of Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University of Jakarta)
BY:
MUTIARA RAHMAH
NIM: 1112014000042
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF EDUCATIONAL SCIENCES
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
v
Hidayatullah State Islamic University of Jakarta).
Skripsi of Department of
English Education at the Faculty of Educational Sciences of Syarif Hidayatullah
State Islamic University of Jakarta, 2016.
Advisor I
: Dr. Ratna Sari Dewi, M.Pd.
Advisor II
: Hapsari Dwi Kartika, M.A. TESOL.
This study aimed at describing
the relationship between students’ vocabulary
mastery and their writing achievement. The population of this study was the
seventh semester students of Department of English Education of Syarif
Hidayatullah State Islamic University of Jakarta academic year 2016/2017. There
were 44 students from A and B classes selected as the sample of this study. This
study used a quantitative method with the correlational study as the research
design of study. The instruments used for collecting data were vocabulary mastery
and writi
ng achievement tests. Both tests were conducted to measure students’
vocabulary mastery and writing achievement. The data which was collected was
calculated by using Pearson Product Moment Correlation to see whether there was
any significant relationship between the two variables. Based on the research
analysis, the relationship between the two variables was found at the 99% level of
confidence (p < 0.01) with the value of rxy was 0.444 which was in the medium or
moderate level. The value was higher than the value of rt in the significant of 1%,
in which 0.444 > 0.384. Moreover, the significance of t contribution revealed that
the result was significant with the value of tcount was 3.210. The value was higher
than the value of ttable
at the level of significance 0.01, in which 3.210 > 2.698.
Hence, the alternative hypothesis (Ha) is accepted and null hypothesis (Ho) is
rejected. In conclusion, there was a significant correlation between students’
vocabulary mastery and their writing achievement at the seventh semester
students of the Department of English Education of Syarif Hidayatullah State
Islamic University of Jakarta 2016/2017.
vi
Hidayatullah State Islamic University of Jakarta).
Skripsi Jurusan Pendidikan
Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri
Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2016.
Dosen Pembimbing I
: Ratna Sari Dewi, M.Pd.
Dosen Pembimbing II
: Hapsari Dwi Kartika, M.A. TESOL.
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mendeskripsikan hubungan antara penguasaan
kosakata dan pencapaian menulis siswa. Populasi pada penelitian ini adalah
mahasiswa semester tujuh Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Islam
Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta tahun ajaran 2016/2017. Sebanyak 44 siswa
dari kelas A dan B yang terpilih menjadi sampel penelitian. Penelitian ini
menggunakan metode kuantitatif dengan korelasi sebagai desain penelitian.
Instrumen penelitian yang digunakan untuk memperoleh data adalah tes
penguasaan kosakata dan tes pencapaian menulis. Kedua tes tersebut dilakukan
untuk mengukur pengasaan kosakata dan pencapaian menulis siswa. Data yang
diperoleh dihitung menggunakan korelasi Pearson Product Moment untuk
mengetahui apakah ada hubungan yang signifikan antara kedua variabel tersebut.
Berdasarkan analisa penelitian, hubungan antara kedua variabel ditemukan level
signifikansi 99% (p < 0.01) dengan nilai dari rxy
adalah 0.444 yang berada pada
level sedang. Nilai tersebut lebih tinggi dari nilai rt
pada tingkat kesalahan 1%,
yaitu 0.444 > 0.384. Selain itu, signifikan nilai t mengungkapkan bahwa hasil
tersebut signifikan dengan nilai dari thitung adalah 3.210. Nilai tersebut lebih tinggi
dari nilai ttabel
pada level signifikan 0.01, yaitu 3.210 > 2.698. Oleh karena itu,
hipotesis alternatif (Ha) diterima sedangkan hipotesis nol (Ho) ditolak. Dapat
disimpulkan bahwa adanya hubungan yang signifikan antara penguasaan kosakata
dan pemcapaian menulis mahasiswa semester tujuh Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris,
Univesitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta 2016/2017.
vii
always be upon the Prophet Muhammad, the savior of the humankind, who has
brought the light onto this world and turned it into a better place.
This
skripsi took a long process and would not have been complete without
help and support of lecturers, institution, family, and friends. Therefore, in this
occasion, the writer is pleasure to acknowledge the help and contributions by
conveying her utmost gratitude to them who have helped her in completing this
skripsi.
First, the writer would like to express a very profound gratitude to her great
parents; her dearest mother, Nurjanah, and father, Dustur, also her sisters; Luli
Akhriyani and Najmil Hayah for their love, support, and moral encouragement in
motivating the writer to finish her study. Next, the writer would like to express the
greatest honor and deepest gratitude to her advisors, Dr. Ratna Sari Dewi M.Pd.,
and Hapsari Dwi Kartika, M.A.TESOL., for patiently guiding her and giving her
the most valuable help, advice, and support during the writing process of this
skripsi.
Moreover, the writer would like to express her gratitude and appreciation to:
1. Prof. Dr. Ahmad Thib Raya, M.A., as the Dean of Faculty of Educational
Sciences.
2. Dr. Alek, M.Pd., as the Head of Department of English Education.
3. Zaharil Anansy, M.Hum., as the secretary of Department of English Education.
4. All lecturers in the Department of English Education who always give
motivation and valuable knowledge during her study.
5. All students of the seventh semester of Department of English Education in
academic year 2016/2015, as the participants of this study.
6. Her best companions; Amalia, Nia Pebriyanti, Poetri Tanjung Prameswara ,
viii
Lastly, the writer realizes that this
skripsi
is still far from being flawless.
Despite the help from the aforementioned people, there are weaknesses and
shortages in this
skripsi
that remain as the writers’ responsibility. She, therefore,
welcomes all kinds of corrections and suggestions for a better writing.
Jakarta, 2 November 2016
ix
Surat Pernyataan Karya Sendiri
... iv
ABSTRACT
... v
ABSTRAK
... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
... vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
... ix
LIST OF TABLES
... xi
LIST OF APPENDICES
... xii
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION
... 1
A.
Background of Study ... 1
B.
Identification of the Problems ... 3
C.
Limitation of the Problems ... 3
D.
Formulation of the Problems ... 3
E.
Objective of the Study ... 3
F.
Significance of the Study ... 4
CHAPTER II. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
... 5
A.
Writing ... 5
1.
Definition of Writing ... 5
2.
Genres of Writing ... 6
3.
