THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MOTIVATION IN LEARNING ENGLISH TOWARDS
STUDENTS’ LEARNING ACHIEVEMENT AT THE ENGLISH EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF UNIVERSITAS MUHAMMADIYAH YOGYAKARTA
A Skripsi
Submitted to the Faculty of Language Education
On a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement to Obtain the Degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan
Author:
Leny Ferayanti (20110540039)
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE EDUCATION
UNIVERSITAS MUHAMMADIYAH YOGYAKARTA
AUTHOR’S DECLARATION OF ORIGINALITY
I hereby certify that I am the sole author of this skripsi and there is no part of this skripsi has been submitted for publication.
I certify that the title of this undergraduated skripsi“The Relationship between Motivation in Learning English towards Students’ Learning
Achievement at the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah
Yogyakarta” is definitely my own work. Others opinion or findings include in this skripsi are quoted in accordance with ethical standards.
I declare that this is true copy of my skripsi, including any final revisions, as approved by my skripsi committee and the Faculty of Language Education, and the skripsi has not been submitted for a higher degree to any other University or Institution.
Yogyakarta, March 5 th, 2016
The Author,
Leny Ferayanti
DEDICATION
In the name of Allah, the most gracious, the most merciful.
I dedicate this writing for:
Mommy (Baiq Rohmatul Hayati) and Daddy (Anwar Fauzi, S.Pd), in every
disappointed, every tear, every smile, and every cheer you were always there for
me. Thank you for all the time, for prays to our lovely God Allah SWT and thank
you for everything that you have done for me. Hopefully, I can make both of them
proud, one day.
My beloved brother (Muhammad Irwan Hadi, S.Pd.T., M.M.) thank you for
supporting me to be enjoyable girl to complete the task. Also, my beloved sister
(Emy Yuliartina, S.Ei), thank you for providing me with all the energy that you
MOTTO
You are never too old to set another goal or to dream a new dream
(C. S. Lewis)
The lateness is not mean a failed because it is a process to achieve the
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Alhamdulillahirabbil’alamiin, my highest gratitude and honor goes to
Allah SWT for always guiding, strengthening and blessing me, so that I could finish my skripsi.
This skripsi would not be completed without having many supports from many people. My deep gratitude and appreciation go to Mr. Puthut Ardianto, S.Pd., M.Pd as my best supervisor who has always been willing to guide me in his fatiguing time. Thank you for your carefully reading, beneficial correction, and valuable suggestion.
I would like to thank to my Examiners, Miss Ika Wahyuni Lestari, S.Pd., M.Hum and Miss Sri Rejeki Murtingsih, S.Pd., M.Ed., Ph.D for encouraging me. I also thank to all lectures of English Education Department of Universitas
Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta for all the knowledge and experience. Thank you for providing a very nice place to learn.
My thankfulness also goes to my respondents who took their valuable time to participate in my research. For my friends, thank you for the togetherness and supports.
TABLE OF CONTENT
COVER PAGE ... i
APPROVAL SHEET ... ii
AUTHOR’S DECLARATION OF ORIGINALITY ... iii
DEDICATION ... iv
MOTTO ... v
ACKNOWLEDGMENT ... vi
TABLE OF CONTENT ... vii
LIST OF TABLES ... x
LIST OF FIGURES ... xi
LIST OF ABBREVIATION ... xii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xiii
ABSTRACT ... xiv
CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION Background of the Research ... 1
Identification of the Problem ... 3
Limitation of the Problem ... 3
Questions of the Research ... 4
Objectives of the Research ... 4
Outlines of the Research ... 6
CHAPTER TWO LITERATURE REVIEW Motivations ... 8
Definition of Motivation ... 8
Types of Motivation ... 9
Motivation in Learning English ... 11
Students’ Learning Achievement ... 12
Definition of Students’ Learning Achievement ... 12
The Measurement of Students’ Learning Achievement ... 13
The Factors Affecting Students’ Achievement ... 14
Relationship between motivation in learning English towards students’ learning achievement ... 14
Review of Related Research ... 15
Conceptual Framework ... 16
Hypothesis of the Research ... 17
CHAPTER THREE METHODOLOGY Design of the Research ... 18
Setting of the Research ... 19
Participants of the Research ... 20
Instruments of the Research ... 21
Variables of the Research ... 27
Validity and Reliability of the Instrument ... 27
Analysis of the Data ... 29
CHAPTER FOUR FINDING AND DISCUSSION
Part I: Analytical result of students’ motivation in learning English ... 32 Part II: Analytical result of the students’ learning achievement ... 34 Part III. Relationship between motivation and students’ learning achievement ... 36
Discussion ... 38
CHAPTER FIVE CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
CONCLUSION ... 41
RECOMMENDATION ... 43
LIST OF TABLE
TABLE 1.1 Adopted Questionnaire TABLE 1.2 Scale of Questionnaire TABLE 1.3 Five percentiles quartile scale
TABLE 1.4 The interpretation of GPA based on the regulation of university (policy)
TABLE 1.5 Reliability Criteria
TABLE 1.6 Validity and Reliability of instrument
TABLE 1.7 Coefficient of relationship and the interpretation TABLE 2.1 Motivation of Students
TABLE 2.2 Component of motivation items TABLE 2.3 Category of motivation
TABLE 3.1 The interpretation of GPA TABLE 3.2 Students’ learning achievement TABLE 4.1 Correlations
LIST OF FIGURE
Figure 1.1 Relationship between motivation towards students’ learning
LIST OF ABBREVIATION
L2 : Second Language
EFL : English as a Foreign Language
AMTB : Attitude Motivation Test Battery
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1 : Adopted Questionnaire
Appendix 2 : Questionnaire of Motivation in Learning English
Appendix 3 : Validity and Reliability of Questionnaire
Appendix 4 : Data of the Research
Appendix 5 : Overall Motivation of Students
Appendix 6 : Descriptive Statistics for each Questions of the Questionnaire
Appendix 7 : Description for Grade Point Average (Students’ achievement)
Appendix 8 : Overall Grade Point Average
ABSTRACT
This research aims to find students’ motivation, revealing the students’
learning achievement and investigating the relationship between motivation in
learning English towards students’ learning achievement at the English Education
Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. There were 49 students’ batch 2012 at the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta who participated in this research. There were two instruments, i.e. questionnaire and document. The questionnaire was statistically analyzed by using
the SPSS 22.0 windows. To measure the students’ learning achievement, it used
the GPA (Grade Point Average) as the document from the students at batch 2012 at the English Education Department. The Pearson product moment correlation coefficient was used to see the relationship between the two variables (motivation and learning achievement). Findings from this research showed that the
motivation in learning English of students at batch 2012 was very high and dominant for instrumental motivation and the learning achievement of students at batch 2012 is at distinction level. There was a significant relationship between
motivation in learning English and students’ learning achievement. In conclusion,
the variables of this research show that motivation in learning English has positive
relationship towards students’ learning achievement. That is why alternative
hypothesis (H1) was accepted.
