AN ANALYSIS OF VERB PHRASE FOUND IN THE SELECTED ARTICLES OF TEMPO MAGAZINE
A THESIS
BY:
RONI ABRAHAM SIMANGUNSONG REG.NO. 090705034
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH
AN ANALYSIS OF VERB PHRASE FOUND IN THE SELECTED ARTICLES OF TEMPO MAGAZINE
A THESIS
BY:
RONI ABRAHAM SIMANGUNSONG REG.NO. 090705034
SUPERVISOR CO-SUPERVISOR
_________________ __________________
Dr. Deliana, M.Hum Drs. Yulianus Harefa, M.Ed. TESOL
Submitted to Faculty of Cultural Studies University of Sumatera Utara Medan in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Sarjana Sastra from Department of English.
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH
Approved by the Department of English, Faculty of Cultural Studies University of Sumatera Utara (USU) Medan as thesis for The Sarjana Sastra Examination.
Head, Secretary,
_________________ _____________________
Accepted by the Board of Examiners in partial fulfillment of requirements for the degree of Sarjana Sastra from the Department of English, Faculty of Cultural Studies University of Sumatera Utara, Medan.
The Examination is held in Department of English Faculty of Cultural Studies University of Sumatera Utara on 23 May 2014
Dean of Faculty of Cultural Studies University of Sumatera Utara
Dr. H. Syahron Lubis, MA NIP. 19511013 197603 1 001
Board of Examiners
Dr. H. Muhizar Muchtar, MS ...
Rahmadsyah Rangkuti, MA. Ph.D ...
Dr. Deliana, M.Hum ...
AUTHOR’S DECLARATION
I, RONI ABRAHAM SIMANGUNSONG DECLARE THAT I AM THE SOLE AUTHOR OF THIS THESIS EXCEPT WHERE REFERENCE IS MADE IN THE TEXT OF THIS THESIS. THIS THESIS CONTAINS NO MATERIAL PUBLISHED ELSEWHERE OR EXTRACTED IN WHOLE OR IN PART FROM A THESIS BY WHICH A HAVE QUALIFIED FOR OR AWARDED ANOTHER DEGREE. NO OTHER PERSON’S WORK HAS BEEN USED WITHOUT DUE ACKNOWLEDGMENTS IN THE MAIN TEXT OF THIS THESIS. THIS THESIS HAS NOT BEEN SUBMITTED FOR THE AWARD OF ANOTHER DEGREE IN ANY TERTIARY EDUCATION.
Signed : ……….
COPYRIGHT DECLARATION
NAME : RONI ABRAHAM SIMANGUNSONG
TITLE OF THESIS : AN ANALYSIS OF VERB PHRASE FOUND IN THE SELECTED ARTICLES OF TEMPO MAGAZINE
QUALIFICATION : S-1/ SARJANA SASTRA DEPARTMENT : ENGLISH
I AM WILLING THAT MY THESIS SHOULD BE AVAILABLE FOR REPRODUCTION AT THE DISCRETION OF THE LIBRARIAN OF DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH, FACULTY OF CULTURAL STUDIES, UNIVERSITY OF SUMATERA UTARA ON THE UNDERSTANDING THAT USERS ARE MADE AWARE OF THEIR OBLIGATION UNDER THE LAW OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA.
ABSTRAK
ABSTRACT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
AUTHOR’S DECLARATION………...i
COPYRIGHT DECLARATION………...ii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT………..iii
ABSTRAK………iv
ABSTRACT……….…….v
TABLE OF CONTENTS………vi
I. INTRODUCTION 1.1Background of the Study……….1
1.2Problem of the Study………...4
1.3Objective of the Study……….4
1.4Scope of the Study………...5
1.5Significance of the Study……….5
II. REVIEW OF LITERATURE 2.1 Definition of Verb Phrase………...6
2.2 Forms of Verb Phrase……….………..8
2.2.1 Active Forms………...8
2.2.2 Passive Forms………..9
2.3 Kinds of Verb Phrase……….………..10
2.3.1 Tense………...10
2.3.2 Aspect………....…...13
III. METHOD OF RESEARCH
3.1 Research Method………...23
3.2 Data and Data Source………....24
3.3 Data Collecting Method………....24
3.4 Data Analyzing Method………....25
IV. ANALYSIS AND FINDING 4.1 Data Analysis...27
4.1.1 Tense...27
4.1.2 Aspect...34
4.1.3 Voice...37
4.2 Finding...50
V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION 5.1 Conclusion...55
5.2 Suggestion...55
ABSTRAK
ABSTRACT
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background of the Analysis
Language is a tool or primary means that used to communicate by human. Beside we often use spoken language, it also often used in writing or written language. Language has relationship with the sentence.
Sentence is a group of words that expresses a statement or expression. A sentence is a group of words which is usually a grammatically complete statement tied together and conveys an idea, event or description. Radford (1988) stated that all sentences have a categorical constituent structure, all sentences are hierarchically structured out of word and phrases, and each the component words and phrases in a sentence belong to a specific category. There are two level categories; they are word level categories and phrasal categories. Words belong to the various categories of different types that are Noun, Verb, Adjective, Adverb and Preposition. Meanwhile, the phrasal categories are Noun Phrases, Verb Pharases, Adjectival Phrases, Adverbial Phrases, and Preposiotional Phrases.
phrase is a group of words that makes sense but not complete sense. Sometimes, a phrase may consist of a single word or a group of words. Most phrases have a central word which defines the types of phrase; the central word is called the “head”. Phrase always has head in each word, it can be analyzed, if knows about types of phrase and knows how to form it.
Verb phrase or VP is a syntax structure composed of predicative element of a sentence and function in providing information about the subject of the sentence. All verbs that function as a predicate is verb phrase. The head of phrase is a verb and constructed from a single verb, however, the verb phrase will consist of various combinations of the main verb and any auxiliary verb, plus optionally specifier, complement, and adjunct.
Douglas (2002:42) says, verb phrase is a phrase with a verb as its head. Verb phrase has a lexical verb or primary verb as their head (i.e. their main verb). It is also called as predicate. Verbs can be grouped into three major classes according to their ability to function as main verbs or auxiliary verbs.
• Lexical verbs (e.g. run, eat, think) have function as main verbs (full verbs)
ex: Children and dog ran from side to side. He barely ate or slept that night
• Primary verbs
Primary verbs (be, have, and do) have function as both auxiliary and main verbs
His dad was an art professor. Every atom has a dense nucleus
*Primary verbs as auxiliary function Ex : He doesn’t look at the numbers. He was wearing a dark ski mask.
