INTERACTIVE TECHNIQUE
(A Classroom Action Research at the Eleventh Grade of SMAN 7 Kota Bekasi)
By :
Catur Wijayanti
1112014000076
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF EDUCATIONAL SCIENCES
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY OF SYARIF
HIDAYATULLAH
JAKARTA
i
IMPROVING STUDENTS’ ABILITY IN USING
CONDITIONAL SENTENCE TYPE III THROUGH
INTERACTIVE TECHNIQUE
(A Classroom Action Research at the Eleventh Grade of SMAN 7 Kota Bekasi)
A “Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Educational Sciences in a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
for the Degree of S.Pd in the Department of English Education
By :
Catur Wijayanti
1112014000076
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF EDUCATIONAL SCIENCES
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY OF SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH
JAKARTA
iv
Education Department. Faculty of Educational Sciences. Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University of Jakarta.
Advisors : Nida Husna, M.Pd., M.A.TESOL. & Atik Yuliani, M.A.TESOL Keywords : Students‟ Ability, Conditional Sentence Type III, Interactive
Technique.
v ABSTRAK
Catur Wijayanti. 2016. Catur Wijayanti. 2016. Improving Students’ Ability in Using Conditional Sentence Type III through Interactive Technique. (A Classroom Action Research at the Eleventh Grade of SMA Negeri 7 Kota Bekasi). Skripsi. Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris. Fakultas Ilmu Pendidikan. UIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
Pembimbing : Nida Husna, M.Pd., M.A.TESOL. & Atik Yuliani, M.A.TESOL Kata Kunci : Kemampuan siswa, Conditional sentence tipe III, Interaktif
teknik.
vi
completing this paper. Sholawat and Salam are given upon our prophet Muhammad SAW who has guided us to the truth way and brought us to the real light of life.
The writer is extremely grateful to the Almighty Allah. He has blessed her with his power and strength at all times until she can accomplish this “Skripsi”. She also would like to express her deepest gratitude to her parents, Mrs. Mariyam, S.Pd and Mr. Supriyono for giving her a motivation, guidance, and pray all the time.
Furthermore, the writer would also like to express her great honour and deepest gratitude to her advisors, Mrs. Nida Husna, M.Pd., M.A. TESOL. and Mrs. Atik Yuliani, M.A. TESOL., for their valuable help, guidance, comments, corrections, suggestions and also their patience to sacrifice their energy and time to assist the writer so that the writer could finish this “Skripsi”
The writer would like to express her special gratitude and give her appreciation to :
1. Dr. Alek, M.Pd. the chairman of the Department of English Education. 2. Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum, the secretary of the Department of English
Education.
3. Teguh Khaeruddin, M.App.Ling , as an academic advisor who has given the writer a motivation, suggestion, and a useful knowledge.
4. All lecturers and staffs of the Department of English Education who have taught the writer the useful knowledge and skills.
vii
6. Eno Sutresno, S.Pd, M.Si, the principal of SMAN 7 Kota Bekasi who has given a permission to the writer to conduct the classroom action research in that school.
7. H. Saud, M.Pd, as the English teacher of SMAN 7 Kota Bekasi who has given the opportunity and chance to be involved in conducting the classroom action research.
8. Ika Retnasari S.Pd and Tri Hariyanto S.Pd, the writer‟s sister and brother who have given the support, motivation, and suggestion for the writer to
finish this”skripsi”.
9. All friends in English Education Department, especially PBI C 2012 who have created a great friendship, support, knowledge, and togetherness. May Allah the Almighty bless them all, so be it.
Finally, the writer realizes that the Skripsi is far from being perfect, but the writer hopes this “Skripsi” will be useful for her, any readers or researchers. Therefore, it is such a pleasure for her to get the critiques and suggestions to make this “Skripsi” better.
Jakarta, 28 Oktober 2016
viii
TABLE OF CONTENT ... viii
LIST OF TABLES ... xi
LIST OF FIGURES ... xii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xiii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Research ...1
B. Identification of the Problem ...7
C. Limitation and Formulation of the Problem ...7
D. Objectives of the Research ...7
E. Signifance of the Study ...7
CHAPTER II THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK A. Conditional Sentence ...9
1. The Definition of Conditional Sentence ...9
2. Types of Conditional Sentence ...10
3. The Function of Conditional Sentence ...19
B. Interactive Technique ...20
1. The Definition of Interactive Technique ...20
2. Interactive Principles ...22
3. Strategies for Interactive Learning ...24
4. Stages of Interactive Technique ...24
C. Teaching Conditional Sentence by Using Interactive Technique ...25
ix
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Place & Time of the Research ...32
B. Method of the Research ...32
C. The Design of the Research ...33
D. Subject of the Research ...36
E. The Role of the Writer in the Research ...36
F. The Instruments of the Data ...36
G. Procedures of Classroom Action Research ...37
1. Planning ...37
2. Acting ...37
3. Observing ...37
4. Reflecting ...38
H. Technique of Data Collection 1. Pre-Interview ...38
2. Observation ...39
3. Questionnaire ...39
4. Test ...40
I. Technique of Data Analysis ...40
J. Trustworthiness ...47
K. Criteria of Success ...47
CHAPTER IV RESEARCH FINDINGS AND INTERPRETATION A. The Description of Data ...49
1. Findings before the Implementation of CAR a) The Result of Pre-Interview ...49
b) The Result of Observation ...51
x
3) Observing ...55
4) Reflecting ...60
b) Cycle 2 ...61
1) Planning ...61
2) Acting ...62
3) Observing ...63
4) Reflecting ...67
3. Findings after the Implementation of CAR a) Questionnaire ...68
b) The Result of Post-Test ...73
B. Analysis of the Data ...75
C. Interpretation of the Data ...79
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusion ...82
B. Suggestion ...83
REFERENCE ...84
xi
LIST OF TABLES
3.1 Blueprint of observational journal ...39
3.2 Rubric of Observation Sheet ...41
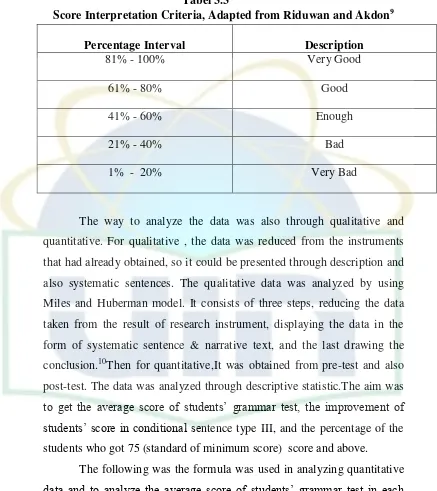
3.4 Score Interpretation Criteria ...45
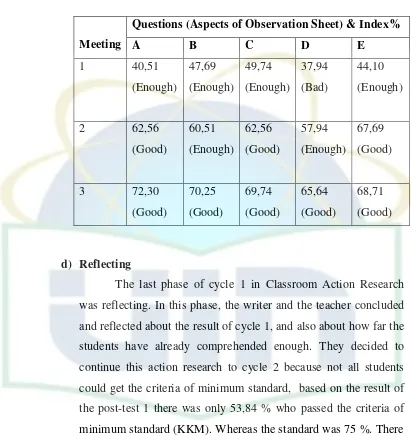
4.1 The Result of Index% Cycle 1 ...60
