Department at SMK Negeri 3 Tangerang)
By:
Dian Novita Sari
109014000175
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHER’S TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC
UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
ii
at SMK Negeri 3 Tangerang)
A Skripsi
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teacher’s Training in a Partial
Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Starta 1 (Bachelor of Art) in
English Language Education
By:
Dian Novita Sari
109014000175
Approved by:
Advisor I Advisor II
Dr. Fahriany, M.Pd Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum
NIP. 19700 611 1991 2 001 NIP. 1976 1007 200710 1 002
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHER’S TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC
UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
iii
ENDORSEMENT SHEET
The Examination Committee of the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’
Training certifies that the “Skripsi” (Scientific Paper) entitled “THE EFFECTIVENESS OF „FIND SOMEONE WHO‟ GAME TOWARD
STUDENTS’ SPEAKING SKILL” (A Pre-experimental Study of First Grade Students of Culinary Department at SMK Negeri 3 Tangerang), written by Dian
Novita Sari student’s registration number 109014000175 was examined by the
Committee on January, 29th 2014. The “Skripsi” has been accepted and declared
to have fulfilled one of the requirements for the degree of “S.Pd” (Bachelor of
Arts) in English language Education at the English Department.
Jakarta, January 30th 2014
EXAMINATION COMMETTEE
CHAIRMAN : Drs. SYAUKI, M.Pd ________ ( )
NIP. 19641212 199103 1 002
SECRETARY : ZAHARIL ANASY, M.Hum ( )
NIP. 1976 1007 200710 1 002
EXAMINER I : Drs. Nasrun Mahmud, M.Pd ( )
NIP. 150 041 070
EXAMINER II: Drs. SYAUKI, M.Pd _______ ( )
NIP. 19641212 199103 1 002
Acknowledge By
Dean of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training
NURLENA RIFA’I, MA, P
h.D
iv
NIM : 109014000175
Jurusan : Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris
Alamat : Griya Merpati Mas Blok C43 No.7 RT 04/RW 05 Gembor,
Periuk, Tangerang, Banten, 15133.
MENYATAKAN DENGAN SESUNGGUHNYA
Bahwa skripsi yang berjudul The Effectiveness of “Find Someone Who” Game toward Students’ Speaking Skill adalah benar hasil karya sendiri di bawah bimbingan dosen:
1. Nama Pembimbing I : Dr. Fahriany, M.Pd
NIP : 19700 611 1991 2 001
Jurusan/Program Studi : Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris
2. Nama Pembimbing II : Zahari Anasy, M.Hum
NIP : 1976 1007 200710 1 002
Jurusan/Program Studi : Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris
Demikian surat pernyataan ini saya buat dengan sesungguhnya dan saya siap
menerima segala konsekuensi apabila terbukti bahwa skripsi ini bukan hasil karya
sendiri.
Jakarta, 22 Desember 2013
Yang Menyatakan
Dian Novita Sari
v
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
All praises be to Allah, the lord of the worlds, the one Who has bestowed
upon the writer in finishing this „Skripsi’ paper. Peace and blessing may always
be upon our prophet Muhammad saw, his family, relatives and all of his followers
until the day after.
First of all, the writer would like to express her greatest thanks to her Advisors
Dr. Fahriany, M.Pd and Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum for their guidance and suggestion
in completing this „Skripsi’. Without their help this „Skripsi’ will mean nothing.
Moreover, the writer also would like to give her gratitude to all people who
have helped her completing this „Skripsi’, particularly to:
1. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd and Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum, the Head and Secretary of
English Education Department, also to all of their staffs, for their
assistance and help which have given lots of contributions for the process
of writing this „Skripsi’.
2. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd, the Academic Advisor of class E of English Education
Department academic year 2009.
3. All the lectures in English Education Department for their encouragement,
guidance, and knowledge for the writer during her study in this university.
4. Nurlena Rifa’i, MA, Ph.D, the Dean of the Faculty of Tarbiyah and
Teachers Training.
5. Drs. H. Surya Mulyana, the Head Master of SMK Negeri 3 Tangerang for
giving the writer permission and authority for doing the research in his
school.
6. Misbahul Munir, S.Ag, M.M, the Responsible of Students Organization of
Intern School (OSIS) in SMK Negeri 3 Tangerang for his help, guidance,
7. Hj. Murtinah, S.Pd, English Teacher of X grade students of academic year
2013- 2014 in SMK Negeri 3 Tangerang for her help, guidance and
suggestion for the writer during the research.
8. Writer’s lovely parents Mr. Gunawan, Mrs. Sugiyatmi and writer’s dearest
brother Adhika Dwi Prastya for all of their help, support and prayer.
9. Writer’s classmates especially: Maret, Nisa, Nervi, Dita, Ma’dah, Hayin,
Neng, for their help, support and accompany for finishing this „Skripsi’.
Finally, the writer realized that this „Skripsi’ is far from being perfect;
therefore the writer hoped that there are many constructive critiques and
suggestion for the writer to make this „Skripsi’ better. Hopefully, this „Skripsi’
can give some contribution to the development of English Teaching and
Learning and there will be further research of it.
vii
Students of Culinary Department at SMK Negeri 3 Tangerang. Skripsi of English Education Department of Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training of State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2014.
Key words: Speaking skill, find someone who game, effectiveness.
This study was aimed to improve students’ speaking skill through the use of
“Find Someone Who” game in the first grade students of SMK Negeri 3 Tangerang academic year 2013/2014. The subject of this study was a class of X (ten) grade students which consisted of 25 students.
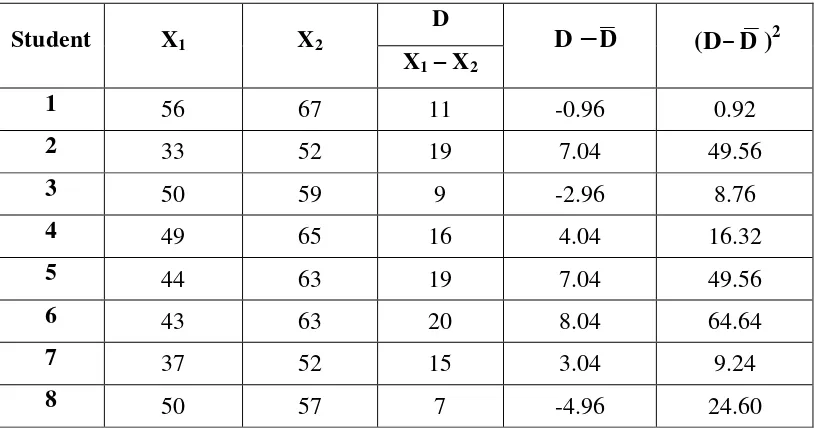
The research design of this study was a pre-experimental research design. In this research the writer used only a class of student as experimental class. The writer used one group pre-test and post-test for collecting the data. The data of pre-test were taken for measuring students speaking skill before the treatment was given and the data were taken from the post-test used for measuring students speaking skill after receiving the treatment using “Find Someone Who” game.
