A Skripsi
Submitted to the Faculty of Language Education as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan
Putri Dian Lestari 20120540030
English Education Department Faculty of Language Education Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta
Supervising Teachers’ Perceptions on Pedagogical Competence of English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah
Yogyakarta’s Student-Teachers in an Internship Program
A Skripsi
Submitted to the Faculty of Language Education as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan
Putri Dian Lestari 20120540030
English Education Department Faculty of Language Education Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta
Statement of Authenticity
I hereby certify that this skripsi is definitely my original work. I am completely responsible for the content of this skripsi. Any theories, findings and research techniques which are not are my own quoted or cited in accordance with the standard referencing practices. Theoretical contribution and findings in this skripsi are truly my original word and have not been submitted for any degrees in other University or Institution.
Yogyakarta, December 28th,2016 The researcher,
Acknowledgement
First of all, I would like to thank to ALLAH Subhanahu wata’ala who
always give me a mercy, blessing, strength, health, and a chance to finish my skripsi writing.
I dedicate this skripsi to my beloved family, especially for my beloved parents, Ibu Suparmi and Bapak Mukiyono who are always loving me and
supporting me to finish my study. I love you so much and thank you for your love and for everything you gave to me. I also place my thanks to my beloved sister, Desy Dwi Lestari, my grandfather, my grandmother and all my big family members who always supporting me. Thank you very much. May Allah always give us His blessing in this world and in the hereafter on paradise. Aamiin.
A special gratitude is also for my great supervisor, Fitria Rahmawati, S.Pd, M.Hum for supporting, guiding and helping me in finishing this skripsi writing. Thank you very much for your patience Mam. I also thank to my second
supervisor, Miss Evi and my examiner, Miss Jeckie for all valuable suggestion and feedback toward my research.
Sincerely, I also place my thanks to my dearest friends, Leha, Nisa, Amel, Harni, Yuli, Nia, Erlin, Lia, Anisa, Kiki and Mba Ina. Thanks for your time, experience and your support. You all are very kind guys. I also do not forget to thank for my beloved friends of EED of UMY Class A 2012. Thanks for the experience we have during the last four years. I love you all and see you on top guys.
Table of Contents
Cover ... i
Approval Page ... ii
Statement of Authenticity ... iii
Acknowledgement... iv
Abstract ... vi
Table of Contents ... viii
List of Table ... xii
List of Figure ... xiii
List of Appendices ... xiv
Chapter One ... 1
Introduction ... 1
Background of the Study ... 1
Statement of the Problem ... 6
Limitation of the Problem ... 7
Research Question ... 8
Objective of the Study ... 8
Chapter Two ... 10
Literature Review ... 10
Pedagogical Competence ... 10
Definition of pedagogical competence ... 10
Aspects of pedagogical competence ... 13
Internship Program ... 16
Definition of internship program ... 18
Significances of internship program ... 19
Problems in internship program ... 22
EED of UMY’s internship program ... 24
Supervising teachers ... 24
Roles of supervising teachers ... 25
Review of related studies ... 27
Conceptual framework ... 30
Chapter Three ... 32
Methodology ... 32
Research Design ... 32
Setting and Participants ... 34
Data Collection Method ... 35
Chapter Four ... 37
Findings and Discussion ... 37
Supervising teachers’ perceptions on EED of UMY’s student-teachers’
competence in understanding characteristic of students ... 37
Supervising teachers’ perceptions on EED of UMY’s student-teachers’
competence in mastering teaching theories and principles ... 41
Supervising teachers’ perceptions on EED of UMY’s student-teachers’
competence in developing lesson plan ... 43
Supervising teachers’ perceptions on EED of UMY’s student-teachers’
competence in conducting teaching activity, ... 45
Supervising teachers’ perceptions on EED of UMY’s student-teachers’
competence in using technology ... 48
Supervising teachers’ perceptions on EED of UMY’s student-teachers’
ocmpetence in facilitating students to actualize students’ potential ... 49
Supervising teachers’ perceptions on EED of UMY’s student-teachers’
competence in communicating to students ... 52
Supervising teachers’ perceptions on EED of UMY’s student-teachers’
competence in conducting assessment and evaluation ... 54
Supervising teachers’ perceptions on EED of UMY’s
Supervising teachers’ perceptions on EED of UMY’s student-teachers’
competence in doing teaching reflection ... 58
Chapter Five ... 61
Conclusion and Recommendation... 61
Conclusion ... 61
Recommendation ... 63
References ... 66
List of Table
List of Figures
Figure 2.1 Kolb’s Learning Cycle ... 12
Figure 2.2 Student-teachers’ problems in practicum program ... 21
Figure 2. 3 The implementation of EED of UMY’s internship program ... 24
List of Appendices
Abstract
Pedagogical competence is important to be mastered by teachers, besides personal competence, social competence and professional competence. As a teacher educational institution, English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta (EED of UMY) facilitates their student-teachers to master this competence by conducting an internship program. This study aims to reveal supervising-teachers’ perceptions on EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ pedagogical competence in an internship program. The perceptions cover ten aspects of pedagogical competence, those are understanding characteristic of students, mastering teaching theories and principle, developing lesson plan, conducting teaching activity, using technology, facilitating students to actualize students’ potential, communicating to students, conducting assessment and
evaluation, utilizing the assessment and evaluation result, and doing teaching reflection.
This study used qualitative research design and specifically employed case study research. The researcher involved five supervising teachers from five senior high schools as participants. Purposive sampling was used by the researcher to choose the participants. The researcher used in-depth interview to gather the data and used member checking to validate the data. In analizing the data, the
researcher used open coding, axial coding and selective coding.
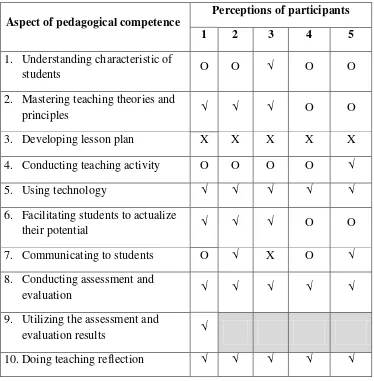
internship program. From the ten aspects of pedagogical competence, the perceptions indicated that EED of UMY’s student-teachers were competent in
three aspects of pedagogical competence. Those are in using technology, conducting assessment and evaluation, and doing teaching reflection. All
supervising teachers had good perceptions on those three pedagogical aspects. In understanding characteristic of students, mastering teaching theories and
principles, developing lesson plan, conducting teaching activity, facilitating students to actualize their potential, and communicating to students, supervising teachers had different perceptions. Some of them argued that EED of UMY’s student-teachers had good competence, the others perceptions indicated that EED of UMY’s student-teachers had less competence. Then, in utilizing the assessment
and evaluation result, one supervising teacher had good perception on the EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ competence. The others had no perception because EED of UMY’s student-teachers not conduct this activity.