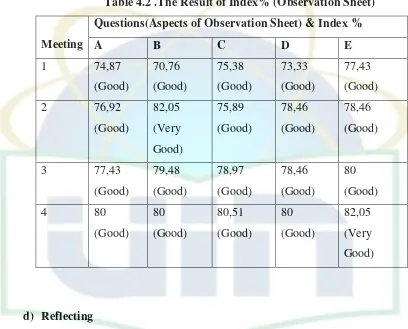
4.2 The Result of Index% Cycle 2 ...67
xii
xiii
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1. Students‟Score ...87
Appendix 2. Interview Guide and Result ...89
Appendix 3. The Instrument of Pre-Test ...92
Appendix 4. The Instrument of Post-Test 1 ...97
Appendix 5. The Instrument of Post-Test 2 ...102
Appendix 6. Observation Journal of Post-Action 1 ...108
Appendix 7. Observation Journal of Post-Action 2 ...111
Appendix 8. Questionnaire ...113
Appendix 9. Result of Questionnaire ...116
Appendix 10 Result of Observation Sheet in Cycle 1 ...120
Appendix 11 Result of Observation Sheet in Cycle 2 ...121
Appendix 12. Lesson Plan ...122
Appendix 13. Surat Bimbingan Skripsi ...163
Appendix 14. Surat Permohonan Izin Penelitian ...165
Appendix 15. Surat Keterangan Telah Melakukan Penelitian ...166
1
identification of the problem, limitation and the formulation of the problem, objectives of the research and the significance of the study.
A. Background of the Problem
Since 1960 until now, teachinggrammar becomes the crucial issue
which invites some controversial in English teaching - learning process.1Whether it is being taught or not, it invites a controversy for students to be able to use communicative competence appropriately. According to Dykes, a grammar teaching is so important because if it is not taught, it will decrease the literacy of people.2 So that‟s why the role of teaching grammar should not be neglected. As Richards & Renandya also emphasized that grammar is more important than to be neglected and a language development of learner will be seriously constrained without a good knowledge of grammar.3 Also, Mart stated that grammar teaching is important because “it holds an important place in foreign language learning to make great contribution to language competence”.4
The demanding existence to communicate properly makes the CLT becomes important too. As Savignon stated that the central idea of Communicative Language Teaching is communicative competence, in term of expression, interpretation, and negotiation of meaning.5 It gives the challenge for the position of grammar teaching to adapt with the development of the process in teaching English. In order to make a
1
Barbara Dykes, Grammar for Everyone, (Victoria : ACER Pres, 2007), p.3. 2
Ibid.
3
Jack C Richards & Willy A Renandya, Methodology in Language Teaching : An Onthology of Current, (Cambridge : Cambridge University Press, 2002), p.145.
4
Cagri tugul Mart, Teaching Grammar in Context : Why and How?, Theory and Practice in Language Studies, vol 3,no.1,2013, pp. 124-129.
5
2
grammar class becomes more communicative and avoid a boredom, a grammar teaching- learning process should get a proper attention.
In the countries where English is EFL (English Foreign Language) such as Indonesia, the debates and discussions about whether we should teach grammar or not is still exist. Here, the writer agree with other experts who believe that we should teach grammar, such as Dykes, Richards & Renandya, and Mart. Teaching grammar should be taught because it can facilitate students to speak accurately, communicatively,
and to understand the language easily. To be able to communicate accurately and to understand the language properly, grammar is important to be learned6. The discussion for those who believe that grammar should be taught mainly focus on whether to teach grammar structure deductively or inductively7, whether to present grammar through communication or not, whether to teach grammar explicitly or implicitly8 and so on. Mostly, “traditional grammar teaching”9 (Grammar teaching which emphasizing the way to learn grammar through memorizing rules or pattern) has existed since a long time ago. However, it gives some problems such as, it might not fulfil the needs in contextuality and sometimes gives a confusion about how to communicate accurately.10
Traditional grammar teaching is often marked with prescriptive , which contains some rules for what is correct and incorrect in a language. So, people also have to follow the rules for usage 11. It makes the students get some difficulties to implement grammar in speaking because they just learn about the language. Students only learn the pattern and try to
6
Ron Cowan, The Teacher’s Grammar of English, (Cambridge : Cambridge University Press, 2008), p. 2.
7
Jack C Richards & Willy A Renandya, Methodology in Language Teaching : An Onthology of Current, (Cambridge : Cambridge University Press, 2002), p.145.
8
Yun, Xiao Yan, Interactive Grammar Teaching, Asian EFL Journal, vol 17.no. 3, 2012,
pp.34-37. 9
Ibid.
10
James E. Purpura, Assessing Grammar, (Cambridge University Press, 2004), p.21. 11
remember the dry memorization of rules without implementation, so it gives negative feelings like boredom and even fear of grammar.12
In Indonesia, grammar becomes one of the important parts in
In eleventhgrade‟s student based on the syllabus, students have to learn about some grammatical theories. They need to achieve the goals in comprehending those materials. They are expected to be able to use some structures such as tenses, active-passive, and also conditional sentence. The way to teach those materials are often explained through traditional grammar.
From those materials in grammar, conditional sentence also becomes one of the parts that is quite difficult for students. According to Covitt, he conducted a survey and found that conditionals ranked fifth (behind articles, prepositions, phrasal verbs, and verbals) among the most difficult teaching problems.14 The material about conditional sentences have some types and various meaning. Therefore, students often get some problems to understand it from the form, meaning, and also the time-tense relationship.15 The third type of conditional sentence is considered as the most complex type that gives the specific problems for students. Pyle also stated that the third type of conditional sentence is difficult to be
http://kemdikbud.go.id/main/?lang=id, syllabus for the eleventh grade, retrieved at 10/06/2016.
14
R.I, Covitt, “Some Problematic Grammar Areas For ESL Teachers”, (M.A Thesis in TESL UCLA : England, 1976), Unpublished.
4
sentence is contrary to the fact.16 For example, if the sentence of conditional sentence is positive, the meaning is actually negative, and so on.
