FREQUENCY OF PEOPLE WITH LEFT-HANDED
PREFERENCE AND THEIR CREATIVITY IN BOGOR
WEST JAVA
WINATI NURHAYU
DEPARTEMEN BIOLOGI
FAKULTAS MATEMATIKA DAN ILMU PENGETAHUAN ALAM INSTITUT PERTANIAN BOGOR
PERNYATAAN MENGENAI SKRIPSI DAN
SUMBER INFORMASI SERTA PELIMPAHAN HAK CIPTA*
Dengan ini saya menyatakan bahwa skripsi berjudul Frequency of People with Left-handed Preference and Their Creativity in Bogor West Java adalah benar karya saya dengan arahan dari komisi pembimbing dan belum diajukan dalam bentuk apa pun kepada perguruan tinggi mana pun. Sumber informasi yang berasal atau dikutip dari karya yang diterbitkan maupun tidak diterbitkan dari penulis lain telah disebutkan dalam teks dan dicantumkan dalam Daftar Pustaka di bagian akhir skripsi ini.
Dengan ini saya melimpahkan hak cipta dari karya tulis saya kepada Institut Pertanian Bogor.
ABSTRACT
WINATI NURHAYU. Frequency of People with Left-handed Preference and Their Creativity in Bogor West Java. Supervised by KANTHI ARUM WIDAYATI and BAMBANG SURYOBROTO.
Individual human shows a preference for using one hand than the other hand. Handedness is influenced by genetic, developmental, and cultural factor. Approximately 10% of humans are left-handed. Most manual activities can be classified into precision and power grips. However, there is no research on the precision and power-grip task of people with left-handed preference. Some suggest that the structure of the brain of sinistral (left-handed) has a larger corpus callosum. It is predicted that the left-handed success reflects their superior divergent thinking. The subjects were 267 female students and 226 male students in Bogor, West Java. Age range of subjects was 6 until 21 years old. In determining left-handed preference, subjects were measured with Rife methods, precision grip, and power grip. In determining of creativity, subjects were measured with Adjective Check List. Male brains are exposed to substantially higher testosterone levels than female brains during prenatal development, so that a sex effect for handedness may be expected. Total frequency of left-handed was 7.3%. Percentage of creative right-handed both females and males was not different, while creative percentage of handed females was higher than left-handed males. The activities and environment impact for creativity is discussed. Keywords: bogor, creativity, handedness, left-handed
ABSTRAK
WINATI NURHAYU. Frekuensi Orang Kidal dan Kreativitasnya di Bogor Jawa Barat. Dibimbing oleh KANTHI ARUM WIDAYATI dan BAMBANG SURYOBROTO.
Setiap manusia lebih menyukai menggunakan salah satu tangan dari pada tangan lainnya. Kebiasaan penggunaan tangan ini dipengaruhi oleh faktor genetik, pertumbuhan dan perkembangan, dan faktor lingkungan. Kurang lebih 10% dari manusia berpreferensi kidal. Mayoritas aktivitas manual dapat diklasifikasikan menjadi ketelitian dan kekuatan tangan. Namun, masih belum ada penelitian mengenai ketelitian dan kekuatan tangan pada orang kidal. Beberapa peneliti menyimpulkan bahwa struktur otak orang kidal memiliki corpus callosum yang lebih besar. Maka dari itu, diprediksikan bahwa kesuksesan orang kidal mencerminkan cara berfikir divergen mereka yang superior. Subjek penelitian ini berjumlah 267 pelajar perempuan dan 226 pelajar laki-laki di Bogor, Jawa Barat. Rentang umur dari subjek yaitu dari umur 6 tahun sampai umur 21 tahun. Preferensi tangan responden diuji dengan metode Rife, uji ketelitian tangan, dan uji kekuatan tangan. Responden juga diukur kreativitasnya dengan daftar kata sifat. Otak laki-laki terpapar testosteron yang lebih tinggi daripada otak perempuan saat perkembangan janin, sehingga diduga ada efek jenis kelamin terhadap kebiasaan penggunaan tangan. Frekuensi total orang kidal 7.3%. Persentase kreativitas orang yang tidak kidal baik perempuan maupun laki-laki tidak berbeda, sedangkan
persentase kreativitas perempuan kidal lebih tinggi daripada laki-laki kidal. Dampak aktivitas dan lingkungan bagi kreativitas didiskusikan.