Key words:Motivation, Instrumental motivation, Integrative motivation,
Chapter One
Introduction
This chapter consists of background of the research, identification of the problem, limitation of the problem, questions of the research, objectives of the research, significances of the research, and outlines of the research.
Background of the Research
Some people believe that motivation is one of the important factors that will determine the success or failure of a person in the learning process. Orio (2013) says that learners who are not motivated are more likely to fail in achieving their goals than those who are motivated. In addition, there are many different goals of language learners in learning a language. Many students learn a language as a foreign language for academic interest and also for social and culture. For instance, learning English to get better jobs, to know more what happen in the world, to communicate, and to study the culture.
language. Both of the components of motivations affect the achievement of students in learning a foreign language. High motivation makes the students possible to achieve high achievement in learning while low motivation may make the students get low achievement in the result of learning.
Motivation is very important for students to learn a foreign language to get goals of the target language. The role of motivation is very important because the motivation will measure the result of the effort of students to learning English. Motivation is significantly related to learning English as a foreign language to see how the students wish for mastering a foreign language. In university levels, particularly at the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta, where the researcher is also a student, students need motivation to learn English and to achieve goals of study.
Based on the researcher’s experience during her study, language learners also have different ability when they learn a language. For example, in a
classroom, there are students who are enthusiastic in learning English as a foreign language and seemed to have high motivation in the teaching and learning
Identification of the Problem
This research focus on the relationship between motivation in learning
English towards students’ learning achievement. There are some problems usually
found in motivation of students. The problem that is usually found is the most of students are lazy to show up their knowledge of learning English in class. The other problems such as anxiety of students, students need for achievement, need to be accepted, and curiosity of English. Language learners have different ability and different goals to learn a language. Many students are learning a language as a foreign language for academic and economic purpose and also learning English for social and culture interest. In addition, these differences will make different
motivation and students’ achievement in the learning process.
Based on the description above, this study will look at the relationship between motivation in learning English towards students’ learning achievement at batch 2012 in English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta.
Limitation of the Problem
This research discusses motivation of students to learn EFL (English as a Foreign Language) as their target language. The limitation of this research is that the researcher wants to know the relationship between motivation towards
students’ learning achievement at the English Education Department. Motivation in learning English is classified into four types (Instrumental, Integrative,
motivation). The researcher chose these components of motivation because based on Gardner’s theory, the two components of motivation categorized as the most influential motivation towards learning English.
Questions of the Research
The problems of the research can be identified in three research questions, they are:
1. How is the students’ motivation in learning English at the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta? 2. How is the students’ learning achievement at the English Education
Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta?
3. What is the relationship between motivation in learning English towards
students’ learning achievement at the English Education Department of
Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta?
Objectives of the Research
Purpose of this research is conducted to answer the research questions, they are:
1. To find out the students’ motivation in learning English at the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. 2. To reveal the students’ learning achievement at the English Education
Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta.
3. To investigate the relationship between motivation in learning English
towards students’ learning achievement at the English Education
Significances of the Research
This research will give some advantages for:
The Researcher. This research can help the researcher to enhance knowledge of the researcher in learning English as a foreign language. Also, the researcher will be able to know more motivations which have a role in making great success in the future of students.
The Students. From this research, students can enhance their knowledge so that the students will understand the role of motivation in learning English. Also, by this research, students will know that motivation has implication towards their achievements. In addition, by knowing the result of the research, students will be able to know the motivation from themselves. It will make their goals of learning becomes more focused.
Teachers. This research also will give benefits for teachers to improve
teaching technique to teach the students based on what students’ needs, the
teachers should know about the students’ objectives of the study. Hence, the
teachers not only seek the instructional design of study but also knowing the characteristic of language learners. It can help the teacher used appropriate teaching strategies.
The Institution. This research will donate a consideration to the
this research shows that the students have low motivation and low achievement, the institution has to look for the solution to improve it.
Outlines of the Research
This research contains of five chapters. Chapter One is introduction that consists of background of the research, identification of the problem, limitation of the problem, questions of the research, objectives of the research, significances of the research, and outline of the research.
Chapter Two is literature review that consists of studies about students’
motivation and the students’ learning achievement. There are several explanations related to the motivation, such as definition of motivation, type of motivation, and motivation in learning English. Meanwhile, related to the students’ learning achievement, there are also several explanations, such as students’ learning
achievement, definition of learning achievement, the measurement of students’
learning achievement, the factor affecting students’ achievement, relationship
between students’motivation and students’ learning achievement at the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. This chapter also presents the conceptual framework, the previous related research, and hypotheses.
Chapter Two
Literature Review
This chapter gives the review of some theories and previous research to
support the researcher’s opinion. Literature review consists of the studies about
students’ motivation and the students’ learning achievement.
Motivations
The independent variable of the study is motivation which is classified into two components (instrumental motivation and integrative motivation) based
on Gardner and Lambert’s (1972) theory. The motivated individual effort is
persistent and attentive to the task at hand, has goals, desires and aspiration, enjoy the activity, experiences reinforcement from success and disappointment from failure (Gardner and Margoret, 2003). The statements show that the motivation in a person will make their goals become more structured. The students will find out why they are successful or fail in learning English.
The definition of motivation. Pintrich (2003) argues that the term
motivation comes from the Latin Verba(to move), which means “driving force of person” (p. 669). The term means that the motivation is the driving force in a person to do certain things to achieve goals or self-satisfaction. The motivation of each individual will move a person to make efforts to realize a desire.
Learning motivation occurs when an individual pursues a higher level of development after basic needs are satisfied (Lee, 2010). In other hand, motivation is an effort of the students to achieve the desired learning targets with the
has a different motivation, ability, and purpose to achieve their goals particularly, in learning English as a foreign language in Indonesia.
Types of motivation. Motivation is classified into four types: instrumental, integrative, resultative, and intrinsic motivation (Ellis, 1997).
Instrumental Motivation. Ellis (1997) stated that learners may make efforts to learn an L2 for some functional reasons – to pass an examination, to get a better job, or to get a place at a university. It means, language learners who have instrumental motivation are motivated to learn English for academic and
economic interests. Instrumental motivation refers to learner’s desire to acquire a
new language for utilitarian reasons and to reflect the practical value and advantages of learning a target language (Gardner & Lambert, 1959). In other words, instrumental motivation is self-motivation that grows in language learners for specific purposes such as for economic interest, career, and academic interest. In addition, this component is important to motivate oneself to learn a foreign language because of this motivation comes from within a person learn. The desire from within oneself is to change the economic situation and for academic interest.
