Informasi Dokumen
- Penulis:
- Diana Hermawati
- Pengajar:
- Mirnawati Sudarwanto, PTS
- Soewarno T. Soekarto
- Fransiska R. Zakaria
- Sofjan Sudardjat
- Fadjar Sumping Tjatur Rasa
- Sekolah: Sekolah Pascasarjana, Institut Pertanian Bogor
- Mata Pelajaran: Sains Veteriner
- Topik: Kajian Aktivitas dan Karakterisasi Senyawa Antimikroba dari Susu Kuda Sumbawa
- Tipe: Disertasi
- Tahun: 2005
- Kota: Bogor
Ringkasan Dokumen
I. Introduction
This section provides the background of the study, focusing on the unique properties of Sumbawa mare's milk, its purported medicinal uses, and the lack of scientific research to support these claims. The introduction highlights the discrepancies in public perception and scientific understanding, setting the stage for the research objectives. It emphasizes the need for a comprehensive study investigating the antimicrobial properties of the milk, addressing the knowledge gap regarding its preservation and potential applications. The study's potential impact on local economies and the wider scientific community is also discussed, positioning the research within a broader context of socio-economic and academic relevance.
1.1 Background
The background delves into the traditional use of mare's milk, particularly in Eastern Europe and Asia, as both a daily beverage and a therapeutic agent. The introduction of Sumbawa mare’s milk, its unique characteristic of remaining unspoiled for extended periods at room temperature, and its subsequent commercialization as a purported cure-all are examined. This section emphasizes the contrast between anecdotal evidence and the lack of scientific validation for its purported medicinal properties. It sets the context for a scientifically rigorous investigation into the composition and antimicrobial activity of Sumbawa mare’s milk, highlighting the importance of bridging the gap between folklore and evidence-based knowledge.
1.2 Research Objectives
This subsection clearly outlines the specific aims of the research. The objectives encompass both field observations of mare's milk production practices in Sumbawa and detailed laboratory analyses to identify and characterize antimicrobial compounds. The objectives are multi-faceted, including verifying antimicrobial activity, investigating the influence of heating and storage, determining the spectrum of antimicrobial activity, identifying the polarity characteristics, and culminating in the isolation, identification, and characterization of the active compounds. This structured approach to investigation is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of the phenomenon and demonstrates a robust research design.
1.3 Benefits of the Research
This section highlights the potential applications and broader impact of the research. The benefits extend beyond the purely scientific realm, encompassing potential economic gains for local communities through the development of new products and improved management practices for Sumbawa mare farming. It also underscores the importance of providing accurate information to address misconceptions surrounding the milk's purported medicinal qualities. The potential contributions to public health and policymaking regarding the use of Sumbawa mare's milk as a potential health product are discussed, connecting the research to real-world implications.
1.4 Hypothesis
This subsection presents the formulated hypotheses guiding the research. The hypotheses are based on preliminary observations and existing literature, focusing on the presence of potent antimicrobial compounds in Sumbawa mare's milk, its broad-spectrum activity, and the likely protein nature of the active compounds. The clearly stated hypotheses provide a framework for interpreting the research findings and demonstrate a structured approach to scientific inquiry. This section is vital in establishing the research's direction and expectations.
II. Literature Review
This section provides a comprehensive review of relevant literature on horses, milk, antimicrobial compounds, and pathogenic microbes. It establishes the theoretical framework of the study by discussing existing knowledge on horse breeds in Indonesia, the composition of various types of milk, the mechanisms of antimicrobial action, and the characteristics of bacteria targeted by the research. The review critically analyzes previous research and identifies gaps in current understanding, emphasizing the originality and significance of the proposed research.
2.1 Horses
This subsection focuses on the origins and characteristics of horses, especially those in Indonesia. The discussion includes the evolution of the horse species, the history of horse breeds in Indonesia, and a specific examination of Sumbawa horses and their traditional farming practices. This lays the foundation for understanding the environmental and husbandry factors that may influence the composition of Sumbawa mare's milk. The historical and geographical background of Indonesian horse breeds is crucial in establishing the context for the unique properties of the Sumbawa variety.
2.2 Milk
This subsection reviews the general composition and properties of milk from different mammalian species. Detailed descriptions of milk components (fats, proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals) are given. The discussion also focuses on the specific composition of mare's milk, comparing and contrasting it with milk from other animals (e.g., cow, goat). The comparison highlights the unique characteristics of mare's milk in relation to its nutritional value and potential functional properties, establishing its unique position within the existing literature.
2.3 Antimicrobial Compounds
This part explores the various types of antimicrobial agents, including antibiotics and naturally occurring antimicrobial compounds from plants and animals. This section examines various antimicrobial mechanisms, focusing on the interactions of antimicrobial agents with bacterial cell walls, membranes, and genetic materials. It also examines specific antimicrobial components found in milk, such as lactoferrin, lactoperoxidase, lactoglobulin, and lactolipids, laying the groundwork for understanding potential candidates for the antimicrobial activity observed in Sumbawa mare's milk.