Type of Structures in Writing ... 7
4.
The Process of Writing ... 8
5.
Writing Achievement ... 10
B.
Vocabulary ... 13
1.
Definition of Vocabulary ... 13
2.
Types of Vocabulary ... 14
3.
Vocabulary Mastery ... 16
C.
Related Previous Study ... 16
D.
Thinking Framework ... 19
x
D.
Instrument of the Study ... 22
E.
Technique of Data Collecting ... 23
F.
Technique of Data Analysis ... 25
G.
Statistical Hypotheses ... 27
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
... 28
A.
Research Finding ... 28
1.
Data Description ... 28
a.
Vocabulary Mastery ... 28
b.
Writing Achievement ... 31
2.
Data Analysis ... 34
a.
Analysis of the Linearity of Tests ... 34
b.
Analysis of the Normality of Tests ... 34
c.
Analysis of the Correlation Coefficient ... 35
d.
Analysis of Determination Coefficient ... 38
3.
Test of Hypothesis ... 39
B. Discussion ... 41
C. Research Limitation ... 43
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
... 44
A.
Conclusion ... 44
B.
Suggestion ... 45
REFERENCES
... 46
xi
LIST OF TABLES
Table 3.1 The Blue Print of Vocabulary Test ... 22
Table 3.2 Analytic Scoring Rubric... 24
Table 3.3 Pearson Correlation ... 26
Table 4.1 The Score of Vocabulary Mastery Test of 7
thSemester of
Department of English Education ... 28
Table 4.2 The Statistical Score of Vocabulary Mastery ... 30
Table 4.3 The Score of Writing Test of 7
thSemester of Department of
English Education ... 31
Table 4.4 The Statistical Score of Writing Achievement ... 33
Table 4.5 The Linearity Test Result of the Data ... 34
Table 4.6 The Normality of the Test ... 35
Table 4.7 The Data Analysis Table of Vocabulary Mastery and Writing
Achievement ... 35
Table 4.8 Pearson Product Moment Table ... 38
xii
LIST OF APPENDICES
APPENDIX 1 Vocabulary Mastery Test ... 49
APPENDIX 2 Writing Achievement Test ... 52
APPENDIX 3 The Vocabulary Mastery Score of 7
thSemester Students of
Department of English Education ... 53
APPENDIX 4 The Writing Achievement Score of 7
thSemester Students of
Department of English Education ... 55
APPENDIX 5 Original Vocabulary Mastery Test (Before Pilot Study)... 57
APPENDIX 6 Output Anates of the Pilot Study ... 61
APPENDIX 7 Statistical Calculation of Vocabulary Mastery Score... 70
APPENDIX 8 Statistical Calculation of Writing Achievement Score ... 71
APPENDIX 9 SPSS Correlation “r” Product Moment
... 72
APPENDIX 10 Pearson Product Moment Table ... 73
APPENDIX 11 T-table ... 75
APPENDIX 12 Surat Permohonan Izin Penelitian ... 77
APPENDIX 13 Surat Proposal Skripsi ... 78
APPENDIX 14 Surat Bimbingan Skripsi ... 79
APPENDIX 15 Lembar Uji Referensi ... 80
1
In Indonesia national curriculum, English is a compulsory subject. It is taught
from elementary up to university level. English has some skills that should be
learned by students which one of them is writing. Through writing, students can
produce a message in a form of written text. As Richard says that writing is one of
active/productive skill, writing requires writers to encode messages or ideas in the
form of written language.
1In order to successfully deliver the messages, many
knowledge and comprehension is needed. Some of the knowledge needed are
grammar, spelling, and vocabulary.
As it requires some knowledge and comprehension, this skill is considered
complex and difficult. If the writer fails to deliver the message, they also fail in
writing. The complexity of composing writing emerges some problems.
Regarding to Sealey that vocabulary is closely related to written language, lack of
vocabulary can be one of factors of difficulty appears in composing writing.
2Vocabulary is a crucial component in acquiring and understanding language.
When students compose writing, their vocabulary mastery will help them in
expressing ideas or messages they have so they can write fluently. Vocabulary is
the stock of words used in a language.
3The more students have stock of words
used in a language, the better their writing performance will be. Mastering
vocabulary is the ability to get or to receive lots of words. By mastering
vocabulary students will be able to deliver ideas and messages in written form
effectively.
Vocabulary is classified into noun, verb, adjective, preposition, synonym,
antonym, etc. The variety of vocabulary can be found in many English sources
1Jack C. Richards and Richard Schmidt, Longman Dictionary of Language Teaching and Applied Linguistics, (4th Ed.), (London: Pearson Education Limited, 2010), p. 322.
2Brian Richard (ed.), Vocabulary Studies in First and Second Language Acquisition, (New York: Palgrave McMillan, 2009), p. 40.
such as newspapers, magazines, televisions and radio programs, or even movies.
Reading and listening to those sources of English vocabulary are the main activity
in enriching language learners’ vocabulary.
Besides giving the input by asking
students to read and listen to English sources, teachers also need to ask students to
speak and write in English so they will not only memorize the words, but also be
able to use them.
Based on the writer
’s
observation in Writing 4 class, some of the students
have difficulties in composing essay. One of the obstacles that obstruct them in
composing an essay is their lack of English vocabulary. Students who lack of
vocabulary have difficulties in composing an essay which leads to getting low
score in Writing subject. Whenever they have an idea about what they want to
write, in their mind, the idea was still in
Bahasa Indonesia. Therefore, to turn it
into English essay, they need many English vocabularies. Moreover, when they
try to compose an essay, they often open up dictionary to find the English word
they need. In other words, having a lot of stocks of English words is needed in
composing a text. So if the stock of words mastered by students related to the
ability of composing writing, there should be relation to their writing achievement
which can be seen in a form of writing score.
Based on some problems above, the writer assumes that there is a relationship
between students’ vocabulary mastery and their writing achievement. The writer’s
assumption is in line with Saadian and Bagheri who in their research had revealed
that grammar and vocabulary have a positive effect on the quality of EFL
learners’ writing performance.
4Students with better vocabulary knowledge will
have better writing performance. It happens because students with better linguistic
knowledge are able to write better, longer, and various sentences. In other words it
can be said that student whose vocabulary mastery will also have better writing
achievement. So, to prove the assumption, the writer would like to conduct a
study with the title: The Relationship
between Students’
Vocabulary Mastery and
4
Hamideh Saadian and Mohammad Sadegh Bahgeri, The Relationship between Grammar
Their Writing Achievement (A Correlational Study at the Seventh Semester
Students of Department of English Education Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic
University of Jakarta in Academic Year 2016/2017).
