Informasi Dokumen
- Penulis:
- Yusnida Febriany. H.
- Pengajar:
- Dr. Dwi Yulianti, M.Pd.
- Dr. Eng., Helmy Fitriawan, S.T., M.Sc
- Dr. Abdurrahman, M.Si.
- Sekolah: Universitas Lampung
- Mata Pelajaran: Magister Teknologi Pendidikan
- Topik: Blended Learning Mata Pelajaran Fisika Kelas XI.TKJ Di SMKN 1 Bakauheni
- Tipe: thesis
- Tahun: 2017
- Kota: Bandar Lampung
Ringkasan Dokumen
I. INTRODUCTION
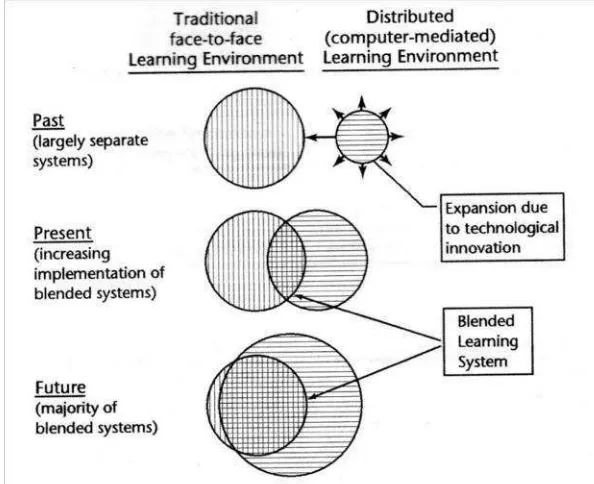
The introduction outlines the rapid development of technology, particularly in Information and Communication Technology (ICT), which has significantly impacted education. It discusses the shift from traditional face-to-face learning to more open and media-based education, emphasizing the potential of distance learning and e-learning through internet networks. The introduction also highlights the research's objective to describe the design, process, evaluation, student responses, and understanding of physics through blended learning for the eleventh-grade TKJ students at SMKN 1 Bakauheni.
1.1 Background
The background section elaborates on the challenges faced in conventional learning methods, particularly in physics education. It emphasizes the need for innovative teaching strategies like blended learning, which combines face-to-face and online learning. The section also discusses the limitations of traditional physics education and the necessity to engage students actively to improve their understanding and interest in the subject.
1.2 Problem Identification
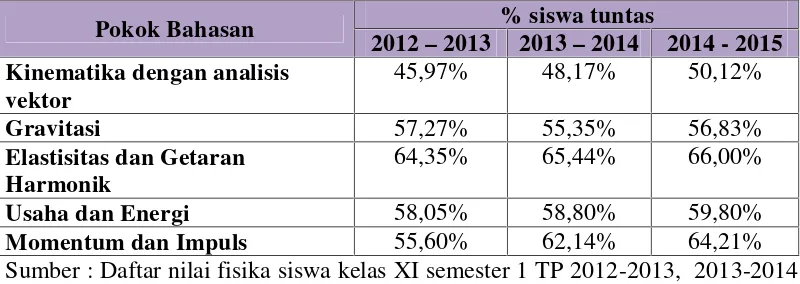
This subsection identifies key issues in physics education at SMKN 1 Bakauheni, including the reliance on conventional teaching methods, student disengagement, and low understanding of physics concepts. It highlights the importance of addressing these problems to enhance student learning outcomes and engagement.
1.3 Problem Limitations
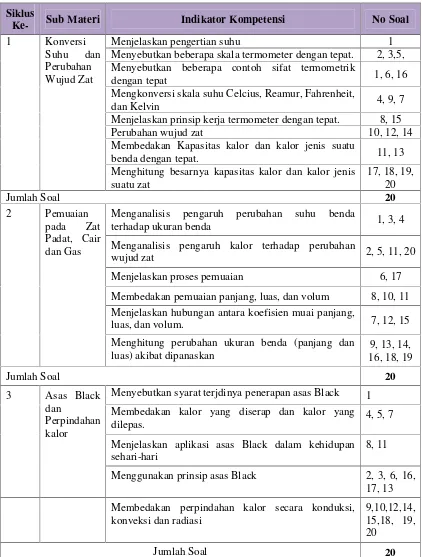
To focus the research, this section limits the study to the application of blended learning in the physics curriculum for eleventh-grade TKJ students during the 2015-2016 academic year. It specifies the topics covered, such as heat and temperature, and the methods used for data collection and analysis.
1.4 Problem Formulation
The formulation of the problem outlines the research questions aimed at assessing the design, process, student responses, and learning outcomes of blended learning in physics education. It serves as a guide for the research objectives and methodology.