Chapter One Introduction
Chapter One provides general information about this study. Those are the background of this study, statement of the problem, limitation of the problem, the research question, the objective of the study and the significance of this study. The background of this study discusses the reason of the researcher why choose the topic on pedagogical competence. Then, statement of the problem and limitation of the problem discuss the focus of problems. Research question presents the question that will be answered by this study. The aim of this study is presented in the objective of the study. Lastly, the benefits of this study are explained in the significance of this study.
Background of the Study
Teachers are very important in education. Chen and Ragatz (2010) argued that the most significant factor in improving the quality of education is the quality of teachers. It is because the teachers’ knowledge and all things they do has a big
teachers’ attitudes and actions can directly influence students’ achievements and
the success of education.
However, becoming a teacher is not easy. McKenzie and Santiago (2005) in Kuswandono (2013) argued, “Teaching is a complex task, and there is not a
single set of teacher attributes and behaviors that is universally effective for all types of students and learning environments” (p. 23). It is because classroom is
filled with students whose learning styles, needs, strengths, and abilities differ (Stronge, Tucker and Hindman, 2004). Moreover, Azeem (2011) said, “Teaching
is an exciting and rewarding activity but like other professions, it is demanding. It requires that its practitioners clearly understand what should be done to bring about the most desirable learning in the pupil and be highly proficient in the skills necessary to carry out these tasks” (p.1). Therefore, teachers need several
requirements and competencies to support them getting success in their job. In Indonesia, regulations about teacher are set in Undang-undang Republik Indonesia Nomor 14 tahun 2005 tentang Guru dan Dosen (Law of Republic Indonesia Number 14 of 2005 on Teachers and Lecturers). This law is arranged to direct teachers and lecturers in achieving the Indonesian national education goal, which is developing students’ potential to be a faithful, healthy, skillful, creative,
independent, democratic and responsive person. The law stated, “Guru wajib memiliki kualifikasi akademik, kompetensi, sertifikat pendidik, sehat jasmani dan rohani, serta memiliki kemampuan untuk mewujudkan tujuan pendidikan
nasional” (Pasal 8 Bab IV). The academic qualification mentioned in Article 8
teachers’ competences are mentioned in Article 10, those are pedagogical
competence, personal competence, social competence and professional competence that acquired from teacher profession education.
Government of Indonesia defined those four teachers’ competences in the
explanation and attachment of Article 10 Verse 1 of Law of Republic Indonesia Number 14 of 2005 on Teacher and Lecturer. The law defines pedagogical competence as an ability of teachers to manage the students’ learning. Personal competence is the ability of teachers to have steady personality, good character and wisdom, so they can be a role model of their students. Professional
competence is the ability of teachers to master the lesson subject widely and deeply. Last, social competence is the ability of teachers to communicate and interact effectively and efficiently with students, other teachers, parents and the surrounding community.
As an educational institution, English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta (EED of UMY) facilitates student-teachers to get an academic qualification and build the competencies. It will be very useful for student-teachers to join a teacher certification program after graduate from this bachelor degree level. To meet all of the competencies, besides giving teaching and learning theories in the classroom, EED of UMY also
Internship program gives some benefits for student-teachers. As stated in the Internship Program Handbook, EED of UMY’s internship program aims to
build student-teachers’ competencies, trains the skill of student-teachers in teaching at real school situation and gives real experience related to the teachers’ duty. Kuswandono (2013) said that internship program in school-based settings is important to develop student-teachers’ professional skill before they enter the real world of teaching. Furthermore, Richards and Crookes (1998) as cited in Riesky (2013) also states:
“By following this kind of activity, student-teachers will have a chance to
experience many valuable things, such as getting practical classroom experience, putting theories into practices, gaining insight from observing experienced teachers, improving lesson planning ability, improving ability in designing and developing materials, sharpening their teaching ability,
strengthening their understanding of teaching in terms of theory and practice, and improving decision-making ability in teaching by looking and exploring into themselves and other’s teaching practices.” (p. 251)
matters. Those are school placement, resources, learners discipline, classroom environment, also supervision and support. It means, there are a lot of things in school that could potentially cause problems for student-teachers during the internship program.
Based on the researcher personal experience and observation, EED of UMY’s student-teachers also faced those problems during the internship program
and the most problems are related with pedagogy. They faced pedagogical problems in all phases of teaching, including pre-teaching, whilst teaching and after teaching. In the pre-teaching, EED of UMY’s student-teachers were difficult to deal with and understand the curriculum also in preparing the appropriate material. In while teaching, they were difficult in delivering material. For the post-teaching, EED of UMY’s student teachers also hard in evaluating the teaching-learning process.
To help student-teachers face problems during the internship program, EED of UMY’s student-teachers are helped by supervising teachers. Those
supervising teachers are experienced English teachers from partner schools who have a main task to guide and help student-teachers in solving problems related to their duty in the school. Cohen, Manion, Morrison and Wyse (2010) mentioned that:
“Supervising teachers have responsibility for advising student-teachers how
advising student-teachers on class management and the planning of curricula and assessment.” (p. 27).
In addition, Norris, Larke and Briers (1990) also said that supervising teacher is the most important ingredient in the student teaching experience beside the student teaching center and it influences the development of student-teachers. Hence, supervising teachers is strictly important in internship program.
From the explanation above, the researcher is interested to conduct a study related with EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ pedagogical competence. The researcher wants to know the pedagogical competence of EED of UMY’s student -teachers’ from supervising -teachers’ perspective. The close relation between
student-teachers and supervising teachers in internship program makes the supervising teachers know more about their student-teachers’ competence
compared to school principle or students’ parents. This study may present results that can reflect the EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ pedagogical competence and
will benefit to improve the quality of EED of UMY especially in the internship program.
Statement of the Problem
As teacher candidates, EED of UMY’s students-teachers should master all teachers’ competences required by the law: pedagogical competence, personal
competence, professional competence, and social competence. In the internship program, EED of UMY’s student-teachers faced problems related to their
to manage the classroom. EED of UMY’s student-teachers feel hesitant about
their pedagogical competence. Therefore, the researcher interested to conduct a study on EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ pedagogical competence in the internship program by revealing supervising teachers’ perceptions. Moreover, a
study about supervising teachers perceptions on EED of UMY’s student-teachers’
pedagogical competence has never been conducted at EED of UMY.