2.4 Pathogenic and Spoilage Microbes
This section provides detailed information on the bacteria used in the study to test the antimicrobial activity of Sumbawa mare's milk. This includes the description of pathogenic bacteria, food spoilage bacteria, Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The choice of these specific bacteria is justified based on their relevance to human health and food safety, providing a basis for understanding the broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity of the milk and its implications.
2.5 Extraction, Fractionation, Isolation, and Characterization Methods
This subsection reviews the methods used for the extraction, fractionation, isolation, and characterization of bioactive compounds. It provides a theoretical foundation for the laboratory techniques employed in the research, such as chromatographic methods (HPLC), electrophoresis, and spectroscopic methods (IR, UV). This detailed description of methodologies is crucial for evaluating the rigor and validity of the research procedures and the reproducibility of the findings.
III. Materials and Methods
This section describes the research design, including the study location, materials (Sumbawa mare's milk, control milk samples, plant samples), equipment, bacterial cultures, and specific research methods. The description provides enough detail to allow for replication of the study. The methodology is presented in a clear, logical order, highlighting the multiple phases of the research, from field observations to laboratory analysis.
3.1 Research Location and Materials
This subsection describes the study areas in Sumbawa and details the materials used, including the collection of Sumbawa mare's milk samples, control milk samples from other sources, and plant material consumed by the horses. The rationale for selecting these materials is clearly stated, highlighting the importance of control groups for comparison and consideration of potential dietary influences on milk composition.
3.2 Equipment and Bacterial Cultures
A list of equipment used in the different phases of the research and the specific bacterial cultures selected for testing the antimicrobial activity is provided. The detailed description of equipment ensures the reproducibility of the study, while the selection of bacterial cultures is justified based on their pathogenic significance and relevance to food spoilage. This section ensures transparency and allows for evaluation of the adequacy of the research tools and materials.
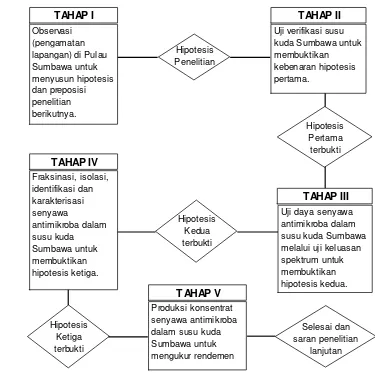
3.3 Research Framework and Methodology
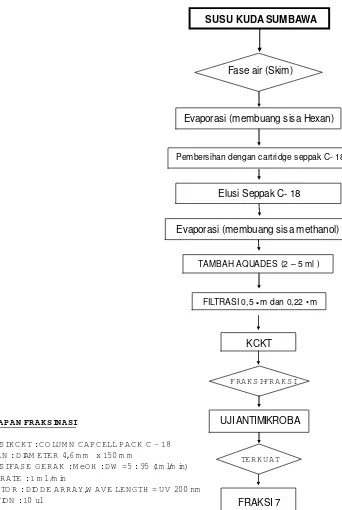
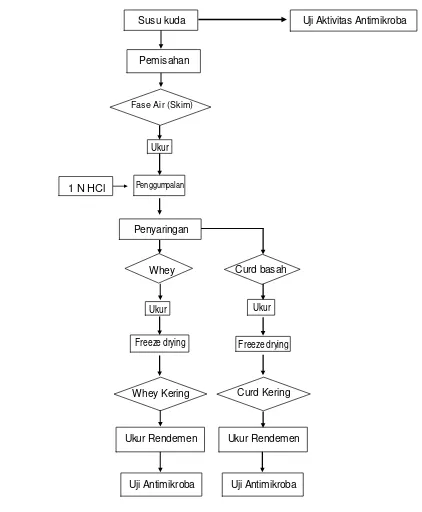
This subsection provides a detailed overview of the research design, including a flow chart or diagram outlining the sequence of research steps. A detailed explanation of the methodology employed in each phase of the study is provided, including data collection techniques in the field and the specific laboratory procedures used for analyzing antimicrobial activity, stability, spectrum, polarity, fractionation, isolation, identification, and characterization of the active compound. The research framework demonstrates a systematic approach to answering the research questions.
IV. Results and Discussion
This section presents the findings of the study, organized according to the research objectives. The results are presented clearly, using tables and figures where appropriate. The discussion section interprets the results in the context of the literature review, addressing the hypotheses presented in the introduction. The discussion also explores the limitations of the study and suggests avenues for future research.
4.1 Field Observations
This subsection presents the findings from field observations regarding the husbandry practices of Sumbawa horses, including details of animal management, milking procedures, and storage and transportation methods for the milk. This information contextualizes the laboratory findings and addresses the unique environmental and cultural aspects influencing the antimicrobial properties of the milk. The detailed description of field observations provides a rich qualitative context for the subsequent quantitative data.