1.5 Research Objectives
This section details the general and specific objectives of the research, which include improving the design and process of physics learning, enhancing student responses, and increasing learning outcomes through the implementation of blended learning strategies.
1.6 Research Benefits
The benefits of the research are discussed, emphasizing its potential contributions to educational practices at SMKN 1 Bakauheni, providing insights for other educators, and serving as a foundation for future research in blended learning and physics education.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
The literature review discusses the concept of blended learning, its definitions, and its relevance in the educational context. It explores various instructional methods and their effectiveness in enhancing student learning experiences. The review highlights the importance of integrating technology into traditional teaching methods to create a more engaging learning environment.
2.1 Concept of Blended Learning
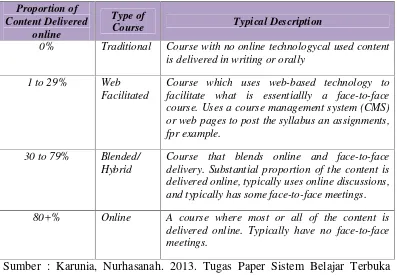
This subsection defines blended learning and its significance in modern education. It explains how blended learning combines face-to-face instruction with online learning, emphasizing its flexibility and effectiveness in catering to diverse learning styles and needs.
2.2 Learning Outcomes
This section outlines the importance of learning outcomes as indicators of educational effectiveness. It discusses how blended learning can enhance students' understanding and retention of physics concepts, ultimately leading to improved academic performance.
2.3 Learning Theories
Theories of learning, including behaviorism, cognitive theory, and constructivism, are examined. The section emphasizes the relevance of constructivist approaches in blended learning, advocating for active student engagement in the learning process.
2.4 Characteristics of Physics Education in Vocational Schools
This subsection discusses the unique characteristics of teaching physics in vocational schools, including the practical applications of physics concepts in technology and industry. It highlights the challenges faced by students in understanding abstract concepts and the need for innovative teaching strategies.
2.5 Relevant Research
A review of previous studies related to blended learning in physics education is presented. This section identifies gaps in the existing literature and underscores the need for further research in this area to enhance teaching practices and learning outcomes.
III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This section outlines the research design, methodology, and data collection techniques employed in the study. It emphasizes the use of classroom action research to implement and evaluate the blended learning approach in physics education.
3.1 Research Location
This subsection describes the setting of the research, specifically SMKN 1 Bakauheni, and the characteristics of the student population involved in the study. It provides context for the research and highlights the relevance of the blended learning approach in this environment.
3.2 Research Timing
The timing of the research is discussed, detailing the duration of the study and the cycles of implementation for the blended learning approach. This section outlines how the research was structured over time to assess improvements in student learning outcomes.
3.3 Research Subjects
This subsection identifies the subjects of the research, focusing on the eleventh-grade TKJ students at SMKN 1 Bakauheni. It discusses the selection criteria and the relevance of this group for studying the effects of blended learning.
3.4 Duration of Action and Success Indicators
The duration of the research action and the indicators for measuring success are outlined. This section details how the effectiveness of the blended learning approach will be evaluated through various assessment methods.
3.5 Research Design
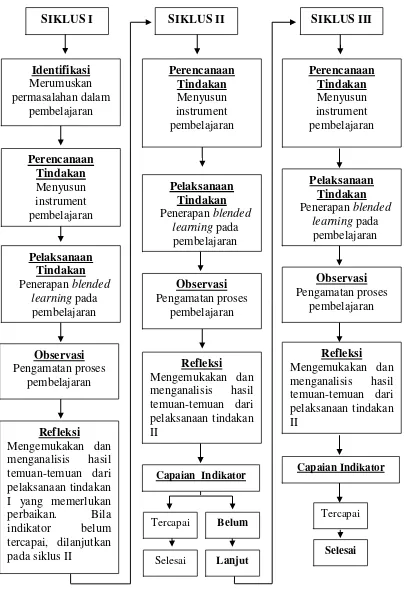
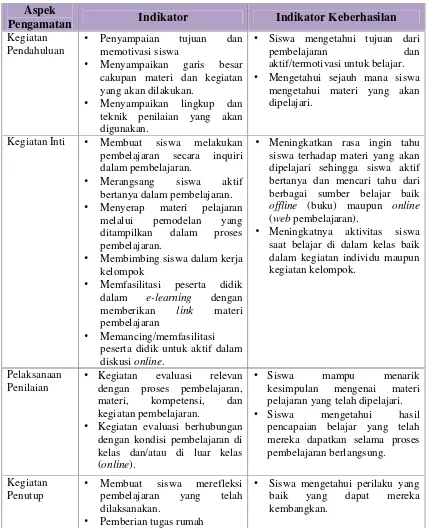
This subsection describes the classroom action research design used in the study, including the planning, implementation, observation, and reflection phases. It emphasizes the iterative nature of the research process and the importance of continuous improvement.