Limitation of the Problem
EED of UMY’s internship program is held along with some partner
schools in Yogyakarta. To make this study more focused, it is emphasized on the perception of supervising teachers in senior high schools (SMA) level. For the pedagogical competence, it refers to Lampiran Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan Nasional Nomor 16 Tahun 2007 tentang Standar Kualifikasi Akademik dan Kompetensi Guru (Attachment of Rules and Regulation of Education Ministry Number 16 of 2007 about Teachers’ Standard Qualification and Competencies).
The law states that Indonesian teachers are considered to master the ten aspects of pedagogical competence: understand characteristic of students, master teaching theories and principles, develop lesson plan, conduct teaching activity, use technology, facilitate students to actualize students’ potential, communicate to
Research Question
The research question being investigated in this study is:
“What are supervising teachers’ perceptions on pedagogical competence of
English Education Department of Universitas Muhamadiyah Yogyakarta’s
student-teachers in an internship program?”
Objectives of the Study
The research aims to identify supervising teachers’ perceptions on
pedagogical competence of English Education Department of Universitas Muhamadiyah Yogyakarta’s student-teachers in the internship program. The perceptions cover ten aspects of pedagogical competence. Those are
understanding characteristic of students, mastering teaching theories and
principle, developing lesson plan, conducting teaching activity, using technology, facilitating students to actualize students’ potential, communicating to students,
conducting assessment and evaluation, utilizing the assessment and evaluation result, and doing teaching reflection.
Significance of the Study
This study would be useful for the researcher, the student-teachers, the institution (EED of UMY), the partner schools and supervising teachers, and other researchers.
indirectly gives a reflection about the researcher’ pedagogical competence as a
student-teacher who participated in the internship program. Last, this study motivates the researcher as a student-teacher to be better in the pedagogical mastery and implementation.
The student-teachers. This study deliberates the information related to the EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ pedagogical competence that may give
direct good involvement for them. This study can aid the student-teachers to know their strength and weakness in pedagogical mastery. Then, it can be used to
enhance the understanding and knowledge about pedagogical competence to be a professional teacher.
The institution (EED of UMY). Firstly, this study can reflect the EED of UMY’s internship program at schools, whether it runs well or not. Secondly, this
study gives information about EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ pedagogical
competence. Last, the research findings may help EED of UMY to do some evaluations to enhance the quality of this program.
The partner schools and supervising teachers. This study gives
information about the pedagogical competence of EED UMY’s student-teachers.
It might be useful for partner schools and supervising teachers to do evaluation, because they have an obligation to facilitate and guide student-teachers during the internship program.
Chapter Two Literature Review
This chapter presents the general review of pedagogical competence, practicum program, and supervising teacher. Some previous studies related to the supervising teachers perception on student-teachers’ pedagogical competence in internship program will also be presented in this chapter. Last, this chapter presents the theoretical framework.
Pedagogical Competence
This sub chapter gives information about pedagogical competence. It is divided into two parts. Those are the definition of pedagogical competence and aspects of pedagogical competence.
Definition of pedagogical competence. To get an understanding about the definition of pedagogical competence, the explanation will be started with the definition of pedagogy. The second is definition of competence. The last part is definition of pedagogical competence.
Competence. Competence is more than knowledge. Hoskins and Crick
(2008) argued that competence is “a complex combination of knowledge, skills,
understanding, values, attitudes and desire which lead to effective, embodied human action in the world, in a particular domain” (p. 4). They believed that
knowledge, skills, understanding, values, attitudes and desire influence one’s
achievement at work. Moreover, Spencer and Spencer (1993) said that competency is a main characteristic of a person related to the effectiveness of individual performance on the job. The characteristics have a causal relationship or a cause and effect with the criteria referenced. By certain criteria, competence
can be used to measure and predict one’s performance in doing a job. Then,
Schroeter (2009) said that competence refers to a potential ability or capability to function in certain situation. It makes one capable to fulfill responsibility in doing a task. So, competence is the ability of an individual to do a job or task properly.
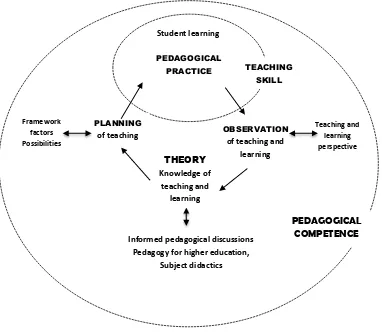
There is a schematic model of pedagogical competence. It is called as
Kolb’s Learning Cycle:
Figure 2.1. Kolb’s Learning Cycle (Kolb, 1984 in Ryegard, et al., 2010)
The scheme explains how theoretical knowledge and pedagogical practice are important in forming pedagogical competence. Pedagogical competence assumes broad and deep. Teaching skill becomes the central part of pedagogical
competence. It is demonstrated the ability of teachers to teach and support
students’ learning actively. Beside pedagogical practice, teachers have to do an
observation of teaching and learning. That is useful for teachers to build their OBSERVATION
of teaching and learning TEACHING SKILL Student learning PEDAGOGICAL PRACTICE PLANNING of teaching THEORY Knowledge of teaching and learning Teaching and learning perspective Framework factors Possibilities PEDAGOGICAL COMPETENCE
Informed pedagogical discussions Pedagogy for higher education,
perspective about teaching and learning. Then, teachers have also understand theory or knowledge of teaching and learning, including informed pedagogical discussion, pedagogy for higher education and subject didactics that crucial to be mastered by teachers. Last, teachers have to plan the teaching activity by
presuming framework factors that possibly influence teaching and learning activity. Those activities are important in shaping pedagogical competence.
Moreover, Indonesian Government in the explanation of Verse 1 Article 10 Law of Republic Indonesia Number 14 in 2005 on Teacher and Lecturer, stated
“Yang dimaksud dengan kompetensi pedagogik adalah kemampuan mengelola
pembelajaran peserta didik”. It means that pedagogical competence is the ability of teacher to manage the learning of students. It includes teaching-learning preparation, teaching-learning implementation and teaching-learning evaluation.
In summary, pedagogical competence is the ability of teachers in mastering and applying theories of teaching and learning. The theories include teaching-learning principles, teaching methodologies and approaches, curriculum, also teaching assessment and evaluation. This competence is required by teachers from preparation, implementation and evaluation of teaching.
Aspects of pedagogical competence. Indonesian government describes pedagogical competence of teacher in the Attachment of Regulation from National Education Ministry Number 16 in 2007 on Academic Qualification
Standard and Teachers’ Competencies. There are ten main aspects of pedagogical
Understand characteristic of students. A good teacher should be able to understand characteristics of students. It is related to the physical, moral, spiritual, cultural, emotional or intellectual aspect of students. Then, teachers have to identify the potential ability of students and their difficulties in learning.
