INCREASING STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY THROUGH PROBLEM SOLVING AT THE FIRST GRADE
SMAN 1 SIMPANG PEMATANG
By
REZA FANDANA
A Script
Submitted in a Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement for S-1 Degree
in
The Language and Arts Education Department of The Faculty of Teacher Training and Education
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY UNIVERSITY OF LAMPUNG
ABSTRACT
INCREASINGSTUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY THROUGH PROBLEM
SOLVING AT THE FIRST GRADE OF SMAN 1 SIMPANG PEMATANG BY
Reza Fandana
Problem solving is a technique that gives students opportunity to express their opinion based on the problem. Problem solving can help students become more interested and active. In problem solving students use their background knowledge and experience to understand their situation and solve the problem.
There are two main objectives of this research namely, 1. To find out whether there is any significant difference of students’ speaking ability after being taught through problem solving. 2. To know which one is the most effective topic for teaching speaking. This research was conducted at SMAN 1 Simpang Pematang. The sample of this research was students of tenth grade, class X1. The study employed times series design by giving three pre-tests, three treatments, and three post-tests. To collect data, the speaking test applied speaking performance. There were two raters to score students’ speaking performance.
The result shows that there is significant difference of students’ speaking ability after being taught through problem solving. It means that problem solving can increase students speaking ability. The result of students’ mean score pre-test 1 is 62.3 up in post-test 1 is 71(gain is 8.7), pre-test 2 is 63.1 up in post-test 2 is 73.4 (gain is 10.3) ,and pre-test 3 is 64.2 up in post-test 3 is 76.8 (gain is 12.6). The reseacher also uses pair sample of SPSS. The result is 1stpair 26.187 (t-value) > 2. 048 (t-table) , 2ndpair 22.079 (t-value) > 2. 048 (t-table), 3rdpair 43.847 (t-value) > 2. 048 (t-table) means that there aresignificant differences of students’ speaking ability after being taught through problem solving. Therefore, the first hypothesis is accepted.
1. Research Schedule... 63
2. Table of Rating Sheet Score Pre-test 1 from Two Raters... 64
3. Table of Rating Sheet Score Pre-test 2 from Two Raters... 65
4. Table of Rating Sheet Score Pre-test 3 from Two Raters... 66
5. Table of Rating Sheet Score Post-test 1 from Two Raters... 67
6. Table of Rating Sheet Score Post-test 2 from Two Raters... 68
7. Table of Rating Sheet Score Post-test 3 from Two Raters... 69
8. Score Table of Pre-test 1 from Two Raters... 70
9. Score Table of Pre-test 2 from Two Raters... 71
10. Score Table of Pre-test 3 from Two Raters... 72
11. Score Table of Post-test 1 from Two Raters... 73
12. Score Table of Post-test 2 from Two Raters... 74
13. Score Table of Post-test 3 from Two Raters... 75
14. Frequencies of Topic 1 ... 76
15. Frequencies of Topic 2 ... 77
16. Frequencies of Topic 3 ... 78
17.Analysis of Students’ scoreEvaluation... 79
18. Lesson Plan 1... 82
19. Lesson Plan 2... 85
20. Lesson Plan 3... 88
21. Pre-test 1... 91
22. Pre-test 2... 92
24. Post-test 1... 94
25. Post-test 2... 95
26. Post-test 3... 96
27. Transcripts of Pre-test 1... 97
28. Transcripts of Pre-test 2... 101
29. Transcripts of Pre-test 3... 106
30. Transcripts of Post-test 1... 110
31. Transcripts of Post-test 2... 116
ABSTRACT ... i
APPROVAL ... ii
ADMITTION... iii
CURICULUM VITAE ... iv
DEDICATION ... v
MOTTO ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT...vii
TABLE OF CONTENT ... ix
LIST OF APPENDICES... x
I. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Background of Problems ... 1
1.2 Identification of the Problems ... 6
1.3 Limitation of the Problems ... 6
1.4 Formulation of the Problems ... .6
1.5 Objectives of the Researchs ... 7
1.6 Uses of the Research... 7
1.7 Scope of the Research... .7
1.8 Definition of Terms ... .8
II. FRAME OF THEORIES 2.1 Review of Previous Related Research ... 9
2.2 Review of Related Literature ... 10
2.2.1 Concept of Speking ... 10
2.2.2 Teaching Speaking ... 18
2.2.3 Concept of CLT ... 19
2.2.4 Problem Solving ... 21
2.2.5 Concept of Pair Work ... 27
2.3 Procedures of Teaching Speaking through Problem Solving ... 27
2.4 Applicability of the Procedure Implementing Problem Solving in English Class ... 29
2.5 Advantages and Disadvantages... 30
2.6 Theoretical Assumption... 31
2.7 Hypothesis... 31
III.RESEARCH METHODS 3.1 Research Design ... 32
3.2 Sample and Population ... 33
3.3.1 Administering the Pre-Test... 33
3.3.2 Administering the Post-Test ... 34
3.4 Research Procedures... 34
3.5 Instrument of the Research ... 37
3.6 Validity and Reliability ... 37
3.7 Data Analysis... 39
3.8 Testing the Hypothesis ... 40
IV. RESULT AND DISCUSSION 4.1 Validity and Reliability of the Test ... 42
4.1.1 Validity of the Speaking Test ... 42
4.1.2 Reliability of the Speaking Test ... 43
4.2 Result of the Research ... 44
4.2.1 Result of Pre-Test ... 44
4.2.2 Result of Post-Test... 46
4.2.3 Hypothesis Testing ... 48
4.3 Findings and Discussions ... 52
4.3.1 Application of the Problem Solving Technique ... 52
4.3.2 The Result of Three Different Topics... 59
V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS 5.1 Conclusions ... 61
5.2 Suggestions ... 62
1
1.INTRODUCTION
This chapter describes background of the problem, formulation of the problems,
objectives of the research, uses of the research, and scope of the research. In order
to avoid misunderstanding , definition or terms are provided in the last part of this
chapter.
1.1 Background of the Problem
In our country, English as a Foreign Language should be learnt by the students
through four skills, namely listening, speaking, reading, and writing.
