TEACIIING DESCRIPTIVE WRITING
(An Experimental Study at the Second Year of SMPN 5 Bekasi)
A"Skripsi"
Presented to the Faculty ofTarbiya and Teachers' Training in Partial Fulfillment of the
Requirements for the Degree of S .Pd (Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education
By: UunHusnah
104014000386
!'i j i't'i•111. ..
d;sri
ᄋイセ、ゥ@
'' ';()'.
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH: EDUC.ATION
THE INFLUENCE OF COOPERATIVE LEARNING IN
TEACHING DESCRIPTIVE WRITING
(An Experimental Study at the Second Year ofSA1PN 5 Bekasi)
A"Skripsi"
Presented to the Faculty ofTarbiya and Teachers' Training in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree ofS.Pd (Bachelor of Arts) in English
Language Education
Approved By Advisor
Drs.H.A.Munir Sonhadji,M.Ed NIP:l50 050 682
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYA AND TEACHERS' TRAINING
SY ARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
LEARNING IN TEACHING DESCRIPTIVE WRITING(An Experimental Study at Second Year of SMPN 5 Bekasi) written by Uun Husnah, student's registration number 104014000386 was examined in the examination session of the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers' Training Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakaita on December 5th 2008. The skripsi has been accepted and declared to have fullfilled one of requirements for the degree of S.Pd (Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education in the Department of English Education.
Jakaita, December 5th 2008
Examination Committee
CHAIRMAN : Ors. Syauki, M.Pd ( )
NIP. 150.246.289
SECRETARY : Neneng Sunengsih, S.Pd ( )
NIP. 150.293.236
EXAMINER I : Ors. Nasrun Mahmud, M.Pd (
"'
)NIP. 150.041.070
Wセ@
EXAMINER II :;Dr. M. Farkhan, M.Pd (
NIP. 150. 299.480
""'
ACKNOWLEDGF113Y
Dean ofTarbiyah and Teachers' Training
,1,
I
Prof. Dr. Ded OS ada M.A
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
In the name of Allah, the Most Beneficent, the Most Merciful.
Praise be to Allah, who gives His blessing and grace: to the writer so that
she can finish writing this skripsi. Peace and blessing be npon to the
prophet Muhammad SAW, the man who had brought us from the darkness
to the lightness and for his families, his companions and followers.
The writer would like to give her gratitude, respect and
appreciation to:
1. Ors.I-I.A.Munir Sonhadji,M.Ed. who has patiently given
valuable advice, suppo1t and guidance to finalize this skripsi.
2. All lecturers in the English Education Department and all its staffs for their encouragement to her.
3. Her beloved parnnts (H.M.Ummm and Siti Adlah) and all
members of her family who always gives their suppo1t and
motivation to encourage her to finish this skripsi.
4. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd, the Chief of the English Education
Department.
5. Neneng Sunengsih, S.Pd, the Secretary of the English
Education Department.
6. Prof. Dr. Dede Rosyada, MA the Dean of Faculty of Tarbiya
and Teachers' Training.
7. I-I. Saiful Bahri, M.Pd the School Principal ofSMPN 5 Bekasi.
8. Salasatul Fatiqiyah, A.Md lmd Rumini, S.Pd the English
teacher and all the teachers and staffs of Sl\1PN 5 Bekasi.
9. The students of the second year (2008-2009) of SMPN 5 Bekasi especially VIII4•6•7 who have helped the writer to get the
Finally, the writer realizes that this skripsi is not perfect enough, therefore the writer would like to accept any cont1ibutive suggestion to make this skripsi better.
