By:
ERMA VELANDA 1110014000121
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAAND TEACHERS’ TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH
Students’ Narrative Writing (An Experimental Study at the Eighth Grade Students of MTs Pembangunan UIN Jakarta, Skripsi, Department of English Education, The Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training, State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
Advisor I : Drs. M. Farkhan Advisor II : Devi Yusnita, M. Pd
Key Word: Guided Questions,Writing, Narrative Text.
The purpose of this research is to investigate the effectiveness of guided questions on students’ writing of narrative text, specifically it is written on the title of this research that is “The Effectiveness of Guided Questions in Teaching Students’ Narrative Writing, An Experimental Study at the Eight Grade Students of MTs Pembangunan UIN Jakarta.”
Experimental research was used as a method in this study. The study was carried out in two classes, one as the controlled class and the other as the experimental class. The data are gathered through tests. The test consisted of the pre-test and post-test.
The research was conducted at the eight grade of MTs Pembangunan UIN
Jakarta on September, 15th until October,30th 2014 of the school year 2014/2015.
The sample used was a student class 8-H as experiment class and 8-G as control classwhich consist of 32 students in each class. The experimental class is taught by using guided questions, whereas in controlled class is taught narrative text as usual, without guided questions technique.After giving the treatment on experimental class and without it on controlled class, the data collected and analyzed by using t-test. According to the result of statistical calculation, it is
obtained the value of to (t-observation) is 7,09 and the value of “tt”(t-table) from
the df (62) on degree of significant of 5% = 1.7 and 1% = 2.4, as known “to” is
higher than “t” table as 1.7< 7,09> 2.4.It means that the null hypothesis (Ho)is
rejected and the alternative Hypothesis (Ha) is accepted.
Based on the finding in this study, it can be concluded that guided questions is effective on students’ writing of narrative text, that showed by result above.
Pembangunan UIN Jakarta). Skripsi, Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah, Jakarta.
Advisor I : Dr. M. Farkhan Advisor II: Devi Yusnita, M. Pd
Kata kunci: Pertanyaan Terbimbing, Menulis, Narrative Teks
Tujuan penelitian ini adalah untuk meneliti keefektifan dari tehnik pertanyaan terbimbing untuk menulis narrative teks bagi siswa kelas delapan di MTs Pembangunan UIN Jakarta.Penelitian ini berjudul“The Effectiveness of Guided Questionsin Teaching Students’ Writing of Narrative Text, An Experimental Study at the Eighth Grade Students of MTs Pembangunan UIN Jakarta”.
Metode yang digunakan adalah penelitian eksperimen. Penelitian ini dilakukan di dua kelas, yakni kelas control dan kelas eksperimen. Data dikumpulkan melalui dua tes. Tes terdiri dari pre-test dan post-test.
Penelitian ini dilaksanakan di kelas delapan MTs Pembangunan UIN Jakarta pada tanggal 15 September sampai dengan tanggal 30 Oktober 2014 tahun pelajaran 2014/2015, sampel yang digunakan adalah kelas 8-H sebagai kelas eksperimen dan 8-G sebagai kelas control dimana masing-masing kelas terdiri dari 32 siswa. Kelas eksperimen mendapatkan perlakuan khusus yaitu menggunakan pertanyaan terbimbing dalam menulis teks narrative dan kelas control tidak mendapatkan perlakuan khusus. Setelah diberikan perlakuan terhadap kelas eksperimen dan tanpa perlakuan di kelas control dan setelah dilakukan pre-test dan post-test maka data yang sudah di dapatkan kemudian di analisa menggunkan formula t-test. Berdasarkanhasil dari kalkulasi statistik, nilai
to atau t-observasi adalah7,09 dan nilai t-table (t-tabel) dengan derajat kebebasan
62 dalam taraf nyata 5 persen adalah 1.7 dan dalam taraf nyata 1 persen adalah
2.4. maka diketahui bahwa to (observasi) lebih tinggi nilainya dari t-tabel,
1.7<7.09>2.4, berdasarkan data hasil penghitungan statistik diatas maka dapat disimpulkan bahwa Null Hipotesis (Ho) ditolak, sedangkan Alternatif Hipotesis (Ha) dapat diterima, yang berarti pertanyaan terbimbing efektif terhadap pengajaran menulis narrative teks siswa kelas delapan.
Berdasarkan penjelasan diatas dapat disimpulkan bahwa pertanyaan terbimbing efektif terhadap menulis narrative teks siswa kelas delapan di MTs Pembangunan UIN Jakartat, yang dapat dilihat dari nilai t-skor diatas.
In the name of Allah, the Beneficent, the Merciful All praises be to Allah the Lord of the worlds
Peace and blessing be upon our prophet Muhammad, his family, his descendants, and his followers
This skripsi is presented to the English Education Department of English
Education Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers’ Training, State Islamic University
Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
In this good occasion, the writer would like to express her greatest
gratitude and appreciation to her beloved father, MintoHadiSlamet, for his
encouragement and support and my beloved mother SitiAsiyahfor being the best
mother I ever known, for everything she has given, for dedicating her whole life
to her children, and for her patience to motivate the writer to finish her study.
Moreover, to my beloved sister AmilatulArifah and my beloved brother
AlfianAfikMaulana for their motivation and praying.To my beloved grandmother
and grandfather, Munayatun (alm) and Affandi (alm) for always loving me and
believe in me. And My aunts SitiFuadah, SitiMaslacha, Khoirunnisa, my uncle
Mustofa and Khairul Anwar for being my other parents and support me.
Her gratitude and honor also go to:
1. Nurlena Rifai as the dean of Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers’ Training
2. Drs. Syauki, M. Pd, the Head of English Education Departement
3. Zahril Anasy, M. Pd, the secretary of Englsih Education Departement, and all
staffs of English Education Departement
4. Dr. M. Farkhan and Devi Yusnita, M. Pd as her advisors who have given their
energy and valuable time for the writer to give consultations with full of help
during the writer developing her skripsi.
English teacher of MTs Pembangunan Jakarta
7. All of teacher in MTs Pembangunan UIN Jakarta
8. Her beloved, MohamadApriliantoHestiawanfor loving, encouraging and
supporting the writer.
9. All of her friends from junior and senior high, RizqiHaqsari, Fadhila
Dian,FaridNurul, and Miftachus Salam for gathering and supporting each
other from over last ten years.
10. All of her friends of English Education Department in year 2010, especially C
class, Nurdina Mecca Zathira, for her huge support by encourage the writer
that they can never finished it by doing nothing and push the writer to start
over, DedeIrosRosmawati, RindaNuraini, Suaeni, and IlfaHidayah, for
gathering and sharing their knowladge, and whose names can not be
mentioned one by one.
May Allah, the Almighty bless them all, so be it. because only Him who
knows and sees how much contribution and motivation received by the writer.
At last, the writer realizes that this skripsi is still far from the perfection, a
criticism and suggestions would be welcomed to make it better.
