MATERIAL SELECTION OF CAR’S TIRE BASED ON DESIGN
FOR SUSTAINABILITY APPROACH
MOHD FIRDAUS HANDY
B 050710014
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA
MATERIAL SELECTION OF CAR’S TIRES BASED ON DESIGN
FOR SUSTAINABILITY APPROACH
This report submitted in accordance with requirement of the Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka (UTeM) for the Bachelor Degree of Manufacturing Engineering
(Manufacturing Design) with Honours.
by
MOHAMMAD FIRDAUS BIN HANDY B 050710014
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA
BORANG PENGESAHAN STATUS LAPORAN PSM
TAJUK: Material Selection of Car’s Tires Based On Design for Sustainability Approach
SESI PENGAJIAN: 2010/11 Semester 2
Saya MOHD FIRDAUS BIN HANDY
mengaku membenarkan t esis (PSM/ Sarj ana/ Dokt or Falsaf ah) ini disimpan di Perpust akaan Universit i Teknikal Malaysia Melaka (UTeM) dengan syarat -syarat kegunaan sepert i berikut :
1. Tesis adalah hak milik Universit i Teknikal Malaysia Melaka dan penulis.
2. Perpust akaan Universit i Teknikal Malaysia Melaka dibenarkan membuat salinan
unt uk t uj uan pengaj ian sahaj a dengan izin penulis.
3. Perpust akaan dibenarkan membuat salinan t esis ini sebagai bahan pert ukaran
ant ara inst it usi pengaj ian t inggi.
4. *Sila t andakan (√)
SULIT
TERHAD
TIDAK TERHAD
(Mengandungi maklumat yang berdarj ah keselamat an at au kepent ingan Malaysia yang t ermakt ub di dalam AKTA RAHSIA RASMI 1972)
(Mengandungi maklumat TERHAD yang t elah dit ent ukan oleh organisasi/ badan di mana penyelidikan dij alankan)
TANDATANGAN PENULIS
DECLARATION
I hereby, declared this report entitled “Material Selection of Car’s Tire Based on Design for Sustainability Approach” is the results of my own research except as cited
in references.
APPROVAL
This report is submitted to the Faculty of Manufacturing Engineering of UTeM as a partial fulfilment of the requirement for the degree of Bachelor of Manufacturing Engineering (Manufacturing Design) with Honours. The member of the supervisory committee is as follow:
i
ABSTRACT
ii
ABSTRAK
iii
DEDICATION
iv
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
v
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Abstract i
Abstrak ii
Dedication iii
Acknowledgements iv
Table of Contents v
2.1 Design for Sustainability 7
2.1.1 Technology Sustainability 9
2.1.2 Environmental Sustaiabilty 10
2.1.3 Architectural Sustainability 10
vi
2.3 Life-Cycle Assessment 12
2.3.1 Goals and Purposes of LCA 14
2.3.2 Cradle-to-Grave 14
2.4 Sima-Pro Software 15
2.8.1 Effects of Under-Inflation 24
2.8.2 Effects of Over-Inflation 24
2.8.3 Effects of Time and Temperature 24
2.9 Tire Making Process 25
3.3.1 Literature Review Analysis 34
3.3.2 Questionnaire Analysis 35
vii
3.3.3 Sima-Pro Analysis 39
3.3.4 CES Edupack Analysis 40
3.4 Gathering Information 41
3.4.1 Online Article, Journal and Conference Pages 41
3.4.2 Reference Books 42
3.4.3 Video Presentation 42
3.5 Best Approach Practice 42
3.6 Discussion of Questionnaire 43
3.7 Conclusion 46
4. MATERIAL ANALYSIS
4.1 Introduction 47
4.2 DFS Principles 47
4.3 Conceptual Design 49
4.4 Current Design (Polyisoprene Rubber) 49
4.4.1 Ziegler-Natta Polymerization 51
4.4.2 Properties, Advantages & Disadvantages 52 4.5 1st Propose Design (Styrene-Butadiene rubber) 53 4.5.1 Properties, Advantages & Disadvantages 55 4.6 2nd Propose Design (Ethylene Propylene Rubber) 57 4.6.1 Properties, Advantages & Disadvantages 59
4.7 3rd Propose Design (Polyurethane) 60
viii
5. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
5.1 Sima-Pro Results 63
5.1.1 Impact Assessment Results 64
5.1.2 Total Material to Rescycle Result 69
5.2 CES Edupack Results 69
5.2.1 Detail Material’s Physical and Chemical Properties Result 70 5.2.2 Tensile Strength and Density Result 79
5.2.3 Price and Tensile Strength Result 80