A particular combination of result has occurred
• Modal verbs (can, could, shall, should, will, would, may, might, must) have
function only as auxiliary verbs Ex : He should be angry for all that. He would probably like it softer.
The main verb can stand alone or be preceded by one or more auxiliary verbs. The auxiliaries further define the action, state, or process denoted by the main verbs. Verb phrases are the essential part of clause, referring to a type of state or action.
interested in analyzing it. It is also hoped that all the readers can be helped to understand about verb phrase well by this thesis.
In helping me doing the analysis, I have chosen a magazine. I chosen Tempo magazine that published in April, 21st 2013 as the source of my data. Magazine is one of literary works and also a written language. In this thesis, I use some of the selected articles Tempo Magazine. The magazine was selected because there are different kinds of verb phrase inside that can help me in writing this thesis.
1.2 Problem of the Study
In this thesis, there are some problems that will be analyzed which are related to analysis of verb phrase. They are :
1. What kinds of verb phrase are found in the selected articles of Tempo Magazine?
2. What is the most dominant kind of verb phrase that found in the selected articles of Tempo magazine?
1.3 Objectives of the Study
Based on the problems above, I try to investigate the objectives of the analysis. They are :
1. To find out kinds of verb phrase that found in the selected articles of Tempo magazine.
1.4 Scope of the Study
The scope of this thesis is about verb phrase. To avoid overlapping, and misleading discussion, I will analyze only three out of six kinds of verb phrase, they are: tense, aspect, and voice that found in the selected articles of Tempo Magazine that published in April 21st,2013.
1.5 Significances of the Study
The significances of this analysis are :
1. Give some knowledge for students to identify the kinds of verb phrase in a certain literature.
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
2.1 Defininition of Verb Phrase
Douglas (2002:42) says that, verb phrase is a phrase with a verb as its head. Verb phrase has a lexical verb or primary verb as their head (i.e. their main verb). It is also called a predicate. The main verb can stand alone or be preceded by one or more auxiliary verbs. The auxiliaries further define the action, state, or process denoted by the main verbs. Verb phrases are the essential part of clause, referring to a type of state or action.
Verb phrase or VP is a syntax structure composed of predicative element of a sentence and has function in providing information about the subject of the sentence. All verbs that function as a predicate is verb phrase. The head of phrase is a verb and constructed from a single verb, however, the verb phrase will consist of various combinations of the main verb and any auxiliary verb, plus optionally specifier, complement, and adjunct.
A main verb can stand by itself as the simple predicate of a sentence. For example : Many different people lived in the American colonies. Word `lived` is the main verb (action). In the sentence “The colonists were hardworking”, `were` has function as main verb (linking).
• Lexical verbs (e.g. run, eat, think) have function as main verbs (full verbs)
ex: - Children and dog ran from side to side. - He barely ate or slept that night
• Primary verbs
*Primary verbs (be, have, and do) have function as both auxiliary and main verbs
* Primary verbs as main verbs function: Ex : - He does my washing.
- His dad was an art professor. - Every atom has a dense nucleus
*Primary verbs as auxiliary function (with main verb underlined) Ex : - He doesn’t look at the numbers.
- He was wearing a dark ski mask.
- A particular combination of result has occurred
• Modal verbs (can, could, shall, should, will, would, may, might, must) have
function only as auxiliary verbs Ex : - He should be angry for all that.
- He would probably like it softer.
In addition, the parts of a verb phrase can be interrupted by adverbs or other adverbial. For example :
- You know the English will always have gardens whereever they find themselves. (verb phrase = will have)
- The current year has definitely started well. (verb phrase = has started)
2.2 Forms of Verb Phrase
Main forms of the verb phrase are : active forms and passive forms.
2.2.1 Active Forms
Active form is form of a verb which shows that the person or thing denoted by the subject does something (does action). It consists of simple, perfect, progressive, and perfect progressive.
2.2.1.1 Simple Sentence
Ex : 1. Present : I love her very much. 2. Past : He drunk coffee yesterday.
3. Modal : She can visits this place every sunday. 2.2.1.2Perfect Sentence
Ex : 1. Present : I have received the flower.
2. Past : I had written the letter before he arrived.
2.2.1.3Progressive Sentence
Ex : 1. Present : The boys are playing a ball.
2. Past : They were listening to the radio all evening. 3. Modal : Every body could be asking some questions.
2.2.1.4 Perfect Progressive Sentence
Ex : 1. Present : I have been sleeping for five hours. 2. Past : He had been writing a novel for two years.
3. Modal : They should have been doing their homework at the time that i called.
2.2.2 Passive Forms
Form of verb which shows that something is done to the person or thing denoted by the subject (receives some action). It consists of simple, perfect and progressive.
2.2.2.1 Simple Sentence
Ex : 1. Present : The ball is kicked by that boy.
2. Past : His letter was received by me a week ago.
3. Modal : His letter should be received by me a week ago.
2.2.2.2Perfect Sentence
Ex : 1. Present : She have been received my flower.
3. Modal : She might have been received my flower.
2.2.2.3Progressive Sentence
Ex : 1. Present : Hockey is being played by Andi .
2. Past : The radio was being listened by him last all evening. 3. Modal : Hockey might be being played by Andi.
2.3 Kinds of Verb Phrase
According to Douglas (2002:149), there are six kinds of verb phrase. They are tense, aspect, voice, modality, negation and finite clause. The writer only focuses on tense, aspect and voice.
2.3.1 Tense
grammatically a present tense but is clearly talking about something which will occur in the future.
1. Simple Present
Azar (1993:36) states that simple present is : something was true in the past, is true in the present, and will be true in the future. It is used for general statements of fact. The simple present is used to express habitual or everyday activity. According to Douglas (2004:151), there are three major meaning for simple present tense when it refers to present time:
• It can describe a state that exists at the present time.
Ex : 1. I want a packet of crisps.
2. The pigment occurs in the epidermal cells. • It can refer to a habitual action
Ex : 1. She`s vegetarian but she eats chicken. 2. He dances and moves about a lot.
• It can describe an action that is happening at the present time.
Ex : 1. Here comes your mother.