Jakarta, January 16th 2015
The Writer
Acknowladgments... v
Table of Content... vii
List of Table... ix
List of Appendices... x
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A.The Background of the Study... 1
B.The Identification of Problem... 6
C.The Limitation of Problem... 6
D.The The Formulation of Problem... 6
E. The Objective of Study... 7
F. The Significance of Study... 7
CHAPTER II THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK A.Literature Review... 8
1. Writing... 8
a. Definition of Writing... 8
b. Classroom Writing Activity... 9
c. Writing Process... 10
d. Purpose of Writing………. 12
2. Guided Questions... 15
a. Definition of Guided Questions... 15
b. Function of Guided Questions... 17
c. Purpose of Guided Questions... 18
d. Indicator of Guided Question for Writing……… 18
3. Narrative... 19
a. Definition of Narrative... 19
b. Purpose of Narrative... 20
c. Kind of Narrative Story... 20
D.Theoretical Hypotheses... 25
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A.Time and Place... 26
B.Research Design... 26
C.Population and Sample... 27
D.Method of the research……….. 27
E. Instrument and Technique of Collecting Data………. 28
F. Technique of Data Analysis... 29
G.Statistical Hypothesis... 31
CHAPTER IV RESEARCH FINDING A.Data Description………... 32
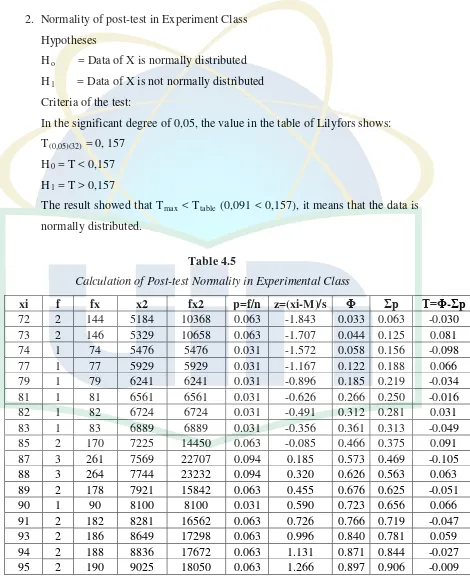
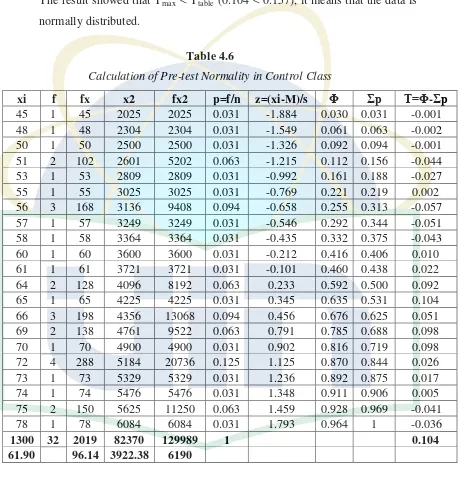
B.Normality of the Data……… 37
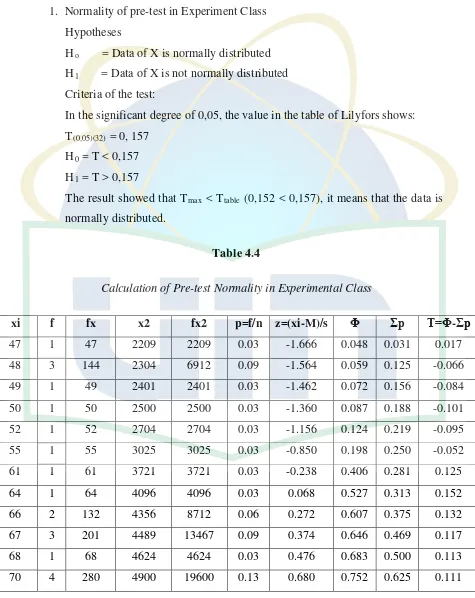
1. Normality of pre-test in Experiment class………. 38
2. Normality of post-test in Experiment class………. 40
3. Normality of pre-test in Control class………. 41
4. Normality of post-test in Control class………. 43
C.Data Analysis……… 45
D.The Testing of theHypothesis... 47
E. Data Interpretation... 48
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusion... 49
B. Suggestion... 50
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 51
APPENDIX... 53
2. The students’ score of the control class……… 34
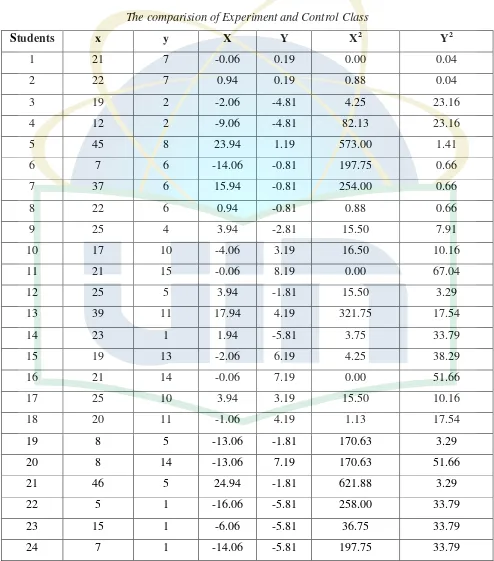
3. The comparison of experiment and control class………. 36
4. Calculation of Pre-test Normality in Experimental Class………. 38
5. Calculation of Post-test Normality in Experimental Class…………..…. 40
6. Calculation of Pre-test Normality in Control Class……….. 42
7. Calculation of Post-test Normality in Control Class……… . 43
3. Appendix 3: Instrument ………. ……… 78
4. Appendix 4:Rubric for Assesing Writing……….... 79
5. Example of Pre-Test
6. Post-Test Form
7. Example of Post test
8. Table of Lilyfors
9. Table of T-test
10. Surat Pengesahan proposal Skripsi
11. Surat Izin Penelitian
12. Nama Siswa
A.Background of Study
Educational side is important for human being. Every school in Indonesia
tries to figure out the best method and technique in order to make the subject
matter easier to understand. This proves that educational background is one of
several factors that influence people’s life; however there are many subjects
that make students hard to master the whole material.
So many subjects in Indonesia that must be mastered by every student,
one of them are English subject. In Indonesia, especially in the eighth grade
students of junior high school, the subject matter of English subject has been
arranged by governor in syllabus. Based on the syllabus, the teachers have to
develop their own way to teach their students and find a good way in order to
make the students understand all of skills in English as well.
In English subject, there are four major skills that student has to know
and master. One of them is writing skill. Writing is the ability of people to
produce words in form of written or printed work in order to deliver some
message to the reader. As other skills, we could not master it in a day. Students
have to write gradually in order to make their writing better and better.
Furthermore, we know that in writing itself, there are many materials we have
to concern.
What make writing difficult is because there are many materials in
writing that students have to understand well, one of those is texts. Writing text
in English is not that simple, the students have to know many part which
support writing, for example grammar and vocabulary. Writing is skill, where
to acquire it students have to do it gradually to make it better. Beside, in
writing text, the students have to know the feature and characteristic of the text
they want to write. Moreover, there are many texts in English. They are
analytical, recount, narrative, descriptive, procedure and so on. Narrative text
becomes one of many texts that students in junior and senior high school
should understand well. Then because of the research will hold in eighth grade
of MTs Pembangunan UIN Jakarta, the writer have to consider the syllabus
which is used there.