The result of the study showed that there was improvement of students speaking skill after being taught using “Find Someone Who” game. Most of students speaking score in post-test were better than their score in the pre-test. The
students’ mean score from pre-test was 47.36 whereas their mean score in post-test was 59.32. After the data from pre-post-test and post-post-test were calculated the result show that t0 (t-observation)= 6.53 and based on degree of freedom (df/dk)=24 at significant level 1% and 5% ttable5% = 2.064 and 1%= 2.797 can be concluded that t0>ttableor 6.53 > 2.797 > 2.064 or Ha was accepted and H0 was rejected. Thus the result of the study showed that “Find Someone Who” game is effective to
viii
ABSTRAK
EFEKTIVITAS “FIND SOMEONE WHO” GAME UNTUK MENINGKATKAN KEMAMPUAN SPEAKING SISWA Penelitian Pre-eksperimen Terhadap Siswa Kelas Satu Jurusan Tata Boga di SMK Negeri 3 Tangerang. Skripsi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan Universitas Islam Negri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2014.
Kata kunci: Speaking skill, find someone who game, effectiveness.
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk meningkatkan kemampuan berbicara siswa melalui pengaplikasian “Find Someone Who” game sebagai sebuah teknik pembelajaran speaking di kelas satu SMK Negeri 3 Tangerang tahun ajaran 2013/ 2014. Subjek penelitian dalam studi ini diperoleh dari siswa kelas X yang terdiri dari 25 siswa.
Design penelitian yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah pre-experimen design dimana peneliti hanya menggunakan satu kelas sebagai kelas eksperimen. Pengambilan data penelitian dilakukan melalui pre-test dan post-test yang berbentuk tes lisan. Data yang didapatkan peneliti melalui pre-test akan digunakan untuk mengukur kemampuan berbicara siswa sebelum perlakuan diberikan, sedangkan data yang didapatkanpeneliti melalui post-test akan digunakan untuk mengukur kemampuan berbicara siswa setelah mendapat perlakuan berupa pembelajaran speaking melalui “Find Someone Who” game.
Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa adanya peningkatan secara signifikan terhadap kemampuan berbicara siswa setelah menerima pembelajaran menggunakan “Find Someone Who” game. Sebagian besar nilai speaking siswa yang di dapatkan melalui post-test menunjukkan peningkatan yang cukup signifikan dibandingkan dengan nilai speaking siswa yang didapatkan melalui pre-test. Nilai rata-rata siswa yang didapatkan melalui pre-test sebesar 47.36 lebih kecil dibandingkan nilai rata-rata siswa yang didapatkan melalui post-test yaitu sebesar 59.32. Setelah proses penghitungan data yang diperoleh selesai didapatkanlah hasil t0 (t-observation)= 6.53 dan berdasarkan derajat kebebasan= 24 dengan tingkat kesalahan/ tingkat signifikansi sebesa 1% dan 5% maka didapatkan ttable5% = 2.064 dan 1%= 2.797 sehingga dapat disimpulkan bahwa t0>ttableor 6.53 > 2.797 > 2.064 atau Ha diterima dan H0 ditolak. Dengan demikian dapat disimpulkan melalui hasil penelitian ini bahwa penggunaan“Find Someone
ix
PAGE OF APPROVAL ... ii
THE ENDORSEMENT SHEET ... iii
CERTIFICATE OF ORIGINALITY ... iv
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... v
ABSTRACT ... vii
TABLE OF CONTENT ... ix
LIST OF THE TABLE ... xi
LIST OF THE APPENDICES ... xii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Identification of the Problem ... 3
C. Limitation of the Problem ... 4
D. Formulation of the Problem ... 4
E. Objectives of the Study ... 4
F. Significance of the Study ... 4
CHAPTER II THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ... 5
A. Speaking ... 5
1. The Nature of Speaking ... 5
2. Types of Spoken Discourse ... 8
3. Techniques for Teaching Speaking ... 10
a. Discussion ... 12
b. Problem Solving ... 13
c. Role Play/Simulation ... 14
4. The Objective of Teaching Speaking in Vocational High School ... 15
5. Teacher Roles in Teaching Speaking ... 19
B. Game ... 22
1. The Definition of Game ... 22
2. Kind of Speaking Games ... 24
a. Information-gap ... 24
b. Describing Pictures ... 26
c. Find Someone Who Game ... 27
3. Benefits of Using Find Someone Who Game ... 29
C. Previous Studies ... 29
E. Theoretical Thinking ... 31
F. Hypothesis ... 32
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 33
A. Place and Time of Study ... 33
B. Research Method and Design ... 33
C. Variable of the Research ... 34
D. Data of the Research ... 34
E. Instrument of the Research ... 35
F. Technique of Collecting Data ... 35
G. Technique of Analyzing Data ... 36
H. Scoring ... 37
G. Hypothesis Statistic ... 41
CHAPTER IV RESULT FINDING AND DISCUSSION ... 43
A. Data Description ... 43
B. Data Analysis ... 45
C. Hypotheses ... 48
D. Data Interpretation ... 49
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 51
A. Conclusion ... 51
B. Suggestion ... 51
REFERENCES ... 53
xi
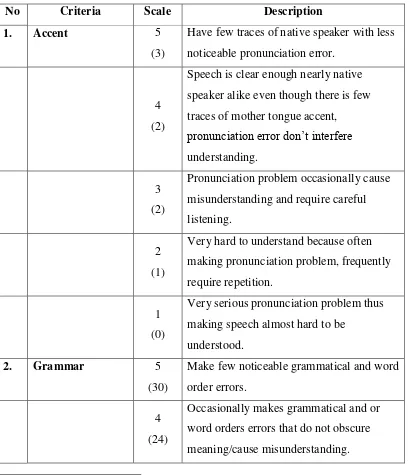
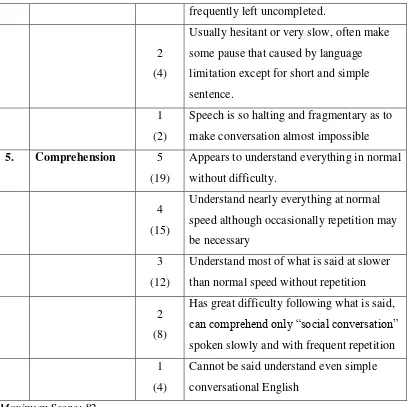
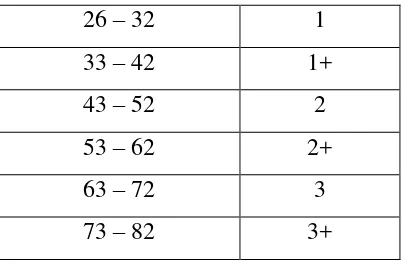
Table 3.2 : Conversion Table ... 40
Table 3.3 : Description of Conversion Table ... 41
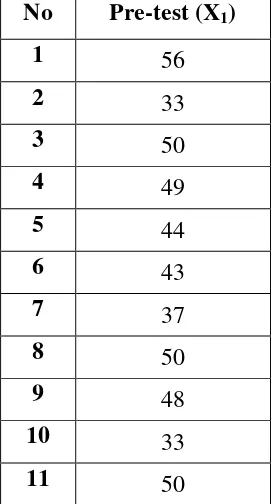
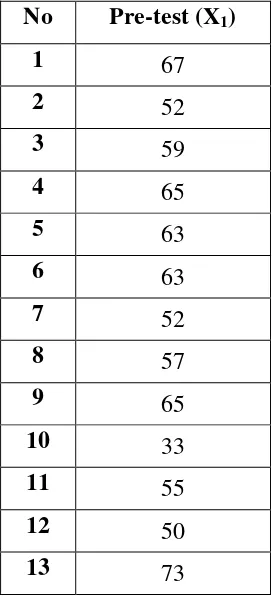
Table 4.1 : Students’ Pre-test Speaking Score ... 43
Table 4.2 : Students’ Post-test Speaking Score ... 44
xii
Appendix 2 : Guidance for Oral-test ... 57
Appendix 3 : The Score Aspect of Students Pre-test ... 58
Appendix 4 : The Score Aspects of Students Post-test ... 60
Appendix 5 : Transcript of Students Pre-test ... 62
Appendix 6 : Transcript of Students Post-test... 63
Appendix 7 : Scoring System ... 64
Appendix 8 : Lesson Plan of Experiment Class ... 70