There are some studies which have already emphasized for students who are using conditional sentence.Pratama17 has revealed that the second type of conditional sentence gave the further problems for students at SMA Dua Mei Ciputat. Students often make the mistakes in using conditional sentence type II because of the time-tense relationship
and also they got the difficulties to understand about the meaning of the sentence. In the second type of conditional sentence, the meaning of the sentence is contrary to the fact, so the students get the difficulties in understanding the meaning of the sentence. Not only him but also Aulia18 found some problems in conditional sentence for university students in Universitas Gadjah Mada, she explained that the problems are on each type of conditional sentence and also about the way to understand the meaning of each type. Both studies emphasize the problems in understanding the meaning of the sentence for each type of conditional sentence. Next, Yusuf19 also stated that conditional becomes one of the problem which appears in students‟ understanding about grammar, especially to differentiate the meaning of conditional sentence for each type.
Considering about this condition, hence, it is urgent to find the appropriate technique to improve the students‟ ability in conditional sentence. Based on some preliminary studies, conditional sentence becomes one of the most difficult parts for students. The paradigm about
16
Michael A.Pyle & Mary Ellen Munoz Page, TOEFL-Preparation Guide Test of English As A Foreign Language, (New Delhi : Wiley, 2002), p.115.
17 Muhammad Ridho Pratama, “Error analysis on the second grade students of senior high school in using type two of conditional sentences at SMA Dua Mei Ciputat”, Skripsi ofUIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, Jakarta, 2011, Unpublished.
18Hernita Ratna Aulia, “
Conditional Sentences in English and Their Problems for First Year Students of Faculty of Cultural Sciences, Universitas Gadjah Mada”, Skripsi of UGM, Yogyakarta, 2013, Unpublished.
monotonous grammar is still exist. Students feel bored and difficult to learn about conditional sentence, especially with the monotonous learning activities in a traditional grammar classroom. Consequently, this problem should be solved, because if there is no solution, students will get further problems in their learning process. The paradigm of traditional grammar must be changed with the new method that can improve students‟communicative competence. The learning process can be achieved through interactive technique.CLT sets the students tend to be
more active to be involved in a learning process. Also, the learning process will be beneficial if it provides fun and interesting activities. The alternative way that should be achieved is through interactive grammar.
Interactive grammar provides a various type of learning. According to Murcia, teaching technique should vary based on the match being emphasized.20 Hence, a various technique in interactive grammar can facilitate students to learn communicatively. By applying this technique in a classroom, it will be easier for students to comprehend the material and also it can make students become more active in learning grammar, especially in conditional sentence type III (past unreal).
There have been several researches conducted to use an interactive grammar for improving students‟ grammar mastery. Yan Xiao Yun has revealed that a traditional grammar teaching can be interesting, inspiring, and creative through an interactive grammar. In addition, Yahya Dkhissi 21 also proves that the system of formal grammar does not give the effective feedback. It means that a various way or technique should facilitate students in learning grammar. Another studies have been conducted by Md. Kawsar Uddin and Tazin Ahmed22 The study reveals that to
20
Marianne Celce-Murcia & Sharon Hilles. Techniques and Resources in Teaching Grammar, (New York : Oxford University Press ), p.11
21
Yahya Dkhssi, An Integrative Model of Grammar Teaching : From Academic to Communicative Needs, International Journal of Language & Linguistics, vol. 2 no. 3,2014. pp 145-153.
22
6
internalize grammar, it should be taught in inductive and contextual approaches interactively.
Therefore, in this study the writer will apply an interactive technique in conditional sentence type III. The writer chooses the technique of interactive because it provides interesting learning activities through various media(eclectic) and students will not only learn and remember about the rules or the pattern only, but also students can know about how to apply it in a contextual way.
The writer will use a classroom action research (CAR) for the design of the research. Classroom action research is suitable to solve the problem of the research, especially in a science 3 of SMAN 7 Kota Bekasi and interactive technique is also considered suitable because it can improve students‟ ability better. This design is also chosen in order to distinguish from the previous preliminary studies at the beginning.
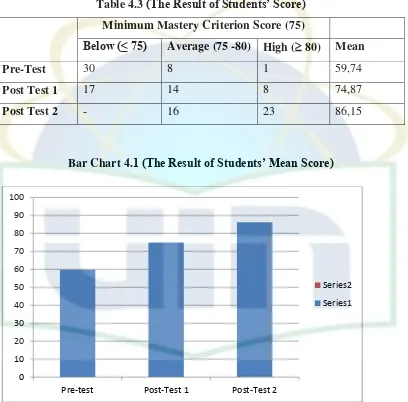
SMAN 7 BEKASI is also choosen becauseat the beginning, the researcher had conducted an interview and observation in that school. Based on those data, the result showed that students got some difficulties in understanding conditional sentence, especially in type III. It could be seen from the minimum mastery criterion (KKM) on that school. The minimum mastery criterion (KKM) on that school is 75, whereas there are many students who got below 75, especially in conditional sentence. It means that the students‟ understanding about conditional sentence was still low. So, the solution will be done in this school. The writer has already confirmed to the English teacher in SMAN 7 BEKASI to conduct a classroom action research in that school and he allowed the writer to do this research.
The writer is interested in conducting a classroom action research by using interactive technique with the title of “Improving Students’ Ability in Using Conditional Sentence Type III Through Interactive Technique in
B. Identification of the Problem
The problem which appears in this research are:
1) Students have some difficulties and confusion in learning about conditional sentence especially type III such as with the form, meaning, and also with the time-tense relationship.
2) The technique or learning style from the teacher in a grammar class does not motivate students to be active and does not fulfil the needs.
C. Limitation and the Formulation of Problem
In this study, the writer limits the problem only to see conditional sentence type III in the eleventh grade of SMAN 7 Bekasi through interactive technique.The formulation problem of this paper is:
1) Does interactive technique improve students‟ ability in using Conditional Sentence (Type III) ?
2) To what extent interactive technique can improve the students‟ ability in using conditional sentence type III at the eleventh grade of SMAN 7 Bekasi?
D. Objectives of the Research
The objectives of the research is to find the evidence whether Interactive technique can improve student‟s ability in using conditional sentence type III and also how significant it is and to see how interactive technique improve students‟ ability in using conditional sentence type (III) at the eleventh grade of SMAN 7 Bekasi.
E. The Significance of the Research
The writer hopes that the result of the research will be beneficial for : Students : The students can learn actively both in a theory and real
8
and monotonous. They can improve their ability into a skillful student and also active.
Teacher : By applying interactive grammar, teachers can explore the students‟ competence comunicatively. Then, also teacher can be more creative to design the learning activities. So, the teacher can also improve their ability in teaching.
