138 Santoso Med J Indones
Percutaneous
transluminal coronary
angioplasty
of
the
very
proximal
left anterior
descending
coronary
artery lesions
Teguh
SantosoAbstrak
I]ntuk menilai hasil angioplasti karoner transluminal perkutan
efCA)
pada segmen yanç amat proksimal dari pembuluh left anterior descending coronary artery U,AD) dilakukan analisisdari
153 penderitayangmenjalani PTCA padapembuluh tersebut. Jarak Iesi dari ostium pembuluh LAD diukur pada proyelcsi angiogramight
anterior oblique. Duapuluh penderita (kelompok I) mempunyai Iesi amat prol<simal ( 0,5 cm dari ostium), 39 penderita (kelompok II) mempunyai lesi intermediate prortmal ( 0,5 cm dari ostium, tetapi sebelum cabang septal pertama) dan 92 penderita (kelompokIII)
mempunyai lesi lebih distal. Lesi berangkai (tandem lesions) yang harus ditiup balonberlcali-kali ditemui padag (40.97o) penderitadari kelompok I, 11 (28,2 Vo) penderita dari kelompokll (tidak termasuk penderita yang sudah dimasukkan dalam kelompok I d.an 23 (25Vo) penderita dari kelompokIII
(tidak termasuk penderita yang sudah dimasukkan dalam kelompokI
danII
). Angka keberhasilan adalah 20 (90,9 7o); 38 (97,4 Vo) dan 82 (89,1 Vo), masing-masing pada kelompokI,
II
danIII.
Perbedaan antar kelompoktilak
bermakna. Luas penyakit, derajad serta beratnya kelninan morfologik tidak mempengaruhi keberhasilan.Tidak ditemui komplikasi pada penderita kelompokI.
Diseksi pembuluh left main stem tidakpernah terjadi-Seorang penderita kelo:mpokIII
mengalami infark dan seorang penderita dari kelompokIII
meninggal. Pada 2;I
dari 9 penderita dari kelompokI,
II
danIII
oklusi total pembuluh tidak dapat dilewati. PTCA pada pembuluh I'AD yang mata proksimal dapat dilakukan secara aman dengan angka keberhasilan yang tinggi.Abstract
To assess the result of percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) of the very prortmal left anterior descending (LAD) Iesions, 153 consecutive patients undergoing PTCA
of
LAD were analyzed. The distance ofthe lesionfrom the origin of LAD was measuredin the right anterior oblique angiogram. Twenty - two patients (group I) hadveryproximallesion( 0.5 cmfromthe origin), 39 patients ( groupII)
had intermediate proximal lesion ( 0.5 cm from the origin, but still before thefirst
septal branch) and 92 patients (groupIII)hadmoredistallesion.Tandemlesionsnecessitating multipleballooninflationwereobservedin9(40.9Vo)patientsof groupI,
1 1 (28.2 7o) patients of groupII
(excluding those already included in group I) and 23 (25 Vo) patients of groupIII
(excluding those already included in groupsI
andII).
Success rates were 20 (90.9 %); 3S (97.4 Vo) and 82 (89.1 Vo) respectively, in group I,II
and III. Dffirences were statistically not significant. Extent of disease as well as degree and morphologic severity did not influence success. No complications occured in any patient of group I. Dissection of the main stem has not observed. One patient of groupIII
developed acute infarction and one patient of groupIII
died. We failed to cross chronic lotal occlusion in, respectively; 2,I
and 9 patients of group I,II
andIII.
PTCA of the very proximal I'AD can be performed safely with a high success rate.Keywords :PTCA, left anterior descending coronary artery.
INTRODUCTION
Proximal
left
anterior
descending
(LAD)
coronary
artery
diseaseis
generally
considered as
a high risk
lesion
associatedwith
an increased ratesof
death andmyocardial
infarction.
However,
treatment
of
such lesion has remainedcontroversial.
Compared tomedi-cal therapy, coronary
artery bypass surgery
hasnot
beenconclusively
demonstrated toimprove survival or
preyent myoc,ardial
intarction
in
thii
sstting.l-3
The
dilemmas
are renewedby
the increasing useof internal
Division
of
Cardiology, Departmentof
Internal Medicine, IJniversityof
Indonesia Medical School/
Dr. Cipto Mangunkus umo H ospital, J aknrta, Indonesiamammary bypass
grafting, which long term
patency
andlow perioperative
infaction
andmortality
has made theprocedure
aneffective
therapy."-'
The recent advent
of
percutaneous
transluminal
coronary angioplasty
(PTCA)
andparticularly
theever
increasing angioplasty operator experience and
con-tinued
improvement
in
methods and equipment
have changedthe
approachsubstantially. Currently PTCA
hasemerged
as analternative
effective
treatment
for
proximal
LAD
diseasewith
ahigh
successrate,
lo'wincidence
of
procedural complication and
excellent
long term
result.s-|2
However,
therisk
of
PTCA of
aVol 7, No 3, July - September l,998
This study
wasundertaken to determined
the immedi-ate success rimmedi-ate andprocedural complication
of
pTCA
of
thevery
proximal LADlesion.
