(A Case Study at the Second Grade of SMP Negeri 13 Tangerang Selatan)
A “Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers’ Training
in a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of S.Pd. (Bachelor of Arts) in
English Language Education
Written By:
Andrian Dwi Prayoga 107014000882
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYA AND TEACHERS’ TRAINING
“SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH” STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
i
Semester 2010/2011 (A Case Study at the Second Grade of SMPN 13
South Tangerang), Skripsi, English Education Department, Faculty of
Tarbiya and Teachers’ Training, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic
University Jakarta.
Key words: Item Difficulty Level, Summative Test
This study is purposed to measure the difficulty level of the English summative test items, tested for the second grade of SMPN 13 South Tangerang at odd semester academic year 2010/2011. Through this study, it can be known which one of the test items is too easy, moderate, and difficult.
This study is included in quantitative research because the researcher uses some numerical data which are analyzed statistically. Also, this study is categorized as descriptive analysis because it is intended to describe the objective condition about the difficulty level of the English summative test for the second grade of SMPN 13 South Tangerang at odd semester academic year 2010/2011.
The findings of this study are that moderate items have highest percentage with 66,7% followed by difficult items with 20% and easy items with 13,3%. Overall, the difficulty level of the test is in moderate level with 0.50. Therefore, this test has a good difficulty level.
ii
Semester 2010/2011 (A Case Study at the Second Grade of SMPN 13
South Tangerang), Skripsi, Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas
Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
Kata kunci: Tingkat Kesulitan Butir Soal, Tes Sumatif
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengukur tingkat kesulitan butir-butir soal dari tes sumatif bahasa Inggris yang diujikan untuk kelas dua SMPN 13 Tangerang Selatan pada semester ganjil tahun ajaran 2010/2011. Dengan penelitian ini, dapat diketahui butir soal mana saja yang terlalu mudah, sedang dan sulit.
Penelitian ini termasuk dalam penelitian kuantitatif karena peneliti menggunakan beberapa data numerik yang dianalisis secara statistik. Penelitian ini juga dikategorikan sebagai analisis deskriptif karena penelitian ini menggambarkan kondisi objektif mengenai tingkat kesulitan tes sumatif bahasa Inggris untuk kelas dua SMPN 13 Tangerang Selatan pada semester ganjil tahun ajaran 2010/2011.
Hasil dari penelitian ini adalah bahwa soal yang sedang memiliki persentase yang paling tinggi dengan 66,7% diikuti oleh soal sulit sebesar 20% dan soal mudah sebesar 13,3%. Secara keseluruhan, tingkat kesukaran soal ini berada pada tingkat sedang dengan 0.50. Oleh karena itu, tes ini memiliki tingkat kesukaran soal yang baik.
iii
and Blessing to the writer, so that this “Skripsi” can be finished completely. Peace
and Salution be upon our prophet Muhammad, his families, companions, and his
followers.
The writer would like to express his gratitude to Mr. Dr. H. Muhammad
Farkhan, M.Pd. as the writer’s advisor who had kindly spent his time to give his
valuable advice, guidance, corrections, and suggestions in composing this
“Skripsi.”
Also, on this occasion, the writer would like to express his greatest
appreciation, honor, gratitude and love to his beloved mother, Mrs. Tri Hastuti,
S.Pd., who has been a great motivator in every condition, and also to his father
Mr. Juraid Umar, M.Pd., who has given him many inspirations. He thanks to them
for their pray, guidance, patience, and encouragement to motivate the writer to
finish his study.
The writer would like to express his highest appreciation and gratitude to all
lecturers of English Education Department, for teaching the precious knowledge,
sharing the values of life and giving the unforgettable study experinces.
The writer dedicates many thanks to Mr. Rohman, S.Pd. as the Headmaster of
“SMPN” 13 South Tangerang, who had given the permission to the writer to do
the research there. Also, his gratitude is sent to Ms. Dahlia Muflikhati, S.Pd. as
one of English teachers in “SMPN” 13 South Tangerang who had given the writer
