i Cover
published in serial conference:
ii Internati onal Scientific Commi ttee (tentati ve*)
1. Prof. John Paul (Kedge Business School, France)*
2. Prof. Varakorn Samakoses (President of Dhurakij Pundit University, Thailand) * 3. Prof. Ranbir M alik Singh (Curtin, Australia)
4. Prof. Dr. Nobuhide Otomo (Kanazawa University, Japan)
5. Prof. Dr. M ohamed Dahlan Ibrahim, (Universiti M alaysia Kelantan, M alaysia) 6. Prof. Dr. Nanang Fattah, M Pd ( UPI, Indonesia)
7. Prof. Dr.Agus Rahayu M P ( UPI, Indonesia)
8. Prof. Dr. Tjutju Yuniarsih SE, M Pd ( UPI, Indonesia) 9. Prof. Dr. Disman M S (UPI, Indonesia)
10. Prof. Dr. Suryana M S ( UPI, Indonesia) 11. Prof. Dr. Eeng Ahman, M S ( UPI, Indonesia) 12. Prof. DR. Ratih Hurriyati, M P (UPI, Indonesia ) 13. Prof. Ina Primiana SE, M T (UNPAD)
14. Prof Lincoln Arsyad, M Ec, PhD (UGM)
15. Prof. Gunawan Sumodiningrat M Ec, PhD (UGM ) 16. Dr. Phil Dadang Kurnia M Sc. (GIZ German) 17. Assoc.Prof. Arry Akhmad Arman, MT, Dr (ITB) 18. Assoc.Prof. Dwilarso , M BA, PhD (ITB)
19. Assoc.Prof. Hardianto Iristiadi M SM E, PhD (ITB) 20. Assoc.Prof. Rachmawaty Wangsaputra, M Sc, PhD (ITB) 21. Assoc.Prof. Teungku Ezni Balkiah, M Sc, PhD (UI) 22. Assoc.Prof. Ruslan Priyadi M Sc, PhD (UI) 23. Assoc.Prof. Sri Gunawan, M BA, DBA ( UNAIR) 24. Assoc.Prof. Yudi Aziz, MT, PhD (UNPAD) 25. Assoc.Prof. Lili Adiwibowo, MM, DR (UPI) 26. Assoc.Prof. Vanessa Gaffar, M BA, DR (UPI) 27. Assoc.Prof. Chaerul Furqon, MM , DR (UPI) 28. Vina Andriany M Ed, PhD (UPI)
29. Tutin Ariyanti, ST, MT, PhD ( UPI)
Chair person
Prof.Dr. Ratih Hurriyati M P,
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, INDONESIA
Technical Chair person
Assoc. Prof. Lili Adiwibowo
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, INDONESIA
Organizing Commi ttee
iii
vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Cover ...i Welcome Message ...iii Table of Cont ents ...vii REPROGRAMMED DEVE LOP ING CREATIVE MANP OWER IN THE 21S T
CENTURY INDUS TRY CONDITIONS
Taehee Kim, Ph.D. ...1 CHA LLE NGES TOWARD DIGITAL COMPA NY
Arry Akhmad Arman ...3
FINANCI AL MANAGEMENT AND ACCOUNTING
THE DE TE CTION OF CORRUP TION AND THE ROLE OF ACCOUNTA NT IN ACHIEVING GOOD PUBLIC GOVE RNA NCE
Rozmita Dewi Yuniarti...4 THE EFFECT OF CORPORA TE TA X GOVERNANCE, AUDIT QUALITY AND TA X E XP OSURE ON A UDIT FEE FOR COMPANIES ENLIS TED IN
INDONESIA S TOCK E XCHANGE
Nelly Nur Apandi,Sidharta Utama, Hilda Rosiet a ...5 THE EFFECT OF EMP LOYEE COMPE TE NCE TO THE RE LIA B ILITY OF
FINA NCIA L STA TEME NTS
R. Ait Novatiani, R.Roosal eh Laksono...6
DEVELOPING STUDENTS’ FINANCIAL LITERACY AND FINANCIAL
BEHAVIOUR BY STUDE NTS EMOTIONAL QUOTIENT
Azizah Fauziyah, Siti Aty Ruhayati...7 THE ANALYS IS OF DIFFE RENCES IN PERSONAL CHA RACTE RIS TICS OF
PUBLIC ACCOUNTANTS AND IT’S IMPACT ON THE IMPLEMENTA TION OF
THE PUBLIC ACCOUNTA NTS E THICS
Amilin ...8 E XECUTIVES CHA RA CTERS, GENDE R AND TA X AVOIDA NCE: A STUDY
ON MANUFA CTURING COMPANIES IN INDONES IA
Nova Novita ...9 RA TE OF PROFIT VE RSUS RA TE OF INTERES T : THEORE TICA L
PERSPECTIVE FOR THE IMPLE MENTA TION OF INTE RS T FREE BANK ING SYSTEM
Trisiladi Supriyanto ...10
THE IMPACT OF TOURISTS’ NUMBER VISIT ON THE REGIONAL OWN
REVENUE IN WEST JAVA PROV INCE YEAR OF 2009-2014
Imas Purnamasari, Gita Dwi Rahmi ...11 THE INFLUENCE OF FINA NCIA L PERFORMA NCE ON S TOCK PRICE IN
INDONESIAN OIL AND GAS COMPANY’S
viii
THE RELA TIONS HIP BE TWEEN LOCAL OW N REVENUES AND GENE RAL FUND ALLOCA TION TO CAPITA L E XPE NDITURE ON LOCA L
GOVERNMENT IN ALL OF WES T JAVA PROV INCE FISCAL IN 2015
Heni Mulyani ...13 PERFORMANCE EVALUA TION OF INDONESIA N BANKS AND FOREIGN
BANKS OPERA TING IN INDONES IA RELA TE D TO CLASSIFICA TION OF CAPITA L
Sugiarto ...14 BUDGE T IMPLEME NTA TION IN HIGHE R EDUCA TION
Asep Kurniawan, Tjutju Yuniarsih, Sumarto ...15 REAL ACTIV ITIES MA NIP ULA TION (RAM) AND ACCRUA L-BASED EARNING MANAGEMENT BEFORE AND AFTER IFRS ADOP TION IN INDONESIA
Dyah Purwanti ...16 FINA NCIA L AND NON FINA NCIAL FA CTORS INFLUENCE ON THE
IMPLEME NTA TION OF INTE RNA TIONAL FINA NCIA L REPORTING STA NDA RD (IFRS)
Icih, Siti Rodiah Qolbiah ...17 INTE RNAL CONTROL APPLICA TION SYSTEM FOR SALA RY PAYMENT
PROCEDURE BASED ON COMPUTE RIZED IN MULIA PLUS SE NIOR HIGH SCHOOL
Novy Anggraini, Arum Rakhmasari Octivaningsih ...18 THE EFFECT OF OPERA TING CAS H FLOW TO THE P ROFIT GROW TH
Agus Widarsono, Mega Rahmawati ...19 THE OPPORTUNITIES AND CHALLENGES OF IS LAMIC ACCOUNTING
LEARNING FOR VOCA TIONA L S TUDENTS A ND ITS APPLICA TION IN ISLAMIC MICROFINA NCE INS TITUTIONS
Arim, Agus Widarsono, Ellina Riennovita ...20 ANALYSIS OF EFFICIE NCY TE CHNIQUE LEVEL OF RURAL BANK BY
USING DA TA ENVELOPME NT ANA LYSIS (DEA)
Wini Welani, Nugraha, Heraeni Tanuatmodjo ...21 INTE RNAL CONTROL AND QUA LITY OF FINA NCIAL REPORTING IN ZAKA T MANAGEMENT ORGANIZA TION
Elis Mediawati ...22 STOCK VALUA TION OF PT. PERUSAHAA N GAS NEGA RA (PERSE RO) TBK IN THE MIDDLE OF GLOBAL ECONOMIC SLOWDOWN
Felix Terahadi, Subiakto Soekarno ...23 ISLAMIC MONE TA RY POLICY A ND ITS IMPA CT TO THE GROW TH OF
ISLAMIC BA NKING
Yoghi Cit ra Prat ama ...24 FEASIBILITY A NALYSIS OF BREEDING BUS INESS OF S HEEP GARUT ON
AL-BAROKAH LIVES TOCK GROUP RAWAMERTA DIS TRICT KARAWANG REGENCY