One of the objectives of teaching English is to make the learners are able to
communicate using the language in the forms of oral and written communication.
It is known that speaking is important for communication in the society to convey
information and ideas , and maintain social relationship. The ability to
communicate is the primary goal of foreign language instruction in which
speaking is put ahead above the other skills. In addition, a large percentage of the
world language learners study English in order to be able to communicate in
Many language learners regard speaking ability as the yard-stick measurement of
mastering a language. They regard speaking as the most important skill that can
acquire and asses their progress in terms of their accomplishment in oral
communication. But almost all students think that speaking is the most difficult
part in learning English.
In early November, the reseacher conducted pre-observation in SMAN 1 Simpang
Pematang. The reseacher asked the students about the problems they faced in
learning speaking, their average score was only 56. The reseacher tried to get
information from some students from that school. When she asked the students
whether speaking was a difficult lesson for them and what problem that they
faced in learning speaking, they said that they got bored in learning English
because they could not speak, they practiced less in speaking, they had less self
confident to speak up, and the teacher mostly taught about grammar.
Inappropriate teaching technique which is used by the teacher in teaching
speaking class may be the cause that English is difficult to be mastered. The
teacher teaches speaking by explaining the form of sentences, drilling it to the
students and asking students to do some written exercises at students’ worksheet or LKS. It makes the students become passive and speaking class become writing
class and students do not have a chance to speak.
Furthermore, in the teaching learning process, the teacher uses conventional
technique. She teaches the lesson by giving the formula of sentence for about
twenty five minutes and then asks the students to memorize the formula and do
3
situation makes most students kept silent. When the teacher asks the students to
show their speaking task in front of the class, only the active students produce
good communication in English. In addition, most of the students’ pronunciation are not clear. It could be seen from the sound, stress and intonation they produced.
According to Hedge (2000), many teacher will say that pronunciation is one of the
most difficult areas for students. To teach them how to pronunce it well, they have
to listen to English conversation for many times to improve their pronunciation.
Actually in studying English, the emphasis is not only on lingustic competence of
the language learners, but also on the development of their communicative ability.
In order to develop the learners’ communicative ability, the teacher needs apply good technique to teach the target language in an active and interesting manner.
To give the students good chance to practice, it is neccesary to take an action by
using approriate technique which gives opportunities and trigger the students to
practice their English in the classroom. A suitable technique can increase
students’ interest and then it will increase their speaking ability. According to Antony (1963) , the technique is a particular trick, stratagem or contrivance used
to accomplish and immediate objective. The technique depends on the teacher.
The teacher can choose a suitable technique for the students which can support the
teaching learning process in order to get better result.
To find a suitable technique, the reseacher promotes problem solving in teaching
speaking. According to Larsen-Freeman (2000), problem solving is included in
communicative language teaching. Problem solving is the process of applying a
conditions and that the problem solver has not seen before, in order to obtain a
satisfactory solution. Problem solving forces the student to think smart and
creatively. In problem solving, there is no right answer, so the student will not be
shy to express their answer to solve the problems. It can give the student more
practice to speak English and the class become an active class.
The researcher modified problem solving procedure from Dewey and Fullerton as
follows: The first step of introducing the problem could be warm-up activity
where the teacher can ask students to answer some questions related to the
problem and thus giving a chance to predict what the problem might be and
motivate the students. It can be a picture shown on the active-board, or a video.
The second step is reading of the story or watching video. Find out what words
are unfamiliar for the students and write down them on the blackboard. Be sure
that the students understand the situation.
The third step is comprehension check. Comprehension check can be done in
different ways, for example as listening or reading exercises. At first the teacher
can ask “yes” or “no” questions then go to special questions and then offers the students to ask their own questions. Or the teacher may offer different statements,
which can be right and wrong and ask students to say whether they are correct or
not and correct the wrong ones.
In order to choose the best solution the teacher may divide students into pair
gruop and ask them to discuss the possible consequences of their decision. In this
5
express his opinion. It is possible for students to come up with new solutions if the
consider them to be more successful. When the groups are ready to come up with
their solution, ask them to sound it and explain why it was chosen. Ask the
students from other pairs if they agree with it or not. Encourage the students to
take active part in this discussion as it develops their ability to persist in opinion,
giving his reasons in the target language.
The next step is discussion. Here the students are encouraged to talk about the
issues presented in the reading and also their personal experience. The questions
may require students to make suppositions and use their judgment. There are no
correct answers. Encourage them to use their imagination and critical thinking to
come up with the possible consequences.
The last is asked the students to come in front of class to give their own opinion
how to solve the problem.
The reseacher had experienced to use problem solving to teach English in Junior
high school at SMPN 1 Jati Agung. They had an increase in speaking ability but
the student had too low vocabulary mastery. So the class became so busy because
most students asked their friend about the vocabulary they would use. They also
mostly used so many word in Bahasa Indonesia. Based n this experience the
reseacher wants to apply problem solving in SMAN 1 Simpang Pematang.
Therefore, since problem solving has not been used in SMAN 1 Simpang
taught through problem solving. She also wants to know which one is the most
effective topic for teaching speaking.
1.2 Identification of the Problems a. The students have low speaking ability.
b. The frequency in learning speaking is not enough.
c. Students do not have any self confidence to speak up.
d. The teacher tends to emphasize student to learn about grammar.
e. The teacher technique in teaching speaking is not appropriate.
f. Students feel bored in learning English.
1.3 Limitation of the Problems
Based on the identification of the problems above, the writer limits her research as
follows:
1. Finding out whether there is anysignificant difference of students’ speaking ability after being taught through problem solving.
2. Knowing which one is the most effective topic for teaching speaking.
1.4 Formulation of the Problems
Referring to the limitation of the problem above, the writer would like to
formulate the problem as follows:
1. Is there any significant differenceof students’ speaking ability after being taught through problem solving?
7
1.5 Objectives of the Research The objective of this research is:
1. To find out whether there is any significant differenceof students’ speaking ability after being taught through problem solving.