"may Allah, the Almighty bless them all. Amin
Jakarta, October 20111 2008
TABLE OF CONTENTS
COVER ··· ··· ... ··· ... I
LEGALIZATION OF ADVISOR ... 11
ENDORSEMENT SHEET ... .iii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... 1v
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... vi
LIST OF TABLES ... vm CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Study ... .1
B. The Limitation and Formulation of Problem ... 3
C.The Use ofStudy ... .4
D. Method ofResearch ... .4
E. The Organization of Paper ... .4
CHAPTER II : THEORETICAL FRAl\1'.EWORK A. Theoretical Descripticn ... 6
1.Writing
... 6
1. Definition ofWriting ... 6
2. Purpose of Writing ... ? 3. The Types ofWriting ... 9
4. The Process of Writing ... 11
2.Descriptive Writing ... 13
CHAPTER III
CHAPTER IV
BIBLIOGRAPHY APPENDIXES
2. Purpose of Cooperative Leaming ... 16
3. Element of Cooperative Leaming ... 17
4. The Steps of Cooperative Le:arning ... 18
B.Conceptual Framework. ... 20
C.Hypothesis ... 21
: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND FINDINGS A. Research Methodology ... 22
I. Objective of the Study ... 22
2. Place and location of Research ... 22
3. The Subject ofResearch ... 23
v4.
Population and Sample ... 23'-' 5. Instrument of research ... 24
, 6. Technique of Data Collecting ... 28
1,-7. Technique of Analyzing Data ... 28
B. Findings ... .30
1. Data Description ... 30
2. Data Analysis ... 43
3. Data Interpretation ... .48
: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A.Conclusion ... 50
LIST OFT ABLES
Page
1. Table 2.1 The Phases of Cooperative Leaming ... .18
2. Table 3.1 Data of Control Class Pre-test Score ... 30
3. Table 3.2 Data of Control Class Pre-test Score of Frequency Distribution ... 32
4. Table 3.3 Data of Control Class Post-test Score ... .33
5. Table 3.4 Data of Control Class Post-test Score ofFrequency Distribution .... .35
6. Table 3.5 Data of Experiment Class Pre-test Score ... 36
7. Table 3.6 Data of experiment class pre-test score of frequency Distribution .... 38
8.Table 3.7 Data of experiment class post-test score ... .39
9. Table 3.8 Data of Experiment Class Post-test Score ofFrequency ... .41
IO. Table 3.9 the Improvement of Students' Achievement in Descriptive Animal Writing in Control Class (without using TPS technique) aind Experiment Class (using TPS technique ) ... .42
11. Table 3.10 Data of Normality Testing of Control Class (pre-test) ... 44
J 2. Table 3.11 Data of Normality Testing of Control Class (post-test) ... .44
13. Table 3.12 Data ofNormality Testing of Experiment Class (pre-test) ... 45
INTRODUCTION
A.
Background of The Study
Language is an effective tool for communication among people all
over the world.
English is international language. It is also a foreign language that should be taught as a compulsory subject at the Jm1ior and Senior High
School. So many people are motivated to learn English as the language of
international communication. People learn English because they have
some reasons. They want to communicate in English orally and written
form.
Learning is acquiring or getting of knowledge of a subject or a skill
by study, experience or instruction.1 It means that learning is a way for someone to learn how to do something, get lmowledge and understand the
lesson that they learned.
Leaming a language is trying to acquire a new skill in mastering a
language as a means of communication.2 Many actual and linguistic
competences involve in the process of mastery skills such as listening,
speaking, reading, writing, grammar, vocabulary, spelling, and
pronunciation. These actual and linguistic competences are studied at
school and in a language course. Both of actual and linguistic competence,
writing is one of the most skill that many people especially students feel
should be learned. It is a complex activity because students challenged to
arrange and to organize writing into a wtゥセエ・ョ@ form. Beside that it is one of
the most difficult skills to master it.
1
• H. Douglas Brown, " Principles of Language Learning and Teaching",( San
Francisco: Addison Wesley Longman, 2000), P. 7
2
2
Many students who study English consider that they do not know
how to write a topic. They are unable to apply English in the written form.
They often face some problems to organize their ideas. They do some
mistakes concerning with the lack of knowledge in vocabulary,
grammatical rules and tenses. Although writing is ッュセ@ of the most difficult
skills, it is an important form for communication. It is a part from a subject
matter at the school.