ix
COGNITIVE BIAS AND RISK PREFE RENCES ANALYS IS OF PONZI SCHEME INVES TORS
Maya Sari, Nugraha...26 EFFECT OF DIV IDE ND POLICIES, MANAGE RIA L OWNE RSHIP, BOARD
SIZE AND PROFITAB ILITY TO FIRM VALUE ON MANUFACTURING COMPA NY IN INDONES IA STOCK E XCHA NE
Suparno (a*); Jaelani (b*); Djoko Pitojo (c*) ...27 THE EFFECT OF CAPITA L S TRUCTURE AND WORK ING CAPITA L ON
PROFITABILITY (CASE S TUDY A T PT. INDOSA T TBK IN THE PERIOD OF 2005-2014)
Ratu Dintha IZFS, Ahim Surachim ...28 SHARIA COMP LIANCE ON MURABA HA FINANCING (S TUDY IN BAITUL
MAAL WA TAMWIL)
Elis Mediawati, Silviana Agustami ...29 THE INFLUENCE OF MA THEMA TICAL THINK ING SKILL
Sakti Alamsyah ...30 REDES IGN, REORIE NTA TION AND RE NEWAL OF INDONES IA ECONOMY
EDUCA TION CURRICULUM CREA TIVE ECONOMY BASED, LOCAL CULTURAL VALUES CHARA CTER PA RADIGM, THROUGH ACA DEMIC, HUMA NIS TIC AND SOCIO-E CONOMIC RECONS TRUCTION APPROA CH
Moch Noviadi Nugroho, M.Pd ...31 CREA TIVE THINKING SKILLS WITHIN ACCOUNTING IN CO LLEGE
CURRICULUM OF INDONESIA
Gayatria Oktalin, Erika Feronika Br. Simanungkali. ...33 THE IMPA CT OF DE LEGA TE D AUTHORITY A ND ORGA NIZA TIONA L
COMMITME NT TOWARD BUDGE T PARTICIPA TION
Ernawaty Usman, Nurhayati Haris, Sugianto ...34 EFFECT OF RE TURN ON ASSE TS AND RE TURN ON EQUITY TO THE
STOCK PRICE ON P T.INDOCEMENT TUNGGAL P RAKARSA TBK
Fitri Sukmawati, Innes Garsela ...35 SMART BUS INESS S TRA TE GY: OPTIMALIZING THE ROLE OF
MANAGEMENT A CCOUNTING
Yoga Tantular Rachman, Sendi Gusnan dar Arnan, Yogo Heru Prayitno ...36 E XECUTIVES CHA RA CTERS, GENDE R AND TA X AVOIDA NCE: A STUDY
ON MANUFA CTURING COMPANIES IN INDONES IA
Nova Novita ...37 VALUA TION OF UPS TREAM OIL AND GAS PROJECTS USING
DIS COUNTED CASH FLOW METHODS. CASE STUDY: “AAX” OIL FIELD DEVELOPME NT PROJECT, “NW NTX” WORKING AREA
Zarpani ...38 ANALYSIS OF RISK OF THE CUS TOME R FOR DEPOS IT PRODUCTS IN
ISLAMIC BA NKING AND CONVE NTIONAL BANK ING WITH VALUE A T RISK METHODS (IN CASE OF BANK SYARIA H MANDIRI AND BANK MANDIRI PERIOD 2011-2013)
x
GREEN BUSI NESS
SRI RICE ORGANIC FARMER’S DILEMMA : BETWEEN ECONOMIC
ASPECTS A ND SUS TA INABLE AGRICULTURE
D.Yadi Heryadi, Trisna Insan Noor...40 THE INFLUENCE OF GREEN MA RKE TING TO PERCE IVED VALUE ON
PERTAMA X P URCHASING DE CISION
Rennyta Yusiana, Arry Widodo ...41 INVES TIGA TION OF THE IMPLEME NTA TION OF GREEN MA NUFA CTURING ON TE XTILE INDUS TRY IN WEST JAVA
Supriyadi, Ratna Ekawati ...42 MARKE TING A RTIFICIAL REEF AS RE CREA TIONAL SCUBA DIVING
RESOURCES: FEASIBILITY S TUDY FOR SUS TA INABLE TOURISM
Harriman Samuel Saragih ...43 THE EFFECT OF E NVIRONME NTAL CORP ORA TE SOCIAL
RESPONS IB ILITY (CS R) DISCLOSURE TO INVES TOR BEHAV IOR: EMPIRICAL STUDY FROM INDONES IA CAPITA L MARKE T
Marsdenia ...44
INNOV ATION, OPERATIONS AND SUPPLY MANAGEMENT STRA TEGY OF PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT A ND PROCESS OF CRE A TIVE INDUS TRIES IN INDONESIA
Ryan Kurniawan (1); Andhi Sukma (3); E vo Sampetua Hariandja (2) ...45
CUSTOMER’S PERCEPTION AND EXPECTATION FOR REVERSE
LOGIS TICS IMPLEME NTA TION
Farida Pulansari, Dwi Sukma Donoriyanto, Nisa Masruroh ...46 LEAN SIGMA APPLICA TION F OR B RIDGE IMPROVEMENT PROJE CT
Prayogi Purnapandhega ...47 EFFECT OF IMPLEMENTA TION P ROBLEM POS ING ME THOD A ND
PROBLEM SOLVING ME THODS OF CREA TIVE THINK ING ABILITY
STUDE NTS (QUAS I-E XPERIME NTAL S TUDY ON ECONOMIC SUB JECTS IN SMA NEGERI 1 LEMBANG)
Nurul Haeriy ah Ridwan, Agus Rahayu ...48 SUPPLY CHAIN OPERA TIONAL CAPABILITY AFFE CTING BUSINESS
PERFORMANCE OF CREA TIVE INDUS TRIES IN INDONESIA
Suryadi Hadi, Benyamin Parubak ...49 PATENT INVES TIGA TION ON PELLE T B IOMASS FROM EMP TY FRUIT
BUNCH TO ENHANCE INNOVA TION DEVELOPME NT OF RE NEWABLE ENERGY
T. Hendrix, A. Wicaksono, F.T. Ajie ...50 EFFECT OF GUIDE D DISCOVERY ME THOD A ND P ROBLEM SOLVING
METHOD FO S TUDE NTS CRITICAL THINK ING SKILLS (QUASI
E XPERIME NTAL S TUDY ON ECONOMIC SUB JECT IN SMA NE GERI 1 CIKA RANG UTA RA)
xi
ALTE RA TION TO FOOD SUPP LY CHAIN: CONSUME R PREFE RENCES
Imanuella Romaputri Andilolo, Ikma Citra Ranteallo...52 GUDEG CA NNE D: TRA DITIONA L FOOD FOR SMALL AND MEDIUM
ENTERP RISES (SMEs)
Asep Nurhikmat, Tommy Hendrix ...53 ANALYSIS OF E CONOMIC TRA NSFORMA TION AND DE TERMINA TION OF
MAIN E CONOMIC SE CTORS OF BANTE N PROV INCE, INDONES IA IN THE FUTURE
Sri Lestari, Samsul Arifin ...54 AN E XAMINA TION OF ORGA NIZA TIONAL DE TE RMINA NTS INFL UE NCING
GREEN P RODUCTION ADOP TION BY SMEs IN MALAYS IA
Mohd Firdaus Ruslan, Marlina Muhamad, Mohd Fazil Jamaludin ...55 THE ANALYS IS OF QUALITY CONTROL IN XXX COMPANY BY US ING
STA TIS TIC IN CONTROLING PRODUCT
Nafila Mayang, Tika Annisa Lestari Koeswandi, Sinta Yulianti ...56 QUALITY CONTROL OF PRODUCT : STA TIS TICA L PROCESS CONTROL
Solehatin Ika Putri, Chandra Budhi Septyandi, Dwi Phayana Rohandani ...57 BLOGSPOT-BASED LEA RNING MODEL TO IMPROVE ECONOMIC SELF
DIRE CTED LEA RNING
Zul Afdal, Disman, Munir ...58 MATE RIA L REQUIREME NTS PLANNING (MRP) ME THODS TO SOLVE
INVE NTORY PROB LEM A T STA RT-UP BUS INESS
Widianingsih, Desy Anisya Farmaciawaty ...59 QUO VA DIS PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT S TRA TEGY OF INDONESIA
MANUFA CTURING COMPANIES?
