ABSTRACT
INCREASING STUDENTS` VOCABULARY ACHIEVEMENT THROUGH DIRECT METHOD AT THE FIRST GRADE OF SMP NEGERI 2
GADING REJO By
SETIO AGUNG WIBOWO
Vocabulary is a component of language containing information about the meaning and the using of words in language. This research was intended to find out whether there was a significant increase of the students` vocabulary achievement related to content words at the first grade of SMP Negeri 2 Gadingrejo before and after being taught through direct method. The pretest and the posttest with one group pretest-posttest, pre-experimental design was applied. The population of the research was the grade VII students of SMP Negeri 2 Gadingrejo in the year 2010/2011. Vocabulary test in the form of multiple choices was used as the instrument of the research and repeated measures t-test was accomplished to analyze the data.
The result shows that the students mean score of the pretest (53.45) while the mean score of the posttest (73.10). After comparing the result of the pretest and the posttest score, it was found that there was significant difference, the increase of mean score of the students was 19.643 after the treatments. Based on the data analysis at the significant level of 0.05, it was noted that p=0.000. It was proved that the students` scores were significantly different (p, 0.05, p=0.000) and the students active learning was better. The result showed that the students taught through direct method seemed to be interested in learning vocabulary since the students could provide a good response during teaching learning process. The teaching learning process motivated the students to compete in asking and delivering the questions.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Alhamdulillah, thanks to Allah SWT the almighty for the eternal blessing, so the writer can accomplish this script. This script is presented to English Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of Lampung University as partial fulfillment for S1 degree.
1.
advisor who has been so benevolent in guiding and giving his advices. 2. Drs. Dedy Supriyadi, M.Pd,
guidance and help to improve this script be better. 3.
guidance during completion this script.
4. Sugito,S.Pd, as the Headmaster of SMP Negeri 2 Gadingrejo Pringsewu for giving his permit to conduct the research.
5. Drs. Hi. Suharwanto, as the English Teacher of SMP Negeri 2 Gadingrejo Pringsewu who has supported the research and all of the students in class VIIB and VIIC.
6. All lecturers of English program, who have contributed their guidance and knowledge for the writer.
7. Hj. Sufiya.), my old sister ( Yunia Eka
Sari, Wahyu Widiastuti, Enita Mariyana), for giving their pray trust and support, and encouragement to finish this script.
8. English 2006 fraternity ( for all support), especially Erlan Heriyanto, Ahmad Sahlan, Eka Setiawan, Jaka Dirgantara, Adi Suratman, Zulpri, Frisca Mei Indah Sari, Lidya Sinta, Victoria, Faradiaswita, Novi, Kharisma, Haris Tamzil, Nuprisyah Heriyanto, Alvin, Seftia, Emil and all my friends who cannot be mentioned one by one (thanks for everything). Nothing in this world is perfect and this final project is no exception. The writer hopes that is final project will be useful and beneficial for this readers, especially those who are involved in English Teaching profession.
Bandar Lampung, 2012 The Writer
(A Script)
By
SETIO AGUNG WIBOWO
LAMPUNG UNIVERSITY BANDAR LAMPUNG
I OCABULARY ACHIEVEMENT TRHOUGH DIRECT METHOD AT THE FIRST GRADE OF
SMP NEGERI 2 GADINGREJO PRINGSEWU
By
SETIO AGUNG WIBOWO
A Script
Submitted in a Partial Fulfillment of The requirement for S-1 Degree
in
The Language and Arts Department of The Faculty of Teacher Training and Education
LAMPUNG UNIVERSITY BANDAR LAMPUNG
: SETIO AGUNG WIBOWO : 0643042039
Department : Language and Arts Education Study Program : English Education
Faculty : Teachers Training and Education
APPROVED BY Advisory Committee
Advisor I Advisor II
Prof. Dr. Cucu Sutarsyah, M.A. Drs. Deddy Supriyadi, M.Pd. NIP 19570406198603 1 001 NIP 19580505198502 1 001
The Head of
Language and Arts Education Department
ADMITTED BY
1. Examination Committee Chairperson
2. The Dean of Teachers Training and Education Faculty
Dr. H. Bujang Rahman, M.Si. NIP 19600315 198503 1 003
A. Background of the Problem
Vocabulary is one of language aspects that are presented in the classroom during
vital The existence of vocabulary has been considered important since it is term that should be acquired to learn four skills namely listening, speaking, reading, and writing. A small number of words can be used effectively to express an enormous number of ideas as in the case with speaking, it is important to get learners be able to make the best use of a small productive vocabulary. An adequate vocabulary is also needed if learners are going to
generate, develop, and present ideas in their writing. The process of writing can be a contributor to vocabulary acquisition by making learners grapple with the
meaning of words as they write.