2. Oh my goodness. There he goes. Look at him walk.
The rule to form the simple present tense :
For example:
1. She watches the television everyday
2. He goes to school
.
everyday. Subject + V1 s/es + N/ Adv
3. They are students.
Adverbs which show time in these forms are as follows:
- Everyday Usually Always - Often Sometimes Seldom - Ever Never Generally, etc
Verbs that usually occur in the present tense :
Bet, doubt, know, matter, mean, mind, reckon, suppose, think, care, differ,
fancy, imply, tend and want.
2. Simple past tense
Simple past tense is most often used to refer to past time or to indicate an action completed in the past. In fictional narrative and description, the use of simple past tense is common for describing imagined past states and events.
Betty (1993:2) states that simple past tense is at one particular time in the past, this happened. It began and ended in the past.
The rule of simple past tense :
- Yesterday, last…. , - ….ago
Subject +V2 + Adj/Adv
For example:
1. I visited my grandmother yesterday
2. She went with him
. last night
3. My father was sick
. two days ago.
Verb that usually occur in the past tense :
Exclaim, eye, glance, grin, nod, pause, remark, reply, shrug, sigh, smile,
whisper, bend, bow, lean, light, park, seat, set off, shake, stare, turn away,
wave, and wrap.
2.3.2 Aspect
Douglas (2004:156) says, aspect adds time meanings to those expressed by tense. Aspect answer the question” is the event/state described by the verb completed, or is it continuing” ?
Aspect is to do with whether an action of state is complete or ongoing, recent or less recent and the length of duration.
There are two aspects in English: perfect and progressive (sometimes known as continuous).
1. The perfect aspect
a. Perfect aspect, present time ( Present Perfect)
Present perfect verbs often refer to past actions with effects that continue up to present time.
Use the following rule to form the present perfect :
The present perfect is used to indicate :
a. To show an action has been finished in the short time. It usually uses the adverb as follows:
- Already, just,
- recently, yet, since
For example: We have just read the book.
b. To show an action which has been done but that action is still has a connection with now.
For example: He has taught English since 2001
c. An action that happened more than once in the past.
For example: George has seen this movie three times.
Verbs that are common in the present perfect :
Has/have been
Ex : Rowlands has been critical of Welsh officials. Has/have got and has/have had
Ex : - Jones has got the letter.
- I have got a problem actually.
Other verbs that are common in present perfect are some of the most common
verbs overall (ex : gone, done, mad, seen, come, said, taken, become, given, shown, thought, called).
Ex : - He`s gone home.
- Experiments have shown that nitrogen deficiency tends to strengthen the lower nodes.
b. Perfect aspect , past time ( Past Perfect)
Past perfect verbs refer to actions in the past that are completed at or before a given time in the past. The actual time is often specified.
The rule to form past perfect :
Adverbs which show the time used in this time form are:
- Already, before, after,
- until, as soon as.
For example :
1. He had gone with them.
2. She had taken it herself.
Verbs that are common in the past perfect :
Like the simple past tense, past perfect verb phrases are especially common in fiction. They are used especially for reference to an earlier period in the middle of a past tense narrative :
He hadn`t even been jealous of her dead husband.
Nancy had gone with them.
He had taken it himself.
The most common verbs with the past perfect are some of the most common verbs overall. These are mostly verbs that describe physical movements and other activities (gone, come, left, given, got, ect.), speech acts (said, told), and mental perceptions or thoughts (see, heard, known).
2. Progressive aspect
Progressive aspect describes an event or state of affairs in the progress or continuing. It also describes activities or events in a progress at a particular time, usually for a limited amount of time.
• Verbs that most strongly associated with progressive aspect :
Activity/physical verbs : bleed ,chase, shop, starve, dance, drip, head (for), march, pound, rain, stream, sweat
Communication verbs : chat, joke, kid, moan, scream, talk Mental / attitude verbs : look forward, study
• Verbs that almost never occur with progressive aspect :
Activity/physical verbs : arrest, dissolve, find, invent, rule, shut, shrug, smash, throw
Communication verbs : accuse, communicate, disclose,exclaim, reply, thank Mental / attitude verbs : agree, appreciate, believe, conclude, desire, know,want, like
Perceptual states/ activities : detect, hear perceive, see
Facilitation/causation verbs : convince, guarantee, initiate, oblige, provoke
a. Progressive aspect, present tense ( Present Continuous)
Present progressive is in the progress at the present time, and probably continue.
The rule is :
Adverbs which show the time used in this time form are: Right now, at this moment/this time, at present
The functions are:
For examples:
1. They are playing kites now.
2. My father is sleeping right now.
b. To state the event or action in mean time
For example : My father is buying a car but he will sell soon.
c. To state the event or action in the future
For example: My mother and my sister are going to Bali tonight.
b. Progressive aspect, past tense ( Past Continuous)
Past progressive is in progress at particular time in the past. It probably continued. It is also used to denote an action going on at some time in the past. It also used, with always, continually etc., for persistent habits in the past. (He was always
The rule :
grumbling )
Adverbs which show the time used in this time form are: When and while
For examples :
1. He was sleeping when
2. That is why I was thinking I might hang onto the Volvo. I arrived.
3. The perfect progressive
Verb phrases can be marked for both aspects (perfect and progressive) at the same time.
a Present perfect progressive ( Present Perfect Continuous)
For an action that began in the past and is still occurring in the present.
The rule:
Adverbs which show the time used in this time form are: for and since
1. I have been waiting here for 10 years.
2. I have been studying for two hours.
b. Past perfect progressive ( Past Perfect Continuous )
The past perfect continuous is used for an action that began for a certain point in the past and continued up to that time.
The rule :
1. I had been studying for two hours before my friends came
2. I had been waiting for you for four hours before you came Subject+Have/Has+been+V-ing+O/C
2.3.3 Voice
Based on the use of verbs, transitive verb has two voice they are active voice and passive voice. Before discussing further about the active and passive voice, it is better to know definition of voice. Martin and Wren (1986:8) state, “voice is that form of a verb which is shows whether, what is denoted by the subject does something of has something done it” . Furthermore, House and Susan (1950:94) defines, “voice is the modification of a transitive verb which indicates whether subject is acting or being acted upon”. From the two quotations above, it can concluded that voice is the form of a verb, which can express the time of an occurrence of the action. Thomson and Martinet (1975:176) stated that the active and passive tense is formed by putting the verb to be into the same tense as the active verb and adding the past participle of the active verb.
1. Active Voices
When the subject of the verb represents the actor (agent), the voice is said as active voice. An active sentence is commonly structured :
For example:
The girls stole the purse
S V O
2. Passive Voices
When the subject receives or denotes the object to which the action is directed, the voice is said as passive voice. The passive voice is a structure that allows making a statement without knowing who performed the action of the sentence.