E vo Sampetua Hariandja ...60 SERVICE INNOVA TION CAPABILITY AND INNOVA TION PERFORMA NCE IN DIS TRIBUTION S TORE AND CLOTHING IND US TRY: A CONCEP TUAL FRAMEWORK
E vo Sampetua Hariandja ...61 PRODUCTIVITY A NALYSIS ON LOCAL GOVERNME NT-OWNED DRINKING WATER COMPANIES (P DAMs) IN INDONES IA AND ITS MA RKET
CHA LLE NGE
Anang Mufftiadi ...62 THE INFLUENCE OF BUDGE T PA RTICIPA TION ON THE PERFORMA NCE
OF LOCAL GOVE RNMENT OFFICIAL WITH BUDGE T EMPHAS IS, BUDGE T GOAL CLARITY, CULTURAL ORGA NIZA TION AND DE CENTRA LIZA TION SYSTEM AS MODE RA TING VA RIAB LES
Nesti Hapsari, Dian Hakip Nurdiansyah...63 VALUE CHAIN ANA LYSIS IN SMALL B USINESS CONTE XT
Mega Iskanti Putri, Budi Harsanto...64 RISK MANA GEMENT DESIGN FOR PRIVA TE, SMALL, AND MEDIUM S CALE MUSICAL CONCE RTS
xii
OVERALL EQUIPMENT EFFE CTIVENESS IMP ROVEME NT WITH TOTAL PRODUCTIVE MAINTENA NCE ME THOD: CASE STUDY FROM A N INDONESIA N PHA RMACE UTICA L COMPANY
Claudia Febianny Susilo, Aditya Andika ...66 ANALYSIS FA CTORS AFFECTING S TUDE NTS SATISFA CTION TO
ACADEM IC SE RVICES BASED ON SERV QUA L
Girang Razati, Sumiyati, Masharyono ...67 MARKETING MANAGEMENT
THE DIFFE RENTIA TION OF UNIQUE EDUCA TION SERV ICES TO THE SUPERIOR CUS TOME R VALUE
Muhamad Adi Suja’i...68 PROPOSE D MODE L FOR SOCIAL CAPITA L RELA TIONS HIP WITH ONLINE
PURCHASE DE CISION IN SOCIAL NE TWORK
Adhi Prasetio; Vanessa Gaffar...69 IDE NTIFYING CRITICAL SUCCESS FA C TORS AFFECT CONSUME RS
PURCHAS ING BEHAV IOR OF POLISHE D GEMS TONES IN INDONESIA
Elimawaty Rombe, Zakiyah Zahara ...70 RE TAILING MIX S TRA TE GY OF HYPERMA RKE T IN BANDUNG CITY
Ria Arifianti ...71 PURCHASE DE CISION P ROCESS OF DOMA IN .ID
Mudji Sabar...72 LIFES TY LE INFLUENCES ON P URCHASE DECISIONS BECOME MEMBERS Aggi Panigoro, Andry Fernandus W, Muhamad Mustofa ...73 THE INFLUENCE OF TELEV ISION ADVERTISEMENT ON P URCHASE
DECISION FA CIAL WASH FOR ME N PRODUCT
Ira Valentina Silalahi, Harini Fajar Ningrum, Rasna Ulfah ...74 THE INCREASE OF DE CIS ON TO VISIT TO GURILAPS DES TINA TION
THROUGH SOCIAL MEDIA MARKE TING MODEL
Arief Budiman, Ayu Krishna Yuliawati, Mokh. Adib Sultan ...75 ANALYSIS OF COMPE TITOR INTE LLIGE NCE AS PRODUCT S TRA TEGY
BUSINESS DEVELOPME NT FOR PRODUCT X LIP I
Syukri Yusuf Nasution...76
CELEBGRAM AND IT’S EFFECTS ON ONLINE PURCHASE DECIS ION
Heny Hendrayati, Vanessa Gaffar, Dea Sintia Dwiyanty ...77 CUS TOMER E XPERIE NCE MANA GEMENT IN HOTE L INDUS TRY:
PRINCIP LES, THEORY A ND PRA CTICE
Bachruddin S aleh Luturlean, Grisna Anggadwita ...78 COMPA RA TIVE ANA LYSIS OF FA CEBOOK AND INS TAGRAM AS WEB
PROMOTION TOOLS
V.Gaffar, H.Hendrayati, M.H.Ifandha...79 VARIA TION OF PRODUCTS AND SWITCHIN G BARRIE R ON CUS TOMER
LOYALTY
xiii
CREA TING S TUDENTS LOYALTY MODEL IN P RIVA TE HIGHE R EDUCA TION
Muji Gunarto, Lili Adi Wibowo , Ratih Hurriyati ...81 CREA TING VALUE CREA TION TO INCREASE MARKETING
PERFORMANCE
Reminta Lumban Batu, Eeng Ahman, Lili Adi Wibowo ...82 BRAND ELEMENT A ND MA RKE TING MIX OF EDUCA TIONA L SERVICES
EFFECT TOWARD BRA ND VALUE OF HIGHE R EDUCA TION INS TITUTION
Puspo Dewi Dirgantari, Agus Ra hayu, Disman, Ratih Hurriyati ...83 THE EFFECT OF PE RCE IVED VALUE TOWARDS BEHAVIORA L
INTE NTIONS
Lili Adi Wibowo, Fuji Nur Fitriani ...84 INS TA GRAM CONTENT FOR S TA RT-UP CULINA RY COMPANY AFFECT
CUS TOMER P URCHASE INTE NTION
Oktaviani Br Sagala, E vy Rachmawati ...85 STUDE NT INTE NTION: THE RELEVA NCE OF THE IMA GE OF
UNIVERS ITIES, TRUS T A ND WORD OF MOUTH AS MODERA TING VARIABLES
Nugraha Saefudin ...86 BRAND ATTITUDE OF SMARTP HONE USER: THE ROLE OF BRA ND
KNOWLEDGE AND SELF-CONGRUE NCE
Ali Mohamad Rezza...87
YOUNG CONSUMER’S PERCEPTION ON E-SE RV ICE QUALITY OF ONLINE
SHOP: AN EVIDENCE FROM BANDUNG
Nina Septina ...88 DE TERMINANTS OF CUS TOME R TRUS T AND ITS IMPLICA TION ON
CUS TOMER COMMITME NT : THE EMPIRICAL S TUDY A T SHA RIA BA NK IN BANDUNG
Nandan Limakris na, Deden Komar Priatna, Winna Roswina ...89 EFFECT OF BRA ND ORIENTA TION ON ENTREP RENE USHIP CREA TIV ITY
Dadan Abdul Aziz Mubarok ...90 MEASURING HABLUMMINALLA H BEHAVIOR IN THE THIRD -ORDE R
CONFIRMA TORY FA CTOR ANALYS IS OF MUS LIM CONSUMERS’ RELIGIOUS BEHAVIOR MODEL
Muniaty Aisyah ...91 FACTORS AFFECTING CUS TOMERS BUY ING INTE NTION
Daffi Ranandi, Mustika Sufiati Purwanegara ...92 THE INTERA CTION BETWEEN DYNAMIC MARKE TING CAPABILITY AND
SERVICE INNOVA TION CAPABILITY AND THE ME DIA TING EFFE CT OF MARKE TING COMMUNICA TION ON PERFORMANCE: A HOTEL INDUS TRY PERSPECTIVE
E vo Sampetua Hariandja ...93 THE IMPA CT OF S TORE IMAGE ON PURCHAS ING DE CIS IONS
xiv
SERVICE E XCELLE NCE IN THE HOTEL INDUS TRY THROUGH DY NAMIC MARKE TING CAPABILITY
E vo Sampetua Hariandja ...95 ANALYSIS OF WEBSITE QUALITY, BRAND AWARENESS ON TRUS T AND
ITS IMPA CT ON CUS TOME R LOYALTY
W.Sastika, B. Suryawardani, F.H. Hanifa ...96 FEASIBILITY A NALYSIS OF BREEDING BUS INESS OF S HEEP GARUT ON
AL-BAROKAH LIVES TOCK GROUP RAWAMERTA DIS TRICT KARAWANG REGENCY
Ina Ratnasari, Dian Hakip Nurdiansyah ...97 THE EFFECT SOCIAL ENV IRONME NT OF THE SWITCHING INTE NTION ON SOCIAL MEDIA FACEBOOK FOR BUSINESS
Safira Rahmalia, Bambang Widjajanta, Girang Razati ...98 THE EFFECT OF B RAND E XPE RIENCE ON CUS TOMER SA TISFACTI ON
AND THE IMPA CT TOWARD REPURCHASE INTE NTION
A. H. Ekaputri, Agus Rahayu, Lili Adi Wibowo ...99 SERVICE QUA LITY A ND REPUTA TION TOWARD CUS TOME R TRUS T IN
LIFE INS URA NCE CORPORA TION
Lisnawati, Girang Razati, Henny Mulyani ...100 REBRA NDING AND PURCHASE INTENTION ON KING THAI TEA
Heny Hendrayati, Ratih Hurriyati, Cipto Putra Daud ...101 ANALYSIS OF SE RVICE QUA LITY TO CUS TOME R SATISFA CTION IN
MUSIC RE CORDING S TUDIO
Harriman Samuel Saragih ...102 FACTORS AFFECTING ONLINE SHOPP ING PREFERA NCE ON SOCIA L
MEDIA OR WEBSTORE THA T INFLUENCE PURCHASE DE CIS ION OF STA RT-UP COMPANY
Atika Sari Pohan, E vy Rachmawati Ch ...103 PUBLIC PERCEP TION AND P REFERE NCE A NALYSIS ON HIGHE R
EDUCA TION REPUTA TION RA TING AGE NCY
Muji Gunarto, Dimas Yudistira Nugraha, Vanessa Gaffar ...104 BEHAVIORAL INTE NTION OF INS TAGRAM AS PART OF TECHNOLOGY
ACCEP TA NCE
Mokh Adib Sultan ...105
ORGANI ZATIONAL BEHAVIOR, LEADERS HIP AND HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT
CONTRA CT EMPLOYEE ARE BETTE R? INFLUE NCE OF ORGANIZA TIONAL CLIMA TE AND JOB SA TISFACTION TOWARDS ORGA NIZA TIONA L
CITIZE NSHIP BEHAV IOUR
Suci Fika Widyana ...106 THE EFFECT OF P RINCIPA L LEADE RSHIP AND SCHOOL CLIMA TE ON
PRODUCTIVITY OF VOCA TIONAL HIGH S CHOOL OF BUSINESS AND MANAGEMENT E XPE RTISE IN BANDUNG CITY
xv
