Informasi Dokumen
- Penulis:
- Harbi D Girsang
- Pengajar:
- Bapak Prof. Dr. Azhar Maksum, M.Ec.Ac
- Bapak Wahyu Ario Pratomo, SE, M.Ec
- Bapak Drs. Syahrir Hakim Nasution, M.Si
- Bapak Irsyad Lubis, SE, M.Soc, Sc, Ph.D
- Bapak Paidi Hidayat, SE, M.Si
- Sekolah: Universitas Sumatera Utara
- Mata Pelajaran: Ekonomi Pembangunan
- Topik: Analisis Strategi Pengembangan Objek Wisata Air Terjun Sipiso-Piso
- Tipe: skripsi
- Tahun: 2013
- Kota: Medan
Ringkasan Dokumen
I. Introduction
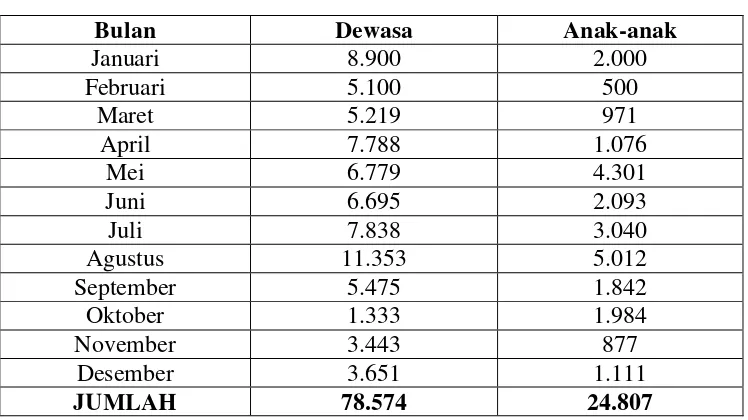
The introduction outlines the significance of developing the Sipiso-Piso waterfall as a tourist attraction in Karo Regency. It highlights the decline in visitor numbers due to inadequate government support, high infrastructure costs, and unfriendly local culture. The importance of strategic tourism development is emphasized, with a focus on leveraging local resources and improving community welfare. The section sets the stage for the analysis of tourism development strategies using methods like SWOT and AHP, aiming to enhance the appeal of Sipiso-Piso to tourists.
II. Theoretical Framework
This section reviews relevant theories and concepts in tourism, including definitions, elements, types of tourism, and the motivations of tourists. It discusses the importance of understanding the tourism market and the various factors influencing tourist behavior. The frameworks provided serve as a foundation for analyzing the potential of Sipiso-Piso as a tourist destination, ensuring that strategies align with both market trends and visitor expectations. This theoretical grounding is crucial for developing effective tourism strategies.
2.1 Definition of Tourism
Tourism is defined as the act of traveling for leisure or business, encompassing various activities and experiences. Understanding this definition is essential for developing targeted strategies that cater to the needs of different types of tourists, particularly in the context of Sipiso-Piso.
2.2 Elements of Tourism
Key elements of tourism include government policy, shopping opportunities, promotions, pricing, transportation, accommodation, attractions, distance, and hospitality. Analyzing these elements helps identify areas for improvement at Sipiso-Piso, such as enhancing local amenities and services to boost tourist satisfaction.
2.3 Types of Tourism
Tourism can be categorized into various types, such as cultural, health, adventure, and ecological tourism. Sipiso-Piso primarily fits into adventure tourism, which can be leveraged to attract visitors seeking unique and immersive experiences in nature.
2.4 Tourist Motivation
Motivations for travel vary among tourists, influenced by physical, cultural, social, and fantasy factors. Understanding these motivations is vital for designing marketing strategies that resonate with potential visitors to Sipiso-Piso, ultimately driving higher visitation rates.