Integrative Motivation. Integrative motivation refers to a learner’s desire
characterized by the learner’s positive attitude towards the target language group
and the desire to integrate into the target language community. This behavior reflects that integrative motivation of a student is able to demonstrate students’ language skills among the communities. It is very influential in the spirit of the students to learn a foreign language as the target language. The researcher concludes the statement above that this component is also important to know because language learners who have integrative motivation will show more curiosity about foreign language.
Resultative Motivation. Ellis (1997) asserts that motivation is the cause of L2 achievement. Based on the statement above, motivation can influence the
students’ achievement in learning English as a foreign language. Ellis (1997)
states that resultative motivation is considered the result of learning when learners who experience success in learning may become more or in some contexts less motivated to learn. It means students with high motivation can get the good result of the study, and students with less motivated can get the low result in learning English.
Intrinsic Motivation. Ellis (1997) stated that motivation involves the
arousal and maintenance of curiosity as a result of such factors as learners’
Motivation in learning English. A large number of studies have investigated the relationship between motivation and English as a foreign
language. Gardner (1985) defined second language motivation as the combination of effort plus desire to achieve the goal of learning the language. It means that the motivation has a very important role in learning English. In addition, students need motivation as driving them to achieve what their goals for learning English.
According to Gardner and Lambert (1972), there are two kinds of motivation: integrative motivation, referring to a holistic learning approach toward the speech and culture of the target language group, and instrumental motivation, referring to language learning for more immediate or practical goals. Despite that fact that both types of motivation are vital factors to success in
learning a second or foreign language, much debate among researchers has been focused on which kind of motivation is more significant for L2 learners (Dornyei, 2001). Integrative motivation was viewed as superior to instrumental motivation for predicting the success of L2 learning (Gass and Selinker, 2001).
The conclusion of the statements above is the researcher chooses two
Students’ Learning Achievement
The dependent variable of the study is learning achievement of students at the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta.
The students’ learning achievement will represent the high and low achievement
in learning English as a foreign language.
Definition of learning achievement. Learning achievement is about how successful the learner can master the materials of the learning object. Hsiang (2013) stated that learning achievement is the result of students’ learning to see how far their abilities during the process of teaching and learning in their study.
Students’ learning achievement is a result of students during the learning process
of students to get the target language in university level. In addition, students’ learning achievement is how far the students learn a foreign language to achieve the personal target to get great or mark achieved. Choosri (2011) says that the result of study may also provide useful guidelines for teachers concerned with developing English language motivation. Learning achievement in this study is divided into two levels, i.e. there are students with high achievement and low achievement.
learning. This happens because the students are motivated to achieve the goals of each individual to learn a language.
Marsh (2008) argues that students with low achievement motivation have feelings of inadequacy and are not willing to stick at a task until it is completed satisfactorily.Students with low achievement levels have problems on the
motivation of each individual. In addition, these motivational effects on students’
achievement that are found students with low achievement motivation levels do not provide maximum ability in their learning.
The measurement of students’ learning achievement. Winkel (1996) found that learning achievement is a proof of success in the process of learning that is measured by a grade or mark that is achieved. In addition, based on academic book of English Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah
Yogyakarta, the institution assesses students’ achievement by grade point average
(GPA). Although GPA is not a perfect measurement of a student’s achievement
and learning, it is the most widely used measure (Pascarella & Terenzini, 2005).
While, Chatriand (2012) stated that grade point average is useful because it provides a quantitative summary of each semester for a student as well as an
overall calculation of the student’s performance in all of her or his classes. Thus,
Grade point Average is the average grade attained by dividing the total of quality points earned by the total of quality hours for courses (Robert, 2003). On the other
hand, students’ learning achievement is grade of students to know how far their
target language. For these reasons, GPA was used as a measurement for student achievement for this research.
The factors affecting students’ achievement. Marsh (2008) stated that
students’ motivation is various and complex and is interrelated with many other factors such as anxiety, need for achievement, need to be accepted, and curiosity. For example, Anxiety of students on their achievement, learning English to get good result, need to be accepted in university, and curiosity of students to learn a language as a foreign language.
According to Yu-mei (2009), motivation is one of several important
factors that may influence students’ English achievement. Learners’ motivation
has been widely accepted as a key factor which influences the rate and success of second/foreign language (Ellis, 1994; Mcdonough, 1983). The researcher
concluded the statements above that motivation has a very important role in determining the success of the students in learning English.
Relationship between motivation in learning English toward student’s
learning achievement
This research focused on relationship between students’ motivation
towards students’ learning achievement at the English Education Department of
Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. The foundation of this research is based
on Gardner and Lambert’s theory about language learners. Tenaw (2013)
mentioned that there are many psychological factors that influence learning achievement, such as attitude, motivation, aptitude, and self-efficiency. Choosri
learning achievement. This research gives the significant study for the researcher
and teacher to improve students’ achievement and develop students’ motivation.
Hsiang (2013) mentioned that learning achievement or EFL are affected by learning motivation. The research discusses about learning motivation is a result of reinforcement and enabling students to obtain achievement is the key to improving students learning achievement in learning process.
Review of Related Research
The researcher found two journals that reveal the relationship between motivation and students learning achievement. These journals are related to this research to support this study based on Gardner and Lambert. The first journal is
entitled “Relationship between Motivation and Students’ English Learning
Achievement: A study of the second-year vocational certificate level Hatyai
Technical College Students” by Chalermporn Choosri & Usa Intharaksa in 2011.
In this journal, there is more impact of motivation towards students’ learning
achievement. This research classified the motivation of students into two parts: instrumental motivation and integrative motivation. The results of this research show the positive relationship between motivation and learning achievement.
The second journal is entitled “The Relationship of Learning Motivation
motivation and previous learning experiences and there are some differences on
gender for students’ learning motivations.
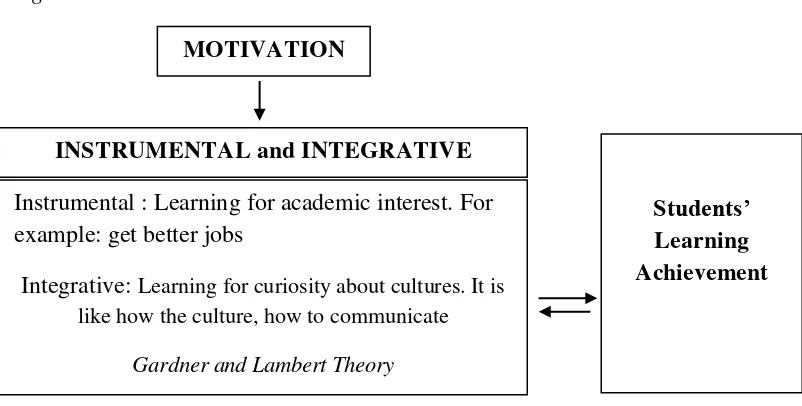
Conceptual Framework
Figure 1.1 Relationship between motivation in learning English towards students’ learning achievement
Based on the conceptual framework above, students’ motivation is one of
factors that can influence the students’ achievement in learning English. The
motivation includes instrumental motivation and integrative motivation. Each motivation has different goals in language learning. Students who have
instrumental motivation have goals to learn language for academic interest, to get better jobs. Students who have integrative motivation have goals in learning language to know how the culture and how to communicate with people using that language. Instrumental and integrative motivations have different goals, but in university levels, there is mark or result of students learning. From this concept, we know that the component motivation has either high achievement or low achievement in learning process.