Master teaching theories and principles. In mastering teaching theories and principles, teachers not only know teaching theories and principles but also have to implement the theories in their teaching activity. They should be able in applying various teaching methods, strategies and techniques when teach. Brown (2007) mentioned some popular methods in teaching second language, such as grammar translation method, direct method, audiolingual method, community language learning, suggestopedia, silent way and total physical response. Then, he also mentioned some approaches in teaching second language, such as
communicative approach (CLT) and task-based language teaching approach (TBLT).
Develop lesson plan. Teachers should be ablo to make a lesson plan to guide them in teaching. In developing lesson plan, teachers should be able to determine goal, objectives, develop indicators, select learning experience and materials that related to the objectives, also make instruments for assessment and evaluation. Brown (2007) said that a good lesson plan is structured of goal, objectives, teaching materials and equipment, procedures and assessment.
Use technology in teaching. Teachers should be able to use technology in teaching. Cohen, et al. (2010) said that there are many kinds of technology that can be used by teachers. Those are word processing, spreadsheets, databases, graphing software, desktop publishing, multimedia, internet, distant
communication also games and simulations. Moreover, They believed that using technology in teaching can help students to raise good achievement, promote higher-order thinking, promote learning for capability and problem-solving, foster collaborative learning and raise students’ motivation significantly.
Facilitate students to actualize students’ potential. Teachers have to
facilitate students to actualize their potential. Teachers should be able to motivate
students in learning and develop students’ creativity to achieve their optimal
result.
Communicate to students. Teachers should be able to conduct a good communication to students. Teachers have to understand the effective, empathic, and well-mannered communication strategy using verbal, written, and / or another form in communication.
Conduct assessment and evaluation. Teachers should be able to conduct assessment and evaluation during the teaching process. Teachers have to
determine the important aspect to be assessed and evaluated, arrange the
assessment and evaluation procedure also develop the instrument of assessment and evaluation.
teachers know the students’ achievement in the subject lesson. Then, they can use
the assessment and evaluation results to design remedial programs.
Do a teaching reflection. After conducting teaching activities, teachers have to do a teaching reflection. This purpose of teaching reflection is to know
teachers’ strengths and weaknesses in teaching. From the teaching reflection
result, teachers should be able to improve their teaching quality.
Internship Program
This sub chapter discusses internship program. Those are the definition of internship program, the significant of internship program and the problems in internship program. This sub chapter also describes the general review of EED of
UMY’s internship program.
Definition of internship program. There are some terms of internship program. Internship program is usually called as teaching practice, teaching practicum, school-based teaching experience, field experience or practicum program. However, the meanings of those terms are same.
Panda and Nayak (2014) explain internship as a program that need to appear by student-teachers before entering to the real profession. Internship provides an opportunity to student-teacher to practice teaching in school. They argue that it is impossible for teacher-education institution attempting a practical and field experience for student-teachers without internship program.
situation in order to practice their teaching skills under the supervision of a supervising teacher. The kind of this activity is practice teaching in a regular classroom. The amount of this direct teaching experience can be full time or half time service in a school. Then, Kiggundu and Niyamuli (2009) mentioned that the
time of teaching practice is depending on the institutions’ policy and school’s
schedule. Some institutions send student-teachers to go for teaching practice once a day each week, others do this over a semester.
Moreover, classroom practice is used by Cohen, Brody and Shavin (2004) to refer to this program. They said classroom practice is a main feature of teacher-education program that takes outside the training institution. Classroom practice allows student-teachers to apply directly the methods and strategies they learned, experienced, and observed at the university. Classroom practice is quick to notice discrepancies between the teaching theories they learned at the university, their observations in actual classrooms and their real teaching experience.
In addition, EED of UMY (2015) defines internship program as an
obligatory subject undertaken by EED of UMY’s student-teachers to achieve their degree of bachelor education. This program is conducted in some schools in Yogyakarta. The program includes preparation, implementation and evaluation.
This program may shape EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ competences which
are required to be a professional teacher.
student-teachers to actualize teaching theories into practice in real school environment.
Significances of internship program. Internship program gives some significances for student-teachers. Some experts explain the significances of internship program bellow:
Firstly, Pinder (2008) said that internship program is significant in facilitating student-teachers to learn about lesson plan and curriculum delivery. They learn by observing and modelling of senior teachers. Then, internship program also provides an opportunity for student-teachers to learn about
themselves. Their learning is occurred from observation and modeling, trial and error, problem solving, and making connections with prior experiences. They learn about self-behavior management which is important to improve their personal competence. Moreover, Pinder also said, in internship program student-teachers have to do interaction with other student-teachers, students, staff and school environment. All interactions that happened in internship program will build student-teachers’ social competence.
Secondly, Brown and Brown (1990) in Azeem (2011) said that internship program is a time for student-teachers to enhance their teaching competence. They try out some ideas which have been developed in university with the different approaches strategies and techniques of teaching raised in real classroom. Then, internship program provides an opportunity for student-teachers to gain
teacher. Moreover during the internship program, student-teachers also learn to solve many problems related to children in real life.
Last, Mirza (2012) in Panda and Nayak (2014) believed that internship program is function as a professional preparation of student-teachers. “It ensures the professional preparation of students in various ways such as understanding of the target profession and future prospects of working conditions in that
profession” (p.62). Internship program helps student-teachers to understand the
target profession and future prospects of working conditions by observing and making interactions with professional teachers at schools. So, internship program is beneficial to build student-teachers’ professional competence.
Therefore, internship program is important for student-teachers in shaping their competencies to be a professional teacher. It gives a chance for student-teachers to build their competencies, including pedagogical competence, personal competence, social competence and professional competence.
Problems in internship program. In internship program, student-teachers face some difficulties. Ganal, Anaya and Guiab (2015) found eight common problems faced by student-teachers in internship program. Those are:
Personal problems. Personal problems can influence student-teachers’ confidence and performance in front of class, such as their clothing not properly groomed. Some student-teachers are also poor of diction that makes them hard in speaking and explaining. The other problem, they are not creative and not
Teacher’s preparation problems. Some student-teachers being unprepared
before they enter the classroom. They are not able to write lesson plan well and not provide a variety of activities. They also do not have sufficient activities and no back up activity, so students do not do anything. Then, they are not well planned on strategies or methods.
Class participation problems. In this case, students are not active and responsive during class discussions or in other related tasks. There is only little evidence of students. They are not attentive or responsive to student-teachers in classroom activities to do interactions with others.
Class management problems. Student-teachers are difficult to handle the discipline of students and hold attention of students throughout the period of classes. They are difficult in managing a classroom independently without assistance from other student-teachers and supervising teachers. They are also unable to perform effectively routine activities, such as: checking of attendance and distributing or collecting papers, books, and workbooks.