B.
Identification of the Problems
1.
Students have difficulties in choosing suitable word to put in their writing
because they have limited stock of vocabulary.
2.
Students have difficulties in putting messages or ideas in written language
because of their lack of vocabulary.
3.
It is supposed that students have low writing achievement because of lack of
vocabulary.
C.
Limitation of the Problem
The writer limited the study on relationship
between students’ vocabulary
mastery and their writing achievement which was conducted at the seventh
semester students of Department of English Education of Syarif Hidayatullah
State Islamic University of Jakarta in academic year 2016/2017.
D.
Formulation of the Problem
Based on the background and limitation above, the writer formulated the
research question as
“
Is there any relationship between vocabulary mastery and
writing achievement at the seventh semester students of Department of English
Education of Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University of Jakarta
?”
E.
Objective of the Study
F.
Significance of the Study
The result of this study is expected to give some significances not only
theoretically but also practically.
1.
For students, this study will encourage to learn vocabulary more in order to
improve their writing achievement.
2.
For teachers, the result of this study can be useful as a reflection that it is
important to help students develop their vocabulary mastery in order to
improve their writing achievement as well.
5
A.
Writing
1.
Definition of Writing
Writing is one of skills learned in language learning. In writing, some
knowledge, such as grammar and vocabulary, are needed. Those knowledge are
needed because in producing a text, ideas need to be expressed so it can be
understood clearly by the reader. Many experts have different point of views in
defining writing.
Oshima and Hogue in their book said that writing is an action which includes
some processes such as thinking, writing, correcting, and revising.
1Along with
Oshima and Hogue, Harmer stated that in writing there are several stages that a
writer goes through in order to produce something in its final written form.
2This
means that writing cannot be produced instantly. Instead, it needs several stages
before it reaches its final form.
In writing, some knowledge, such as grammar and vocabulary, are needed.
Those knowledge are needed because in producing a text, the writer needs to be
able to express ideas so it can be understood by the reader. This is why Browne
agreed that writing is considered as a complex activity.
3Moreover, Sealey says
that says that vocabulary is closely related to written language.
4This means that
vocabulary plays an important role in the process of producing written language
since it has a close relation to writing.
In conclusion, writing is an activity of turning ideas or thoughts into visible
form which also can be the medium of communication. As a complex process it
1Alice Oshima and Ann Hogue, Introduction to Academic Writing, (New York: Pearson Longman, 2007), p. 15.
2Jeremy Harmer, How to Teach Writing, (Cambridge: Longman, 2004), p. 4.
3Ann Browne, Teaching and Learning Communication, Language and Literacy, (London: Paul Chapman Publishing, 2007), p. 81.
4Brian Richard (ed.), Vocabulary studies in First and Second Language Acquisition, (New
needs combination of good grammatical structures, vocabularies, punctuation and
spelling knowledge. Due to its complexity, it should be learned and mastered
through continuous practice.
2.
Genres of Writing
Each type of writing has features that separate them from another. As students
are asked to produce many different types of text, it is important for students to
know that writing has many genres. According to Brown, there are some most
common genres that students might produce; academic writing, job-related
writing, and personal writing.
5Academic writing is kind of writing used in high school and college classes.
6In other words, academic writing is any writing done to fulfill a requirement for
high school or college classes. Academic writing includes paragraphs, usually
introductory paragraph, paragraphs that develop a thesis, and concluding
paragraph. Academic writing has some characteristics. First, formal tone. In
academic writing, the author is expected to investigate a research problem from
authoritative point of view. Therefore, to make it strong, the argument must be
presented in accurate and appropriate language to avoid loaded and biased
language.
Second, the consideration of the use of third-person rather that first-person
perspective. The use of third person rather that first person perspective is
considered because the focus in academic writing usually not to who is doing the
action, but who is receiving or experiencing the result of the action. To make the
readers focus on the person, thing, or place affected by the action, sentences in the
form of passive voice can be used. The other thing that should be considered
while writing an academic writing is references. An academic writer must be
responsible to any claims made. Therefore, a list of references as either footnotes
or endnotes is a very important aspect of academic writing. Besides, citing sources
5H. Douglas Brown, Language Assessment: Principles and Classroom Practices, (New York: Pearson Education, 2003), p. 219.
is also important as it makes reader easier to identify the source that is being used.
Many kind of texts are classified as academic writing. Some of them are papers
and general subject reports, essays, academically focused journals, short-answer
test responses, technical reports (for example like laboratory reports), theses, and
dissertations.
The next genre, job-related writing, is writing which is written for the
necessity of a job. Phone messages, letters, emails, memos, and manuals are some
examples of job-related writing. And the last one, personal writing, is writing that
shows feeling, reactions, and experience that one has ever had. Unlike, academic
writings, points that writer’s
has in personal writing does not need to be proven.
Some examples of personal writing are letters, greeting cards, invitations, notes,
and personal journals.
3.
Type of Structures in Writing
Crème and Lea divide ways of organizing writing into some kind of
structures which is commonly used in university writing:
a.
Chronology Writing
This structure follows time with a sense of the sequence of events, one
following another. This structure makes the writer write a text based on events
that happens. The events are related in chronological order or time sequence
which the events took place.
b.
Description Writing
c.
Cause-Effect Writing
This structure relates events to each other. Unlike the chronology writing,
cause and effect writing relates each other by explaining problem’s cause and
the effects that result.
d.
Compare/Contrast Writing
This structure shows similarities and differences between two things. In other
words this type of structure explains that two things are similar in some ways
but different in others. When similarities and differences are reflected, a
deeper understanding of the items, like their relationship to each other and
what is most important about them, is gained.
e.
Summary Writing
This structure presents briefly about someone says. This is necessary because
a lot of university writing is specifically about discussing what the authors
have said about a topic. In other words this type of structure needs a large
reading. Summary writing does not mean rewriting the original one, instead it
aims to present basic ideas of the original reading.
7There are many kinds of structure in producing a text as mentioned above. In
summary, the way writers choose the structure depends on the purpose and
writers’ point of view of the topic itself.
In choosing the structure, writers have to
choose the appropriate one so the reader can see clearly what the writers try to
present.
4.