METHODS
Patients
The study groups included
153 consecutive
patients undergoingPTCA
of
theLAD.
Their
ages rangedfrom
3I
to
12 years and
1 18were
male.
A
history of prior
myocardial
infarction
was notedin
37 (24.2Vo)patients.The
left
ventricular function,
as
assessedby
contrastventriculography
wasnormal
(EF 55Eo)inI0I
(66.0Vo)patients,impaired
(EF
>30-55
Vo)in 43 (28.I
Eo)patients and
poor (EF
<
30Vo) in
9 (5.9
Zo) patienrs. Patients who had angioplastyfor
treatmentof
an
acuteevolving
myocardial
infarction
were
excluded.The distance
of
thelesion
from
theorigin
of
LAD
was measuredin
theright
anterior oblique angiogram.
Theproximal
LAD
lesion
was defined
asextending
from
the
vesselorigin to
the
take-off
of
the
anatomic
first
septal
perforator
branch.The patients were
divided into
3groups depending
tothe site
of
the
LAD
stenosis. Group
I
comprised
of
patients
with very proximal
lesion, that
was less than0.5 cm
from
the
vesselorigin but still
before
thefirst
septal
branch.
Group
II consisted
of
patients with
proximal
lesion of
greater than 0.5 cmfrom
theorigin.
Group
III
hadmore distal
lesion.
patients
with
tandemlesions were classified according
to
their proximal
stenosis.
Defïnitions
Extent
of
coronary artery
diseasewas defined
as thenumber
of
epicardial
vessel
(ormajor
branches)
with
>70Vo stenosis
by
visual
estimation.
Single
vesseldisease
referred to > 70%
stenosisof
theLAD.
Severity
of
lesion
was
classified
astype
A, B,
or
Caccording
to
the recommendation
of
the
American
College
of
Cardiology/American Heart
Association
Task
Force.Successful
coronary dilatation
wasdefined
as less than 507oresidual
stenosis
with
>
20Voreduction
of
theoriginal
stenosis
in
the
absenceof
infaction,
urgent
bypass
surgery or
death.Angioplasty Procedure
Unless contraindicated, medications given
before
PTCA usually consisted of
nitrates,
calcium
channelPercutaneoustransluminalcoronaryangioplasty
I39
blocker, aspirin
andticlopidine. Angioplasty
was
at-temptedfirst
todilate
themost severely
disease vesselsupplying
the greatest amount ofjeopardized
myocar-dium.
If
this primary
target
vesselwas
theLAD
andthe lesion were
multiple, PTCA
was
startedfrom
themost distal
vesselupstream.
During
balloon
inflation,
care
was
takennot to
obstruct the
left main
coronary
artery. However,
to achieve anoptimal
result
occasio-nally dilatation
had
to
be
performed with part
of
theballoon in
theleft
maincoronary artery;
an attemptthat
was
only
possible
if
the sizeof
theleft
main coronary
artery
wasbig
enough toallow
unhindered
flow
to theleft
circumlex coronary
artery. A
goodflow
to theleft
circumflex coronary artery after
contrast
injection in
the absence
of
a sudden dropof blood
pressure securedthat
this
artery
wasnot compromised. In
no
instancewas
adouble guide
wire
technique
used. During
theprocedure, intravenous heparin and intracoronary
nitrates
were
used.
After PTCA
patients
were
main-tained on heparin
for
<
24 hours,
and
continued
toreceive nitrates
for
>
24
hours,
a
calcium
channelblocker
for
>
6
months and
antiplatelet indefinitely.
No
stents, lasersor
atherectomy devices were
usedin
this
study.Statistical Analysis
Univariate
analysesbetween groups
were
performed
by
using the
t-test.RESULTS
Twenty-two
patients belonged to group
[,
39 patientsto
group
II and
92
patients
to
group
III.