MTs Pembangunan UIN Jakarta is a school which uses two kind of
curriculum. In seventh grade, 2013 syllabus is used and in eighth and ninth
grade, KTSP is still used. Back to English subject, the problem is focus on
writing ability of the students about text, especially writing narrative in eighth
grade. Thus, because of the school still use KTSP, the writer refers the standard
competence and base competence of KTSP curriculum. Stated in the syllabus,
in eighth, tenth, eleventh, and twelfth of standard competence, point 8.2, 10.2,
11.1, 11.3, and 12.2 in base competence. One of them is “Merespon makna
yang terdapat dalam monolog pendek sederhana secara akurat, lancar, dan berterima untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar dalam teks berbentuk
narrative dan recount” and “Mengungkapkan makna dalam monolog pendek
sederhana dengan menggunakan ragam bahasa lisan secara akurat, lancar, dan berterima untuk berinteraksi dengan lingkungan sekitar dalam teks berbentuk recount dan narrative”. Stated in that syllabus, the purpose is that the students should know the whole part of narrative and make sure that the
students will understand well in the end of the study.
The reason why this research is conducted and the problem is choosen is
because when the writer do teaching learning practice in this school, the
students in eighth grade have some difficulties in writing narrative text. They
have to understand the generic structure and the plot well to write narrative
story especially fiction because in this grade they learn narrative only in fiction
story. The purpose of writing for this point of standard competence is teaching
students to write narrative in well organized and well grammatically even there
are many purposes in teaching writing.
In order to achieve the purpose, formal educations always try to find a
way to make writing narrative easier for their students. Yet, before it, the
teachers have to recognize the problem in learning and the factors which make
Formal educations always try to find an effective way to teach every skill
in English, including writing skill. Teaching English is not as easy as people
say. We could see this statement is true from so many methods, technique and
curriculum in Indonesia that change gradually. This situation has purposed to
make teaching and learning English understandable and usable. On the other
hand, we could see that teaching and learning English in Indonesia fails, the
writer does not expect to look from the national examination result, but from
secondary graduated students who could not use English as what they had been
expecting, for example; to understand some reference books in English when
they become university student.
Failure and success come from many factors. There are four important
factors in learning foreign language. First is ‘who’ factor, the first person who
determines the successful of learning process. A student is the first person who
takes in charge in their understanding. The ability to memorize, inner
motivation and their willingness to absorb the material are really significant
aspect to make them learn. We can ask students come to the class, do their task,
give them any homework and many other school activities, but remember when
they do not like it, and do not want to absorb it; it would be useless, because
they will forget it easily. We could not push them to understand and process
the information to their long-term memory.
Students have to memorize the pattern, vocabulary, and grammatical
rule. “The greatest barrier to second language learning seems to boil down to a
matter of memory: if you could just remember everything taught and heard,
you would be a very successful language learner.”1 This statement are require
the great memory of the students and tell us that learning language is not like
learning geography, when we learn new material, we could save the previous
material. Learning English is like arranging the brick, every single brick we
had pile up is important, one brick lost, the whole building will collapse,
because it is an accumulation process. “Language teaching cannot be built on
1
Harold Brown, Principles of Language Learning and Teaching Forth Edition, (New York: Longman, 2000), p 100.
what the learner knew; it can only be built on what he knows.”2 This quotation
from William Mackey supports the previous quotation from Harold. Students
do not expect forgetting, even a little part of language learning. What students
know in the past is not important anymore because when they forgot it, it
would be useless and could not help them to communicate. Their ability is
what they know right when they need it.
The second factor after ‘who’ is ‘how’. The method to teach in
teaching-learning process is important, but not always fit for every situation. Harmer
says in his book, “Many approaches and methods are based on a very western
idea of what constitutes ‘good learning’”. Some people think the best way how
to learn English is by changing the new method or technique especially that
successfully applying in western education, but actually method and technique
is only the tools for teacher to make their students understand. Method and
technique are important, but it will not become the first and the only factor to
make students easy to write something in target language. “There is no one
way to teach, no one method that is clearly the best.”3 The explanation of this
quotation is really clear that English has many sub-skills and component that
would encourage us to find an effective technique in order to learn them, but
let’s emphasize that there is no technique could overcome all situation. We
have to find the exact technique, which proper with what we want to learn. To
find the best technique, we have to consider these two important things, firstly
we have to consider and remember that there is no method that suit for all
teaching learning problem. Second, in the classroom, we have heterogenic
students who have different mind, intelligent, emotion, interest and types of
learning.
Many techniques in teaching learning process that developed by many
teachers to make student easy in writing. They are using video, picture, story
and many other media and technique. Writing narrative text as one of many
texts in junior high school should consider the feature and characteristic. As a
2
William F. Mackey, Language Teaching Analysis, (New York: Longman, 1967), p. 8
3
Stephen Krashen, Principles and Practice in Second Language Acquisition, (California: Pergamon Press, 1987), p. 27
story, narrative has to be organized well in order to make the reader easy to
read and understand the content. From so many techniques, one of them is
guided questions.
Guided questions is series of question which guide the student to write
the paragraph in good organizing. Thus, with this technique, the students can
hopefully write narrative text well organize as well as grammatically correct.
The third factor is ‘where’. Even formal education or some informal
instances like course always have certain place where to study. They always
prepare a class for teaching and learning process. Starting from fifteen people
per class till forty people per class is available. We could not make it in
language learning. Language is wider. The students only have several hours a
day in class and the entire hours will be their native language role. When
someone gets their native language, they did it naturally. They hear and write it
again and again every day since they did not even know another language.
Comparing to acquisition in second language, it would be a tiny portion of time
if we just concern in classroom learning. “Second language classes are best
thought of as places to gain comprehensible input in early stages.”4This means
that classroom activities are only to prepare students to make next movement in
learning second language. Using guided questions is hopefully encouraging
students to make the almost same pattern of question in writing narrative not
only in school but also in their own home.
The last factor is ‘when’. The last factor is to support the third factor that
students could write narrative and practice it by using guided question
everywhere, even in their own house by making the same pattern question. If
every student could do some practice outside gradually, it would be-at
least-almost equal with mother tongue acquisition.
To sum up from the four factors above, we can see that the students’ is
the first way to attract student in learning. They would follow the subject
efficiently if they know where the material goes. Thus, the teacher should be
4
Stephen Krashen, Principles and Practice in Second Language Acquisition, (California: Pargamen Press, 1987), p. 16
creative in adapting a useful and enjoyable classroom activity but also can
encourage students to focus in what they have to learn.
From many methods and technique to improve, develop, and understand
target language (English), and many problem rises in teaching learning activity
to learn foreign language, the writer uses guided questions technique in
increasing students’ writing of narrative text in eighth grade students of junior
high school, with hope that this will encourage the students’ confidence to
answer with their own words, and also indirectly, it would make them
automatically memories the pattern and easier to write their own story.
By those statements, guided questions as a series of question to guide the
students in writing the organized story by their own, the question is raised.
Then, rising from much explanation above, the researcher would do research
entitle “THE EFFECTIVENESS OF GUIDED QUESTION IN
TEACHING STUDENTS’ NARRATIVE WRITING”.
