The
correlation
between
histologic placentitis and amnionitis and the
amniotic
fluid's inflammatory
cytokines
in
case
of spontaneous
pre-term
labor
\ryith
intact
membrane
Agus Abadi
Abstrak
Persalinan preterm diperkiral<an sebagai akibat penjalaran infeksi genitalia bagian bawah kc atas, terutarnn lcc
jaingan
desidua dan korioamniotik. Respons tubuh terhadap jejas semacam ini antara lain dengan diekspresil<annya protein-protein yang berperan dalam proses inflamasi. El<spresiIL-|p,
IL-6, IL-8 dan TNF-x, alan meninglat pada kcadaan infelui. Sitokin-sitokin ini mungkin mempunyai peran yang mendasar terhadap patofrsiologi terjadinya persalinan preterm spontan dengan lcctuban yang masihintak
Penelitian observasional ialah untuk membuktilcan hubungan antaraI
histologik amnionitis dan plasentitis dengan lcejadian persalinan preterm, 2) ekspresi IL-l P, IL-6, IL-8 dan TNF-x, dalam air kctuban dengan kejadian persalinan preterm, 3) derajat histologik amnionitis dan plasentitis dengan l<adarIL-I8, IL-6, IL-]
dan TNF-ry, dalamair
lcetuban pada lasuspervlinan
preterm spontan dengan ketuban yang masih intak. Terhadap kasus-kasus persalinan pretenn spontan dengan kcnban yang masih intak dil"akul@n amniosentesis transabdominal pada saat masuk l<amar bersalin dan selanjutnya dirawat sesuai dengan protap untuk lcasus dengan persalinan preterm dengan ketuban yang masih intak. Semua kasus yang mengikuti penelitian diobservasi sampai dengan terjadinya persalinan a[elrn maupun preterm. Spesimen selaput kctuban dan plasenta untuk pemeril<saan histologik diambil pasca persalinan, kemudian dilakukan pemeiksaan adanya tanda-tanda suatu inflamasi akut berdasarlankiteria
Salafa. KadarIL-Ip, IL-6, IL-8
dan TNF-x, dalamair
ketuban dianalisis secara kuantitatif dengan metoda Elisa. Pada penelitian ini ditemulcan bahwa derajat histologik amnionitis dan plasentitis, kadar IL-I P, IL-6, IL-8 dan TNF-a dalamair
ketuban pada persalinan pretenn lebih tinggi dibanding pada persalinan aterrn (p<0,05) dan ditemukan juga adanya korelasi yang positip antara derajat inflamasi dengan kadar IL-l p,L-6, IL-8
dan TNF-a dalamair
ketuban (Spearmann Rank"Conelation test: p<0,05). Disimpullcan bahwanwkin
tinggi derajat inflamasi pada amnion dan plnsenta, makin tinggi kadarIL-Ip,
IL-6, IL-ï dan TNF-a dalamair
ketuban alcan makin tinggi pularisiko terjadinya persalinan preterrn. Korelasi yang ditemukan pada penelitian
ini
menunjukkan penjalaran proses inflamasidai
selaput ketuban dan plasenta ke dalam air ketuban pada kts4s persalinan preterm spontan dengan selaput ketuban yang masih intak. (Med J Indones 2001; 10: 203-9)Abstract
Pre-term
labor is
presumedto
resultfrom
spreadingof lower genital
infectionto
upperpart,
subsequentlyto
decidual andchoioamniotic tissues. Host response
to this injury
include the expression of protein whichis
responsibleto the
inflammatory reactions. The expression of the inflammatory cytokines such asIL-IP, IL6, IL-8
and TNF-a increasein
case of infection. These cytokines may play an essential rolein
the pathophysiology of spontaneous pretem labor with intact membrane. An observational analytic cohort study wascaried
out on cases of spontaneous pre-tefln labor with intact membrane. The objectivesof
this study areto
examine the relationship betweenl)
the histologic amnionitis and placentitis and the incidence of preterm delivery,2) the expression of amnioticfluid's
IL-I B, IL-6, IL-9, TNF-r and the incidence of preterm delivery, 3) the level of amnioticfluid's
IL-t p, IL-6' IL-9, TNF-T and the grade of histologic amnionitis and placentitis in case of pre-term labor with intact membrane. Casesof
spontaneous Pre'teftn labor with intact membrane which underwent transabdominal amniocentesis at admission and managed as standard procedure for pre-term labor with intact membrane. Atl of the cases were observed until the delivery of the baby, eithir pre-term or term. The membrane and the placentawere cut postnatally and then the histologic acute inflammation eyaluated based on thecriteria of Salafia.The level of amniotic