9
of conditional sentence, the function of conditional sentence. This chapter will also present about the definition of interactive technique, interactive principles, strategies for interactive learning, stages of interactive technique,
and the previous of related studies.
A. Conditional Sentence
1. The Definition of Conditional Sentence
Conditional sentence or if clause is one of the materials in English grammar. Espino and Santamaria explain that a conditional is a declarative sentence which has two propostions by using the connective “if”. It has a main clause and a subordinate clause (if clause).1 Another expert, Cowan states that conditional sentence contains a proposition or condition and the result clause contains about what happens if the conditional is fulfilled.2
Celce - Murcia and Larsen - Freeman also conclude that a conditional is a complex sentence that consists of a main clause and a subordinate clause and begins with the adverbial subordinator if.3
Moreover, according to Cobuild, conditional clause is a subordinate clause that usually begin with “if”. The event described in the main clause depends on the condition described in the subordinate clause.4
Therefore, it can be summarized that conditional sentence is a sentence which contains two clauses, the if clause and the result of the clause if it is fulfilled. There are three different types of conditional
1
Orlando Espino & Carlos Santamaria, Initial Models in Conditionals : Evidence from Priming, The Spanish Journal of Psychology, vol.11. no.1, 2008, pp. 36 - 47.
2
Ron Cowan, The Teacher’s Grammar of English, (Cambridge : Cambridge University Press, 2008), p.449.
3
. Marianne Celce- Murcia & Diane Larsen-Freeman, The Grammar Book, (Newyork : Heinle, 1998 ), p.546.
4
10
relationship, factual conditional, future or predictive conditional, and imaginative conditional relationships. The explanation about the types of conditional will be discussed further.
2. Types of conditional sentences
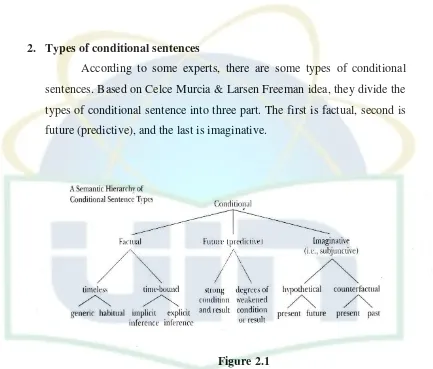
According to some experts, there are some types of conditional sentences. Based on Celce Murcia & Larsen Freeman idea, they divide the
types of conditional sentence into three part. The first is factual, second is future (predictive), and the last is imaginative.
Figure 2.1
A Semantic Hierarchy of Conditional Sentence Types Adapted From The Grammar Book5
Cowan is also agree with Celce-Murcia & Larsen-Freeman, he categorizes the similar type of conditional sentence.6 Those parts are also separated into smaller unit. Factual conditional contains of timeless and bound. In timeless, there are generic and habitual factual conditional sentence. A relationship of sentence which is true or based on the fact is
5
Marianne Celce- Murcia & Diane Larsen-Freeman, The Grammar Book, (Newyork : Heinle, 1998 ), p.548.
6
called generic factual conditional sentence. Whereas, habitual factual conditional sentence is not bounded with time, it is based on the repeated action which we often do regularly which is called habit.
The next part of factual time bound deals with implicit and explicit inference conditional sentence. Implicit conditional deals with indirect meaning and explicit with directed meaning. The other experts such as Plye defines a different term to give the label of the first conditional sentence into real conditions.7 The real condition indicates an action or
event which is possibly true and it is categorized into future time, habitual, and command. The future time predicts the event that will happen, whereas for habitual, it mainly focus on the repeated event or action which is routine, the last is command it actually asks someone to do something.
Another term of the first conditional sentence is also stated by Sofyan in his book of Kiat Sukses Lulus Ujian Bahasa Inggris, he defines the first conditional sentence as present real. It tells about an event that will happen today or in the future if the condition is fulfilled.8 However, in the book of Grammar for English Language Teachers, The first conditional sentence has the different term with previous experts. It is called as “first” or “future” conditional.9 In that book, Parrot also expands the first conditional into some various form, such as in imperative, present continuous, present perfect, and the use of “should” for emphasizing the formality.
The writer summarizes some similarities and differences of term for the first conditional sentence. The similarities between Celce Murcia and Pyle, define the same term of habitual. Next, the term of real
7
Michael A.Pyle & Mary Ellen Munoz Page, TOEFL-Preparation Guide Test of English As A Foreign Language, (New Delhi : Wiley, 2002), pp. 116 - 117.
8
Fahmi Sofyan, Kiat Sukses Lulus Ujian Bahasa Inggris, (Jakarta : Pustaka Tarbiyah Baru, 2008), p.50.
9
12 others do not mention about it. Third, Pyle and Parrot have the smaller part of first conditional sentence, it is command or imperative. Both experts mention that command or imperative is included in real conditions, on the
other hand the others do not explain about it.
Based on the semantic hierarchy of conditional from Celce -Marcia & Larsen - Freeman, the next category of conditional sentence is called as future (predictive). They divided into strong condition & result and the degrees of weakened condition of result. Strong condition & result express future plans and contingencies. Whereas, degrees of weakened condition of result express that the result clause is not always possibly strong, the prediction can be weak by substitute the word of “will” with “may or should”. According to the writer, this term is still similar with the others‟ expert thought about conditional sentence, but the position is still in the first conditional sentence or in present real.
The next semantic hierarcy from CelceMarcia and Larsen -freeman is called imaginative. According to them, imaginative conditional is the most problematic conditional than the others because of the tense used. The past tense refers to the present time and the past perfect tense refers to past time.12 In imaginative conditional, they divided into hypothetical (present - future) and counterfactual (present - past). Hypothetical conditionals express the speaker‟s belief about events to be
10
Martin Hewings, Advanced Grammar in Use, (Cambridge : Cambridge University Press, 2002), p. 198.
11 Mark Foley & Diane Hall, Advanced Learner’s Grammar : A Self
- Study Reference & Practice Book with Answers, (Harlow : Longman, 2003), p. 120.
12
unlikely yet possible. In contrast, counterfactual conditionals express impossible events or states.
Another expert such as Pyle states the second conditional sentence as unreal conditions. It shows that the events result will be not true. Hewings is also agree with Pyle‟s idea about the second conditional sentence, which is called as unreal conditionals, whereas present unreal is categorized by Sofyan as the second conditional sentence. According to him, the result event of present unreal will be contrary to the fact with
present condition. However, Foley & Hall define the second conditional sentence as the unlikely or improbable conditional. Another expert such as Parrot give the label of the second conditional as hypothetical or unreal conditional. It is used to speculate about something which is impossible or contrary to the fact. There are also some similarities and differences from the experts‟ thought about second conditional sentence. The similarities arise from Pyle and Hewings, they categorize it into unreal conditions. Second, Parrot defines the similar term with Celce-Murcia&Larsen Freeman about hypothetical conditional. However, the different term of second conditional sentence is mentioned by Folley & Hall as improbable conditional.