great contribution and corporation while he was doing this research.
His gratitude also goes to Mr. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd. as the Head of English
Education Department, Ms. Neneng Sunengsih, S.Pd. as the Secretary of English
Education Department. Also, his thanks is given to the staffs of English Education
Department, specially for Ms. Aida Ainul Wardah, S.Pd. who always gives
excellent service and contribution to the writer.
The writer would like to express his thanks and love to all his beloved friends,
iv
while studying together.
Finally, the writer realizes that this “Skripsi” is still far from being perfect.
Constructive criticism and suggestion would be welcomed to make it better.
Jakarta, November 2011
v
ABSTRAK... ii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT... iii
TABLE OF CONTENTS... v
LIST OF TABLES... viii
CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION... 1
A. Background of the Study... 1
B. Limitation of the Study... 4
C. Statement of the Problem... 4
D. Objective of the Study... 5
E. Significance of the Study... 5
F. Method of the Study... 5
CHAPTER II : THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK... 6
A. Test... 6
1. Definition of Test... 6
2. Types of Test... 7
a. Achievement Test... 7
1. Placement Test... 8
2. Formative Test... 9
3. Diagnostic Test... 10
4. Summative Test... 11
b. Proficiency Test... 11
c. Progress Test... 12
d. Aptitude Test... 12
B. Categories of Good Test... 13
1. Validity... 13
a. Content Validity... 14
vi
2. Reliability... 15
3. Practicality... 16
C. Types of Test Item... 17
1. Objective Test... 17
a. Selection-Type Test Item... 18
1. Multiple Choice... 18
2. True-False... 21
3. Matching... 23
4. Rearrangement... 24
b. Supply-Type Test Item... 25
1. Short-Answer... 25
2. Fill-in... 27
2. Essay Test... 29
D. Item Analysis... 31
1. Definition of Item Analysis... 31
2. Kinds of Item Analysis... 32
a. Level of Difficulty... 33
b. Discriminating Power... 36
c. The Effectiveness of Distractors... 38
E. The Importance of Item Analysis... 38
CHAPTER III : THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE RESEARCH... 41
A. Research Methodology... 41
1. Purpose of the Study... 41
2. Place and Time of the Study... 41
3. Population and Sample... 41
4. Method of the Study... 42
vii
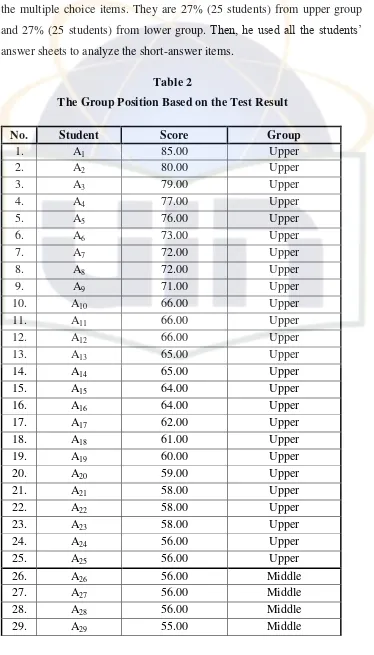
1. Data Description... 44
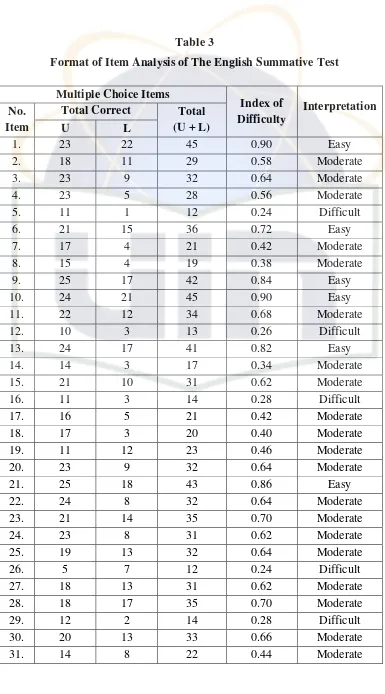
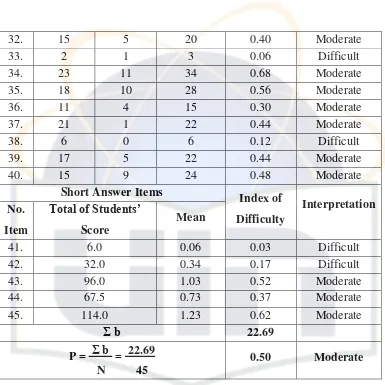
2. Data Analysis... 47
3. Data Interpretation... 52
CHAPTER IV : CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIONS... 53
A. Conclusion... 53
B. Suggestions... 53
BIBLIOGRAPHY... ix
viii
Table 2. The Group Position Based on the Test Result... 45
Table 3. Format of Item Analysis of the English Summative Test... 48
Table 4. Classification of Items Based on the Proportion of Difficulty Leve...49
Appendix
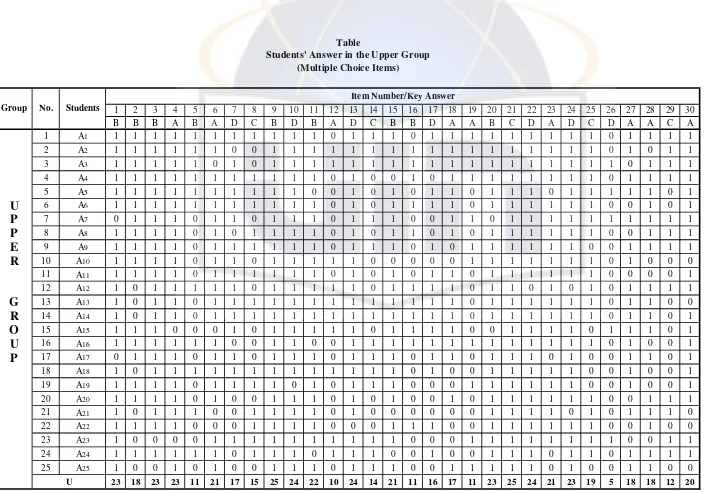
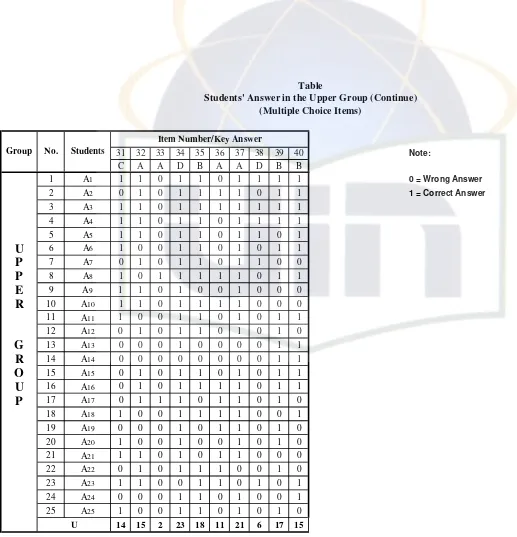
Table 5. Students’ Answer in the Upper Group (Multiple-Choice Items)
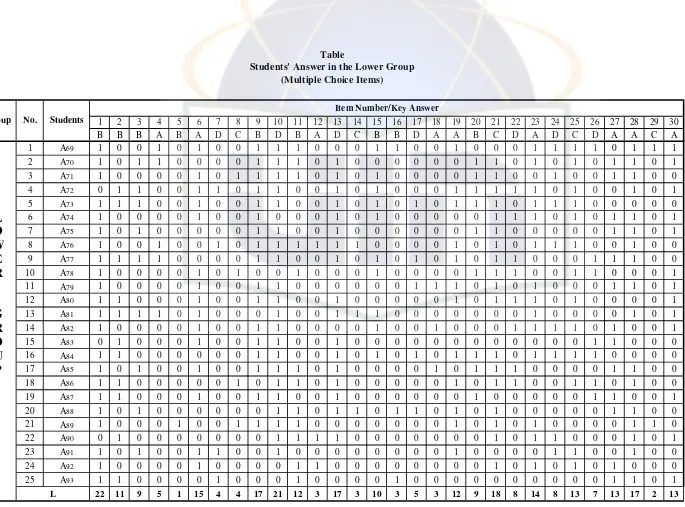
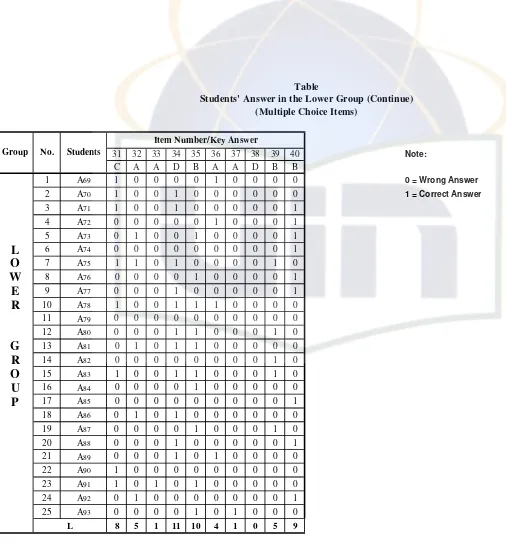
Table 6. Students’ Answer in the Lower Group (Multiple-Choice Items)
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter discusses and presents background of the study, limitation of the
problem, statement of the problem, objective of the study, significance of the
study, and method of the study.
A. Background of the Study
Evaluation plays an important role in every stage of education. It is
integrated in the school program so it contributes directly to the teaching and
learning process. According to Norman E. Gronlund, “Carefully collected
evaluation data help teachers understand the learners, plan learning
experiences for them, and determine the extent to which the instructional
objectives are being achieved.”1
Evaluation refers to the process of making conclusion from a study of
data gathered to describe value judgments about student’s performance. Lyle
F. Bachman quotes that, “evaluation can be defined as the systematic
gathering of information for the purpose of making decisions.”2 In summary, evaluation takes the very important role because it is a must for teachers to
always concern with the quality of their instructional process and whether
students have reached the instructional goals which have been stated before.