fluid IL-IP,
IL-6, IL-8 and TNf-a were analyzed quantitatively by Elisa method. This study showed thet the degree of histologic amnionitis and placentitis, and the level of amnioticfluid's
IL-lp,
IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-a were significantly higher in pre-term compared to terrn deliveries (p<0.05) and lhere were a positive correlation between the gradeof
histoLogic inflammation and the level of amniotic
fluid's
cytokines (Spearmann Rank Conelation test; p<0,05) in cases of preterm labor with intact membrane. The higher the grade of histologic amnionitis and placentitis, the higher the level of arnniotic fluid'sIL-lp,
IL-6, IL-9 and TNF-a resulting in a higher rtsk of pre-tenn delivery in case of prererm labor with intact membrane. These correlation moy indicate a progression of inflarvnation from placenn and membrane into the amniotic cavity. (Med J Indones 2M1; I0: 203-9)
Keywords : Inflarntnation, Preterm Lab our
Division of Fetomatemal Medicine, Department
of
204
AbadiThe incidence
of
preterm delivery
variesfrom
country
to
country
and remain unchangedduring
the lasttwo
to three decades.lIn
developed countries, the incidenceof
pretermdelivery probably
lies between 5to
107oof
all
births.
In Dr.
SoetomoGeneral Hospital
of
Surabaya,the incidence
of
preterm delivery
is about
19.4Vo.2In
Indonesia, preterm
delivery
accountsfor
about
70
to SOVoof
total
perinatal
death without
congenital malformation.Mortalify
ratesfor
prematureinfant in
thefirst
yearof live
rangefrom 40 to
70Vo. Further more, there arestill high
incidenceof
short term complicationsof
prematureinfants
becauseof
biologically
immatureorgans
such
as respiratory
distress,
intraventricular haemonaghe and necrotizing enterocolitis. The long term handicap causedby
prolonged
fetal
hypoxia
(hypoxicischemic encephalopathy)
with
varied
clinical
manifestations
such as
cerebral palsy,
blindness, deafness andmentally
retardation arestill
aproblem
of
expences
in
developing countries,
however,type of
care are
consideredlow
priority.t'o
Th"
aetiology
of
preterm
labor is poorly
understood
but certain associated factors areknown. In
the past decadethere had been
mounting
evidenceof a link
betweengenital infection
and preterm labor. The previous studyfound about
7O
to
SOVopreterm
labor had a posifif
conelation
with
vagino-cervical
infection.s'6 Joesoef etal,
in
bacterial
vaginosis studyon
preterm deliveriesin
Indonesia
found higher
incidenceof
preterm deliveriesin
the earlier gestational
age (20,5Va), as compared towomen
who
hadbacterial vaginosis
in
late
pregnancy (lO,77o).7 There were manyclinical
evidence explainedthe role
of
inflammation
in
the
patophysiology
of
preterm labor. Preterm labor is presumed to resultfrom
the
spreadingof infection of
tract
lower
genital
to
theupper
uchorio
ecytoki
scytokines may play an
essential
role
in
the
pato-physiology
of
preterm labor
with
intact
membrane. These cytokinesmight
activate the biochemical cascadeof
prostaglandinesbiosyntesis
(PGE-2
and PGF-24),
which
leadto myometrial
contraction, cervical changes andinitiating
the labor.rrChorioamnionitis
and
intraamniotic infection
Generally, chorioamnionitis
is
defined
as
aninflarnmatory reaction
of
the chorioamniotic tissue
asa
response
to injury
caused
by
trauma,
infection,
Med J Indones
chemicals and
neoplasma.In
caseof infection,
mostof
the vaginal
microbes produce mucinase
and sialidase, enzymesthat may alter the
immune
systemin
the cervical
mucous.
In
this
condition,
themicroorganisms
may gain
accessto cervical
canal,membrane,
placenta
and
intraamniotic
cavity.
Moreover,
thesemicroorganisms
directly or indirectly
stimulate collagenase
and elastase
activity.