MOTIVATION
INSTRUMENTAL and INTEGRATIVE
Instrumental : Learning for academic interest. For example: get better jobs
Integrative: Learning for curiosity about cultures. It is like how the culture, how to communicate
Gardner and Lambert Theory
Students’
Hypothesis of the Research
Alternative hypothesis (H1): There is a significant relationship between motivation in Learning English towards students’ learning achievement at the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta
Chapter Three
Methodology
This chapter presents the methodology of this research. This chapter contains the design of the research, setting of the research, participants of the research (population and sample of the research), technique of data collection, instruments of the research (document and questionnaire), variable of the research (independent and dependent variable), validity and reliability of the instrument, and analysis of the data.
Design of the Research
Research design was a plan of the researcher to collect data and analyze the data to be feasible data. In using research design, the researcher made data become valid and reliable. It could make feasible data for research for the
researcher. Research design helped the researcher collect data that the researcher would analyze. Quantitative research as a method based on the philosophy of positivism; Method is used to examine the specific populations or samples; the sampling technique is usually done by calculating the specific sampling
Setting of the Research
The location of this research was at the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. There were two reasons why the research was conducted at the English Education Department. The first reason was because motivation topic taught under LLA (Language Learning & Acquisition) at the English Education Department. Specifically was the EFL (English as a Foreign Language) course at the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. English Department motivated students to learn English as a foreign language by showing how to teach, how to learn and interact with other people. For example, teachers shared the experience in English, how to get better jobs, and soft-skill programs in every semester. Hence, the researcher was interested to find out the relationship between motivation in
learning English towards students’ learning achievement.
The second reason was the accessibility. The researcher took this place as the setting of the research because the researcher was also studying at the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. Setting of the research was actually to facilitate the researcher to investigate the relationship
between motivation in learning English and learning achievement in students’
Participants of the Research
Population of the research. Population was the generalization consisting of the object or subject that has certain qualities and characteristics that are
applied by researchers to learn and then draw the conclusion (Sugiono, 2011). The population of this research was the students at batch 2012 at the English
Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. Students at batch 2012 were divided into three classes (class A, B, C). The total numbers of students at batch 2012 were 97 students. The researcher got the total number of students from the administration staff that was also approved by the head of the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta.
Sample of the research. Sample was taken as part of the overall object studied and considered to represent the entire population (Notoadmodjo, 2010). Sample size in this study was determined based on the formula of Notoadmodjo as follows:
) )
Explain:
n = Large sample N = Large Population
d = Level of confidence/accuracy desired (0.1)
)
Based on the formula of Notoadmodjo above, and referring to some previous research, the researcher took 49 respondents as the number of sample.
Sampling method in this research was using a non-probability sampling. It was a sampling technique that did not provide opportunities or equal opportunity for each element or member of the population to be selected into the sample (Sugiono, 2011). The researcher took students at batch 2012 because they had already passed at least seven semesters at the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. It meant that their result of learning was visible and suitable; this was supposed to make the data collected by researchers valid and reliable.
Instrument of the Research
The research instrument was a tool used to measure the natural and social phenomena observed (Sugiono, 2011). The researcher used a questionnaire as the
research instrument to measure the students’ motivation. In addition, the
researcher also used document to measure students’ learning achievement at the
English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. The researcher applied the two instruments in this research. The first instrument was the questionnaire to collect the data. This instrument made the researcher know how the motivation of students batch 2012. The second
Questionnaire. Questionnaire was the supportive instrument to gain the information which was related to the perception, opinion, and expectation or other resembles things (Creswell, 2012). The questionnaire of this research was a survey of different opinions from the people. The questionnaire was actually using anonymous replies; it helped the researcher to collect data from large number of people.
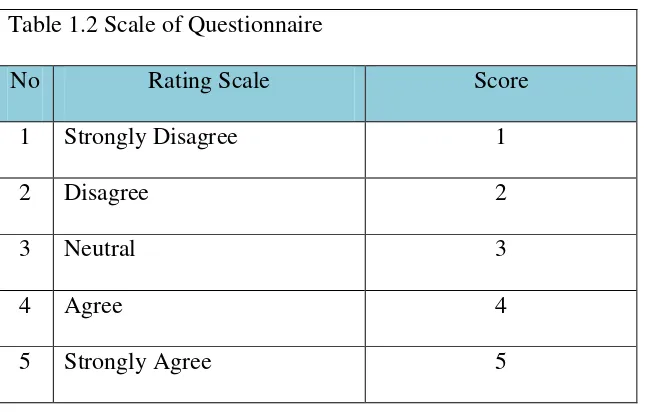
All the items except the background questionnaire items was placed on a 5-point Likert scale ranging from “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree”. Sanusi (2011) said, Likert Scale was a scale which was based on amount of respondents to respond to the statements relating to the variable that was being measured.
The researcher did measure the motivation using the international (AMTB) The Attitude Motivation Test Battery. The total questions of the
international AMTB are 116 questions about attitude and motivation. According to Gardner (1985), the AMTB was designed to assess the non-linguistic goals of second language program. He claimed that emphasize aspect as improved understanding of the other community, desire to continue studying the language, and interest in learning other languages and AMTB was reported to have good reliability and validity. In this research, the researcher uses the international manual AMTB to measure the students’ motivation because this manual AMTB was classify the questions into each category. In addition, the category of the international manual AMTB includes the attitude, interest, integrative,
motivation towards learning achievement. The questionnaire were administered in the mother tongue along with the English original. The questionnaire items were translated into Indonesian and being proofread by a translator to make the participant clearly understand each question.
Table 1.1 Adopted Questionnaire
No
Integrative Motivation
Theory Statement
1 Integrative motivation refers to
a learner’s desire to learn more
about culture community of the target language or to assimilate in the target community
(Gardner & Lambert, 1959).
Q1. Studying English can be important to me because it will allow me to be more at ease with other people who speak English
Q2. Studying English can be important for me because it will allow me to meet and converse with more and varied people
Q3. Studying English can be important for me because it will enable me to better understand and appreciate English art and literature
Q4. Studying English can be important for me because I will be able to
No
Instrumental Motivation
Theory Statement
2 Instrumental motivation refers
to learner’s desire to acquire a new language for utilitarian reasons and to reflect the practical value and advantages of learning a target language (Gardner & Lambert, 1959).