1
Norman E. Gronlund, Measurement and Evaluation in Teaching, (New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1981), 4th Ed., p. 3.
2
There are many ways for collecting data as information in the process of
evaluation. One of them is by using a test. A test is a set of question, each of
which has a correct answer, which examinees usually answer orally or in
writing.3 There are several types of the test. One of them is achievement test which is designed to know how successful student has mastered the
knowledge, abilities, and skills in the past learning activity.
According to Wilmar Tinambunan, there are four types of achievement
test which are commonly used. First, a placement test is done at the beginning
of learning to know student’s early performance. Next, a formative test is
used to monitor student’s progress during the learning process. Third, a
diagnostic test is intended to detect student’s weaknesses during instruction.
Finally, a summative test is used to show the standard that students have
reached in relation to other students at the same stage.4 In this research, the test that the writer would like to analyze is the summative test.
As one of methods to measure students’ achievement in learning process,
a test should be well constructed. A well constructed test should have three
main characteristics which involve validity, reliability, and practicallity. Valid
in language testing means that how the test really evaluates what we actually
want to measure. Whereas, reliability means that a test has to be consistent
and reproducible. While, practicallity is concerned with a wide range of
factors of economy, convenience and interpretability.5
Making a well constructed test is the teachers’ responsibility because
Wilmar Tinambunan, Evaluation of Students Achievement, (Jakarta: Depdikbud, 1988), p. 3.
4
Wilmar Tinambunan, Evaluation of Students ...p. 7-9.
5
Robert L. Thorndike and Elizabeth Hagen, Measurement and Evaluation in Psychology and
particular classes. More of these tests are administrated than any other kind.
Unfortunately, they are carelessly constructed and interpreted.”6
Based on the explanation above, teachers need to evaluate the
effecetiveness of the test items because it is necessary for teachers to know
whether the test items work well or not. Meanwhile, Harold S. Maiden
explains that “the selections of appropriate language items are not enough by
itself to ensure a good test. Each question needs to function properly;
otherwise, it can weaken the exam. Fortunately, there are some rather simple
statistical ways of checking individuals’ items. This procedure is called as
item analysis.7 This is done by analyzing the students’ response to each item. Items analysis of a test can be a valuable activity that can improve the
test’s reliability and validity. Items analysis procedures provide information
for evaluating the functional effectiveness of each item and for detecting
weakness, which should be corrected. This information is useful when
reviewing the test and it is indispensable when building a set of high quality
items for the next test.
Items analysis has three main components; they are level difficulty,
discriminating power, and effectiveness of the distracters. The difficulty level
procedure provides data how many percentages of students who answer an
item correctly. Discriminating power means whether the test can discriminate
the students’ ability or not. The last one means whether all the alternatives of
items function well or not.
The writer limits the problem of the study that he will discuss; he only
focuses on the difficulty level of the test. The test should have the difficulty
level whether it is included as easy, moderate, or difficult test. Besides, he
needs to analyze how many percentages of items which are easy, moderate,
and difficult. Moreover, it is able to distinguish between the students who
have studied well and those who have not.
6
J. Stanley Ahmann and Marvin D. Glock, Evaluating Pupil Growth Principles of Tests and
Measurement, (Boston: Allyn and Bacon, Inc, 1967), p. 17.
7
The writer intends to analyze the difficulty level of English summative
test because he found some problems at the second grade of SMP Negeri 13
Tangerang Selatan. First, some students commented that the test is too
difficult or too easy and so forth. Also, the main problem is that many
students got low score. The writer tried to investigate about this problem. He
wants to know how difficult the test is.
Based on the description given previously, the writer would like to
perform items analysis toward the English Summative Test items for the
second grade of SMP Negeri 13 Tangerang Selatan. The writer did the
research under the title “AN ANALYSIS ON THE DIFFICULTY LEVEL
OF ENGLISH SUMMATIVE TEST FOR SECOND GRADE OF
JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL AT ODD SEMESTER 2010/2011 (A Case
Study at the Second Grade of SMP Negeri 13 Tangerang Selatan)”.
B. Limitation of the Study
To make this study easier to understand, the writer limits the study as
follow:
1. The research focused only on the difficulty level of English Summative
Test at the odd semester 2010/2011
2. The test which is analyzed is English Summative Test for the second grade
at odd semester, 2010/2011 academic year
3. The research focused only on the second grade students of SMP Negeri 13
Tangerang Selatan
C. Statement of the Problem
From the limitation of problem which has been explained above, the
writer formulates the statement of the problem in this research as follow:
“Does the English Summative Test for the second grade of SMP Negeri 13 Tangerang Selatan at the odd semester 2010/2011 fulfill the criteria of a good
D. Objective of the Study
In line with the limitation of the problem, the objective of the study is to
measure the quality of English Summative Test for second grade of SMP
Negeri 13 Tangerang Selatan at the odd semester 2010/2011 and to know the
difficulty level of each item.
E. Significance of the Study
The result of this study is expected to have some benefits in English
teaching. It suggests to the test makers or classroom teachers when they find
an item test which has a high or low difficulty. They could review which
items that make the test too easy or too difficult and it can be followed up by
rearranging the test. So, this study can give contributions or a useful input and
feedback as bases for improving English Summative Test.
Besides the purpose above, the study will fulfill the writer’s final
assignment for his bachelor’s degree. Finally, other researchers who are
interested in analysis on the difficulty level can get basic information from
this study to do the further research.
F. Method of the Study
The methods used in the research are descriptive analysis and
quantitative. The writer took the English Summative Test paper and students’
answer sheet, then analyzed the difficulty level of each item. Quantitatively,
the writer used some numerical data which is analyzed statistically. The
writer also did library research by studying a number of references and
literatures related to the topic of discussion to support the theoretical aspect of
6 CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
In this chapter, the writer tries to give clear description of theoretical
framework which covers definition and types of test, types of test item,
characteristics of good test, definition and types of item analysis, and the
importance of the item analysis.
A. Test
1. Definition of Test
In the process of evaluation, one of the method that can be used to
gather data is a test. Many experts have stated some definitions of test. In
his book, Educational Test and Measurement an Introduction, Anthony J.
Nitko writes “Test is a systematic procedure for observing and describing
one or more characteristics of a person with the aid of either a numerical
scale or category system.”1
Another opinion states that test is a technique or way consisting of
some questions, statements, or tasks that are delivered to students in term
of measuring their performance or behavior.2 Victor H. Noll also writes
1
Anthony J. Nitko, Educational Test and Measurement, an Introduction, (New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Inc., 1983), p. 6.