Kata kunci: bogor, penggunaan tangan, kidal, kreativitas
Skripsi
sebagai salah satu syarat untuk memperoleh gelar Sarjana Sains
pada
Departemen Biologi
FREQUENCY OF PEOPLE WITH LEFT-HANDED
PREFERENCE AND THEIR CREATIVITY IN BOGOR
WEST JAVA
WINATI NURHAYU
DEPARTEMEN BIOLOGI
FAKULTAS MATEMATIKA DAN ILMU PENGETAHUAN ALAM INSTITUT PERTANIAN BOGOR
BOGOR 2015
PRAKATA
Puji dan syukur penulis panjatkan kepada Allah SWT atas segala rahmat dan karunia-Nya sehingga karya ilmiah ini dapat diselesaikan. Skripsi ini disusun berdasarkan hasil penelitian yang berjudul Frequency of People with Left-handed Preference and Their Creativity in Bogor West Java yang dilaksanakan sejak Desember 2014 sampai Febuari 2015.
Terimakasih kepada Dr Kanthi Arum Widayati dan Dr Bambang Suryobroto sebagai dosen pembimbing atas bimbingan dan saran yang diberikan. Terimakasih kepada Kantor Kesatuan Bangsa dan Politik serta Dinas Pendidikan Kota Bogor yang telah memberikan izin pengambilan data. Terimakasih banyak kepada Papa, Mama, Roro, Bilal Ibnu Wahid, Kak Au, Dian, Citra, teman-teman Biologi 48, Jakarta Community 48, dan Zoo Corner family untuk bantuan dan dukungannya selama ini.
Semoga karya ilmiah ini bermanfaat.
DAFTAR ISI
DAFTAR TABEL xii
DAFTAR GAMBAR xii
DAFTAR LAMPIRAN xii
INTRODUCTION 1
Background 1
Aim 2
MATERIALS AND METHOD 2
Time and place 2
Subjects 2
Collecting Personal Data 2
Left-handed Preference 2
Determination of Creativity 4
RESULT 4
Frequency of left-handed people 4
Creativity 7
DISCUSSION 8
CONCLUSION 9
REFERENCES 9
APPENDIX 11
RIWAYAT HIDUP 15
DAFTAR TABEL
1 Percentages people of self-confessed about handedness in Bogor 4
2 Percentages people of handedness based on age 5
3 Percentage people of hand preference in unimanual activities 5 4 Percentage people of precision grip of left-handed 6
5 Percentage people of power grip of left-handed 6
6 Percentages people with creativity based on handedness and gender 8
DAFTAR GAMBAR
1 Tools for precisian grip measure 3
2 Precision grip measure 3
3 Power grip-D device 3
4 Power grip measure 3
5 Numbers of people with left-handed preference based on Rife method
total score in females and males 6
6 Numbers of left-handed people with creativity 7
7 Numbers of right-handed people with creativity 7
DAFTAR LAMPIRAN
1 Research questionnaire 11
2 Handedness questionnaire 12
3 Creativity determination 13
4 Positive and negative items on ACL 14
INTRODUCTION
Background
Individual human shows a preference for using one hand than the other hand (Llaurens et al. 2009). Handedness corresponds with cerebral asymmetry and right-handedness indicates a dominance of the left hemisphere for motor function (Scerri et al. 2011). Left-handedness is related with reductions or reversals of brain asymmetries. Approximately 10% of humans are left-handed (Fauri et al. 2005). A study in Padang, West Sumatra had found that left-handed frequency is 20% (Sari 2014).
Handedness is influenced by genetic, developmental, and cultural factor (Llaurens et al. 2009). So far, only two specific genes have been suggested as a candidates for handedness, such as LRRTM1 (Leucine-rich repeat transmembrane neuronal) and PCSK6 (Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 6). LRRTM1 is identified as the X-linked androgen receptor. PCSK6 is known as key role in regulating both the anteroposterior and left–right axes, so it become a highly attractive candidate gene for involvement in handedness (Scerri et al. 2011). Cerebral lateralization theory of Geschwind-Galaburda posits that high testosterone intrauterine levels promote the development of left-handedness, for left brain hemisphere maturation is delayed (Tran et al. 2014). Moreover, early brain insult may cause the individual to switch to the opposite hand for unimanual activities. Cultural factors could change hand preference in three ways. First, changing the hand used for some activities (e.g. writing, eating). Second, reducing the degree of hand preference, when weak pressure applies to all unimanual activity. Third, changing the overall preferred hand, when strong pressure applies to all unimanual activity (Llaurens et al. 2009).