Q5. Studying English can be important
for me because I’ll need it for my
future career
Q6. Studying English can be important for me because it will make me a more knowledge person
Q7. Studying English can be important to me because I think it will someday be useful in getting a good job
Q8. Studying English can be important for me because other people will respect me more if I have knowledge of a foreign language
The researcher used following scale to give the questionnaire a score from 1 to 5 for each of the questions.
Table 1.2 Scale of Questionnaire
No Rating Scale Score
1 Strongly Disagree 1
2 Disagree 2
3 Neutral 3
4 Agree 4
5 Strongly Agree 5
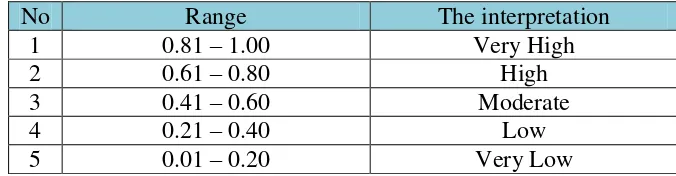
Based on five percentiles quartile scale in the SPSS, the range of the interpretation motivation in learning English is as follow:
Table 1.3 Five percentiles quartile scale
No Range The interpretation
1 0.81 – 1.00 Very High
2 0.61 – 0.80 High
3 0.41 – 0.60 Moderate
4 0.21 – 0.40 Low
Document. Cohen et al (2011) had found that a document can be defined concisely as a record of an occurrence, an incident or process. Documentation was a method to obtain data using note/transcript to gain the theories related to the research. In documentation, there were books, magazine, document of students’
scores, and school’s notes (Arikunto, 2013). In this research, the researcher used
the GPA (Grade Point Average) as the document from the students at batch 2012 at the English Education Department. The researcher had gotten the permission using the permission letter from administration staff that was also approved by the head of the English Department.
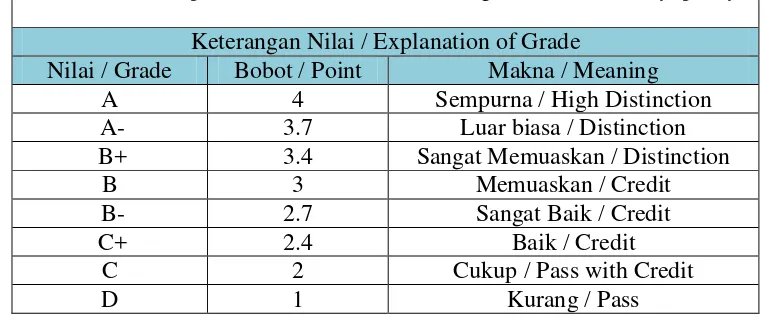
Table 1.4 The interpretation of GPA based on the regulation of university (policy)
Keterangan Nilai / Explanation of Grade
Nilai / Grade Bobot / Point Makna / Meaning
Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. Third, the researcher explained how to answer the questionnaire. Fourth, the researcher gathered the data from respondents. The next step, the researcher asked permission letters to administration staff that had been approved by the head of the English Department for document school scores or GPA of students at batch 2012.
Variables of the Research
According to Cohen et al (2011), “A variable is a condition, factor or quality that, as its name propose, can vary from one case to another case; it is the
reverse of a constant, which does not diverge between cases” (p. 606). In this
research, there were two variables that were going to be correlated. The variables included the independent variable and dependent variable.
Independent Variable (x). Cohen et al, (2011) found that a independent variable was an input variable, which caused, in part or in total, a particular result; it was a stimulus that affects response, an antecedent or a factor that may be modified (e.g. under experimental or the other situations) to influence a results (p.
607). The independent variable of this research is the students’ motivation
because students’ motivation can influence the students’ learning achievement.
Dependent Variable (y). Cohen at el (2011) found that a dependent variable is the result variable, which is caused, in total or in part, by the input, antecedent variable. It is the consequence, the influence of, or response to, an independent variable (p. 607). The dependent variable of this research was
students’ learning achievement because learning achievement was the effect of
Validity and Reliability of the Instrument
Validity. Validity was the degree to which all of the evidence points to the intended interpretation of the test scores for proposed purpose (Creswell, 2012). Test the validity of the data item was a test instrument to determine how close an item in measuring what to be measured. Item could be said valid if it had
significant correlation with the total score. The test of validity that was used by the researcher was correlation or skewness/kurtosis and KMO and Bartlett's Test using SPSS version 22.0. This test was to identify the validity of the instrument used to measure the variable of indicator of this research. An instrument could be said valid if the data of variable was able to measure what the researcher want from research. Since the questionnaire was taken from the previous research, the instrument of the researcher was valid.
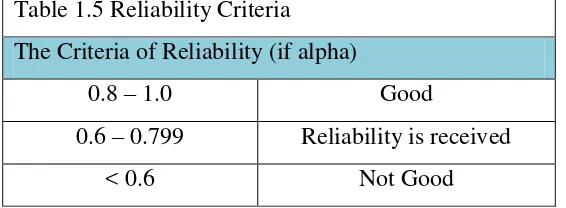
Reliability. Sekaran (2006) stated that a research instrument was indicated adequately reliable if the cronbach alpha coefficient is greater than or equal to 0.60. Reliable measurements showed consistency, meaning that repeated measurement would get the same result.
Meanwhile, Sekaran (2000) decided the three levels of reliability indicator are as follow:
Table 1.5 Reliability Criteria
The Criteria of Reliability (if alpha)
0.8 – 1.0 Good
0.6 – 0.799 Reliability is received
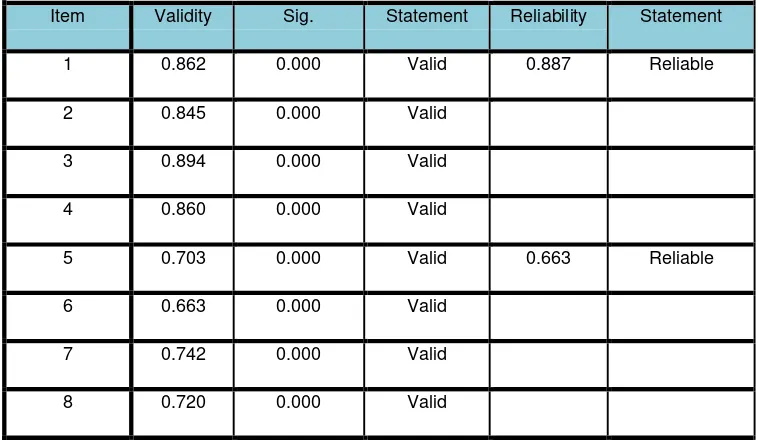
Table 1.6 Validity and Reliability of instrument
Item Validity Sig. Statement Reliability Statement
1 0.862 0.000 Valid 0.887 Reliable
The researcher used SPSS software as the tool to analyze the data
collected from respondents. The data analysis included: descriptive statistics and Pearson product moment correlation coefficient. The purpose of this research was to find out the relationship between motivation in learning English towards
students’ learning achievement. Therefore, the researcher analyzed the data using
descriptive statistic. The first question was “How is the students’ motivation in
learning English at the English Education Department of Universitas
Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta?” second question was “How is the students’
learning achievement at the English Education Department of Universitas
Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta?”