Based on the Guidelines of SMP Curriculum of English (KTSP for English), graduates of Junior High School are supported to master vocabulary in order to be able to communicate whether in spoken or written form. The first year students of Junior High School are expected to master 1000 words after finishing their study. But in fact, based on experience when the researcher is in Junior High School, it seems difficult to be reached since the students often
2
like other subject, learning on the book only without any practice. Sometime, the teacher taught vocabulary the same as they teach reading, structure, writing, speaking or listening without using certain method.So it made the students lack of vocabulary. And as the result, they got a difficulty in comprehending the meaning of sentences and to express their idea whether in spoken or written form.
In this research, the researcher chose vocabulary as the topic of this research because vocabulary is an important part of learning a language. Vocabulary is one of the important aspects that should be acquired in learning four language skills. Vocabulary is divided into four types, these are content words, function words, substitute words and distributed words. From these type of English vocabulary, the content words (noun and verb) are taken as the material in English teaching vocabulary since it is appropriate with Junior High School Students.
Besides that, based on Junior High School National Final Examination
(Depdiknas, 2006) that vocabulary earned the highest score (4 of 10 points) in speaking and writing test, 40 percent in listening test score, and 30 percent in reading test score.
The researcher assumed that it is also caused of the teacher teaching strategy. In Teaching learning process the teacher should consider the way of teaching in order to get better result of students score. It is the teacher`s responsibility to determine an appropriate way of teaching which is easier and more useful for teaching, so that the students will be interested in learning English. An interesting way in teaching will encourage the students to learn easily.
Beside four skills that should be considered in scoring, one of the terms that also earns in the scoring is vocabulary. Thus, vocabulary teaching that encourages the
attention and motivation in learning should be taken into consideration, in order to get better result of students` score.
junior high school where the researcher will conduct the research, most of the students especially the first grades at the first semester of class VII have limited vocabulary. The students have problems to understand the reading texts, such as, paragraph, sentences and meaning of words. In speaking class, the students cannot express their idea clearly. When the teacher asks them to do a short conversation about asking and giving information in front of the class, they are confused and cannot tell their idea clearly. All of these were because the students were lack of vocabulary since vocabulary is one of important language aspects.
4
motivation to study. Sometime the teacher asks the students to memorize the list of vocabulary without training them well in developing their vocabularies. So they are bored in learning English.
Based on the research result of Jayanti (2006:47) stated that in memorizing word list, the students cannot remember the word immediately, but need a process, perhaps, after remembering words from list of words students are able to remember them, but the words stay in the students mind just for a while. It is because learning word list does not pass through some steps or strategies that make the meaning of the words will stick in students mind.
Based on the explanation above, the researcher wanted to apply direct method in teaching vocabulary. Direct method is a way of teaching a foreign language insists that only the target language should be used in the class and meaning should be communicated directly. This method employs realias, pictures, and pantomimes as teaching media. Teaching English vocabulary through Direct Method will make the students able to learn directly because in Direct Method Vocabulary is
acquired more directly than memorizing words list. The researcher conducted the research at SMP Negeri 2 Gadingrejo since the research about it has not
B. Formulation of the Problem
Referring to the background above, the problem of the research is as follows: Is there any significant increase of student s vocabulary achievement of the first grade of SMP Negeri 2 Gadingrejo after being taught through direct method?
C. Objective of the Research
Concerning to the problem above, the objective of this research is to find out whether:
To find out whether there is any significant increase of student s vocabulary achievement of the first grade of SMP Negeri 2 Gadingrejo after being taught through direct method.
D. Significances of the Research
The significances of this research are:
1. Practically, the result of this research can be used by English teacher as information in order to select suitable technique or method in teaching vocabulary in junior high school.
2. Theoretically, as the information whether the result of this research is relevant or not to the theory. Moreover it can be used to verify the previous theories dealing with the theories in this research and also as a reference for further research.
6
F. Definition of Terms
Some terms are defined in order to give basic understanding of the related variables and concepts. These are stated below:
1. Vocabulary is a set of words known to a person or entity, or that are part of a specific language which will make the language meaningful.
2. Direct Method is a way of teaching a foreign language insists that only the target language should be used in the class and meaning should be
communicated directly by associating speech forms with realia, picture, and pantomime.
3. Vocabulary achievement is
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
This chapter discusses about the description of vocabulary, the description of teachingvocabulary, the description of direct method,procedure of teaching English vocabulary through direct method, theoretical assumption, and hypothesis.
A. Description of Vocabulary
Vocabulary can be defined as a set of lexeme including simple words, compound words, and idioms (Lamb, 1963:19). According to lamb, a simple word is a single word that may or not may have a prefix and/or suffix, for example: book, chair, table, etc. While a compound word is a word join from two or more other words, as supported by Trask (1999:120) states that compound word is two or more existing words, which are simply combining. Compound word can be written as one word, two words or as a hyphenated word, such as fireman, policeman, putdown, etc. Idiom is a group of words with a meaning, which is different from the individual words and often difficult to understand from the individual words, look at, give up, carry out, etc.