Theactivation
of
macrophages and other cells, will
expressthe inflammatory mediators
or
cytokines
such asIL-1p, IL-6, IL-8
andTNF-cr.rt't3 Chorioamnionitis
and intraamniotic infection are
presumed
to
result
from the
invasion
of
abnormal growth
of
cervicovaginal facultative microorganisms to
uppergenital
tract,
and
subsequentlythe gestational
tissues(decidua,
chorion
and amnion),
intraamniotic
cavity.
Another pathway,
thernicroorganims may gain
accessto
the fetus through
the cord blood
circulation
(funiculitis,
choriovasculitis).
I aThe objectives
of this
study are toprove
:l.
the
relationship between
the
evidence
of
histologic amnionitis
and placentitis
and
theincidence of
pretermlabor
with
intact
membrane.2.
the
relationship between
the
expression of
amniotic
fluid's
tr--1P,
IL-6, IL-8,
TNF-tx
and the incidenceof
pretermlabor
with
intact
membrane.3.
the correlation between
the level
of
amniotic
fluid's
tr--1P,
IL-6, IL-8,
TNF-cx andthe
gradeof
histologic amnionitis and placentitis
in
case
of
pretermlabor
with
intact
membrane.I\{ETHODS
The
designof
this
study was anobservational analytic
cohort study
with
internal control, conducted
in
casesof
spontaneouspreterm labor
with intact
membrane presumed causedby
infection.15The
study
wasperformed
in
the
delivery
room
of
theEmergency Care Instalation
of Dr.
Soetomo
GeneralHospital,
Surabaya, Indonesia.uterine anomaly,
fetal anomaly and gynecologic tumor.
Transabdominal amniocentesis
was
performed
atadmission
and
managed
as
standard procedure
for
pretermlabor
with
intact membrane.
All
of
these caseswere
observeduntill
the delivery
of
the
baby,
eitherpreterm
or
term.
The
membrane
was
cut
2 to
3 centimetersarround the tear and
the placenta
was cut
the
whole thickness
3 to 5 cm anound the cord and thenthe
histologic inflammation
of
the
membranes
andplacentas
were
evaluated
based
on the
criteria of
Salafia.
Twenty
mililiters
of the amnioticfluid
was centrifuged at 1500rpm
for
l0
minuæs, the supematant was collectedand incubated
in -
80o Celcius. The level ofILlp,
IL-6,
IL-8
and
TNf-cr
were analyzed quantitatively
by
Elisamethod (Millenia, End Point
Enzpe
ImmunometricAssay,
GmBH Biermann) simultantly
(50 cases).The
standardprocedure
of
managementon
pre-term
labor with intact
membrane were hospitalization
andbed rest,
parenteral betamethasone
16
mglday
intramuscularly
for
two
consecutive
daysto
promotefetal lung
maturation, parenteral
ampicillin
sulbactam1,5
glday
intravenously
for
two
days, proceeded by
750
mg/day
orally
in
two divided
dosesfor 5
days.Tocolytic
agent was given, startingwith
1000 mcgof
parenteral
Terbutaline
in
500
ml
NaCL
O.9Vo.The
initial
dose
was
was
I
mcg/minute
or
10
drops/minute,
increased
by
0.5
mcg/minute
or
5drops/minute
in
every
15 minutesuntil
the contractiondisappeared
or
serious
matemal
or
fetal side
effect
developed.
Maximum dose was
5
mcg/minute
(50 drops per minute).As
the contraction disappeared, thetherapeutic
level
should be maintained
until
onehour
and then decreasethe dose 5 drops
every
15 minutes.The
maintenance dose
was
10-20 drops/minute
for
8hours.
If the
contraction
reappeared
during
maintenance,
the dose should be
increased
and
theprevious
procedures repeated.It
is
recommended that2000
mcg/
1000rnl NaCL
0.9Vo astotal
dose may begiven. Oral terbutaline
of
7.5 mglday
in
three divideddoses
was given
for 5
days
and
started
30
minutes before parenteralterbutaline
were stopped.During
thetocolytic treatment, the matemal
side effect (tachycardiaand pulmonary
oedema)
and sign
of
fetal
hypoxia should be monitored continuously.As
the sign
of
sideeffect
appear,
the
tocolytic
treatment should
bestopped
instantly and the patient
supported
againstcomplications.
