team,"The
Meaningof
Working",
Dlugos, G. andWeimair,
K.
@ds.), Management UnderDrffering
Yalue Systems.Berlin,
New
York:
Walter de Gruyter, 1991, 565-630.Wanous, John
P.,
'i4'
Causal-CorrelationalAnalysis
of
the Job
$atisfaction and Performance Relationship-',Jotrnal
of
Applied
P sychologt,
zA0/., 59 (2),139-144.