THE INNOVA TION LEADERS HIP THROUGH MAPPING WITH HUMAN RESOURCES INFORMA TION SYSTEM TOWARDS SUS TA INABILITY DEVELOPME NT GOA LS
Dian Ambarwati; Gidiono Tirtoadisurja ...108 CAUSALITY ANA LYSIS IN BEHAV IORAL PERSPE CTIVE OF S TRA TEGIC
HUMA N RESOURCE MA NAGEMENT: THEORE TICAL MODEL
Audia Junita ...109 THE ROLES OF LECTURERS IN E DUCA TION SERVICE: IN BETWEEN
PERCEP TION AND BEHAVIORS
Meta Arief, Umar Faruk, Leny Yulianti ...110 THE ROLE OF TALE NT MANAGEME NT AS DIS TINCTIVE CAPABILITIES
FOR ORGA NIZA TION: AN EMP IRICAL S TUDY OF FURNITURE RA TTA N COMPA NY IN INDONES IA
Annisa Ciptagustia, Kusnendi ...111 THE CHALLE NGES OF HUMA N CAP ITAL PERFORMANCE IN DEVELOPING
BAITUL MAAL WAT TAMWIL IN INDONES IA : USING THE ANALY TICA L NE TWORK PROCESS (A NP)
Aas Nurasyiah, Suci Aprilliani Utami, Firmansyah ...112 INDONESIA HUMA N CAP ITAL COMPE TITIVENESS IN THE ASEAN
ECONOMIC COMMUNITY (AE C) E RA
Acep Durahman ...113 GAINING COMPE TITIVE ADVANTA GE THROUGH TA LENT MA NAGEME NT
Rofi Rofaida ...114 ACCOUNTABILITY IN ELEMENTA RY SCHOOL
Yahya Sudarya, Elis Mediawati ...115 THE EFFECT OF PE RCE IVED ORGA NIZA TIONAL SUPPORT FOR
INNOVA TION ON INNOVA TIVE WORK BEHAVIOR WITH LEADE R-MEMBER E XCHA NGE MEDIA TION ON THE LECTURER OF CIVIL AND PLANNING FACULTY INS TITUTE SEPULUH NOPEMBER
Anis Eliyana, Diah Yovita Suryarini, Ria Mardiana Yusuf, Dwijo Sumarno ...116 THE IMP LEMENTA TION OF CAREE R TRA CK
Suharto, Yohanes Wibowo ...117 THE ANTE CEDE NT FACTOR OF EMPLOYEE ENGA GEMENT FROM A
SELF-DE TE RMINA TION THEORY PERSPECTIVE
Cattleya Rejito, Mery Citra Sondari ...118 THE EFFECT OF FAMILY E NVIRONME NT AND SCHOOL ENVIRONME NT
ON ECONOMIC LITE RACY (S URVEY ON THIRD GRADE S TUDE NT IN SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL NO 1 LUBUK BESAR, CE NTRAL BANGKA REGENCY, BANGKA BELITUNG A RCHIPELAGO P ROV INCE
Muhammad Haris Munandar (a*), Agus Rahayu(b), Suwatno (b) ...119 AN ANALYS IS OF RE CRUITMENT A ND JOB TRAINING ME THOD
EFFECTIVENESS TO EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT IN BANDUNG CULINARY STA RT-UP
xvi
INFLUENCE SITUA TIONA L LEADE RSHIP AND WORK ENV IRONMENT TO EMPLOYEES PERFORMANCE IN SERV ICES AND BUS INESS
DEVELOPME NT HOLDING OFFICE RRI BANDUNG WEST JAVA
B. Lena Nuryanti, Rani Rahmawati ...121 THE INFLUENCE OF O RGA NIZA TIONA L CHANGE (BANK MERGER) ON
EMPLOYEE’S ATTITUDE RESPONSE
Achmad Supriyanto ...122 FACTORS THA T INFLUENCE ENTREPRE NEUR INTENTION TOWARDS
STA RT-UP GROW TH
Febrian Ulfa Ayu Romadhani ...123 THE CHARA CTERIS TICS OF IDEAL HUMAN IN ISLAMIC PERSPECTIVE
Dudung Abdurrahman, Atih Rohaeti Dariah, Aminuddin Irfani ...124 HUMA N RESOURCE PLA NNING AND USE OF TE CHNOLOGY TO
COMPA NY EFFICIE NCY AND EMPLOYMENT CREA TION
Muhammad Calvin Capnary ...125 POLITICAL MA NAGEMENT OF COMMUNITY ORGANIZA TION TOWARD
COSMOP OLITAN DEMOCRA CY
M Yahya Arwiyah, AMA Suyanto, Runik Machfiroh ...126 MODEL OF EFFECTIVE SCHOOL MANAGEME NT A T VOCA TIONA L HIGH
SCHOOL IN WES T JAVA
Yayat Supriyatna, Nugraha, M Arief Ramdhany ...127 THE INFLUENCE OF COMPENSA TIONS AND SOCIA L ASSURA NCE ON
JOB PERFORMA NCE: STUDY ON CONTRACT EMPLOYEES’ PALM COMPA NY
Rahmi Widyanti, Basuki ...128 PATTE RN OF P UBLIC POLICY IN THE PERSPECTIVE OF
IMPLEME NTA TION OF REGIONAL COMP ULS ORY GOVERNMENT AFFA IRS Muhamad Nur Afandi ...129 JOB PERFORMA NCE AFFECTE D SKILL VARIE TY, TASK IDENTITY, TASK
SIGNIFICANCE, OTONOMY AND FEEDBA CK?
Syamsul Hadi Senen, Sumiyati, Masharyono, Nida Triananda ...131 PROFESSIONA L EDUCA TOR WORK ATTITUDE VS WORK LIFE BENEFITS
Ifada Rahmayanti ...132
MANAGEMENT STUDENTS’ ATTITUDES TOWARD BUSINESS ETHICS AND
SOCIAL RESPONS IBILITY
Dyah Purwanti, Edy Purwanto ...133 INTE NS IFICA TION OF MADRASA CULTURE AND COMMUNITY
PARTICIPA TION: EFFORTS TO MANA GE THE DEVELOPMENTA L CHANGE M. Arief Ramdhany, Akhmad Buhaiti ...134 BUREA UCRACY, LEA DERS HIP AND PEOPLE CHA RACTE RIS TICS
(A REVIEW OF COMMUNICA TION PUB LIC OFFIC IAL AFTER POLITICAL REFORMA TION)
xvii
SOCIAL CAP ITAL ANA LY ZE ON AGRIBUS INESS MICROFINANCE INS TITUTION PERFORMA NCE IN SUKAB UMI CITY
Amalia Nur Milla ...136 ENVIRONMENTA L INFLUE NCES PHYS ICA L AND DISCIPLINE WORK
AGAINS T PRODUCTIV ITY EMPLOYEES PRODUCTION LINE
Toyib, Sumiyati, Masharyono ...137 THE INFLUENCE OF SOCIAL WORK ENV IRONMENT A ND THE QUA LITY
OF WORK LIFE ON EMPLOYEE PRODUCTIVITY DIV IS ION FIRM PRODUCTION MANUFACTURING
Kevin Fajar P ratama, Sumiyati, Ridwan Purnama, Masharyono...138 JOB SA TISFA CTION AND ORGANIZA TIONAL COMMITME NT AS
DE TERMINANTS OF TEA CHE R PERFORMA NCE
Rini Anggraeni, Rasto ...139
STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT, ENTREP RENEURSHIP AND CONTEMPORARY ISSUES
THE STRA TEGY TO IMP ROVE THE PROFESSION COMPE TE NCE THROUGH K NOWLE DGE MANAGEME NT TO A CHIEVE CORPORA TE PERFORMANCE
Yoke Prima Hendrawan, ST. MM. IA I., Dr. Ir. Umi Rusilowati, MM.,
Dr. Hadi Supratikta, MM ...140 INFLUENCE OF COMPE TITIVE ADVA NTAGE S TRA TE GY FOR B USINESS
SUCCESS (CASE S TUDY OF KARTIKA SARI BANDUNG)
Anny Nurbas ari, Nisa Hanum Harani ...141 EMPOWERMENT OF CREA TIVE SMALL A ND ME DIUM ENTE RPRISES
(SMES) THROUGH THE MICRO FINANCIA L S TRUCTURE STRENGTHE NING
Chairul Furqon, Suryana, Budhi Pamungkas ...142 DIGITA L CITIZENS HIP STUDENTS FROM DIGITA L COMMERCE ASPECT
Rini Triastuti, Dasim Budimansyah, Sapriy a ...143 EFFECT ADVE RSITY INTE LLEGE NCE TO READINESS INS TRUMENT OF
ENTREP RENE URS HIP
Kurjono ...144
ANALYZING PREFERENCES OF HONDA BEAT MOTORCYCLE’
CONSUME RS IN KELURAHA N PADAS UKA, BANDUNG
Hadi Alamdhien (a), Hamdan Ardiansyah (b), Bagus MDES (c) ...145 RESOURCE-BASED V IEW AS A COMPETITIVE ADVA NTAGE OF THE
COMPA NY: AN EMPIRICAL REV IEW
Heru Basuki Purwanto ...146 THE INFLUENCE OF INTE RES T INCOME OF TYPE OF CREDIT ON TOTA L
INCOME FROM CRE DIT INTERES T
Sri Suartini, Dian Hakip Nurdiansyah ...147 THE EFFECT OF E NTREPRENE URSHIP ORIE NTA TION AND E -WORD OF
MOUTH TO SME’S PERFORMA NCE
xviii
OPTIMIZE OF QA RDHU HASAN ISLAMIC BA NKING FOR RE DUCING POVERTY IN BANDUNG CITY
Amir Machmud, Eeng Ahman, Navik Istikoma h ...149 EN ROUTE FOR NOBILITY A ND SUPE RIORITY: PRESE RVING
INDIGE NOUS CULTURA L INHE RITANCES AND SUS TAI NING COMPE TITIVE WORLD MUS IC
Harriman Samuel Saragih ...150 FOS TERING AND ADVANCING INCLUS ION AND DIVERS ITY AS
CORPORATE’S KEY STRATEGIES TO SUSTAIN IN GLOBAL
COMPE TITIVENESS
Priyo Yantyo; Syahrizal Maulana ...151 STUDE NT ENTREPRE NE URS HIP E DUCA TION EFFORT THROUGH KOPSIS Yana Rohmana, Neti Budiwati ...152 THE INFLUENCE OF COMPANY RESOURCES AND ABSORP TIVE
