i
IMPROVING STUDENTS’ UNDERSTANDING IN LEARNING PASSIVE VOICE OF PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE THROUGH
ARRANGE WORD GAME
(An Action Research Study at First Grade at SMAI Al-Azhar 1 Jakarta)
By:
HIJRI RAHMAN 206014000132
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
ii
Jl. Ir. H. Juanda No.95 Telp: (62-21) 7443328, 7401925
Ciputat 15142 Jakarta Email: [email protected]
SURAT PERNYATAAN KARYA SENDIRI
Saya yang bertanda tangan dibawah ini,
Nama : Hijri Rahman
Tempat/Tanggal lahir : Tangerang, 4 September 1988
NIM : 206014000132
Program Studi : Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris
Judul Skripsi : Improving Students’ Understanding in Learning Passive Voice of Present Continuous Tense through Arrange Word Game (An Action Research Study at First Grade at
SMAI Al-Azhar 1 Jakarta)
Dosen Pembimbing : Drs. Syauki, M.Pd
Dengan ini menyatakan bahwa skripsi yang saya buat benar-benar hasil karya saya sendiri dan saya bertanggung jawab secara akademis atas apa yang saya tulis. Pernyataan ini dibuat sebagai salah satu syarat menempuh Ujian Munaqasah.
Jakarta, 30 Mei 2011 Mahasiswa Ybs
iv
v
All praise be to Allah, the beneficent and the merciful, who has given the writer His love and compassion to finish the last assignment in his study. Peace
and salutation be upon to the prophet Muhammad SAW, his family, his companion, and his adherence.
In this occasion, the writer would like to say his great honor and deepest
gratitude to his beloved parents: Drs. H. Memed Rahmatullah and Lismalinah,
S.Pd, his lovely brother Dzikri Fauzan and Adi Nurfuadi, his lovely sister Eni
Nuraini, SH and Yulia Merlisari, S.Ag, and whole family who always gives their
love, support, motivation, and advice in accomplishing his study.
The writer also would like to express her sincere gratitude to his advisor,
Drs. Syauki, M.Pd who has patiently given his valuable help, guidance, and
corrections to finish this skripsi.
The writer also realizes that he would never finish writing this skripsi
without the help of some people around him. Therefore, he would like to say a lot
of thanks to:
1. All lecturers and staffs of English Education Department.
2. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd., the head of English Education Department.
3. Neneng Sunengsih, M.Pd., the secretary of English Education
Department.
4. Prof. Dr. Dede Rosyada, M.A., the Dean of the Faculty of
Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training Syarif Hidayatullah State
Islamic University Jakarta.
5. Drs. Sumarwanto, the head master of SMAI Al-Azhar 1 Jakarta
6. Mariyam, SS., the English teacher of SMAI Al-Azhar 1 Jakarta.
7. All friends in English Department 2006/2007, his beloved friends
Dian Harry Maulana, Zulmi Alfarabi, Fikriandi, Latifah, Neneng
Qofiah, Ahmad Efendi, Akbar Khadafi, Joko Susanto, Ady
Mulyanto, Ryan Nurdin, Rina Maryana, Hudaf Mandhaga and all
vi
contributions on this skripsi. May Allah SWT protect and give them happiness
throughout their life. Finally, the writer realizes that the skripsi is far from being
perfect. It is a pleasure for him to receive constructive critiques and suggestions
from the readers.
Jakarta, May 2011
vii
ABSTRACT
Hijri Rahman. 2011. Improving Students’ Understanding in Learning Passive
Voice OF Present Continuous Tense through Arrange Word Game (An Action
Research Study at First Grade at SMAI Al-Azhar 1 Jakarta), Skripsi, English
Education Department, The Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta.
Advisor: Drs. Syauki, M.Pd.
Keywords: Students’ Understanding, Passive voice of present continuous tense, Arrange word game technique
This study is aimed to know whether arrange word game technique
improve students’ understanding of passive voice present continuous tense at class X.3 of SMAI Al-Azhar 1 Jakarta.
This study is categorized as the Classroom Action Research (CAR) method in which it is used to identify and to solve the problem on students’ understanding of passive voice present continuous tense. In this Classroom Action Research, the writer implements the Hopkins’s design. Meanwhile, the data derived from the interview, questionnaire, observation, and test (pretest and posttest).
viii
Voice OF Present Continuous Tense through Arrange Word Game (An Action
Research Study at First Grade at SMAI Al-Azhar 1 Jakarta), Skripsi, English
Education Department, The Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training, Syarif
Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta.
Pembimbing: Drs. Syauki, M.Pd.
Kata Kunci: Pemahaman Siswa, Passive voice present continuous tense, Tehnik permainan acak kata.
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui apakah tehnik permainan acak kata dapat meningkatkan pemahaman siswa terhadap passive voice present continuous tense.
Penelitian ini dikategorikan sebagai Penelitian Tindakan Kelas (PTK); untuk mengidentifikasi dan mengatasi permasalahan pemahaman siswa pada materi passive voice present continuous tense. Adapun model Penelitian Tindakan Kelas yang digunakan menganut pada model penelitian Hopkin. Data yang diperoleh berasal dari wawancara terhadap guru, angket untuk murid, observasi di kelas, dan test (pretest dan posttest).