Tandemlesions necessitating
multiple ballon inflations
wereobserved
in9
(40.9Vo) parienrsof
group
I,
tl
(2g.ZEo)p-ât-rents
of
group
II
(excluding
thosealready included
in
groupI
) and 23 (25Vo) patientsofgroup
III
(exclud-ing
thosealready included
in
group
I
andII).
All
groupsof patients were
similar with
respect to theextent
and degree ormorphologic
severity
of
coronary
artery
disease(Table
l).
Success
rates were
90.9Vo
i
97.4Vo
and
89.lTo
in,
respectively, group
I,
II
and
III.
No
complications
occurred
in
anypatients
of
group
I. Dissection
of
theleft
main coronary artery
wasnot noted.
One patient
of
group
III developed
an
acute
infarction
and
onepatient
of
group
III
died.
None required
emergencybypass
grafting
and
no patient
experienced
a
stroke.We
failed
to
crosschronic total
occlusions
in,
t40
SantosoTable 1. Extent and moehologic severitJ.
Group I Group II Group III
Med J Indones
coronar)
revascu\adzation, randomized
tria\
compar-ing
bypassgrafting
andPTCA
islacking.
Furthermore
the
results
of
anon
matched
patient
series
in
which
heterogeneous
patient
groups undergo
PTCA
or
bypass
surgery
based
on
physician
and patient
preference are not
conclusive.lo
In
arandomized
trial
comparing
PTCA
andmedical
therapyin
thetreatment
of
single
vessel
disease,PTCA
is
reported
to
offer
earlier
and more completerelief
of
angina thanmedical
therapy
andis
associatedwith
better performance
onthe
exercisetest. However PTCA
treatment involves
asmall immediate
risk of
acutemyocardial
infarction
and acute
coronary occlusion
leading to bypass surgeryand a later
needfor redilatation to
treat
restenosis.20The relatively small number
of
patients recruited in
this
trial
does
not allow
analysis
to
be
done
on
theimpact
of
PTCA
on
theLAD.
Earlier
studies
of
PTCA
for LAD
stenosis reoorted
clinical
successrates
of
only
84.5
EoBto
90.6
Eo,ge
incidence
of
myocardial
infarction
was Vo)8 anda
greatér
proportion
of
patients
hospital
bypass surgery (7 .7 Vo to 8.3 Vo).6'eThe lower
successrates and the greater number
of
in-hospital
eventsreflect
thetime period of
the studies.In
both
studies
no particular attention was paid
onlesion
in
thevery proximal
part
of
the LAD.
Recent studies showed that ahigher
success rate (around95%)
and a
lower
proceduralcomplication
(less than 3Vo)can
beachieved.ll'12
In
the
present study
we
specifically
analyzed
theresults
of
PTCA
of
the very proximal
LAD
lesions,which
may
carry
ahigher
risk
if the procedure result
in
occlusive
dissection
with
involvement
of the
mainstem.
Regardlessof
number
of
vesselsinvolved
and
the
degreeor
morphologic
severity
of
the lesion,
the
successrate
of in
patients
with
very
proximal
stenosis
did
not differ with
those
having more
distal
narrowing
(s).
In this small
seriesof
patients we
did
not
observe any
complication including
dissection
of
the
left
main
stem.
Comparison
with
other
recent
reports
yields similar
find-ings.ll'12 Technical
im-provements
with
stents,
lasers, atherectomy (DCA,
rotablator,
TEC device) may offer better results for
specific lesions,
i.e.
DCA
appears
well
suited
for
stenosis
which
are eccentric, ulcerative
or
contain
small-moderate
amountsof thrombus.
The rotablator
may
be
of
benefit when
moderate
angulation or
cal-cification
is
present,but
should be avoided when
clot
is evident.2l
There
has beenconsiderable discussion regarding
therelatively high
restenosis
rate
(up
to 40
Vo)of
theproximal LAD, in
comparison
with
other locations
in
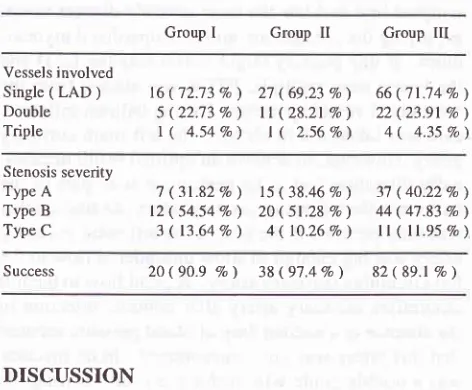
Vessels involved
Single ( LAD )
Double
Triple
16(72.73
Eo)
27 (69.237o)
66 ('n;14Eo)5(22.73Vo) ll(28.21 Vo)
22(23.91 Eo)r(
4.54Eo)
I (
2.56Vo)
4(
4.35Vo)Stenosis severity Type A
Type B Type C
7
(31.82Eo)
15(38.468o)
3'l (40.22Vo)12(54.54Eo) 20 ( 51.28
Vo)
44 (47.83 Eo) 3(13.648o) 4(lO.26Vo)
ll (ll.95Eo)
Success 20(90.9
Eo)
38(97.4%) 82 ( 89.1 Eo )DISCUSSION
A proximal
LAD
stenosis is respectedby cardiologists
and
cardiac
surgeon becauseofits
distinctive negative
influence on
morbidity
andmortality.