Passive voice is the change of position of the sentence. It means that in the passive forming, there is transformation process or shortly the passive voice is transformed from the active voice. There are some steps in forming the passive voice, the steps are as follows:
1. put object of the active in front of the passive voice
(Object of the active becomes the subject of the passive)
2. object of the passive becomes pronoun(i.e. personal pronoun as object)
3. add “to be” in passive which is suitable with it tense
4. put them main verb of the active after auxiliary (to be) in the verb past participle form (V3)
5. Put the agent “by” after the verb past participle.
6. For example:
- They sent James to prison for two years (active)
- James was sent to prison (by) them for two years (passive)
passive of an active tense is formed by putting the verb to be into the same tense as the active verb and adding the past participle of the active verb. The subject of the active verb becomes the agent of the passive verb. The agent is very often to be mentioned, it precedes by “by” and placed at the end of the sentence. So generally the pattern of passive voice is :
Verbs that are common in the passive voice :
Aligned (with), based (on), born, coupled (with), deemed, effected, entitled
(to), flattened, inclined, obliged, positioned, situated, stained, subjected (to),
approved, associated (with), attributed (to), classified (as), composed (of),
confined (to), designed, diagnosed (as), distributed, estimated, grouped
(with), intended, labeled, linked (to/with), located (at/in), plotted, recruited,
stored,and viewed.
CHAPTER III
METHOD OF RESEARCH
3.1 Research Method
Research method is one of the important things of scientific studies in analyzing the problems. In this thesis, some theories and opinion are applied. Research method which is used in this research is Library Research, that is by reading and studying some books also research findings concerned with the topic of the problem.
According to Nawawi (1991: 30), the activity of library research is conducted by collecting the data from some literatures, either in library or in other places. We can also use the documentation materials, magazines, newspaper, and so on, which are written as Nawawi (1991:30) says,
3.2 Data and Data Source
Source of data that used in analyzing the verb phrase is a magazine. I choose Tempo Magazine that published in April, 21st 2013. There are four articles chosen in doing the analysis. They are Bribery In Room 1201 (page 14 – 18), Fingerprints on ID Cards (page 20 – 21), Budget Master In Senayan (page 22 – 23), New Threat
From Obsolete Clause (page 31 -34). Four articles of the magazine could represent
the whole of magazine in helping me to find the kinds of verb phrase.
3.3 Data Collecting Method
Nawawi (1991:144) states that sample is a part of population to represent the whole population. The data was taken by using Purposive sampling method. According to Nawawi (1991:157) in this technique, sampling is adjusted with the purpose of the research. In other word, sample is adjusted with the certain criteria, which is decided based on the purpose of the research as Nawawi (1991:157) says,
“Purposive sampling adalah teknik pengambilan sampel yang disesuaikan dengan tujuan penelitian. Ukuran sampel the tidak dipersoalkan sebagaimana di dalam accidental sampling. pembatasan sampel hanya mengambil unit sampling yang sesuai dengan tujuan penelitian.” (Purposive sampling is a technique of taking the sample which is suitable to the purpose of research. The count of the sample is no problem as in acccidental sampling. The scope of the sample only take the unit of sample that is appropriate to the purpose of research.)
3.4 Data Analyzing Method
In writing and analyzing the data, a descriptive quantitative method was used. According to Nawawi (1991:32), this method can be used while research uses the data like numbers with some classification such as frequency, average mark, percentage, the dominant variable, and so on. The data processing as done through mathematical calculation with a certain formula. I will use it to collect the data and analyzes them to determine the kinds of verb phrase, whether tenses, aspects or active and passive voice.
The data is analyzed in two steps. First, the data was identified. Second, the kinds of verb phrase that found in each article was categorized and classified. The classification is done by grouping the data depending on kinds of verb pharase. The purpose of grouping here are to find out the kinds of verb phrase in Tempo Magazine.
The formula that used to count the percentage is :
� =XY x 100 %
In which:
N= the percentage of types of verb phrase X= the number of types of verb phrase.
Y= the total number off all types of verb phrase. 100%= standart percentage.
CHAPTER IV
ANALYSIS AND FINDING
4.1 Data Analysis
The data which will be analyzed are taken from the selected articles of Tempo Magazine in April 21st , 2013. There are four articles chosen in doing the analysis. They are Bribery In Room 1201 (page 14 – 18), Fingerprints on ID Cards (page 20 – 21), Budget Master In Senayan (page 22 – 23), New Threat From Obsolete Clause (page 31 -34).
4.1.1 TENSE
1. Simple Present
Article 1 Bribery In Room 1201 (page 14 – 18)
1. Lukman Abbas clearly recalls a meeting held in Room 1201 of the Nusantara I Building at the House of Representatives (DPR) in early February last year. 2. We suspect there are traces of meeting here.
Article 2 Fingerprints on ID Cards (page 20 – 21) 1. Paulus suspects Setya was behind the change.
2. He also claims that he does not know Andi Agustinus.
4. They all work.
Article 3 Budget Master In Senayan (page 22 – 23) 1. He knows how to build a network.
2. In Golkar circles, Setya often holds `classes` for members of the DPR`s budget body.
3. Being in two worlds, politics and business, Setya often finds himself in perilous situations.
4. Many of his colleagues say he is untouchable.
Article 4 New Threat From Obsolete Clause (page 31 -34)
1. So no party contesting the election becomes dominant, the regulations limit the frequency and duration of presentation of each candidate`s advertising. 2. The KPU also prohibits the media from selling the packages outside
advertising slots for campaigning.
3. The KPU also prohibits the media from accepting ads from sponsors of particular candidates.
4. The Broadcasting Commission and Press Council fail to report the application of penalties, the Election Commission will then itself apply penalties to the election candidate involved.
5. Nezar Patria says the KPU ought not to over-regulate the media, particularly in reporting.
2. Simple Past
Article 1 Bribery In Room 1201 (page 14 – 18)
1. They met their host, Golkar Party faction chairman Setya Novanto. 2. The guests arrived just before lunchtime.
3. Some Golkar DPR members were already in Setya`s office.
4. Lukman also saw Sudikerta, chairman of the Bali branch of the Golkar Party. 5. The Governor immediately introduced us to Pak Setya.
