Informasi Dokumen
- Sekolah: SMP Kartikatama Metro
- Mata Pelajaran: English Education
- Topik: The Implementation of Self Directed Dialogue Technique in Speaking Class at the Second Year of SMP Kartikatama Metro (Classroom Action Research)
- Tipe: classroom action research
- Kota: Metro
Ringkasan Dokumen
I. INTRODUCTION
This section introduces the significance of speaking in communication, emphasizing its role in social interaction and the challenges faced by students in developing this skill. The background highlights the importance of effective communication in English, especially in a global context. Observations from SMP Kartikatama Metro reveal that many students struggle with speaking, leading to low proficiency levels. The need for an effective teaching technique, such as Self-Directed Dialogue, is established to enhance students' speaking abilities and engagement.
1.1 Background of the Problem
The background outlines the critical role of speaking in communication, referencing key theorists like Byrne and Melty. It discusses the objectives of the 2006 Educational Unit Level Curriculum (KTSP) for speaking skills, stating the expectations for students' abilities in conversation and expression. The observed reluctance and difficulties faced by students at SMP Kartikatama Metro are highlighted, indicating a gap between expectations and actual speaking proficiency.
1.2 The Formulation of the Problem
This subsection formulates specific research questions aimed at investigating how the implementation of Self-Directed Dialogue Technique can improve speaking achievement, student participation, and the quality of teaching performance. These questions set the stage for the research objectives and the classroom action research approach.
1.3 The Objectives
The objectives of the research are clearly stated, focusing on the effectiveness of the Self-Directed Dialogue Technique in enhancing students' speaking achievements, increasing participation during lessons, and improving the quality of the teacher's instructional performance. These objectives align with the identified problems and the research questions.
1.4 Uses of the Research
The research outlines both theoretical and practical uses, aiming to validate existing theories on Self-Directed Dialogue and provide a reference for future studies. It also aims to assist English teachers in improving students' speaking abilities and engagement through effective teaching strategies.
1.5 Scope of the Research
This section defines the scope of the research, specifying that it focuses on second-year students at SMP Kartikatama Metro, comprising 30-36 students. It highlights the choice of Self-Directed Dialogue as the primary teaching technique and the specific aspects of speaking (grammar, fluency, vocabulary, and pronunciation) that will be assessed.
II. FRAME OF THEORIES
This section provides a theoretical foundation for the research, discussing key concepts related to speaking and the Self-Directed Dialogue technique. It emphasizes the importance of speaking as a communicative skill and the need for effective teaching strategies to enhance students' speaking abilities.
2.1 Concept of Speaking
The concept of speaking is explored through definitions from various theorists, emphasizing its nature as a two-way communicative process. The importance of speaking in English for global interaction is highlighted, reinforcing the need for effective speaking skills in modern society.
2.2 Concept of Speaking Skill
This subsection delves into the components of speaking skills, including pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary, and fluency. It underscores the significance of mastering these elements for effective communication and the teacher's role in facilitating students' speaking practice.
2.3 Previous Research on Speaking through Self-Directed Dialogue
The relevance of dialogue in improving speaking skills is discussed, highlighting its effectiveness in providing real-life communication practice. The concept of Self-Directed Dialogue is introduced as a method that encourages student engagement and language use in a supportive environment.
2.4 The Procedure of the Self-Directed Dialogue Technique
This section outlines the procedural steps involved in implementing the Self-Directed Dialogue technique, detailing how students are paired, given props, and guided to create conversations. The emphasis is on fostering student autonomy and creativity in language use.
2.5 Procedure of Teaching Speaking through Self-Directed Dialogue Technique
The teaching procedure is described in detail, covering pre-activities, while activities, and post-activities. The importance of engaging students in communicative tasks and providing feedback is emphasized, showcasing how the technique can enhance speaking skills.
III. RESEARCH METHOD
This section outlines the research design and methodology used in the study, focusing on classroom action research as a means to address the identified speaking difficulties faced by students. The approach includes planning, implementing, observing, and reflecting on the teaching process.
3.1 Research Design
The research design is established as a classroom action research aimed at identifying and addressing speaking difficulties among second-grade students. The rationale for selecting class VIII A, with its lower speaking test scores, is explained.
3.2 General Description of the Research
This subsection discusses the characteristics of classroom action research, emphasizing the iterative nature of the process and the importance of problem identification and solution implementation. The role of the researcher as an observer is also highlighted.
3.3 Research Procedures
The procedures for conducting the research are outlined, detailing the stages of planning, implementing, observing, and reflecting. Each stage is described to illustrate the systematic approach taken to improve students' speaking skills.
3.4 Indicator of the Research
Indicators for measuring the success of the research are established, focusing on both learning processes and products. The expected levels of student participation and speaking proficiency are defined to assess the effectiveness of the Self-Directed Dialogue technique.
3.5 Instrument of the Research
The instruments used for data collection are described, including observation sheets, speaking tests, and questionnaires. Each instrument's purpose and method of implementation are explained to ensure comprehensive data gathering.
3.6 Data Analysis
The data analysis process is outlined, detailing how both learning products and processes will be evaluated. The use of qualitative and quantitative methods to assess student performance and engagement is emphasized.
IV. RESULT AND DISCUSSION OF THE RESEARCH
This section presents the findings of the classroom action research conducted over two cycles. The results indicate improvements in students' speaking skills, participation, and overall engagement in the learning process through the implementation of the Self-Directed Dialogue technique.
4.1 Cycle I
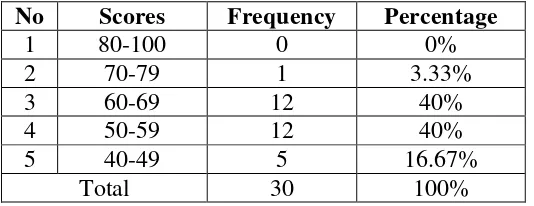
The first cycle's implementation is described, detailing the planning, action, observation, and reflection stages. The challenges faced during the initial implementation and the responses from students are discussed, highlighting areas for improvement.
4.2 Cycle II
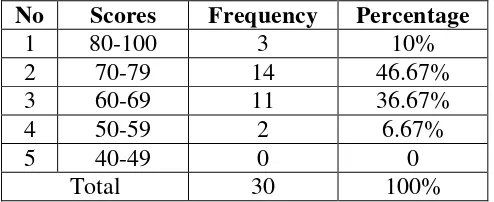
The second cycle builds upon the findings from the first cycle, incorporating feedback and adjustments to enhance the teaching approach. The outcomes of the second cycle are analyzed, demonstrating the effectiveness of the Self-Directed Dialogue technique in improving students' speaking abilities.
Referensi Dokumen
- Swain (1985) ( Swain )
- Arikunto (1993:210) ( Arikunto )
- Depdiknas; 2006 ( Depdiknas )