The
LAD
sup-plies the anterior part
of
the interventricular
septum andthe anterior wall
of
the
left
ventricle.
This
con-stitutes
40Voof
the
left
ventricular
myocardium.14LAD
diseaseis
acommon
finding
in
autopsy
studiesof
patients who
die
of acute
myocardial infarction.
Proximal
LAD stenosis occured
in
2lVo
of
patientswho
died
of
non cardiac
"uor"rl5
and23%oof patientswho died
of
acute
myocardial
infarction.l6 In
con-trast, acutethrombotic coronary
eventsin
theproximal
LAD
accounted
for
6l
Vaof
fatal myocardial
infarc-tion, in comparison
with
8 Vo oT acute lesionsoccurring
in
the
mid or distal
segments.
Also,
theincidence
of
acute
thrombotic
eventsin
other coronary
arteries wasmuch
lower,
being
6
Voin
the
left circumflex, 7
Vo i1'tthe
left
main and
Ig
Eointhe right
coronary
artery.16In
survivors
of
myocardial
infarction, the mortality
tate
at 30months
was2J
Vo in patientswith proximal
LAD
and
only
4
Voin
Thosewithout proximal LAD
disease.'
'
In
another studyof
survivors of myocardial
infarction,
it
hasbeen shown
that
at
3
year,the
mor-tality
rate
from
cardiac
causesand
the incidence
of
recurrent
myocardial infarction in
patients
with LAD
disease was
similar
to thatin patients
with
multivessel
disease. I 8
Because
of
these reason, anotheralternatives to
medi-cal
treatment
arechosen.
These are
coronary
artery bypasssurgery
andPTCA or
related
procedures suchas stenting,
atherectomy
and
lasers.
The
Coronary
Artery
Surgery Study reported
a
1O-yearsurvival
ad-vantage
in
operated patients
with
proximal LAD
[image:3.595.53.289.102.297.2]VoI7, No 3, July - September 1998
the same vessel
or
in
theother
vessels.ll'22
Horv"uer,
such as
rate
is
basedon incomplete angiographic
fol-low
up andreflects
thehigher
probability
of
restudyin
symptomatic
patients.
Thenumber of
patientsrequir-ing a
second revascularization procedure
is
also
aclinically
relovant
measure oflong
term success. In onestudy
it
wasreported
to bel9
Eo.Ytlnour
studymany
of
the
patients
did not
undergo repeat cardiac
catheterization,
sono
data can beprovided
regarding
long term
results.The available
data
in the literature
suggestthat
bothPTCA
and bypasssurgery
canprovide excellent long
term results
with
low risk of
cardiac death andmyocar-dial
infarction.
Regardles sof
theinitial
revasc:ulariza-tion
strategy employed,
it
appears
that the
5-year
survival
rate
without
cardiac
deathor myocardial
in-farction
has anupper
limit
that borderson 95
Vo.8'9'rrIn
conclusion,
in
most patients
with
very proximal
lesion
of
theLAD,
PTCA
can beperformed
with
avery
high overall
successrate
andlow
risk.
However,
theprocedure has
to be performed
with the
full
under-standing
that
a
second revascularization
proceduremay
berequired
for
recurrence.Acknowledgement
The author wishes to acknowledge the
collaboration
of
Drs.
H.B. Trisnohadi
andM.
Wangge.REFERENCES
1. European Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery Study Group.
Prospective randomized study
of
coronary artery bypasssurgery in stable angina pectoris. Lancet 1980.2:491-5.
2. Mock MB, Ringqvist I, FisherLD et al. Survival of
medical-ly
treated patientsin
the Coronary Artery Surgery Study(CASS) registry. Circulation 1982;66:562-8.