Teaching English writing needs many kinds of technique, because
the students often feel too bored in learning English writing in the
classroom. To make teaching and learning process will be more effective
and the students are motivated in learning English writing, the teacher
needs a suitable technique. Discuss a technique for teaching English
writing is an interesting problem, the technique used by teacher has crucial
role, beside that the teacher role is not just give the information for the
students in the classroom but also the teacher can arise students'
motivation in learning and create student learning ᄋセクー・イゥ・ョ」・N@
Because the teacher has important role, the teacher must find
suitable technique in order to the teaching and learning process will be
more fun and the purpose oflearning can be achieved.
As the students' problem in English writing and the role of teacher
m teaching English writing, the v.>riter wants to apply an alternative
technique in teaching English writing that can improve students' ability in
learning English writing.
Cooperative learning 1s a learning model, it is adopted by
constructivists, it uses small group that consist of 4 until 6 members of
student in group. Cooperative learning is required to work together, to
maximize students' problem in learning. In coopt:rative learning, the
students work an assignment into their small group. Cooperative learning
TPS (Think Pair Share) technique is an effective way to make
condition of classroom discussion has more time to think, to respond and
to help each other in pairs.3 It means that student ca:n work together with
their partner and make the classroom condition more enjoyable.
The applied technique hopefully can help students to organize and
to produce the sort of descriptive writing. By using TPS technique the
students have opportunity t-0 discuss their own writing, share their
mistakes that they will be made in their writing, make them easier in
learning descriptive writing and also they can improve their achievement
in learning descriptive writing.
As the explanation above, the writer hopes both of teacher and
students feel easily to apply and to praci;ice mis technique in teaching and
lea.ming descriptive writing. Moreover, the influence of TPS technique is
not merely to help students to improve their achievement in English
writing skill. At the same time it can also improve students' ability in
writing. The writer would like to choose a · title under" THE
INFLUENCE OF COOPERATIVE LEARNING IN TEACIDNG
DESCIUPTIVE WIUTING". (An Experimental Study At the Second
Year of SMPN 5 Bekasi).
B. The Limitation and Formulation of Problem
I. Limitation of Problem
According to the background above, the writer limited the study
focuses on the teaching English writing concerning with the
descriptive writing about animal by using TPS (Think Pair Share)
technique.
2. Formulation of Problem
The writer formulated the problem of stuc\y as follows: "How
4
C. The Use Of Study
The result of this study is expected to be useful for:
1. Teacher
The result of this study is to give the iufonnation for th.e English
teacher that TPS (Think Pair Share) teclmique is able to improve student
ability in learning descriptive writing.
2. Student
The result of this study is to give an easy technique for students in
learning and understanding descriptive writing and they can reinforce their
knowledge of English or all aspects of English language that they have
been learned.
D. Method of Research
To support this study, the writer used some reference books and
other resources that related with the subject from library. In the field
research the writer conducted an experimental study at the second year of
SMPN 5 Bekasi which consists of two classes, they are experiment and
control class.
E. The Organization of Paper
The writer divides this paper into four chapters; Chapter I is
Introduction, including background of the study, the limitation and
fommlation of problem, the use of study, method of research and
organization of paper.
Chapter II is Theoretical framework, this chapter discusses about
Theoretical Description, it consists of Writing, definition of writing, the
purpose of writing, kinds of writing, the steps in writing process.
Learning, background of cooperative learning, purpose of cooperative
learning, basic elements of cooperative learning, steps of cooperative
learning. Conceptual Framework. Hypothesis.
Chapter III is the research methodology and findings, it consists
of the objective of research, place and location of research, the subject of
research, Population and Sample, Instrument of research, technique of data
collecting, technique of analyzing the data, the description of data, the
analysis of data, test of hypothesis and interpretation of data.
The last, the conclusion and suggestion will be described m
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAJ.., FRAMEWORK
A. Theoretical Description
1.
Writing
The ability to write in English language is impo1iant in global
communication because English is an international language. Advance in
transportation and technology allow people to interact with each other.
Communication across language becomes more essm1tial; as a result, the
ability to write a foreign language is widely recognized as an imp01iant
skill for education, business, Science and technology.