Most manual activities can be classified into precision and power grips (Napier 1956). The precision grip is the manipulation of small objects with the flexor aspects of the finger and the opposing thumb. Many right hemisphere nodes are more active in the precision-grip task. It means that they are located in the hemisphere ipsilateral to the operating hand. The power grip is a palmar opposition grasp in which all fingers are flexed around the object, counter pressure being applied by the thumb lying more or less in the plane of the palm. The power-grip tasks are associated predominately with contralateral primary sensory and motor cortex (Ehrsson et al. 2000). However, there is no research on the precision- and power-grip task of people with left-handed preference.
2
individual utilizes this advantage in divergent thinking, which moves outward from conventional knowledge into unexplored association. It is predicted that the left-handed people success in this field reflects their superior divergent thinking (Coren 1995).
Aim
The aim of this study is to collect the data and to determine frequency of people with left-handed preference and their creativity in Indonesia, specifically in Bogor, West Java.
MATERIALS AND METHOD
Time and place
The research was held on December 2014 until February 2015 in Bogor, West Java. Sampling was conducted in six senior high schools and six junior high schools which are located in six different sub districts. Sampling was also conducted door to door visits to find elementary students. Data was analyzed at Biosystematics and Ecology of Animals, Department of Biology, Bogor Agricultural University.
Subjects
The subjects were 493 individuals consisted of 267 female students and 226 male students in Bogor, West Java. Age range of subjects was 6 until 21 years old. Subjects were elementary students, junior high school students, and senior high school students.
Collecting Personal Data
Respondents were asked personal information such as name, address, gender, and self-confessed about handedness (Appendix 1).
Left-handed Preference
3 hand is checked, -0.5 point is given each time either hand is checked, and 0 point is given each time right hand is checked.
Respondents were measured precision grip and power grip of either hand. The precision grip measure used tweezers, 6 pegs, and board with 21 holes (Figure 1). Respondents were asked to move the pegs with tweezers from the first hole to the next hole one by one until the pegs were moved to the last hole (Figure 2). This movement was done with one hand and was repeated 3 times. The value of precision grip is the summary of movement duration. The power grip measure used power grip-D device (Figure 3). Respondents were asked to grip the device lever as strong as they can four times with one hand (Figure 4). The value of power grip is an average of four times grip.
Figure 1 Tools for precisian grip measure
(A) Tweezers, (B) 6 pegs, and (C) board with 21 holes
Figure 2 Precision grip measure Respondents were asked to move the pegs with tweezers one by one
Figure 4 Power grip measure Respondents were asked to grip the device lever as strong as they can four times with one hand
(A) (B)
(C)
(A)
4
Determining the score of grip used estimation index which is from percentage either grip toward right grip. In scoring power grip, right grip average minus left grip average, then divide with right grip average. In scoring precision grip, left grip average minus right grip average, then divide with right grip average. Thus, the equation results three indexes. Negative index means the left hand is more powerful or more precise. Neutral index means the left hand and right hand are equal. Positive index means the right hand is more powerful or more precise.
Determination of Creativity
Determination of creativity used the Adjective Check List (Gough 1979). Respondents were given a questionnaire containing 30 adjectives and were asked to checklist adjectives that describe themselves (Appendix 3). In the Adjective Check List (ACL), there are 30 adjectives that consist of 18 positive items and 12 negative items (Appendix 4). In scoring Adjective Check List, 1 point is given each time one of 18 positive items is checked, and -1 point is given each time one of 12 negative items is checked. The theoretical range of scores is therefore -12 to +18. If respondents had score ≤ 3 they are categorized as not creative, while had score > 3 are categorized as creative (Gough 1979).
RESULT
Percentage of left-handed people
Percentages people of self-confessed about handedness are shown in Table 1. Total frequency of left-handed people was 7.3%. Frequency of left-handed females was 5.6% whereas frequency of left-handed males was 9.3%.