Appendix 9 : Treatments ... 98
Appendix 10 : The Value of t-table... 103
Appendix 11 : The Evidence Letter of the Research ... 104
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the StudyLanguage is one of the means of communication that plays an important role
in human interaction. People around the world use language to convey their
messages, communicate their feelings and needs whether in spoken form or in
written form. Nobody can avoid the interaction through language
(communication) with people around them. Because of the necessity of
communication in humans’ life, speaking skill considers as one of important language aspects that have to be acquired in order to convey their verbal messages
precisely and communicate their purpose successfully.
Lately, as the development of modern world the necessity of mastering
English language especially the ability to communicate in English language has
encouraged the Ministry of Education in Indonesia to develop some curriculum
that emphasis on developing communicative skill in the term of transactional and
interpersonal interactions. Turning back to the past even there are some previous
curriculum that already emphasized on communicative activities in the class such
as Kurikulum Berbasis Kompetensi (KBK) and Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan
Pendidikan (KTSP). Nowadays, the Ministry of Education develops the newest
curriculum which is known as Kurikulum 2013. This curriculum hopefully can
refine the latest curriculum for integrating some important aspects of education
that has not been existed in its predecessor.
Based on core competency (Kompetensi Inti) and basic competency in
Kurikulum 2013, there are some differences between Kurikulum 2013 and its
predecessor KTSP. In KTSP competencies that should be mastered by students
were separated in specific lesson but in Kurikulum 2013 every lesson being taught
in school supports each competency including affective competency, aptitude
scientific approach uses as teaching approach that requires students’ active
participation in offering critical question about the lesson and theirs participation
in analyzing and in summarizing learning points. Another differences come from
the integration of some learning aspects such as moral value, religious value,
social value, culture, science, and technology.
Even though the aim of teaching English in Vocational High School had been
well established in Indonesian National Curriculum but most of learners in SMK
Negeri 3 Tangerang still find speaking as a difficult skill to be mastered. This
situation happened because English language is not used as communication
language in their society. Another problem which causes consideration that
speaking is a difficult skill to be mastered comes from the implementation of
grammatical competence that should be transformed into communicative
competence. Speaking, as productive skill, is considered as the most difficult skill
to be mastered by most of language learners around the world because speaking is
transient and dynamic thus speeches exchange between the speakers occur in very
limited time.
Fortunately the process of teaching English in SMKN 3 Tangerang has been
conducted by using communicative approach before the implementation of
Kurikulum 2013. This condition caused students’ communicative skill in SMKN 3
Tangerang are well established. Furthermore, based on writer’s observation on X
grade students can be found that there are some problems which caused students’
speaking performance less than good. First of all, students’ previous knowledge
about English language; this problems comes from how English language has
been taught in students’ previous school thus indirectly influence their capability in constructing well-forms spoken utterances and in implementing language
function. Another problem comes from teacher routine on using dialogue practice
for teaching speaking. Even though it is not a serious problem but dialogue
practice which is known as pre-communicative activity had caused students’
misconception on practicing the target language in real-life communication
for making simple daily interpersonal communication. The other problem comes
from students’ vocabulary mastery. Students’ incapacity in using English vocabulary actively makes them need a great amount of effort for selecting the
vocabulary in order to convey the desired meaning.
In consequence, after observing these phenomena, the writer saw the
necessity of providing a learning technique which can facilitate students with
real-life alike communicative activity and can bring the needs for communicating to
the students during learning process. Based on that reason therefore the writer
chose a kind of communication game named “Find Someone Who” (FSW) for teaching speaking and improving students speaking skill in X grade students of
Vocational High School. Other than that, most of experts agree that learning a
language is a hard process; therefore facilitating students’ with kind of activity
which can bring some joyful feeling such as game is very important. Another
reason for using FSW as a teaching technique is the interesting and playfulness
feeling that was brought by game. Moreover, there is no doubt that most of
teenagers love game; therefore the writer tries to engage students’ attention, involvement, and cooperativeness during learning process in order to provide a
great amount of communicative practice and target language exposure into
learning activity for improving students’ speaking skill.