I. Definition of Writing
Writing is one of four languages skills such as listening, speaking
and reading. It has always formed part of syllabus in teaching English at the Junior and Senior High School. There are a Jot of definitions about
writing that have been given by experts: some of them are Penny Ur. She
said that: writing is a learned skill.1 It can be taught and learned. From this definition the writer get a meaning that writing is a learned skill like
driving, cooking and typing. It can be learned. S1udents who want to master it, they must take the intensive practice because writing is not an
automatic skill. It is need some knowledge such as vocabulary, grammar, punctuation and spelling.
Marianne Celce Murcia and Elite Olshtain viewed that "writing is a
language skill used for communication. 2 It means that writing used for communication when someone wants to commtmicate in different
situation.
1
• Penny Ur, ," A C'ourse in language Teaching",(United Kingdon1: Ca1nbridgc
As Penny Ur, Marianne Celce Murcia and Elite Olshtain points of view about writing. Tricia Hedge said that, V.'Titing is process of composing.3 It means that Miting has given certain process. When students at the first time write something down, エィQセケ@ have already been thinking and finding the idea, putting idea into sentences, organizing sentences into paragraph, revising and reviewing writing with correct punctuation and grammatical function.
Meanwhile, Sandra Cornbleet and Ronald Carter in their book "the Language of Speech and Writing". They said that" \li/riting is planned".4 It means that writing takes time. As the students write a sentence, they can think each word before they Mite it and then they can always go back and correct it until they were satisfied. Before they can write anything, they need time to think.
Based on the definitions above, it can be said that Miting is a complex process, it is done in a series of steps, such as preMiting, writing, revising, reviewing and editing. Beside that, writing is a skill that is needed a lot time to practice and need some knowledge to produce a coherent writing.
2. Purpose of Writing
Students frequently have more time to think in writing, they can go through what they know in their minds, consult dictionaries, grammar books or other reference material to help them to make a good Miting.
8
book, "A Course in Language Teaching" she explained that " the purpose of writing, in principle is the expression of ideas, the conveying of a message to the reader, so the ideas themselves should arguably be seen as the most aspect of the writing ". 5
Tricia Hedge mentioned the purpose of writing as follows "A good deal of writing in English language classroom is undertaken as an aid of learning for exan1ple: to consolidate the learning of new strnctures or vocabulary or to help student remember new items of language".6
Jeremy Harmer on his book, "How to Teach 'Writing" he said that: "writing has always been used as a means of reinforcing language that has been taught ". 7 It means that teacher asked students to write sentence by using grammar that the students have been learned, for example, students can be asked to write a sto1y about something that happened to them. It is a good way for students to practice their knowledge of language aspects that they have been learned besides that writing can encourage students to focus on accurate language use. Clearly, the aim of writing activity i8 to give students opportunities to think about grammar and vocabulary.
Afte1wards Jeremy Harmer stated on his book, "How to Teach English", " the reasons for teaching English WTiting to students of foreign language. They are reinforcement, language development, learning style and most importantly, writing as a skill in its 0Vv11 right". 8 All is clearly explained in the following points:
5
• Penny Ur," ... , P. 163 6
P. 82
1. Reinforcement
Some students easily requirt' language items through oral way but most of them find it easier when they see it. Thus, when they write down, writing reinforces students to acquire language indirectly.
2. Language Development
The actual writing process helps students to learn the language directly.
3. Learning Style
For many learners, writing gives the time to think to produce language in a slower way.
4. Writing as skill
Because the writing is an important skill, it can be learnt, students learn to know how to use it for a daily life.
From the description above, it is clear that the writing can help
students to acquire the abilities of the foreign language that they are
studied. When students do writing activity, at the same time they leamed
many things in the target language beside that they can express the ideas
and convey some written infonnation to the readers.
3. The Types of Writing
Generally, writing divided into five types; they are narrative,
descriptive, expository, persuasive, and argumentative:.9
I. Narrative
Narrative writing is a type of writing which present events
in a related series. It is a story which can be real and imagined. 10 It
can be a personal experience or it can be the experience of another
person. It is to amuse, to entertain and to deal with actual or various experience in different ways.