The first and second research questions were analyzed using descriptive
general tendencies in the data (mean, minimum, maximum), the spread of scores
(variance, and range)” (p.182). The data was directly taken from the data source
and the data was analyzed using SPSS (statistical package for the social science) version 22.0 for windows.
The correlation technique was using by the Pearson product moment
correlation coefficient for relationship between motivation and students’ learning
achievement. According to Wikipedia, “Pearson product moment correlation coefficient is a measure of the linear correlation between two variables X and Y,
giving a value between +1 and -1 inclusive, where 1 is total positive correlation, 0
is no correlation and -1 is total negative correlation”, it was developed by Karl Pearson.
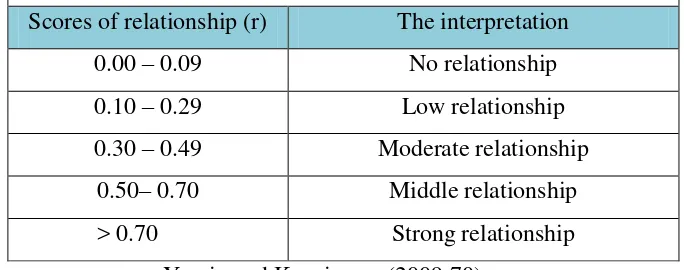
Table 1.7 Coefficient of relationship and the interpretation Scores of relationship (r) The interpretation
0.00 – 0.09 No relationship
0.10 – 0.29 Low relationship
0.30 – 0.49 Moderate relationship 0.50– 0.70 Middle relationship
> 0.70 Strong relationship
Chapter Four
Findings and Discussion
In this chapter, the researcher presents the finding and discussion of the research. The findings answered the research questions proposed in this research. The researcher reports the findings of the research obtained from the analysis and discussion of the result of this research. The findings are presented in the
following sections:
Findings
This part deals with several findings related to the statistical analysis. The findings were obtained from questionnaire and the data documents reporting of the students’ learning achievement. This part presents the data of questionnaire
motivation towards students’ learning achievement at the English Education
Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta.
The first data was collected by questionnaire from the students of batch 2012 at the English Education Department. The second data came from the
students’ learning achievement at the English Education Department of
Analytical result of students’ motivation in learning English. Based on the results of testing instruments, integrative and instrumental motivation
variables has a value of significance (2-tiled) is smaller than the value of α by 5 percent. It can be concluded that the entire instrument statement of integrative and instrumental variables used are valid and can be used in the research. The results of reliability test shows that Cronbach Alpha of the integrative and instrumental motivation variable is greater than 0.6. Thus it can be stated all the statements of instrument used in this research met the criteria of reliability as a tool of collecting data.
To answer the research question on “How is the students’ motivation in
learning English at the English Education Department of Universitas
Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta?” The researcher used the result of tabulating the
gain scores of the students’ motivation. The result is presented in the following
table:
Table 2.1 Motivation of Students
Mean Minimum Maximum Range
Maximum /
Minimum Variance Item
Means
The total number of respondents was 49 respondents. The data were obtained using a scale of motivation which consists of 8 items. The research measured two components of motivation, integrative and instrumental motivation.
Table 2.2 Component of motivation items
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Q6 Q7 Q8 IPK
N Valid 49 49 49 49 49 49 49 49 49
Missing 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Mean 4.94 4.61 3.98 3.71 4.80 4.43 4.96 4.04 3.3892
Sum 242 226 195 182 235 217 243 198 166.07
Firstly, Integrative motivation includes studying English to be more at ease with other people who speak English (4.94%), to meet and converse with more and varied people (4.61%), to better understand and appreciate English art and literature (3.98%), to participate more freely in the activities of other cultural groups (3.71%). Second, Instrumental motivation include studying English for the future career (4.80%), for make a person more knowledge (4.43%), for getting a good job (4.96%), to make other people will respect if have knowledge of a foreign language (4.04%). The total scores for integrative motivation and
instrumental motivation was 17.24% and 18.23%. It means that the motivation of students at batch 2012 dominant for instrumental motivation.
The table 2.1 shows that the mean scores of students’ motivation were
4.443. The total scores of students’ motivation were divided by the 5 Likert scale
of instrument’s motivation, which is 4.443 divided by 5 equals 0.88. In addition,
division of the mean of motivation and the maximum score, which equal to 0.88. Based on five percentiles quartile scale in the SPSS, the range of the interpretation is as follow:
Table 2.3 Category of Motivation
No Range The interpretation
1 0.81 – 1.00 Very High
2 0.61 – 0.80 High
3 0.41 – 0.60 Moderate
4 0.21 – 0.40 Low
5 0.01 – 0.20 Very Low
The five percentiles quartile scales in the SPSS are useful for giving the relative standing of an individual in a group. Percentiles are essentially
normalized rank between 80% of the lower scores and 20% of the highest score, from very high interpretation until very low interpretation.
The descriptive statistic above showed that the mean scores of overall motivation of students at batch 2012 are 0.88. In other word, it can be said that the motivation of students in learning English at the English Education
Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta is very high motivation and the dominant motivation of students at batch 2012 was instrumental
motivation.
Analytical result of the students’ learning achievement. To answer the
research question on “How is the students’ learning achievement at the English
Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta?” The
by the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. In this research, a measurement of the learning achievement used the grade point average (GPA) of students at batch 2012.
Table 3.1 The interpretation of GPA
Keterangan Nilai / Explanation of Grade
Nilai / Grade Bobot / Point Makna / Meaning
Based on the regulation of university on the table 3.1, it can be seen the learning achievement of students at batch 2012 in the following table:
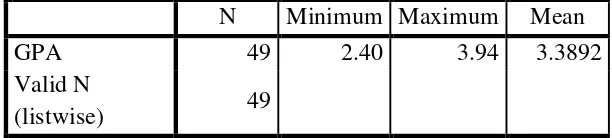
Table 3.2 Students’ learning achievement
N Minimum Maximum Mean
GPA 49 2.40 3.94 3.3892
Valid N
(listwise) 49
The majority of respondents had a very good achievement. This is reflected in the GPA of students who reached the maximum scores 3.94 and
minimum scores were 2.40. The mean scores of students’ learning achievement
Relationship between motivation and students’ learning achievement.
To answer the research question on “What is the relationship between motivation in learning English towards students’ learning achievement at the English
Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta?” The purpose
of the analysis was to determine the relationship of integrative and instrumental
motivation on students’ learning achievement at students’ batch 2012. The results
of analysis using SPSS to the scores of the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient analysis to test the hypothesis presented in the following table.