The
exposures(independent variables) are
the
gradeof
histologic
inflammation of
membrane and placentabased
on
the
criteria
of
Salafia and
the
level
of
amniotic
fluid
IL-lp,
IL-6, IL-8
andTNf-c,
analyzedquantitatively by Elisa.
The
outcomes (dependent
variables)
are
preterm
deliveries
with
gestational
age
of
<
37
weeks,according
to
the last period and Dubowitz
score
atbirth
and
term deliveries
with
gestational
ageof
37weeks or more, according to the last period at
birth.
Salafia's grading system
for
histologic inllammation of the membrane and placenta.l6Inflammation of the membrane.
Grade
I :
One focus ofat least 5 neutrophyls.Grade2
:
More than one focus of gradel,
or at least onefocus of 5-20 neutrophils.
Grade
3
:
Multiple or confluents foci of grade 2. Grade4 :
Diffuse and dense acute inflammation.Inflammation of the placenta.
Grade
1
:
One focusof
at
least5
neutrophilsin
sub-chorionic hbrine.
Grade
2
:
Multiple foci of gradeI
in subchorionic fibrine.Grade
3
:
Few
neutrophils
in
connectivetissue
or chorionic plate.Grade
4
:
Numerous neutrophilsin
chorionic plate andsign of acute inflammation
of
chorionic vessels ( chorionic vasculitis)The
chi
square test or student t-test were carried out toevaluate
the
homogeneity
between groups.
Risk
analysisstudy was done
to know the risk
of
specific exposuresand
SpearmannRank
Correlation test
wascanied
out for
correlation
among
exposures(inflammation
and cytokines expression).RESULTS
Fifty
casesof
spontaneouspreterm
labor
with
intact
membrane,who
fulfilled
the inclusion
and exclusion
criterias were
included
in
this study.
206
Abadiage
of 37.7
+
1.3
weeks,
birth
weight
of
2772.5
+
277.4
gramsand delivered
at
40.4
+
15.4 days
afterarffliocentesis.
The distribution
of
casesaccording
tomaternal age,
parity, education
and
occupationbetween
groups (preterm
and
aterm)
were
not
significantly different,
but
there
was a
difference
onthe gestational
ageat admission (p<0,05). The earlier
the gestational
age
at
admission
the
higher
theincidence
of
preterm
delivery
in
caseof
spontaneouslabor
with
intact
membrane.The
role
of
histologic qmnionitis
and
placentitis
onthe incidence of
preterm delivery
in
caseof preterm
labor with
intact
membrane.The histology
of
acuteinflammation of
membrane andplacenta
were divided
into
4
grades
of
Salafia's
criteria.
To
evaluate therole of
these exposures and to make easier thestatistical
analysis,it
were categorizedinto
:First Category
:if
there was
ainflammation.
if
there
was
noinflammation.
Med J Indones
with mild
andno inflammation of
the placenta (df.2;
p<0,01).
It
showed
clearly
the role
of the
grade
of
histologic inflammation
in the incidence
of
preterm
delivery
in
case
of
preterm
labor
with
intact
membrane.According to
this
phenomena, thehigher
the gradeof
inflammation, the higher the
risk
of
preterm delivery
(RR.4.11
vs
2.50
for
the
inflammation
of
themembrane and
RR.2.40
vs
1.55for
the inflammation
of
the
placenta).
Single table
analysis
of cases
with
mild
andno inflammation
showedno significant risk
on the incidence
of
preterm
delivery.
Sowe
concludethat
only
cases
with severe inflammation lead
tosignificant
risk
of
preterm delivery
in
caseof
preterm
labor
with
intact
membrane(p<0.05).
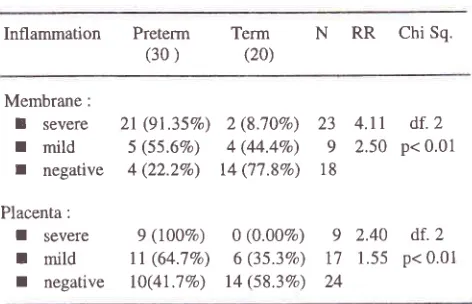
Table
l.