Nan·ative writing must have a good plot that can attract
readers' attention, it has interesting characters that appear alive and
9
10
credible in order to hold the readers' attention and it also uses the lively and humorous dialogue, at the same time the readers does not feel that the dialogue is monotonous.
2. Descriptive
Descriptive writing 1s a writing which make the readers' see things, or to perceive the special quality of them. It makes them see in the sense of visualizing. 11
Descriptive writing serves only to describe. It is to describe a pmiicular person, place, animal or thing. It is required to give the reader a detailed, vivid picture of a person, place, scene, object or anything that is described.
3. Expository
Expository writing is a 'witing orderly setting out of facts and ideas.12 It is not imagination or dramatizes writing because the exposition writing is presented in a clear, accurate and factual facts and ideas. It is a form which explains a subject. Its purpose is to make the reader understm1d.
4. Persuasive
Persuasive writing is used to convince. 13 It is the art of getting other people or readers to do and believe something. It may attempt to convince something to follow a certain action or accept a belief position.
Persuasive writing relies on reasoning and clear logic. It aims is to persuade the readers of the reasonable of the writers view.
11
• Richard. W. Weaver, "Composition: A Course in Writing and Rhetoric",(United State
5. Argumentative
Argwnentative is a logical way that the writer's belief,
position, conclusion is valid and that ofuers are not. 14It is to persuade reasonable people to agree with the writer's belief and
position. Argwnentative writing usually requires proving that a
statement is true so the argument must be logical; bofu of points
and facts are relevant.
Argumentative and persuasive are related, but they are not
the san1e. Persuasive getting other people to change their minds
relies on appeals to emotion, to self interest, and to reason.
Argumentative in its form is the appeal to reason and refutes
opposing opinions.
4. The Process of Writing
Writing is a complex process which is neither easy nor
spontaneous for many students. To make a good writing students need
strategies to manage fueir writing process. Although 'writing process is not
a set procedure, the writing process has been observed as having distinct
five stages. In general, every writing process includes prewriting, drafting,
revising and editing.15 I. Prewriting
In fue prewriting stage, the students take time to think about
their topic and generate ideas. In this stage, sometimes the students
are frustrated because they cannot think of anything to say about a
topic. To make students feel easy in this stage, there are some
14
• Laurie G. Kirszher and Stephen R. Mandell, "Patterns for College Writing: A
12
techniques like brainstorming, free writing, WH Question, and
clustering.16 The following points explained clearly: a. Brainstorming
It is a way to associate idea and stimulate thinking to
brainstorm. Start with a word or phrase. In this process, the
students do not attempt to think logically but they write a list of
ideas as quickly and possible.
b. Free Writing
It is writing without stopping. It means that the students write whatever comes to their mind.. 'Without worry about
whether the ideas are good and the grammar is correct.
c. WH Question
The students can use who, what, when, where, why and
how questions to generate material for their writing. In this
process, the students write out as many WH question as they
can, then they answer them as fully as they can.
d. Clnstering
It is making a visual map of the students' ideas. It may allow students to think more creatively.
In
this technique, the students begin with their topic circled in the middle of a sheetof paper. Then draw a line out from the circle and write an idea
associated with the topic. Continue to map or cluster m1til the
students can not think of any more ideas.
2. Drafting
Drafting is a way to discover more ideas about the topic. It
is a planning tool to expand outline into a text with full sentences.
Use full sentences whenever possible and don't worry abont
Drafting is also transforming the ideas into sentences. It
purposes are to let ideas develop and expand. Drafting is primarily
a stage of discovery and exploration.
3. Revising
Revising is one of the most important phases of the writing
process. It is focus on how well the ideas are expressed and
organized to sentence structure. It:; purposes are to rethink ideas,
refine and develop them. During this stage the students reshape
ideas, expanding, deleting and clarifying.
4. Editing
Editing is the last phase. It involves correcting all of
mistakes in writing. It is require examining ideas, details words,
grammar and punctuation. It also emphasizes not only accuracy but also on correctness.