The Process of Writing
Writing, as a product, does not appear all in a sudden. As there are ideas that
will be delivered there, there are some steps that a writer goes through in order to
produce a text and make the ideas delivered to the reader. According to Harmer,
there are four elements in the process of writing. Those elements are planning,
drafting, editing, and final draft.
a.
Planning
Planning helps writers think more clearly about a topic. Planning effectively
also helps writer to write effectively, which means writer will have less editing
to do later on. Making detailed notes, jotted down few words or plan in their
heads are some ways in doing planning which can be done by writers. In
planning, there are three main issues. First, the purpose of the writing.
Considering the purpose of writing becomes important because it will
influence not only the type of the text which will be produced, but also
language used, and information provided. Second, writers also need to think of
the audience or the reader. They have to consider the target audience as it will
influence the shape of the writing and the choice of language. Third, writers
also have to consider the content structure of their writing. This means that
writers have to choose accurately the best way of delivering their ideas,
arguments or facts which are become the contents of the writing.
b.
Drafting
Many students, when they are asked to make writing for assignment, submit
their first draft to their teacher. The draft is often written the night before the
assignment is due. Consequently, when they see comments or feedback from
the teacher, some of them regret that what they writer should not be that way
–
structure chosen, words used, etc. This happens because writers sometimes
change their mind on one or more occasion. First version of a piece of writing
called draft. But in writing, it is possible to have more than one draft before
final version of the writing is produced.
c.
Editing
d.
Final Version
After doing three steps above, students are expected to make the final version
of their writing. The final version is written text which is ready to be shown to
the audience.
8From the explanation above, the writer concludes that writing is a process that
involves several steps: planning, drafting, editing, and final version. Planning is
when the writers set up the outlines of their writing which can be in a form of
detailed notes, and jotted down few words. The next process, drafting, is along
with editing. Writers make drafts as they edit their works. And the last one, final
version, is the writing which has gone through those steps and intended to the
reader or audience.
5.
Writing Achievement
Achievement, according to Pearson Education in Longman Dictionary of
American English, is success in doing or getting what you worked for.
9In other
words, achievement is the result that students get in the end of a learning process.
According to Brown, there are some types of test and one of them is achievement
test.
10Achievement test is a test which the purpose is to determine whether course
objectives addressed in a curriculum within a particular time have been met. With
achievement test, teachers get the evidence of the measurement of students’
ability from the class that they have taught.
Students’ achievement in writing can be measured by many kinds of writing
assessment. According to Brown, there are many types of writing assessment.
11The types of writing assessment are divided into four based on the types of
writing performances; imitative, intensive, responsive, and extensive writing.
8Jeremy Harmer, How to Teach Writing, (Essex: Pearson Education Limited, 2007), pp. 4-6. 9Pearson Education, Longman Dictionary of American English, (Harlow: Pearson Education, 2009), p.9.
10Brown, op. cit., p. 219.
Imitative writing intends students to be able to produce written language in
the fundamental basic tasks including writing letters, words, and punctuation. In
this stage, students focus on the form, therefore meaning and context become
secondary concern. In this category there are some designs of assessment which
can be used like copying, and form-completion tasks.
In copying, students will be provided examples of letters, words or
punctuations. Then the students will copy the letter or words or punctuation using
their own handwriting. While in form-completion tasks, students will be provided
pictures of simple form which asks for name, address, phone number and other
data. Then, they will be asked to write their name and address.
Intensive writing intends students to produce appropriate vocabulary and be
aware to grammatical features up to a length of a sentence. In this category of
writing performance, students focus on the form still, but unlike the imitative one,
correctness and appropriateness of every words being written is more concerned
since it determine the context and meaning of a sentence.
In assessing intensive writing, there are some designs of assessment that is
appropriate. Some of them are; picture-cued tasks and ordering tasks. In using
picture-cued tasks, teacher will provide some pictures and students will be asked
to write a brief sentence related to the pictures. In ordering tasks, students will be
provided some disordered sentences and what they have to do is to arrange those
sentences into the correct ones.
In the next type of writing performance, responsive writing, the tasks require
students to connect sentences into paragraph and develop the paragraphs and
make them logically connected. Or in other words, students have mastered basic
sentence level and become more focus to make a written text.
sure that the organization of ideas, grammatical forms and many of small errors
that might occur are minimized.
There are many designs which can be used by teachers in assessing students’
responsive and extensive writing. One of them is paragraph construction tasks. In
this assessment, students develop a topic into paragraphs. In writing the
paragraphs, students have to make sure that every paragraph has a topic sentence,
the topic is developed and connected within paragraphs, and every paragraph has
main idea and some supporting ideas.
Responsive and extensive writing has three major approaches for scoring
writing performance which are; holistic, primary trait, and analytical scoring:
a.
Holistic Scoring
Each point on a holistic scale is given systematic set of descriptors and the
reader-evaluator matches an overall impression with the descriptors to arrive
at a score. In other words, teacher or test maker reads the writing quickly then
judged the score against a rating scale or a scoring rubric that outlines the
scoring criteria.
b.
Primary Trait
Primary trait scoring focuses on particular aspect of writing and allows the
test-maker to focus on the feedback specifically. For example if test maker
asks students to make a text which the purpose is to entertain the reader, then
the score will depends on the accomplishment of that function.
c.
Analytical Scoring
In using analytic scoring, test maker will evaluate students’ writing based on
five major elements of writing; organization, logical development of ideas,
grammar, punctuation/spelling/mechanics, and style and quality of expression.
By evaluating the writing specifically, students are enabled to identify their
weaknesses and strengths.
12In short, rubrics or scoring guides can help teachers assess or evaluate
students’ writing. Besides, it also can help students know what they have to do in
order to achieve success in writing. This happens because rubrics or scoring
guides consists of a list of criteria relevant to the specific assignment.
In conclusion, achievement is the accumulative result of learning process
which can be seen in a form of score. So, writing achievement can be described as
the result of learning process of writing in a form of score. In getting the score,
many types of assessment which is used by test-taker depends on the needs. In
addition, as the types of assessing are vary, the scoring style are also vary and are
also chosen depends on the needs.
B.
Vocabulary
1.
Definition of Vocabulary
Something expressed and told need words. These words are called
vocabulary. Vocabulary plays an important role in improving communication
skill. Without having enough vocabulary, communication will end up in
unpleasant situation and make the students difficult to continue their sentences or
ideas, therefore it is essential for English teachers to help their students master
vocabulary.