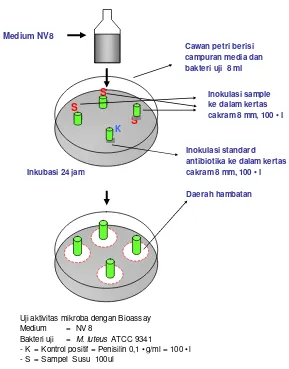
4.2 Verification of Antimicrobial Activity
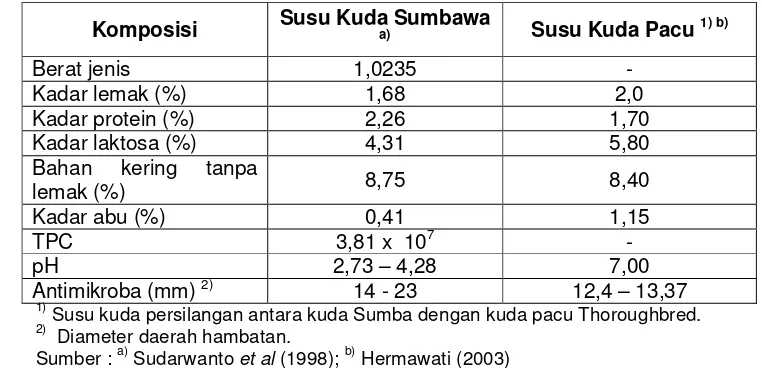
This subsection presents the quantitative results of the antimicrobial activity tests conducted on Sumbawa mare's milk. The data, presented in tables and figures, would show the zone of inhibition, indicating the effectiveness of the milk against various bacterial strains. This section directly addresses the first hypothesis, providing evidence for or against the presence of potent antimicrobial agents.
4.3 Stability, Spectrum, and Polarity of Antimicrobial Compounds
This subsection presents results on the stability of the antimicrobial activity of the milk under different conditions (heating, storage), the spectrum of antimicrobial activity against various bacterial species, and the determination of the polarity characteristics of the active compounds. This section would demonstrate the robustness of the antimicrobial activity and provide insights into the chemical nature of the active components.
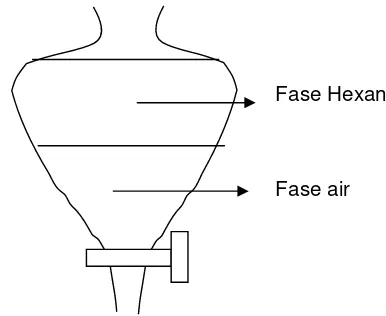
4.4 Fractionation, Isolation, Identification, and Characterization of Antimicrobial Compounds
This subsection presents the findings from the fractionation, isolation, identification, and characterization of the active antimicrobial compound(s). The results from HPLC fractionation, protein identification methods (e.g., Bradford assay, electrophoresis), and spectroscopic analyses (IR, UV) would be presented, leading to the identification and characterization of the active compound(s). This section provides crucial evidence to support the third hypothesis concerning the protein nature of the active compounds.
4.5 Development of a Concentrated Antimicrobial Product
This subsection presents the findings and discussion concerning the development of a concentrated antimicrobial product from Sumbawa mare's milk. The results would detail the procedures and outcomes of developing a commercially viable product, highlighting the practical application of the research findings. This section directly addresses the applied aspects of the research, emphasizing its potential economic and societal benefits.
V. General Discussion
This section synthesizes the key findings of the study, placing them within the broader context of the literature and highlighting their significance. This section might also discuss unexpected results or findings that require further investigation. The general discussion section integrates the findings from different sections, linking the field observations with the laboratory results and providing a holistic interpretation of the data. It could also discuss the implications of the findings for various fields, such as veterinary science, food science, and public health.
VI. Conclusion and Recommendations
This section summarizes the main conclusions of the study based on the findings and discusses the implications of the research. Recommendations for future research are presented, suggesting potential avenues for further investigation and application of the findings. The conclusion section concisely summarizes the key findings, reiterating the significance of the results and addressing the research questions. Recommendations for future studies would propose potential avenues for expanding on the current research to address remaining questions or explore new applications.
6.1 Conclusion
This subsection summarizes the main conclusions drawn from the study's results, providing a concise and clear statement of the main findings. It confirms or refutes the hypotheses presented in the introduction, summarizing the evidence supporting the conclusions. This section offers a clear and concise summary of the research's impact.
6.2 Recommendations
This subsection presents specific recommendations based on the study's findings. These recommendations might include suggestions for further research, focusing on specific aspects that require additional investigation, or propose practical applications for the identified antimicrobial compounds and their potential commercialization or incorporation into health products. This section concludes the study by highlighting its implications and proposing directions for future work.