Table 4.1 Correlations
Based on the result of relationship on the table 4.1, it can be seen there are
two variables i.e. motivation and students’ learning achievement. The Pearson’s
for the relationship between motivation and students’ learning achievement
variable is 0.140. The coefficient result between motivation and students’ learning
Table 4.2 interpretation of relationship
Scores of relationship (r) The interpretation
0.00 – 0.09 No relationship
0.10 – 0.29 Low relationship
0.30 – 0.49 Moderate relationship 0.50– 0.70 Middle relationship
> 0.70 Strong relationship
Yamin and Kurniawan (2009:70)
It means that there is strong relationship between two variables in this research. The first variable has strong relationship between the second variable.
On the table 4.2, Pearson’s correlation is 0.140 so, the researcher concluded that
there is a strong relationship between motivation and students’ learning
achievement at the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta.
Motivation and students’ learning achievement have Pearson scores
positive (+) so, if the motivation of students increases, the students’ learning achievement also increases in value. Similarly, if the motivation of students
decreases, the students’ learning achievement also decreases in value. Pearson
Discussion
The second part presents the discussion of the research which gave the additional information that is related to the findings. This part discusses the interpretation and analysis of the statistic as demonstrated in the findings section in order to answer the research question. This research identified several
significant results.
Motivation. The researcher gathered the data of motivation in learning English from the questionnaire. The data that were analyzed were used to identify
the students’ motivation. To reveal the motivation of students’ batch 2012 at the
English Education Department, the researcher used the mean scores to know the category of motivation which can be seen on table 2.3.
The findings of this research showed that the mean score of the overall motivation was 0.88. So, based on the result of the data analysis above, the researcher can conclude that the motivation of students at batch 2012 at the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta is very high motivation. The participants mentioned that they have studied English for
getting a good job. So, the students’ motivation in learning English is dominated
by the instrumental motivation than integrative motivation.
In conclusion, motivation is important to be success in learning English. It
is supported from Gardner’s theory (1985), he claimed that two components of
in teaching and learning process at the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta will explained in discussion bellow.
Students’ Learning Achievement. The report of table 3.2 shows that the grade point average (GPA) of students at batch 2012 is in distinction level. In fact, there are more students who are in distinction level in learning English as a
foreign language. In addition, the majority of students at the English Education Department had GPA between 2.40–3.94. The mean score of students’ learning achievement was 3.4. The researcher categorized the students’ learning
achievement based on the regulation of the university, which can be seen on table 3.1.
Based on the categories of students’ achievement on table 3.1, the result of
the analysis for students’ learning achievement is in distinction level. In addition, when students have motivation in learning English, it will be the force of students to get the purpose of students to learn will structure. McMillian (2010) found that when students focus on improvement and progress, they are more likely to adopt the mastery goals and develop high self-efficacy and expectations for success. It
means the students’ motivation as a driving force of students to get good result in
The relationship between motivation in learning English towards
students’ learning achievement. The data analysis revealed that there is a strong and significant relationship between motivation in learning English towards
students’ learning achievement. Based on table 4.1, it shows that the two
components of motivation here have positive relationship towards students’
learning achievement because the score of the SPSS analysis has positive sign (+) on the table. The fact shows that students who got a high grade point average (GPA) in English course for the individual reasons. Individual reasons here mean students focus on improvement English based on the purpose of students to learning English. The researcher can conclude that the motivation of students at batch 2012 shows very high level of motivaton in learning English as a foreign language. In addition, the final result of students at batch 2012 at the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta is distinction level. Finally, there is a strong and significant relationship between motivation in
learning English towards students’ learning achievement.
In this study, based on the findings, the hypothesis was answered. Alternative hypothesis (H1) that stated that there was significant relationship
between motivation in learning English towards students’ learning achievement at
the English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta was accepted. Contrary, null hypothesis (H0) that stated that there was no
significant relationship between motivation towards students’ learning
Chapter Five
Conclusion and Recommendation
The last chapter of this research report is conclusion and recommendation. This chapter is divided into two sections consisting of conclusion and
recommendations. The conclusion presents the summary of this research. Then, the second section presents several recommendations for the institution, for students, for teacher and for other researchers.
Conclusion
Generally, this study revealed three points that answered the first, second and the third research questions. They are the students’ motivation in learning
English, the students’ learning achievement, and the relationship between
motivation in learning English towards students’ learning achievement at the
English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. The research focused on two components of motivation i.e. instrumental motivation and integrative motivation. These components are based on the purpose of
students in learning English, for utilitarian reasons or curiosity of students to learn English for social and culture. The research discusses about the motivation in
learning English and students learning achievement of students’ batch 2012 at the
English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. The Pearson product moment coefficient correlation ware use to analysis the
relationship between two variables here (Motivation in learning English and
The first thing that is exposed is the motivation in learning English of students at batch 2012 was very high motivation. Regarding to the components of motivation on the questionnaire, students at batch 2012 were more motivated by instrumental motivation than by integrative motivation. All of the students mentioned that English is very important for their future.
Second thing, the descriptive analysis result shows that most of the
students’ achievement is in the highest level. The researcher found the minimum
score of students’ achievement is 2.40 and the maximum score is 3.94. The
students have a score in a distinction level because the mean score of students learning achievement is 3.4. The criteria score is based on level score at
Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. It shows that the students’ learning
achievement of students at batch 2012 at English Education Department in an distinction level.
The final achievement of students at batch 2012 is highest achievement
because the mean scores of student’s GPA who has distinction level in learning
English. The result shows that there is significant relationship between motivation
towards students’ learning achievement. It means that the hypothesis H1 is partly
true. The integrative and instrumental motivation has positive significant
relationship between students’ learning achievement. The score of positive significant relationship is 0.140, the data did not put negative sign to the result, it can be called the independent and dependent variables have positive relationship.
Recommendation
The relationship between motivation in learning English and students’ learning achievement there is significant relationship. Two components of
motivation here have positive significant relationship towards students’ learning
achievement. In addition, this research can give some suggestion to students, teachers, the institution and other researchers. The suggestions are as follow:
For students. The students should become self-motivated independent learners. Motivation will lead the students to be successful in learning English. Besides that, the students can be more motivated in learning English and also can
improve their students’ learning achievement.
For teachers. English teacher should apply effective teaching and learning
strategies to develop students’ motivation. This research encourages the lecturers
to provide the appropriate method in order to understand the characteristic of students, it can make the teaching and learning process is successful.
For the institution. The English Education Department should enhance
the students’ motivation for the better and effective perception in language
For other researchers. The researcher realized that this research is far from being perfect. Therefore, the researcher suggests to other researchers who
will conduct the similar research “The relationship between motivation in learning
English towards students’learning achievement” to increase the students’
REFERENCES
Arikunto, S. (2013). Prosedur Penelitian. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta
Chatriand, C. M. (2012). The effect of selected campus connection programs on GP A and retention. Graduate College.