B. Identification of the Problems
According to writer’s observation of X year students of SMK Negeri 3
Tangerang there are some identification of problems:
1. Students’ incapability to speak English caused by their previous
knowledge about the language and the way English being taught in their
previous school.
2. Students need more communicative activity for improving their speaking
skill and practicing English language in real-life communication.
3. Students’ lack vocabulary mastery causes their incapability on conveying
C. Limitation of the Study
In order to be more specific, the writer will limit this study on investigating
the effectiveness of a kind of game “Find Someone Who” to increase students’ speaking skill at grade X of Vocational High School.
D. Formulation of the Problems
Based on limitation of the problems stated above, this study will focus on
answering the following question: “Does teaching speaking through ‘Find Someone Who’ game effective in increasing students’ speaking skill?”
E. Objectives of the Study
According to the formulation of problems mentioned above, the aim of this
study is to observe whether “Find Someone Who” is effective for increasing
students’ speaking skill in speaking class.
F. Significances of the Study
Depends on the objective of study has been mentioned above, this study will
give several significant not only for students but also for teachers.
First of all, for teachers his study will give some benefits such as improving
their teaching technique and creating more interesting and more joyful learning
process in their speaking class.
Moreover, this study also gives some benefits for the students such as
reducing their stress and burden that caused by their obligation to catch all of
learning points being taught by their teacher during learning process. Since
language learning considers as one of difficult subjects to be learned a joyful
learning process through game can make them capable of catching more learning
5
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A.
Speaking
1.
The Nature of Speaking
Speaking refers to the communication activity that requires the interaction
between at least two people. In this situation, someone who involve in
speaking activity can give simultaneous contribution to the communication
discourse that occurs in particular situation and they also can change and
develop the topic of discussion being discussed as the communication takes
place.
According to Carter and Nunan speaking defines as reciprocal and
physically situated face-to-face interaction. Reciprocal means that speakers
can give simultaneous contribution to the discourse and respond to each
contribution as soon as possible. Whereas, physically situated face-to-face
interaction means that speakers can see each other thus they can understand
some physical context and physical signal to show their attention to the
interaction and their intention for responding the utterances.1
The definition above explains that speaking is a reciprocal action which
means that the speaker and the interlocutor can make direct contribution to the
discourse or to the information exchange. This situation will bring the
speakers to the topic development or exchange because in oral communication
people usually make less predictable interactions such as making initiation for
developing topic, making clarification about some information, or closing the
interaction. Moreover, beside of its unpredictable activity speaking is known
also as dynamic and transient activity because in speaking activity
conversations occur immediately and these utterances/conversations are
impermanent which can change as soon as the speaker produces the other
1
utterances. Furthermore, speaking also defines as physically situated
face-to-face interaction which means that both of speaker and interlocutor can see
each other. They can use physical context and physical signal for indicating
their attention or intention to the interaction and for making some contribution
or for responding the topic being discussed.
On the other hand, McDonough and Shaw see that speaking is not an oral
form of written language because it requires learners’ ability to use its
sub-skills to form a complete competency of spoken language.2 With this argumentation can be concluded that speaking differs from oral form of
written language because to achieve speaking competency learners are not
only required to be able to speak but they also need to be able to master
speaking sub-skill such as pronunciation, stress, intonation, turn-taking ability,
and so on. When the speakers involve in speaking activity, speaking sub-skills
will give some important contributions for maintaining or managing speakers’
relation with the other speakers in speaking activity. This relation is useful for
delivering their message clearly and for communicating successfully.
Furthermore, spoken language differs from written language not only
because of the involvement its sub-skill but also because of its different
characteristics. Spoken language is considered as more dynamic and transient
activity than written language; therefore as the spoken discourse has been said
it will disappear as soon as possible and it cannot be exactly repeated in the
same way. Meanwhile, written language is permanent that the readers can read
it anytime they want or they can reread it many times without worrying about
missing any essential information in the text. This argumentation derives from
Hughes explanation that the nature of speaking is different from the nature of
writing in the aspects of production and in the social aspects. In aspect of
production spoken language is context dependent, unplanned, transient,
2
oral/aural, and dynamic; whereas in the social aspect spoken language is locus
of change, inter-personal, informal, stigmatised, rhetorical, and primary.3 From that statement can be elaborated that the characteristic of spoken
language in the aspect of production can be changed depends on its context.
Spoken language is unpredictable that speakers can easily move from one
topic to the different topic. Moreover, spoken discourse is temporal which
means that the utterances being spoken can’t be repeated in the same way
because they disappear as soon as the speakers said them and it delivers
through oral/ aural communication which makes spoken language dynamic
and actively change for its spontaneous material. This condition makes the
materials being discussed in speaking activity can be changed easily based on
speakers’ willingness. On the other hand, in the social aspects the characteristics of spoken language not only require topic exchange between
speakers but also topic exchange between discourse and the things around it.
Moreover, the interaction in speaking activity always occurs between more
than one people and commonly using informal language; therefore, the
speakers not only need the ability to adapt themselves with other speakers or
the ability to repairs misunderstanding that occur between them but they also
need to understand communication style which used by the speakers in order
to communicate in effective way.
Furthermore, in “A Communicative Grammar of English” Leech and Svartvik remark that a conversation is not limited on giving and receiving
information only but also including social interaction and participant
cooperation as the basic characteristic of conversation.4 This statement explains that communication between the speakers aimed not only for
exchanging information but also for maintaining social interaction and
speakers’ cooperation during the conversation thus demand the speakers to
master the ability for managing turn-taking technique in communication.
3
Rebecca Hughes. Teaching and Researching Speaking. (Harlow: Pearson Education Limited, 2002), pp. 9- 11.
4
Therefore, founded on the three definitions of speaking above can be
concluded that the characteristics of spoken language is different from the
characteristics of writing language in the aspect of production and in the social
aspects. Speaking is known as a communicative activity that requires
reciprocal and physical face-to-face interaction between at least two speakers
and in order to master speaking competency learners not only have to be able
to master speaking skill but also to be able to master its sub-skills for
maintaining social interaction between the speakers and for achieving a
successful communication.
2.
Types of Spoken Discourse
There are two kinds of discourse that commonly used in Indonesian
English National Syllabus; transactional discourse and interactional discourse.