2
that a test usually includes the use of several certain instrument or set of
instruments to determine a specific quality or trait.3
Moreover, Jum C. Nunnally states that, “A test is a standardized
situation that provides an individual with a score.”4
Based on some definitions above, it can be concluded that a test is a
method or way to measure the behavior or performance of individuals and
it consists of some systematic procedures for gathering data about their
achievement. It is usually carried out under standardized situation in
teaching and learning process.
2. Types of Test
There are many types of test used to measure students’ achievement.
However, there are four basic types of language tests: achievement tests,
proficiency tests, progress tests, and aptitude tests.5
a. Achievement Test
In his book, Language Testing, Tim McNamara writes,
“Achievement tests accumulate evidence during, or at the end of, a course of study in order to see whether and where progress has been made in terms of the goals of learning. They relate to the past in that they measure what language the students have learned as a
result of teaching.”6
Furthermore, Nunnally states that, “The purpose of achievement
test is to measure progress in school up to a particular point in time.
Achievement test is based on the core educational objectives shared by
the educators across the country.”7
3
Victor H. Noll, Educational Measurement, (Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company, 1965), 2nd Ed., p. 13.
Tim McNamara, Language Testing, (New York: Oxford University Press, 2000), p. 6.
7
In addition, according to Rebecca M. Valette, “achievement tests are usually not built around one set of teaching materials but are
designed for use with students from a variety of different schools and
programs.”8
In the writer’s opinion, achievement test is a test which is designed
to know how successful students have mastered the previous materials
of a long period of course and whether they have achieved the
educational objectives. So, by achievement test, it is able to compare
among individual students, classes and school progress with others
across the country.
According to Wilmar Tinambunan, there are four types of
achievement test: placement, formative, diagnostic, and summative
test.9 the top class. In other centres the students’ ability in different skills such as reading and writing may need to be identified. In such a centre a student could conceivably be placed in the top reading class, but in the bottom writing class, or some other combination. In yet other centres placement test may have the purpose of deciding whether students need any further tuition
at all.”10
Also, a quote by James Dean Brown in his book Testing in
Language Programs states that the purpose of this test is to make a
group of students who are in the same level of ability so teachers
can focus and only concentrate on the problems or learning points
suitable for that level.11
Moreover, placement tests provide information that helps to
place students in the part of learning program most appropriate
with their levels of ability. They are most successful in term of
their use when they are constructed for particular situations.12 Most placement tests constructed by classroom teachers are pretests
which function to know the readiness of students to begin the
instruction and to place the students in the part of learning activity
with the proper instruction.
2. Formative Test
Norman E. Gronlund writes that “formative tests are given
periodically during instruction to monitor pupil learning progress
and to provide ongoing feedback to pupils and teachers.”13
It
usually covers some parts of instruction, such as unit, chapter, etc.
In line with the opinion above, formative tests are carried out
while the instruction is ongoing to identify learning progress
students have made and to give the continuous feedback in term of
strengths and weaknesses of learning activity.14 Furthermore, “the formative test is given during the course of instruction; its purpose
to show which aspects of the chapter the student has mastered and
where remedial work is necessary.”15
11
James Dean Brown, Testing in Language Programs, (New Jersey: Prentice Hall Regents, 1996), p. 11.
12
Arthur Hughes, Testing for Language Teachers, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003), 2nd Ed., p. 16-17.
13
Norman E. Gronlund, Measurement and Evaluation in Teaching, (New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1981), 4th Ed., p. 125.
14
Wilmar Tinambunan, Evaluation of Students..., p. 8.
15
Its result gives the information about how well students have
mastered a particular material and provides them immediate
feedback. With feedback, students can determine their learning
errors or weaknesses then they can revise with or without teachers’
help.
Thus, in the writer’s opinion, formative test is designed to
check students progress during the instruction in mastering one
particular learning point and to give students feedback directly.
3. Diagnostic Test
The result of diagnostic test is intended to show the specific
weaknesses and strengths in a particular material or skill.16 It can be said that it is much comprehensive and detailed because it
identifies the major causes of learning difficulties and then helps
prepare a plan for remedial activity.
In his book, Testing for Language Teachers, Arthur Hughes
states that, “Diagnostic tests are used to identify learners’ strengths
and weaknesses. They are intended primarily to ascertain what
learning still needs to take place.”17In addition, “a diagnostic test is
designed to determine the degree to which the specific instructional
objectives of the course have been accomplished.”18
Therefore, by using diagnostic tests, teacher knows what
students have mastered and what areas in which a student needs
further help. It is made while students are learning the language.
So, diagnostic tests are typically delivered at the beginning or in
the middle of a language course.
16
Robert Lado, Language Testing, The Construction and Use of Foreign Language Tests, (London: Longman Group Limited, 1961), p. 369.
17
Arthur Hughes, Testing for Language ..., p. 15.
18
4. Summative Test
According to Wilmar Tinambunan, “the summative test is
intended to show the standard which the students have now reached
in relation to other students at the same stage. It typically comes at
the end of a course or unit of instruction.” 19
To support the opinion above, summative assessment methods
are made to determine what a students has accomplished at the
beginning or the end of a language course, then teachers can give a
final mark to students.20 Moreover, Rebecca M. Valette states that,
“the summative test is usually given at the end of a marking period
and measures the “sum” total of the material covered.”21
In conclusion, the summative test is a test that is usually
administered at the end of a language course, a semester or an
academic year to know how successful students has achieved a
wide range of material within a certain period. On this type of a
test, students are usually ranked and graded.
b. Proficiency Test
James Dean Brown writes, “a proficiency test assesses the general
knowledge or skills commonly required or prerequisite to entry into a group of similar institutions. Such tests are very general in language. The content of a proficiency tests, therefore, is not based on the content or objectives of language courses that people taking the test may have followed. Rather, it is based on a specification of
19
Wilmar Tinambunan, Evaluation of Students ..., p. 9.
what candidates have to be able to do in the language in order to be
considered proficient.”23
To sum up, proficiency tests measure someone’s general ability in
a language and they are not related to some previous courses of
instruction. The proficiency tests usually consist of standardized
multiple-choice items on grammar, vocabulary, reading
comprehension, aural comprehension, and sometimes on writing.
c. Progress Test
Based on the book Language Test Construction and Evaluation,
“progress tests are given at various stages throughout a language
course to see what the students have learnt.”24
Meanwhile, another opinion states that, “the progress test measures
how much the student has learned in a specific course of instruction.
The tests that the classroom teacher prepares for administration at the
end of a unit or end of a semester are progress tests.”25
Thus, progress test is used to check students progress in learning
one particular lesson and teacher can administer it at anytime of
language course.
d. Aptitude Test
According to Robert Lado, “aptitude tests are designed to predict
the degree of success that individual students will have in studying a
tests imply prediction. They give us a basis for predicting future level
of performance.”28
Because it functions to measure the potential capacity of an
individual, aptitude test can be used to decide how long students will
master a foreign language sufficiently. Also, it is often used in
selecting individuals for language training, for jobs, for scholarships,
and for many other purposes.