Table 1 Percentages people of self-confessed about handedness in Bogor
Handedness Female Male Total frequency of
handedness
Left-handed 5.6 %(15) 9.3%(21) 7.3%(36)
Right-handed 94.4%(252) 90.7%(205) 92.7%(457)
Total 100%(267) 100%(226) 100%(493)
( ): Number of respondents
5 Table 2 Percentages people of handedness based on age
Handedness Age (years)
6-10 11-15 16-21
Left-handed 4%(1) 8%(24) 6%(11)
Right-handed 96%(27) 92%(278) 94%(162)
Total 100%(28) 100%(302) 100%(173) females and males were almost equal for each activity.
Table 3 Percentage people of hand preference in unimanual activities
Task
marbles 4.5% 3.0% 92.5% 6.2% 2.7% 91.2%
Bowling or
scissors 4.9% 4.1% 91% 8.4% 3.5% 88.1%
6
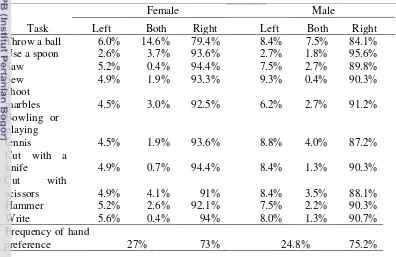
Figure 5 Numbers of people with left-handed preference based on Rife method total score in females and males
Percentages people of precision grip of left-handed are shown in Table 4. All of left-handed females had negative index which means their left hand was more precise. On the other hand, one left-handed male had positive scale which means their right hand was more precise. The other left-handed males had negative scale of precision grip.
Table 4 Percentage people of precision grip of left-handed
Scale of precision grip Female Male
Negative 100% 95.2%
Neutral 0% 0%
Positive 0% 4.8%
Total 100% 100%
Percentages people of power grip of left-handed are shown in Table 5. All of left-handed females had negative scale which means their left hand was more powerful. On the other hand, one left-handed male had neutral scale which means their left and right hand were same powerful. Six other left-handed males had positive scale which means their right hand was equal. The other left-handed males have negative scale of power grip.
Table 5 Percentage people of power grip of left-handed
Scale of power grip Female Male
Negative 100% 66,7%
Neutral 0% 4.8%
Positive 0% 28.6%
Total 100% 100%
Rife method total score Number of respondents
7 Creativity
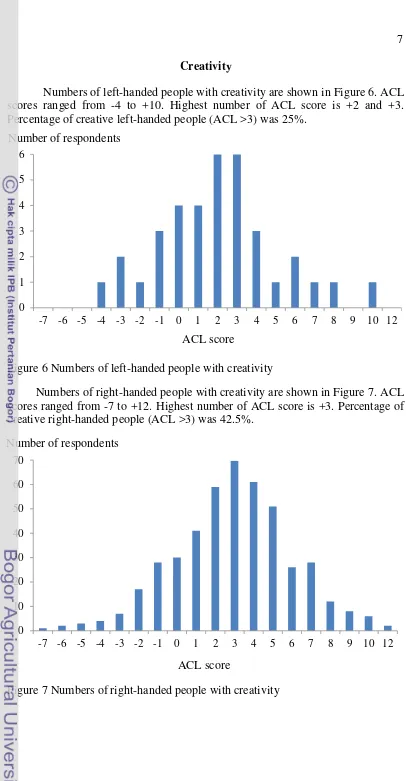
Numbers of left-handed people with creativity are shown in Figure 6. ACL scores ranged from -4 to +10. Highest number of ACL score is +2 and +3. Percentage of creative left-handed people (ACL >3) was 25%.
Figure 6 Numbers of left-handed people with creativity
Numbers of right-handed people with creativity are shown in Figure 7. ACL scores ranged from -7 to +12. Highest number of ACL score is +3. Percentage of creative right-handed people (ACL >3) was 42.5%.
Figure 7 Numbers of right-handed people with creativity
8
ACL scores ranged from -7 to +12. Percentages people with creativity based on handedness and gender are shown in Table 6. The creative left-handed females were 40% while creative left-handed males were 14.3%. The creative right-handed females were 40.1% and creative right-handed males were 45.4%. This result showed that percentage of creative females with left-handed preference was higher than males, while creativity in females and males with right-handed preference was not different.