B.The Identification of the Problem
Based on the background above the problem that covered the research
can be identified as followed:
1. There are many skills in English that students have to master
2. Students have difficulties in memorizing the material
3. Students find difficulties in writing some texts in English subject
4. Students do not understand well some features of text
5. Students find difficulties in mastering narrative text
6. Teachers are difficult in selecting the appropriate technique in teaching
writing
C.The Limitation of the Problem
From the identification of the problem, this research would have the
limitation in order to make the research focus. Thus, the problem would be
limited on: the effectiveness of guided questions in teaching students’ narrative
D.Formulation of the Problem
The writer would analyze whether the using of guided questions
technique is appropriate in teaching writing of narrative text in eighth grade
students of MTs Pembangunan UIN Jakarta. The writer proposes the general
question “is the guided questions technique effective in teaching narrative
writing for eighth grade students’?”
E.The Objective of the study
The objective of the research is trying to investigate whether or not the
guided questions technique effective in teaching students’ writing of narrative
text, especially in eighth grade students of MTs Pembangunan Tangerang
Selatan.
F. Significant of the Study
This research hopefully will give any advantage for some people:
1. The English teacher, the people who will hold the English lesson in
class and would have the first responsibility in increasing students’
ability in English skills
2. The formal institution, for example school, and especially MTs
Pembangunan Tangerang Selatan, it could be a consideration in
increasing students’ writing of narrative text if the research proves that
the technique is effective.
3. The next research, as a reference and also consideration to hold
A.Literature Review 1. Writing
a. Definition of Writing
Talking about definition of writing, it would be include some book
and some expert. Writing as a skill of English is a process of discovery,
involving a series of steps. It is way of remembering and way of thinking
well. We usually know that writing is formal form of speaking. When slang
and informal grammar is used in speaking, writing considers many aspect of
the language itself.
Raymond defined, “Writing is an instrument of both communication
and self-expression” 1. This statement is supported by Grenville when she
said that writing was when you let your surrounding quite enough, chewed
the pan, and put all of you thought and what in your mind on a piece of
paper.2 It means that writing is used as an instrument to communicate and
show one’s self-expression which comes from personal thinking. Someone
may have some ideas or feeling that sometimes it can not be showed as
speaking. Writing is another instrument to communicate besides speaking.
Another definition comes from Byrne in a “Teaching Writing Skill”,
stated that “Writing can be said to be the act of farming these symbol
making marks on a flat surface of some kind.”3 Then, in another book which
has almost same idea said that writing is work on paper or onscreen.4 Both
of theory emphasize on media of writing. People can put their idea on paper
or onscreen using particular symbol in their own understanding. In this case,
1
Anita Pincas, Gillian and Charles Hadfield, Writing in English, (London: The Macmillan Press Limited,1982), p.100
2
Kate Grenville. Writing from Start to Finish, A Six Step Guide, (Miller St: Griffin Press, 2001), p. 6-7
3
Dom Byrne. Teaching Writing Skill. (London: Longman. 2006), p. 156
4
Paul Kei Matsuda and Christine M. Tardy. The St. Martin’s Handbook, (Boston: St. martin’s, 2010), p. 23
understanding means the language and the rule that people used and they
know it well in their area.
In Ryan book’s, he said, “writing is a skill, and skills are learning by
doing.”5 We can’t learn writing by the theory. We have to understand every
part of writing itself. In writing narrative, we have to understand the
characteristic and have to arrange it grammatically well. Besides, we can not
only write once then master it; we have to write gradually in order to make
it better and better.
From the other book, writing defined as a way of remembering and a
way of thinking as well. Writing makes words permanent, and that expand
the collective memory of human beings from the relative small store. 6
From many definitions the writer infer that writing is a human
communication besides speaking through particular rule with particular
equipment such as paper and pen in order to show people feeling and to
produce people’s mind into a work, and in the process it can help people to
sharpen their memory.
b. Classroom writing activity
In teaching writing, the researcher should consider what kind of
writing activity in the class room. Some of writing activity is explained by a
book with a title “From Language Learner to Language Teacher”, they are:7
1) Copying
Vincent Ryan Ruggiero. The Art of Writing. (California: Alfred Publisher. 1981), P. 12-13
6
James C. Raymond, Writing Is an Unnatural Act, (New York, Harper & Row Publisher Inc), p.2
7
Snow, Don. an Introduction to Teaching English as a Foreign Language, (Venice: TESOL Publications, 2007), p. 152-157
From that book, there are seven activities that students can do in
classroom. One of them is story. In the story, students in eighth grade will
focus on recount and narrative. Recount retell their activities or experiences
about past even, when narrative usually will amuse or entertain them with
classical and fairytale story.
c. Writing Process
Another important thing in writing is the process, because writing is
not one time over activity. The idea could come anytime, and we would try
to make our written as good as possible. There are several stages from
several books about process of writing; the first one is from Carol: 8
1) Prewriting
Prewriting occurs before the writer produces the first rough draft, is
a planning and preparation stage. In prewriting, the writer selects a
subject and begins to discover what she wants to say about it and how
best to present her thoughts to her audience intended. It provides the
foundation for any discoveries made in the writing process; it is the
germination or gestation period for the paper, the stage in which ideas
begin to take shape.
2) Writing
In this stage, the writer will try to write down their idea on a paper.
It will be the first draft of the idea. The writer could make up the idea in
the next stage.
3) Rewriting
Continuing in this part of writing, the writer revises the draft
produced in the writing stage, is an important part of writing that is at
times neglected by many student writers. This stage requires the writer to
make decisions that determine the final shape and effectiveness of her
writing. It involves both editing for grammatical and mechanical
correctness.
8
Carol A. Binder. Writing in Process: Strategies for organization and Development, (Singapore: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2005), p. 6-8
When Carol divided the process into three, Seow divided it into five
stages. They are:9
1) Planning
Planning here is almost same with pre-writing. The students have
some activities which show that they are in the beginning of the stage to
write. The activities will encourage and stimulate them to start. Starting
by brainstorming when the students think their ideas spontaneity then
continues to cluster the idea. The students have to choose the linked
detail to support the main idea. After that, the students can make a note
and rapid free writing about the main idea and details. To make them
easy to write in well organize, they can use wh-question to guide them
about what they want to add in the details.
2) Drafting
In the drafting, the writers are focus on the fluency of writing and
not bothering with the grammatical rule and the neatness of the draft.
They only have to develop their idea in planning. In here, the writers
have to consider about visualize and audience. In this stage, the genre of
writing must clear. The purpose of writing should be emphasizing,
whether the writers want to write narrative, expository, or argumentative.
3) Responding
Responding means that the first drafting will be given to the
teacher or a friend, so they can read and giving some comment. The
respond can be oral or written. The response can cover about
grammatical, spelling, and vocabulary. Teachers may have much
consideration when read their students work, they can use many rule in
assessing writing, but some students maybe do not even concern about it,
so it will be better if peer review involve some list in the table so every
students have the same rule how to response their friends work. Yet, the
students also can add some personal opinion about the writing.