Vocabulary knowledge is an important aspect of study success in foreign
language.
13This means that one who masters enough vocabulary will find fewer
difficulties than those who have less vocabulary. When they read a certain text,
they will easily get information from it since they can understand every word in
the text. Experienced teachers of English as a foreign language know very well
the importance of vocabulary. They know that the students need to learn thousand
of words that speakers use. Fortunately, the need for vocabulary is one point on
which teachers and students agree. Without vocabulary, students could not be able
to understand how the language is. The role of words is important to know how
the language is used, practiced, and communicated.
According to Jack. C Richards and Willy A. Renandya, vocabulary is a core
component of language proficiency and provides much of the basis for how well
learners speak, listen and write.
14In other words, the first thing we have to learn
when we learn a language is we have to master the vocabulary, because with
vocabulary, we can learn another language easier and will be useful for the
process of achieving language teaching objectives, in other word, vocabulary is
the important subject in language learning, if students lack of vocabulary, they
will face many obstacles.
In conclusion, vocabulary is a total words or phrases that maintain all
information used by a person, class, or profession in communication and it is
important for students who are learning a language to make them easier in
learning it.
2.
Types of Vocabulary
There are many kind of vocabulary and many experts divide them into
different categories. Read divided them into receptive and productive vocabulary.
While, Fromkin, Rodman, and Hyams classify words into content and function
words. This is in line with Radford et. al. who classify words into two categories
which are lexical and functional words.
Receptive vocabulary, sometimes called as passive vocabulary, defined as the
vocabulary associated with reading and listening materials, whereas the
productive vocabulary refers to the vocabulary used as learners are learning the
writing or speaking skills. While productive vocabulary defined as words which
are familiar or easy to recognize and often used by individual, particularly in
writing and speaking; while in contrast, receptive vocabulary are less used by
students and not recognizable as students listen or read.
15Meanwhile, content words are words used to describe things such as actions,
objects, attributes and ideas. This kind of word has full meaning and provides
links between sentences. It consists of noun, verb, adjective and adverb. In
contrast with content words, function words are words which do not have clear
14Jack C. Richards and Willy A. Renandya, Methodology in Language Teaching, (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2002), p. 225.
concept of meaning and are only used in the terms of grammatical function. In
other words, it only has full meaning when they are integrated with other words.
This kind of word includes articles, pronoun, and preposition.
A word does not always have one meaning. Sometimes, a word can have
many meaning. Moreover, Harmer said that what a word means is also defined by
its relationship to other words.
16This means that sometimes students cannot guess
a meaning of a word by a word itself. They have to see its relationship with the
other words. The relationship makes a word sometimes has more than one
meaning. Those relationships are synonym, antonym, and hyponym.
Synonym is a word having the same or nearly the same meaning as another
word in certain context, for example; depressed, sad, and miserable are synonym
because they have one same meaning which is unhappy. Antonym is a word that
has contradicted meaning with other words. for example if someone asks what is
the opposite of hard then the answer will be soft. But one word can have more
than one opposite. Therefore, teachers should lead students to aware about the
relationships between words and make them realize that it is possible for a word
to have more than one antonym. Hyponymy is relationship where one word
includes others within a hierarchy, so there are superordinate words and
subordinate words. For example, there is a word ‘flower’, which is the
superordinate words, and ‘rose’ and ‘orchid’ being the subordinates hyponyms of
‘flower’. Thus, ‘flower’ and ‘rose and orchid’ are co
-hyponyms of each other.
In conclusion, there are many types of vocabulary. Some of them can be
categorized by the division of language skills, such as receptive vocabulary which
is associated with receptive skills, while productive ones compromised with
speaking and writing skill. Besides, vocabulary also can be classified based on its
parts of speech or word classes such as verb, noun, adjective, and etc. Then,
beside classified based on part of speech, it also classified from its relationship
with other words.
3.
Vocabulary Mastery
Vocabulary is one of language aspects which should be learned. Learning
vocabulary is important as learners need it in order to be able to speak, wrote, read
and listen to a language. According to Cameron, a person is said to know a word
if they can recognize its meaning when they see it.
17It means that in learning
vocabulary it is important to know not only the meaning but also its use in a
particular context.
According to Read, vocabulary is knowledge of knowing the meanings of
words and therefore the purpose of a vocabulary test is to find out whether the
learners can match each word with a synonym, a dictionary, or an equivalent word
in their own language. In learning vocabulary students have to know the meaning
of the words and be able to use it in sentences depends on the context.
18English has many words or even words families. According to Sebastian,
here are the number of words need to be learned by English as a Second Language
Students;
a.
1000 to 2000 high frequency words for basic conversations and everyday
texts;
b.
8000 words for advanced conversations;
c.
10,000 to 20,000 word families (excluding phrases and expressions) to read at
a university level.
In conclusion, vocabulary mastery can be defined as a number of words in a
language which contains information about meaning, form, and usage in context.
Vocabulary mastery is not a spontaneous process which is easy to be done.
Students have to read, and hear a lot of words and do a lot of practices expressing
it whether in spoken or written form.
17Lynn Cameron, Teaching Languages to Young Learners, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001), p. 78.
C.
Related Previous Study
The following are the previous studies related
to the variables of the writer’s
study comprising vocabulary mastery and writing achievement. First, a study
entitled ‘
The Relationship between Grammar and Vocabulary Knowledge and
Iranian EFL Learners’ Writing Performance’
was conducted by Saadian and
Bahgeri. The study was conducted to find out grammar and vocabulary
knowledge and its relationship with
learners’ writing performance
. This study
used correlational design. The instruments used were tests. The total participants
of this study were 42 students. The data analysis of the study used Pearson
product Moment correlation. Based on the findings of the study it was found that
there was a significant correlation between grammar and vocabulary knowledge
and their writing quality.
19In addition, Staehr investigated
Vocabulary Size and the Skills of Listening,
Reading, and Writing. The aim of this study was to find out the relationship
between vocabulary size and the skills of listening, reading, and writing in English
as a Foreign Language (EFL). There are 88 EFL learners as participants of this
study. Tests were distributed as the instruments in collecting the data. Two tests in
a form of multiple choices were used to measure reading and listening
comprehension. Next, in measuring the writing skills, a 450-word composition
was used. And, to measure the vocabulary size, VLT in improved version by
Schmitt, Schmitt, and Clapham was used. The result of analyzing data of this
study revealed that reading skill was found to be the most dependent on
vocabulary size, followed by writing skill which was found to correlate
significantly and fairly highly with vocabulary size. Then, in contrast, listening
showed the weakest association with vocabulary size.