CAPABILITY ON VALUE CREA TION AND THE IMP LICA TION ON BUSINESS PERFORMANCE IN THE COURIER SE RVICE INDUS TRY IN INDONES IA
Hana Suryana ...153 BUILDING CAPAB ILITY AND CAPACITY IN THE PRERA RA TION OF
ESTABLISHING POS T LOGIS TICS BY SPINNIN G OFF LOGIS TIC BUS INESS UNIT
Hana Suryana, Lili Adi Wibowo...154 ADVERS ITY QUOTIENT EFFE CT OF ACHIEVEMENT AND ITS IMPACT ON
STUDE NT ENTREPRE NE URS HIP INTE NTIONS
Rizqita Qiyaski Buhari, Eded Tarmedi, Hari Mulyadi ...155 DIS COVE RY LEARNING MODE L DEVELOPME NT TO GROW
ENTREP RENE URIAL MINDSE T ON COLLE GE STUDENTS IN B USINESS MANAGEMENT E DUCA TION A T UNIVE RSITY OF EDUCA TION INDONESIA Dr. B Lena Nuryanti, M.Pd., Drs. Rd. Dian H. Utama, M.Si., Drs. Girang Razati,
M.Si., Drs. H. Eded Tarmedi, MA ...156 POP MUSIC RIVALRY IN INDONES IA: PAST, PRESENT A ND FUTURE
TRENDS
Harriman Samuel Saragih ...157 DE TERMINANTS OF ONLINE COMMERCE PLA TFORM ANA LY ZED WITH
WEBSITE QUALITY THE ORY (CASE STUDY: LAZA DA INDONESIA)
Mahir Pradana...158 THE EFFECTIVENESS OF E NTERP RENE URS HIP LEARNING IN
DEVELOP ING STUDENTS’ ENTREPRENEURIAL INTENTIONS
Kakang Harudi n, Nanang Fattah, Eeng Ahman ...159 THE INS TITUTIONAL S TRA TEGY IN INCREAS ING THE PUB LICA TION
PERFORMANCE AS A VALUE OF HIGHER EDUCA TION (S TUDY A T UNIVERS ITAS WIDYA TAMA, BANDUNG)
Eriana Astuty*a), Alfi Nura*b), Muji Gunarto*c) ...160 COMME RCIALIZA TION TYPE DE TE RMINA TION STRA TEGY OF RESEARCH RESULTS IN ORDER TO TECHNOLOGY TRA NSFER: S TUDY CASE IN LIP I
xix
MITIGA TION ON PRODUCT LA UNCH FAILURE; CASE STUDY : BRAND X NUTMEG JUICE PRODUCT
Adityo Wicaksono, Firman Tri Ajie, Tommy Hendrix ...162 ENTREP RENE URIAL ORIENTA TION MODEL IN CLUS TER DEVELOPME NT
OF AGRIBUS INESS POTA TOES IN THE PROVINCE OF ACEH
Lukman Hakim, Tomy Perdana, Maman Haeruman K, Yosini Deliana...163 A CASE STUDY TO CREA TE INDONESIA N INTERNA TIONAL
ENTERP RENE URS HIP BY SPECIAL ON THE JOB TRA INING IN EUROPHEA N
Jamhadi, Haryo Santosa and Iwan Tjahjo ...164 OPTIMIZA TION OF CAS H WAQF IN DEVELOP ING INDONESIA CREA TIVE
INDUS TRY : AN EFFORT TO CREA TE SHA RIA -CREA TIVEPRE NEURS
Neni Sri Wulandari, Rida Rosida, Aneu Cakhyaneu ...165 GEOTOURISM RES OURCES AS PART OF S US TAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
IN INDONESIA’S GEOPARK
Ayu Krishna Yuliawati, Mohamad Sapari Dwi Hadian, Krishna Nur Pribadi ...166 ANALYSIS EFFICIE NCY PRODUCTION AND STRA TEGIES OF SMALL
-MEDIUN SCALE ENTE RP RISES : EVIDE NCE FROM A SURVEY OF ENTERP RISES IN ME DAN CITY
Dede Ruslan ...167 INTE GRA TE D COMMUNITY PROGRAM TO S TRE NGTHEN S UBSEA CABLE
SECURITY A ND E NVIRONMENTA L SUS TA INAB ILITY IN THE OFFSHORE OIL AND GAS INDUS TRY
Harriman Samuel Saragih ...168 THE INFLUENCE OF E XTERNAL E NVIRONTME NTAL FORCES AND
STRA TEGIC ORIENTA TION ON VALUE CREA TION AND THE IMPLICA TION ON BUS INESS PERFORMA NCE
Hana Suryana ...169 ENTREP RENE URS HIP PROCESS AND B USINESS INCUBA TOR IN
PANGALE NGA N, WEST JAVA - INDONES IA
Zoel Hutabarat ...170 THE ROLE OF CRAFT AND ENTREPRE NEURIAL SUB JECTS IN FOS TER
CREA TIV ITY, INTE RES T AND FOS TE R THE ENTREPRE NE URIAL SPIRIT
Arie Septiningrum, Ridna Ardiana ...171
UNIVERSITY’S PRESS MANAGEMENT TO INCREASE THE QUALITY OF
EDUCA TION IN UNIVE RSITY
Kundharu Saddhono, Budhi Setiawan ...172 ROLE ISLAM FOR DEVELOPMENT IN INDONES IA
Muhammad Sholahuddin ...173 MANAGEMENT S TRA TEGY IN POKEKEA MEGALITH TOURISM A T BEHO’A
VALLEY
Tabitha R. Matana and Gitit I.P. Wacana...174 CSR S TRA TEGY IN INDUS TRIAL CITY TO AC HIEVED COMPE TITIVE
ADVANTAGE
xx
DEVELOP ING TRA DITIONA L MARKE T S TANDARD: A SOCIO-E CONOMICS-ENVIRONMENT APP ROA CH
Budi Supriatono Purnomo, Alfira Sofia, Denny Andriana3, R. Nelly Nur A pandi ...176 ENTREP RENE URS HIP EDUCA TION AND ENTREPRE NEURIAL INTE NTION
ON ENTREPRE NE URS HIP BEHAV IOR OF S TUDE NTS IN SHA RIA BANK ING PROGRAM; A CASE STUDY
Adhitya Ginanjar...177 ENTREP RENE URS HIP INTENTION TO TRIGGE R ENTREPRE NEURS HIP
ORIENTA TION (S URVEY ON BUS INESS MANA GEMENT E DUCA TION COLLEGE S TUDE NTS AT E DUCA TION UNIVE RSITY OF INDONES IA) Drs. Rd. Dian H. Ut ama, M.Si., Dr. B Lena Nuryanti S.,
M.Pd., Dra. Hj. Neni Sutarni, M.Pd...178 STRA TEGY MODEL OF RAIS ING COMPE TITIVE NESS OFFICE
MANAGEMENT COMPE TE NCE
Uep Tatang Sontani, Adman ...179 ENTRE UPRE UNEURSHIP S TRA TE GY OF SELLE R AND RES TAURANT
OWNER
Thriwaty Arsal ...180 SHARIA MICRO FINA NCING FOR WOMEN POVERTY REDUCTION : AN
EMPIRICAL S TUDY OF RURAL AREAS OF KUNINGAN –WES T JAVA – INDONESIA
Dr. Ayus Ahmad Yusuf, M.Si. Rina Masruroh, ME.Sy. Neni Nurhayati, M.Si.Ak...181 THE CONS UMER PERSPE CTIVES ON SERV ICE QUALITY AND
PERFORMANCE OF ROAD INFRAS TRUCTURE ASSE TS
Katharina Priyatiningsih, Ratih Hurriyati ...182 THE ROLE OF THE E NTREP RENE UR INNOVATION IN THE ECONOMIC
DEVELOPME NT OF A COUNTRY
Ari Riswanto...183 ANALYSIS OF POULTRY FEED EFFE CIENCY: LOCAL EFFORTS TO
REDUCE RELIANCE ON IMPORTE D FIS H MEAL IN INDONES IA
Hilda Monoarfa, Chalil, Sri Sarjuni, Edhi Taqwa ...184 THE DIMENS IONS OF ENTREP RENE URIAL ORIENTA TION AND ITS
IMPACT ON BUS INESS PERFORMANCE OF RES TA URA NT INDUS TRY
Hart elina ...185 ECOPRE NE URS HIP IMPLEME NTA TION FOR E NVIRONME NT AND
ECONOMIC S US TAINABILITY: A CASE STUDY OF SMALL BUSINESS IN BANDUNG, INDONES IA
Sony Sasongko, Grisna Anggadwit a ...186 THE CORPORA TE S TRA TE GY-BASED ON CONS UMERS IN A GLOBAL
COMPE TITION
Judi Achmadi, Katharina Priyatiningsih ...187 BUSINESS ANALYS IS ON SWEET CONDE NSED TEMPE H AS A FUNCTIONA L FOOD
xxi
CITIZE NSHIP AND GOOD GOVERNANCE IN INDONESIA: PUBLIC PARTICIPA TION IN ME DIUM -TERM LOCA L DEVELOPMENT PLA N
Rusnaini ...189 BUILDING ENTREPRE NE URS HIP ON PERFORMING ARTS INDUS TRY
THROUGH THE MODEL OF INCUBATION
Juju Masunah, Rita Milyartini ...190 A MODEL OF CORPORA TE UNIVE RSITY FOR AN INTE RNA TIONA L
BUSINESS SCHOOL IN INDONES IA
Indra Santosa, Jamhadi and Syahril Majidi ...191 HOW BUSINESS PROCESS MANAGEME NTS IMPA CTS DE CIS ION MAKING
PROCESS OF FASHION S TA RT UP BUS INESS IN BANDUNG
Nia Alprilia, Manahan Siallagan ...192 IMPACT OF E XCHA NGE RA TE CHA NGE ON IMPORT P RICE IN INDONESIA Sri Isnowati, Mulyo Budi Setiawan ...193
THE EFFECT OF CAMPUS ENVIRONMENT TOWARDS STUDENTS’
ENTREP RENE URS HIP ATTITUDE AND BEHAV IOR
Neiny Ratmaningsih...194 MUSIC FOR THE GE NERA TION-Z, QUO VADIS ?
Harriman Samuel Saragih ...195 IDE NTIFICA TION OF THE MAJOR AGRICULTURA L POTENTIA L AND
COMMODITY POTE NTIAL OF MAJOR FOOD PLANT A ND ITS GROW TH IN OKU RE GENCY
Munajat and Fifian Permat a Sari ...196 TE CHNOLOGY TRANSFE R OF CREA TIVE INDUS TRIES IN RIA U