2. To know which one is the most effective topic for teaching speaking.
1.6 Uses of the Research The uses of this research are :
1.Practically,
As consideration for english teachers that problem solving can be used as an
alternative technique to increase students’ speaking ability.
2.Theoretically,
To contribute useful information for the future research of teaching speaking.
1.7 Scope of the Research
This research was conducted at SMAN 1 Simpang Pematang and the subject was
class X 1 which consists of 30 students The focus of the research areon students’ speaking ability and the writer applied problem solving as a technique in her
teaching and learning process. The topics of the teaching learning are Friend,
Family, and Holiday. This research was carried out for about four weeks. Each
meeting consists of 90 minutes. Therefore, the score of the test was based on three
aspects to be tested, such as pronunciation, fluency, and comprehensibility. The
1.8 Definition of Terms Increase
Increase is a process of becoming larger or longer or more numerous or more
important . In this research the researcher intends to make the students ability
better.
Speaking
Speaking is a productive skill in which the speaker produce and use the language
to express the ideas when the learners try to get the ideas.
Ability
Ability is a skill or power required to do something and the quality of being able
or competence in doing something.
Problem solving
Problem solving is the process of applying a method–not known in advance-to a problem that is subject to a specific set of conditions and that the problem solver
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
This chapter discusses about the review of previous related researches, review of
related literature, concept of speaking, teaching speaking, concept of CLT,
problem solving, procedures of teaching speaking through problem solving,
advantages and disadvantages, theoretical assumption and hypothesis.
2.1 Review of Related Reseach
Speaking is an important skill in language teaching. But speaking is difficult for
the language learners because it is as the productive skill. Teaching speaking is a
very important part of second language learning. The ability to communicate in a
second language clearly and efficiently contributes to the success of the learner in
school and success later in every phase of life. There are some previous research:
Asep Rahmat Hidayat, this research entitled “Teaching Speaking Skill Using
Problem-Solving at Class Tenth of SMA Bina Muda Cicalengka” . The objective
of this research was to find out whether teaching speaking skill using problem
solving could increase the students’ speaking skill at class tenth of SMA Bina
Muda Cicalengka. The research used a quantitative method with one group
of this research was 47 of students of tenth grade of SMA Bina Muda Cicalengka.
The sample was the entire population. The data of this research were collected by
using the pretest and posttest to the students’ sample. The results of the data analysis showed that: the mean of pretest score was 53.51, the mean of posttest
score was 75.74, and t-observed was 10.10. The t-critical value with degree of
freedom (df) = 46 and significance level at 0.05 was 2.3. Based on the analysis
above, the alternative hypothesis of this research was accepted, because the
t-observed was bigger than t-critical value (10.10 > 2.3). It could also be concluded
that teaching speaking skill using problem-solving increased the students’
speaking skill.
In the other hand, Beverly talking about thingking aloud pair on problem solving
in Science Education journal to make an effective technique better than individual
problem solving. Reviews research is relevant to the problem of unsatisfactory
student problem-solving abilities and suggests a teaching strategy that addresses
the issue. Author explains how she uses teaching aloud problem solving (TAPS)
in college chemistry and presents evaluation data. Among the findings are that the
TAPS class got fewer problems completely right, but they also got fewer
problems completely wrong.
Donald tried to describes the problem hapened in problem solving in his research.
He describes problems in teaching problem solving and summarizes research in
this area. He Presents Guided Design or Guided Decision Making as a
problem-solving approach in which groups of students work their way through a model of
11
2.2 Review of Related Literature 2.2.1 Concept of Speaking
According to Bryne (1984), speaking is an oral communication, the two way
process between speaker and listener and involves productive and receptive skills
of understanding. According to Welty (1976), speaking is the main skill in
communication. In same lines, According to Irawati (2003), speaking is one of the
central elements of communication of an interactive process in which an
individual alternately takes the roles of speakers and listeners used to
communicate an information, ideas, and emotions to other using oral language.
Meanwhile according to Brown (2001:250), speaking is an interactive process of
construction meaning that involves producting, receiving, and processing in
formation. Based on this idea, there are three important points that must occured
to the participants of communication (speaker and listener) to construct the
meaning during the interaction among them.
According to Chaney (1998:13), speaking is the process of building and sharing
meaning through the use of verbal and non verbal symbol, in a variety of context.
Therefore, speaking can take place if the speaker uses verbal symbol like word
and non verbal symbol like gesture and body language to convey the intention.
In speaking process, especially in dialogue, it needs at least two people. One
becomes the speaker who produces information and other become the listener
Speaking must fulfill the following aspects, they are :
1. Fluency
Fluency can be defined as the ability to speak fluently and accurately. Nunan
(2003) said that fluency is use the language quickly and confidently with few
unnatural pauses. Fluency is the smoothness or flow with which sound, syllables,
word, and phrases are joined together when speaking. It means that when a person
makes a dialogue with another person, the other person can give respond well
without difficulty. For example, A and B : “Hi how are you today?”, B will be
answer “ As always, happy .” It is answered well and quickly.
2.Accuracy (Grammar and Pronociation)
Accuracy focuses on an issues of aprroriateness and other formal factors. It
relates to the use of grammar and pronunciation. According to Heaton ( 1978: 5),
definition of grammar is the students ability to manipulate structure and to
distinguish approriate grammatical form in approriate ones is needed for students
to arrange correct sentences in conversation, while pronunciation refers to the
ability to produce easily comprehensible articulation (Syakur:1987).
3. Comprehension
According to Syakur (1987), defines comprehension for oral communication that
requires a subject to respond to speech as well as to initiate it. Comprehensibility
13
There are some factors related to the speaking ability ( Heaton, 1991) :
a. Fluency
According to Gilman (1968 :45) the characteristic of voices is commonly
described as pitch, loudness, fluency, duration and quality.
b. Pronunciation
According to Brown (2001:198), teaching pronunciation are separated into
two levels, there are :
1. The beginning level: The learner hopefully can surface that they should
beneath which pronunciation detracts from their ability to communicate.