ix
TABLE OF CONTENT
TITLE ... i
SURAT PERNYATAAN KARYA SENDIRI ... ii
APPROVAL ... iii
2. The Understanding of Present Continuous tense ... 11
3. The Passive Voice of Present Continuous tense .... 12
B. Arrange Word Game ... 16
E. The Classroom Action Research (CAR) Procedures ... 29
x
2. Observation Sheet of Learning Activities ... 35
3. Questionnaires ... 35
1. Before Implementing the Action ... 39
xi
c. The Result of Post Test ... 64
B. Data Interpretation ... 68
1. The Interpretation of Interview ... 68
2. The Interpretation of Observation ... 69
3. The Interpretation of Questionnaire ... 70
4. The Interpretation of Test ... 70
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 72
A. Conclusion ... 72
B. Suggestion ... 72
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 73
xii
Table 3.2 The Blueprint of Pre Questionnaire ... 34
Table 3.3 The Blueprint of Post Questionnaire ... 34
Table 4.1 The Result of Pre Questionnaire ... 42
Table 4.2 The Result of Pre Test ... 46
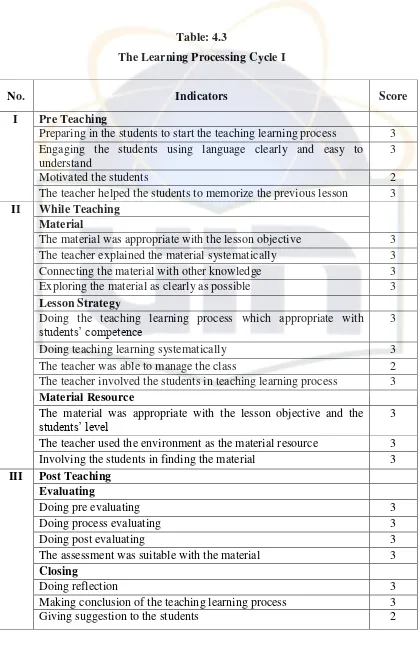
Table 4.3 The Learning Processing Cycle I ... 49
Table 4.4 The Activity of the Teacher and the Students in Cycle I ... 50
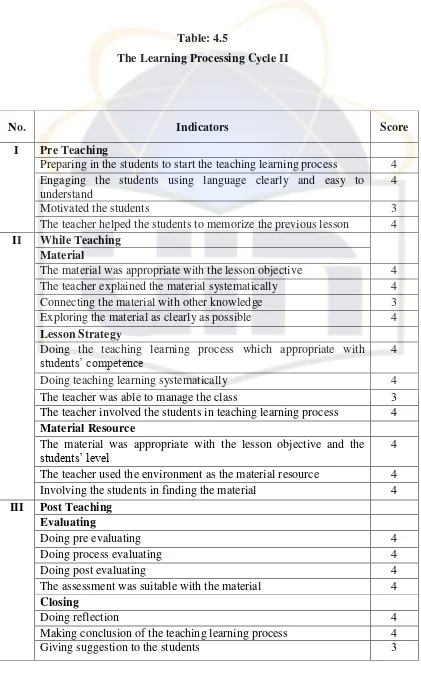
Table 4.5 The Learning Processing Cycle II ... 55
Table 4.6 The Activity of the Teacher and the Students in Cycle II .... 57
Table 4.7 The Result of Post Questionnaire ... 61
xiii
LIST OF FIGURES
xiv
Appendix 2a The Lesson Plan of Cycle 1 ... 78
Appendix 2b The Lesson Plan of Cycle 2 ... 82
Appendix 3 The Questionnaire for Students Before the Action ... 86
Appendix 4a The Blueprint of Pretest ... 88
Appendix 4b The Blueprint of Posttest 1 ... 89
Appendix 4c The Blueprint of Posttest 2 ... 90
Appendix 5a The Item Analysis of Pretest ... 91
Appendix 5b The Item Analysis of Posttest 1 ... 93
Appendix 5c The Item Analysis of Posttest 2 ... 95
Appendix 6a The Question of Pretest ... 97
Appendix 6b The Question of Posttest 1 ... 100
Appendix 6c The Question of Posttest 2 ... 103
Appendix 7a Arrange Word Game Material Cycle 1 ... 106
Appendix 7b Arrange Word Game Material Cycle 2 ... 107
Appendix 8a Arrange Word Game Answer Sheet Cycle 1 ... 108
Appendix 8b Arrange Word Game Answer Sheet Cycle 2 ... 109
Appendix 9a Observation Sheet of Cycle 1 ... 110
Appendix 9b Observation Sheet of Cycle 2 ... 112
Appendix 10a Field Note Cycle 1 ... 114
Appendix 10b Field Note Cycle 2 ... 116
Appendix 11 The Questionnaire for Students after the Action ... 118
Appendix 12 The Student’s Score ... 120
Appendix 13 The Graph of Students’ Score ... 122
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents the general account of the present study. It covers
background of the study, formulation of the problem, objective of the study,
method of the study and significance of the study.
A. Background of the Study
People use language for doing things with each other, and their use of
language itself a join action.1 By language, they understand each other, and interest as part of a society. There are many languages used in this world, such as
Indonesia, English, Arabic, French, Chinese, Japanese, and many others. One of
languages used in this world is English language, and now English becomes an
international language.
Every human being who speaks a language knows its grammar. When
linguists wish to describe a language, they attempt to describe a language.2 Grammar is one of the important aspects in teaching and learning English. Every
student has to understand English grammar, because grammar has the core
position in learning English language, without learning grammar, the student
cannot use English well. Obviously, for example the students need to know about
tenses, they may have difficulty to differ between present tense, past tense, and
future tense, and any other grammar materials.
And one of tenses which make student confused is present continuous
tense, because when they are demanded to speak based on the tenses, they have to
be aware about the time and the verb forms, and also they have to differ between
where the time and the verb forms are regardless. Beside of that present
continuous tense is stated in curriculum for the first grade of SMA.
Generally, the student felt confused to change an active voice of present
continuous tense into a passive voice of present continuous tense, because in the
passive voice, the object of an active verb becomes the subject of the passive
verb.3 Passive voice is generally difficult to be understood because of its rule and formula which are dissimilar with active voice. So they felt confused, and
sometime they made many mistakes in placing an object and a subject.
One of the important aspects in learning foreign language is the method of
teaching. The method of teaching can help the teacher to solve the student‟s
learning problem. Teaching methods can best be defined as the types of principles
and methods used for instruction. There are many types of teaching methods,
depending on what information or skill the teacher is trying to convey. For
effective teaching to take place, a good method must be adopted by a teacher. A
teacher has many options when choosing a style by which to teach. The teacher
may write lesson plans of their own, borrow plans from other teachers, or search
online or within books for lesson plans. When deciding what teaching method to
use, a teacher needs to consider students' background knowledge, environment,
and learning goals. Teachers are aware that students learn in different ways, but
almost all children will respond well to praise. Students have different ways of
absorbing information and of demonstrating their knowledge. Teachers often use
techniques which cater to multiple learning styles to help students retain
information and strengthen understanding.4
Many methods are used in teaching English language, such as grammar
translation method, direct method, oral approach, situational language teaching,
audio-lingual method, total physical response, the silent way, communicative
3
language teaching, natural approach, cooperative language teaching,
competency-based language teaching, games method, collaboration method and any others
method.