Table 6 Percentages people with creativity based on handedness and gender
Female Total Male Total
Frequency of left-handed people in Bogor, West Java was 7.3%. Frequency of left-handed females was 5.6% while frequency of left-handed males was 9.3%. The result showed frequency of left-handed males is higher than females. Male brains are exposed to substantially higher testosterone levels than female brains during prenatal development. The cerebral lateralization theory of Geschwind-Galaburda (Tran et al. 2014) posits that high intrauterine levels of testosterone promote the development of left-handedness because of left brain hemisphere maturation is delayed, so that a sex effect for handedness may be expected (Tran et al. 2014).
Highest percentage of Rife method total score in females was -9, while in males was -9 and -8. Females were designated left-handed when they use left hand for 5 activities or more, while males use left hand for 2 activities or more. This result showed left-handed males were more adaptable to use right hand than left-handed females. Males are apt to have the greatest growth in the planum temporale or any other affected areas of the brain due to male fetuses are more likely to be exposed to the higher levels of testosterone. This means that any benefit derived from changes in the normal pattern of neurological development would be expected to be more visible in males than females (Coren 1995).
9 Left-handers live in a world above the usual challenges afforded to right-handed. These challenges require left-handers to make special adaptations in dealing with the environment that may foster creative behavior (Newland 1981). However, the result showed the right-handers were more creative than left-handers. Because of the respondents were the school students, their creativity still developing due to their activities at school. Many of right-handed students often did their hobby such as drawing, singing, dancing, or playing music instrument. These kinds of hobby may foster creativity (Fleith 2000). Creativity was a result of the interaction between person and environment. Classroom characteristics which inhibit creativity such as: the use of one right answer, no mistakes, ignored ideas, competition, evaluation, discipline, drill work, emphasis on curriculum, and lack of time (Fleith 2000). So it is predicted that classroom characteristic made creativity of students both left- and right-handed did not develop. The result of this research showed that percentage of creative females and males with right-handed preference is not different, while percentage of creative left-right-handed females is higher than of males. Perhaps females tend to elaborate more than males, which elaborate is one of creativity subscales (Newland 1981).
CONCLUSION
Frequency of left-handed males in Bogor, West Java was higher than females. The right-handers were more creative than left-handers. Percentage of creative right-handed both females and males was not different, while creative percentage of left-handed females was higher than left-handed males.
REFERENCES
Coren S. 1995. Differences in divergent thinking as a function of handedness and sex. TheAmerican Journal of Psychology 108(3): 311-325.
Ehrsson HH, Fagergren A, Jonsson T, Westling G, Johansson RS, Forssberg H. 2000. Cortical activity in precision- versus power-grip tasks: An fMRI study. J. Neurophysiol 83: 528-536.
Fleith DS. 2000. Teacher and student perception of creativity in the classroom environment. Roeper Review 22(3): 148-153.
Fauri C, Schiefenhὂvel W, le Bomin S, Billiard S, Raymond M. 2005. Variation in the frequency of left-handedness in traditional societies. Current Anthropology 46: 142-147.
Gough HG. 1979. A creative personality scale for the Adjective Check List. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 37(8): 1398-1405.
Llaurens V, Raymond M, Faurie C. 2009. Why are some people left-handed? An evolutionary perspective. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B. 364: 881-894.
10
Napier JR. 1956. The prehensile movements of the human hand. J. Bone Joint Surg. 38B: 902-913.
Newland GA. 1981. Differences between left- and right-handers on a measure of creativity. Perceptual and Motor Skills 53: 787-792.
Rife DC. 1940. Handedness, with special preference to twins. Genetics 25: 178-186.
Sari MD. 2014. Frequency of left-handed people and their creativity in Padang West Sumatra [skripsi]. Bogor (ID): Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Scerri TS, Brandler WM, Paracchini S, Morris AP, Ring SM, Richardson AJ, Talcott JB, SteinJ, Monaco AP. 2011. PCSK6 is associated with handedness in individuals with dyslexia. Human Molecular Genetics 20(3): 608-614.