The last type of conditional sentence is categorized by Celce-Murcia & Larsen - Freeman as counterfactual conditionals. However, Sofyan indicates the third conditional sentence as past unreal. It means that the result event will be contrary to the fact with the past. All in all, the writer concludes that the type of conditional sentence are categorized into three. Present real - Present unreal - and Past unreal. Eventhough some experts use the different term of each types, they still have the same
meaning and intention.
14
a) Generic Factual Conditional Sentences
Generic factual conditional express relationship which is true or unchanging. The systematic form of this type is present tense, it also occurs in both clauses. For example :
If we heat the water, it boils. If it rains, the soil gets wet. If you heat ice, it melts.
If today is 17 August, Indonesia celebrates an Independence Day. If Jakarta is the capital of Indonesia, the central goverment is on it.
Those examples, show that a general truth is never changing so the form is always in simple present tense.
b) Habitual Factual Conditionals
Habitual Factual Conditional is not bounded in time. The relationship is based on the habit. Habit is a repeated action which we often do regularly.
For example :
If Zahra wakes up early, she comes on time to school. If Zafitri always studies hard, she gets a scholarship.
If the students often collect their work on time, they get a good
mark.
If Zulaika always eat carrots, her eyes is healthy.
If Hanif &Hanifah often do an exercise, they will be more healthy
and fresh.
The examples above show that the activity becomes the habit, so the form is still in present tense for both sentences (if clause - main clause).
c) Implicit and Explicit Inference Conditionals
time is not directly connected, meanwhile for the timebound. The time is connected, for example in the implicit and explicit inference.
Implicit inference use much wider range of tense and aspect markers, they also occurs with certain modal auxiliaries. For example :
If smog can be licked in Jakarta, it can be licked everywhere. If someone’s at the door, it must be Siska.
If we can reduce the pollution, we can get the fresh air everywhere.
The if clause indicates an event that is bounded in time, and the result
clause refers to an action that can be logically inferred.
Meanwhile, explicit inference means there is no strict parallelism of tense, aspect, or modal in both clauses. For example :
if that call is for me, it should be Zidan. If someone’s at the door, it must be Hanif.
If he has a luxury car, he must be rich.
An explicit inference is made on the result- clause, about some time-bound event , action or fact. The result clause also contains an inferential modal, using must or should.
d) Future Conditional Sentences (Strong Condition and Result)
This type of conditional sentence shows future plans or something that might possibly happen in the future, that usually „causing problems‟ or „making further arrangements necessary‟. For example :
If it rains, I’ll stay at home.
If you attend the class, you will get a further explanation about the
lesson for quiz.
If Zaskia borrows some books at the library, she will work until
16
e) Future Conditional Sentences (Degrees of Weakened Condition or Result)
The result of main clause is not sufficiently enough to warrant the use of will or be going to. Sometimes a weaker modal of prediction such as may or should can be used. For example :
If you finish your vegetables, I may buy you some ice creams.
From the example, the result clause is weaker than the use of „will‟. . The scale of prediction can be categorized as :
will, be going to = certain (strong result) should = probable
may = possible (stronger than might) might = possible (weaker than may).
f) Imaginative Conditional Sentences
There are two types of imaginative, there are hypothetical and counterfactuals conditional sentences. Hypothetical conditional express what the speaker‟s belief to be unlikely yet possible events. For example :
If I got a wedding invitation, I would go there. If my friend came, I would learn together with her
For the counterfactual, it refers to impossibilities events or states. For example :
If my grandfather had still been alive in 1993, he would have been
85 years old.
If she had studied English, she would have gotten a good carrier in
her job.
g) Present Real Conditional Sentence
circumstances in the main clause are met.13 The first type of conditional sentence is :
For example :
If a website is popular, people will talk about it. If it is winter, the weather will be cold.
If you mix yellow and blue, you will get green.
The other experts such as Leech & Svartvik give the label of this type as an open condition.14 It means that the truth or the falsehood of the sentence is unknown exactly. For instance, I will help him, if he needs it. From the example of the sentence, the meaning can be true or false depend on the context. That‟s why it is called as “open”.
h) Present Unreal Conditional Sentence
Unreal conditional expresses a situation that would take place if the circumtances expressed were in the past. The result of the action is also contrary to the fact. Blass et al conclude that this type of conditional describe imagined situations. The second type of conditional sentence :
For example :
If I had the time, I would go.
(The fact is : I don’t have the time so I will not go). If today were Sunday, they would go to the beach.
13
Michael A.Pyle & Mary Ellen Munoz Page, TOEFL-Preparation Guide Test of English As A Foreign Language, (New Delhi : Wiley, 2002), p.114.
14
Geoffrey Leech & Jan Svartvik, A Communicative Grammar of English, (America : Pearson, 2003), p.207.
If Clause (Simple Present Tense), Main Clause (Simple Future Tense)
18
(The fact is : Today is not Monday so they will not go to the
beach).
If I had alot of money, I would go around the world.
(The fact : I don’t have alot of money so I will not go around the world).
Hewings reports that in unreal conditionals, we can also use could/might.should (have) instead of would (have).15 For example, if I lived out of town, I could take up gardening. We also call it as
hypothetical. Hypothetical conditional express what the speaker perceives to be unlikely yet possible events or states in the if clause.
i) Past Unreal Conditional Sentence
The third conditional sentence also an action which happened in the past (past perfect). and it is also contrary to the fact. Blass et al define that past unreal conditionals express situations that were not true in the past. They describe something that was possible but did not happen. The third conditional sentence is :
For example :
If she had seen the movie, she would have told you.
(The fact is : she didn’t see the movie so she would not tell you). If you had come ontime, you would not have missed the train.
(The fact is : You didn’t come ontime, so you would miss the train).
If Zaskia had won the first prize, she would have bought a new
house.
(The fact is : Zaskia did nit win the first prize, so she would not buy
a new house).
15
Martin Hewings, Advanced Grammar in Use, (Cambridge : Cambridge University Press, 2002), p. 208.
According to Pyle, the third type of conditional sentence is difficult for foreign students to understand because the fact of the sentence is the opposite of the sentence which appears. When the conditional sentence is negative, the meaning is actually positive and so on. 16 This type is also called as counterfactual. Counterfactual conditionals refer to impossibilities with reference to the present or the past.