The outcomeof
the deliveryby
thel't
category ofinflammation
lnflammation
Preterm Term N
RR
Chi Sq.(30)
(20)sign
of
Salafia's
sign
of
Salafials Membrane(+)
26(81.3%)Membrane
(-)
4(22.2Vo)6(l8.7Vo)
32
3,66
df.l
14(77.8Vo)18
p<0,01r
Positive
:r
Negative
:Second Categories :
r
Severe
:if
there was a sign of
Salafia's
inflammation
grade 2 to 4.if
there was a sign of
Salafia's
r
Mild
inflammation
gradel.
I
Negative
:
if
there
was
no
sign
of
Salafia's
inflammation.
Based
on
the
first
category (table 1), there was
asignificant difference
in
the outcome
of
delivery
(preterm and term). There
were
8l.3%o and 76.9Voof
preterm delivery
with
a
sign
of
inflammation,
ascompared
to
only
22.2Vo and4l.7Vo with no
sign
of
inflammation of
membrane and placenta (df.1; p<0,01).Moreover,
it
was
found
that
the
inflammation
of
themembrane lead
to
a higherrisk of
preterm delivery thanthe inflammation
of the placenta (RR. 3,66
versus 1,85).Based
on
the 2"dcategory
(table2),
therewas
9I.35Voand
IOOVocases
of
preterm deliveries
with
severeinflammation
of
membrane and placenta
respectivelywhile
only 55.67o and
22.2Vo
with mild
and
noinflammation
of
the
mernbrane and 64.7Vo and 4l.7VoThe
increase
of
the expressionof amniotic
fluid's
IL-LP,
IL-6,
IL-8
and
TNF-a
in case
of spontaneous
preterm labor
with
irutact membrane.The
basic understandingof
the mechanismof
preterm
labor
caused by
infection
was
the
host
responsePlacenta
(+)
20(76.9%)Placenta(-)
l0(4l.7Eo)6(23.tVo)
14(58.3Vo)
1,85
df.1 p<0,01 2624
Table
2.
The outcomeof
the category.delivery based
on
the secondInflammation
Preterm (30 )N RR
Chi Sq.Term (20)
Membrane:
I
severer
mildr
negativePlacenta :
I
severeI
mildI
negative2t
(9r.3s%) 5 (55.6Vo)4 (22.2%)
9 (100Vo)
tl
(64.7Vo) lO(41.7Vo)2 (8.70Vo)
4 (44.4Eo)
14 ('17.\Vo)
0 (0.00%) 6 (35.3Vo)
t4 (s8.3%)
23
4.ll
df.2
9
2.50
p< 0.0118
9
2.40
df.2 [image:4.612.309.543.346.449.2] [image:4.612.310.546.489.641.2]Vol 10, No 4, October
-
December 2001against
injury.
The
expression
of
inflammatory
cytokines
mayplay
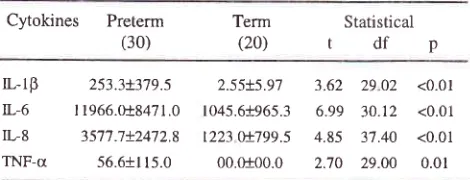
an essential role.Table 3. The level
of
amnioticfluid's
IL-lp, IL6,
IL-8
andTNF-c
in
preterm and term deliveryin
case of preterm labor with intact membrane.Histologic placentitis - amnionitis
conelation
207Table
4.
Spearmann Rank Conelation analysis on the grade ofhistologic amnionitis and placentitis and the level of amniotic
fluid's
IL-lp,
IL-6,
IL8
andTNF-a
in cases of preterm labor with intact membrane.Cytokines N Amnionitis
rp
rp
PlacentitisCytokines
Preterm (30)Statistical
tdfp
0.3751
0.5968
0.010.010.5731
0.010.3828
0.010.4740
0.010.4340
0.010.5136
0.010.4307
0.01Term (20)
L.lB
IL-6 IL.8 TNF-a50 50 50 50
L-rp
253.3+379jIL-6
I 1966.018471.0IL8
35'77.'.7+2472.8TNF-a
56.6+115.02.55+5.97 3.62
29 02 <0.01 1045.61965.36.99 30.12
<0.01t223
0!7995
4.85 3't.40
<0.0100.0100.0 2.70
29.00 0.01
Table
3
showed that the
level
of
arnniotic
fluid's
IL-1P,
IL-6,
IL-8
andTNF-c
weresignificantly higher in
preterm than
term deliveries (p<0.05).