Based on basic competition of Kurikulum 2013 especially in the term of social
competition the objective of teaching English in Vocational High School is
achieving ability to use English language for transactional and interactional
function.5 Therefore, based on that statement students of Vocational High School in Indonesia are required to be able to produce and to understand both
of transactional and interpersonal discourse.
The classification of English language discourse in Kurikulum 2013 is
similar with Richard’s statements about the classification of spoken discourse. According to Richard, spoken discourse are classified into two: interactional
and transactional. Interactional discourse gives more attention on maintaining
good interaction between the participants than on giving the information to the
participants. On the contrary, transactional discourse focuses on using
language to communicate the information to other participant.6
Based on the explanation above can be summed up that interactional
discourse is social interaction oriented. It means that the purpose of
communication is to build a good interaction among the participant and less
5
Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan Republik Indonesia, Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan Republik Indonesia No. 70 Tahun 2013, p. 86.
6
concern on communicating the information itself. On the other hand,
transactional discourse is message oriented, it means that the purpose of
communication among the speakers is communicating the information in
effective, accurate and coherence way.
On the other hand, as stated by Nation and Newton speaking interactions
classify into transactional speaking and interactional speaking. Transactional
speaking is known also as formal speaking; whereas interactional speaking is
known as informal speaking.7 This argumentation shows the classification of speaking based on the degree of formality of the language being used in
speaking and the purpose of speaking itself. In interactional speaking,
speakers commonly use informal language. In this interaction building
relationship among the speakers seems more important than conveying
speakers’ message. On the contrary, in transactional speaking, speakers commonly use formal language and give more focus on using language items
for conveying their message to the other speakers than maintaining social
relationship among the speakers.
Furthermore, Nation and Newton explanation about transactional and
interactional speaking which has been mentioned before is similar with Farrell
statements in his book “Succeeding with English Language Learners”. He said that there are two reasons why people engage in communication: first is
interpersonal reason and second is transactional reason.8 Through that statement can be concluded that there are some reason why people keep
communicating: the first reason is they want to socialize with people around
them (interpersonal reason) and the second reason is they want to exchange
the information about something specific with people around them
(transactional reason).
Furthermore, there are other spoken discourse which is known as
long-turn and short-turn spoken discourse. Brown and Yule in their book
7
I. S. P Nation, J. Newton, Teaching ESL/EFL Listening and Speaking, (New York: Routledge, 2009), pp. 120- 121.
8
“Teaching the Spoken Language” explain that a long-turn discourse consists
of a long utterance that may end as long as hour’s lecture; meanwhile a short-turn discourse consists of only one or two utterances. A short-turn speaking
discourse commonly unburden the speakers while producing its structure;
whereas a long-turn speaking discourse commonly demanding the speakers
while producing its structure because they have to be responsible to produce a
sequence of well-structured utterance for helping their listeners to draw a
coherent representation of their messages.9
The explanation above shows that spoken discourses are classified into
two: short-turn and long-turn spoken discourse. Short-turn spoken discourse
consists of short utterances and because of its simple form the speakers
commonly do not find any serious difficulties while creating its discourse. On
the contrary, long-turn spoken discourse consists of longer utterances than its
predecessor and because of its complicated form the speakers can feel a
burdensome feeling for producing long and complicated structure. Speakers’
burden when producing long-turn spoken discourse not only comes from
speakers’ responsibility for achieving cohesion and coherence of the discourse but also comes from speakers’ responsibility for assuring that their listeners
achieve their messages clearly.
In consequence, from the explanations of experts above can be concluded
that there are many kinds of speaking discourse based on its function, they are:
transactional discourse which concerns on information exchange,
interactional discourse which concerns on maintaining social relationship
among the speakers, long-turn discourse and short-turn discourse which
concern on the length and the complexity production of conversational
structures.
3.
Techniques for Teaching Speaking
Before discussing about the techniques of teaching speaking skill, it is
essential to know that based on linguistic study human are born with the
9
ability for acquiring the language. This basic ability is given by God through
the existence of human brain. In the early age of human development, the
process of acquiring first language begin by receiving language input through
the interaction of the language users around them. Furthermore, by the
development of their speech organ human begin to produce utterances from
the language input which is known as language output.
Based on input and output theory Harmer suggests the three stages of
language teaching and learning to teach productive skill such as speaking that
aimed for increasing communicative competence: first, Introducing new
language; second, practice; third, communicative activities.10 From that classification can be elaborated that in the first stage teachers should explain
clearly the information about the target language including: its meaning, the
way to use the language, the grammatical form of the language, then the
pronunciation and the written form of the target language. Moreover, in the
second stage, teachers should provide a chance for learners to practice the
language. In this stage learners will practice to communicate using the target
language in more controlled way. Finally, in the third stage teachers should
stimulate the communication between learners and learners or between
learners and teachers through learning activities. In this activity learners will
practice to use the target language in less controlled way or they are allowed
to modify the target language based on their own creativity.
In addition, Woods reports that according to Cajkler and Addelman there
is a current model of language teaching which consists of presentation,
practice, and communicative activity. They point out that teachers’ oral input,
learners’ practice, and oral’s model repetition are essential for acquiring the target language. On the other hand, Woods adds that without a sufficient target
language input teachers’ cannot expect target language output from their learners.11 This argumentation shows about the importance of input and output
10
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching, Third Edition, (New York: Longman Publishing, 1991), pp. 50-51.
11
language exposure for learners’ successful achievement of the target language
acquisition. This argumentation upholds the previous opinion about the three
stages of language learning based on input and output theory.
Moreover, there are also some useful and joyful techniques for teaching
speaking according to some experts:
a.
Discussion
Discussion is one of language teaching technique that emphasizes on
giving language learners opportunity to practice communicating through the
target language. According to Ur, discussion considers as “the most natural and effective way for learners to practise talking freely in English is by
thinking some problem or situation together through verbal interchange of
idea”.12
This statement shows that discussion is the most natural and effective
learning activity for the language learners practicing their speaking skill. In
this activity they can share their idea orally and freely through communication
activity which is at the same time learners also can get the opportunity for
practicing the target language.
In Getting Students to Talk Galebiowska defines discussion as “a
communicative activity in which learners retain their own personalities and
views. Their task is to come to an agreement regarding an issue which is
introduced by the teacher.”13
From that definition can be summed up that
discussion is a kind of communicative activity that requires learners’ effort on
upholding their views and argumentations. In this activity learners usually will
be asked to reach an agreement through communication activity depends on
the issue which is given by their teacher.