Dancygier and Sweetser state that the meaning of counterfactuality is not directly means as the form sentence mentioned, but it depends on the
contextuality and inference of the sentence.17
3. The Function of Conditional Sentences
Cobuild defines the use of conditional sentence into several points there are 18
To talk about a situation that sometimes exists or existed. For
example : If they lose weight during an illness, they soon regain it
afterwards.
To talk about a situation that you know doesn‟t exist. For example : If Indonesia had a winter, the weather would be different.
To talk about a situation when you do not know whether it exists or
not. For example : If she is right, it would be possible for the company to find an inovation.
To talk about a situation that may exist in the future.
For example : If I stay in Batam for several years, I will spend a
high cost for a life.
The other experts such as Foley and Hall define the function of
conditional sentence based on each type into some points below19 :
16
Michael A.Pyle & Mary Ellen Munoz Page, TOEFL-Preparation Guide Test of English As A Foreign Language, (New Delhi : Wiley, 2002), p.115.
17
Barbara Dancygier & Eve Sweetser, Mental Spaces in Grammar - Conditional Constructions, (Cambridge : Cambridge University Press,2005), p.71.
18
20
The first conditional sentence emphasizes about the possible future
events or situation and the results.
For example : If you work hard in examination, you will get the
best score.
The second conditional sentence describes about the improbable
future event or situation. The condition is unlikely to be fulfilled because the future event is unlikely to happen.
For example : If I were you, I would not reach my dream to be
true.
(The fact means : Iam not you, so I will reach my dream to be
true).
The third conditional sentence express the hypothetical in the past.
The event happen in the past, and the meaning is contrary to the fact.
For example : If Indonesia had had a winter, it could have been
snow everywhere.
(The fact is : Indonesia did not have a winter so it could not be
snow everywhere).
B. Interactive Technique
1) Definition of Interactive Technique
Interactive technique is one of the technique which is familiar in CLT (Communicative Language Teaching). Brown defines that interactive is collaborative exchange of thoughts, feelings, or ideas between to or more people and it gives a reciprocal effect on each other.20 According to Savignon, the central idea of Communicative Language Teaching is
communicative competence, in term of expression, interpretation, and
19 Mark Foley & Diane Hall, Advanced Learner’s Grammar : A Self
- Study Reference & Practice Book with Answers, (Harlow : Longman, 2003), pp. 121 - 123.
20
negotiation of meaning.21 Xiao Yan also states that communicative competence can be achieved through interactive classroom teaching.22 She also said that an eclectic approach can make the learning process becomes interactive. Brown also agree with her that communicative competence is actually deals with interactive.23 So, the way to create an interactive classroom teaching can be achieved through eclectic.
Another expert such as Brown, explains in his book of “Teaching by Principles” that eclectic approach includes some basic principles of learning and teaching which can be designed and evaluated for classroom lesson.24 It means that eclectic in English language teaching is a teaching-learning process where various media are used in a classroom. The variations of the learning can create an inspiring and motivating the students to learn communicatively.25 This is an alternative way to teach grammar actively, not only just for testable but also can stimulate students to be communicative. The students will have more involvement and responsibility for the learning process.26 The characteristic of interactive technique is the student can be motivated to use their knowledge and also in a contextual way . To use this technique is also needed lots of examples, so that patterns of the usage can be seen and the students will easily use it communicatively.27
The current era of Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) demands student to be able to speak communicatively and interactively. Considering to that era, interactive learning is needed.
21
Sandra J. Savignon, Interpreting Communicative Language Teaching-Contexts and Concerns in Teacher Education, (London : Yale University Press, 2002), p.1.
22
Yun, Xiao Yan, Interactive Grammar Teaching, Asian EFL Journal, vol 17.no. 3,
2012, pp.34-37. 23
H. Douglas Brown, Teaching by Principles, (Sanfransisco : Pearson, 2000), p.48. 24
22
2) Interactive Principles
There are 7 principles of interactive learning. All of those principles can be a beneficial guideline to create an interactive learning.
a. Automaticity
The first principle of interactive is automaticity. Automaticity means when we talk to each other, we don‟t need to think about the grammatical or rigid rules of language. Automaticity also creates the communication or interaction naturally. The
paramount thing in interaction is the message or the meaning. It becomes one of the important principle of interactive because if the interaction don‟t happen automatically, the atmosphere of interactive will not occur, because there is no reciprocal communication. For example, if we are accustomed with a language of our mother tongue, it has already become an
automaticity for us in delivering the speech. We don‟t need to think about the language when we want to interact with each other.
b. Intrinsic Motivation
Intrinsic motivation is a basic characteristic of a person which can create an enthusiasm for doing something. It becomes one of the important principle of interactive because when students can engage with each other in speech acts of fulfillment, it can give a satisfied feeling for students.So, they will try to appreciate their own competence by developing a system of self reward. It also can be beneficial for students‟ learning. When they have already implemented this principle, students
will practice and train to be better in every occasion. c. Strategic Invesment
how to say or write or interpret language, and to make repairs when communication pathways are blocked. The first nature of interaction is automaticity. It is related with this principle. When the interaction happens, the spontaneous of automaticity is needed, so the strategic invesment play a big role for production and comprehension of a language.
d. Risk - Taking
The next category of interactive principle is risk-taking. The
basic principle of interaction is spontaneous of automaticity. It means that interaction also requires the risk of failing to produce intended meaning, of failing to interpret intended meaning. So, being laughed, or rejected when the mistake of the interaction happen is not totally false. The essential thing is the nature of interactive communication.
e. The language - Culture Connection
The language of culture connection is always related with the interaction because every people is actually different. They come from the different region and also different mother tongue. It gives a cultural loading for the interactive speech. Therefore, someone who is involved in an interaction give a various cultural content.
f. Interlanguage
The next principle of interactive is interlanguage. The previous principle has already mentioned about the language - culture connection. It is still related to each other, because of the cultural content in communication, the complexity of
24
g. Communicative Competence
The last principle of interactive is communicative competence. It becomes one of the important thing in interaction because all of the elements of communicative competence are involved in human interaction. For example, based on grammatical, pragmatic, strategic, or meaning are become the part of
communicative. All aspects must work together to make an interactive situation.
3) Strategies for Interactive Learning
One of the best ways to develop an interactive learning is through creating the strategies of questions. There are several steps which can be achieved :
a. The questions should give the opportunity for the students to produce language comfortably.
b. The questions can serve to iniatiate a chain reaction of student interaction among themselves.
c. The questions should give the instructor immediate feedback about student comprehension. After that, the teacher can diagnose the linguistic or content difficulties from student‟s response.
d. The questions should also provide the opportunities to find out what they think by hearing what they say.