5.2.4 Combustion Carbon Dioxide and Tensile Result 81
5.3 Discussion 82
5.3.1 Impact Assessment Analysis 82
5.3.2 Detail Material Properties Analysis 84 5.3.3 Graph Tensile Strength versus Density Analysis 85 5.3.4 Graph Price versus Tensile Strength Analysis 85 5.3.5 Graph Combustion CO2 versus Tensile Strength Analysis 86
5.3.6 Material Decided 87
6. DISCUSSION
6.3 Discussion 89
ix
LIST OF TABLES
3.1 Flow chart of PSM 1 & PSM 2 32
3.2 The three levels of the materials and processes database 41
5.1 Table and graph of comparison of impact assessment every material 68
5.2 Table of detail material’s properties 78
x
LIST OF FIGURES
1.1 Three circle of sustainability 2
1.2 Tire-wear-pattern and its cause 5
2.1 The stages of a process from-cradle-to-grave 13
2.2 Example of CES Edupack Analysis 16
2.3 Tire and its symbol 18
2.4 Instruction of tire symbol 19
2.5 Load Index 21 3.3 Percentage of respondent that know how the tyre making process 37 3.4 Percentage of respondents that agreed to improve tire’s sustainability 38
4.1 Polyisoprene rubber chemical bonding 50
4.2 Hevea tree and its latex 50
4.3 Example product by isoprene rubber 51
4.4 Isoprene chemical bonding by Ziegler-Natta 51
4.5 Styrene-Butadiene rubber chemical bonding 54
4.6 Example product by styrene-butadiene rubber 55
xi
4.8 Example product by ethylene propylene rubber 58
4.9 Polyurethane rubber chemical bonding 60
5.1 Polyisoprene’s graph of damage assessment 64
5.2 Styrene-butadiene’s graph of damage assessment 65 5.3 Ethylene propylene’s graph of damage assessment 66
5.4 Polyurethane’s graph of damage assessment 67
5.5 Polyisoprene properties 70
5.6 Styrene-butadiene properties 72
5.7 Ethylene propylene properties 74
5.8 Polyurethane properties 76
5.9 Graph tensile strength vs density 79
5.10 Graph price vs tensile strength 80
xii
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
DFE - Design for Environment DFS - Design for Sustainability
EIA - Environment Impact Assessment SEA - Strategic Environment Assessment LCA - Life Cycle Assessment
LCC - Life Cycle Costing IE - Industrial Engineering
VE - Value Engineering
MAUT - Multi Attribute Utility Theory EPD - Environment Product Declarations CES - Cambridge Educational Selecter TBM - Tire Building Machine
PSM - Projek Sarjana Muda
IR - Polyisoprene Rubber
1
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
This first chapter discussed about the introduction of design for sustainability (DFS) principles and approaches for new improvement on the car tires. In this part, the briefing of the background, problem statement, objectives, scope, and the expected of the study are discussed.
1.1 Introduction
Design for Sustainability (DFS) is the process of designing goods and services that takes into account all the dimensions of sustainable development and particularly environment, economic and social factors. Design for Sustainable is also much related to Design for Environment (DFE) which means the systematic consideration during design, of issues associated with environment safety and health over the product life cycle. Both of these design takes many product development aspects:
(a) Material selection (b) Energy use
(c) Extended component life cycle (d) Disassembly
(e) Reuse (f) Recycling
2
Sustainability is commonly defined as capable of being maintained at a steady level without exhausting natural resources or causing ecological damage. When considering the sustainability of any design, it must consider all elements of the product’s production, lifecycle and system in which it operates in order to properly understand the entire impact upon resources of the product. It is only when we understand the impact of the product that we can begin to even think about tackling and reducing this impact to improve the sustainability of the product.