2. Descriptive Writing
1. Definition of Descriptive Writing
There are some definitions about descriptive writing. John
E. Lincoln stated that "descriptive is writing about way
persons, animals or things appear".17
Laurie G. Kirszer and Stephen R. Mandell in their book with the title "Patterns for College Writing: A Rhetorical
Reader and Guide". They mentioned "Descriptive is writing
tells what something looks like, feels like, smells like, sotmds
like or tastes like.18
14
that they have been described clearly and use all five senses in order to the description that is described alive and interesting to the readers.19
As some Experts view about descriptive writing. Richard M. Weaver stated that "Descriptive is a form of writing that makes the reader sees in the sense of visualizing. It is focus on the appearance of an object".20
Based on the explanation from some experts about descriptive writing, the writer concluded that descriptive writing is a writing that gives readers the objects such as persons, animals or things that is described alive and the readers feel interesting because it emphasizes imagery and figures of speech such as see, hear, taste, smell and. feel.
2. Purpose of Descriptive Writing
Anyone write a descriptive writing is to give a description about an object that they described clear and alive because the purpose of descriptive writing is to make the readers feel how the object looks, feels, smells, tastes and sounds. Thus, in descriptive wTiting, the readers have been given detailed object, vivid picture and use five senses or use concrete words that will enable the readers to see, foe:l, hear, taste, touch or smell what the object is describing.
3. The Characteristics of Descriptive Writiing
A descliptive writing serves only to describe an object. There are some characteristics about descriptive writing. The following characteristics of descriptive wliting such as:
1. Using of figures of speech (see, hear, taste, smell, touch). In this way the description will appear alive and interesting.
3. Using variety of words. It means that use of variety of adjectives,
nouns, adverbs, and phrases to suggest colors, movements, expressions
and feeling.
4. Using any details. If anyone want to describe an. object. They should not describe just its physical features but also its habit, its
characteristics and its relationship.
5. Using the simple present tense.
6. Using adjective to describe the feature ·:if the subject.
3. Cooperative Learning
1. Background of Cooperative Learning
The challenge in education today is to teach students the subject
matter effectively. Teachers expected to teach in a way that enables
students to learn assignment in the classroom cooperatively. The aim is to
be more concentrated of student centered. Cooperative learning is one of
learning model that focus on student centered. Essentially cooperative
learning represents a shift in educational paradigm from teacher centered
to a more students centered in a small group. 21
It creates opportunity for students to help the:ir group members to solve their learning problems which in small group students feel more
comfortable asking for help. In cooperative learning students can work
their assignment together. Cooperative learning grounded in the belief that
learning is most effective when students are actively involved in sharing
16
Miswati, et al assumed that "cooperative karning is a learning
strategy that uses students grouping into small group which each student
have different achievement". 22
Cooperative learning is a learning process that emphasizes in social
aspect and use a small group which consists of 4 until 6 students. In
cooperative learning students will be easier understood their knowledge
about the subject matter because they can discuss their faced problem with
their pmtner. 23
Based on description above, the writer means that cooperative
learning is a learning model which focuses on students grouping. Each
group consists of 4-6 students. In group they can do their assignment cooperatively.
2. Purpose of Cooperative Learning
The cooperative learning model has been developed to achieve at
least three important instrnctional objectives such as academic
achievement, improved race relation a11d cooperative problem solving
skills.24
1. Academic Achievement
Cooperative learning aims at improving student
performa11ce on important academic tasks. The belief is that the
model cooperative incentive structure raises the value placed on
academic learning and change the norm associated with
achievement.
In addition to changing norms associated with achievement,
cooperative learning can benefit low achieving and high achieving
22
students who work on academic material together. High achievers
tutor low achievers. In the process, high achievers gain
academically because serving as a tutor requires thinking deeply
about the relationships and meanings of a particular subject.
2. Improved Race Relation
In the second effect of cooperative learning is the students
have wider tolerance and acceptance of people who are different by
virtue of their race, culture, social class and ability.