According to Asser, an important condition for successful language
learning is the absence of stress. First language acquisition takes place in
stress-free environment, whereas the adult language learning environment often causes
considerable stress and anxiety.5 And many methods can be used for reducing the stress, one of them is game technique, because game is suitable for all levels and
students will fell fun and happy. The teacher can make his own game to make his
students understand the lesson and also they fell very fun and happy.
SMAI Al – Azhar 1 Jakarta is one of the schools which are conducting
games in teaching learning process. According to the English teacher, games are the way to eliminate students‟ saturation and it makes them interested to learn6
. One of the games that the writer has made is “arrange word game”. Arrange word game is the game which the words are jumbles, and the teacher asks
the students to arrange the jumble word into a complete sentence as much as
possible. The writer thinks this game will be very useful for making easy student
understanding in learning tenses. The writer has used this game in two schools
that the writer has taught in it. And the writer thinks this game will make first
grade student of SMAI Al-Azhar 1 Jakarta easy to understand passive voice of
present continuous tense. According to the writer‟s experience the most benefit of
this game enables the students to have strong memory in remembering the form of
passive voice present continuous tense, and they will not forget the form of
passive voice present continuous tense.
The writer thinks that it is necessary to find out an alternative way to create suitable and interesting techniques related to students‟ condition. They need to be delivered any practices to assist them in increasing grammar comprehension.
5
Jack C Richard and Theodore Rodgers, Approaches and methods in language teaching, (New York: Cambridge university press, 2007), p.75.
6
For the need of research, the writer chooses the first grade class because,
according to the curriculum this class has to learn passive voice. Therefore, the students‟ grammar comprehension needs to be developed. In this research, the writer focuses on passive voice of present continuous tense. It is based on the
recommendation from the teacher. Then, the writer realizes that all of those
problems are impossible to be solved in a time. That is why the writer tries to find
out an appropriate strategy to increase students‟ grammar understanding better
that is through arrange word game which considered as one way of grammar
comprehension techniques toward passive voice of present continuous tense.
Here, the writer‟s basic assumption is students need to learn how to make a
sentence of passive voice of present continuous tense by finding jumble words
and arrange them intro many sentences of passive voice present continuous tense
to make easy their understanding. In other words, through the ability to make a
good sentence, to arrange any words into a good sentence, to increase their
creativity, and it enables them to have a strong memory of remembering the form
of passive voice present continuous tense.
B. Formulation of the Problem
To make the study easy to understand, the writer formulates the problem as follows: “Can arrange word game increase students‟ understanding in learning passive voice of present continuous tense?” In addition, “How does arrange word
game increase students‟ understanding in learning passive voice of present
continuous tense?”
C. Objective of the Study
The objectives of the study are to know whether arrange word game can increase students‟ understanding in learning passive voice of present continuous tense for the first grade of SMAI Al – Azhar 1 Jakarta, and to describe how the
implementation of arrange word game in increasing students‟ understanding of
5
D. Method of the Study
In this research the writer takes classroom action research (CAR). The
writer will conduct several meeting in teaching passive voice present continuous
tense. He will give the student test of passive voice present continuous tense
(pre-test) before the action research in the class. The pre-test is not the same as the
post-test. The pre-test held to know whether the students have same level of
knowledge. And the post-test will take twice test, to know whether the students
understand the passive voice present continuous tense.
E. Significance of the Study
The contributions of this technique are conveyed to: First, for the teacher.
It gives the alternative solution in teaching grammar skill. Second, is for students.
It assists them to solve their problems in making a sentence of passive voice
present continuous tense and it can help them to improve creative thinking skills.
Third, is for the institution of SMAI Al – Azhar 1. It can be beneficial regarding
6
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
This chapter covers some theories related to the study. The discussions
focus on passive voice of present continuous tense, and arrange word game.
A. Passive Voice of Present Continuous Tense 1. The Understanding of Passive Voice
Passive voice is the opposite of active voice in sentence pattern, as writer
told in the first chapter, in the passive voice, the object of an active verb becomes
the subject of the passive verb1, in other word the object in the active sentence moved into subject position in the passive sentence. Both show different
understanding and function and have dissimilar rule in use. In case of this
research, there will be only passive voice is explained more rather than one.
In forming passive voice, there are three ways of forming passive voice,
such as (1) The object in the active sentence moved into subject in position in the
passive sentence, (2) the subject moved to the end of the sentence and by was
inserted before it – the sentence now has an agent by phrase, (3) The main verb
was changed to its past participle form and the appropriate form of be was inserted
before it.2 As example bellow:
Active voice “I eat the rice”
Changed into passive voice:
“The rice is eaten by me”
A verb is said to be in the active voice when it expresses an action
performed by its subject. A verb is in the passive voice when the action it
1
Betty Schrampfer Azhar, Understanding and Using English Grammar, (New York: Longman, 2002), p.208
2
7
expresses is performed upon its subject. The object of the active sentence has
become the subject of the passive one. The subject of the active sentence is
expressed in the passive sentence only in prepositional phrase. In fact, it can be
omitted from the passive sentence altogether. The verb in a passive sentence is
always a verb phrase that includes a form of the verb be and the past participle of
the main verb. If other helping verbs appear in the active sentence, they must also
be included in the passive3. Here some examples of related active and passive
sentences:
S O
ACTIVE : Willa Cather wrote My Antonia
S
PASSIVE : My Antonia was written by Willa Cather
S O
ACTIVE : Tono has made a cake
S
PASSIVE : A cake has been made by Tono
In the sentence above, Willa Carter and Tono are the subjects who perform the action which is wrote and made. It will be different if the active sentence above changed into the passive voice. Willa Carter and Tono as the subject of active sentence will become an object who receives the action or in
other words, it can be said that the action it expresses which is wrote and made are performed upon its subject which is Willa Carter and Tono.
Every sentence, at least, contains of a subject and a verb. Based on the
explanation above, a sentence which has no object, or it is usually called
intransitive, will not be able to be turned into passive voice. This occurs because in
passive sentence, its subject is derived from the object of active sentence. As what
3
Azar writes, “Only transitive verbs are used in the passive. It is not possible to use intransitive verbs in the passive”.4
The passive occurs in all tenses, with all the verb phrase combination5, for
example:
9
progressive is be +being + past participle, the form of present perfect is has/have
+been + past participle, the form of simple past is was/ware + past participle, the
form of past progressive is was/were +being + past participle, the form of past
perfect is had +been + past participle, the form of simple future is will/going to
+be + past participle, and the form of future perfect is will +have + been + past
participle,.