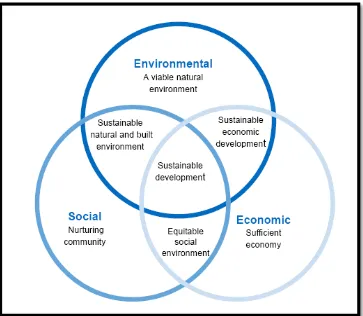
Sustainability is also means the capacity to endure. For humans it is the potential for long-term maintenance of well being, which in turn depends on the well being of the natural world and the responsible use of natural resources. Sustainability contains three elements which are economy, society and environment. Sustainable design also known as philosophy of designing physical objects, the built environment, and services to comply with the principles of economic, social, and environment sustainability.
Figure 1.1: Three circle of sustainability
3
There are four Designs for Sustainability principles, which are;
(a) Low-impact materials: choose non-toxic, sustainably produced or recycled materials which require little energy to process.
(b) Energy efficiency: use manufacturing processes and produce products which require less energy.
(c) Quality and durability: longer-lasting and better-functioning products will have to be replaced less frequently, reducing the impacts of producing replacements.
(d) Design for reuse and recycling: Products, processes, and systems should be designed for performance in a commercial 'afterlife'.
A set of sustainability principles for engineers was then developed, based on the long term viability of the planet, intra- and inter-generational equity, and a holistic view for projects and engineering practice, integrating environmental, social, and economic issues. Practical tasks and requirements for engineers, including a checklist were then drawn up to provide further direction to practicing engineers. (Boyle and Coates, 2005)
4
1.2 Problem Statement
Nowadays, the automotive industry has already known as a very competitive industry. But, automotive industry has been related to environmental issues such as air pollution, water pollution and sound pollution. Furthermore, tires and wheels are one of the most critical parts of any road vehicle. Their quality will dictate speed, road handling, fuel economy and road safety. Critically, their standard will have a significant effect on stopping distance in an emergency.
The most problem that the users always had is about tread damage before its due date. For example, tires that are under inflated or over inflated can affect tread damage and also effect tire life, driving comfort, traction and braking. Under inflation generates excessive flexing of the tire casing, which results in overheating, increase of rolling resistance and premature wear. In short word, under inflation can cause tire damage at tread. Likewise, over inflation can reduce tire life, reduce grip and create irregular wear. As we know, road hazards like potholes, glass and rocks are usually unavoidable. However, there are three most problem that we always had, incorrect inflation pressure, speeding and overloading.
Driving at high speeds has a greater chance of causing tire damage than at low speeds. If contact is made with a road hazard, it has a greater chance of causing tire damage. Driving at speed will cause the tire a greater build up of heat, which can cause tire damage. It can also contribute to a sudden tire destruction and rapid air loss if the tires are not properly maintained. If a tire experiences sudden air loss, it can lead to an accident to us.
5
Figure 1.2: Tire-wear- pattern and its cause (Screenshot from google.com)
1.3 Objectives
The main purpose of this project is to research and analyze the sustainability of tires that able to give an improvement on tire’s quality and user safety. The objectives of this study are:
(a) Identify and study what the problem that always happened. (b) Analyze the existing car tires and its making process.
(c) Study and do a research about the detail properties of other rubber and the existing rubber in tires.
(d) Analyze the material selection of car’s tire using Design for Sustainability (DFS) approach and techniques.
1.4 Scope
6
(a) The investigation base on literature study from many sources.
(b) Analyze the conceptual new designs that fulfill the engineering of Design for Environment specification.
(c) The current tires must be analyzed to improve the sustainability based on Design for Sustainability and Green Technology.