20Another study conducted by Novikasari with the titl
e ‘
The Correlation
between Students’ Vocabulary Mastery and Their Translation Ability of the
19Hamideh Saadian and Mohammad Sadegh Bahgeri, The Relationship between Grammar and
Vocabulary Knowledge and Iranian EFL Learners’ Writing Performance (TOEFL PBT Essay),
International Journal of Language Learning and Applied Linguistics World, Vol. 7 (1), 2014, p. 12.
20Lars Stenius Staehr, Vocabulary Size and the Skills of Listening, Reading, and Writing,
Second Year Students of Senior High School’
has found that the correlation
coefficient between two variables (vocabulary and translation ability) is higher
(0.749) than the table value (0.361) which means that there is a significant
positive correlation between the two variables. Same as the previous one, this
study has more differences that similarities compared with the writer’s. The
similarities are only in the method and design, and sampling technique. The
differences are in the time, place, population and sample. The instrument used is
different as well as Novikasari used only test while the writer will use both test
and documentation.
21Furthermore, a study under the title
The Effect of Blogging on EFL Writing
Achievement was conducted by Emrah Ozdemir and Selami Aydin. It was
conducted in ELT Department of Balikesir University in Turkey. The total
participants were 40 EFL students. They were divided into two groups; control
and experimental group. The instruments used were questionnaire and writing
achievement pre-test and post-tests. The experimental group was given a
treatment involving some process-based writing instruction; meanwhile
participants from the control group completed task in traditional pen-paper writing
process. The findings of this study mentioned that the participants who received
process-based writing instruction attained greater improvement in their writing
achievement. It was shown from the experimental group who outperformed the
control group in terms of writing achievement.
22In comparison with the previous studies discussed and reviewed above, this
study has similarities and differences from those relevant previous studies. First,
although Saadian and Bahgeri carried out study with similar design to this study
(correlational design), the inspection of their study is not specifically limited to
vocabulary but they also investigated grammar knowledge. On the other hand, this
study is conducted to find out vocabulary knowledge in relation to writing
21Yuanita Novikasari, The Correlation between Students’ Vocabulary Mastery and Their
Translation Ability of the Second Year Students of Senior High School, (Skripsi, Faculty of Language and Arts, Semarang State University, 2011).
22Emrah Ozdemir and Selami Aydin, The Effect of Blogging on EFL Writing Achievement,
performance. Next, in comparison with study conducted by Staehr, this study also
carried out similar design to this study, but the inspection is broader than this
study. Staehr investigated vocabulary in relation to some skills which are
listening, reading, and writing. However, it had same type of instruments used as
this study, i.e tests.
Then in comparison to another study conducted by Novikasari, although the
design applied was the same as this study, the variables studied were not all the
same i.e. vocabulary and translation ability. Next, in the comparison to a study
conducted by Ozdemir and Aydin, although the study investigated the same
dependent variable, i.e. writing achievement, they applied different design from
this study. T
he study’s design was categorized as an experimental d
esign since the
study was intended to find out the effect of blogging towards the writing
achievement. By any considerations of the reviews of related previous studies
above, it can be considered that this study is not a replica of the previous studies,
instead it is an expansion as well as a more specific research focusing on
vocabulary mastery and writing achievement as the variables of this study.
D.
Thinking Framework
Based on theories above, writing is one of language skills which is important
to be learned. In language learning, students can express their ideas and message
through written language by writing. Writing is defined as an activity of turning
ideas into written form. Writing is not only jotting down some words, more than
that, it also a complex process which needs a combination of many kinds of
knowledge. Moreover, when students compose writing, they need many words to
be able to express their ideas or messages effectively.
better in writing. It happens because when students write, they think about what
word will be used in the writing. Students may be able to write effectively as they
know adequate English words. In other words, if students have mastered English
vocabulary, their language learning, especially in writing, will be well facilitated.
Therefore, the writer assumes that student
s’ vocabulary mastery has a relationship
with students’ writing achievement.
E.
Theoretical Hypotheses
The theoretical hypothesis of this study is that there is a relationship between
21
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A.
Place and Time of the Study
This study conducted at Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University of
Jakarta which is located at Jl. Ir. Juanda No. 95, Ciputat, Tangerang Selatan,
started form February 14
th, 2016 to November 2
nd, 2016.
B.
Method and Design of the Study
A quantitative method with correlational design was used for this study.
The method and design were selected because the aim of this study was to prove
whether there wa
s a relationship between students’ vocabulary mastery and their
writing achievement. In this study, the variable which was explained and affected
by another variable, or usually known as X variable, was
“
vocabulary mastery
”.
While the variable which was being affected by the independent variable, or
usually known as Y variable was “writing achievement”
.
C.
Population and Sample
The population of this study was 64 students of seventh semester students
of English Education Department of Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University
of Jakarta in academic year 2016/2017. Those 64 students were divided into three
classes; 7A, 7B, and 7C. 7A and 7B were consisted of 22 students each, while 7C
was consisted of 20 students. Then, to choose the sample, the writer used
purposive sampling technique. The sample chosen were 7A and 7B. So in total,
there were 44 students participated in this study as samples.
D.
Instrument of the Study
In collecting the data, test were used as the instruments of this study.
There are two tests: vocabulary test and writing test. Both tests are conducted by
the writer. The content of the vocabulary test was arranged based on syllabus of
Vocabulary II. Vocabulary II was one of the subjects in Department of English
Education of Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University of Jakarta. The subject
was chosen as it was the highest vocabulary subject taught in Department of
English Education of Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University of Jakarta.