The increaseof
these
levels,
might
suggest theimportant role
of
thosecytokines
on the
patophysiology
of
preterm
labor
caused
by infection.
The
correlation
betvveen the level of amnioticfluid's
IL-1P,IL-6,
IL-\
and
TNF-a
and
thegrade of
histologiginflammation af
the membrane andplacenta
in
caseof
preterm labor with
intact membrane.The
evidences above (table2
and3),
showed that, thehigher
grade
of
histologic
inflammation
of
themembrane and placenta, and
level
of IL-IB, IL-6, IL-8
and
TNF-cr were
found
in
preterm delivery
ascompared
with
term
delivery.
It
might
give
an impression that there was a basic reasonof
theinitiation
of
spontaneouspreterrn
labor with intact
membrane.Furthermore,
we
had
to
appraise
the
correlation betweenthe grade
of
histologic inflammation
and the increase of thelevel of
amnioticfluid's
cytokines.Spearmann
Rank Correlation
analy,sis wascarried
outto
seewhether
anycorrelation
between the increaseof
the grade
of histologic inflammation
andthe
level of
amniotic
fluid's IL-1P, IL-6, IL-8
andTNF-a in
caseof
preterm
labor with
intact membrane.'It was found
that there was a
positive corellation
between the gradeof
inflammation and the level
of
amniotic
fluid's
cytokines (p<0.05) (table
4).
It
could
be
concluded that thehigher
the gradeof histologic inflammation
of
membrane and
placenta,
the
higher
the level
of
amniotic
fluid's IL-lP,
IL-6, IL-8
andTNF-a,
in
casesof
pretermlabor
with
intact
membrane.DISCUSSION
Preterm
labor
may be dueto
anormal signal occuring
too early
in
pregnancy,but it is
more
likely
to
be dueto
an
abnormal
signal,
and
there
is
increasingevidence
that infection may
be
such
a
trigger.rT'rsSince
the last
two
decadesthe incidence
of
pretermdelivery
did not
reduce
significantly.
The
decline in
perinafal
morbidity
andmortality
is
largely
attributableto
improved neonatal intensive care,
which
has beenachieved at great expense.
However,
to prevent pretermdelivery before the
clinical sign
of
labor
extend
mayreduce the cost
of
neonatal
care
and
decrease theperinatal
morbidity
and mortality.3Most
investigators
found
an increasing evidence
thatgenital
infection in
themother
may be responsiblefor
a
proportion
of
spontaneous
preterm
labor
andpremature
rupture of
the membrane. These evidence isbased
on the
organisms
found
in
vagina,
cervix
andamniotic
fluid
of
women
in
preterm
labor,
theevidence
of
chorioamnionitis among women with
pretermbirth
andthe reduction
of
prematurity
among pregnant women treatedwith
antibiotics.rePreterm
labor is
presumedto
result
from migration of
lower
genital
infection to
upper
part,
subsequently todecidual
andchorioamniotic
tissues.Host
response tothis injury include the
expression
of
proteins
which
are
responsible
for
the
inflammatory
reactions.Decidual
and
chorioamniotic cells
express
the
basalcytokines.20'2'
The
"^pression
of
the
inflammatory
cytokines such
as
IL-
IP, IL-6, IL-8
and
TNF-cx increasedin
caseof
infection.l'e'10'22In
previous
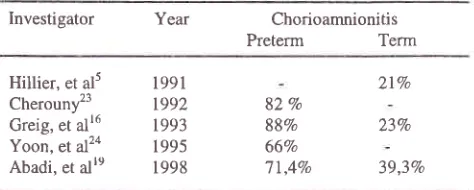
cross [image:5.612.305.538.133.226.2] [image:5.612.48.283.165.255.2]I
Hillier, et al5 Cherouny23 Creig, et alr6 Yoon, et al2a Abadi, et alre
208 Abadi
not prove the
causal
relationship
between infection
and preterm labor.
Table
5.
Several investigators' reporton
the
incidence ofchorioamnionitis in preterm and term deliveries,
Investigator
Year ChorioamnionitisPreterm
TermMed J Indones
So,
the
level of
the amniotic
fluid's
tr--lp,
6,
IL-8
and
TNF-û might indicate
the grade
of
histologic
amnionitis and placentitis.