Instructional problems. The problem includes preparing visual aids and instructional materials. Then, some student-teachers are difficult in making an effective introduction and motivation in the beginning of activity. In conducting the activity, student-teachers do not give clear direction and logical explanation on what students should do. The other instructional problems, student-teachers are
difficult to guide students’ attention to important points in summarizing and
Problems on evaluation. Kinds of problem on evaluation such as student-teachers are difficult in creating different types of questions and choosing
appropriate activity in assessing students’ learning. Then student-teachers also
confused in constructing different types of questions and interpreting test results using simple statistics.
Emotional problems. The emotional problems are depression or feeling very low, feeling of timidity and immaturity. Student-teachers also feel high
anxiety in working so hard at winning the students’ trust. Then they feel scared or
insecure of being a novice teacher.
[image:36.595.120.497.534.676.2]Problems on adjusting to students. The problem on adjusting to students is student-teachers to focus on how to be accepted by students. They are to focus to work effectively with different kinds of students that makes them forget their identity. Student-teachers also affraid to being unpopular to some students. Then, student-teachers feel insecure in a class where students come from prominent families. The problems above are presented in the figure below:
Figure 2. 2. Student-teachers’ problems in practicum program (Ganal, Anaya and Guiab, 2015, p. 65)
Student-teachers Personal problems
EED of UMY’s internship program. Internship is a compulsory subject for all teachers at EED of UMY. This program is taken by
student-teachers from the first semester until the sixth semester. This sub chapter explains the objectives of internship program, place and time of internship, and the stages of internship implementation.
The objectives. In general, EED of UMY’s internship program aims to shape a professional teacher with the required competence. Specifically, this program has three main objectives. Firstly, it shapes student-teachers’ pedagogical competence, professional competence, Islamic personality, social competence and technological competences. Secondly, it trains the teaching skill of
student-teachers in real term of school. Lastly, it provides a real experience related to the teachers duties.
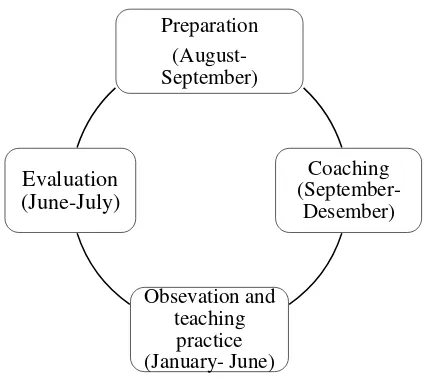
Time and place. Internship is held on odd and even semester in every year. The first half semester is held on September to December, then the second half is held on January to June. The first semester is conducted in the form of preparation and coaching of student-teachers before they practice to teach in the second semester. Coaching is conducted eight times in the odd semester and the results are lesson plan and teaching materials. Whereas, in the second semester student-teachers have to do observations and teaching practice in classroom. At the end of the second semester, student-teachers have to report the implementation of their practical activities.
EED of UMY’s student-teachers conduct internship program in some
junior high school and senior high school (including vocational school and
Muhammadiyah boarding school). All of the schools are agreed to cooperate with EED of UMY.
The implementation. Activities covered in the implementation of
internship program are preparation, coaching, observation and teaching practice, and evaluation. Those activities are explained below:
Preparation. Preparation includes socialization, registration, licensing, coordination with partner schools and coordination with supervising teachers. Preparation of internship program is held every August to October under the coordination of EED of UMY.
Coaching. Coaching is aim to prepare student-teachers before practice teaching in real classroom. Coaching is scheduled in September to December. This coaching is taught by supervising teachers and accompanied by the
supervisor from EED of UMY. Coaching is held eight meetings with 90 minutes for each meeting. In coaching, student-teachers have to make lesson plan and teaching materials.
Observation and teaching practice. Before student-teachers practice to teach, they have to do some observation. In the observation student-teachers do not only observe the school environment as general, but also observe the classroom activity. The observation aims to orient the student-teachers to learn more about the condition of the school where they practice. Then, student-teachers are expected to observe the teaching and learning process in the
teachers and students, and student interaction in the classroom. After that, student-teachers must undertake teaching practice at least three times in one semester. This phase is conducted around January to June.
Evaluation. Evaluation of internship program is held by EED of UMY in coordination with partner schools. The evaluation is conducted in the end of semester around June or July.
[image:39.595.223.436.331.520.2]In the summary, the implementation of internship program is showed in the figure below:
Figure 2. 3. The implementation of EED of UMY’s internship program
Supervising Teacher
There are some terms used to refer to supervising teachers. They are usually called as cooperating teacher, classroom teacher, tutor teacher, mentor or adviser. Supervising teachers are experienced teachers who guide student-teachers directly in internship program.
Preparation (August- September)
Coaching (September-
Desember)
Obsevation and teaching
practice (January- June)
Becoming a supervising teacher is not simple enough. According to Deane (2011), there are some points to be fulfilled. Firstly, supervising teachers should be ready to be a model in teaching. Then, they should be able to use methods and strategies that put the student-teachers and their students at center of learning. They also must knowledgeable in their subject matter and able to manage the schedule of internship program. Then, supervising teachers have to use appropriate resources to stimulate and facilitate the development of student-teachers. The last, supervising teachers should be able to observe and assess student-teachers objectively.
Roles of supervising teachers. Supervising teachers have some important roles in internship program. Gower, Philips and Walter (2005) said that there are three main roles of supervising teachers in internship program. Firstly, they help student-teachers with lesson preparation, Then, they observe student-teachers critically. The last, they give helpful feedback for student-teachers.
Moreover, Payant and Murphy (2012) argued that supervising teachers have four main roles. Those are as communicator, demystifier, catalyst for identity shifts and mentor.
Communicator. As a communicator, supervising teachers have to build good communication with student-teachers and university. They act as an effective communicator of both. Supervising teachers have to clarify the teacher
internship program. Thus, the students will get clearer understandings of what they need to be achieved.
Demystifiers. Supervising teachers have the potential to serve as
demystifiers. The term means supervising teachers should help student-teachers in understanding all things related to the internship program. Lesson plan is one example of a common confusing thing in internship program. So, supervising teachers come to guide student-teachers in making the lesson plan by clarifying procedures and processes. Supervising teachers must be generous in sharing insights about teaching with student-teachers and try to make things as transparent as possible. They can also discuss and work together with student-teachers to arrange meeting times.