2. The advance level: The learners focus on elements that entrance
communication intonation features that go beyond basic patterns, voice of
quality, phonetic distinction between registers and other refinements that
are far more important in the several stream of clear communication than
rolling the English/r/or getting vowel to perfectly imitate a native speaker.
c. Comprehensibility
According to Carrel (1984:332), comprehension is a process in which the
readers use their formal schemata (rhetorical structure language knowledge)
and content (background knowledge of context) in order to get meaning of
However in this research, the components of speaking that are observed were
pronunciation, fluency, and comprehension. According to Heaton (1991), there
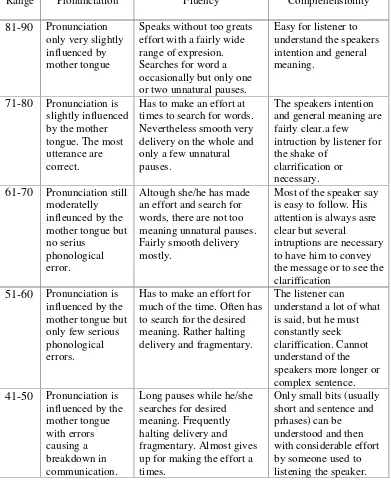
[image:23.595.114.505.219.702.2]are some criteria for analyzing oral ability as follows:
Table 2.1 Rubric of Scoring System
Range Pronunciation Fluency Comprehensibility
81-90 Pronunciation only very slightly influenced by mother tongue
Speaks without too greats effort with a fairly wide range of expresion. Searches for word a occasionally but only one or two unnatural pauses.
Easy for listener to understand the speakers intention and general meaning.
71-80 Pronunciation is slightly influenced by the mother tongue. The most utterance are correct.
Has to make an effort at times to search for words. Nevertheless smooth very delivery on the whole and only a few unnatural pauses.
The speakers intention and general meaning are fairly clear.a few intruction by listener for the shake of
clarrification or necessary. 61-70 Pronunciation still
moderatelly infleunced by the mother tongue but no serius
phonological error.
Altough she/he has made an effort and search for words, there are not too meaning unnatural pauses. Fairly smooth delivery mostly.
Most of the speaker say is easy to follow. His attention is always asre clear but several
intruptions are necessary to have him to convey the message or to see the clariffication
51-60 Pronunciation is influenced by the mother tongue but only few serious phonological errors.
Has to make an effort for much of the time. Often has to search for the desired meaning. Rather halting delivery and fragmentary.
The listener can
understand a lot of what is said, but he must constantly seek clariffication. Cannot understand of the speakers more longer or complex sentence. 41-50 Pronunciation is
influenced by the mother tongue with errors causing a breakdown in communication.
Long pauses while he/she searches for desired meaning. Frequently halting delivery and fragmentary. Almost gives up for making the effort a times.
15
The interpretation of grading system are as follows :
81-89 : excellent
71-80 : very good
61-70 : good
51-60 : fair
41-50 : moderate
According to Brown (2001: 250), the type of oral language is classified in two
parts, such as monologue and dialogue. The first is monologue, Monologue is
situation when one speaker uses spoken language, as in speeches, lectures’ reading, news broadcast, etc. The listener have to process long streches of speech
without interrupting the stream of speech that will go on whether or not the
listener comprehends. In planned, as it opposed to unplanned, monologue differs
considerably in their discourse structures. Monologues are divided into two kinds:
• Planned usually manifest little redundancy and are therefore relatively
difficult to comprehend.
• Unplanned exhibit more redundancy, which makes for ease in
comprehension, but the presence of more performance variables and other
hesitations, can help or hinder comprehension.
The second is dialogue, dialogue is divided in two parts such as interpersonal and
transactional. Dialogue involves two or more speakers and can be subdivided into
those exchanges that promote social relationship (interpersonal) and those for
Transactional dialogue, which is carried out for the purpose of conveying or
exchanging specific information, is an extended form of responsive language.
Conversation, for example, may have more of a negotiation nature for them than
responsive speech does.
According to Brown (2001), type of classroom speaking performances are:
1.Imitative
Practicing an intonation contour or try to pinpoint a certain vowel sound is an
example of imitative speaking. The imitation is carried out not for the purpose of
meaningful interaction, but for focusing on some particular elements of language
forms.
2.Intensive
Intensive speaking includes any speaking performance that is designed to practice
some phonological or grammatical aspect of language. It goes one-stop beyond
imitative speaking.
3.Responsive
A good deal of students speech in the classroom is responding short replies to the
teacher or students-initiated question or comments. These replies are usually
sufficient and do not extend into dialogues. Such speech can be meaningful and
authentic.
4.Transactional
Transactional dialogue is carried out for the purpose of conveying or exchanging
18
Conversation, for example, that may have more negotiate nature for them than
does responsive speech does.
5.Interpersonal
Interpersonal dialogue carried out more for maintaining social relationship than
for the transmition of facts and information. The conversation are little trickier for
the learners because they can involve some or all of the following factors: a casual
register, colloquial language, emotionally charged language, slag, ellipsis,
sarcasm, and convert “agenda”.
6.Extensive
Extensive monologue is extended monologues in the form of oral reports,
summaries, or perhaps short speeches. In this case, the register is more formal and
deliberative. This monologue can be planned or impromtu.
2.2.2 Teaching Speaking
Teaching speaking is teaching the way to use the language for communication or
transferring ideas, etc. One important thing in teaching speaking technique or
strategy of the teacher. According to Rivers (1978:6), speaking is developed from
the first context of the language. Thus, we have to introduce speaking with the
language we are learning, because speaking is the process for the students to
express their emotions and everything in their mind. According to Brown and
Yule (1995), learning to talk in the foreign language is often considered being one
of the most difficult aspects of language learning for the teacher to help the
language is human activity in the part of the individual to make him understood
by another. It means that communication is very important for everyone.
The reseacher used monologue unplanned as her oral speaking type and extensive
as her speaking performance . The reseacher assumed that monologue unplanned
and extensive are suitable for problem solving technique and can explore the
students’ speaking ability .
The reseacher also used familiar topic, it makes the students understand what
teacher’stalking about. Daily life topic makes the students have more background
knowledge about the topic and it can help students in learning speaking ability to
try speak in English and they get motivation to increase their ability.