Moreover, passive voice has two types of passive sentence, they are:
a. Passive without agent by – phrase
Usually the passive is used without agent by –phrase. The passive is most
frequently used when it is not known or not important to know exactly who
perform an action. 6 For example: “Rice is grown in India.”
From the example, the writer assumes that the rice is grown in India by
people, by farmer, or by someone else. It is not known or important to know
exactly who grows rice in India.
Passive without agent by – phrase is also called short passive. There are
many reasons why a native speaker may decide to use short passives in speech and
writing includes the following:
The most obvious reason for not including the agent is that the speaker does
not know who the agent is.
For example: “His car was stolen in Detroit”
The speaker does not want to reveal who the agent is. For example, he or
she may use the agentless passive to avoid assigning blame, as in:
“Rather than dwelling unnecessary on the causes of this fiasco, let‟s just say that mistakes were made.”
The identity of the agent can be assumed or understood, so it is not
necessary to mention the agent.
For example: “Our grapes are usually harvested in late August.”
6
The speaker is interested more in the action being reported than in the
agent that carries it out.
For example: “The animals were first given a cue for an orientation, and than a series of grating was presented”7
b. Passive with agent by – phrase
The by –phrase is included only if it is important to know who perform an
action8. For example:
“That poem was written by Emily Dickenson.”9
The example told the agent of the poet writer, where the sentence by Emily
Dickenson is an important information.
Else, subject of passive sentences in the corresponding active sentence may
be:
Direct object
The professor was dismissed by the dean
Indirect object
Suzy was given many presents by her father
Object of preposition
This bed has been slept in by president
Object complement
That he had special privileges was resented by everyone10
7
Ron Cowan, The Teacher’s Grammar of English, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2008), p. 394 – 395 Educational series, 2006), P.172
10
11
2. The Understanding of Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous expresses an activity that is in progress at the
moment of speaking. It is a temporary activity that began in the past, is continuing
at present, and will probably end at some point in the future.11
According to Ron Cowan, present continuous tense is formed with a
present form of be (i.e., am, is, are) and the present participle of the main verb12, for example:
John is sleepingright now.
I need an umbrella because it is raining
The students are sitting at their desks right now
The formation of preset continuous tense is concluded as below:13
SUBJECT + BE + VERB+ING
Furthermore, here are some functions of usage present continuous tense
declared by Marianne and Celce and Diana Larsen:
11
Azar, Understanding …, p. 13
12
a. Activity in progress:
He is attending a meeting now.
b. Extended present (action will end and therefore lacks the permanence of the
simple present tense):
I am studying geology at the University
c. A temporary situation:
Phyllis is living with her parent
d. Repetition or iteration in a series of similar ongoing action:
Henry is kicking the soccer ball around the backyard
e. Express future (when event is planed; usually with a future – time adverbial)
She is coming tomorrow
f. Emotional comment on present habit (usually co-occurring with frequency
adverb always or forever):
He is always wearing the glasses (approving)
He is forever acting up at these affairs. (disapproving)
g. A change in progress:
She is becoming more and more like her father14
In addition, other perceptions of the usage of present continuous tense sated by Ron Cowan are:
h. Giving statement more emotional strength and intensity:
This operation is really costing a lot of money
i. Focusing on behavior as a change from the norm
You are being stubborn15
3. The Passive Voice of Present Continuous Tense
As they have already been explained, passive voice is a sentence which is
formed by to be, followed by past participle and composed by transitive verbs,
14
Marianne Celce Murcia and Diane Larsen Freeman, The Grammar Book, (New York: Heine and Heinle publishers, 1999), p.117
15
13
while the present continuous tense is a tense expresses an activity that is in
progress at the moment of speaking. If both are fused, there will be a new
definition that passive voice of present continuous tense is an expression of present
continuous tense in form of passive.
As it has mentioned above, the form of passive voice present continuous
tense is be +being + past participle. The passive voice subject determines whether
the verb be is singular or plural.
Present Active Passive
Continuous Students are making a cake A cake is being made by students
Tense Sinta is buying three books Three books are being bought by Sinta
Here, there will be a classification of sentence as an example above
according to its words composition.
The sentence : Students are making a cake Subject to be V-ing Object
Analysis : The sentence has subject (students), to be + V-ing (are making)
and object (a cake). Its verb belongs to present continuous tense and
transitive verb because there is an object follows. Thus, it may
become passive and it is shown as follows:
The Sentence : A cake is being made by students Subject to be + V-ing past participle
Analysis : Subject in passive sentence (a cake) is derived from object of active sentence as shown above. And, object in passive is taken
from subject of active sentence. Object may be involved or not. It is
based on the purpose whether the original doer is important or not
to be known. Furthermore, as it has been demonstrated, the
transformation of verb belongs to passive present continuous tense.
It is recognized that the formula is to be + V-ing + past participle
(V3). To be is decided by subject whether it is singular first person
(I), plural first person (we), singular second person (you), singular
cake) is singular third person; therefore it applies to be as illustrated
affirmative, negative, and interrogative form.
To make passive voice present continuous tense in affirmative
sentence, the following formula is: subject + to be (am /is /are) + being +
past participle + by agent. To make passive voice present continuous tense
in negative sentence, the following formula is: subject + to be (am /is /are)
+ not + being + past participle + by agent. To make passive voice present
continuous tense in interrogative sentence, the following formula is: to be
15
Subject V-ing Past object Complement
B. Arrange Word Game
1. The Understanding of Game
Game is an activity which is entertaining and engaging, often
challenging, and an activity in which the learners play and usually interact
with other.16
According to the statement above, it means that any activity which
is interesting, sometimes challenging, and which can make the students
enjoy playing and interacting each other can be called a game.