B. Categories of Good Test
Test as an instrument of obtaining information should have a good quality.
The quality of a test will influence the result of the test itself. Once the test has
a good quality, the right information will be gained and used to make accurate
decision to the students achievement.
intended.”30 Also, Norman E. Gronlund writes that, “validity refers to the
extent to which the results of an evaluating procedure serve the particular
uses for which they are intended.”31
So, validity of a test means that the test really measures what it is
supposed to measure. According to some experts, three types of validity
have been identified and are commonly used in educational measurement.
28
Howard, B. Lyman, Test Scores and What They Mean, (Boston: Allyn and Bacon, 1998), 6th Ed., p. 22.
29
David P. Harris, Testing English as a Second Language, (New York: McGraw-Hill Inc., 1969). p. 13.
30
J. Stanley Ahmann and Marvin D. Glock, EducatingPupil Growth Principles of Tests and
Measurement, (Boston: Allyn and Bacon, 1967), 3rd Ed., p. 285.
31
a. Content Validity
A test can be said to have content validity if it is built with a
representative sample of the language skills, structures, etc. which it is
meant to be concerned.32 In line with that, Anthony J. Nitko writes
that, “content validity is the extent the items on a test are representative
of the domain or universe that they are supposed to represent.”33
Thus, the degree of content validity in a test relates to how well the
the test measures the content of subject matter that students studied
before. Therefore, it is important to make sure that the test covers all
the areas of material that are supposed to be assessed. For example, a
grammar test should be made up of items relating to the knowledge of
grammar.
b. Construct Validity
This type of validity relates to any underlying ability that is
formulated in a theory of language ability. Construct validity is “the
extent that a test measures the trait, attribute, or mental process it
should measure, and whether descriptions of persons in terms of such
constructs can follow using the scores from that test.”34
Moreover, Arthur Hughes writes that, “it is a matter of empirical
research to establish whether or not such a distinct ability exsists, can
be measured, and is indeed measured in that test.”35
In other words, it can be said that a test has construct validity if it is
able to measure certain specific characteristics agreeable with a theory
of language and behavior in learning.
c. Criterion-Related Validity
Criterion-related validity relates to the extent how agreeable the
results of the test with the results come from the another independent
32
Arthur Hughes, Testing for Language ..., p. 26.
33
Anthony J. Nitko, Educational Test ..., p. 413
34
Anthony J. Nitko, Educational Test ..., p. 413.
35
and trustworthy assessment of student’s competence.36
In addition, in
his book, Educational Tests and Measurement, An Introduction,
Anthony J. Nitko states that, “criterion-related validity questions
concern the extent to which scores on a test permit inferences about
examinees’ likely standing on another measure called a criterion.”37
This type of validity can be divided into two parts; namely,
individual’s test scores with his other assessment taken at about the
same time.
2. Predictive Validity
Predictive validity is intended to predict how well someone
will perform in the future. It is supported by a quote, “predictive
validity concerns the degree to which a test can predict candidates’
future performance.”39
To do this validition, the earlier test scores from individual
students are correlated with grades made at the end of the first
semester.
2. Reliability
Consistent measurement is a necessary condition for high quality
educational testing. This consistency of a test is called as reliability.
36
Arthur Hughes, Testing for Language ..., p. 27.
37
Anthony J. Nitko, Educational Test ..., p. 422.
38
J. Stanley Ahmann and Marvin D. Glock, EducatingPupil ..., p. 288.
39
“Reliability refers to the consistency of measurement – that is, to how consistent test scores or other evaluation results are from one measurement
to another.”40
According to Desmond Allison, “the reliability of a test concerns the
accuracy and trustworthiness of its results. Reliable test results will
accurately reflect each student’s understanding of whatever is being
tested.”41
To sum up, a test is reliable if it consistently produces the same, or
nearly the same result or rank for the same individual taking the test
several times on the different occassion.
3. Practicality
The last quality that a good test should have is practicality or usability.
In selecting a test and other instruments, practical considerations cannot be
neglected. These are some factors relevant to the practicality when
In addition, ease of administration involves the simple and
clear directions, the subtests in minimum numbers and the easy timing.
b. Time Required for Administration
The test’s length is directly related to the reliability of a test, so the availability of enough time should be taken. “A safe procedure is to
40
Norman E. Gronlund, Measurement and Evaluation ..., p. 93.
41
Desmond Allison, Language Testing ..., p. 85.
42
Norman E. Gronlund and Robert L. Linn, Measurement and Evaluation in Teaching, (New York: Macmillan Publishing Company, 1990), 6th Ed., p. 102-103.
43
allot as much time as is necessary to obtain valid and reliable
results.”44
c. Ease of Interpretation and Application
If the test is interpreted correctly and applied effectively, teacher
can make accurate educational decisions about students performance.
d. Availability of Equivalent or Comparable Forms
Equivalent test measure the same aspect and is alike in content,
level of difficulty, and other characteristics. It is useful if teacher wants
to remove the factor of memory when retesting students on the same
domain. Comporable forms are especially useful in measuring the
progress of the basic skills.
e. Cost of Testing
The factor of the cost is actually not really important in selecting
test. Testing is relatively inexpensive. However, the point is the test
should be as economical as possible in cost.
C. Types of Test Item
An item is the basic unit of language testing. According to James Dean
Brown, the definition of the item “is the smallest unit that produces distinctive
and meaningful information on a test or rating scale.”45
The items used in clasroom tests are commonly divided into two broad
categories: (1) the objective item, and (2) the essay test.
1. Objective Test
In constructing an achievement test, the test maker may choose from a
variety of item types. One of them is referred to as objective item. This
kind of item types can be scored objectively. Furthermore, “equally
competent scorers can score them independently and obtain the same
44
Wilmar Tinambunan, Evaluation of Students ..., p. 23.
45
results.”46 In addition, Rebecca M. Valette defines objective test as “any
item for which there is a single predictable correct answer.”47
Thus, when scoring this test, any subjective judgement from the scorer
is pushed aside because every item in that test has only one absolutely
right answer. So, although the test is scored in several different times by
one scorer or another, it will obtain the same result.
The objective item can be classified into two types, which are
selection-type test item and supply-type test item.
a. Selection-Type Test Item
1. Multiple Choice
According to Anthony J. Nitko, “a multiple choice item
consists of one or more introductory sentences followed by a list of
two or more suggested responses from which the examinee
chooses one as the correct answer.”48
The other responses which
are as incorrect answers function to distract students’ attention
away from the correct answer in case they are uncertain of the
answer.
In line with that quote, “multiple choice items are made up of
an item stem, or the main part of the item at the top, a correct
answer, which is obviously the choice that will be counted correct,
and the distractors, which are those choices that will be counted as
incorrect.”49
For example:
Budi has been here ____________ half an hour.