6. Lukman spoke about this meeting to investigators at the Corruption Eradication Comission (KPK).
7. Setya Novanto also confirmed that the meeting took place.
8. He said Rusli and his subordinates arrived and were inhis office for 10 minutes.
9. A week after that meeting, Lukman again flew from Pekanbaru to Jakarta. 10.Over the telephone, Kahar asked him to go the capital city.
11.kahar said that he had studied the proposed additional to be added to the 2012 Revised State Budget.
12.He then convened a meeting at Plaza Senayan in South Jakarta, with contractor firms working on construction of the PON project.
13.He asked the contractors to share in giving funds for the first bribe payment of US$850,000 to the DPR members, which was given the code word `beard`. 14.Dicky Eldianto, former Operational Manager of Riau branch of Adhi Karya
16.Lukman still recalled that on February 23 last year, at around 5pm, he received a message from Kahar through his blackberry.
17.Lukman then sent a message to Kahar, informing that the money had been collected near midnight.
18.Lukman said that he reported everyting he did to Rusli Zainal.
19. After midnight he called the boss, informing him that the money asked for had been collected and was ready to be turned over.
20.Lukman left Kahar`s office and contacted Heriyadi by cellphone to inform him that they had to bags.
21. After completing the first transaction, Lukman tried to think of a way to think of a way to raise the additional payment of US$200,000.
22.Traces of PON funds at the legislature in Senayan also showed up through events which transpired at the KPK building.
23. He called up two employees of contarctors asking them to get that money ready in four days` time.
24. With money in hand, Lukman visited Kahar again.
25.The house member again sent Wihaji to pck up the US$200,000 in the basement parking area of Nusantara 1.
26. A Tempo source in the DPR said that kahar reported the entire request and receipt of funds from Lukman to Setya Novanto.
27.On March 15 last year, Juhaini Alie, a member of Democrat Party faction, returned Rp700 million which he received to the KPK`s Bonuses Directorate.
29.Kahar declined to comment when we met him at the office of the Golkar Central Leadership Board in Slipi, West Jakarta.
30.Earlier, he denied ever receiving money from Lukman, emphasizing that he never had a personal assistant named Wihaji.
31.Lukman casually responded to Kahar denying ever having a personal assistant named Wihaji.
32.At the end of the last month, 22 KPK investigators searched Setya and Kahar`s office.
Article 2 Fingerprints On ID Cards (page 20 – 21)
1. He headed for a house in the Kebayoran area of South Jakarta.
2. Sandipala received a share of the work to print 172 million electronic e-KTP cards.
3. The work consisted of printing blank cards and filling them out with individual data.
4. They also met once in Setya`s office on the 12th floor of Nusantara I Building at the DPR.
5. This meant that the fee would be taken fromthe value of the ID card printing subcontracts which PNRI gave to other companies.
6. Not long afterwards, on December 19, 2011, the Home Affairs Ministry held a meeting with all members of the consortium, except Sandipala company. 7. The ministry saw that PT Sandipala`s performance was low.
8. Paulus filed a lawsuit against the ministry and PNRI, but soon withdrew it. 9. According to Paulus, he called off the lawsuit because he was promised
10.Setya claimed not to know about the KTP project.
11.However, a director of one company in the consortium said that a third of those cards do not work.
Article 3 Budget Master In Senayan ( page 22 – 24)
1. After graduating, Setya moved to Surabaya to study accounting at Widya Mandala University.
2. They met five years later in Jakarta, when Setya continued his studied at the Economics Faculty of Trisakti University.
3. At that time, he had a degree in accounting.
4. Setya paid for her expenses and tuition in Surabaya by selling rice and honey at Keputren Market in Surabaya.
5. He also worked as a salesman at an automobile dealership, and even strode down catwalk to model clothing.
6. He continued to work odd jobs to pay for his education.
7. He washed cars, opened a photocopy service, even formed an business alliance with Hayono.
8. He did not feel uncomfortable to, for instance, carry the bags of senior military officers, such as General Wismoyo Arismunandar.
9. Twenty seven years ago, Setya completed the Nagoya Plaza Hotel project in Batam.
10.He decided he had to get close to Sudwikatmono, a cousin of Presiden Soeharto.
12.Siti Hardijanti Rukmana alias Tutut, Soeharto`s oldest child, appointed Setya to preside over Citra Permatasakti Persada, a service company that managed the driving license business.
13.Then Elsye Sigit, wife of Sigit Harjojudanto Suharto worked with him in the ID card computerization business.
14.Hayono decided to leave Golkar and establish the Justice and Unity Party before finally joining the Democrat Party.
15.Setya established Kosgoro 1957 and became a part of the Golkar leadership under Akbat Tanjung.
16.Yorry Raweyai, a Golkar politician and former Budget Body member verified such meeting take place.
17.This case broke after Bank Bali transferred over Rp500 billion to Era Giat Prima.
18.Setya denied involvement in the Riau PON case.
19.Golkar Secretary General Idrus Marham asked that all slides respect the law.
Article 4 New Threat From Obsolete Clause ( page 31 -34)
1. Last Friday, the Network`s lawyer in Padang, Jakarta and Surabaya issued a joint satatement.
2. They demanded the KPU immediately withdraw its Implementation Guidelines for Election Campaigns for Legislative Assembly Members.
3. The KPU promulgated its Regulation No.1/2013 on January 10.
5. After meeting the legislators earlier in the day, the same evening the KPU ratified the campaign regulations.
6. Understandably so, as two days earlier, the KPU announced which parties had passed verification.
7. The Court held that penalties of revocation of media licenses in the Election Law contravened the Broadcasting and Press Law.
8. They merely copied old campaign regulations that in turn referred to old laws.
9. He declared he had only realized there was a problem after the regulations had been ratified.
10.We only found out after the regulations had been ratified.
11.Deputy Chief of the DPR`s Domestic Governance Commission, Arif Wibowo confirmed the House was consulted on the KPU`s regulations.
12.However, he rejected the suggestion that they did not provide input.
13.From the outset, we reminded the KPU not to interfere with freedom of the press.