9
Ann Raimes, Techniques in Teaching Writing, (New York: Oxford University Press, 1983), p. 315-319
4) Revising
When students revise, they review their texts on the basis of the
feedback given in the responding stage. They reexamine what was
written to see how effectively they have communicated their meanings to
the reader. It is done to improve global content and the organization of
idea so that the writer’s intent is made clearer to the reader.
5) Editing
In editing, the writers make the final draft of their writing. All of
the aspects in writing have to consider in order to make the reader get the
whole idea of the passage.
Both theory about infer the same idea, that someone who write
something have to consider what they want to write first. They have to
classify the idea and collect the data to support the idea. In writing, the
genre and the purpose have to fit with the audience. When someone starts to
write, they do not need to afraid whether their writing right or false, they
only need to focus on their idea and the purpose. First writing is not the
final; they have to share it with other in order to examine the weakness of
their writing. if they know the weakness and the lack of it, they can rewrite
it and make it as a better writing work in final.
d. Purpose of Writing
When the students do their writing, they certainly have some
purposes. They have to consider the purpose of their writing since this will
influence, not only to the type of text they wish to produce, but including
the language they use and the information that they choose. The purpose
will guide the writer to what kind of writing they want to write. In the stage
in writing is clear that the beginning stage, the writers have to consider
about the purpose.
David Nunan wrote in his book that written language serves a range of
1) Primarily for action
Public signs, e.g. on roads an stations; products labels and
instructions, e.g. on food, tool or toys purchased; recipes; television
and radio guides; bill; menus; telephone directories; ballot papers;
computer manuals, monitors and printouts.
2) Primarily for information
Newspapers (news, editorials) and current affairs magazines;
hobby magazines; nonfiction books, including text books; public
notes; advertisement; political pamphlets; scholastic, medical, etc.
reports; guidebooks, travels literature.
3) Primarily for entertainment
Light magazine, come stripes; fiction book; poetry and drama;
newspapers features; film subtitles; games, including computer
games.10
Different from Nunan, Robert have many more purpose in writing.
They are:
1) Writing to understand experience
Experience is personal memory. Writer does not write to tell
what happened but write to underline what the point and what the
important of the experience had been occurred. Because it is writing
about their own lives, so it uses first person view. Yet, although they
are writing about themselves, they are also writing to share their
experience with readers. Writing to understand experiences rely on
thought and reflection more that on emotion and confession.
2) Writing to report information
Writing to report information is to educate the readers about a
topic of which someone has some knowladge. Informative writing
comes from published sounds. It is usually given in university course.
10
3) Writing to explain information
Explaining means we need to analyze and classify information
first, examine causes and consequences, and define concept by
distingushing them from other, similar ones. Explanation is an
essential skill for making sense of the world around us.
4) Writing to evaluate something
Writing to evaluate requires writer to determine the nature or
quality of what he/she is judging. Evaluation also means determining
importance, benefit or worth.
5) Writng to analyze images
Writing to analyze images requires the ability to discern the
difference between the effective and the ineffective of an image and to
explain why you have made that judgment. This writing will help the
reader to why some images are memorable while the others go
unnoticed.
6) Writing to analyze text
Writing to analyze text is not really different from writing to
analyze the images. Writing to analyze the text is aimed to analyze the
certain text instead of image.
7) Writing to persuade others
This writing is aimed to persuade other people to do something
you want for yourself. In persuasive writing, comparison and contrast
is often used to develop a topic. Example of this kind of writing is
exposition, news item, and argumentative.
8) Writing to inspire others
Writing to inspire others is aimed to make the reader cheer up or
move to the case of something. It is mostly about the motivation that
the readers’ need. The general example of it is biography or
autobiography. It is usually about importance or influence people in
9) Writing to amuse others
This writing gives opportunities for the writers to give a
pleasure for the readers. We usually find the amusing text in story,
especially narrative. 11
The last theory will be presented is by Micheline. There are three
purpose of writing which can be abbreviated into “PIE”:
1) P: Persuade
In this era, persuasive is the tool in achieving the goal. We who
live in a capitalist society are bombarded with exposure of the power
of persuasion on television, radio, newspapers, magazines, snail mail,
internet and the market place. This is a good opportunity to teach
critical viewing skills, not to mention out the “inventors” in the class.
2) I: Inform
People sometimes do not realize just how informative they can
be. Almost everyday people will ask something to someone and
answer the question from someone else. Bigger than that, people who
write for information usually include the important information which
may help people and give knowledge to the reader.
3) E: Entertain
When we focus on entertain, the first thing that come across our
mind is story. Fiction is one of genre of the story. Fiction comes from
imagination and the writer will write that reflect their feeling,
experience and that which they like to read. Fiction or other kind of
story for example short story or even novel is amusing readers for
their light reading.12
2. Guided Question
a. Definition of Guided Question
There are many definition of guided question. Charles and Rise stated
that guided question is a technique for teaching which the teacher gives
11
Robert Keith Miller, Motives for Writing, (New York: McGraw-Hill, 2005), p. 609
12
Randy Stone. Best Practice for Teaching Writing: What Award-Winning Classroom, (San Fransisco: Corwin Press, 2007), P. 33-35
some questions to the students applied to a topic in teaching. The series of
question is given to the students in order to make them produce their written
language. They also said that asking questions about a problem or topic is a
way to learn about it and decide what to do or say. It is a useful and
systematic approach to explore a topic. There are several steps in using
questions for invention. They are:
1) Think about your subject. It means any event, person, problem,
project, idea, or issue. In other words, anything you might write about.
We usually define it as main topic of the whole writing.
2) Start with the first question, and move right through the list. Try to
answer each question at least briefly with a word or phrase. This will
make the story organize well.
3) Write your responses quickly, without much planning.13 This is
because of the stage of writing. We will have time to rewrite after we
revise it.
Raymond said that questions can be a way to help exploring topic in
writing skill. Asking questions can be a way of playing with material before
deciding what you want to make of its shape.14 Meanwhile, John Langan
said that you can generate ideas and details by asking questions about your
subject. Such questions include Why, When, Where, Who, and How. In other
hand, Fred also said the needs to know the topic might consider using the
questions. He called this method by 5Ws and the H grid. It works because
the question generates and provides a wraparound understanding of the
topic.15
From three definitions from the experts above, infer that the purpose
of guided question is to guide the students. Guide them to write in right
13
Rise B. Axelrod and Charles R. Cooper. The ST. Martin’s Guide to Writing, (New York: ST.Martin Press, 1985), p. 475.
14
James C. Raymond. Writing is Unnatural Act, (New York: Harper & Row Publisher, 1980), p. 15-16.
15
Fred D. White, The Writer’s Art, (Los Angeles: Wadsworth Publishing Company, 1986), p. 61-62.
sequence, guide them to expand the first main idea to the other, and guide
them to tell story in the right plot.
Moreover, Lois Robinson called this method by guided writing or
controlled writing. He said that guide or controlled writing is writing in
which one cannot make a serious error so long as he follows directions.16 In
here, direction means the series of question that had been made by the
teacher so the students have the same border to write the story. This is the
same method which gives some questions about a topic which are called
question paragraph, then, turning the questions into a paragraph of
affirmative statements. The answer of the question can be combined into a
paragraph with some improvisation from the writer.
b. Function of Guided Question
By using guided questions before doing writing activities, we can get
some advantages from them. Sadley stated in his book,”… If you learn to
use the question technique, you will sometimes discover not only the idea,
but also built-in ‘blueprints’ for organizing these ideas into essay”.17 By
considering that statement, using guided question will help students to write
their idea organized.