The multiple choice item is commonly recognized as the most
applicable and useful type of objective test item. It can be used to
measure both knowledge outcomes and many types of skills. In
addition, it can measure a variety of learning outcomes from simple
to complex material.
The multiplce choice item is included in discrete point test.
Discrete point test takes language skill apart. Oller states that,
“discrete items attempt to test knowledge of language one bit at a
time.”50
It means that language knowledge can be divided into a
number or components, such as grammar, vocabulary spelling,
punctuation, pronunciation, intonation, and stress. This test only
measures the knowledge of language in one particular component.
Actually, it is not too difficult for test maker or teacher to
construct multiple choice item test. However, there some
suggestions that they shoul consider in constructing this type of test
items:51
a. The stem of the item should be meaningful by itself and should show a specific problem.
b. The item stem should include as much of the item as possible and should be free of irrelevant material.
c. A negatively stated item stem can be used only when significant outcomes need it.
d. All of the alternatives should be grammatically consistent with the stem.
e. An item should contain only one clearly correct answer. f. Items used to measure understanding should contain some
novelty, but beware too much. g. All distracters should be plausible.
h. Verbal associations between the stem and the correct answer should be avoided.
i. The relative length of the alternatives should not provide a clue to the answer.
j. The correct answer should appear in each of the alternative positions and in equal number but in random order.
50
John W. Oller, Language Tests ..., p. 37.
51
k. The special alternatives such as “none of the above” or “all
of the above” can be used sparingly.
l. Do not use multiple choice item when other item types are more appropriate.
Although it can be said as the most applicable and useful type
of test item, multiple choice item has some limitations, such as:52 a. The technique tests only recognition knowledge. A multiple
choice item gives a quite inaccurate result of students’
ability in productive and receptive skills.
b. Guessing may have a considerable but unknownable effect
on test scores. We never know what part of any individual’s
score comes through guessing. So, we cannot identify the answer, no correct answer, the obvious clues in the options, ineffective distractors.
e. Backwash may be harmful. Practice at multiple choice items will not usually be the best way for students to improve their command of a language.
f. Cheating may be facilitated. The fact that how to response on a multiple choice item is so simple makes students easy to communicate each other non-verbally.
Beside its limitations, multiple choice item also has some
advantages. Wilmar Tinambunan writes the advantages of multiple
choice item as follow:53
a. The multiple choice item can be used for subject matter content
in any different levels of behaviour, such as ability to reason,
discriminate, interpret, analyze, infer, and solve problems.
b. It has less chance for students to guess the right answer than the
true-false item does because it is followed by four or five
alternatives.
52
Arthur Hughes, Testing for Language ..., p. 76-78.
53
c. One advantage of the multiple choice item over the true-false
item is that students also know what is correct rather than only
know that a statement is incorrect.
In the writer’s opinion, multiple choice item includes at least
three components, which are the stem, the distractors, and the
correct answer. The stem can be the direct question or incomplete
statement which students have to response. The distractors are
presented to distract the students who do not study well for
choosing the answer correctly. This type especially useful for
measuring learning outcomes that require the understanding,
application, or interpretation of factual information.
2. True-False
In the book, Criterion-Referenced Language Testing, true-false
item “requires student to respond to the language by selecting one
of two choices, for instance, between and true and false or between
correct and incorrect.”54
In line with that opinion, Norman gives
the definition of true-false item as follow:
“True-false item is simply a declarative statement that the student must judge as true or false. There are modifications of
this basic form in which the student must respond “yes” or “no,” “agree” or “disagree,” “right” or “wrong,” “fact” or
“opinion,” and the like. Such variations are usually given the
more general name of alternative-response items. In any event this item type is characterized by the fact that only two
responses are possible.”55
For example:
Direction: Read each of the following statements, if the statement
is true grammatically, circle the T. If the statement is
false gramatically, circle the F!
54
James Dean Brown and Thom Hudson, Criterion-Referenced Language Testing, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002), p. 66.
55
T F 1. Toni usually help her mother in cooking.
T F 2. Every student must bring their own book.
T F 3. If I had much money, I would buy a house.
T F 4. She is smarter in our classroom.
T F 5. The men are gathered in a conference room.
The most common use of the true-false item is to measure the
ability to identify the correctness of statement of fact, definition of
terms, principles, etc and to distinguish fact from opinion.56 It is
a. Include only one central, significant idea in each statement b. Word the statement so precisely that it can be judged true
or false unequivocally
c. Keep the statement short, and use simple language structure d. Use negative statements sparingly, and avoid double
negatives
e. Statements of opinion should be attributed to some source f. Avoid extraneous clues to the answer
Moreover, Anthony J. Nitko states that this item type has some
advantages and criticisms.58 Here they are: Advantages:
a. Certain aspects of the subject matter lend themselves to verbal prepositions that can be judged true or false
b. Such items are relatively easy to write c. They can be scored easily and objectively
d. They can cover a wide range of content with a relatively short period of testing
56
Wilmar Tinambunan, Evaluation of Students ..., p. 70.
57
Norman E. Gronlund, Constructing Achievement ..., p. 55-56
58
Criticisms:
a. They are often used only to test specific, frequently trivial, facts
b. They can be ambigiously worded
c. They can be answered correctly by blind guessing
d. They may encourage students to study and accept only oversimplified statements of truth and factual details
Thus, true-false item is the item type which contains a single
written statement and then it must be decided by students whether
it is true or false. It is constructed to check and measure whether a
simple particular point has been comprehended or not.
3. Matching
“The matching item consists of two paralell coloumns with
each word, number, or symbol in one coloumn being matched to a word, sentence, or phrase in the other coloumn. The items in the coloumn for which a match is sought are called premises and the items in the coloumn from which the selection is made are called responses. They are useful in measuring students ability to make associations, discern relationship, make
interpretations or measure knowledge of a series of facts.”59
In other words, this item type presents students with two
coloumn of information in which they have to match the correct
option or response to premise. It is typically used to measure
factual information or knowledge based on simple relationship.
Therefore, when learning outcomes concern on the ability to
identify the relationship between two things, matching item should
be the most appropriate. For example:
Match the following words on the left with their synonyms on the
right!
4. ( ) Appear d. Accept
5. ( ) Improve e. Accomplish
Furthermore, James Dean Brown formulates three guidelines
that teachers should apply in constructing matching items:60
a. More responses should be supplied than premises so that students cannot narrow down the choices as they go along by simply keeping track of the options that they have already used.
b. The responses should usually be shorter than the premises because most students will read a premise and then search through the options for then correct match.
c. The premises and responses should be logically related to one central theme that is obvious to the students.
Moreover, matching item has some advantages to be carried
out in testing. The first advantage is “its compat form, which
makes it possible to measure a large amount of related factual
material in a relatively short time.”61 Secondly, “the effects of
guessing is reduced since the student will have one chance out of a
number of responses available of guessing correctly.”62
At last, it
has ease of construction.