Zoel Hutabarat ...197 ANALYSIS OF FA CTORS INFLUE NCING THE STUDE NT'S INTERES TS TO
PARTICIPA TE ENTREP RENE URIA L STUDENT P ROGRAM UP I PERIOD 2013-2015
Gugun Ruslandi, Hari Mulyadi, Eded Tarmedi ...198 ENTREP RENE UR SK ILLS ON BUS INESS PERFORMANCE OF SMALL A ND
MEDIUM ENTE RP RISE
Page 91 of 220 MEASURING HABLUMMINALLAH BEHAVIOR IN THE THIRD-ORDER
CONFIRMATORY FACTOR ANALYSIS OF MUSLIM CONSUMERS’ RELIGIOUS
BEHAVIOR MODEL
Muniaty Aisyah
Faculty of Economics and Business
State Islamic University (UIN) Syarif Hidayatullah Jakart a - Indonesia Email : [email protected]
ABSTRACT
This research is intended to measure the consumers’ hablumminallah behavior within the third-order confirmatory factor (CFA) model of Muslim Consumers’ Religious Behavior (MCRB) framework. The concept of hablumminallah behavior is precisely about Muslim religi ous behavior which formed from cognition, affection and conation behavior in Faith and Wors hip as pects of a Muslim in his or her relationship wit h God. Different with many other previous researches about Muslim religiosity that mostly still apply a one to one measurement of Christian or wertern terminologies, this researc h applies an Islamic concept of measurement that derived from the holy Al Qur\'an and Hadit h. To measure the propos ed model, 390 data sets were generated through a survey which were analyzed by using the structural equation modeling with Amos 22. 0 software. The finding shows that Indonesian Muslim consumers have high levels of hablumminallah behavior and when a t hird -order CFA model was performed on
MCRB’s constructs, it proved to be valid and reached a goodness-of-fit model. This
study was the continuity of previous researches which implemented the first -order CFA model of hablumminallah behavior and the second -order CFA model of MCRB framework. Because religious behavior is viewed as an important factor that affect consumers purchase pattern in so many ways, by analyzing the level of MCRB allowing marketers to plan a suit able marketing strategy. Since the Indonesian Muslim consumers have high levels of hablumminallah behavior, it is strongly recommended for marketers to assure the halalness (lawfulness) of their products accordingly t o the
Islamic law. This research is limited to only measuring the consumers’ hablumminallah
behavior, while both consumers’ hablumminannas behavior and the third-order CFA
model of MCRB framework measurements will be analyzed later in another further researches.
Measuring Hablumminallah Behavior in
The Third-Order Confirmatory Factor Analysis of
Muslim Consumers’ Religious Behavior Model
Muniaty Aisyah
Fakultas Ekonomi dan BisnisUniversitas Islam Negeri (UIN) Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta Indonesia
Abstract— This research is intended to measure the consumers’ hablumminallah behavior within the third-order confirmatory factor (CFA) model of Muslim Consumers’ Religious Behavior (MCRB) framework. The concept of hablumminallah behavior is precisely about Muslim religious behavior which formed from cognition, affection and conation behavior in Faith and Worship aspects of a Muslim in his or her relationship with God. Different with many other previous researches about Muslim religiosity that mostly still apply a one to one measurement of Christian or western terminologies, this research applies an Islamic concept of measurement that derived from the holy Al Qur'an and Hadith. To measure the proposed model, 390 data sets were generated through a survey which were analyzed by using the structural equation modeling with Amos 22.0 software. The finding shows that Indonesian Muslim consumers have high levels of hablumminallah behavior and when a third-order CFA model was performed on MCRB’s constructs, it proved to be valid and reached a goodness-of-fit model. This study was the continuity of previous researches which implemented the first-order CFA model of hablumminallah behavior and the second-order CFA model of MCRB framework. Because religious behavior is viewed as an important factor that affect consumers purchase pattern in so many ways, by analyzing the level of MCRB allowing marketers to plan a suitable marketing strategy. Since the Indonesian Muslim consumers have high levels of hablumminallah behavior, it is strongly recommended for marketers to assure the halalness (lawfulness) of their products accordingly to the Islamic law. This research is limited to only measuring the consumers’ hablumminallah behavior, while both consumers’ hablumminannas behavior and the third-order CFA model of MCRB framework measurements will be analyzed later in another further researches.
Keywords— Muslim, religious, consumer behavior, third-order cfa model, hablumminallah
I. INTRODUCTION
Culture is a comprehensive concept that includes almost everything that influences an individual’s thought process and behavior [1]. As one of particular sub culture that develops among classes of societies, religion gives identification of its member, influencing their behavior that include their
preferences and purchasing decisions [2]. Consumer behavior is found to be mediated through several factors, including consumer’s religious affiliation, commitment to religious beliefs and practices which used in marketing strategy [3].
As a country with the highest Muslim population in the world, Indonesian law requires halal (lawful) products intended for consumption, use, or wear to be in accordance with Islamic Law. Since religiosity is viewed as the degree to which beliefs in specific religious values and ideals are held and practiced by an individual that also affect buying consumption pattern in so many ways [4], it is important for marketers to analyze the Muslim Consumers ‘Religious Behavior in targeted Muslim marketplaces such as in Indonesia.
There were lots of studies about religious behavior or religiosity in psychology, anthropology or sociology including in human resource management and marketing. Even though several studies have been carried about Muslim religious behavior, however the study usually still associated with Christian religion or Western tradition that measures as one-to one translation into Islamic terminology [5]. Therefore, this study tries to propose a new model of Muslim Religious Behavior in related to the emerging of Islamic marketing theory that mainly derived from the Holy Quran and Hadith as the two main sources of Islamic of teaching.