According toDiamond andGuthlon(2006)Vocabulary is the knowledge of words and word meanings. As Stahl (2005) puts it, "Vocabulary knowledge is
knowledge; the knowledge of a word not only implies a definition, but also implies how that word fits into the world." Vocabulary knowledge is not something that can ever be fully mastered; it is something that expands and deepens over the course of a lifetime. Instruction in vocabulary involves far more than looking up words in a dictionary and using the words in a sentence.
Vocabulary is acquired incidentally through direct exposure to words and intentionally through explicit instruction in specific words and word-learning strategies.
10
As stated by Fries (1975:45), vocabulary can be classified into some types, namely:
1. Content Words represent the name of subject or things, that is: noun (doctor, farmer, and door), action done by those things, that is: verbs (drive, plant, and teach), and the qualities of those things, that is: adjectives (tall, sweet, delicious, etc).
Example:
- You play football Noun - They sing a song
Verb
2. Function words are those words used as a means of expressing relation of grammar/structure, such as conjunction (and, however, but), article (a, an, the), and auxiliaries (do, did, does).
Example:
- Tia and Tata are at home, they do not go to the movie.
Conj Aux
3. Substitute words, those represent not to the individual things or specific action, but function as substitutes for whole form classes of words. In this group, there are personal pronoun (me, you, etc), infinitive (somebody, everybody, anybody, etc), negative expression (nobody, nothing, etc), and quantity of number (each, both, etc).
Example:
- You can trust on me (personal pronoun) - Everybody has problems
Example:
- John does not drink milk either.
Macfayden (2007: 1-21) divides content words into some categories: verb, noun, adjective, and adverb. Verb is perhaps the most important part of the sentence. A verb asserts the most important part of the sentence and expresses actions, events, or states of being. The verb or compound verb is the critical element of the predicate of a sentence. Verb fall into three categories: transitive verbs,
intransitive verbs, and linking verbs. Transitive verb is a verb, which needs direct
meanwhile intransitive verb is a verb, whichdoes not need direct object. For example: arrive, come, go, stay, cry, etc. while linking verbs, e.g. my elder brother become an engineer. This verb does not show action, for example: be (am, is are, was, and were), become, seem, etc.
12
non-count nouns if the substance is placed in a countable container, e.g. glass of milk, two glasses of milk, etc.
For example:
- This is one of the food that my doctor has forbidden me to eat. (Non-countable) - We painted the window blue and the door red. (Countable noun)
The next category is adjectives. Adjective fall into two categories: descriptive and limiting. Descriptive adjective are those, which describe the colour, size, or quality of person or thing (noun or pronoun). For example: beautiful, large, red, interesting, important, colorful, etc. It means that an adjective modifies a noun or a pronoun by describing, identifying, or quantifying words. An adjective usually precedes the noun or the pronoun, which it modifies. Limiting adjectives place restriction on these and those are plural form. For example: cardinal numbers (one, two), ordinal numbers (first, second) possessives (my, your, his),
demonstratives (this, that, these, those), quantity (few, many, much), articles (a, an, the). All others remain the same whether the noun is singular or plural. For example:
- Vianca is a nice girl - Dany is a naughty boy
The last category is adverb. Heather Macfadyen says that an adverb can modify a verb, an adjective, another adverb, a phrase, or a clause. An adverb indicates manner, time, place, cause, or degree and answers questions such as how, when, where, how much. Many descriptive adjectives can be changed to adverbs by adding-ly suffix to the adjective base. Unlike an adjective, an adverb can be found in various places within the sentence.
- She walks slowly Adv
- He was driving carefully Adv
In this research, the material of teaching English vocabulary will be taken from the content words (noun and verb) since the researcher assumes that it is appropriate with Junior high School students.
B. Description of Teaching Learning Vocabulary
Considering the importance of vocabulary in language teaching, teaching vocabulary should be taken into account. The teaching process of vocabulary needs a good technique in order to help the students to get the meaning and to use the words. As stated by Allen and Vallete (1983:116-117) in Gnainoska
(1998:12), teaching vocabulary can be meaning full if the teacher can conduct the teaching process by combining the available techniques of teaching. It is hoped that a good technique will be more enjoyable, interesting and motivating so that the students will not be bored in process of learning. It means that the teacher has to be aware with the kinds of teaching techniques that she will use to achieve the goal of teaching learning process. Beside the technique that should be considered, the teacher also should be considered to the vocabulary will be taught. The teacher must select the vocabulary based on the curriculum.
Nation (1990:18) states that when a teacher teaches a word, she or he has to teach three things, they are; the teacher should:
a. Teach the shape, or form of the word. b. Teach the meaning of the word.
14
As stated by Nation (1990:51) that the meaning of words can be communicated or taught in many different ways such as by using picture or demonstration. Nation also stated that some people criticize translation in mother tongue as way of communicating or teaching meaning of word. Their objections are:
- There is usually no exact correspondence between one language and another. - Translation in mother tongue is indirect.