4. Rearrangement
“Rearrangement items require the pupil to put into some
specified order a series of randomly presented material.”63
In the
book, Measurement and Evaluation in the Schools, Louis J.
Karmel states that any kind of specified order may be called for,
such as chronology, order of difficulty, order of importance,
length, weight, logic, and so on.64
60
James Dean Brown, Testing in Language ..., p. 57.
61
Norman E. Gronlund and Robert L. Linn, Measurement and Evaluation ..., p. 159.
62
Wilmar Tinambunan, Evaluation of Students ..., p. 65.
63
H. H. Remmers, et. al., A Practical Introduction ..., p. 243.
64
For example:
Rearrange these following sentences into a good paragraph!
1. Suddenly, it was getting dark and he realized that he got lost
2. Once upon a time, there was a bee named Bumbee
3. Bumbee could get home and gathered with his family happily
4. One day, he felt so happy and flew alone in the forest
5. Fortunately, a butterfly appeared and she liked to help him
b. Supply-Type Test Item
1. Short-Answer
According to Norman E. Gronlund in his book, Constructing
Achievement Test, he states that, “the short answer (or completion )
item is the only objective item type that requires the examinee to
supply, rather than select, the answer.”65
In line with that opinion,
this item type “generally requires the students to examine a
statement or question then respond to it with a phrase or two, or a
sentence or two, in the space provided.”66
Both short answer item and completion item can be answered
by a word, phrase, sentence, number, or symbol. In the short
answer item, the question is presented as a direct question:
For example:
a. What is the capital city of West Java? (Bandung)
b. Who invented the lightbulb? (Thomas Alfa Edison)
Whereas, the completion item requires student to supply the
answer in an uncomplete statement.
For example:
a. The capital city of West Java is ... (Bandung)
b. The name of the man who invented the lightbulb is ...
(Thomas Alfa Edison)
65
Norman E. Gronlund, Constructing Achievement ..., p. 57.
66
It seems obvious that short answer item or completion item
order not to make the items in a careless way:67 a. Require short, definite, clean-cut answers
b. If several correct answers (synonyms) are possible, count
e. Specify the terms in which the response is to be given f. In testing for a knowledge and understanding of definitions,
it is often better to provide the term and require a definition than to provide a definition and require the term
g. Direct questions are probably preferable to incomplete declarative sentences
h. Hints concerning the correct answer, in the form of the first letter of a word, or a number indicating the number of letters in a word, should generally not be given
i. The space for the response should usually be at the right of the question
j. Allow enough space for the responses to permit legible writing
k. Arranging the answer spaces in a coloumn at the right-hand margin of the page makes scoring more convenient
Furthermore, short answer item has some advantages and
disadvantages like Arthur Hughes writes in his book, Testing for
Language Teachers:68
a. Advantages:
1. Guessing will (or should) contribute less to test scores 2. The technique is not restricted by the need for
3. Cheating is likely to be more difficult
4. Though great care must be taken, items should be easier to write
contents or parts are removed. Then, students are asked to fill those
blank spaces. As James Dean Brown and Thom Hudson write,
“this format provides a language context of some sort and then removes part of the context and replaces it with a blank. The
student’s job is to fill in that blank.”69
For example:
1. He failed another exam, __________ he had studied very hard.
2. She does not come today. She __________ be sick.
3. Once upon a __________, there was a farmer living in a small
village in England. His __________ was Jack. He was a kind
and wise man. He liked to help his neighbors. Jack __________
a mill machine. People came to his place to __________ their
grain. Jack served them happily. However, his wife was a very
__________ woman. She often complained. She __________
angry every time Jack __________ some food to the
neighbors.70
69
James Dean Brown and Thom Hudson, Criterion-Referenced ..., p. 73.
70
In addition, fill-in item measures the student’s ability to
produce a language, even if a small amount of language. However,
to make the measurement by fill-in item result the valid data, it is
prominent to tell clearly to students that only one word can be put
in each blank or gap.
For more advanced, in order to use fill-in item in an efficient
way for measuring students’ performance, there are five
considerations issued by James Dean Brown that teachers should
remember:71
a. Teachers should check to make sure that each item has one very concise correct answer
b. Teacher should make sure that enough context has been provided that the purpose, or intent, of the item is clear to those students who know the answer
c. All the blanks in a fill-in test should be the same length d. Teachers should also consider putting the main body of the
item before the blank in most of the items so that the students have the information necessary to answer the item once the encounter the blank
e. In situations, where the blanks may be very difficult and frustrating for the students, teachers might consider supplying a list of responses from which the students can choose in filling in the blanks
Furthermore, as one of types of test item, fill-in item has some
advantages and limitations:72 Advantages:
a. It is relatively easy to construct
b. It is flexible to use from a test writer’s point of view
c. It requires a short amount of time to administer
Limitations:
a. It is generally very narrowly focused on testing a single word
or short phrase at most
b. It may have a number of possible answers
71
James Dean Brown, Testing in Language ..., p. 58-59.
72
2. Essay Test
According to J. Stanley Ahmann and Marvin D. Glock on the book,
Educating Pupil Growth Principles of Test and Measurements, “an
essay test item demands a response composed by the pupil, usually in one or more sentences, of a nature that no single response or pattern of responses can be listed as correct, and the accuracy and quality of which can be judged subjectively only by one skilled and informed in
the subject, customarily the classroom teacher.”73
In addition, the major characteristic of essay test is the freedom of
response it provides. It means that students have to produce their own
answer.74 To support the opinion above, Wilmar Tinambunan states that,
“the essay-type question requires the examinee to read the question,
formulate his response and express the response in his own words.”75
Essay question can be classified into two types, which are:
a. Restricted Response Type
The student is not given a complete freedom to make his response.
“it usually limits both the content and the response. The content is
usually restricted by the scope of topic to be discussed. Limitations of
response are commonly indicated in the question.”76 For example:
1. State the main differences between the objective test and the
subjective test according to Norman E. Gronlund!
2. Explain two advantages and two disadvantages of using the
multiple choice item in testing English as a foreign language!
b. Extended Response Type
In this type, student is given the freedom completely in composing
his response. “it allows pupil to select any factual information that they
think is pertinent, to organize the answer accordance with their best
73
J. Stanley Ahmann and Marvin D. Glock, EducatingPupil ..., p. 157.
74
Norman E. Gronlund, Constructing Achievement ..., p. 71.
75
Wilmar Tinambunan, Evaluation of Students ..., p. 56.
76
judgment, and to integrate and evaluate ideas as they deem
appropriate.”77
For example:
1. Why is English so important nowadays?
2. Describe the roles of the teacher in language testing!
Moreover, building the essay item as a measurement of complex
learning outcomes should be done in a proper and careful way. Here are
some suggestions to construct a good essay item:78
1. Make definite provisions for preparing students for taking essay examinations
2. Make sure that questions are carefully focused 3. Structure the content and length of questions
4. Have a colleague review and critique the essay questions
5. Avoid the use of optional questions, except when one is assessing writing ability where a choice of questions is desirable
6. Restrict the use of the essay as an achievement test to those objectives for which it is best
As a method to measure the complex learning outcomes, essay item
has several advantages and weaknesses.