11 Appendix 1 Research questionnaire
KUISIONER PENELITIAN
FNUM :
Data Pribadi Tanggal : Nama Lengkap : Jenis Kelamin : P / L Alamat : Hair Whorl :
No. Hand Phone : PRCS(1/2/3) :
Suku (Sunda) : PWR(KA/KI) :
Kidal : ya / tidak Tempat / Tanggal Lahir :
Usia :
Anak ke- : dari bersaudara Data Orang Tua
Nama Ayah : Nama ibu :
Asal : Asal :
Suku (Sunda) : Suku (Sunda) :
Nama Ayah dari Ayah : Nama Ayah dari Ibu :
Asal : Asal :
Suku (Sunda) : Suku (Sunda) :
Nama Ibu dari Ayah : Nama Ibu dari Ibu :
Asal : Asal :
Suku (Sunda) : Suku (Sunda) :
12
Appendix 2 Handedness questionnaire
Ceklis ( √ ) tangan mana yang nyaman dan biasa anda gunakan dalam melakukan kegiatan berikut :
No Kegiatan Tangan yang digunakan
Kiri Kanan
1 Melempar
2 Bermain bowling / tenis /
bulutangkis
3 Bermain kelereng
4 Memotong dengan pisau
5 Makan dengan sendok
6 Memalu
7 Menggerggaji
8 Menjahit
9 Menulis
13 Appendix 3 Creativity determination
Ceklis ( √ ) semua sifat dibawah ini yang anda anggap mendeskripsikan
diri anda.
___mampu ___jujur
___mudah terpengaruh ___cerdas
___pintar ___sopan
___berhati-hati ___ketertarikan luas
___yakin ___berdaya cipta
___egois ___asli, tidak mencontoh
___lumrah ___ketertarikan sempit
___suka bercanda ___berpikir panjang
___tradisional ___tulus
___tak-bergantung ke orang lain ___banyak akal ___biasa, menurut adat ___percaya diri
___tidak resmi ___sexy
___tidak berpuas-diri ___patuh
___berwawasan ___tinggi hati
14
Appendix 4 Positive and negative items on ACL
Positive Negative
mampu mudah terpengaruh
pintar berhati-hati
yakin lumrah
egois tradisional
suka bercanda biasa, menurut adat
tak-bergantung ke orang lain tidak berpuas-diri
tidak resmi jujur
berwawasan ketertarikan sempit
cerdas sopan
ketertarikan luas tulus
berdaya cipta patuh
asli, tidak mencontoh curiga
berpikir panjang banyak akal percaya diri seksi
tinggi hati
15
RIWAYAT HIDUP
Penulis lahir di Jakarta pada tanggal 24 Januari 1994 dari pasangan Drs Edwin Tirani dan Sabarniati Hambawani sebagai anak pertama dari dua bersaudara. Penulis menyelesaikan pendidikan di SMA Negeri 29 Jakarta pada tahun 2011 dan melanjutkan studi pada Jurusan Biologi, Fakultas Matematika dan Ilmu Pengetahuan Alam, Institut Pertanian Bogor melalui jalur Undangan SNMPTN.
Selama masa studi di IPB, penulis aktif di berbagai organisasi mahasiswa. Sejak tahun 2011, penulis aktif sebagai anggota di Organisasi Mahasiswa Daerah Jakarta. Penulis juga aktif sebagai anggota Gentra Kaheman pada periode 2011/2012. Penulis juga aktif sebagai anggota di Divisi PSDM (Pengembangan Sumber Daya Mahasiswa) Himpunan Mahasiswa Biologi (Himabio) IPB pada periode 2012/2013. Penulis juga aktif sebagai bendahara di Divisi Event Organizer Unit Kegiatan Mahasiswa (UKM) MAX!! pada periode 2012/2013. Penulis terlibat dalam beberapa kepanitiaan kegiatan kampus seperti Panitia MAX!! Corner, Erasmus Huis MAX!!, Grand Biodiversity, Masa Orientasi dan Informasi Biologi (MORFOLOGI) Angkatan 49, Kunjungan Industri Biologi, serta Pesta Sains Nasional 2012 dan 2013. Penulis pernah meraih penghargaan juara II lomba Aerobik di Olimpiade Mahasiswa IPB 2014 bersama Fakultas Matematika dan Ilmu Pengetahuan Alam. Penulis pernah menjadi pengisi acara di beberapa kegiatan kampus bersama Gentra Kaheman IPB.