- The use of the mother tongue takes time which could better be spent in using English.
All of the criticisms are true. But they can also be applied to the use of pictures, drawings, demonstration, and the use of real object.
In direct method, the form of the words and the meaning of the words are able to be given to learners by demonstration, picture and realia. The teacher should demonstrate, it is desirable that students make a direct association between the target language and the meaning.
C. Description of Direct Method
Direct method has one basic rule, which is no translation is allowed (Larsen-Freeman, 1986:18). The teacher should not translate when she or he teaches the material. In other words, the researcher can say that the native language should not be used in the classroom. When the teacher introduces new target language word or phrase, the teacher demonstrates its meaning through the use of realia,
target language and the meaning. So in direct method, meaning is to be connected directly with the target language, without using the process of translating into the students` native language. The method relies on a step-by-step progression based on question-and-answer sessions. It provides a motivating start as the learner begins using a foreign language almost immediately.
Since, no translation is allowed in Direct Method, objects (such as, real, picture etc) presented in the immediate classroom environment should be used to help students understand the meaning (Larsen-Freeman, 1986:22).
Like other methods, direct method also has assumptions about language learning. The following are basic assumption about language learning of the direct method. They are:
Meanings are made clear by presenting realia, picture, and pantomime. Translation may be an easy way to make meaning clear but it will not make the students learn the target language directly.
Self-correction is more emphasized than teacher correction. This will make the students think in the target language, not do parroting. This can be done by asking them to make a choice between what they said and an alternative answer provided by the teacher. Self correction also can be done by repeating what they said in a questioning voice to signal to the students that there is something wrong.
16
Teaching another language means taking a role as a partner of the students in communications. The interaction between the teacher and the students are two-way interaction. The teacher can ask the students and vice versa. Besides functioning as a partner, the teacher also a facilitator; he/she can show the students what errors they have made and how they correct the error.
Larsen-Freeman (1986:22) states some principles of
1. Reading in the target language should be taught from the beginning of the language instruction.
2. Object (e. g, realia or pictures) presented in the immediate classroom environment should not be used to help students understand the meaning.
3. The native language should not be used in the classroom.
4. The teacher should demonstrate through the use of realia or picture. It is desirable that students make a direct association between the target and the meaning.
5. The students should learn to think the target as soon as possible. Vocabulary is acquired more naturally if the students use it in full sentences, rather than memorizing word lists.
6. The purpose of language learning is communication (therefore students need to learn how to ask question as well as answer them).
7. Pronunciation should be worked on the right form the beginning of the language instruction.
9. Lesson should contain some conversational activity-some opportunity for students to use language in real contexts students should be
encouraged to speak as much as possible.
10. Grammar should be taught inductively there may never be explicit grammar rule given.
11. Writing is an important skill, to be developed from the beginning of the language instruction.
12. The syllabus is based on situations on topics, not usually on linguistic structures.
13. Learning another language also involves learning how speakers of that language live.
Based on Freeman`s principles of direct method the writer has proposed some sequences of the principles of Direct Method in teaching vocabulary in the classroom. They are:
1. Object (e. g, realia or pictures) presented in the immediate classroom environment should not be used to help students understand the meaning. 2. The native language should not be used in the classroom.
3. The teacher should demonstrate through the use of realia or picture. It is desirable that students make a direct association between the target and the meaning.
18
5. Lesson should contain some conversational activity-some opportunity for students to use language in real contexts students should be encouraged to speak as much as possible.
6. The syllabus is based on situations on topics, not usually on linguistic structures.
D. Teaching Vocabulary through Direct Method
The basic assumption about language in this method is that language is seen as a set of grammatical rules and its vocabulary in real situation. Grammatical rules and its vocabulary are presented in the texts: oral or written texts. Language teacher should use the grammar and vocabulary in contexts and then relate them to the situations in the classroom. In this method vocabulary is emphasized over grammar. If language learners do not understood some words, the language teacher will demonstrate in the target language to make the students understand the meaning through realia, pictures and pantomime.
Based on the theories the writer has explain above, the writer find some
advantages and disadvantages of teaching vocabulary through direct method are:
The students pay more attention to word and grammar used in oral communication.
The teacher and the students are like partner in teaching learning process organized in question and answer.
Using oral communication skills makes the teaching learning process misunderstanding for the students because oral communication skills often use questions.
E. Procedure of Teaching English Vocabulary through Direct Method
Teaching English vocabulary through Direct Method can be done by having the following procedures (Larsen Freeman, 1986:18);
1. Choose a particular situation (situation as at the school) or particular interesting topic (such as at the market) and write a short passage or a dialogue on the theme we have chosen.
2. Brings the students to real conditions if it is possible. If it is possible we can bring some objects or pictures to the classroom.