Another definition about the game is an activity with rules, a goal
and an element of fun.17
Wolfgang Kramer states in his article that “In the German language, a game is any activity which is executed only for pleasure and
without conscious purpose. In this definition every activity that brings pleasure is a game.”18
Sometime teaching English grammar can be hard going for the teacher and students. It doesn‟t have to be difficult of faithful, however. English teacher can teach English using fun, attractive, and communicative
games. This way makes the students willing to learn English grammar. Enjoyment of games is not restricted by age. Some individuals,
regardless of age, may be less fond of games than others. But so much
depends on the appropriateness of the games and the role. Young learner
and adult are very willing to play games.19
In addition, by using the game, the teacher can create the attractive
and fun situation, if the teacher can create situations like those suggested
16
Andrew Wright, Games for Language Learning; Third Edition, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006), p. 1
17
Jill Hadfield, Advanced Communicative Games, (Hong Kong: Nelson House, 1987), P.iii
18
Wolfgang Kramer, what is a Game. This article is accessed on October 29, 2008 from http:www.thegamesjournal.com/articles/WhatIsaGames.html
19
17
above, such students will find themselves drawn into an atmosphere in
which they can forget about their lack of confidence and begin to take part
alongside the less shy or the more competent students.20
Furthermore, the objective of games must be clear that the students
know what they are expected to do in the activities. Sometimes the teachers
use a strategy in playing game to make them interesting. It is according to Oxford Learner’s Pocket Dictionary, game is “a secret plan or trick.”21 It means that the teachers can make the games more interesting by tricks.
They can also have an unlimited goal as a secret plan that is the grammar
item to be acquired by the students, if it is connected to the language
teaching activity.
There are many reasons why English teachers are using game
techniques in their teaching, such as:
1. Language learning is hard work
Language learning is hard work. One must make an effort to
understand, to repeat accurately, to adapt and to use newly
understood language in conversation and in the written composition. Effort is required at every moment and must be
maintained over a long period of time. Games help and encourage
many learners to sustain their interest and work.
2. Experiencing language
Games also help the teacher to create contexts in which the
language is useful and meaningful. The learners want to take part,
and in order to do so must understand what others are saying or
have written, and they must speak or write in order to express their
own point of view or give information. Games provide one way of
20
L.A. Hill and R.D.S. Fielden, English Language Teaching Game, (London: Evans Brothers Limited, 1974) p.iv
21
helping the learners to experience language rather than merely
study.
3. Repeated use of language item
Many games cause as much use of particular language items
as more conventional drill exercises; some game do not. What
matters, however, is the quality of practice.
The contribution of drill exercises lies in the concentration
on a language form and its frequent occurrence during a limited
period of time. Many games similarly provide repeated occurrence
and use of a particular language form. By making language convey information and opinion, games provide the key feature of „drill‟ with the added opportunity to sense the working of languages as
living communication. Games involve the emotions, and the
meaning of the language is thus more vividly experienced. It is, for
this reason, probably better absorbed than learning based on
mechanical drill
4. Central to learning
If it is accepted that games can provide intense and meaningful practice of language, then they must be regarded as central to a language teacher‟s repertoire and not merely a way of passing the time.22
Teacher should be careful to choose situations that are interesting
for the students, since this device helps them to arrange new sentence. It is
very useful so that teacher can convey the meaning and context in very
clear and easy ways.
In learning foreign language the most important thing, is the feeling
19
students win and other lose which sometimes can be destructive for some students. In challenge, everyone feels inspired to „have a go‟ and do their best.
The role of games in teaching and learning grammar cannot be
denied. However, in order to achieve the most from grammar games, it is
essential that suitable games are chosen.
To use games in language teaching learning activity effectively and
successfully, as the teacher of English, we should think carefully about the
selection of games we want to implement at the classroom.
There are so many games can be used in teaching grammar.
Therefore, in this paper the writer only uses one game, it is arrange word
game.
According to Andrew Wright, there are eight main games in
language learning such as:
1. Icebreakers and warmer
Before beginning of the lesson, the teacher can do ice
breaker games with a new class and warmer. Games and
playfulness as a way of warming people and helping them to focus their minds.
2. Mainly speaking
The games in this section offer a reason for speaking, and
thus they can give learners a confirmation and confidence resulting
from the successful use of the language or a warning signal on the
unsuccessful use of the language.
3. Mainly listening
This game is used for non–verbal response, that is to say, „listen and do‟. The „doing‟ shows, in a fair and accurate way, the extent to which the learner has listened and understood.
4. Mainly writing
The games in this section assume the close relationship
5. Mainly reading
Two important skills are concentrated on this game, namely
skimming for gist, when the learner find out at speed what content a
text contains, and scanning, when they search a text for some
particular item.
6. Mainly vocabulary and spelling
The aim of this section is to help the learner experience the
meanings of the words in contexts. Occasionally, it may be
necessary to draw attention to the form of a word as well as its
meaning.
7. Mainly grammar
The games in this section focus on particular points of
grammar and give the learner the opportunity to experience the
language in use in contexts that are meaningful and enjoyable, and
to practice using them over and over again.
8. Solo games
This game is helpful to give the learners an opportunity to
experience how to select and apply different types of game to suit their specific needs.23
Besides that, Andrew Wright has stated in his book there are seven
types of game, such as:
1. Care and share
„Caring and sharing game include all those games in which the learner
feels comfortable while sharing personal information with other learner.
2. Do : Move, mime, draw, obey
The learner is expected to do something non-verbally in response to a read
or a heard text.
3. Identify: Discriminate, guess, speculate
23
21
The learner is challenged to identify something which is difficult to
identify or to hypothesis about something which is then compared with the
facts.
4. Describe
The learner is challenged to describe something to another learner, by
speaking or writing.
5. Connect: Compare, match, group
The learner is challenged to connect, compare match, or group various
items of information, perhaps pictures or texts, objectively or subjectively.
He or she uses language to describe or comment on the pairs or groups of
information.
6. Order
The learner is challenged to put various bits of information into an order of
quality and importance, subjectively or objectively, or to put texts,
pictures, objects, into a development sequence, also subjectively or
objectively.
7. Remember
The learner tries to remember something and then communicate what he or
she has remembered.
8. Create
The learner is challenged or invited to make a story, write a poem or
produce some kind of material using their imagination.24
Finally, let the writer sums up, games are any kind of the interesting
activities, sometimes challenging, which have rule – even the simple one
and can be done in the classroom and accommodate the lesson that make
pleasant atmosphere that students enjoy being involved in and motivated.