4) Stages of Interactive Technique
Xiao-Yun defines an interactive grammar as an eclectic approach. The way to create the interactive technique is through a various
media28. Firstly, Yun used some media such as pictures for comparing the prepositions (on, above, under, and over). She provided some
28
different pictures and after that give some trigger questions for the students for answering that questions by comparing the prepositions.
She also used different colors and fonts in reviewing tenses. The text was projected onto the screen and the students were asked to write three sentences of different tenses with the verbs that were given and check the sentences by doing a peer-correction.
Another media which was used by Yun was video clips. They were inserted in the power point slides in order to add a touch entertainment
and variety and also to encourage the students to notice the language form in watching movies. Those media were provided in order to encourage the students to actively participate in the interactive activities. 29
C. Teaching Conditional Sentence by Using Interactive Technique
The following are the stages to achieve interactive technique through various media, there are :
Preparing the media
In the first stages, preparing the media becomes the inital way that should be done. Eclectic means combining a various media which is useful and interesting. So, some attractive media should be prepaped such as references from bookflix and e-materials from the internet. The others media are text, tables, pictures, songs, and printed material.
Demonstrating the media
i. The first, through a text. The text is projected into the screen with the emphasis clearly and it is also illustrated in
different colors and fonts. The purpose of this step is to provide a lot of examples about conditional sentence. So, here the students will see the pattern and shape their own
29
26
thinking about the types of every conditional sentence. Students are also have to differentiate each type through the text. For example :
If it rains, she will go to the theatre.
If they came, they would discuss about the meeting.
If Zaskia had had alot of money, she would have gone around the world.
ii. Second, table is also used in controlled response exercises as well as communicative activities. In this step, the students will an answer and mention the type of conditional sentence in a table.
First Second Third
If she comes, I will go with her,
If she ... If she had come, I would have gone with her
If Zidan... If Zidan finished the duty ontime, he wouldnot be in rush.
If Zidan...
If it ... If it ... If it had rained, it would have been cold.
iii. The third is through pictures.
sentence of conditional sentence through a picture. When the picture is given, students have to complete the blank of the sentence based on their idea in the pictures. For example :
If it rains, ...
28
If Zidan..., He ... get...
The picture above also can motivate students to illustrate the condition event. For example the sentence can be : If Zidan had not learned hard, he would not have gotten won the science competition. (type 3)
The students can be asked to make their own conditional sentence in every type and also give the label so they can
differentiate each type, so they will also speak well in using conditional sentence.
The students will speak interactively to complete the sentences of conditional sentence through a picture.
iv. The next stages is through song.
In this step, the students will also practice in another skill area such as listening. So, the students will listen to the song which have some lyrics of conditional sentence. After they hear the song, the will complete the lyric of the song which have the blanks of conditional sentence. It can be a solution for the audio learner to learn about grammar, the learning process will be fun and interactive through a song.
v. The last is printed material.
Printed materials are often used in a learning process. These materials can be obtained through a textbook or e-material. It can contain about a piece of paper with examples.So, the
Here, the students will not only learn about the theory of grammar, but also they can feel a fun learning with an interactive grammar.
D. Previous Related Studies
There have been several researches conducted to use an interactive grammar for improving students‟ ability. The first is Yan Xiao-Yun30. She discusses about some techniques for teaching interactive grammar in a
traditional grammar classroom. Yan also believes that interactive grammar teaching can encourage active participation in communication through grammar class.
The researcher has conducted a 16-week experiment of interactive grammar teaching. The author used an eclectic approach for the traditional grammar class, the aids of this experiement are text, tables, pictures, video clips, objects, and printed materials. The first, the students get a treatment about the text which was projected onto the screen with emphasis the example of some sentences with different colors and fonts. Tables were also used in controlled response exercise. Third, pictures were used to assist interactive activities such as showing the prepostion. Next, video clips were inserted in power point slides to add a touch of entertainment. Fifth, objects were used to give students a deep impression of how adjectives are arranged in front of a noun. The last is printed material used as a handout. All of the aids proves that grammar can be interesting, inspiring, and be a creative and interactive activities for the traditional grammar classroom.31 Hence, the way to teach grammar will become meaningful and more active if interactive technique (inductive learrning) is
provided in the classroom. The researcher has revealed that inductive grammar is effective to make an interactive grammar teaching.
30
Yun, Xiao Yan, Interactive Grammar Teaching, Asian EFL Journal, vol 17.no. 3, 2012, pp.34-37.
31
30
Moreover, Yahya32 also discusses about a foregrounding subject in language teaching namely grammar teaching. With regard to the critical situation of grammar teaching in his English departments in Morocco, this research is based on the assumption that formal grammar teaching does not provide the expected output that the teaching-learning enterprise requires from both teachers and learners. Therefore, the aim of this study is to review the grammar teaching methods and find out the practical solutions for the following problems: lack of coordination and consistency of
methods, lack of communicative grammar text books, the difficulties in students‟ mastery of the English grammar even when students get plenty comprehensible input, and finally the teaching of grammar according to syllabus not students‟ needs. At the end finally the study proves that with a new model that engages students in a more practical, comprehensible and useful method of grammar teaching: the Exploration, Production and Integration Model.33 It states more clearly that the old fashioned of traditional grammar or the formal grammar is not effective. Exploration, Production, and Integration Model becomes a unity part that must be involved in a learning process, in order to achieve the interactive grammar teaching.
In addition Md. Kawsar Uddin & Tazin Ahmed34 also reveal that to internalize grammar, it essentially should be taught in inductive and contextual approaches. The experiment was conducted in Bangladesh which at the first time English is taught separately and deductively through rules memorization. This was an experiment that was conducted in summer 2012. At the beginning of the semester, a class of 30 students of the Department of English was asked for sit for a proficiency test. The result
showed that students were divided into 2 category based on their learning
style. Group A was conducted in a deductive grammar during the learning process. Whereas Group B, was applying an inductive grammar. The result showed that at the first time, Group A is higher but during the process, at the end of the semester Group B got a better score than Group A. So, not only given a treatment of experiment by providing inductive approach (rule discovery, learner-centered, self-directed and bottom up teaching). But , after that this study also conducted a short survey to measure the impact of inductive approach. The methodology includes field work and critical study
for data collection and data analysis. At the end it showed that inductive grammar improve the students‟ ability and also they feel more confident and active.
32 CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter presents and discusses about the description of the research method used in this study, including place and time of the
research, method and design of the research, researcher‟s role, instrument of the research, data collecting technique, data analysis technique,
trustworthiness, and criteria of the success.
A. Place and Time of the Research
The research was held in SMAN 7 Kota Bekasi.It is located in Jl. Lingkar Tata Kota No.107, Jatisampurna, Kota Bekasi. The research was conducted for a month started from September to October 2016.