3. Introduce the method we are going to use (the rule) and tell what they are going to learn (vocabulary).
4. Ask the students to prepare their notebook, pen, etc.
5. Demonstrate the parts (the meaning) of the words through the use of
6. Repeat the process of demonstration the parts (the meaning) of the words through the use of realia, picture, or pantomime several times. 7. Ask the students if they have question. Try to create questions and
answers sessions.
20
Based on Freeman`s procedure the writer has proposed some sequences of the implementation of Direct Method in the classroom. They are:
1. The teacher
prepares the media. In this case, the teacher uses pictures of occupation.
2. Tell what they are going to learn (vocabulary).
3. Start the research activity (teaching English vocabulary about occupation. First, the teacher shows the picture; in these steps the teacher puts the pictures on the white board). Finally, to know whether the students understand the lesson or not, the teacher ask about
occupation.
4. Repeat process of describing and demonstrating several times. 5. Ask if the students have any questions.
6. Carry out question answer session several times.
7. To know the result of the students` acquisition of the lesson, the teacher asks the students to do the test based on the material.
F. Theoretical Assumption
the picture and etc. therefore the students can easily remember the vocabularies because they are acquired directly. The students use the vocabularies in full sentences rather than memorize a word list.
III. RESEARCH METHODS
A. Research Design
This research is a quantitative study which hasone group pretest-posttest design. The researcher selected one class as the experimental group using simple
probability sampling. The aim of this research is to find out whether Teaching using Direct Method can increase the students` vocabulary achievement significantly. The design of the research is represented as follows:
T1 X T2
T1 = Pretest X = Treatment T2 = Posttest
(Hatch and Farhadi in Setiyadi, 2006:131)
B. Population and Sample
The population of the research was grade VII students of SMP Negeri 2
Gadingrejo. There were four classes in grade VII in first semester and 2011/2012 school year. The researcher selected one class as the sample of the research by using simple random probability sampling, which is by using lottery. The selected class consisted of 42 students as the experimental group.
The data of the research was the student` vocabulary achievement of occupation before and after the treatments in term of score.
The instrument of the research was objective vocabulary test in the form of multiple choice items, where the researcher gave pretest and posttest in order to evaluate, to measure the vocabulary achievement of occupation related to content words (noun and verb).
In collecting Data, the researcher used the following procedures:
1. Pretest
The pretest was conducted before treatments. It was used to know how far the students had mastered the vocabulary before the treatments were given. The pretest used by researcher is an objective test of the multiple choices. The number of item in the test is 40 items and each item has four options of answers. One is the correct answer and the rests are the distracters.
2. Posttest
24
questions. The posttests consisted of 40 items with four options. One is the correct answer and the rest were the distracters.
D. Steps in Collecting Data
1. Determining the sample of the research
The sample of the research was selected by using simple probability
sampling, which was by using lottery. The researcher took one class of four classes of the first year students at SMP Negeri 2 Gadingrejo as the research sample. Each class consists of 42 students. The sample of the research follows pretest, treatment, and posttest.
2. Selecting instrument materials
In this research, there was one pretest that is proper to the grade VII students It focuses on vocabulary, which is classified in to content words (noun and verb). The materials will be taken based on the educational unit level curriculum of English for Junior High School.
3. Conducting try out
The try out was conducted in the different class of the experiment class in first class of SMP Negeri 2 Gadingrejo. Try out was conducted to measure the reliability of pretest and posttest. It was administered for 60 items in 90 minutes. The aim of try out was to know the quality of the test which will be used as the instrument of the research, and determine which item should be revised for the pretest and posttest.
Pretest was conducted for 40 items in 60 minutes. It is held to measure student
5. Conducting the treatment
After giving pre test, the students was given three times treatments by using direct method based on the lesson plan which has been prepared. Each treatment is held for 90 minutes.
6. Administering post test
The post test will be administered after the application of direct method approach. It will be conducted for 40 items in 60 minutes and the aim was to find out the students` vocabulary achievement after the implementation of direct method.
7. Analysis the Test Result
After conducting pretest and posttest, the researcher analyzed the data. The data was analyzed by using T-test. It was used to know whether direct method is able to increase the students` vocabulary achievement
significantly. The date will compute through the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS).
8. Reporting the Result
In reporting the result, the data were arranged systematically based on the pretest and posttest to see whether there is an increase on the students` vocabulary achievement.
E. Instrument of the Research
26
instrument of the research. The pretest was given in order to know the students vocabulary before the treatments. The posttest was given in order to know the students vocabulary achievement after the treatments.
The form of the try out test, pretest and posttest is objective test. The total number of the items of the try out test is 60 items, and the total number of the items of the pretest and posttest was determined from the result of the try out test. The validity of the instrument concerns with the content, construct and face validity in which the questions represent the vocabularies stated in the process of teaching
F. Try Out of the Test
In this research, to prove whether the test has good quality, it must be tried out first. The test can be said has good quality if it has a good validity, reliability, level of difficulty, and discrimination power.