This study will provide a deeper understanding of the statistical measurement of religious behavior of Muslim consumers by testing the factorial validity of Muslim consumer based religious behavior scale using a third-order CFA model of Muslim Consumers’ Religious Behavior (MCRB) framework, as continuity of previous researches of first-order CFA model of hablumminallah and hablumminannas behavior, and the second-order CFA model, of MCRB framework, which is relevant for marketers or companies in general and for marketing management field in particular.
This research will establish whether:
• Indonesian Muslim consumers have high level of hablumminallah behavior.
• It is possible to validate the Muslim consumers’ religious behavior measurement model by using a third-order factorial validity;
• The third-order CFA model for factorial validity of Muslim consumers’ religious behavior has a goodness-of-fit.
This research will have organized as follows: first section presents a literature review from previous Muslim consumers’ religious behavior researches. Second section provides a description of the structural equation modeling used in this article, and the hypothesized model. Third section presents the methodology, the data sources, as well as the model estimations. The last section provides summaries and discussions of the results.
II. THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Muslim Consumers’ Religious Behavior (MCRB)
Religious behavior is attitudes, intensity and a person way to become religious which develop and grow in external environments like family, schools and societies that gain through a learning process and experiences, either deliberately or not that cultivating, educating and adapting the religion of teachings on a person daily life [6]. Islam as a way of life is interpreted as a human effort to achieve welfare in his/her life and hereafter [7] that is accordance with Islamiclaw which is derived from the holy AlQur’an and Hadith of the Prophet Muhammad [8]. Allah already gave guidance through His messengers that include everything humans need in order to obtain their welfare in accordance to aqidah (faith), akhlak (manner) and sharia (Islamic law). Aqidah and akhlak are constant and not changing from time to time. Meanwhile,
sharia is always changing accordance with the people needs
and civilization which appropriate in every different period of time. Sharia in Islamic teaching emphasizes on ibadat (worshiping God) and muamalat (human interaction) with a good and proper way by understanding its etiquette and implement them in everyday life in order to be a good Muslim [7]. Ibadat emphasizes on Islamic provisions and procedures of human interaction with God which namely as hablumminallah behavior. Meanwhile, muamalat emphasizes on Islamic provisions and procedures of human interaction with others which namely as hablumminannasbehavior.
Based on the criteria which are expected to be owned by Muslim, the proposed theory of Muslim Consumers’ Religious Behavior (MCRB) are developed from two constructs, those are hablumminallah behavior (having a good relationship with God) and hablumminannas behavior (having a good Islamic personality with others) where each indicator within the two constructs are in accordance with the two mainly Islamic law resources, AlQur’an and Hadith.
The concept of hablumminallah behavior is precisely about Muslim religious behavior which formed from cognition, affection and conation behavior in Faith and Worship aspects of a Muslim in his relationship with God, which clearly written in the two Islamic foundations, the six Pillars of Iman (Faith) and the five Pillars of Islam (Worship) [9,11,12,13]. While hablumminannas behavior is essentially about the fact of nature
of human life, human personality, habit, event, and ikhwal/ causes [10, 11, 12, 13].
B. Hablumminallah Behavior
Hablumminallah behavior is measured from three dimensions: 1) having knowledge of the Pillars of Faith and Worship, 2) attitude or believe in the truth of Faith and Worship, and 3) practicing the Faith and Worship [9, 12, 13].
Knowledge of Faith is measured from one’s knowledge about the six Pillars of Iman, those are: knowledge of faith in Allah, Allah’s angels, Allah’s holy books, Allah’s messengers, Allah’s providence and the hereafter. Knowledge of faith in Allah is the knowledge about God’s existence. A human being can learn about God’s existence by paying attention to every phenomenon occurs in the universe. This also applies into other five knowledge of faith. While knowledge of Worship is measured from one’s knowledge about the five Pillars of Islam, those are: knowledge about shahadah (Islamic profession of faith), the mandatory and procedure requirements in ritual activities of sholat (pray), fasting, zakah (tithe), and hajj (pilgrim) [12, 13].
Attitudes of Faith is measured from one’s belief in the truth of the six Pillars of Iman which can be define from one’s belief in Allah and His perfect natures, belief in Allah’s angels and their duties, belief in prophets as Allah’s messengers, belief in Allah’s holy books, belief in Allah’s providence and belief in hereafter life. Meanwhile attitudes of Worship is measured from one’s belief in Allah as the only creator and Muhammad as His last prophet, belief in prayers that could make life more optimist, healthier and well-organized; belief in fasting that could increase one’s concern about fellow human being, self-control and health; belief in zakah (tithe) that could ease problems and avoid disasters; belief in hajj (pilgrim to Mecca) that could manage ukhuwah islamiyah (brotherhood) among fellow Muslims from all over the world [12,13].
Practice of Faith and Worship is one’s actual actions in following God’s commands and desist God’s prohibition by standing firmly on the Pillars of Iman and Islam. Practice of Faith is measured from how often a Muslim starting and finishing jobs by mentioning Allah’s name, how hard one’s effort to maintaining their five senses from doing the bad deeds, how hard one’s effort to imitate the Prophet Muhammad’s behavior, how much one’s eagerness to read and learn the Qur’an, how much one’s eagerness to do the good deeds and how hard one’s effort to act and to be in harmony with the order of the world. Meanwhile practice of Worship is measured from one’s effort to obey all the commitments of Islam in their life, like one’s effort to read the Qur’an and shalawat (prayers up on the Prophet Muhammad), how hard one’s effort to carrying out the five fardhu (obligatory) prayers a day, fasting in Ramadhan month, sunnah fasting, pay zakah (tithe/ the alms tax) or give infaq/shadaqah (charity), undertake a pilgrimage to Mecca [12, 13].
The higher the knowledge, attitude and practice of Faith and Worship aspects, the higher the hablumminallah behavior. The higher the hablumminallah behavior, the higher the hablumminannas behavior. Details of hablumminannas
Hablumminallah
Attitude of Faith and Worship
Practice of Faith and Worship
behavior measurement will be explained later in the next research.
III. RESEARCH FRAMEWORK
A. Structural Equation Modeling
There are two basic types of factor analysis, exploratory factor analysis (EFA) and confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) [14]. For the purposes of this research only CFA was considered. Confirmatory factor analysis is used when the researcher has theoretical knowledge of the underlying latent variable structure [15]. The theory represents causal processes which generate observations on multiple variables [16]. The hypothesized model is tested statistically in a simultaneous analysis of the whole system of variables to determine the extent to which it fits with the collected data. The model supports the plausibility of postulated relations among variables if goodness-of-fit is adequate [14].
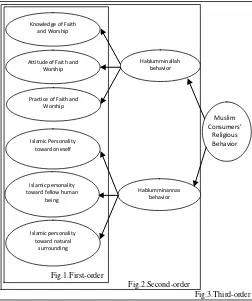
Following the Muslim Consumers’ Religious Behavior (MCRB) framework introduced in this research (Fig. 1), is formed from the two factors (hablumminallah behavior and
hablumminannas behavior) which operated as independent
variables; each could be considered to be one level, or one unidirectional arrow, away from the observed variables. Such factors are termed first-order factors.
Fig.1.First-order
Fig.2.Second-order
Fig.3.Third-order
Fig. 1-3. Conceptual framework of MCRB
For the Second-order factors, although the model schematically portrayed in Fig. 2 has essentially the same with the first-order factors, it differs in a higher order of Muslim Consumers’ Religious Behavior (MCRB) factors which is
hypothesized as accounting for or explaining all variance and covariance related to the first and second-order factors. As such, Muslim Consumers Religious Behavior then is termed the order factors in Fig.3. To determine whether a third-order factor represents the most appropriate factorial structure of Muslim Consumers Religious Behavior it was necessary to specify the model and empirically confirm its goodness-of-fit.
B. The Hypothesized Model
The CFA model to be tested in this study hypothesized a priori that (a) responses to the Muslim Consumers’ Religious Behavior (MCRB) scale can be explained by 6 first-order factors (knowledge, attitude, practice of Faith and Worship, Islamic personality towards oneself, fellow human being and natural surrounding), 2 second-order factors (hablumminallah and hablumminannas behavior), and 1 third-order factor (MCRB); (b) each indicator has a non-zero loading on the first-order factor it was designed to measure, while having zero loadings on the other first-order factors; (c) error terms associated with each item are uncorrelated; and (d) covariation among the six first-order factors is explained fully by their regression on the second-order factor.
As suggested in literature, in an initial check of the hypothesized model, it is recommended to determine a priori the number of degrees of freedom associated with the model under test to ascertain its model identification status. In relation to the model shown in Fig. 4, there are 1431 pieces of information contained in the covariance matrix, and 134 parameters to be estimated, thereby leaving 1297 degrees of freedom.