The reseacher concluded that the teacher must give real situation, opportunity and
motivation for the students to practice in many context and applied in the
classroom.
2.2.3 Concept of Communicative Language Teaching (CLT)
Communicative Language Teaching aims broadly at applying the theoretical
prespective of the communicative approach by making communicative
competence the goal of language teaching and by acknownledging the
interdependence of language and communication (Larsen-Freeman, 2000: 121).
According to Widdowson (1983:118), communication only takes place when we
make use of sentences to perform a variety of different acts of an essentialy social
20
record, to classify, and so on. It means teacher procedures should consider the
formal structures in situational settings in the classroom.
The emphasis on the communicative makes the proponents of this approach pay
attention to function as well as structural aspect of language. It is believed that no
single set procedures or texts are accepted as typical procedure of CLT.
Larsen-Freeman (2000: 129), the most obvious characteristicis of CLT is that almost
everything is done with a communicative intent. The students use the language
through communication with different people. People have interpreted the concept
of combination of functional and structural aspect of language in different ways
(Richard and Rodgers, 1986: 66). For some CLT means an intergration of
grammatical and functional teaching while for others, the approach means using
procedures where learners work in pairs or groups employing available language
resources in problem solving.
There are several types of communicative language teaching based on
Larsen-Freeman (2000):
1. Authentic materials
2. Scrambled sentences
3. Language games
4. Picture strip story
5. Role play
6. Information gap
7. Jigsaw
9. Picture (noting similarities and differences)
10. Working out sequence of picture
11. Following direction
12. Problem solving
13. Debates
14. Seminar
15. Panel discussion
2.2.4 Problem Solving
A problem is an opportunity to make things better, in a situation where the way
something is now does not match your goal for the way you want it to be. Solving
is to find a solution, explanation, or answer for solve the problem. Problem
solving is the process of working through details of a problem to reach a solution.
According to Ormond (2006:111), problem solving is using existing knowledge
and skills to address an unanswered question or troubling situation, while problem
based learning is approach to instruction in which students acquire new
knowledge and skills while working on a complex problem similar to those in the
outside world. During a process of problem solving the students convert the actual
now-situation into their desired goal-situation. Mayer (1995) notes that insight
occurs when a problem solver moves from a state of not knowing how to solve a
problem to knowing how to solve a problem. During insight, problem solvers
devise a way of representing the problem that enables solution
Problem solving is one of the techniques that give the opportunity for the students
22
require students to be reasonable and logical and help students to learn language
in an interesting way are the types of problem-solving. In problem solving, the
problems may be based on real or imaginary situations, and students are expected
to find possible solutions for the problems. Problem solving can help students
become more interested and active.
There are two type of problem solvings, i.e. real problem and imaginative
problem. In this research the reseacher uses imaginative problem. The reseacher
use imaginative problem because imaginative problem is more interesting for the
students. The real problem is also too difficult for the students to solve it.
The process of teaching learning in a classroom has a tendency to meet the
boredom. The boring situation in the classroom can happen . There are some
instructional strategies in problem solving based on Centre for teaching
excellence in University of Waterloo :
• Model a useful problem solving
Problem solving can be difficult and sometimes tedious. Show students by
teachers’ example how to be patient and persistent and how to follow a structured method, such as Woods’ model described. Articulate the
method as teacher use it so students see the connections.
• Teach within a specific context
Teach problem-solving skills in the context in which they will be used .
• Help students understand the problem
In order to solve problems, students need to define the end goal. This steps
is crucial to succesful learning of problem solving skills.
• Take enough time
When planning a lecture/tutorial, budget enough time for : understanding
the problem and defining the goal, both individually and as a class; dealing
with a questions from you and your students; making, finding, fixing
mistakes; and solving entire problems in a single session.
• Ask question and make suggestions
Ask students to predict “ what would happen if....” or explain why something happened. This will help them not only to develop analytical
and deductive thinking skills, But also ask question and make suggestions
about strategies to encourage students to reflect on the problem solving
strategies they use.
According to Dewey (1910) the reflective of solving the problem, namely an
active thinking process, be careful, which is based on thought process towards
definitive conclusions through five steps:
1. Student identified the problem, the problem came from outside the student's
own.
2. The next student would investigate and analyze the difficulty and determine the
issues it faced.
3. And then he connected these essays is the result of analysis or each other, and
the possibilities to solve such problems in the act he was led by his own
24
4. Then he considered the possibility of an answer or a hypothesis with the
consequences of each.
5. Then he tried to practice the one that he considered the best possible solutions.
Results will prove whether the solution solve the problem, when the solution is
not quite right, it would be tried on other possibilities to be find solving the
right solution to the problem.
On the other hands, Fullerton (1992) suggests that teacher will also need to be
able to engage in the following activities.
1. Formulating the problem
You must help the students to examine the problem from a number of
perspectives so that they will understand exactly what the problem is.
2. Analyzing the problem
Before students try to solve a problem, you need to get them to break
down the problem into its various components and assess the importance
of each component.
3. Generating Ideas
When you present students with open-ended problems (rather than
problems that have a specific answer), one of your major tasks will be to
help students generate ideas or data that can be used for solving the
problem. To do this you might : • Help students to relate the problem
situation to real situation • Help students to develop or explore analogies
4. Evaluating ideas
When solving open-ended problems, students may have difficulty deciding
on the relative merits of various ways of approaching the problem and/or
the merits of various suggested solutions.
Then, we can divide the process of problem-solving into several steps:
• The first step of introducing the problem could be warm-up activity where
the teacher can ask students to answer some questions related to the
problem and thus giving a chance to predict what the problem might be
and motivate the students. It can be a picture shown on the active-board, or
a video.
• The second step is reading of the story or watching video. Find out what
words are unfamiliar for the students and write them down on the
blackboard. Be sure that the students understand the situation.
• The third step is comprehension check. Comprehension check can be done
in different ways, for example as listening or reading exercises. At first the
teacher can ask “yes” or “no” questions then go to special questions and then offers the students to ask their own questions. Or the teacher may
offer different statements, which can be right and wrong and ask students
to say whether they are correct or not and correct the wrong ones.