3. Murphy ML, Hultgreen HN, Detre K, Thomsen J, Takaro T.
Treatment of chronic stable angina : a preliminary report of
the survival data of the randomized Veterans Administration
Cooperative Study. N Engl J Med 1977;297:621-7.
4. Sing RN, Sosa JA, Green GE, Long term fate
of
internalmammary artery and saphenous vein grafts. J Thorac
Car-diovasc Surg 1983;86:369-63.
5. Okies JE, Page US, Bigelow JC, Kraude AH, Salomon NW.
The left intemal ammary artery : the graft of choice.
Circula-tion 1989;7- (suppl.I): 1.213-21.
6. Tector AJ, Schmah TM, Canino VR, Kallies JR, Sanfilipo
D. The role of the sequential intemal mammary artery graft
in the coronary surgery. Circulation 1984 70 (suppl
.l):1.225-5.
7 . LytIe BW, Loop FD, Cosgrove DM, Ratliff NB, Easley K,
Taylor PC. Long term (two
to
12 years) serial studies ofPercutaneoustransluminalcoronaryangioplasty
l4l
internal mammary artery and saphenous
vein
coronarybypass grafts. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg1985;89:248-58.
8. Talley JD, Hurst JW, King SB
III
et al. Clinical outcome 5years after attempted percutaneous transluminal coronary
angioplasty in 247 patients. Circulation 1988;77:820-9.
9. Kramer JR, Proudfit WL, Loop FD et al. Late follow-up
of
781 patients undergoingpercutaneous transluminal coronary
angioplasty
or
coronary bypass graftignfor
an isolatedobstruction in the Ieft anterior descending coronary artery.
Am Heart J 1989;l 18:1144-53.
10.
Ellis
SG, FischerL,
Dushman-Ellis, et al. Comparison ofcoronary angioplasty with medical treatment for single-and
double vessel coronary disease with left anterior descending
coronary involvement
:
long-term outcome basedon an
Emory-CASS registry study. Am Heart J 1989;l l8:208-20.
1 I . Frierson JH, Dimas AP, Whitlow P et al. Angioplasty of the
proximal
left
anterior descending coronary arteru:
initialsuccess and long-term
follow-up.
J Am Coll
Cardiol1992;19:745-51.
12. Piovaccari G, Fattori R, Marzocchi
A
et al. Percutaneoustransluminal coronary angioplasty of the very proximal left
anterior descending coronary artery lesions
:
immediateresults and follow-up. Int J Cardiol 1991;30:
l5l-5.
I 3. ACC/AHA Task Force Report. Guidelines for percutaneous
transluminal coronary angiplasty.
J Am Coll
Cardiol1988:12:529-45.
14. Edwards WD, Tajik AJ, Seward JB. Standardized
nomencla-ture and anatomic basis for regional tomographic analysis
of
the heart. Mayo Clin Proc 1981;56:479-97.
15.
Vlodaver
Z,
Edward JE. Pathology
of
coronary
atherosclerosis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 197 1 ;14250-7 3.
16. Schuster EH, Griffith LSC, Buckley BH. Preponderance of
acute proximal
left
anterior descending coronary arteriallesions
in
fatal myocardial infarction :A
cliniopathologicstudy. Am J Cardiol
l98l ;47:
1 189-96.17. Taylor GJ, Humphries JO, Mellits ED et al. Predictors of
clinical course, coronary anatomy and left ventricular
func-tion after recovery from acute myocardial infarction
Circula-tion 1980;62:960-70.
18. De Feyter PJ, VanEenlge MJ, Dighton DH et al. Prognostic
value
of
exercise testing, coronary angiography, and leftventriculography 6-8 weeks afer myocardial intàrction.
Cir-culation 1982;66:527 -36.
19. Chaitman BR, Ryan TJ, Kronmal RA, Foster ED, Frommer
PL,
Killip T
and the Cass investigators : Coronary ArterySurgery (CASS)
:
Comparabilityof
l0
year survival inrandomized and randomizable patients. J Am Coll Cardiol
1990;16:107 l-8.
20. Parisi
AF,
FollandED,
HartiganPH,
on
behalfof
theVererans
Affairs ACME
Investigators.A
comparison ofangioplasty with medical therapy in the treatment of single
vessel coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 1992;326:1O-6.
21. Freed MS. Osital stenosis,
in :
Manualof
InterventionalCardiology
;
FreedM,
GrinesC
(eds), Birmingham,Michigan : Phyisician's Press
:
1992, 11,128-34.22
Rubin GS,King
SB, Douglas JJ. Restenosis afterper-cutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. The Emory
University Hospital experience.
Am
J Cardiol