Fig.4. Hypothesized Third-order Modification Model of Factorial Structure for the MCRB Framework
These include the following 123 variables (53 observed variables and 70 unobserved variables):
• Observed variables (53): 53 MCRB items
• Unobserved variables (70): 53 error terms, 6 first-order factors, 2 second-order factor, 1 third-order factor and 8 residual terms
• Exogenous variables (62): 53 error terms, 1 third-order factor, and 8 residual terms
• Endogenous variables (61): 53 observed variables and 6 first-order factors, and 2 second-order factor
Fixed parameters (71):
• Weights (70): 53 error term regression paths (fixed to 1.0), 9 factor loadings (fixed to 1.0), and 8 residual regression paths (fixed to 1.0)
• Variances (1): 1 third-order factor Unlabeled parameters (134):
• Weights (52): 52 factor loadings
• Covariances (21): 41 21 factor covariances
• Variances (61): 53 error variances and 8 residual variances
IV. RESEARCH METHODE
A. Sample and Procedure
To examine whether the implementation of a third-order CFA model for the factorial validity of MCRB is feasible, data was collected using a standardized survey. In total, 500 questionnaires were collected. As recommended in literature, data screening and detecting univariate outliers were performed [17]. Non-valid data and data profile causing outliers were excluded from the analysis, resulting in a total of 390 valid data. The survey was administered in Ciputat, South Tangerang.
The items in this study were measured using a five-point Likert scale. Knowledge of Faith and Worship was measured using 18 items, attitude of Faith and Worship was measured using 16 items and practice of Faith and Worship was measured using 13 items, Islamic personality toward oneself was measured using 12 items, Islamic personality toward fellow human being was measured using 21 items and Islamic personality toward natural surrounding was measured using 9 items.
B. Measurement Precedures and Results
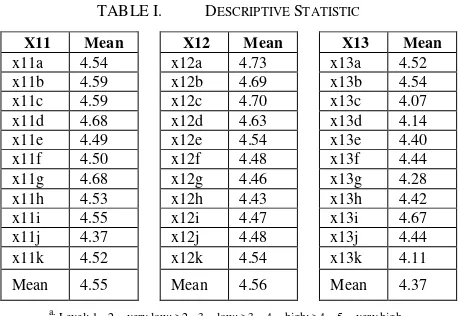
Descriptive statistics are used to describe consumers’
hablumminallah behavior level by using the mean or average
as the type of estimate of central tendency [18, 19, 20]. The results show that Muslim consumers have very high levels of hablummianallah behavior with total 4.49 mean. These include the attitude or believes as the dominant one (4.56), follow by the knowledge (4.55), and the practice or implementation (4.37) of their Faith and Worship aspects (Table I).
All independent and dependent latent variables were included in one single multifactorial CFA model in AMOS 21.0 software. After modification, the model demonstrated goodness-of-fit and marginal fit (Fig.4). The Chi-square/df value was 1.889 (cmin/ df < 2), the root mean square error of approximation value was 0.048 (RMSEA≤0.08), the root mean
square residual value was 0.030 (RMR≤0.05), the goodness of fit index (0.80≤GFI<0.90), the comparative fit index value was 0.839 (0.80≤CFI<0.90), the Tucker-Lewis coefficient was 0.833 (0.80≤TLI<0.90), the incremental fit index value was 0.840 (0.80≤IFI< 0.90). Therefore, the given values reach the permitted threshold accepted in literature [14, 16, 21, 22].
TABLE I. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTIC
X11 Mean X12 Mean X13 Mean
TABLE II. STANDARDIZED REGRESSION WEIGHTS
Factor Loading Factor Loading X1 <--- X .984 x12b <--- x12 .750
Reflective measurements were used to evaluate the conceptual model. Confirmatory factor analysis was performed to ensure the validity of the scales. All factor loadings exceed the 0.50 level for the constructs used in the analysis (Table II). All of the items in each scale loaded on single factor suggesting that MCRB constructs are unidimensional [14].
V. CONCLUSSION
The descriptive analysis used to measure the level of Muslim consumers’ hablumminallah behavior achieved very high levels. Since the Muslim consumers have high levels of hablumminallah behavior, it is strongly recommended for
marketers to assure the halalness (lawfulness) of their products accordingly to the Islamic law.
The Muslim consumers’ religious behavior framework, introduced and examined in this research that used two dimensions and three indicators each with total 53 items, was tested using a single third-order factor CFA model. The two scales used to measure the constructs achieved high levels of factor loadings proving to be valid, and when a high order CFA was performed on the two constructs, the goodness-of-fit and marginal fit model was reach. This concludes that it is possible to validate the Muslim consumers’ religious behavior measurement model by using a third-order CFA model because the factorial validity of Muslim consumers’ religious behavior has a goodness-of-fit, thus, the model could measure the Muslim consumers’ religious behavior significantly which offers further understanding about Muslim religious behavior in many other marketplaces and societies.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research was financially supported by the author and the Faculty of Economics and Business, State Islamic University (UIN) Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, Indonesia.
REFERENCES
[1] Hawkins, Del I. and David L. Mothersbaugh, Consumer Behavior: Building Marketing Strategy, 11th Ed. New York: McGraw-Hill. Inc.,
2010.
[2] Essoo, N., & Dibb, S., Religious Influences on Shopping Behavior: An Exploratory Study. Journal of Marketing Management, vol.20 (7/8), pp.683-713, 2004.
[3] Lawan A. Lawan and Ramat Zanna., Evaluation of Socio-Cultural Factors Influencing Consumer Buying Behavior of Clothes in Borno State, Nigeria, International Journal of Basics and Applied Sciences, vol.01(03), pp. 519-529, Jan 2013.
[4] Delener, N., The effects of Religious Factors on Perceived Risks in Durable Goods Purchase Decision, The Journal of Consumer Marketing, vol.7 (3), pp.27-36, 1990.
[5] El-Menouar, Yasemin and Bertelsmann Stiftung, The Five Dimensions of Muslim Religiosity: Results of an Empirical Study, Methods, Data, Analyses, Vol.8(1), pp.53-78, 2014
[6] Magill, F. N. (Editor), Survey of Social Science: Psychology Series,
Vol.16. Pasadena, California: Salem Press, 1993
[7] Antonio, Muhammad Syafi’i, Islam sebagai Agama yang Lengkap dan Universal, Bank Syariah Suatu Pengenalan Umum, Jakarta: Tazkia Institute, Chap. I, pp.37-40, 2006
[8] Temporal, Paul, Islamic Branding And Marketing: Creating A Global Islamic Business, John Wiley and Sons (Asia) Pte. Ltd., Solaris South Tower, Singapore, 2011
[9] Mansoer, Masri, Perilaku Keberagamaan Remaja pada Siswa SLTA di Jakarta Selatan, Sukabumi dan Lebak, Disertasi Pascasarjana, Institut Pertanian Bogor, 2008
[10] Husaini, Ardian, Konsep Ilahiah, Sahabat Mizan Amanah, Jakarta, pp.19-20, Mei 2013
[11] Hidayat, Mohamad, Pengantar Ekonomi Islam, PKES, 2009.
[12] Aisyah, Muniaty, The Influence of Religious Behavior on Consumers Intention to Purchase Halal- Labeled Products, Journal Business and Entrepreneurial Review, vol.14(1), pp.15-31, Oct 2014
[13] Aisyah, Muniaty, Peer Group Effects on Moslem Consumer’s Decision to Purchase Halal-Labeled Cosmetics, Journal Al-Iqtishad, vol.VII (2), pp.165-180, July 2015
[14] Byrne, Barbara M., Structural Equation Modelin with AMOS: Basic concepts, applications, and programming, second Ed., Taylor and Francis Group, New York, 2010
[15] Schivinski, Bruno, Implementing Second-Order CFA Model for The Factorial Validity of Brand Equity, PhD Interdisciplinary Journal, DS no.020352, pp.105-111, Faculty of Management and Economics, Department of Marketing, Gdansk University of Technology, 2013 [16] Bentler, P., EQS 6 Structural Equations Program Manual, Multivariate
Software, Encino, 2006
[17] Carter, Nancy J., Neil C. Schwertman and Terry L. Kiser, ‘A Comparison of Two Boxplot Methods for Detecting Univariate Outliers which Adjust for Sample Size and Asymmetry’, Statistical Methodology, pp. 604–621, 2009.
[18] Ghozali, Imam (2011), Multivariate Analysis Application with IBM SPSS 19 Program, Diponegoro University Publisher: Semarang, Indonesia
[19] Trochim, William M.K., Descriptive analysis, Research Methods of Knowledge Base, 3rd Ed., All Rights Reserved, 2006
[20] Morgan, G. A., Gliner, J. A., & Harmon, R. J., Measurement and descriptive statistics. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 38(10), 1313-1315, 1999
[21] Wijanto, Setyo Hari, Structural Equation Modelling dengan Lisrel: Konsep Tutorial, Garaha Ilmu: Jakarta, 2008
[22] Haryono, Siswoyo and Parwoto Wardoyo, Structural Equation Modelling untuk Penelitian Manajemen Menggunakan Amos 18.00,
Intermedia Personalia Utama, Bekasi, Jawa barat, 2012