Furthermore, based on Harmer’s argumentation discussion is a useful
activity to promote the fluent use of language. He adds that teacher should
consider some important things before beginning the discussion such as giving
thinking time for each participant and giving each group enough time for
12
Penny Ur, Discussion that Work, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007), p. 2. 13
preparing their argumentation.14 From that statement can be concluded that discussion can be used as a language learning technique which promotes
language practice for learners. Before beginning the discussion teachers
should prepare and encourage their learners to speak by giving them enough
time for thinking about the topic that will be discussed.
In consequence, the three argumentations of the experts above show that
discussion is a kind of activity which prompts the language practice for the
learners. In this activity learners will be asked to reach an agreement through
verbal communication and they also will be asked to share their opinion about
the topic that will be discussed. Moreover, before using this technique for
communication practice in the class teachers should consider some necessary
things to do such as giving some thinking time for learners before beginning
the discussion.
b.
Problem Solving
Problem solving is one of teaching speaking technique that brings the
communicative purpose into learning. According to McDonough and Shaw
problem solving technique provides the opportunity for the learners to discuss
in small group or pairs. In this activity learners can decide and discuss some
reasons for each case which is provided by their teacher.15 From this statement can be concluded that problem solving activity is a kind of activity that
provides the opportunity for practicing the use of target language in
communicative way and for increasing learners’ involvement and cooperativeness during learning process.
Moreover, problem solving is also known as a kind of activity which
insists on using the target language for solving the task and for finding the
solution for each problem which is given by their teacher. This explanation is
taken from Harmer’s statement in his book “The Practice of English
14
Jeremy Harmer, How to Teach English, (Essex: Pearson Education Limited, 2007), p. 128.
15
Language Teaching”, he said “problem solving activities encourage students to talk together to find a solution to (a set of) problems or tasks.”16
In consequence, from the explanation above can be concluded that
problem solving activity can provide language learners with the opportunity
for practicing the target language. Moreover, it also can provide the learners
with the opportunity for solving and finding the solution of problem which is
given by their teacher through small group or pair discussion.
c.
Role Play/Simulation
Role play or simulation is one of language teaching technique that gives
learners opportunity for practicing the language in similar condition of
real-life situation. Harmer states that “simulation and role-play can be used to
encourage general oral fluency or to train students for specific situation,
especially when they are studying English for specific purposes (ESP)”.17 Based on the statement mentioned before role-play and simulation is one of
language teaching technique that emphasizes on giving learners opportunity
for doing communication practice in specific situation. In this activity, firstly
teacher will set up the condition of classroom based on learning topic then
learners will be asked to play different roles or character such as act as a
secretary, director, officer, or so on in order to accomplish learning task.
According to Ur, role-play likely to be a small group discussion that each
member of group will be given situation and roles to act and will be asked to
explore their roles. Role-play also can increase the learners’ opportunity for
doing communication practice based on real-life situation.18 From that statement can be concluded that in role-play learners will work in small group
or pairs and will be given a situation then they will be asked to play and to
explore their role creatively. Furthermore, role-play not only can give learners
16
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching, Third Edition, (New York: Longman Publishing, 1991), p. 129.
17
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching, Fourth Edition, (Essex: Pearson Education Limited, 2007), p. 352.
18
an experience of practicing communication in real-life situation but also can
improve learners’ opportunity for using the target language.
In “Materials and Methods in ELT” McDonough and Shaw informs that role-play is one way to make learners speak in different social context and to
experience some variations of social role. Role-play is considered as a „social
interaction activity’ that requires learners’ ability for maintaining and
establishing social relationship among the participant.19 This statement shows that role-play is useful not only for giving learners opportunity to speak in
different social context and to play different roles in society but also for giving
learners the opportunity to use the target language for maintaining and
establishing social relationship.
Therefore based on the explanation from the experts above can be
concluded that role-play can provide learners with communication practice of
the target language and give them the opportunity to use that language not
only in real-life situation but also in social context thus they can learn useful
technique for maintaining social relationship among the participants.
4.
The Objective of Teaching Speaking in Vocational High School
Since the development of modern world and competitiveness among
global countries, the need for developing educational quality in Indonesia
seems to be important. The intention for developing Indonesian educational
quality can be seen from Educational Ministry serious action on developing
Indonesian educational curriculum in simultaneous way.
The newest curriculum which is used in Indonesia is Kurikulum 2013 that
using PP No. 70 Tahun 2013 as its basic foundation for developing its
syllabus and its learning materials. Based on PP No. 70 Tahun 2013 the
objectives of teaching speaking in Vocational High School are stated in
Kompetensi Dasar (KD): students are required not only being competent on
explaining, questioning, and responding the information about themselves
19
through the target language in order to achieve social functions but also
required being communicative competence for greeting, praising, questioning
about someone’s purpose, responding to someone’s regard, and
communicating about past and future event.20 From that regulation can be summed up that the objective of teaching speaking in Vocational High School
is achieving transactional and interpersonal function.
Moreover, based on PP No. 32 Tahun 2013 pasal 77K, teaching English in
Vocational High School is considered as a general content subject that must be
taught to the learners.21 The elaboration of this regulation appears in PP No.70 Tahun 2013 that in order to assimilate the learning contents in both of Senior
High School and Vocational High School; therefore the Ministry of Education
in Indonesia develops a structural curriculum which is known as ‘Struktur
Kurikulum Pendidikan Menengah’.22 Based on that curriculum the allocation for teaching English subject in Vocational High School is once a week and as
the result of the generalization of learning objective which is stated in
Kurikulum 2013 most of English Teachers in Vocational High School
especially in SMKN 3 Tangerang decided to support their learners competency
in mastering English language by initiating the enrichment of learners’
vocabulary mastery based on their majority.
Furthermore, there are some experts’ argumentations about the objective
of teaching speaking. Most of them agree that the objective of teaching
speaking should be speaking competency or on the other word capability to
communicate through the target language. In Fluency and its Teaching,
Guillot instructs that fluency on the foreign language point of view is known
as a degree in communication proficiency that consists of: (1) capability in
producing both of spoken and written form of language easily; (2) capability
in speaking with a good intonation, vocabulary, and grammar; (3) capability in
20
Menteri Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan Republik Indonesia, Op.cit., pp. 86- 92. 21
Presiden Republik Indonesia, Peraturan Pemerintah Republik Indonesia No. 32 Tahun 2013, p. 26.