1. Validity
The test can be said valid if the test measures the object to be measured and it is suitable with the criteria (Hatch and Farhady, 1982:250).To measure whether the test has a good validity, this research will use content and construct validity.
a. Content Validity
Content validity is concerned with whether the test is sufficiently
representative and comprehensive for the test. In the content validity, the material is given suitable with the curriculum. Researcher used the
vocabulary that is supposed to be comprehended by grade VII students. In this research, the researcher arranged the instrument based on the material that will be given, which is vocabulary, and the researcher makes
28
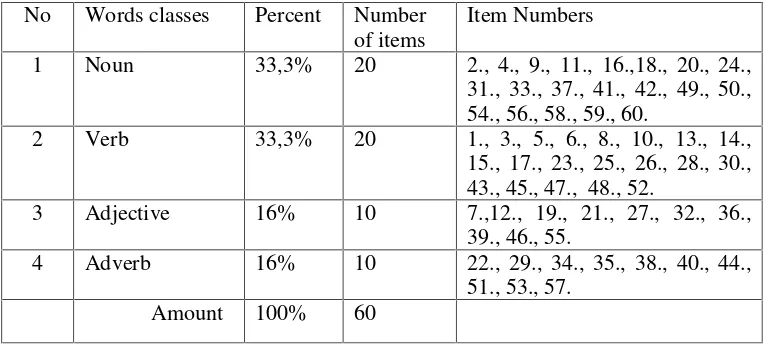
they were noun and verb. The content of try out test is presented in the table of specification below:
Table 1. Table of specification of the Test
b. Construct Validity
Construct validity is concerned with whether the test is true reflection of the theory of the trait in our case language which is being measured. It means that the items should really measure the students` vocabulary achievement. In this research, the researcher used the vocabulary that is supposed to be comprehended by the grade VII students of Junior High School. The material is under topic of occupation which is representative of vocabulary material based on the curriculum used in Junior High School; KTSP Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan) 2006. No Words classes Percent Number
2. Reliability
Reliability of test can be defined as the extent to which a test produces consistent result when administered under similar conditions (Hatch and Farhady,1982:243). To compute the reliability of test, split half method is used. It is done through dividing the test into two parts, odd and even number. To measure the coefficient of the reliability, the researcher used the Person Product Moment Formula below:
2
r : coefficient of reliability between odd numbers and even numbers items x : total numbers of odd numbers items
y : total numbers of even numbers items
n : numbers of students who take part in the test
x2
: square of x
y2 : square of y
x
: Total score of odd number itemsy : Total score of even number items
(Arikunto, 1997:69)
30
0.00 0.19 : very low
Then, to compute the coefficient correlation of the whole items, the researcher use Spearman Brown Prophecy Formula.
rk= rl rl
1 2
r k : reliability of a full test rl : reliability of half test
The criteria of reliability are: 0.90 - 1.00 : high
0.50 0.89 : moderate 0.00 0.49 : low
3. Level of Difficulty
Difficulty level related to how easy or difficult the item is from point of view of the students who take the test. This is important since test items, which are too easy, tell us nothing about differences is discarded. To see the level of difficulty, this research will use the following formula:
LD = N
L U
Where:
LD : level of difficulty U : upper group students L : lower group students The criteria are:
<0.30 = difficult 0.30-0.70 = average
<0.70 = easy
32
4. Discrimination Power
The discrimination power (DP) refers to the extent to which the item differentiates between high and low level students on the test. A good item according to this criterion is one which good students do well on and bad students fail
To know the discrimination power of the test, the writer will use the following formula:
U : the proportion of upper group students L : the proportion of lower group students N : total number of students
The criteria were:
Dp: 0.00-0.19 = Poor
Dp: 0.20-0.39 = Satisfactory Dp: 0.40-0.69 = Good Dp: 0.70-1.00 = Excellent
Dp: - (Negative) = Bad items, should be omitted
5. Scoring System
In scoring the students result of the test, this research used Arikunto`s formula. The total score of pre-test and post tests were calculated by using formula as follows:
R : the total of the right answers N : the total items (40)
(Arikunto, 1997:212)
G. Data Analysis
After conducting pretest and posttest, the researcher analyzed the data. It is used
to know whether mastery.
The researcher examines the students score using the following steps; 1. Scoring the pretest and posttest
2.
measures T-test
3. Drawing conclusion from the tabulated result of the pretest administering, that is statistically analyzed using SPSS (Statistical Program for Social Sciences) in order to test whether increase of the students gain is significant or not.
34
The hypothesis testing is used to prove whether the hypothesis proposed in this research is accepted or not. The hypotheses of this research are:
1. There is significant increase of student s vocabulary achievement of the first grade of SMP Negeri 2 Gadingrejo after being taught through direct method? 2. There is no significant increase of student s vocabulary achievement of the first
grade of SMP Negeri 2 Gadingrejo after being taught through direct method?