In an article, entitle “Improving Writing with a Focus on Guided
Question”, guided question have some function as followed:
1) Enables the teacher to tailor the teaching to the needs of the
students;
2) Facilitates the teaching and learning of individual children,
although the activities is arranged is a group
3) Activity focused on the needs of the students, the teacher is able to
observe and respond to the needs of individuals within the group;
4) Provides the teacher with the opportunity to extend and challenge
the students;
16
Lois Robinson, Guided Writing and Free Writing, (New York: Harper and Row Publisher, 1967), p. 2.
17
Dorothy Sedley. College Writer Workbook, (Ohio: Charles E. Merrill Publishing Company, 1981), p.11
5) Encourages the students to be active participants in discussions
about writing;
6) Builds confidence – the students are all grappling with the same
issues;
7) Allows the teacher to give immediate feedback on success and the
opportunity to discuss further areas for improvement.18
c. Purpose of Guided Question
Based on the definition and function of guided questions above, the
purposes of using guided questions are:
1) To encourage students in writing by using their own word with the
same instruction each students.
2) To make students easier organize the sentence into a paragraph and
the paragraph into a story with the right plot.
3) To build students’ confidents by ask them answer the question.
4) To facilitate the students rewrite the story they already know in the
right feature (narrative feature).
5) To ask the students to be active in class by arrange the puzzle of
story by asking and arranging the answer
6) The teacher will get the exact result about the ability of the students
by bordering their range with the questions
d. Indicator of Guided Question for Writing
There is no exact rule for using guided question in writing text,
especially in writing narrative. Yet, some books had explained clear enough
to say that 5W+1H is the key to write the useful information in a passage.
Meanwhile, the generic structure of narrative text can be the indicator in
making a series of question, because the generic structure of narrative text is
included the information from the question using 5W+1H.
Using wh-question is explored by Raymond. If someone wants to
write about event, the simples question can be used is: “Who?”, “What?”,
18
Primary National Strategy. Improving Writing with a Focus on Guided Writing. (Oxford: Department for children, schools, and Families, 2007)
“When?”, “Where?”, “Why?”. These are easily remembered as five Ws.
Sometimes, “How?” is added to the list.19 This statement support by
Axelrod when he said in his book that action came from method, the
technique an actor used, it referred to whatever makes thing happen. Each of
these points suggests a simple invention question, they are: ‘What (Action)’,
‘Who (Actor)’, ‘When and Where (Setting)’, ‘Why (Motive)’ and ‘How
(Method)’.20
3. Narrative
a. Definition of Narrative
Sometimes, we could not differ between story and narrative, because
these two terms is almost always refer to the same idea, but if we want to
analyze it more, story is wider than narrative. Cambridge dictionary, define
narrative as a story or a description of a series of events. It is almost same as
Mattix’s definition of narrative as “the representation of story relates an
event or anecdote. The writer often sets the scene first, telling who or what,
when, and where.”21 Narrative is a story which has a conflict within the
event. In a narrative, it could be have one or more event which supports the
plot of the story. The event in narrative usually calls as complication.
Narrative is a text that tells a story and in doing so, entertains the audience.
Narrative can be presented as written or spoken text. 22
We always find a narrative from place to place even we do not relies
it. Some children usually say to their mother before they sleep to tell them
any story. Some show in television gathering children among an adult role
and say, “tell me a story.” That situation requires them to tell a story, and
majority, the story is narrative. Narrative is one of children favorite, but it
does not stop the older to enjoy it. This is like what The National Strategy
says,
Betty Mattix Dietsch. Reasoning and Writing Well: A Rhetoric, Research Guide, Reader, and Handbook, (New York: Mc Graw Hill, 2006), p. 86
22
Mark Anderson and Kathy Anderson. Text Type in English 3, (Canbera: Mac Millan, 1998), p.3
“Narrative is central to children’s learning. They use it as a tool to
help them organize their ideas and to explore new ideas and experiences.
Composing stories, whether told or written, involves a set of skills and
authorial knowledge but is also an essential means for children to express
themselves creatively and imaginatively.”23
These definition can be conclude that narrative is a kind of story about
particular event, which have particular feature, in written or oral form with
the purpose of amusing the audience.
b. Purpose of Narrative
The purpose of narrative is to amuse the reader or listener. This
purpose clearly stated in Text Type in English 3 that the purpose of
narrative is providing entertainment, and making the audience think about
the issue, teach them a lesson, or excite their emotion. Barbara Said,
“Narrative text is to entertain, to express the feelings, to inform and to
persuade the reader.”24 These is the simple one, which the entire article,
book, and other resource say the same even in different word. Moreover,
considering the various genre of narrative, the purpose may be different
depend on the genre itself.
Furthermore, Betty stated that there are two purposes in narrative.
First is general purpose, to entertain and establish camaraderie whether the
account is fiction or fact, and specific purpose, is to inform other people and
the main idea, fact or event will often stated first.25
c. Kind of Narrative Story
Kind of narrative is various. It could divide into two big branch, they
are fiction and nonfiction. The writer state that because even narrative is a
story which commonly unreal, sometimes, the story is believed real in some
faith. More widely than two branch of narrative, it divides to:26
23
The National Strategies. Support for writing, Fiction. © Crown copyright 2008
24
Barbara Fine, Pattern for Purpose, (New York, McGraw Hill, 2003), p. 160
25
Mattix. Op. cit., p. 124
26
1) Legend
Legend is story about parentage of one place or one special
event in a particular area. The purpose of legend is to tell someone
about the origin of something and amuse them. The example is the
legend of Toba Lake
2) Myth
Myth is genres of narrative which consist of fictional
explanation for natural phenomena. Many cultures use myths to
explain the world and its mysteries by handing them down from one
generation to the next. Myths can also pass on cultural, religious or
spiritual beliefs and traditions.
3) Fable
Fable is story about animal. This story present that animal have
life as human, which in this story consist of moral value and message.
The examples of fable are three little pig, the crocodile and deer, and
the lion and the mouse.
4) Adventure
Adventure tells us the story about the journey which teaches the
role some special experience. The example is the adventure of Tin Tin
5) Mystery
Mystery is one of narrative story which include a horror part and
build curiosity.
6) Science Fiction
Science fiction story built its story under the development of
science and technology. It means that in the story we will find some
part that tells us about technology; it could be in temporary work or
7) Fantasy
Fantasy story is the story that happened beyond imaginary. It
could be about magic and some unusual creature which much of them
do not exist in the real world
8) Historical
It is like the term, history is about something happen in the past.
Thus, this story include the past even about something which could be
real or not.
9) Dilemma
The story plot is show as about the dilemmas of the role and
maybe could influence the audience, and feel like the dilemma is real.