22
communicating idea in an effective way; and (4) capability in continuing
speech without obstructing the comprehensible of information or breaking the
communication.23
The statement above elaborates that fluency in speaking considers as a
skill or an ability to communicate easily with a good but not necessary perfect
intonation, vocabulary and grammar. It also requires both of the ability to
deliver an idea in an effective way and the ability to control the conversation
flow as good as possible. Therefore, in order to achieve the objective of
learning speaking (speaking fluency) learners are required to be able to
communicate easily and effectively in the target language.
Furthermore, in Getting Students to Talk, Colebiowska states that the aim
of teaching English should encourage the learners to be able to communicate
in English language therefore preparing the learners with a task which
concerns with a real-life communication considers as a very important aspect
for achieving a successful communication.24 From that explanation can be concluded that providing learners with real-life communication task can help
them developing their communicative skill. This condition occurs as the effect
of their familiarity with the communication in the target language which also
can improve the successful of communication practice among the learners in
the class.
On the other hand, Byrne declares that the main goal of teaching speaking
is oral fluency which defines as the ability to express someone or some idea
clearly, wisely, accurately without so much confusion.25 The argumentation about oral fluency as the objective of teaching speaking derives from the fact
that in communication process sometimes people experience a communication
breakdown. Communication breakdown can occur because the listeners
uninterested with the topic had been discussed or get impatient to wait the
other speakers' responds. Therefore, in order to avoid communication
23
Marie-Noelle Guillot, Fluency and its Teaching, (Clevedon: Multilingual Matters Ltd, 1999), p. 26.
24
Colebiowska, Op.cit., p. 1. 25
breakdown and to possess the ability to speak fluently, bringing the learners
from model imitation stage or drilling practice to the communicative stage or
communication practice in less controlled way is very useful for giving the
learners an opportunity to do communication practice in the target language
and for expressing their idea freely.
In addition, Hammerly reports that most of second-language advocates do
not care about students’ mispronunciation because it can be reduced through communicative classroom interaction. In contrast with Hammerly’s
argumentation, Ur asserted that the aim of improving pronunciation is not for
achieving native alike accent but for achieving accurate pronunciation in order
to be understandable and comprehensible enough for other speakers.26
The argumentation above up holds the argumentation of communicative
approach advocates. They state that in the beginning of learning stage
developing learners’ vocabulary is considered very important and focusing on the accuracy of language structure production is considered less important
because students’ mistake in pronouncing words, in using inappropriate
affixes, and in making incorrect grammatical sentences will disappear
gradually through communicative activity in the class. This condition appears
as the result of students’ familiarity of the target language structure. On the
contrary, another expert argued that improving students’ pronunciation
considered very important. Even though the aim of improving students’
pronunciation not to achieve native alike pronunciation but improving
students’ pronunciation is important to achieve a successful communication activity among the speakers and to avoid misunderstanding between them as
the result of mispronouncing words.
In consequence, some of experts’ argumentations about the objective of
teaching speaking which have been mentioned above lead to the conclusion
that most of experts agree that the objective of teaching speaking is
developing communication competency or fluency in speaking. On the other
hand, cannot be neglected that some of speaking sub-skills also give some
26
contributions to the successfulness of communication even though these
sub-skills are not the main objective of teaching speaking. The argumentations
about the objective of teaching speaking according to the experts actually in
line with the objective of teaching speaking in Indonesia that aimed to achieve
transactional and interpersonal function.
5.
Teacher Roles in Teaching Speaking
According to some experts, teachers need to play some roles during
speaking activity for making their learners speak fluently and for achieving a
successful learning process. The following explanation will focused on
describing teachers’ role in speaking class based on some educational experts’
argumentation:
a) Prompter
When acting as prompter teachers are responsible on helping the learners
come over their problem when they get stuck on the idea they are going
to say in the middle of the activity. Teachers also have to make sure that
their help shouldn’t break up the activity or make it out of the role in
order to prevent students’ frustration feeling.
b) Participant
Sometimes teachers also can take a role as participant, they can
participate in learners’ activity by informing them about new information
in order to keep the activity running on its track. Teachers also have to
maintain learners’ engagement on the activity by setting up an interesting
and clear task. They also should provide a creative learning environment
by giving their learners some suggestion in the middle of activity without
making themselves as a dominant participant during learning process.
c) Feedback provider
Teachers as feedback providers need to be aware of different effect from
different feedback approach, for instance, teachers over correction on
learners’ performance can cause the absence of communicativeness from learning activity because students especially who is over corrected by
quite instead of speaking up and making another mistake. On the
contrary, teachers should make gentle correction which can help their
students overcome from difficult situation such as misunderstanding or
hesitation during learning process.27 d) Controller
When teachers acting as controller they have to walk around the class to
ensure that their students are performing their tasks well and doing their
task on the right track. Teachers also have to check out students’
performance in the small group or pairs and see whether their students
need their help or not. Moreover, they also have to make sure that their
students share the same opportunity for making contribution during
learning process.
e) Observer/ analyzer
Teachers’ role as observer or analyzer is observing or analyzing students’ problem during learning process. Teachers should make some observation
on students’ performance in order to ensure that their students are capable
of expressing themselves in the target language and in order to provide
sufficient opportunities for the students for practicing the target language
in the class and outside the class.28 f) Assessor
Teachers’ obligation as assessor is assessing students’ performance thus with this action teachers will know how well students understanding
about the materials which have been taught and how well students
perform their task. Another obligation that should be done by teachers as
the assessor are correcting students mistakes during learning activity and
organizing feedback for their students in order to point out students
successful or failure in performing their task and then when students find
some problems in the middle of learning process, teachers can help
students to solve their problem.
27
Jeremy Harmer, Op.cit.,pp. 347-348. 28
g) Organizer
Teachers’ role as organizer considers as a difficult role to play because
teacher skill in organizing the class will determine both of successful and
failure of a learning process. Teachers are expected to be a good
organizer in setting up learning materials and students’ activity in the
class. Teachers also have to make sure that students get clear information
about the task that will be performed by them during the activity in order
to achieve a successful learning process.
h) Tutor
Teachers’ role as a tutor is acting as a coach and students’ resource; then while students find any difficulties or problems in their project they can
ask their teachers to give some advice or guidance to help them solving
their problems. Teachers’ role as a tutor considers as a broader role than
others because as a tutor teacher required to be able to integrate the other
roles such as organizer, prompter, and students’ resource.29
In conclusion, from the explanation above can be concluded that teachers’
ability for doing their roles in the class are very important to establish and to
determine a successful of language teaching process in the class.