• In order to choose the best solution the teacher may divide students into
pair group and ask them to discuss the possible consequences of their
decision. In this activity the teacher gives the chance to shy students who
26
come up with new solutions if the consider them to be more successful.
When the groups are ready to come up with their solution, ask them to
sound it and explain why it was chosen. Ask the students from other pairs
if they agree with it or not. Encourage the students to take active part in
this discussion as it develops their ability to persist in opinion, giving his
reasons in the target language.
• The next step is discussion. Here the students are encouraged to talk about
the issues presented in the reading and also their personal experience. The
questions may require students to make suppositions and use their
judgment. There are no correct answers. Encourage them to use their
imagination and critical thinking to come up with the possible
consequences.
• The last is asked the students to come in front of class to give their own
opinion how to solve the problem.
Larsen-Freeman (2001: 134) says that the activity just described is an example of
using a problem-solving tasks work well in CLT because they usually include the
three features of communication. What’s more, they can be structured so that
students share information or work together to arrive at a solution. Therefore,
problem solving uses their background knowledge to understand their situation
2.2.4 Concept of Pair work
The reseacher used pair work in this reseach. Pair work in work on two (Kerr :
1986). It is learnt to solve the task or problem between two people. Pair group
work provides greatly exchange opportunity for communication between students
and mostly in the communication. The atmosphere in working in groups can
reduce their fear in making mistakes while speaking in English. The students in
the group can support the others team needing help.
There are some advantages of pair group such as:
• The students can help each other
• The students can share their ideas and knowledgement
• The students are more involved and active in the classroom.
2.3 Procedures of Teaching Speaking through Problem Solving
The researcher modified problem solving procedure from Dewey and Fullerton as
follows:
a. Pre-teaching
• The teacher greets the class.
• The teacher gives the question about the topic to warm up the
students.
b. While teaching
• The students read the text they get from the teacher.
28
• The teacher gives chances to the students to state their opinion
about that problem.
• The teacher asks the students to give their solution.
• Then the teacher gives other problems to the students and gives
ten minutes for them to prepare their solution .
• The teacher asks them in pair to come in front of class and give
their solution.
• The teacher evaluates thestudents’ speaking ability, such as,
pronunciation, fluency, and comprehensibility by using oral test
sheet consist of students’ score based on their oral production.
c. Post activities
• The teacher gives comment and explains necessary things.
• The teacher provides a chance for the students to ask a question
and try to answer them.
• The teacher asks the students represantative to conclude that
lesson.
2.4 Applicability of the Procedure Implementing Problem Solving In English Class
a. Teacher
This study might give contribution to develop of teaching English. This result of
the study could be useful for additional information that could be applied by
general English teacher in teaching and implementing problem solving.
In the procedure of implementing problem solving in the class the researcher was
as teacher. She asked the question about related problem to warming up. After
that, giving a chance to predict what the problem might be and motivate the
students.
She distributed the case problem text. She asked the students the difficult word in
text to sure that students understand about text. She also check their
comprehension use “yes” or “no” question. Next shedivided them into pair group.
Then the student discussion. Here the students are encouraged to talk about the
issues presented in the reading and also their personal experience. The questions
may require students to make suppositions and use their judgment. There are no
correct answers. Now the students are ready to identify the problems and to find
the solutions and talk about the consequences. Encourage them to use their
imagination and critical thinking to come up with the possible consequences.
The last is asked the students to come in front of class to give their own opinion
30
b. Students
In the first treatment, they were looked ashamed. It caused we had the first
meeting, so their confidence were not explored yet, but after first pair come in
front of class to give their own opinion about how to solve the problem, they were
looked so friendly. The students had a good intention with the case studies from
the researcher. In the second treatment, the students had looked interested to
discuss the problem. They were looked active in the class. In the last treatment
they had looked interested to discuss and give their own opinion about how to
solve problem.
2.5 Advantages and Disadvantages
Problem solving promotes language acquciation through the types of language
and interaction they require. Such as :
1. The students are able to learn how to solve problems in which they are
involved.
2. Problem solving is the technique that gives chance for the students get some
speaking practice in front of class.
3. Problem solving can make the students creative in solving a problem.
4. Under the roles, the students can be free to speak English in giving a solution.
5. The students are more active and more motivated in English lesson.
But on the other hands, problem solving also has disadvantages, such as :
2.6 Theoretical Assumption
English teaching is regarded to increase thestudents’ ability in using English as a means of communication. According to school based curriculum for the first
grade of SMA, the students are expected to increase their language skills such as
listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills. One of the ways to increase
students speaking skills is by asking them to practice speaking more often. The
reason to recommend problem solving in teaching speaking is that the problem
solving teacher assumes a responsibility for determing and responding to learner
language needs. From the literature review above, the reseacher assumes that
problem solving technique can increasethe students’ speaking ability.
2.7 Hypothesis
Regarding the theories and assumption above, the reseacher would like to
formulate hypothesis as follows:
H1: There is a significant difference of students’ speaking ability after being
taught through problem solving.
H0: There is nosignificant difference of students’ speaking ability after being
32
III.RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter describes the design of the research, how to collect the data from the
sample of the research and how to analyze the data. This chapter also describes
the research procedure, validity, and reliability of the instrument, data treatment
and hypothesis testing.
3.1 Research Design
In this research the reseacher used quantitative research. Quantitative research is
used to examine the research question that can from the answered by collecting
statistically analyzing data that are in numerical form (Crowl, 1991:10). This
quantitative research intends to find out whether there is any significant difference
of students’ speaking ability after being taught through problem solving. In conducting the research, the researcher used time series design by giving different
topics for each treatment and every test. The researcher used one class where the
students were given three times pre-test, three times treatment, and three times
post-test. The research design is described as follows:
T1 T2 T3 X T4 T5 T6
Note: T1 T2 T3 :Pre-test
T4 T5 T6 :Post-test (Setiyadi,2006: 131)
Pre-test was administered before the treatment of teaching speaking through
problem solving technique was implemented in order, to see the students’ basic
speaking ability. Then, the researcher gave treatment that is teaching speaking
through problem solving technique. The reseacher also used treatment to know the
effective topic for teaching speaking. The post-test was adminstered afterward, to
analyze how the improvement of their speaking ability through problem solving
technique.