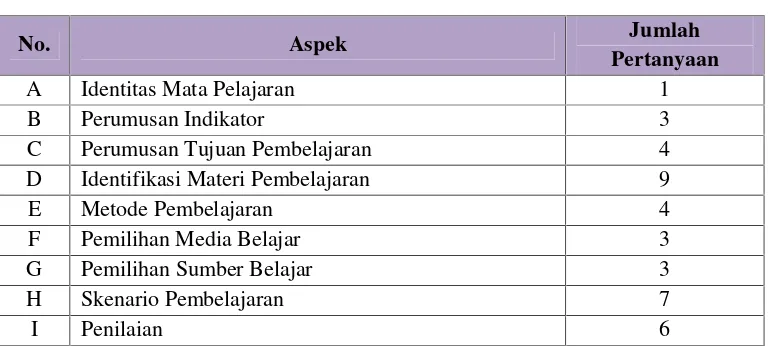
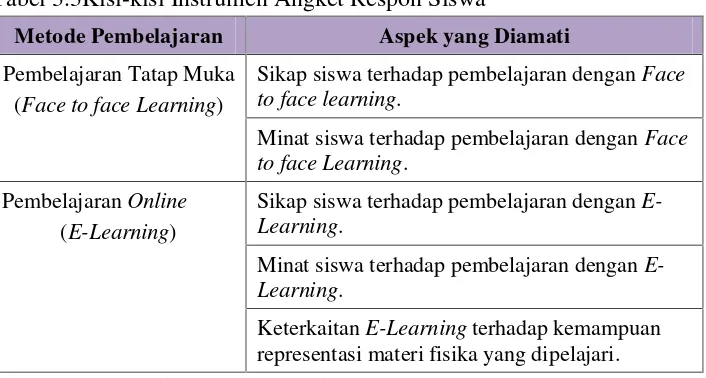
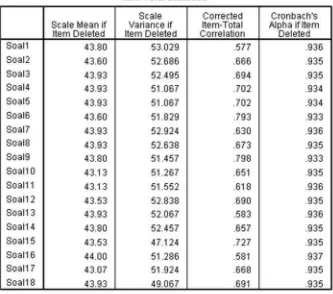
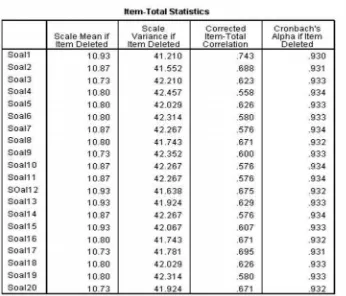
3.6 Data Collection Instruments
The instruments used for data collection are detailed, including lesson plans, observation sheets, student response questionnaires, and learning outcome assessments. This section emphasizes the importance of using diverse methods to gather comprehensive data.
3.7 Data Analysis Techniques
This subsection discusses the techniques used for analyzing the collected data, including quantitative and qualitative methods. It highlights the importance of using appropriate analysis techniques to draw meaningful conclusions from the research findings.
IV. RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This section presents the findings of the research, including the results of implementing blended learning in physics education. It discusses the improvements observed in lesson planning, teaching activities, student responses, and learning outcomes.
4.1 Research Findings
This subsection presents the key findings from the research, including improvements in lesson planning, teaching activities, and student engagement. It highlights the effectiveness of blended learning in enhancing the overall educational experience.
4.2 Discussion of Findings
The discussion section analyzes the findings in relation to the research objectives and existing literature. It explores the implications of the results for teaching practices and the potential for blended learning to transform physics education.
4.3 Limitations of the Research
This subsection acknowledges the limitations of the research, including challenges faced during implementation and potential biases in data collection. It emphasizes the need for further research to address these limitations and enhance the validity of the findings.
V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIONS
The conclusion summarizes the key findings and their implications for physics education. It emphasizes the importance of blended learning in improving student engagement and understanding of physics concepts. Suggestions for future research and practical applications of the findings are also provided.
5.1 Conclusion
This subsection summarizes the main conclusions drawn from the research, emphasizing the positive impact of blended learning on student learning outcomes in physics education. It highlights the effectiveness of integrating online and face-to-face learning.
5.2 Suggestions
The suggestions section provides recommendations for educators and policymakers on implementing blended learning strategies in physics education. It emphasizes the need for ongoing professional development and support for teachers to effectively utilize blended learning approaches.
Referensi Dokumen
- Multimedia for learning: methods and development ( Alessi, S.M., & Trollip, S.R. )
- Learning To Teach ( Arends, Richard )
- Dasar – Dasar Evaluasi Pendidikan ( Arikunto, Suharsimi )
- Media Pembelajaran ( Arsyad, Azhar )
- The Online Teaching Survival Guiding ( Boettcher, Judith, V., Conrad, Rita-Marie )