A. Conclusions
Having conducted the research at the first grade of SMP Negeri 2 Gadingrejo and analyzing the data, some conclusions were given as follows:
1. There was significant increase of the students` vocabulary achievement after being taught through direct method. It can be proved from the increase of the students` mean score in the pretest and the posttest. The result of the posttest was higher than the result of the pretest. There was an increase from the mean score of pretest (53.45) to posttest (73.10). The result of hypothesis test shows that the alternative hypothesis was accepted (p<0.05, p=0.000).
2. Teaching English vocabulary through direct method can attract the students` motivation and interest. It can be seen from their enthusiasm in learning English. The student was given more chances to be involved much in the teaching learning process, so that the students understand more about the material taught and they can get better achievement.
43
Considering the conclusions, some suggestions were proposed as follows: 1. Considering
achievement, it is suggested to the English teacher to use direct method in teaching vocabulary, because i
learn. In this case, the teacher should use English most of the time. 2. The teacher must have a good preparation by using or implement an
The writer is Setio Agung Wibowo , he was born on September 5th, 1987 in Pringsewu, Pringsewu. He is the fourth daughter of happy Moslem couple Mr. Hi. Sudiyono. KS and Mrs. Hj. Sufiyah. He lives on Jl.Pelita I Bulukarto Gadingrejo Pringsewu. He graduated from
DEDICATION
With all of my heart and love , I dedicate this script to :
1. My beloved father and mother, your constant and guidance make me who and what I am today, thank for your pray patience and support.
2. My beloved brother and sister, Sigit Prihantoro, Suratman, Hasyim Asagaf, Yunia Eka Sari, Enita, and Wahyu who always pray and support to get me succsess.
3. My beloved lecturers, Prof. Dr. Cucu Sutarsyah., M.A., Drs. Sudirman, M.Pd., Drs. Deddy Supriyadi., M.Pd.
4. My beloved friends especially Bang Erlan, Alan, Eka, Jaka, Kharisma, Ajis, Nupri, Adi, Zulpri, Alpin, and Frisca, Yudi , Dani, who always give me support an motivation. 5. My beloved special girl friend Nuriya Wijayanti who always gives me pray, support, and
motivation.
LESSON PLAN 1
The students are able to understand and use vocabularies related to occupation
B. Basic Competence
1. The students are able to mention the names of occupations or the words related to occupations given.
2. The students are able to answer the questions related to the occupations.
C.Indicators
1. The students are able to complete the sentences by using the alternative words mentioned based on the picture given.
2. The students are able to mention the meaning of the words of occupation. 3. The students are able to define the occupations.
D. Material
Vocabulary of occupation The words related to occupation:
- Gardener (noun) - Singer (noun) - Secretary (noun) - Reporter (noun) - Police Officer (noun) - Librarian (noun) - Report (verb) - Painter (noun) - Stewardess (noun) - Nurse (noun) - Paint (verb) - Sing (verb)
- Water (verb) - Photographers (noun) - Director (noun)
48
1. The teacher greets the students
2. The teacher asks the students to pray before starting the activity. 3. The teacher che
4. The teacher asks the students to prepare the book, pen, etc. 5. The teacher introduces the rules of the activity.
6. The teacher gives the leading question by asking what they have known about occupation.
7. The teacher shows picture to the students and ask several questions. 8. The teacher informs the students what they are going to learn and the
objective of the learning.
9. The teacher teaches English vocabulary about occupation by using pictures and demonstration
Here, the teacher shows the pictures and asks the students to remember picture and words.
10. The teacher shows the picture again to the students and asks them to repeat after her to mention or pronounce the words.
11. The teacher asks the students by using pictures and body movement. 12. The teacher repeats question and answer several times.
13. The teacher asks one or more students to express some words of occupation on his own sentences.
14. The teacher lets the students discuss the lesson with their friends. 15. The teacher gives the task and asks to do it.
16. The teacher asks the students about what they have learnt. 17. The teacher closes the class.
F. Media
- Picture, note book, pen.
G. Evaluation
Material (First meeting)
- Gardener (noun) - Singer (noun) - Secretary (noun) - Reporter (noun) - Police Officer (noun) - Librarian (noun) - Report (verb) - Painter (noun) - Stewardess (noun) - Nurse (noun) - Paint (verb) - Sing (verb)
- Water (verb) - Photographers (noun) - Director (noun)
1. Gardener is a person who works in a garden.
2. Police officer is the men or women belonging to the department of government concerned with the keeping of public order or a person who uses gun and handcuffs to do her work.
3. Singer is a person who can sing songs sweetly.
4. Secretary is a person with the job of preparing letters, keeping record, arranges meeting in the company.
5. Librarian is a person who can help you find a good book to borrow. 6. Stewardess is a woman who attends to the needs of passengers in a
ship or airliner.