III. Research Methodology
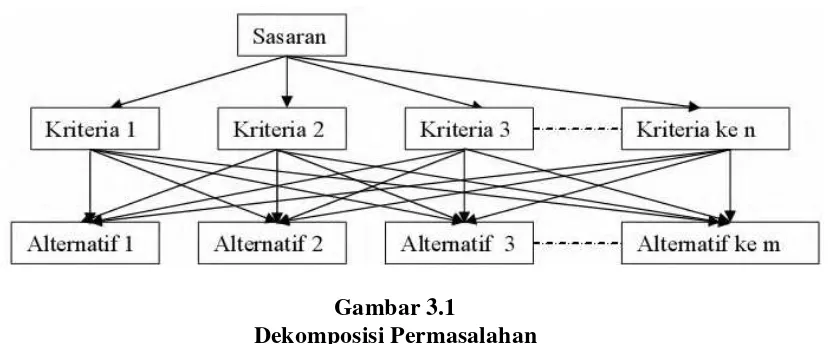
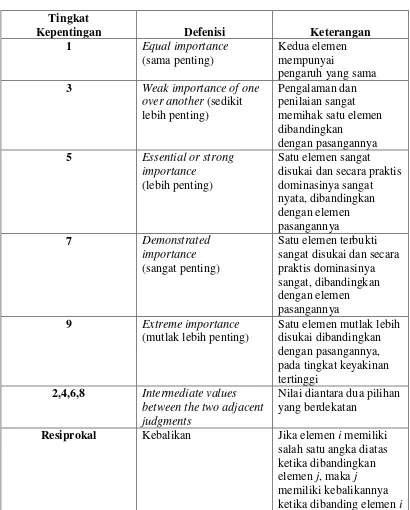
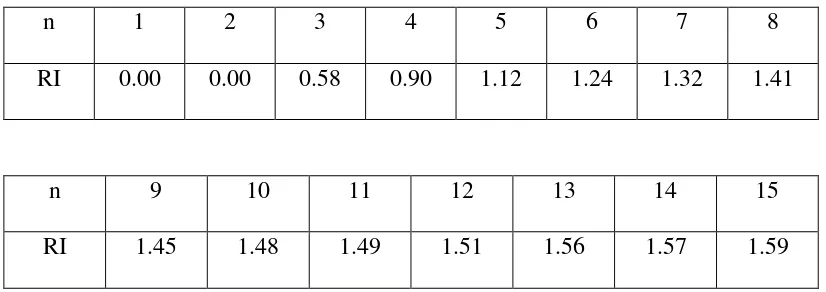
This section describes the research methods employed in the study, including data collection techniques and analytical frameworks. The Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP), EFAS-IFAS, and SWOT analysis are highlighted as key tools for evaluating the tourism development strategies for Sipiso-Piso. This methodological rigor ensures that the findings are credible and actionable, providing a solid basis for recommendations.
3.1 Research Methods
The study utilizes qualitative and quantitative research methods to gather comprehensive data on the tourism potential of Sipiso-Piso. This mixed-methods approach allows for a nuanced understanding of both visitor experiences and stakeholder perspectives.
3.2 Data Collection Locations
Research was conducted in Karo Regency, focusing on the Sipiso-Piso area. This localized approach ensures that the findings are relevant to the specific context and challenges faced by the region in terms of tourism development.
3.3 Data Sources
Data was collected from various sources, including surveys, interviews with local stakeholders, and existing literature on tourism in the region. This diverse data set enriches the analysis and supports robust conclusions.
IV. Discussion
The discussion section synthesizes the findings from the analysis, addressing the current state of the Sipiso-Piso tourism sector. It explores the morphological conditions of the waterfall, the role of local government, community perceptions, and the effectiveness of existing tourism strategies. This comprehensive discussion informs the strategic recommendations for enhancing tourism at Sipiso-Piso.
4.1 Morphological Conditions
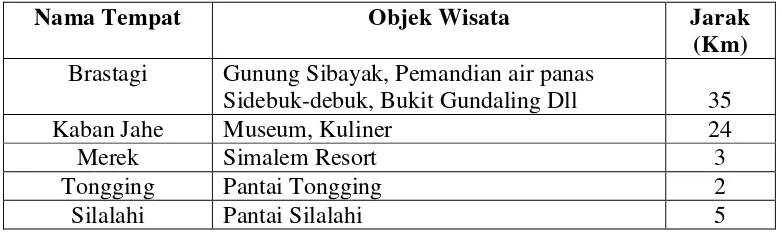
The geographical and climatic conditions of Sipiso-Piso are analyzed to understand their impact on tourism. The area's natural beauty and accessibility are crucial factors that can be leveraged in promotional strategies.
4.2 Community Perceptions
Understanding local community perceptions regarding tourism is essential for fostering a supportive environment for development. Engaging the community in tourism initiatives can enhance both visitor experiences and local livelihoods.