B. The Method of the Research
The researcher employed aqualitative design of Classroom Action Research (CAR). The rationale to use this method was because, first there were some problems in a classroom especially about the understanding for students in english grammar (conditional sentence) and it needed to be solved. Second, the learning process should be achieved by the improvement of students ability.As Burns states that the central idea of action research is to intervene the problematic situation in order to bring changes or improvements.1 So, improving students‟ ability in grammar can be achieved through action research. Third, the teacher‟s ability in teaching about this subject need to be improved.
The writer implemented a combination of qualitative and quantitative design becausenot only a primary data of qualitative which was needed in this study, but also the numerical data of quantitative was important to support the data. Sometimes, the primary data of qualitative
1
was not enough to address or answer the research problem, so mixed method was also needed. The secondary data of quantitative was needed to extend, elaborate, or explain the primary data2. Gall is also agree that action research is not only deals with the collection of qualitative data but also it can include quantitative data.3 So, this study employed qualitative as the primary and quantitative as the secondary data. The writer conducted the research through interview, observation, questionnaire, and test which can measure the students‟ ability.
C. The Design of the Research
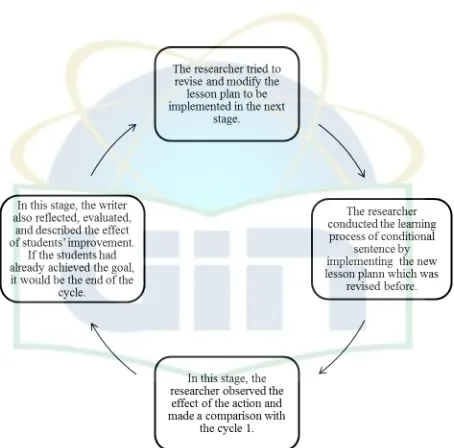
The researcher used the spiral model of action research proposed by Kemmis and McTaggart. The spiral of self-contained cycles of planning, acting, observing, and reflecting . The reason about choosing the spiral model appealing was because the steps are convenient and the process of each phase is not too rigid. The cycles done in two cycles.
Figure 3.1 Cyclical AR model
based on Kemmis and McTaggart4
2
John W. Creswell, Educational Research “Planning, Conducting, and Evaluating Quantitative amd Qualitative Reseacrh”, (United States : Pearson, 2011), p.535.
3
Meredith D. Gall. et al., Educational Research, (New York : Pearson Education, 2003), p.582.
4
34
Figure 3.2
The explanation about those cycles will be explained below :
Figure 3.3
36
D. Subject of the Research
The subject of this researchwas students at the eleventh grade in SMAN 7 Kota Bekasi, which consisted of 39 students.
E. The Role of the Writer in the Research
The role of the writer was not only as an observer but also as a teacher. It meant that the writer was involving, living in the context, and also being a part of it. As Kemmis & Mctaggart reported that participatory
research could create the condition for practitioners to understand and develop the ways of the research that was conducted by the researchers.5 The writer collaborated with the English teacher. The writer prepared the lesson plan, media of the teaching and also taught in the classroom. Whereas, the teacher worked together with the writer to observe the learning process in the classroom.
F. The Instruments of the Data
The data of this research was students‟ ability in using conditional sentence type III. In order to get the data, the researcher needed some instruments. The first instrument was pre-interview. It was conducted at the beginning of the study. The aim of pre-interview was to analyze and diagnose the initial problems about the teaching of conditional sentence. The type of the interview was semi-structured, and it was chosen because according to Arikunto6, some guideline of the interview questions couldbe used, but the researcher still could explore and develop that questions which were not stated on the list, in order to get the explanation in more details. The guideline interview‟s question contains of 10 questions on the
list.
Next, to obtain the data the researcher gave a pre-test and post-test. It contained of 30 questions of multiple choice for each test that was made
5
Stephen Kemmis, Robin Mctaggart & Rhonda Nixon, The Action Research Planner, (Singapore : Springer, 2014), p.5.
6
by the researcher. The reference was also adapted from “Kiat Sukses Lulus Ujian Bahasa Inggris”. Then, the questions were eliminated into 20
questions. Pre-test was given at the beginning of the study, in order to see about the initial problems in understanding conditional sentence and also see how far that the students have already understood. Post-test was given at the end of the study, in order to see the progress of the students in understanding the use of conditional sentence. Third, questionaire was also used in this study. It was conducted at the end of the study. The aim
was to get the data from the students‟ point of view. The last was observation (observation journal and observation sheet).. Observation was also conducted in order to get the data in real situation which happened during the learning process.
G. Procedures of Class Action Research 1. Planning
The researcher identified the problems in SMAN 7 Bekasi. After she interviewed the teacher, observed, and also gave pre-test for students, the writer designed a lesson plan to be implemented in the next step.
2. Acting
In this step, the researcher conducted the learning process of conditional sentence in the classroom by implementing the lesson plan which had already designed before.
3. Observing
After giving a treatment, the researcher observed the result from the action, the researcher also made an observation journal and
38
4. Reflecting
The researcher tried to reflect, evaluate, and describe the effect from the action before and also in this phase, the researcher would see the failure or progress from the students‟ improvement. The writer would go back to the next cycle if it did not yet fulfill the criteria, but if it had already achieved the goal, the researcher could stop the cycle.
H. Technique of Data Collection
Technique of collecting data in this research were using pre-interview, observation, questionnaire, pre-test and post-test. Pre-interview and pre-test were conducted at the beginning. Pre-interview conducted, in order to know about the problems of conditional sentence and pre-test to
see the students‟ ability in using conditional sentence type III before
implementing interactive technique. For the post-test, it was conducted at the end of the study in order to measure students‟ ability in using conditional sentence type III through interactive technique.
1) Pre - interview
The first instrument was interview. It was conducted at the beginning. The reason for choosing pre-interview was because it provided powerful evidence for presenting the data from the person resource directly. The writer interviewed the teacher to see what were the problems and about how the students dealt with those problems., together with the observation. The writer used semi-structured interview, it contained of 10 questions, but it could still be developed. The data that will be obtained in pre-interview is about the opinion or fact from about the problems
2) Observation
The writer observed the learning process and also the students in a classroom to see the condition directly, in order to know about the problems. The observation wasdone by using structural and open observation. Structural observation was done through observation sheets, in order to know about the three aspects that need to be observed. Whereas, for open observation was used through observation journal. The aim of observation journal was
to get the further information which was not provided in observation sheet. The observation was conducted both for the writer and also the teacher.
Table 3.1 Observation Journal
Cycle Meeting Date Activities Findings
I
I
II
III
3) Questionnaire
Questionnaire was conducted by the writer at end of the meeting
in order to know about students‟ opinion about the learning