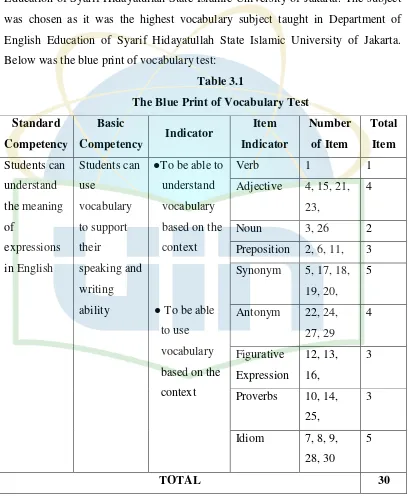
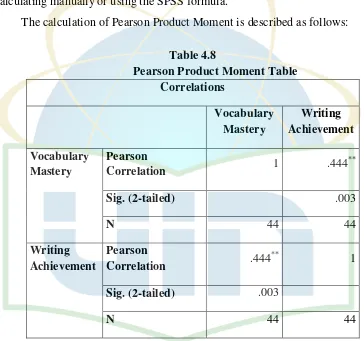
[image:34.595.109.517.229.725.2]Below was the blue print of vocabulary test:
Table 3.1
The Blue Print of Vocabulary Test
Standard
Competency
Basic
Competency
Indicator
Item
Indicator
Number
of Item
Total
Item
Students can
understand
the meaning
of
expressions
in English
Students can
use
vocabulary
to support
their
speaking and
writing
ability
●
To be able to
understand
vocabulary
based on the
context
●
To be able
to use
vocabulary
based on the
context
Verb
1
1
Adjective
4, 15, 21,
23,
4
Noun
3, 26
2
Preposition
2, 6, 11,
3
Synonym
5, 17, 18,
19, 20,
5
Antonym
22, 24,
27, 29
4
Figurative
Expression
12, 13,
16,
3
Proverbs
10, 14,
25,
3
Idiom
7, 8, 9,
28, 30
5
The second test, writing test was arranged based on syllabus Writing IV.
Writing IV was also one of the subjects taught in Department of English
Education of Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University of Jakarta. The content
of Writing IV syllabus was used as Writing IV was the highest writing subject that
they had passed. Based on the syllabus, students of Department of English
Education of Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University of Jakarta must be able
to make an argumentative essay. Therefore, the writer asked the students to make
an argumentative essay.
E.
Technique of Data Collecting
Before collecting the data, the writer conducted a pilot study for the
vocabulary test. Pilot study was used to try out and check the validity and the
reliability of the instrument. The writer used Anates software to find out the
validity and the reliability. Based on the calculation, the validity and the reliability
of the test were 0.52 and 0.68 which mean that the test was valid and reliable.
After being analyzed, from 45 items, 30 of them were chosen to be included in the
vocabulary test as the instrument to collect the data.
After conducting a pilot study, the writer distributed the tests and started
collecting the data. The writer used test as the instruments to measure vocabulary
mastery and their writing achievement. The data for the writing achievement were
taken first. After that, the writer collected the data of vocabulary test. In scoring
Table 3.2
Analytic Scoring Rubric
1Score
Level
Criteria
Content
30-27
EXCELLENT TO VERY GOOD: knowledgeable
●
substantive ● through development of thesis ●
relevant
to assigned topic
26-22
GOOD TO AVERAGE: some knowledge of subject
●
adequate range ● limited development of thesis ●
mostly relevant to topic, but lacks detail
21-17
FAIR TO POOR: limited knowledge of subject
● little
substance ● inadequate development topic
16-13
VERY POOR: does not show knowledge of subject ●
non-
substantive ● not pertinent ● OR not enough to
evaluate
Organization
20-18
EXCELLENT TO VERY GOOD: fluent expression
●
ideas clearly stated/sup
ported ● succinct ● well
organized ● logical sequencing ● cohesive
17-14
GOOD TO AVERAGE: somewhat choppy
● loosely
organized but main ideas stand out ●limited support ●
logical but incomplete sequencing
13-10
FAIR TO POOR: non-fluent
● ideas confused
or
disconnected ● lacks logical sequencing and
development
9-7
VERY POOR: does not communicate
● no organization
● OR not enough to evaluate
Vocabulary
20-18
EXCELLENT TO VERY GOOD: sophisticated range
● effective word/idiom choice and usage ● word
form
mastery ●appropriate register
17-14
GOOD TO AVERAGE: adequate range
● occasional
errors of words/idiom form, choice, usage but meaning
not obscured
13-10
FAIR TO POOR: limited range
● frequent errors of
word/idiom form, choice, usage ● meaning
confused or
obscured
9-7
VERY POOR: essentially translation
● little knowledge
of English vocabulary, idioms, word form ● or not
enough to evaluate
Score
Level
Criteria
`Language
Use
25-22
EXCELLENT TO VERY GOOD: effective complex
constructions
● few
errors of agreement, tense, number,
word order/function, articles, pronouns, prepositions
21-18
GOOD
TO
AVERAGE:
effective
but
simple
constructions
● minor problems in complex
constructions ● several errors of agreement, tense,
number, word order/function, articles, pronouns,
prepositions but meaning seldom obscured
17-11
FAIR TO POOR: major problems in simple/complex
constructions
●frequent errors of negation, agreement,
tense, number, word order/function, articles, pronouns,
prepositions and/ or fragments, runs-ons, deletions,
●meaning confused or obscured
10-5
VERY POOR: virtually no mastery of sentence
construction rules
● dominated by errors ● does not
communicate ● OR not enough to evaluate
Mechanics
5
EXCELLENT TO VERY GOOD: demonstrates
mastery of conventions
● few errors of spelling,
punctuation, capitalization, paragraphing
4
GOOD TO AVERAGE: occasional errors of spelling,
punctuation, capitalization, paragraphing but meaning
not obscured
3
FAIR TO POOR: frequent errors of spelling,
punctuation, capitalization, paragraphing
● poor
handwriting ● meaning confused or obscured
2
VERY POOR: no mastery of conventions
● dominated
by errors of spelling, punctuation, capitalization,
paragraphing ● handwriting illegible ● OR not enough
to evaluate
6. Technique of Data Analysis
After collecting the data needed, the writer started analyzing the data by
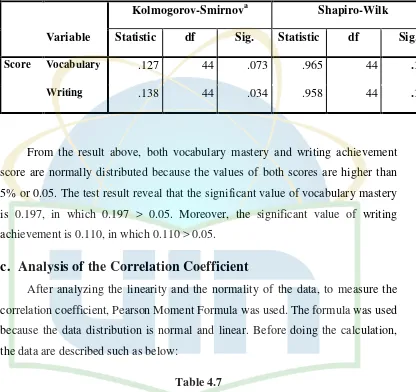
testing the normality and linearity. In calculating the correlation, a formula called
Product Moment from Pearson was used. These steps are along with Susetyo who
said that to study a correlation between two variables a test of normality and
linearity are necessary to be conducted and can use Product Moment from Pearson
to calculate the correlation.