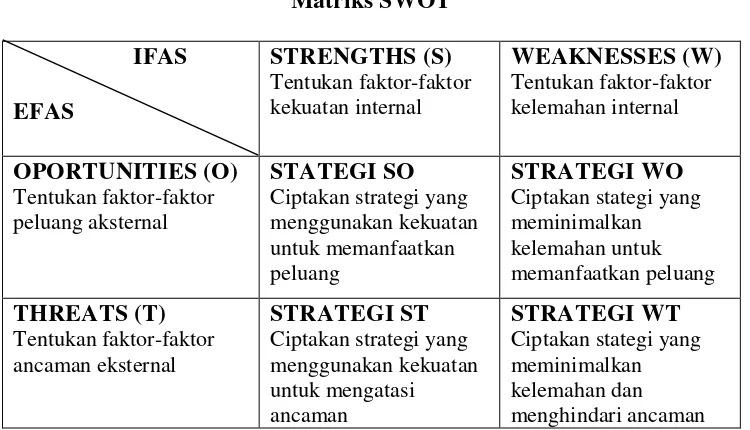
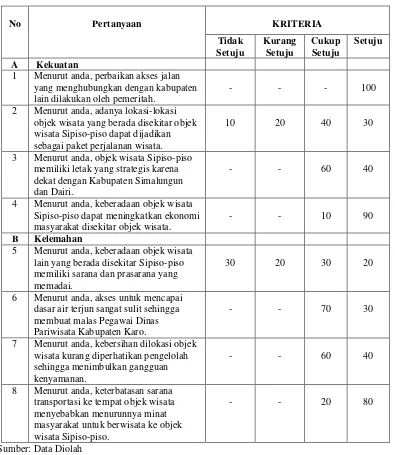
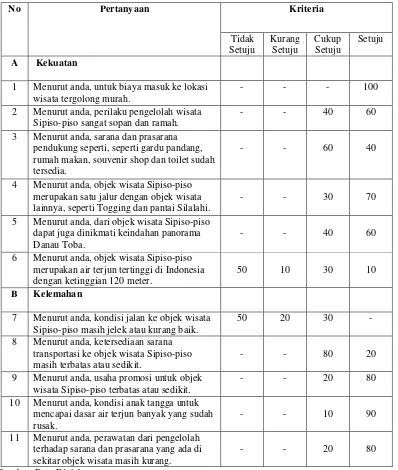
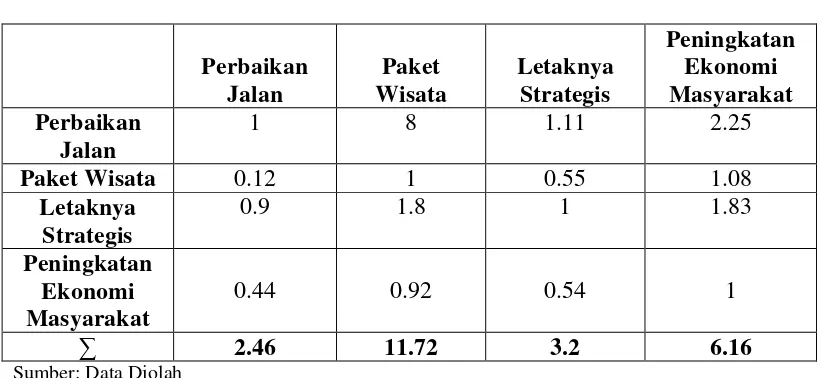
4.3 SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis identifies the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to Sipiso-Piso tourism. This framework provides insights into strategic areas for improvement and potential growth avenues.
V. Conclusion and Recommendations
The concluding section summarizes the key findings of the study and offers actionable recommendations for the development of Sipiso-Piso as a premier tourist destination. Emphasis is placed on the need for collaborative efforts among stakeholders, improved infrastructure, and targeted marketing strategies to enhance tourist attraction and satisfaction.
5.1 Conclusions
The study concludes that with strategic planning and community involvement, Sipiso-Piso can significantly increase its attractiveness as a tourist destination, benefiting both visitors and the local economy.
5.2 Recommendations
Recommendations include enhancing infrastructure, promoting local culture, and establishing partnerships between government and local businesses to create a sustainable tourism ecosystem at Sipiso-Piso.
Referensi Dokumen
- Psikologi Pelayanan Wisata ( Gramedia )