24
2. Arrange Word Game
According to Elayne Masters, teachers can fill a vocabulary lesson
plan with a variety of learning resources, including games, workshops, and
other activities. The goal is to make learning vocabulary fun.25 This statement inspired the writer to make a game for language teaching.
As it has already been mentioned in the first chapter, one of the games that the writer has made is “arrange word game”. Arrange word game is the game which the words are jumbles, and the teacher asks the
students to arrange the jumble word into a complete sentence as much as
possible.
According to the writer‟s experience, this game is very useful for
making easy students‟ understanding in learning passive voice present
continuous tense.
The procedures in using arrange word game are:
a. The teacher explains passive voice of present continuous tense. b. The teacher asks the student whether the students have any question. c. The teacher presents many jumble words to the students, as example
bellow:
25
Elayne Masters, Create Fun Vocabulary Lesson with Word Game. This article is accessed on December 01, 2008 from http://www.suite101.com/content/create-fun-vocabulary-lessons-with-word-games-a81517
The fish is by being
read is The ball being
is is The book me
is being my sister by
23
d. The teacher asks the students to arrange those jumble words into five sentences (or more) of passive voice present continuous tense.
e. Than the students arrange those jumble words into five complete sentences of passive voice present continuous tense, as example
bellow:
taken The magazines my mother
f. After finishing, the students collect their assignment to the teacher. g. Than the teacher corrects the student‟s assignment.
25
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter presents the method of research, subject, and object of the study,
the research setting, research design, the Classroom Action Research (CAR) procedures
technique of collecting data, the research instrument, test validity analysis, technique of
the data analysis, and criteria of the action success.
A. The Method of Research
The method used in this study is Classroom Action Research (CAR). According
to Richard Sagor, Classroom Action Research (CAR) is a discipline process of inquiry
conducted by and for those taking the action. The primary reason for engaging in action
research is to assist the “actor” in improving and/or refining his/her action.1 It means that to begin the Classroom Action Research (CAR), the researcher or the teacher needs
to find an alternative way for improving students‟ understanding.
B. The Subject and the Object of Study 1. The Subject of Study
The subject of this study is the students at first grade of SMAI Al – Azhar I
Jakarta, academic year 2010/2011. The number of the students consists of 31 (thirty
one). The research is chosen based upon pre-research interview result with the
English teacher at that class proving that they have the lowest achievement of the
test among the other first grade classes. That is why they need an appropriate
strategy to help them in improving their scores toward passive voice of present
continuous tense.
1
2. The Object of Study
The object of this study is arrange word game technique to improve students‟ understanding in learning passive voice present continuous tense.
C. The Research Setting
1. The Writer’s Role on the Study
In this role, the writer is not only as the observer whilst the action but also he
prepares a lesson plan and the assessment or test before Classroom Action Research
(CAR) pre-test and after Classroom Action Research (CAR) post-test in each final
cycle. Else, the writer also collects and analyzes data then reports the result of study.
On the other side, the English teacher as an observer when the writer was a teacher and
he was a teacher when the writer as an observer.
2. The Time and Place of the Study
This research is carried out for 3 (three) months started from March up to May
2011. The place is at first grade of SMA Al – Azhar Jakarta VIII, academic year
2010/2011.
D. The Research Design
The Classroom Action Research (CAR) procedure used in this research is
Hopkins design. It consists of two cycles in which each cycle contains four phases;
27
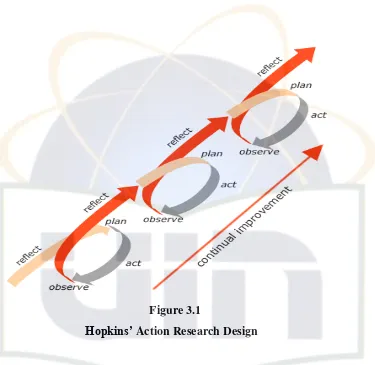
Figure 3.1
Hopkins’ Action Research Design
Based on the Hopkins action research design above, the writer would like to
describe further concerning the implementation of Classroom Action research (CAR) in
the cycle one and cycle two as following:
A. Pre-research which includes the following activities: a. Prepare the research instrument
b. Interviewing the teacher to know the subject of the research condition.
c. Giving a pre-test to the students
d. Giving pre-questionnaire to the students
B. Cycle I
1. Planning, which includes the following activities:
a. Curriculum study, programming and planning of learning which
involves the application of the meetings
c. Prepare lesson plan
d. Prepare evaluation tools
2. Acting, which includes the following activities:
a. Doing learning activity of passive voice present continious tense
material through arrange word game with implementation plan learning
b. Giving post-test cycle I to the students
3. Observing, which includes the following activities:
a. Observing the students activities during learning activities
b. Rewriting the events that appear on the students during learning
activities
c. Observation data collected during the execution of learning activities
4. Reflecting, which includes the following activities:
a. Analyzing data from the implementation of action
b. Evaluating the implementation of measures that have been done on the
cycle I
c. Planning the actions for the second cycle
C. Cycle II
1. Planning, which includes the following activities:
a. Planning the learning implementation consisting of one meeting
b. Making the game instrument
c. Prepare the research instrument
d. Prepare the evaluation tools
2. Acting, which includes the following activities:
a. Implementing learning activity of passive voice present continious tense
material through arrange word game
b. Giving the post-questionaire
c. Giving post-test cycle II to the students
3. Observing, which includes the following activities:
a. Observing the students activities during learning activities
29
c. Observation data collected during the execution of learning activities
4. Reflecting, which includes the following activities:
a. Analyzing data from the implementation of action
b. Evaluating the implementation of measures that have been done on the
cycle II
E. The Classroom Action Research (CAR) Procedures
The Classroom Action Research using Hopkins‟s design consists of four phases
within one cycle. Those are planning, acting, observing, and reflecting. After
accomplishing the first cycle, it will be probably found a new problem or the previous
unfinished problems yet. Therefore, it is necessary to continue to the second cycle in
line with the same concept of the first cycle.