4.1.2 ASPECT
1. Perfect Aspect
a. Perfect Aspect, Present Time
1. Some of them have damaged chip. (article 2)
3. The Press Legal Aid Network has also reacted. (article 4)
4. The KPU has reproduced obsolete regulations that can potentially fetter the press. (article 4)
5. This is actually not the first time such muzzling articles have surfaced in election regulations. (article 4)
6. The Press Council has taken a similar stance. (article 4)
b. Perfect Aspect, Past Time
1. He had gone there with two of his colleagues from the Riau provincial government to accompany Governor Rusli Zainal. (article 1)
2. The governor had projected Rp290 billion, in order to cover a Rp164.6 billion payment to shortage to a contractor, and Rp125 billion for the constuction of the stadium . (article 1)
3. The governor had already approved the proposed budgetary addition. (article 1)
4. He had studied the proposed additional funds to be added to the 2012 Revised State Budget. (article 1)
5. I had only followed development in the media. (article 1) 6. As of 8pm he had managed to raise US$805,000. (article 1)
7. Sandipala had only printed 4 million of the target 67 million cards. (article 2)
8. They had not received any resident data. (article 2)
2. Progressive Aspect
a. Progressive Aspect, Present Time
1. We are purchasing new machines. (article 2)
2. The KPU is meddling too far into media matters. (article 4)
3. This week the Press Council is discussing the regulations and will then take a stance of them. (article 4)
4. It is threatening any media violating the regulations with multiple penalties. (article 4)
5. The KPU is handling over the campaign supervision of the media to the Indonesia Broadcasting Commission (KPI) and the Press Council. (article 4)
6. It is willing to cooperate provided the KPU makes rules of the game that comply with the Broadcasting law and its secondary regulations. (article 4)
b. Progressive Aspect, Past Time
1. Setya was reportedly manipulating the project. (article 2)
2. Setya was finding it easier to enter the circle of power. (article 3) 3. Indeed, they were racing to meet a deadline. (article 4)
3. Perfect Progressive Aspect
a. Perfect Progressive Aspect, Present Time
1. His business has been growing ever since. (article 3)
2. His career has been growing till the leadership of the Aburizal Bakrie. (article 3)
b. Perfect Progressive Aspect, Past Time
1. Setya Novanto, the host, had been waiting there with his colleague, Andi Agustinus alias Andi Narogong. (article 2)
4.1.3 VOICE 1. Active Voice
Article 1 Bribery In Room 1201 (page 14 – 18)
1. Lukman Abbas clearly recalls a meeting held in Room 1201 of the Nusantara Building.
2. We suspect there are traces of meeting here.
3. They met their host, Golkar Party faction chairman Setya Novanto. 4. The guests arrived just before lunchtime.
5. Some Golkar DPR members were already in Setya`s office.
6. Lukman also saw Sudikerta, chairman of the Bali branch of the Golkar Party.
8. Lukman spoke about this meeting to investigators at the Corruption Eradication Comission (KPK).
9. Setya Novanto also confirmed that the meeting took place.
10.He said Rusli and his subordinates arrived and were inhis office for 10 minutes.
11.A week after that meeting, Lukman again flew from Pekanbaru to Jakarta. 12.Over the telephone, Kahar asked him to go the capital city.
13.kahar said that he had studied the proposed additional to be added to the 2012 Revised State Budget.
14.He then convened a meeting at Plaza Senayan in South Jakarta, with contractor firms working on construction of the PON project.
15.He asked the contractors to share in giving funds for the first bribe payment of US$850,000 to the DPR members, which was given the code word `beard`.
16.Dicky Eldianto, former Operational Manager of Riau branch of Adhi Karya company, confirmed that the first meeting took place at Plaza Senayan.
17.He handed over Rp100 million at the first meeting at Plaza Senayan. 18.Lukman still recalled that on February 23 last year, at around 5pm, he
received a message from Kahar through his blackberry.
19.Lukman then sent a message to Kahar, informing that the money had been collected near midnight.
20.Lukman said that he reported everyting he did to Rusli Zainal.
22.Lukman left Kahar`s office and contacted Heriyadi by cellphone to inform him that they had to bags.
23. After completing the first transaction, Lukman tried to think of a way to think of a way to raise the additional payment of US$200,000.
24.Traces of PON funds at the legislature in Senayan also showed up through events which transpired at the KPK building.
25. He called up two employees of contarctors asking them to get that money ready in four days` time.
26. With money in hand, Lukman visited Kahar again.
27.The house member again sent Wihaji to pck up the US$200,000 in the basement parking area of Nusantara 1.
28. A Tempo source in the DPR said that kahar reported the entire request and receipt of funds from Lukman to Setya Novanto.
29.On March 15 last year, Juhaini Alie, a member of Democrat Party faction, returned Rp700 million which he received to the KPK`s Bonuses Directorate.
30.As a Democrat Party factionmember of the Budget body, Juhaini received a share of the bribes which he immediately deposited at the KPK.
31.Kahar declined to comment when we met him at the office of the Golkar Central Leadership Board in Slipi, West Jakarta.
32.Earlier, he denied ever receiving money from Lukman, emphasizing that he never had a personal assistant named Wihaji.
34.At the end of the last month, 22 KPK investigators searched Setya and Kahar`s office.
35.He had gone there with two of his colleagues from the Riau provincial government to accompany Governor Rusli Zainal.
36.The governor had projected Rp290 billion, in order to cover a Rp164.6 billion payment to shortage to a contractor, and Rp125 billion for the constuction of the stadium .
37.The governor had already approved the proposed budgetary addition. 38.He had studied the proposed additional funds to be added to the 2012
Revised State Budget.
39.I had only followed development in the media. 40.As of 8pm he had managed to raise US$805,000.
Article 2 Fingerprints On ID Cards (page 20 – 21) 1. Paulus suspects Setya was behind the change.
2. He also claims that he does not know Andi Agustinus.
3. Reydonnyzar Moenek claims that there is nothing wrong with the cards which have been distributed to residents.
4. They all work.
5. He headed for a house in the Kebayoran area of South Jakarta.
6. Sandipala received a share of the work to print 172 million electronic e-KTP cards.
8. They also met once in Setya`s office on the 12th floor of Nusantara I Building at the DPR.
9. This meant that the fee would be taken fromthe value of the ID card printing subcontracts which PNRI gave to other companies.
10.Not long afterwards, on December 19, 2011, the Home Affairs Ministry held a meeting with all members of the consortium, except Sandipala company.
11. The ministry saw that PT Sandipala`s performance was low.
12.Paulus filed a lawsuit against the ministry and PNRI, but soon withdrew it.
13.According to Paulus, he called off the lawsuit because he was promised compensation.
14.Setya claimed not to know about the KTP project.
15.However, a director of one company in the consortium said that a third of those cards do not work.
16.Some of them have damaged chip.