10) Fairy tales
We usually find it in Barbie story. The stories which include a
fairy that becomes an important role in the story.
d. Element of Narrative
1) Generic structure
Generic structure of narrative can be drawn as triangle to present the
correlation between one part to another,
Figure 2.1
Generic Structure Triangle Climax
Falling Action Rising Action
The generic structure we usually know is:
a) Introduction: this part is usually mentioned the role, the place, and the
time of the story. In introduction, the reader or listener will find
‘who’, ‘where’, and ‘when’ of the story
b) Complication : complication is the beginning problem that build the
story and preface to the climax
c) Climax: climax is the summit of the problem that may occur and
happen to the character of the story.
d) Resolution: in the triangle, the resolution is placed after falling action,
when the climax start to overcome, but in some story, the resolution
could be the part when the character find a problem solving in the
story
e) Coda: if any coda in the story, it would show the changes of the
character and usually imply the moral value and suggestion from the
story.27
2) Language use
Narrative is the stories which happen in the past. According to the
rule, narrative use past tense, the pattern is:
The characteristic of narrative also use adverb of time, such as: Ones
upon a time, Long ago, A hundred years ago, and so on.
B.Previous Study
There are some previous studies that dealing with the research which is
conducted. These have correlation with the variable in this research.
27
Sanggam Siahaan & Kisno Shinoda, Generic Structure Text¸(Yogyakarta, Graha Ilmu, 2008), p. 73
Subject + verb II + complement Subject + was/were + complement
Nurfazriah, conducted classroom action research entitles “Improving
Students’ Descriptive Writing through Guided Questions”. She conducted the
research in SMPN 207 Jakarta. From her research, she get the result that guided
question technique has been proven could improve students’ descriptive writing.
Post-test in first and second cycle showed that the result is higher than pre-test. 28
The second study was conducted by Iwan, from Faculty of Teacher Training
and Education, Lampung University under the title “Developing the Students’
Ability in Writing Recount Text through Guiding Questions Technique at the
Second Year Students of SMPN 1 Terbanggi Besar Lampung Tengah.” From his
study, he found that the students’ score in writing recount text has improved by
applying guiding questions technique.29
Another study was held by Kurniawan. His research is about using pictures
and guided questions in teaching descriptive text. The goal of this research is to
know the students’ improvement in learning descriptive writing by using picture
and guided questions. The result showed that the implementation this technique
can improve the students’ ability in writing descriptive.30
Different from the previous study, in this research the writer will focus on
guided questions for narrative writing using a quasi-experimental method. By
previous study above, the writer will know whether guided question also effective
or not for narrative writing just like for writing description and recount.
C.Conceptual Framework
Writing as one of important skill in English. Writing is a process in telling
the reader about the writers ideas which usually display in a paper or on screen in
order to delivered the message and have particular purpose with some rule which
have to be followed, like grammar, punctuation, spelling and so on. This skill has
28
Nurfazriah, “Improving Students’ Descriptive Writing through Guided Question”, skripsi in UIN Syarifhidayatullah, 2011, unpublished.
29
Iwan, “Developing the Students’ Ability in Writing Recount Text through Guiding Questions Technique at the Second Year Students of SMPN 1 TerbanggiBesar Lampung Tengah”, 2012, unpublished.
30
Irwan Kurniawan, “Using Picture and Guided Questions in Teaching Descriptive Writing”, Skripsi of UIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta: 2009. Unpublished.
to master by the students. Yet, students find difficulties in mastering writing and
teaching find difficulty in using the appropriate technique. Many techniques are
used in order to make students write well. Some techniques are appropriate but
some techniques are not. In order to make the students writing, especially
narrative text, guided questions is used to analyze whether this technique is
appropriate or not in eight grade of junior high school in MTs Pembangunan
Jakarta.
Guided question is series of questions to guide students’ in writing narrative
text, because by the answer from those questions, they can arrange their own
words into their own story but still in right plot. Whereas, narrative is one of some
texts in junior high with the purpose is to amuse the reader. By that consideration,
the writer purpose two hypotheses, they are hypotheses null and hypotheses
alternative.
D.Theoretical Hypothesis
Based on the problem statements that presented by the writer, the research
hypothesis is stated as follows:
1. Hypothesis Alternative (Ha): there is significant effectiveness in
students’ narrative writing by using guided questions technique
2. Hypothesis Null (H0): there is no significant effectiveness in students’
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
A. Place and Time
This research is conducted at MTs Pembangunan Tangerang Selatan, Jl.
Ibnu Taimia IV Complex Lecturer UIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta in
academic year 2014/2015. The writer conducted this research for one month
and half , it began from September, 15th to October, 30th 2014.
B. Research Design
This is an experimental research; the design is depend on control and
experiment class. An experimental research is one of the most powerful
research methodologies that researchers can use. It is the only type of research
that directly attempts to influence a particular variable, and, when properly
applied, it is the best type for testing hypotheses about cause and effect
relationship.
In this research the writer will conduct some step, they are:
1. Two classes will be chosen, one become control class and another one
become experiment class
2. Pre-test will be given by asking the students to write narrative text.
The writer has chosen the text entitle “Rudi and the Golden
Compass”.
3. The treatment is given in experiment class by giving the students
series of question that will guide them to write narrative text organize.
4. The treatment will be conducted three times
5. After each treatment, the students will be given some explanation
about narrative –the features and characteristic.
6. Short review is given in every treatment
7. Post-test is conducted in order to know the effect of the technique in
writing narrative. Both classes will have post-test without guided
questions in order to make the result more objective.
C. Population and Sample
In this research, the population and sample is clear. The population of
this research is the eighth grade students at MTs Pembangunan Tangerang
Selatan, academic year 2014/2015, which consist of eight class, from A to
8-H.
The writer took two classes as research sample, they are H and G.
8-G is a control class and the 8-H experiment class. There are 32 students in 8-H
and 8-G, the presentation of the girls and boys is equal.
The sampling technique that used in this research is purposive sampling,
because the writer chooses two classes in equal level. Both of 8-G and 8-H are
bilingual classes, where both of the classes have almost same ability in English
and have same number of students.
D. Method of Research
In this research, experimental study is used; this is one of quantitative
research.The designed of experiment and control class by Arikunto for
conducting the result, as followed:
Figure 3.1
Control group, pre-test, post-test design Where:
E : Experimental Class
K : Controlled Class
01&03 : Pre-test
X : Treatment
02&04 : Post-test.1
1
Sugiyono , Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif, Kualitatif dan R&D, (Bandung: Alfabeta, 2009), p.76
E 01 X 02
K 03 04
The pre-test, to ensure the equivalency of the control and the experiment
group before conducting the treatment and a post test to see if there is any
statistically significant difference of students’ ability in writing skill after using
guided questions technique. The dependent variable in this study was students’
writing in narrative text whereas the independent variable was the use of
guided questions technique.
E. Instrument and Technique of Collecting Data
In collecting the data, the writer made instrument and the instrument is
written pre-test and post-test. According to Donald, instrument is an important
device for collecting data in a research. Usually, a test is used as the instrument
to measure the students` achievement in education. From a certain kind of a
test, the researcher would be able to collect the data in the form of scores which
could be used to identify, classify, or evaluate the test takers. He also adds that
the test in a more inclusive definition is a means of measuring the knowledge,
skills, feeling, intelligence or aptitude of an individual or group.2
1. Pre-test
Pre-test in conducted before the treatment in control class. Both
classes will write narrative story entitle “Rudy and The Compass”. In
this pre-test, the writer would not explain anything about narrative.