Catalyst for identity shifts. Supervising teachers facilitate student-teachers to find their identity as a teacher. It is from learner-of-teaching to one that
includes as classroom teacher. Supervising teachers ask student-teachers to
imagine their own identities as shifting from one of an observer-of-teaching to one more closely approximating a classroom teacher. It is important to inform and remind student-teachers that they need to grow beyond toward more of a teaching role and away from the observer role.
by suggesting course topics. Next, supervising teachers and student-teachers begin to negotiate the content and plans for practice-teaching. This preparation stages can be face-to-face, by telephone, or by e-mail. While the student-teachers are practice-teaching, supervising teachers act as an observer. They keep note for possible improvement. In the post teaching, supervising teachers shares their observation notes with the student-teachers and discuss the strengths, areas for teaching improvement, and modifications for future implementation.
In conclusion, supervising teachers are important in internship program. They have responsibility to guide student-teacher at school during the internship program and act as communicator, demystifier, catalyst for identity shifts and mentor.
Review of Related Study
Some researchers conduct some studies in the same topic with this study. Firstly, Trisandra (2014) conduct a research entitled “The Tutor Teacher’s Perceptions of Pedagogical Competencies on Student of Field Experience Program (FEP) Department of Electrical Engineering Education”. This study aims to explain the pedagogical competence of student-teachers in field
every student-teacher in guide. Pedagogical competence focuses on the ability of students in planning the learning and the ability in implementing the learning. The
result shows that the students’ capabilities in planning and implementation of
learning measured as competent or in good criteria.
Secondly, Damayanti and Suwanda (2015) conduct a research entitled
“Perceptions of Tutor Teachers and Students on Student-Teachers’ Competencies
in Learning Management Program (PPP), Batch 2012 of Universitas Negeri
Surabaya (UNESA) at SMK Negeri 12 Surabaya”. This research aims to (1)
(PPP) in terms of pedagogical competence indicates percentage of 79.40% who classified as good category.
The other study is conducted by Suganda (2014) entitled “Classroom
Teachers’ Perceptions toward Student-teachers in Penjasorkes Subject at Senior
High Schools in Padang”. This study aims to determine how is the perception of
classroom teacher toward student-teachers’ skills in teaching Penjasorkes at senior high schools in Padang. This research is descriptive research. The
population in this study is all teachers of Penjasorkes in SMAN Padang. Samples are with a total sampling, as many as 24 teachers. The result shows that in pre-teaching student-teachers obtained at 81% in the category of "very well", in while teaching obtained at 85% and in the final achievement obtained at 83% is in the category "very well". It means student-teachers’ skills in teaching Penjasorkes at senior high schools in Padang is very well.
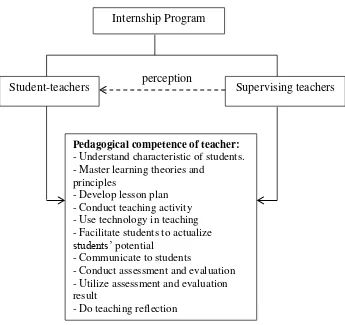
Conceptual Framework
Teachers have to master pedagogical competence. Indonesian government
defines ten aspects of teachers’ pedagogical competence in the attachment of
Regulation from National Education Ministry Number 16 in 2007 on Academic Qualification Standard and Teachers’ Competencies. Those are understand characteristic of students, master teaching theories and principles, develop lesson plan, conduct teaching activity, use technology, facilitate students to actualize
students’ potential, communicate to students, conduct assessment and evaluation,
utilize the assessment and evaluation result, and do teaching reflection.
EED of UMY has a program called internship program that facilitate EED
of UMY’s student-teachers become a professional teacher. During the internship
program, EED of UMY’s student-teachers are guided by supervising teachers
from school. The close relation between supervising teacher and EED of UMY’s
student-teachers makes supervising teacher easier in analyzing EED of UMY’s student-teachers competences. Therefore, the researcher want to reveal the
perception of supervising teachers on EED of UMY’s student-teachers’
Internship Program
Student-teachers perception Supervising teachers
Pedagogical competence of teacher:
- Understand characteristic of students. - Master learning theories and
principles
- Develop lesson plan - Conduct teaching activity - Use technology in teaching - Facilitate students to actualize
students’ potential
- Communicate to students
- Conduct assessment and evaluation - Utilize assessment and evaluation result
[image:46.595.121.466.107.432.2]- Do teaching reflection
Chapter Three Methodology
This chapter discusses the method used in this research. There are some parts of this chapter. Firstly, it discusses the research design used in the study. Secondly, it presents the setting and participant of the study. The next part discusses the data collection method. Finally, this chapter explains the data analysis.
Research Design
The aim of this study was to reveal supervising teachers’ perceptions on
EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ pedagogical competence in an internship
program. Qualitative study was used by the researcher as the method of this study. Cresswel (2009) described that qualitative study is suitable to explore the
perception, believe or opinion of individuals or groups. Then, Mack, Woodsong, Queen, Guest and Namey (2005) stated that qualitative research is able to provide multifarious textual descriptions about how people experience an issue about humans. Moreover, Dawson (2009) also believed that qualitative research can explore attitudes, behavior and experiences through such methods as interviews or focus groups. This method was appropiate for the researcher to know the
perception of supervising teachers.
in depth a program, event, activity, process on one or more individuals. Moreover, Gillham (2000) stated that case study can investigate the specific answer of
research questions and seeks different kinds of evidence to get the best possible answers to the research questions. Hence, by using this method the researcher got the real explanation about EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ pedagogical
competence.
Setting and Participant
Setting. This study was conducted in five senior high schools as EED of UMY’s partner schools for internship program. The researcher chose the schools
randomly to generalize the data. Senior high schools was chosen because of some reasons:
Firstly, senior high school is the last step of EED of UMY’s student
-teachers in conducting internship program. Therefore, the result of this study can reflect the EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ pedagogical competence in general
before they graduate from EED of UMY.
Secondly, the researcher had done an internship program at senior high school in the third year of education and still found difficulties in dealing with pedagogical problem. It also happened with the majority of EED of UMY’s
student-teachers who conducted the internship in other schools.
Participants. Purposive sampling was used in choosing the participants of this study. Mcnaill and Chapman (2005) said that purposive sampling is used when a researcher knows the type to be wanted of particular groups or places to study. Moreover, Mack, Woodsong, Queen, Guest and Namey (2005) said that purposive sampling is one of the most common sampling strategies, groups participants according to preselected criteria relevant to a particular research question. Then, Dawson (2009) argued that purposive sample is better to be used if description is the goal of a study. Hence, purposive sampling was appropriate for this study.
The participants of this study was chosen by two criteria. Firstly, he or she was an English teacher who guided EED of UMY’s student-teachers in the last EED of UMY’s internship program. Then, he or she was the most senior
supervising teachers who guided EED of UMY’s student-teachers in the last EED of UMY’s internship program. Based on the criteria, the researcher involved five
participants. They were two male participants and three female participants. All participants have experiences of teaching English more than eight years and have experience of supervising student-teachers more than three times.