Advantages:79
1. It measures complex learning outcomes that cannot be measured by other means
2. It emphasize on the integration and application of thinking and problem-solving skills
3. It is regarded as a device for improving writing skills
4. It has ease of construction. Most teachers can formulate several essay questions in a matter of minutes
Weaknesses:80
1. There are not many samplings of achievement because only a small
number of questions can be included in essay test
77
Norman E. Gronlund and Robert L. Linn, Measurement and Evaluation ..., p. 213.
78
Kenneth D. Hopkins, et. al., Educational and Psychlogical Measurement and Evaluation, (Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice Hall Inc., 1990), 7th Ed., p. 216.
79
Norman E. Gronlund and Robert L. Linn, Measurement and Evaluation ..., p. 216.
80
2. Scoring the essay test is influenced by student’s writing ability. Poor
expression and errors in punctuation, spelling, grammar usually lower
their score
3. While scoring essay test, the standards can be shifted because of
variations in the content of the answers from paper to paper
4. It requires much time to score the answers81
Thus, in essay item, students are asked to demonstrate their ability to
select, organize, integrate and review ideas to response the question in the
freedom. In addition, this item type is scored subjectively since it will
presents the different results when it is scored by the different person. The
people who are assigned to score the answers are typically influenced by
their own judgment or opinion.
To sum up, based on the previous explanation, an essay test is used to
measure student’s comprehension of a certain knowledge and student is
asked to answer by expressing his own words effectively and organizing
their own ideas, using information from his own background and
knowledge.
D. Item Analysis
1. Definition of Item Analysis
Obtaining the valid data as information is very valuable to give the
clear judgment about student’s performance in evaluation activity. In case
of that, the test should have a good quality and every item functions
properly. Teacher or test maker should know whether the test can be
included as a good test or not by evaluating every item in that test. This
activity is called as item analysis.
According to Anthony J. Nitko, “item analysis refers to the process of
collecting, summarizing, and using information about individual test
items, especially information about pupil’s response to item.”82
81
In addition, “item analysis as a whole will be defined here as the
systematic statistical evaluation of the effectiveness of individual test items. Item analysis is usually done for purposes of selecting which items will remain on future revised and improved versions of the test. Sometimes, however, item analysis is performed simply to investigate how well the items on a test are working with a particular group of students, or to study which items match the language domain of
interest.”83
Moreover, Arthur Hughes proposes the purpose of item analysis
which is “to examine the contribution that each item is making to the test.
Items that are identified as faulty or inefficient can be modified or
rejected.”84
Although item analysis is done primarily for response-choice item, it
is available for teacher to use several of the techniques described with any
items that are scored dichotomously (simply as correct or incorrect).85
In the writer’s opinion, item analysis is statistical evaluation to know
the quality of a test by identifying whether every item on a test works
appropriately or not. It is done by collecting students’ responses to each
item so that it can also be known which items are included as a good one
and which items that weaken the test. It is very useful for teacher to
performs item analysis since it can be a device for test improvement.
2. Kinds of Item Analysis
Item analysis usually concentrates three vital features: level of
difficulty, discriminating power, and the effectiveness of each alternative.
“Thus, item analysis can tell us if an item was too difficult or too easy,
how well it discriminated between high and law scores on the test, and
whether all the alternatives functioned as intended.”86
82
Anthony J. Nitko, Educational Test ..., p. 284.
83
James Dean Brown and Thom Hudson, Criterion-Referenced ..., p. 113.
84
Arthur Hughes, Testing for Language ..., p. 225.
85
Anthony J. Nitko, Educational Test ..., p. 286.
86
a. Level of Difficulty
The first area in item analysis is level of difficulty which concerns
on how easy or difficult each item is. According to Kathleen M.
Bailey, difficulty level is “an index of how easy an individual item was
for the people who took it. It is typically printed as a decimal, ranging
from 0.0 to 1.0. It represents the proportion of people who got the item
right.”87
Furthermore, in the book, Language Tests at School, “difficulty
level (or item facility) has to do with how easy (or difficult) an item is
from the viewpoint of the group of students or examiness taking the
test of which that item is a part.”88
In writer’s opinion, level of difficulty deals with how many
percentage of students who response an item correctly and those who
response incorrectly. By analyzing the difficulty level of each item, it
can be inferred whether an item is included as easy, moderate or
difficult item.
Level of difficulty is interpreted in the form of percentage. The
larger the percentage of the correct answer, the easier the item is. Then,
the fewer the students who answer correctly, the more difficult the
test and the valid data of information about student’s achievement will
not be acquired.
In addition, level of difficulty analysis can be applied for either
large group of students or the small one.
87
Kathleen M. Bailey, Learning about Language Assessment: Dilemmas, Decisions, and
Directions, (New York: Heinle & Heinle Publishers, 1998), p. 132.
88
As a quote, from Lyle F. Bachman, states that, “to conduct an item analysis, we first arrange the scored test papers or answer sheets in order from the highest score to the lowest score. Next, we separate the papers into upper and lower groups, according to their total test scores. For large groups, we would choose the upper and lower 27 percent, while for smaller groups, we would typically choose the upper and lower one-third.”89
The formula used for analyzing the difficulty level of each item in
large group is stated below:
In which:
TK : Index of difficulty
U : The number of students in the upper group who answer the
item correctly
L : The number of students in the lower group who answer the
item correctly
T : The number of students in upper and lower group90
Next, for the small group, teacher or test maker can easily evaluate
an item by using all the students’ answer sheets. Then, the formula is:
89
Lyle F. Bachman, Statistical Analyses for Language Assessment, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004), p. 123.
90
M. Ngalim Purwanto, Prinsip-Prinsip dan Teknik Evaluasi Pengajaran, (Bandung: Remadja Karya, 1986), p. 153.
B
P = JS
In which:
P : Index of difficulty
B : The total number of students who got the item correct
JS : The number of students who took a test91
The formula above is commonly used for multiple choice item. For
the short-answer item, Zainal Arifin states as follows:92
After analyzing each item and obtaining its difficulty level, the next
thing to do is finding out the difficulty level for whole items in a test. It
is performed by using the following formula:
In which:
P : Difficulty level for whole items
b : Difficulty level of each item
Σ : Sigma (Total)
N : Total number of test items93
91
Suharsimi Arikunto, Dasar-Dasar Evaluasi Pendidikan, (Jakarta: PT. Bumi Aksara, 2006), p. 208.
92
Zainal Arifin, Evaluasi Pembelajaran ..., P. 135.
The total of student’s score for each item Mean =
The number of students
Mean Index of difficulty =
Maximum score of each item