17.Sandipala had only printed 4 million of the target 67 million cards. 18.They had not received any resident data.
19.We are purchasing new machines.
20.Setya was reportedly manipulating the project.
Article 3 Budget Master In Senayan ( page 22 – 24) 1. He knows how to build a network.
2. In Golkar circles, Setya often holds `classes` for members of the DPR`s budget body.
3. Being in two worlds, politics and business, Setya often finds himself in perilous situations.
4. Many of his colleagues say he is untouchable.
5. After graduating, Setya moved to Surabaya to study accounting at Widya Mandala University.
6. They met five years later in Jakarta, when Setya continued his studied at the Economics Faculty of Trisakti University.
7. At that time, he had a degree in accounting.
8. Setya paid for her expenses and tuition in Surabaya by selling rice and honey at Keputren Market in Surabaya.
9. He also worked as a salesman at an automobile dealership, and even strode down catwalk to model clothing.
10.He continued to work odd jobs to pay for his education.
11.He washed cars, opened a photocopy service, even formed an business alliance with Hayono.
12.He did not feel uncomfortable to, for instance, carry the bags of senior military officers, such as General Wismoyo Arismunandar.
13.Twenty seven years ago, Setya completed the Nagoya Plaza Hotel project in Batam.
15.He wrote the book Manajemen Soeharto after meeting with and interviewing Presiden Soeharto.
16.Siti Hardijanti Rukmana alias Tutut, Soeharto`s oldest child, appointed Setya to preside over Citra Permatasakti Persada, a service company that managed the driving license business.
17.Then Elsye Sigit, wife of Sigit Harjojudanto Suharto worked with him in the ID card computerization business.
18.Hayono decided to leave Golkar and establish the Justice and Unity Party before finally joining the Democrat Party.
19.Setya established Kosgoro 1957 and became a part of the Golkar leadership under Akbat Tanjung.
20.Yorry Raweyai, a Golkar politician and former Budget Body member verified such meeting take place.
21.This case broke after Bank Bali transferred over Rp500 billion to Era Giat Prima.
22.Setya denied involvement in the Riau PON case.
23.Golkar Secretary General Idrus Marham asked that all slides respect the law.
24.He had recognized the island`s potential as a tourist area. 25.Setya was finding it easier to enter the circle of power. 26.His business has been growing ever since.
Article 4 New Threat From Obsolete Clause ( page 31 -34)
1. So no party contesting the election becomes dominant, the regulations limit the frequency and duration of presentation of each candidate`s advertising.
2. The KPU also prohibits the media from selling the packages outside advertising slots for campaigning.
3. The KPU also prohibits the media from accepting ads from sponsors of particular candidates.
4. The Broadcasting Commission and Press Council fail to report the application of penalties, the Election Commission will then itself apply penalties to the election candidate involved.
5. Nezar Patria says the KPU ought not to over-regulate the media, particularly in reporting.
6. Last Friday, the Network`s lawyer in Padang, Jakarta and Surabaya issued a joint satatement.
7. They demanded the KPU immediately withdraw its Implementation Guidelines for Election Campaigns for Legislative Assembly Members. 8. The KPU promulgated its Regulation No.1/2013 on January 10.
9. However, journalists and press freedom activist only realized the danger the regulation posed some time later.
10.After meeting the legislators earlier in the day, the same evening the KPU ratified the campaign regulations.
12.The Court held that penalties of revocation of media licenses in the Election Law contravened the Broadcasting and Press Law.
13.They merely copied old campaign regulations that in turn referred to old laws.
14.He declared he had only realized there was a problem after the regulations had been ratified.
15.We only found out after the regulations had been ratified.
16.Deputy Chief of the DPR`s Domestic Governance Commission, Arif Wibowo confirmed the House was consulted on the KPU`s regulations. 17.However, he rejected the suggestion that they did not provide input. 18.From the outset, we reminded the KPU not to interfere with freedom of
the press.
19.Unwilling to take the threat of being muzzled lightly, a number of jurnalist and press freedom activist have quickly closed ranks.
20.The Press Legal Aid Network has also reacted.
21.The KPU has reproduced obsolete regulations that can potentially fetter the press.
22.This is actually not the first time such muzzling articles have surfaced in election regulations.
23.The Press Council has taken a similar stance. 24.The KPU is meddling too far into media matters.
25.This week the Press Council is discussing the regulations and will then take a stance of them.
27.The KPU is handling over the campaign supervision of the media to the Indonesia Broadcasting Commission (KPI) and the Press Council.
28.It is willing to cooperate provided the KPU makes rules of the game that comply with the Broadcasting law and its secondary regulations.
29.Indeed, they were racing to meet a deadline.
30.The drafting team from the KPU Secretariat was simply taking the easy road.
2. Passive Voice
Article 1 Bribery In Room 1201 (page 14 – 18)
1. Five months later he was indicted in a corruption case of a constuction project for the XVIII National Sports Week (PON) in Riau last year. 2. A detailed breakdown of the required additional funds had been sent
ahead of time.
3. Essentially, the budget increase had been previously approved.
4. That was to be devided among certain DPR members, to ensure that the revised PON budget with the additional funds would be easily approved. 5. A similar admission was made by Anil Salbir Singh Gill, CEO of Orindo
Prima, a contracting film.
6. The bribe money was packed in two bags and put in the baggage area of Toyota Harrier with license plate B-282-LUK.
7. The additional bribe money was finally collected on March 22 last year. 8. The execution of the allocation of the Revised National Budget is fully
9. Packed in a cardboard box, the money was brought to him by someone claiming to be a cadre of the Democrat Party, at Juhaini`s office in Nusantara 1 Building.
10.That package was given as a token of thanks for my duties and functions. 11.A Tempo source said this money which this younger brother of DPR
speaker Marzuki Ali gave to the KPK was part of bribe paid out by the Riau Government.
12.According to KPK spokesman Johan Budi S.P., this search was carried out as a part of the investigation into rusli Zainal.
Article 2 Fingerprints On ID Cards (page 20 – 21)
1. As chairman of the Golkar faction, Setya Novanto is suspected of being involved in securing the budget for the project at the legislature.
2. When he was contacted again last week he again did not make any outright denial.
3. Three other meetings were held at Setya`s house.
4. At these meetings, Setya was nearly always accompanied by Andi Agustinus.
5. At a meeting in the Equity Tower, Setya was accompanied by Chairuman Harahap, also a politician, and another businessperson.