It
is
the
same
as
theprevious study where there was a
significant
positive
corellation
between
the grade
of
histologic
chorio-onitis and the level
of
Interleukin-6
in
preterm
16.24
ery.
CONCLUSION
In
such patients
with
spontaneouspreterm
labor
andintact
membrane,there
areevidence that the
gradeof
histologic amnionitis
and
placentitis
are
significantly
higher
in
preterm
than term delivery. The levels of
amniotic
fluid's
tr--lp,
IL-6,
IL-8
and
TNF-o
aremarkedly increased
in
preterm compared
to
term
deliveries and there
is significant positive
corellation
between the grade
of histologic inflammation
and thelevels
of
amniotic
fluid's
inflammmatory
cytokines.These correlations
may
indicate
a
progression
of
inflammation
from
placenta
and
membrane
into
theamniotic
cavity. Assuming that most
inflammatory
lesions
of
the
membrane
and
placenta
were due
toinfection,
it
strongly
suggest
that
infection
of
gestational tissue may be responsiblefor
the incidenceof
pretermlabor
anddelivery.
REFERENCES
l.
Lamont RF. The role of infectionin
the pathogenesis ofpreterm labor. In: Progress on Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Vol
10. Churchill & Livingstone; 1995. p. 135-58.2.
Abadi
A,
SulistionoA.
The
difference of histologicmembranitis and placentitis between preterm and term deliveries. Maj Obstet Ginekol 1998; 7: 30-5.
3.
Mc
GregorJA,
FrenchJL.
PretermBirth.
Therole
of infection and inflammation. Medscape Women Health 2(8). Medscape Inc. 1997.4.
Wiknjosastro G. Antenatal Infection and Preterm Labor. JPed Obstet Gynecol i998:24:27-30.
5.
Hillier
SL,
Krohn
MA,
Kiviat
MB,
Watts
DH, EschenbachDA.
Microbiologic
causesand neonatal
outcomes. Associatedwith
chorioamniotic infection. Amer J Obstet Gynecol. 1991; 165: 955-61.6.
Gibbs RK, Romero R,Hillier
SL, Eschenbach DA, SweetRL.
A
review
of
prematurebirth and
subclinical infection. Amer J Obstet Gynecol. 1992;166:1515-28,'7
.
Joesoef MR, Hillier SL, Utomo B, Wiknyosastro G, LinnanNM,
KandunM.
Bacterial Vaginosis and Prematurity in Indonesia. Associated in Early and Late Pregnancy. Amer J Obstet Gynecol. 1993; 169: 175-8.82 Vo
88Vo 66Vo 77,4Vo
2t%
23Vo
39,3Vo
This
presentstudy
had shownthat
in
casesof preterm
labor with
intact
membrane,
the
grade
of
histologic
amnionitis
andplacentitis
and thelevel of
IL-lp,
IL-6,
IL-8
and
TNF-o were significantly
increased. Basedon
the
l't
category
of
inflammation
(presence
andabsence
of
inflammation)
it
had been proven
thatthere were
significant
differences between
theincidence
of
preterm delivery
with
and
without
inflammation
of
the membrane(8l.3Vo
vs22.2Vo)
andplacenta (76.9Vo
vs
4l.7Vo).
Looking
at
the 2"d
category
of
inflammation (severity, mildness
andabsence
of
inflammation),
it
showed
that only
caseswith
severe
inflammation
(grade
2
-
4
of
Salafia's)
lead
to
the
significant
risk
for
preterm
delivery
(p<0.05). The mild
(grade
I
of
Salafia's)
and
thosewithout inflammation
had
no
significant
risk
for
preterm
delivery (p>0.05).
It
can be
concluded
thatthe higher
the
grade
of
histologic inflammation,
thehigher
the possibility
for
preterm delivery.
As
weknow,
the designof this
study was prospective cohort,most likely to prove the
causalrelationship
betweenthose
inflammation
and preterm delivery.15In
this
study we found that the level
of
amniotic
fluid's IL-18,
IL-6,
IL-S
and TNF-cr significantly
increasedin
preterm deliveries
ascompared
to
tbosein
term. This result showed that the
inflammatory
response
was stronger
in
preterm than.term delivery.