3.2 Sample and Population
This research was conducted at SMAN 1 Simpang Pematang. There are four
classes of second grade and every class has the same opportunity. The sample was
class X1 consisting of 30 students that had been chosen through lottery drawing.
3.3 Data Collecting Techique
The data of this research was in the form of students’ speaking ability in performing transactional dialogue in terms of pronunciation, fluency, and
comprehensibility under three topics: which topics are Friend, Family and
Holiday. In collecting the data, the researcher used the following steps:
3.3.1 Administering the Pre-test
The pre-test was administered to the students before the treatment of teaching
34
conducted in order to know the students’ basic speaking ability. Meanwhile, before conducting the pre-test, the researcher explains the topic that would be
tested. The tests were focused in oral test.
3.3.2 Administering the Post-test
The post-test was administered to the students after the treatment of teaching
speaking technique through problem solving technique will be implemented. It is
a subjective test and focused in oral test. The researcher gives three topics in every
test for the students to performance.
3.4 Research Procedure
In collecting the data, the resercher followed the following steps:
1. Determining the Subject
There are four classes at first grade of SMAN 1 Simpang Pematang
which consisted of about 30 - 38 students for each class. The sample of
this reseacher was chosen by using probability sampling technique as
the control and experimental class.
2. Selecting the Materials
The researcher chosen the materials from the students’ book based on the syllabus. The material was about understanding and using a
problem that they have to solve. The researcher conducted three
3. Conducting Pre-test
The pre-test was adminstered to the students before the treatment of
teaching speaking through problem solving technique being
implemented in order to know the students’ basic speaking ability. Meanwhile, before administering the pre-test, the researcher explained
the topic that would be tested. The tests were focused on oral test. The
researcher was conducted three times test by giving topics in each test,
they are, first pre-test (1st topic: Friend), second pre-test (2nd topic: Family ), and the third pre-test (3rdtopic: Holiday). It was a subjective test and focused in oral test. The reseacher explained generally the test
and asked the students to make a group of two. The researcher gave a
problem that they have to solve and tell it in front of the class. In
performing the test, the students were asked to speak up clearly since
the students’ voice would be recorded. Futhermore, the researcher and another English teacher judgedthe students’ performance.
4. Treatments
In this research, the treatments were administered in three meetings in
which 90 minutes that conducted three different topics in every
meeting. The topic used in the first treatment was about “ Friend”, the
second was about “ Family”, and the third was about “Holiday”. At the
first treatment the resercher asked the a question related to the
problem. She also explains the material by using Problem solving
36
problem with their pair group. The procedure of teaching speaking
through problem solving technique as follows:
a. Pre Activities
b. While Activities
c. Post Activities
5. Administering Post-test
The post-test was conducted after the treatment. The post-test was used
to know the progress of speaking ability after using problem solving
technique. Based on the research design that is time series design, the
post-tests was conducted in three times, after three meetings /
treatments. The reseacher used a subjective test in oral test.
Futhermore, the researcher gave different topics in every test. The
researcher gave a problem for the students to be solved. In giving their
solutions, the students were asked to speak clearly since the students’ voice would be recorded. Moreover, the researcher and the English
teacher “Miss Liza” judgedthe students’ performance.
6. Analyzing Data
After conducting the final test, the reseacher analyzed the data. After
collecting the data, the students’ score were analyzed subjectively by
both reseacher and teacher. Then, the reseacher analyzed the mean of
every test by comparing from the two raters based on the test. The
mean of the pre-tests and the post-tests were used to know the increase
mean of treatment also uses to know which one is the most effective
for teaching speaking.
3.5 Instruments of the Research
There are some instrument used in research. The reseacher used two kinds of test
as the instrument of the research; pretest which was given to the students before
the writer gave the treatment, and posttest which was given after the students got
the treatment.
3.6 Validity and Reliability
Setiyadi (2006: 29) mentions that in order to make research valid and reliable,
quantitative research is focused on the collected data. Therefore, because the
researcher used quantitative research, some considerations were also going to be
taken as follows:
a. Validity of the Test
Validity refers to the appropriateness, meaningfulness, and useful of the
interences a researcher makes (Fraenkel and Wallen, 1990:126). It means that
validity refers to the extent to which an instrument will give us the information
that we want. Meanwhile, Setiyadi (2006: 24) mentions that the test should reflect
all the areas to be assessed in suitable proportions and represent a balanced
sample.
Other source says that validity is a matter of relevance; it means that the test
38
validity, it has to be analyzed from content and construct validity. In the content
validity, the material and the test are composed based on the indicators and
objectives in syllabus of KTSP curriculum. The materials that are taught based on
the students’handbook for Senior high school. While, the construct validity focuses on the kind of the test that isuse to measure the students’ ability.
b. Reliability of the Test
Reliability refers to the extent to which the test is consistent in its scores, and it
gives an indication of how accurate the scores of the are. Heaton (1988 :162)
states that reliability is a necessary characteristic of any good test: to be valid, a
test first should be reliable as a measuring instrument .
To ensure the reliability of the score and to avoid the subjectively of the
researcher, inter rater reliabilities applied in this research. Inter rater reliability is
used when score of the test is independently estimated by two raters. To achieve
such reliability and to score the in the students’ speaking performance, the researcher:
1.Used a speaking criteria based on Heaton (1991). The focus of speaking skills
that have been assesed are:
a. Pronunciation
b. Fluency
c. Comprehensibility
2.Involved second rater in using the profile to give judgement for each students’
experienced in rating the students’ speaking ability. It was done to provide the consistent and fair judgement.
3.7 Data Analysis
Data analysis is a process for organizing the data in order to get the explanation
form. The reseacher analyzed the data by using these following steps:
1. Transcribing the Students’ Spoken
The reseacher recorded the students’ spoken, the reseacher transcribed the record into written form.
2. Scoring the Data
Each rater scored the students’ speaking performance of the test. After that, the two counted the avarage score that was going to be the final score.