6.
The Characteristics of Successful Speaking Activity
Every teacher expects to accomplish a successful learning process and in
order to know whether their learning process success or fail, teachers need to
know the characteristics of a successful learning process. In “A Course in
Language Teaching” Ur reports that a successful speaking activity has some characteristic such as: (1) learners talk a lot; (2) participation is even; (3)
motivation is high; and (4) language is of an acceptable level.30
Therefore, from the explanation above can be elaborated that in a
successful speaking activity learners will talk a lot during the learning process
29
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching, Third Edition, (New York: Longman Publishing, 1991), pp. 236- 242.
30
and there is no domination of minority students in speaking activity and every
learner participate actively during learning process or on the other words
learners will equally share the opportunity to talk and to make contribution
during learning process. Moreover, learners’ motivation to speak during
speaking activity is high because they are interested in the topic being
discussed then they want to give an active contribution in order to accomplish
learning objective. The last characteristic is learners’ mastery of acceptable
language level which means that learners’ language are easy to understand
with the other participants and they level of language accuracy are good
enough.
In addition, McDonough and Shaw stated: “successful completion of this
type of activity (communication game activity) clearly depends on the
effective communicative use of the language and of the sharing of information
amongst the participants”.31 From that statement can be elaborated that in communication game activity the objective of speaking activity only can be
accomplished successfully if learners can communicate effectively through the
target language thus with this ability they also can share the information
successfully.
In conclusion, based on the elaboration of the experts above a successful
speaking activity can be indicated by some characteristic such as the amount
of communication that occurs between the learners, learners’ active
contribution during learning process, learners’ motivation to accomplish the
learning objective, and learners’ ability to communicate effectively through the target language.
B.
Game
1.
The Definition of Game
Most of people love to play games because of the joyful and the
interesting feeling which provided by games. In Games for Language
31
Learning, game defines as an exciting and joyful activity which sometimes
challenges its players to play and to interact with others players.32
Points out the definition of game stated above can be summed up that in
spite of exciting and joyful sensation provided by game, it also more
emphasizes on the challenging aspect rather than competitive aspect in its
activity because in competition students against each other and the strongest
party considers as a winner and the weakest party considers as a looser thus
the gap between the winner and the looser can decries the looser participation
during this activity. In contrast, a challenging activity will inspire the
participants to do their best without worrying too much of being not good
(looser) in doing this activity.
Moreover, the idea of game as an interesting and joyful activity also
supported by the other expert such as Ur; in “Five Minutes Activities” Ur and Wright define game as “amusing item to round off the lesson with a smile.”33 From that statement can be concluded that game is an entertaining activity
which can make learning process full of happiness. When teaching a new
language in the class teachers need to include some points such as a new
grammatical point, grammatical exercise, or text reading and when those
learning points being taught in monotonous technique learners will feel bored;
therefore to avoid this problem teachers can initiate to use game as their
teaching technique.
Furthermore, Harmer’s explanation about game in “The Practice of English Language Teaching” also similar with the explanation that has been mentioned above; Harmer defines games as an important equipment for
teachers because of their usefulness for language practice and their relaxing
effect for learners. Moreover, he adds that game can provide a challenging and
interesting activity and also capable of cheering up students’ English class
even in the end of a long day.34 From that statement be summed up that games
32
Wright et al, Op.cit., p.1. 33
Penny Ur, Andrew Wright, Five-Minutes Activity, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007), p. x.
34
consider as teachers’ important tools in language teaching. This argumentation
comes from the usefulness that provided by game such as: the opportunity for
learners to practice the target language, game brings joyful feeling while
learning a language, game also can make learning activity more challenging
and interesting which making learning process more cheerful even at the end
of session.
Moreover, game considers also as highly motivated activity because of its
amusing and challenging characteristic. Game not only gives students break
time from a hard and frustrating learning process but also give them a chance
for practicing language skill.35 From that statement can be concluded that game is very useful because it can motivate students through its challenging
and interesting activity, it can give students a break from a hard learning
process and an obligation for catching lots of learning points, and it also can
give students opportunity for practicing the target language.
In consequence, under pinned the definitions mentioned by some experts
above game considers as an interesting and joyful activity which gives a lot of
advantages for language learners such as cooperative work among the
students, challenging feeling for every learner which can prompt their effort
for doing the best to complete their task, and moreover can make learning
process becomes an interesting activity which makes their English class more
entertaining and provides more opportunity for practicing the target language.
2.
Kind of Speaking Games
Some of educational practitioners and experts such as Harmer, Ur,
McDonough, Shaw, and so on agree that there are many kind of games which
can be used as speaking activity such as information-gap game, describing
pictures, and find someone who game.
a.
Information-gap
One of purpose of communication is interchanging information between
the speakers or on the other word there is a gap of information between one
35
speaker and the other speaker. Therefore in order to provide communication
practice activity to the learners information gap is adopted as one of teaching
technique in speaking. According to Harmer information gap is “where two
speakers have different bits of information, and they can only complete the
whole picture by sharing that information because they have different
information, there is a „gap’ between them”.36
Based on that statement can be
elaborated that information-gap is a kind of activity which requires the act of
sharing information among the learners in order to accomplish their learning
task. In this activity each learner will be given a different piece of information.
In Teaching and Assessing Skill in Foreign Languages Scrivener reports
that the aim of information-gap activity is to make the students using the
language which is taught in the class to interact in real and meaningful
situation by exchanging the information.37 From that statement can be summed up that information-gap activity is a kind of activity which provides
the learners with an opportunity for doing communication practice in real and
meaningful situation. In this activity learners are required to exchange the
information with their friends in order to complete their task.
Moreover, Harmer in his book The Practice of English Language
Teaching explains that information-gap activity is a kind of communication
game which urges one learner to talk to a partner in order to solve a puzzle, to
describe and to draw a picture, and so on.38 This statement explains that information-gap activity prompts learners’ willingness to talk to their friends
in order to seek for useful information which is used for completing their task.
Consequently, by the statements’ of the experts above can be summarized
that information-gap activity is an activity that prompts learners to use the
target language in real and meaningful situation for completing the gap of
information that occurs between them.
36
Jeremy Harmer, How to Teach English, (Essex: Pearson Education Limited, 2007), p. 129.
37
Woods, Op.cit., p. 47. 38
b.
Describing Pictures
In this activity learners will be divided into small group and ach group will
be given a picture which can be seen by all of members of the group. Each
member will be asked to