Data Collection Method
This study was used interview to collect the data. It was related to the aim of the study which is to reveal the perceptions of participants. This study
experiences, particularly when sensitive topics are being explored” (Mack, et.al,
2005, p. 2). Then, Gillham (2000) believed that the strength of face-to-face interview is the richness of the communication that is possible to do and the answer can be more complex than simply yes or no.
In conducting the interview, the researcher used interview guideline. The guideline helped researcher to more focus with the interview goals. The researcher also made an appointment to meet the before conducting the interview by phone or text message. Before making the appointment, the researcher explained the aim of this study.
During the interview, recorder tool was used by the researcher. That was beneficial to keep the interview data. The researcher chose Bahasa Indonesia as the language in the interview, because it was the first language of both,
interviewer and interviewee. By using the first language, hopefully there was no misunderstanding in interpreting questions and answers. First language also helped the participants to explore their answers deeper. The interview was conducted around fifteen to thirty minutes.
Data Analysis
participants to validate the data. In the member checking, all particpants clarified that the data have beed appropiate with their statements in the interview. Then, after getting the feedback and valid data, the next step was coding, including open coding, axial coding and selective coding. Strauss & Corbin (1990) in Cohen & Crabtree (2006) said open coding is the process of breaking down, examining, comparing, conceptualizing, and categorizing data. Then axial coding is making connection between categories. Last, selective coding is selecting the core
Chapter Four Finding and Discussion
This chapter presented the finding and discussion of this study. This study aimed to reveal the supervising teachers’ perceptions on pedagogical competence
of EED of UMY’s student-teachers in an internship program. The perceptions
covered EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ competence in understanding
characteristic of students; EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ competence in
mastering teaching theories and principle; EED of UMY’s student-teachers’
competence in developing lesson plan; EED of UMY’s student
-teachers’competence in conducting teaching activity; EED of UMY’s student
-teachers’ competence in using technology; EED of UMY’s student-teachers’
competence in facilitating students to actualize students’ potential; EED of
UMY’s student-teachers’ competence in communicating to students; EED of
UMY’s student-teachers’ competence in conducting assessment and evaluation;
EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ competence in utilizing the assessment and
evaluation result; and EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ competence in doing
teaching reflection.
Supervising Teachers’ Perceptions on EED of UMY’s Student-teachers’ Competence in Understanding the Characteristic of Students
The first purpose of this study was to know the perception of supervising
teachers on EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ competence in understanding the
characteristic of students. The researcher found that supervising teachers had
understanding the characteristic of students. Firstly, one participant mentioned
that EED of UMY’s student-teachers were good in understanding the
characteristic of students. Then, the other participants said that EED of UMY’s
student-teachers had different abilities in understanding the characteristic of students.
Finding 1: EED of UMY’s student-teachers were good in
understanding the characteristic of students. Candra mentioned that EED of
UMY’s student-teachers had no problem in understanding the characteristic of
students. It was because the gap between EED of UMY’s student-teachers and students age at that school was not too wide. He said, “I think there was no problem on the understanding of EED of UMY’s student-teachers about the
characteristic of students, because their age gap was not too wide”. Moreover,
Candra also mentioned that EED of UMY’s student-teachers were easy to
understand the characteristic of students. They only need two meetings for observations to identify the characteristics of their students. He said, “After some meeting, maybe only two meetings for observations, then they know which students who hyperactive, stolid, calm and other kind of characters”.
Finding 2: EED of UMY’s student-teachers had different abilities in understanding the characteristic of students. Four participants mentioned that
EED of UMY’s student-teachers had different abilities in understanding the
students. Some of EED of UMY’s student-teachers only need two meetings, while
the others need three meetings to understand the characteristic of students.
The other participant, Berta said that EED of UMY’s student-teachers had
different abilities in understanding the characteristic of students. Although there was one EED of UMY’s student-teacher who was easier to understand the characteristic of students, most of EED of UMY’s student-teachers stated that they were difficult to understand the characteristic of students. Berta also said that understanding the characteristic of students was not easy because they needed long time and process. Unfortunately, EED of UMY’s student-teachers only had few meetings to conduct the internship program, so they did not have enough time to understand the characteristic of students. This condition influenced their
performance in managing the classroom. Berta mentioned that EED of UMY’s student-teachers had low ability in managing the classroom because they did not
understand the characteristic of students well. She said, “Based on my own
observation, when I guide them in teaching, most of them were difficult to understand the characteristic of students, so they had low ability in managing the
classroom”.
The next participant, Ani also said that EED of UMY’s student-teachers
had different abilities in understanding the characteristic of students. Some EED
of UMY’s student-teachers tried to understand the characteristic of students, but
the others did not care. They used appropriate teaching methods when they
understand students’ characteristic well. Ani said, “Student-teachers use teaching
talk, active and noisy in the classroom, then they will use method which is
appropriate with the students’ active level”. It was related to the statement of
Stronger, Tucker and Hindman (2004) who argued that classroom is filled with students whose learning styles, needs and ability differ. Therefore, teachers should be able to apply various teaching methods related to the characteristic of students.
The last participant, Dika also said that EED of UMY’s student-teachers
had different abilities in understanding the characteristic of students. He
mentioned that some EED of UMY’s student-teachers were able to understand the characteristic of students. They can directly intense in handling the students. For example, some EED of UMY’s student-teachers were able to accost and motivate passive students to be more active in learning. However, the other EED of UMY’s student-teachers did not care to their students, so that they cannot handle the students well.
In summary, there were two perceptions of supervising teachers on EED of
UMY’s student-teachers’ competence in understanding characteristic of students.
One participant said that EED of UMY’s student-teachers were good in
understanding the characteristic of students. It was because the age gap between
EED of UMY’s student-teachers and students was not too wide. The other
participants said that EED of UMY’s student-teachers had different abilities in
understanding the characteristic of students. Some EED of UMY’s student
Supervising Teachers’ Perceptions on EED of UMY’s Student-teachers’ Competence in Mastering Teaching Theories and Principles
The second purpose of this study was to know the supervising teachers’
perceptions on EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ competence in mastering
teaching theories and principles. There were two findings. Firstly, EED of UMY’s
student-teachers were good in mastering teaching theories and principles.
Secondly, EED of UMY’s student-teachers were good in mastering teaching
theories and principles but still lack in the implementation.
Finding 1: EED of UMY’s student-teachers were good in mastering teaching theories and principles. Three participants had good perceptions on
EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ competence in mastering teaching theories and
principles. Firstly, Ani said that EED of UMY’s student-teachers were good in
mastering teaching theories and principles. She mentioned that EED of UMY’s
student-teachers already know how to teach students well. In teaching their
students, EED of UMY’s student-teachers did not only use explaining method, but
also used some teaching media, such as Power Point Presentation (PPT), video and flashcard.