What students need to know is the story itself.
2. Post-test
Post-test is conducted after treatment. Both control and experiment
class will write narrative entitle “The Empty Pot”. Moreover, just like
in pre-test, actually every story they write, they have to know the plot
so they can answer the question in each treatment in experiment class
and can write the story in this post-test.
2
Donald Ari. Introduction to Research on Education, (New York: Rinehart and Winston, 2007), p. 127
F. Technique of Data Analysis
First of all, the research will do pre-test to know the basic ability of the
student and to know the students writing of narrative text. After doing pre-test
the writer treated them in order to analyze the effectiveness of guided questions
on student’s writing of narrative text in experiment class. After conducting the
treatment, the writer will give them post-test to see the significantly effect of
the technique on students’ writing.
After the data is collected, the writer will analyze the normality of the
data in order to make sure whether or not the data is normally distribute in this
research. This normality calculation is using Lillyfors, the data was
transformed into the basic value. The maximum dispute (T) got from the
calculation must be in absolute value (+). The result of normality can be seen
by comparing the value of Tmax to Ttable With formula as followed:.3
Accept Ha if T > Ttable
Accept Ho if T < Ttable
After get the data from pre-test and post-testand after the normality is
proved, they will be analyzed and processed by using statistic calculation of the
T-test formula with the significance degree 5% and 1 % and Gained Score. The
result will be scored by using rubric. The T-test formula is used to calculate the
differential significance made by pre-test and post-test. Moreover, gained score
formula is used to calculate the degree of its effectiveness. The T-test formula
is stated as follows, which X is the data from experiment class and Y is the
data from control class.
1. Determining Mean with formula:
��R = the average of variables score
���′ = sum of frequency multiply the student’s score
� = number of students
3
Susetyo budy. Statistika Untuk Analisis Data dan Penelitia, ( Bandung: PT Refika Aditama, 2010), p. 148
�
�=
�
�+
�
�
∑ ��
′
� �
2. Determining Standard Deviation score with formula:
��� = standard deviation of gained score
∑ ��′2 = sum of squared gained score
∑ ��′ = sum of gained score
� = number of students
3. Determining of Standard Error mean with formula:
���� = standard error mean of gained score
��� = standard deviation of gained score
� = number of students
4. Determining Standard Error Mean of variable X and variable Y with
formula:
5. Determining t-observation (t0) with the formula:
6. Determining t-table in significant level 5% and 1% with degree of freedom
(df), with formula:
�� = (�1 +�2)−2
�� = degree of freedom
� = number of students
���=��∑ �� ′2
� − �
∑ ��′ � �
2
���� = ���
√� −1
���1�2= ����1+���2
G. Statistical Hypothesis Ho: to < tt
Ha: to > tt
If to < tt : The alternative hypothesis (Ha) is rejected, and null
hypothesis (Ho) is accepted. It means that there is no effect and significant
difference between the result after teaching narrative writing by using guided
questions and without using guided questions at the eighth grade students of
MTs Pembangunan UIN Jakarta
If to > tt : The alternative hypothesis (Ha) is accepted, and null
hypothesis (Ho) is rejected. It means that there is an effect and significant
difference between the result after teaching narrative writing by using guided
questions and without using guided questions at the eighth grade students of
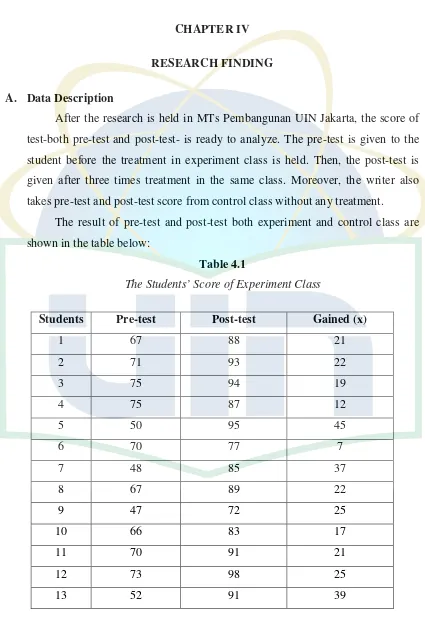
A. Data Description
After the research is held in MTs Pembangunan UIN Jakarta, the score of
test-both pre-test and post-test- is ready to analyze. The pre-test is given to the
student before the treatment in experiment class is held. Then, the post-test is
given after three times treatment in the same class. Moreover, the writer also
takes pre-test and post-test score from control class without any treatment.
The result of pre-test and post-test both experiment and control class are
shown in the table below:
Table 4.1
The Students’ Score of Experiment Class
Students Pre-test Post-test Gained (x)
1 67 88 21
2 71 93 22
3 75 94 19
4 75 87 12
5 50 95 45
6 70 77 7
7 48 85 37
8 67 89 22
9 47 72 25
10 66 83 17
11 70 91 21
12 73 98 25
13 52 91 39
14 73 96 23
15 70 89 19
16 72 93 21
17 48 73 25
18 70 90 20
19 74 82 8
20 66 74 8
21 48 94 46
22 68 73 5
23 73 88 15
24 78 85 7
25 64 88 24
26 71 89 18
27 73 95 22
28 61 81 20
29 55 87 32
30 67 72 5
31 49 79 30
32 73 87 14
∑ � = 2017 ∑ �= 2670 ∑ �= 674
��= 65.13 ��= 86.19 ��= 21.06
From the table above, the average of post-test in experiment class is much
higher than in pre-test. Every student got gain value more than 5. The higher gain
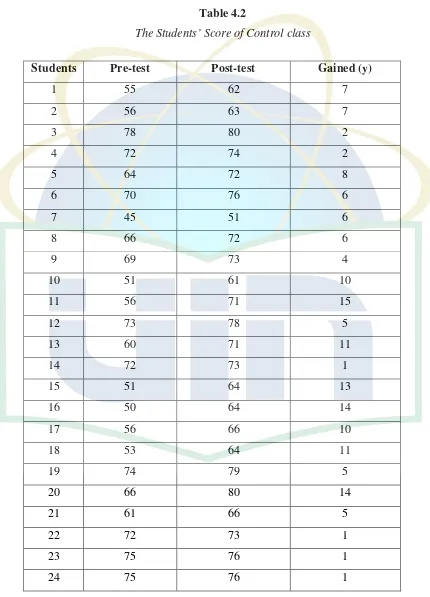
Table 4.2
The Students’ Score of Control class
Students Pre-test Post-test Gained (y)
1 55 62 7
2 56 63 7
3 78 80 2
4 72 74 2
5 64 72 8
6 70 76 6
7 45 51 6
8 66 72 6
9 69 73 4
10 51 61 10
11 56 71 15
12 73 78 5
13 60 71 11
14 72 73 1
15 51 64 13
16 50 64 14
17 56 66 10
18 53 64 11
19 74 79 5
20 66 80 14
21 61 66 5
22 72 73 1
23 75 76 1