6. The ministry was represented by, among others, Secretary General Diah Anggareni and the commitment-making official, Sugiharto.
7. The meeting was held upon the request of the ministry.
9. According to Paulus, he called off the lawsuit because he was promised compensation.
10.CEO of PNRI Isnu Edhi Wijaya said that the printing of their share of the card was being done on their own, and was not being subcontracted. 11.Of these millions, 130million cards have been distributed.
Article 3 Budget Master In Senayan ( page 22 – 24)
1. Setya is suspected of being involved in the budget markup case for the XVIII National Sports Week (PON) in Riau last year.
2. His office on the 12th floor of the Nusantara 1 Building at the DPR was searched by investigators from the Corruption Etadication Commission (KPK).
3. Unfortunately, the most strategically-located land in that area, in the Nongsa Beach area, was already controlled by businessman Sudwikatmono, Ciputra, and Liem Sioe Liong.
4. In October 2009, he was appointed chairman of the Golkar Party faction in the DPR.
5. He was also said to be involved in the smuggling of toxic waste in Batam in 2006.
6. Setya has also been mentioned in connection with the disputeover the bidding on the electronic ID card project.
Article 4 New Threat From Obsolete Clause ( page 31 -34)
1. Buried for years, clauses offensive to press freedom are now being resurrected.
2. The regulation has only been started to be heatedly debated,, including through discussions on various social media sites, since middle of last week.
3. The draft campaign regulations had been discussed with theHouse of Representatives (DPR) Commission II.
4. The draft was sent to the DPR on December 8.
5. Because of the House recess, the consultative meeting was only held on January 10, 2013.
6. If they had been limited to just controlling media ads, the KPU`s steps could well not have been strongly opposed.
7. But those articles were later cancelled by the Constitutional Court in 2009.
4.2 Findings
After analyzing the data, the writer found some results and the results is made in table form. The following table shows the occurrences of each kind of verb phrases found in the articles of Tempo Magazine.
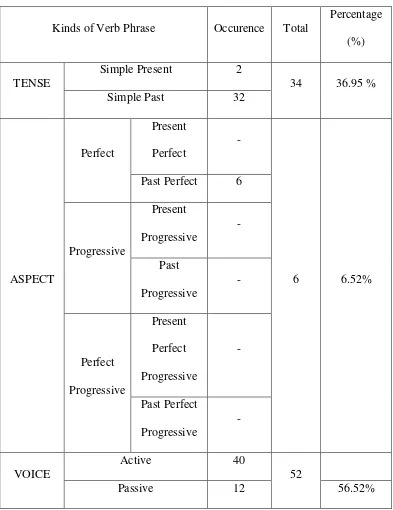
1. The article entitled Bribery In Room 1201 of Tempo Magazine, edition of 21st April 2013
Kinds of Verb Phrase Occurence Total
2. The article entitled Fingerprints On ID Cards of Tempo Magazine, edition of 21st April 2013
Kinds of Verb Phrase Occurence Total
3. The article entitled Budget Master In Senayan of Tempo Magazine, edition of 21st April 2013
Kinds of Verb Phrase Occurence Total
4. The article entitled New Threat From Obsolete Clauses of Tempo Magazine, edition of 21st April 2013
Kinds of Verb Phrase Occurence Total
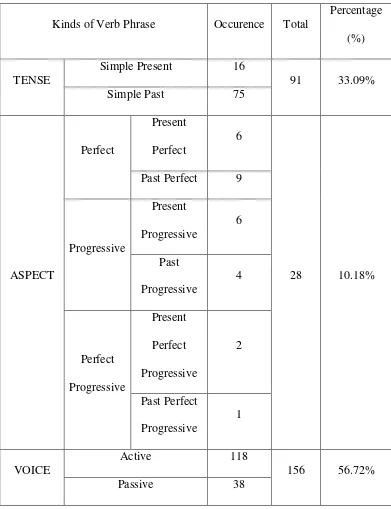
Table of frequency and percentages of all kinds of verb phrases found in four articles that found in Tempo Magazine :
Kinds of Verb Phrase Occurence Total
Percentage (%)
TENSE
Simple Present 16
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
5.1 Conclusion
After analyzing three of six kinds of verb phrase in the articles of Tempo Magazine, I can conclude that :
1. There are 275 sentences in this magazine that relate with verb phrase. 2. Tense, aspect and voice can be found in the Tempo Magazine.
3. The most dominant verb phrase in the Tempo Magazine is voice with the percentage 56.72 % (active voice 42.9% and passive voice 13.81%), the second is tense with the percentage 33.09% (simple present tense 5.81% and simple past tense 27.27%), the third is aspect with the percentage 10.18% (perfect aspect 5.45%, progressive aspect 3.63% and perfect progressive 1.09%).
4. It can be concluded that active voice is more frequently used than passive voice and simple past is more frequently used than simple present in Tempo Magazine.
5.2 Suggestions
Based on the conclusion, there are some suggestions for all the people who are
REFERENCES
Azar, Betty. 1993: Understanding and Using English Grammar. Jakarta : Binarupa Aksara.
Biber, Douglas et.al. 2002. Longman Student Grammar of Spoken and Written English. England : Pearson Education Limited.
Chomsky, Noam. 1961. Syntatic Structures. 2nd Edition. The united States of America: The Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Frank, Marcella. 1972. Modern English. United States of America : Prentice Hall.
Fromkin and Rodman, 1983. An Introduction to Language. (third edition). Sidney: Holt, Rinehart, and Winston.
Hornby, A.S. 2000. Oxford Advanced Learner`s Dictionary. United Kingdom : Oxford University Press.
Hurford, James and Heasley, Brendan. 1983. Semantics: A Course Book. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Frank, Marcella. 1972. Modern English : a practical reference guide. USA : New York University.
Leech, Geoffrey. Et. Al. 1985. English Grammar for Today. London: Macmillan Publishers.
Meliani, Vivi. 2011. An Analysis of verb phrase found in the selected article of The Jakarta Post. Unpublished Thesis. Medan : USU.
Miller, Jim. 2002. An Introduction to English Syntax. Edinburgh : Edinburg University Press.
Nawawi, H. 1993. Metode Penelitian Bidang Sosial. Yogyakarta: Gajah Mada University.
O`Grady, William et.al. 1997. Contemporary Linguistics. United Kingdom: Pearson Education Limited.
Wren and Martin. 1990. High School English Grammar and Composition. New Delhi : S.chand.
APPENDIX Article I
Article II
Article III
Article IV