The next participant, Berta said that EED of UMY’s student-teachers
principles was closely related to the implementation of various methods, strategies and techniques in teaching.
In addition, Candra also said that EED of UMY’s student-teachers were
good in mastering teaching theories and principles. Although it was the first time
for EED of UMY’s student-teachers to teach in the senior high school level, but
they did it well. He said, “In mastering the theories, student-teachers were very good. Although this became the first time for them to teach at senior high school level and they found a little problem, but after some meetings they did it well”.
Finding 2: EED of UMY’s student-teachers were good in mastering teaching theories and principles but less competent in implementing the theories. The different perceptions came from Dika and Eni. They argued that
EED of UMY’s student-teachers were good in mastering teaching theories and
principles but still lack in the implementation. Dika mentioned, “For the theories,
they mastered 90% of the theories, but less competent in delivering the teaching materials. It was because they still learn, sometimes they made students
understood, sometimes they made students confused”. Moreover, he also said that
when delivering the teaching materials, EED of UMY’s student-teachers still
looking up for the best way to teach their students.
The other participant, Eni said that EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ were
good in mastering teaching theories, but they lacked in implementing the theories.
She mentioned, “Okay, they were good for the theories, because they had learned
argued that implementing teaching theories was not an easy thing, it needed time and process to learn. Moreover, Eni believed that the more EED of UMY’s student-teachers practice, the more they will master.
In summary, EED of UMY’s student-teachers were good in understanding teaching theories and principles but still need an improvement in the
implementation. In the other side, Lovat (2003) said that pedagogy is a complex blend of theoritical understanding and practical skill. It means a good knowledge of teaching theories and principles would be meaningless if it is not offset by a good implementation. Therefore, it is important for student-teachers to be able in both, knowing the theories and implementing the theories well.
Supervising Teachers’ Perceptions on EED of UMY’s Student-teachers’ Competence in Developing Lesson Plan
This study also revealed supervising teachers’ perceptions on EED of
UMY’s student-teachers’ competence in developing lesson plan. All participant
mentioned that EED of UMY’s student-teachers still found difficulties in
developing lesson plan. Some EED of UMY’s student-teachers were difficult to
develop some parts of lesson plan, such as difficult to write apperception in introduction, determine main activity and divide time for teaching. Then, the other
EED of UMY’s student-teachers did copy paste.
The first participant, Ani said that the lesson plan from university and
the lesson plan applied in the school. Then, Ani mentioned that EED of UMY’s
student-teachers still found difficulties in developing lesson plan, such as dividing time for teaching, writing apperception in the introduction, choosing the learning materials and writing the learning resources. Ani stated:
“Student-teachers usually difficult to divide time of teaching. Then, there
was no apperception in the introduction. Sometimes the teaching material was too little and they did not write the sources from internet completely.
They only write „internet’, there was no http, www, and what time they
accessed”.
The next participant, Berta said that EED of UMY’s student-teachers had
different abilities in developing lesson plan. Some of EED of UMY’s student
-teachers can directly made a good lesson plan, while the others need more than
once. Then, Berta also mentioned that some EED of UMY’s student-teachers only
do copy-paste. She said, “Some EED of UMY’s student-teachers only did the copy-paste from their friends. I found that many times. Moreover, the did not change the name in the lesson plan”.
Then, Candra also reported the same point. He said that EED of UMY’s student-teachers need to learn more in making lesson plan. Much of them did the copy-paste and unwilling to make their own lesson plan. He mentioned, “In making lesson plan, I think they need to learn more. Because when we read their lesson plan, much of them did copy-paste and unwilling to make their own lesson
In addition, Dika and Eni mentioned that EED of UMY’s student-teachers
found difficulties in developing their lesson plan. Dika said that EED of UMY’s
student-teachers feel confused in determining main activities in teaching. Then, Eni argued that the difference lesson plan from university and school made some
EED of UMY’s student-teachers confused and difficult to determine teaching
activities. Eni said, ”In developing lesson plan, because the lesson plan from
university and school were different, so they felt difficult”.
In summary, all supervising teachers argued that EED of UMY’s student
-teachers still found problems in developing lesson plan. Some of EED of UMY’s
student-teachers had difficulties in writing some parts of lesson plan and the others only copy-paste. The difference lesson plan from university and school also became the reason why EED of UMY’s student-teachers were getting confused. This finding was suported by the statement of Ganal, Anaya and Guiab (2015) who mentioned that difficult to make lesson plan became one of the most common problem faced by student-teachers in an internship program.
Supervising Teachers’ Perceptions on EED of UMY’s Student-teachers’ Competence in Conducting Teaching Activity
The next purpose of this study was to reveal supervising teachers’
perceptions on EED of UMY’s student-teachers’ competence in conducting
teaching activity. There were two perceptions coming from supervising teachers.
activity. Secondly, EED of UMY’s student-teachers had different abilities in
conducting teaching activity.
Finding 1: EED of UMY’s student-teachers were good in conducting teaching activity. One participant, Eni said that EED of UMY’s student-teachers were good in conducting teaching activity. It was caused by they apply the lesson
plan well. Eni said, “Most of them were good, because they used lesson plan as
the guide when teaching in the class”. This statement was related to the argument
from Brown (2007) who said that lesson plan was useful for teachers as the guideline while teaching. It helped teachers to achieve the learning goal.
Finding 2: EED of UMY’s student-teachers found some problems in conducting teaching activity. The other participants said that EED of UMY’s student-teachers still found problems in conducting teaching activity, such as lack in time management, too much use Bahasa Indonesia when teaching and feel nervous while teaching. Firstly, Ani mentioned that in conducting teaching
activity EED of UMY’s student-teachers found problems in time management.
Although they were able to use appropiate teaching material, but they were difficult to manange time of teaching. For example, they finished the teaching
activity earlier than their plan. Ani said, “For the material has been appropriate,
but for the implementation was not according to the time allocation, sometimes
The next participant, Berta and Dika mentioned that EED of UMY’s student-teachers found personal problem in conducting teaching activity. They feel sweaty, clumsy and nervous. These are their statements:
(Berta) “In the classroom, some student-teachers were sweaty when facing
their students”.
(Dika) “The material was okay. But sometimes they feel clumsy or
nervous when teaching.”
Then last participant, Candra said that EED of UMY’s student-teachers
still found problems in having communication with the students. Actually, EED of
UMY’s student-teachers were good in speaking English, but when interacting
with the students they used Bahasa Indonesia too much. This is his statement:
(Candra) “The ability in speaking English is good. Sometimes we need to
adjust to the students’ language and