To
assess
the
relationship between
the
grade of
histologic inflammation
and
the
increaseof
the level
of
the
inflammatory cytokines,
Spearmann
RankCorellation analysis was carried out. This
analysisshowed
significantly positive corelation (table 4). It
means
that
the
higher
the
grade
of
hystologic
inflammation
of
membrane and placenta,
the
higher
the level of amniotic fluid's
inflammatory
cytokines.1991
r992
[image:6.612.47.284.155.250.2]8.
Lockwood CJ. The Diagnosisof
preterm labor and theprediction of preterm delivery. Clin Obstet Gynecol 1995;
38: 675-87.
9.
KellanJA,
ColemanM,
Mitchell
MD.
The Molecularmechanism
of
term and preterm labor. Recent progressand clinical implcation. J Clin Endocr Metab 1996; 81:
25'79-86.
10.
Kunkel
SL,
LukacsN,
StrieterRM.
Cytokines andinflammatory disease.
A
cause and cure. J. Clin Immunol 1992',12:61.ll.
Cunningham FG, Mac Donald PC, Gant NF, Leveno KJ.Parturition. Preterm labor.
In:
William's Obstetrics. 20thEd. Chapter 11. London, Appleton
&
Lange. 1997; p.306-13.
12.
BeckerrnanLP.
Reproduction and the immune system.Basic and clinical immunology. Stites et al (eds). 8th Ed.
Section
III.
London, Appleton & Lange 1994.p.552-67.13.
PimentelE.
Tumor Necrosis Factors.In:
Handbookof
growth factors. Vol.
I[. Hematopoietic growth factors
andcytokines. Chap. 5. 1994. p. 241-61.
14.
Romero R, Yoon BH, MazorM,
Gomez R, Diamond M,Kenney
J.
The
Diagnosticand
prognosticvalue
ofamniotic
fluid
white blood cells count,
Glucose,Interleukin-6 and Gram stain
in
patientswith
preterm labor and intact membranes. Amer J Obstet Gynecol 1993;169:805-l 6.
i5.
GordisL.
More
on
risk.
Estimating the potential forprevention. In: Epidemiology. Chapter 10. Phyladelphia.
WB Saunders Co. 1997. p. 155-62.
16.
GreigPC,
EmestJM,
Teot
L,
EricksonI,
Talley R.Amniotic
fluid
interleukin-6
level
corellated
withhistologic chorioamnionitis and amniotic fluid cultures in
patients of premature labor with intact membrane. Amer J
Obstet Gynecol 1993; 169: 1035-44.
Mitchell
DM,
TrautmanMS,
Dudley
DJ.
Immuno-endocrinology
of
preterm labor and delivery. Balliere'sClinical Obstetric & Gynecology 1993 ; 7 : 553-75. Herman
AA,
Carrey
JC. The role
of
infection
in precipitating pretermlabor.
Obstetric&
GynecologicInfectious disease. Pastorek (ed)
II.
New York
RavenPress. 1994. p.267-74.
Abadi
A.
The inflammationof
the membrane, placentaand amniotic
fluid's
interleukin-6 as determinant factorfor preterm delivery
in
case of preterm labor with intactmembrane. Disertation; I 999.
Hamblin AS. Cytokines and cytokine receptors. Oxford
University Press. Inc New York. 1993;
p.2l-40.
Maradny
E,
KanayamaN,
Abdul Halim,
Maehara K,Sumimoto
K.
Interleukin-8 induce cervical ripening inrabbit. Amer J Obstet Gynecol 1994; 17l:77-83.
Bernal
AL,
Watson
SP,
Phaneuf
S,
Finner
GN. Biochemistryand
physiologyof
pretermlabor
anddelivery. Balliere's
Clinical
Obstetric&
Gynecology. 1993;7:523-52.Cherouny P, Pankuch G, Applebaum P. The presence of
amniotic
fluid
leucoattractantaccurately
identifies histologic chorioamnionitis and predict tocolytic efficacy in patients with idiophathic preterm labor associated withinfection. Amer J Obstet Gynecol 1992;167:683-8.
Yoon BH, Romero R,
Kim
CJ, Jun JK, Gomez R, ChoiJH, Syn HC.
Amniotic
Fluid Interleukin-6.A
SensitiveTest
for
Antenatal Diagnosisof
Acute
InflammatoryLesion
of
Preterm Placenta and Predictionof
PrenatalMorbidity. Amer J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:960-70. 17.
l8
19
20
2t
22.
23.