2a.
Finding the number of correlation using formula
3:
N= the number of respondent
X= the students’ score in vocabulary
Y= the students’ score
in writing
ΣX = the sum of vocabulary scores
ΣY = the sum of writing score
ΣX
2= the sum of the squared scores of grammar
ΣY
2= the sum of the squared scores of writing
ΣXY = the sum of multiplied score between X and Y
The formula above is used in finding
index correlation “r” product
moment between X variable and Y variable (r
xy).
[image:38.595.113.512.174.733.2]To interpret the index scores of “r” correlation, product moment (rxy
) the
interpretation such as below is used:
4Table 3.3
Pearson Correlation
The Score of “r”
Product Moment (r
xy)
Interpretation
0.00 - 0.19
There is a relationship between X and
Y, but the correlation is very weak or
little so it is ignored or it is considered
no correlation in this rating.
0.20
–
0.39
There is a relationship between X and
Y, but it is weak or little.
0.40
–
0.69
There is a relationship between X and
Y. The value is medium.
0.70
–
0.89
There is high relationship between X
and Y.
3Ibid. 4
The Score of “r”
Product Moment (r
xy)
Interpretation
0.90
–
1.00
There is a very high relationship
between X and Y.
7. Statistical Hypotheses
1.
If r
ois the same as or higher than r
t, the H
ais accepted which means that
there is a relationship between vocabulary mastery and writing
achievement.
2.
If r
ois lower than r
t, the H
sis rejected which means that there is no
28
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
A.
Research Finding
1.
Data Description
The research was conducted at Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University
of Jakarta in which the seventh semester students of Department of English
Education were involved as the participants of the research. There were two
different tests conducted in this study; vocabulary mastery test and writing
achievement test.
The tests were conducted in order to get data of students’
vocabulary mastery and their writing achievement. The data was described as
follows:
a.
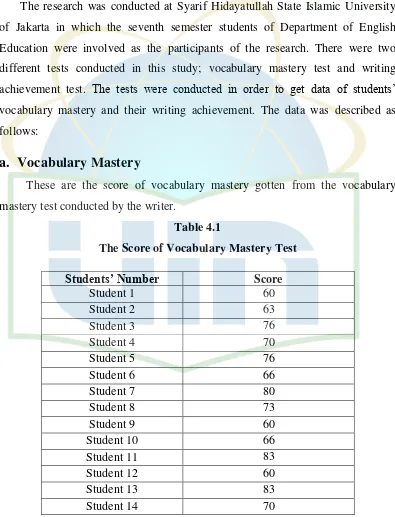
Vocabulary Mastery
These are the score of vocabulary mastery gotten from the vocabulary
[image:40.595.114.509.235.752.2]mastery test conducted by the writer.
Table 4.1
The Score of Vocabulary Mastery Test
Students’ Number
Score
Student 1
60
Student 2
63
Student 3
76
Student 4
70
Student 5
76
Student 6
66
Student 7
80
Student 8
73
Student 9
60
Student 10
66
Student 11
83
Student 12
60
Student 13
83
Students’ Number
Score
Student 15
83
Student 16
66
Student 17
83
Student 18
63
Student 19
83
Student 20
66
Student 21
73
Student 22
70
Student 23
83
Student 24
70
Student 25
56
Student 26
76
Student 27
86
Student 28
76
Student 29
80
Student 30
70
Student 31
76
Student 32
80
Student 33
63
Student 34
86
Student 35
80
Student 36
66
Student 36
80
Student 38
73
Student 39
90
Student 40
76
Student 41
76
Student 42
73
Student 43
86
Student 44
93
These scores were gotten by dividing the number of correct answer with the
total number of the item and it was multiplied by 100. There were three students
who got score 60, three students who got 63, five students got 66, five students
got 70, four students got 73, seven students got 76, five students got 80, six
students got 83, three students got 86, one student got 90, and one student got 93.
From the data, it is known that the total number of the students is 44.
Then, to count the statistical score of vocabulary mastery, the writer used
to know the mean, median, mode, maximum and minimum score, and sum. The
[image:42.595.118.504.212.590.2]data is described as follows:
Table 4.2
The Statistical Score of Vocabulary Mastery
Statistics
Vocabulary
N
Valid
44
Missing
0
Mean
74.27
Median
76.00
Mode
76
Minimum
56
Maximum
93
Sum
3268
From the descriptive statistic above, the respondents of this study are 44
students. The mean of vocabulary score is 74.27, which means that it is the
average score obtained by the students. The median score of the vocabulary
mastery is 76. Then, the mode of score is 76, which means that most students
obtained 76 in vocabulary mastery test. Then, the lowest score of vocabulary
mastery is 56 while the highest is 93.
In Department of English Education, score is characterized as follows:
80
–
100 = A
70
–
79 = B
60
–
69 = C
A is characterized as an excellent score. It is the highest score a student can
obtain if they pass a test excellently. Then, B is characterized as a good score.
Next, C is characterized as a medium score, or the test takers passed but it is
recommended to retake the test or have a remedial test. The last, D, is
characterized as a bad score or means that the test takers failed to pass the test.
Based on description above, it can be concluded that the seventh semester
students of Department of English Education in academic year 2016/2017
obtained good scores in vocabulary mastery. It can be seen that most of students
obtained score 76, in which score 76 is characterized as B, the good score.
Overall, the seventh semester students of Department of English Education at
Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University of Jakarta in academic year
2016/2017 have good vocabulary knowledge.
b.
Writing Achievement
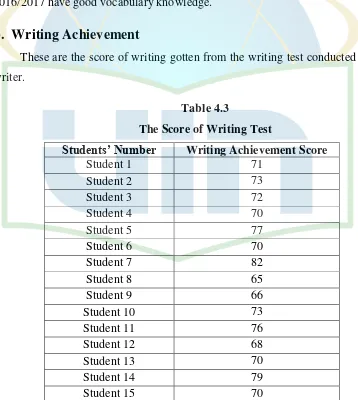
These are the score of writing gotten from the writing test conducted by the
[image:43.595.120.478.346.746.2]writer.
Table 4.3
The Score of Writing Test
Students’ Number
Writing Achievement Score
Student 1
71
Student 2
73
Student 3
72
Student 4
70
Student 5
77
Student 6
70
Student 7
82
Student 8
65
Student 9
66
Student 10
73
Student 11
76
Student 12
68
Student 13
70
Student 14
79