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2011). Research Methodology Education 7th edition. Roudledge
Creswell, J. W. (2012). Educational Research. Boston: Pearson Education
Dornyei, Z. (2001). Teaching and researching motivation. Longman: New York.
Ellis, R. (1997). Second Language Acquisition. New York: Oxford University Press.
Masgoret, A.M. and Gardner, R. C. (2003, March). Attitudes, Motivation, and Second Language Learning: A Meta-Analysis of Studies Conducted by Gardner and Associates. Language Learning.
Gardner, R.C. (2004). Attitude/Motivation Test Battery: International AMTB Research Project (English Version). The University of Western Ontario, Canada.
Gardner, R. C., & Lambert, W. E. (1959). Motivational variables in second language acquisition. canadian Journal of Psychology, 13, 266-272.
Gardner, R. C. (1985). Social psychology and second language learning: the role of attitudes and motivation: Baltimore, Maryland: Edward Arnold.
Gass, S., and Selinker, L. (2001). Second language acquisition: An introductory course. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Hadavi, Z. H. (2014, September 01). Exploring the roles of integrative and instrumental motivation on English language acquisition among Iranian medical and dentistry students. International Journal of Language and Linguistics.
Hsiang-Yung Feng, J.-J. F.-Z. (2013). The Relationship of Learning Motivation and Achievement in EFL: Gender as an Intermediated Variable. Educational Research International, 2.
Intharaksa, C. C. (2011, April 2). “Relationship between Motivation and Students’
English Learning Achievement: A study of the second-year vocational certificate
level Hatyai Technical College Students”. The 3rd International Conference on
Humanities and Social Sciences.
Lee, I.-C. (2010, December). The Effect of Learning Motivation, Total Quality Teaching and peer assisted Learning on Study Achievement: Empirical Analysis from Vocational Universities or Collages' Students in Taiwan. The Journal of Human Resource and Adult Learning.
McDonough, S. (1983). Psychology in foreign language teaching. George Allen & Unwin: London.
Notoadmodjo, Soekidjo. (2010). Metodologi Penelitian Kesehatan. Jakarta: P.T Rineka Cipta
Orio, S. F. (2013). Motivation and Second Language Acquisition. Universidad De La Rioja
Pintrich, P. P. (2003). A Motivational Science Perspective on the Role of Student Motivation in Learning and Teaching Contexts. Journal of Educational
Psychology, 3.
Pascarella, E. T., & Terenzini, P. T. (2005). How college affects students: A third decade of research (Vol. 2). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Pui-Wa L., Dina., Matthew B. (2001). Alternatives to the Grade Point Average as a Measure of Academic Achievement in College. ACT Research Report .
Sekaran, Uma (2006). Research Methods for Business, Buku 2, Edisi 4, Penerbit Salemba Empat, Jakarta
Salvia, J., Yssldyke, J. E., & Bolt, S. (2007). Assessment (10 edition). Houghton Mifflin
Sugiyono. (2011). Metode penelitian pendidikan kuantitatif kualitatif R & D. Bandung: Alfabeta
Tenaw, Y. A. (2013). Relationship between self-efficiency, academic, genders in analytical chemistry at Debre Markos Collefe of teacher education. AJCE, 3-28.
Weisberg, S. (2005). Applied linier regression. Canada: Wiley interscience.
Winkel, W. S. (1996). Psikologi Pengajaran. Jakarta: PT Gramedia TESOL Quarterly 21 (1), 1987, pp. 87-111.
Yu-mei, L. (2009). On motivation and college English learning: Sino-US English Teaching, 6, 57-65
learner’s desire to learn more about
culture community of the target
language or to assimilate in the target
community (Gardner & Lambert, 1959).
because it will allow me to be more at ease
with other people who speak English
Q2. Studying English can be important for me
because it will allow me to meet and converse
with more and varied people
Q3. Studying English can be important for me
because it will enable me to better understand
and appreciate English art and literature
Q4. Studying English can be important for me
because I will be able to participate more freely
in the activities of other cultural groups
No
Instrumental Motivation
Theory Statement
2 Instrumental motivation refers to
learner’s desire to acquire a new
language for utilitarian reasons and to
reflect the practical value and
advantages of learning a target
language (Gardner & Lambert, 1959).
Q5. Studying English can be important for me
because I’ll need it for my future career
Q6. Studying English can be important for me
because it will make me a more knowledge
person
Q7. Studying English can be important to me
because I think it will someday be useful in
getting a good job
Q8. Studying English can be important for me
because other people will respect me more if I
Kuesioner
Petunjuk Pengisian:
1. Kuesioner ini bertujuan untuk memperoleh data yang sesuai dengan penelitian “Hubungan
antara motivasi belajar bahasa Inggris terhadap hasil belajar siswa di Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta”
2. Bacalah petunjuk secara seksama sebelum mengisi kuesioner ini
3. Isilah kolom di bawah ini dengan dengan memberikan tanda (x) pada kolom pilihan jawaban. 4. Terima kasih atas kerjasama dan kesediaan Anda untuk mengisi kuesioner ini
5. Identitas Responden
Nama : NIM Responden :
1 = Sangat tidak Setuju 3 = Netral 5 = Sangat Setuju
2 = Tidak Setuju 4 = Setuju
NO Pertanyaan 1 2 3 4 5
1 Belajar bahasa Inggris penting untuk saya karena memudahkan saya berbicara dengan orang yang menggunakan bahasa Inggris
Studying English can be important to me because it will allow me to be more at ease with other people who speak English
2 Belajar bahasa Inggris penting untuk bertemu dan bercakap-cakap dengan berbagai macam orang
Studying English can be important for me because it will allow me to meet and converse with more and varied people
3 Belajar bahasa Inggris penting untuk lebih memahami dan menghargai seni dan sastra bahasa Inggris
Studying English can be important for me because it will enable me to better understand and appreciate English art and literature
4 Belajar bahasa Inggris penting untuk lebih ikut serta dalam kegiatan keompok budaya lain
6 Belajar bahasa Inggris penting untuk saya agar menjadi orang yang lebih berwawasan
Studying English can be important for me because it will make me a more knowledge person
7 Belajar bahasa Inggris penting untuk saya karena suatu saat bahasa Inggris berguna dalam mencari pekerjaan
Studying English can be important to me because I think it will someday be useful in getting a good job
8 Belajar bahasa Inggris penting untuk saya karena orang lain akan lebih menghargai saya jika saya bisa berbahasa Inggris
Studying English can be important for me because other people will respect me more if I have knowledge of a foreign language
Appendix 3 : Validity and Reliability of Questionnaire
Item Validity Sig. Statement Reliability Statement