7. Painter is a person who paints pictures, artist or workman who paints woodwork, walls, buildings, ships, etc.
8. Reporter person who reports news for a newspaper or on radio or television.
9. Nurse is a person who helps a doctor to give medical treatment to the patients.
50
I use picture of occupations as the first introduction to `he` and `she`. - What is he? He is a gardener.
- What is he? She is a secretary.
2. What are they?
I use picture of occupations as the first introduction to `they` after the students have learned them singularly.
- What are they? They are police officer.
3. Where does she work?
I use this first set to practice `where` - Where does she/he work?
4. Introducing some places around town.
These also use for introducing some places around town.
I use `
- He worka as a cook at the restaurant.
I use these to talk about what people do at their jobs. It is a great way to introduce a lot of verbs.
- He works as a clothing store. He helps customers, sells and cleans the store.
No Occupations Place of work
1 Gardener Garden
2 Police officer Police office
Part 1
Choose the correct answer by crossing a, b, c, or d!
1. Painter is a person whose job draws something for living. 3. Singer is people who can songs.
a. sing c. make b. create d. dance 4. He uses gun and handcuffs to do
her work. If there are bad guys, he will chase them and put them in jail. He is library. She can help you to find a good book to borrow.
a. navigator c. library b. postman. d. mechanic
Part 2
Mention the meaning of the words and make definition of the
following words in English!
Read the following sentences and then write down which job each of the Following people have!
52
2. This person works in department of government concern with the keeping of public order or a person who uses gun and handcuffs to do her work. 3. This person can sing a song sweetly.
4. The person who attends to the needs of passengers in a ship or airliner. 5. If you need good a book to borrow in library you can come to this person. 6. This person works in the hospital to help a doctor to give medical treatment to
the patient.
7. This person work in a garden.
8. This person reports news for a newspaper or on radio or television. 9. This person works in painting pictures, artist or workman who paints
woodwork, walls, buildings, ships, etc. 10. He takes ph
The Pictures!
Gardener
Reporter
Stewardess Nurse
Secretary
Singer
Painter
MOTTO
learning stays young. The greatest thing in life is to keep your mind
Arikunto,S .1997.Dasar-Dasar Evaluasi Pendidikan.Jakarta: Bina Aksara Bismoko, J. 1976. An Introductory Reader to Method of Teaching English in
Indonesia.Yogyakarta: IKIP Sanata Dharma. Burton, John.1982. Intelligent Tutoring System.
http:/www..cse.msu.edu/groups/cse 101/ITS/its.html Depdiknas. 2006.Curriculum for Junior High School Student.
Jakarta: Depdiknas.
Diamond, Linda and Linda Gutlhohn. 2006.Teaching Vocabulary. http://www.readingrockets.org/teaching vocabulary.
Fries, C. C. 1975.Teaching and Learning English as Foreign Language. An Arbor: The University of Michigan Press.
Gnainoska, Anna C. 1970.Teaching in colour. English Teaching Forum. http://www.Exchanges.state.gov/forum.
Harmer, Jeremy. 1999.The Practice of English Language Learning: New Edition. London: Longman.
Hatch, E. and Hossein Farhady. 1982.Research Design and Statistic for applied Linguistic. London: New Burry House. Inc.
Heaton, J. B. 1975.Writing English Language Test. London: Longman. Hornby, A. 1986.Oxford Advances Learnes` Dictionary of Current English.
New York: Oxford University Press.
Jayanti, Prisda. 2006.A Comparative Study of Teahing English Vocabulary through Deducing Meaning from Context and Memorizing Word List at second year of SMA Wijaya Bandar Lampung: Unpublished Script. Kridalaksana, H.1982.Kamus Linguistic Bahasa Indonesia.Jakarta: Gramedia. Marion Minerva Lamb. 1963.Word Studies. Ohio: South Western Publishing Co. Larsen-Freeman, D. 1986.Techniques and Principles in Language Teaching
Nation, I. S. P. 1990.Teaching and Learning Vocabulary.New York: Heinle & Heinle. publishers.
Rivers, Wilga. M. 1970.Teaching Foreign Language Skill. Chicago: The University Chicago press.
Schaefer, Pat. 2002.The practice: Vocabulary Development.The Education Alliance at Brown University.
http//:www.knowledgeloom.org.
Setiyadi, Ag. Bambang. 2006. Metode Penelitian untuk Pengajaran Bahasa Asing: Pendekatan Kuantitif dan Kualitatif. Yogyakarta: Graha Ilmu Publish.
Shohamy, E. 1985.A Practical Handbook in Language Testing for the Second LanguageTeachers.Tel Aviv: Tel Aviv University press.
Trask, R. L. 1999.Key Concept in Language and Linguistics. New York: Routledge publishers.
Wallace, David Foster, 1986.Vocabulary.
http://www.answer.com/topic/david foster Wallace. Universitas Lampung. 2006.Format Penulisan Karya Ilmiah.