To make clear what happens in every phase. Here are the explanations:
1. Planning Phase
Planning involves thinking about what the researcher wants to improve,
how he goes about it, and how he evaluates what he has done. In the following
sections, the process of planning an action research study is organized into four
steps. The first step involves formulating an initial research question by
reflecting on puzzling student behaviors, pressing problems, or needs identified
by his school district. The second step is „search for a new teaching strategy
though his observation of students‟, his dialog with other teachers, and his
professional development activities. The third step requires a search of the
educational literature for the purpose of further exploring new strategies and
finding research evidence that supports their use in the classroom. Forth and
finally he needs to consider what method of data collection he will need to
evaluate the effectiveness of his teaching strategies.
In this phase, the researcher also explains about what, why, when, where,
by whom, and how the research is done. In the preparation stage of this research,
attention to be observed, and then make an instrument analysis to help him
recording the facts that occurred during these procedures.
2. Acting Phase
In this phase, both the writer and the teacher collaborates to carry out the
planned action. The teacher uses the determined strategy as he is teaching while
the writer observes the class condition during teaching learning activity. Here, it
begins the process of going more deeply into the issue being researched.
Related to the condition of limited teaching learning period, that is why the
writer and the teacher take the action phase during two weeks within two cycles
in which each cycle consists of two meetings in action. The schedule is as
follows:
Table 3.1
Schedule of the Research
No Activities
Month and Week
March April May
1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
1 Interview X
2 Observation X X
3 Proposal X X X X X X
4 Instrument X
5 Cycle I X
6 Cycle II X
7 Report X
3. Observing Phase
This phase is done by the observer. Both observing and acting will take
place in the same time. The second step (action) is given to provide opportunity
31
action, he did not have the time to analyze the event while it is happening.
Therefore when observing, the observer should notice and note all of activities in the physical classroom. It may be about the teacher‟s performance, class situation, students‟ response, etc. In this phase, it also collects the data derived from evaluation or post-test.
4. Reflecting Phase
This phase is aimed to restate what has been done. This activity is very
appropriately when the teacher completed the action based upon data that have
been collected, and then it is necessary to hold evaluation for completing the
next cycle. This phase is carried out collaboratively, that is to discuss further
some problems occurred in the class. Thus, the reflection is able to be
determined after implementing the action and observation outcomes. If there
still might have found some problems, so it needs to move to the next cycle
concerning re-planning, re-acting, and re-observing. Therefore, the unfinished
problems yet could be solved.
F. The Technique of Collecting Data
In collecting data, classroom action research (CAR) uses qualitative data
(experience-based) and quantitative data (number-based). The qualitative data consists
of observation within the physical activity in the classroom and interview to be
presented for the teacher. On the other side, the quantitative data uses pre-test and
post-test.2 The completely explanation as follows:
a. Observation
Firstly, the writer uses the unstructured or opened observation. to know
the occurrences within learning process. It may be about the teacher‟s
performance during Classroom Action Research (CAR, and students‟ response
concerning the use of arrange word game technique. In general, all of the need
2
aspects that should be noticed are to make sure whether the teaching learning
processes in line with the lesson plan or not.
b. Interview
Before implementing Classroom Action Research, the writer asks the
teacher whether the students have difficulties in learning passive voice of
present continuous tense, and the method or kinds of strategies usually used by
the teacher in teaching grammar. The interview also will be carried out after
accomplishing Classroom Action Research (CAR) to know the teacher‟s
response toward the idea of arrange word game technique.
c. Test
The test used in this study is pre-test and post-test. The pre-test is done
before implementing arrange word game technique. It is to measure students‟
understanding in learning passive voice of present continuous tense at first.
Meanwhile, the post-test is implemented after using arrange word game
technique. In this study, the test is done in form of multiple choices, true false,
matching and arranging word. The test is held on every second action of each
cycle.
Next, to know the validity of test items, the writer uses discriminating
power and the difficulty item. The use of discriminating power of the tests item
is to know the difference response between the proportions of the high and low
groups to the item.3 The following is the formula to calculate the discriminating power:4
3
Kathleen M. Bailey, Learning about Language Assessment: Dilemmas, Decisions, and Direction, (London: Heinle & Heinle Publisher, 1998), p.135
4
33
D = The index of Discriminating power.
U = The number of pupils in the upper group who answered the item correctly.
L = The number of pupils in the lower group who answered the item correctly.
N = Number of pupils in each group.
Then, the discriminating scale uses:5
DP Remark
0.6 – 1.0 Very good
0.4 – 0.6 Good
0.1 – 0.3 Ok
-1 – 0.0 Bad
Furthermore, the difficulty item analysis concerns with the proportion of comparing students who answered correctly with all students who follow the
test. To know the difficulty item of the test, the following formula is used:6
P = Index of difficulty.
R = Total number of students who selected the correct answer.
T = Total number of students including upper and lower group
The following is the criterion of index difficulty:7
5
J. B. Heaton, Classroom Testing, (New York: Longman Inc, 1990), p. 174
6
Norman E. Grondlund, Costruction Achievement Test, (New York: Prentice Hall, 1982), p.102.
D = U-L
N
P = R
ID Remark
0 – 0.30 High
0.30 – 0.79 Medium
0.80 – 1.00 Low
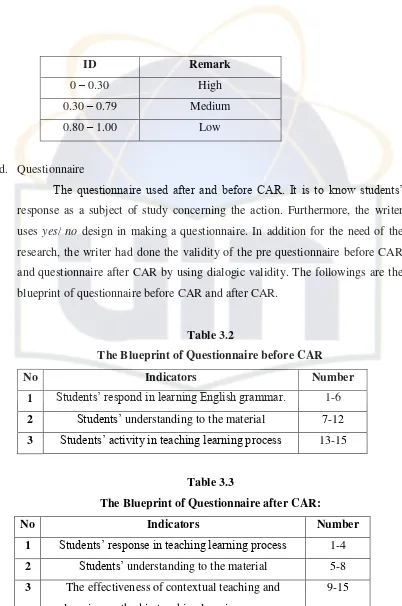
d. Questionnaire
The questionnaire used after and before CAR. It is to know students‟ response as a subject of study concerning the action. Furthermore, the writer
uses yes/ no design in making a questionnaire. In addition for the need of the
research, the writer had done the validity of the pre questionnaire before CAR
and questionnaire after CAR by using dialogic validity. The followings are the
blueprint of questionnaire before CAR and after CAR.