3. Calculating the Mean
The reseacher calculated the data such as the minimum score and the
maximum score to know the mean of the test. Then the reseacher maked a
graphic based on that data. At least, the reseacher compared both pre-test
and post-test to know the increasing. The mean of the test was illustrated
40
Figure 3.1. The Example Graphic Line of Problem Solving
Line 1 indicated that problem solving had a good effect or positive effect
in teaching speaking. Line 2 indicated that problem solving that was
implemented by using problem solving had a negative effect. And then
line 3 indicated that there was no significant difference on students’ speaking ability before and after the application of problem solving.
3.8 Testing the Hypothesis Hypothesis of this research was:
H1= Tvalue> Ttable
H0= Tvalue< Ttable
H1: There is a significant difference of students’ speaking ability after being taught through problem solving.
H0: There is nosignificant difference of students’ speaking ability after being taught through problem solving.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6
1
2
This hyphotesis was statistically analyzed by comparing the mean of both pre test
and post test using excel manually, Pair Sample T-Test of SPSS 16 and then
61
V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
This chapter draws about the conclusions of this research and the reseacher’s
suggestions.
5.1 Conclusions
To answer the formulation of the problem and referring to the results the
researcher draws the following conclusions:
1. There is a significant difference of students’ speaking ability after being taught through problem solving. It means that problem solving can
increase students speaking ability. It can be seen from the finding of the
research. The total gain score of students’ speaking achievement from
pre-test to post-pre-test is; students’ mean score pre-pre-test 1 is 62.3, pre-pre-test 2 is 63.1
gain of , pre-test 3 is 64.2. Meanwhile, the result of mean score from
post-test 1 is 71, post-post-test 2 is 73.4 and post-post-test 3 is 76.8. The reseacher also
using pair sample of SPSS. The result is 1st pair 26.187 (t-value) > 2. 048 (t-table) , 2nd pair 22.079 (t-value) > 2. 048 (t-table), 3rd pair 43.847 (t-value) > 2. 048 (t-table) means that there are significant differences of
2. Regarding the three topics given are; Friend, Family, and Holiday. The
result of mean score for Friend topic is 66.86 and is up to 67.66 in Family
topic and then the last topic, Holiday is up 68.18 . The most effective
topic for teaching speaking is the third topic Holiday. It might be due to
the very familiar material to every student.
5.2 Suggestions
Based on the findings, the reseacher suggests that:
1. After having the research of problem solving in helping the students to
enhance their speaking ability, the reseacher suggests that the English
teachers apply problem solving technique in the classroom for
teaching.
2. Since pronunciation got the lowest increase, the teacher should give
more attention to students who have difficulties in pronunciation. After
the students come in front to speak, give the example to the students
how to pronunce the vocabulary that they had wrong to pronunced.
3. The researcher suggests to apply problem solving in the other skill and
use interesting topic such as imaginative topic or something which is
close to their daily life to increase students’interest and activate them
REFERENCES
Anthony, E. M. 1963. Approach, Method and Technique: English Language Teaching 17: 63-71.
Botti, J.A. & Mayers, R. 1995.Exploring the Environment: a Problem-Based Approach to Learning about Global Change. Geoscience and Remote Sensing symposium, 1, July 10-14, 391-393
Brown, H. Douglas. 2001. Teaching Educational Research: An interactive Approach to Language Pedagogy. New York: Longman.
Brown, G., & Yule, G. 1995. Teaching the Spoken Language. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Bryne, Don. 1984.Teaching Oral English. New Jersey: Longman Group Ltd.
Business.fullerton.edu/problemsolving/problemsolvingrubric3.docx Retrieved on: May, 1th 2013
Carrell, P. 1984.The Effect of Rhetorical Organization on ESL Readers. TESOL Quarterl,(18(3)), 441-469.
Channey, A. L. 1998.Teaching Oral Communication in Grades K-8. Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Crowl, Thomas K. 1996.Fundamental of Educational Research. London: Brown and Bench Mark Production.
Cte.uwaterloo.ca/teaching_resources/tips/teaching_problem_solving_skills.html Retrieved on: December, 18th 2012
Dewey, J. 1910.How We Think. Lexington, MA: D. C. Heath
Fraenkel, J. R and Wallwn, N. E. 1990.How to Design and Evaluate Research in Education. New York: McGraw-Hill Companies.
Gilman, Richard. 1968. “It’s a Show”.New Republic 159, no. 19 (9 november
1986): 29ff.
Jespersen, O.1965.The Philosophy of Grammar. New York: Norton.
Kilpatrick, J., Swafford, j., and Findell, B. (Eds.). (2001). Adding it up:Helping Children Learn Mathematics. Washington, DC: National Academic Press.
Larsen- Freeman, D. 2000. Techniques and Principles in Language Teaching. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Nunan, D. 2003.Practical English Language Teaching. New York : McGraw-Hill Companies.
Ormond, J.E. 2006.Essentials of Educational Psychology. Pearson Merrill Prentice Hall.
Pestel, Beverly C. 1993. Science Education:Teaching Problem Solving without Modeling through "Thinking Aloud Pair Problem Solving." v77 n1 p83-94
Universitas Lampung.2008.Pedoman Penelitian Karya Ilmiah. Bandar Lampung: Lampung University Press.
Rahmat, Asep. 2012.Teaching Speaking Skill Using Problem-Solving at Class Tenth of SMA Bina Muda Cicalengka. ( A script ). STKIP Siliwangi Bandung.
Richard, J., C., & Rodger, T., S. 1986.Approaches and Method in Language Teaching. Cambridge University Press.
Rivers, Wilga 1978. Teaching Foreign Language Skill. Chicago: the University of Chicago.
Setiadi, Ag. B. 2006. Metode Penelitian untuk Bahasa Asing. Jogjakarta: Graha Ilmu.
Syakur. 1987. Language Testing and Evaluation. Surakarta: 11 Maret University Press.
Welty, Don., and Doroty R. Welty. 1976. The Teacher Aids in the Instruction Team. New York: Mc. Grew Hill.
Widdowson, H. G. 1983. Learning Purpose and Language Use. Oxford: Oxford University Press.