Table 3.2
The Blueprint of Questionnaire before CAR
No Indicators Number
1 Students‟ respond in learning English grammar. 1-6 2 Students‟ understanding to the material 7-12 3 Students‟ activity in teaching learning process 13-15
Table 3.3
The Blueprint of Questionnaire after CAR:
No Indicators Number
1 Students‟ response in teaching learning process 1-4 2 Students‟ understanding to the material 5-8 3 The effectiveness of contextual teaching and
learning method in teaching learning process.
9-15
7
35
G. The Research Instrument
The instruments which are used in this research are:
1. Lesson Plan
Lesson plan is a plan that describes the procedures and organization of
learning to achieve basic competence under standard content and has been
described on the syllabus. Lesson plan consists of the lesson identity, time
allocation, competency standards, basic competency, indicators, aim of the
study, the materials, learning steps, tools/source, and evaluation.
2. Observation Sheet of Learning Activities
a. Observation sheet of learning management by using arrange word game,
to observe the ability of teachers in managing learning
b. Observation sheet of the students and teacher activity, to observe the
activity of teacher and students during learning activity.
3. Questionnaires
a. Questionnaire of interview, this questionnaire is used for the teacher to
determine whether the learning of passive voice present continuous
tense though arrange word game is effective.
b. Questionnaire of interview, this questionnaire is used for the students to
determine whether the learning of passive voice present continuous
tense though arrange word game can improving their understanding.
4. Test
There are three kinds of test: pre-test, post-test cycle I, and post-test
cycle II. The question is about 60 questions, consists of 20 questions for
H. Test Validity Analysis
Before carrying out data collection through research is a test instrument, and to
get a good test, the data must be tested and analyzed. Tests conducted on students
outside of the target research, and test analysis was conducted on the:
A. Difficulty Level
Difficulty level is used to determine about the level of test difficulty.
Analysis of the problem shows that the test contained: 12 questions is low
41 questions is medium 7 questions is high
B. Distinguishing
Distinguish is an analysis to identify characteristics of the ability to
distinguish between students with high and low ability learners. From an
analysis of the test criteria obtained 60 good questions, therefore the test used
has been qualified from all aspects, such as validity reliability difficulty level
and distinguish.
I. The Technique of Data Analysis
The analysis qualitative data used in this study is the observation of students‟ activities during teaching learning process, and the interview before and after
Classroom Action Research (CAR). In this case, the writer collected the entire data
which have gained. In analyzing the numerical data, first the writer tries to get the
average of students‟ score per action within one cycle. It is used to know how well students‟ score as a whole on reading skill. It uses the formula:8
_ X : mean
8
Sudjana, Metoda Statistika, (Bandung: PT. Tarsito, 2002), p. 67.
37
x : individual score n : number of students
Second, the writer tries to get the class percentage which pass the minimal
mastery level criterion (KKM) considering English subject gains score 75 (seventy
five) which is adapted from the school agreement at SMA Al-Azhar9. It uses the
comprehension from pre-test up to posttest score in cycle 1 and cycle 2. In analyzing
that, the writer uses the formula:11
P : percentage of students‟ improvement y : pre-test result
y1 : post-test 1
P : percentage of students‟ improvement y : pre-test result
y2 : post-test 2
9
Taken from the interview with the English teacher on 2 nd March 2011.
10
Anas Sudijono, Pengantar Statistis Pendidikan, (Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo Persada, 2008), p. 43.
11
David E. Meltzer, The Relationship between Mathematics Preparation and Conceptual Learning Gains in Physics: A Possible Hidden Variable in Diagnostic Pretest Scores, (Iowa: Department of Physics and Astronomy, 2008), p.3.
J. Criteria of the Action Success
The criteria of action success if it can exceed the criteria which have been
determined, and fail if it is cannot exceed the criteria which have been detained. In this
study, the research will succeed when there is 70% numbers of students who pass the
Kriteria Ketuntasan Minimum (KKM) which is 75, they could achieve some
improvement scores from the pre-test until the second post-test in cycle two. If the
criterion of the action success achieved, it means that the next action of the Classroom
Action Research (CAR) would be stopped, but if this condition has not been reached
39
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS
This chapter presents the result of the research findings based on the
analysis of data collected from the implementation of arrange word game
technique in improving students’ understanding passive voice of present
continuous tense at grade first grade of SMAI Al – Azhar 1, Jakarta academic year
2010/2011. Related to the discussion of the result, it is divided into three parts.
Those are before implementing the action, the implementation of the action and
discussion of the data after implementing the action.
A. Data Description
There are three general parts of data description including before
implementing the action research, the implementation of the action research, and
the result after implementing the action. Those descriptions as following:
1. Before Implementing the Action
Three parts related to before implementing the action are: pre interview,
pre observation, and pretest. Those explanations bellow:
a. The Result of Pre Interview
Pre interview held on 2nd March 2011. Here, the writer asked some questions to the teacher related to the teaching learning process of passive
voice present continuous tense. The questions divided into three
categories. Those were the general conditions in English class primarily on
students’ performance and students’ achievement, the difficulties faced by students in understanding passive voice of present continuous tense, and
Related to the first category, the teacher said that some of students
though that English is difficult subject and it influenced their motivation
and performance in learning English. Furthermore, those conditions affect
to the students’ achievement. Some students who did not like English subject are hardly to pass the criterion of minimum completeness (KKM),
it is seventy five (75).
The second category discussed about the students’ difficulties in
understanding passive voice of present continuous tense. It was related to
the students’ difficulties in understanding the formula of the sentence and
remembering the past participle. The teacher said students usually forgot
about the usage of passive voice present continuous tense.
The third category was related to the strategy used by the teacher to
solve students’ difficulties in understanding passive voice of present continuous tense. The teacher said he usually gave a brief explanation and
focused on students’ who really have difficulties in understanding passive
voice of present continuous tense. She also gave some exercises from the
students’ hand book (LKS) or English text book, and some time she took the material from internet. Unfortunately, it did not really solve the
problem. Then, the writer suggested using arrange word game technique to
solve the problem. Because through arrange word game technique,
hopefully students are able to understand passive voice of present
continuous tense easily. Finally, the teacher and the writer agreed to use
arrange word game technique in teaching passive voice of present
continuous tense.
b. The Result of Pre Research
Pre research was conducted to know the process of teaching
learning passive voice of present continuous tense before implementing
arrange word game technique. It was conducted at first grade of SMAI