3. Cooperative Problem Solving Skills
A final effect of cooperat[ve learning is that students learn
skills of cooperation and collaboration. These are important skills
in a society where much adult work is carried out in large,
independent organization and where communities become much
more global in their orientation.
3. Element of Cooperative Learning
Cooperative learning organizes instruction according to the
principles of positive interdependence, individual accountability,
promotive interaction and group processing. 25 All of these points explained clearly:
1. Positive Interdependence means that the success of the students is
linked with the success of their team members. The success one
learners is dependent on the other learners.
2. Individual Accountability means that teacher should assess the
amount of effort that each member is contributing these can be
done by giving an individual test to each student and randomly
calling students to present their group's work. The perfo1111ance of
each member is assessed and results are given to the team and the
individual so that the team members cannot get a free ride on the
No
1
2
3
4
18
3. Promotive Interaction means that individual can achieve promotive interaction by helping each other, exchanging resources, challenging each other's conclusion, and providing feedback. Beside that team members share, encourage and support each other's efforts to succeed.
4. Group Processing means that teachers must also provide opportunities for the class to assess group progress. The team members perform group processing to reflect how well the team is fw1ctioning. Group processing enable group to focus on good working relationship, facilitates the learning of cooperative skills and ensure that members receive feedback.
4. Steps of Cooperative Learning
[image:26.595.40.444.94.702.2]Arends has identificated the general steps of cooperative learning. Generally, there are five phases in cooperative learning.26 See the following table below.
Table. 2.1
The Phases of Cooperative Learniing
Phases Teacher's activity
Serving the object and The teacher states the objective to motivate the teaching materials students to learn, to serve the object and make
the teaching materials
Giving the information Teachers gives the information to the students verbally and written
Organizing the students to Teacher explains to the students how to constrnct the group-work construct the group work
5
work and learn working to do the task
Evaluation Teacher evaluates the result of the discussion about the materials they have learned or each group presents the result of the discussion
In cooperative learning model, there are at least five techniques that are commonly used in teaching and learning process. It is used as a tool of learning at various levels of education and in various subject matters. Cooperative learning has many kinds of technique. One of the cooperative learning technique is TPS(Think Pair Share). TPS (Think Pair Share) is one of the kinds of cooperative I.earning technique. In this technique, the students do their assignment that is assigned by teacher cooperatively.
Think Pair Share initially developed by Frank Lyman and his colleagues at the University of Maryland. It is an effective way to change the discourse pattern or condition of classroom discussion. It is also give students more time to think, to respond and to help each other. There are some steps in TPS (Think Pair Share) technique. The following steps are:
Step I
Step JI
: Thinking. The teacher poses a question associated with the lesson and asks students to spend 5 minute thinking alone about answer.
: Pairing. The teacher asks students to pair off and discuss what they have been thinking about. Interaction in this period can be sharing answer if a question has been posed. Teacher allow no more than 10 minute:s for pairing.
20
B. Conceptual
Framework
In a traditional classroom, the teacher asks a question and only one
or two students have opportunities to respond. TPS (Think Pair Share)
technique offers all students an opportunity to express their response to a
question or topic discussion. By Using TPS (Think pair Share)teclmique
the teacher gives the students' time to think, share c01Tect answers with
partner, allow all students to respond then students are invited to share
their responses with the whole class.
Writing is one of the languages skills. In writing activity students
often face some problems because students challenged to organize ideas,
arrange writing into written form and they also do some mistakes in
vocabulary and tenses. To create English writing session in the classroom
more effective, the writer wants to apply TPS (Think Pair Share) teclmique
as a tool of teaching descriptive English writing. The purpose is to make
students enjoyable in learning descriptive writing beside that they can help
each others. They also can discuss some faced problems either to find
appropriate vocabulary or use a grammatical rule.
Because of some purposes about the TPS (Think pair Share)
technique in teaching descriptive writing, the writer applies it in the
following steps:
Step I
l. The teacher divided students into a small group
2. The students sit down with their group.
3. The teacher explains the descriptive writing material about animals
that involved their parts of body, colors, sizes, or shapes
vocabularies and another that they may be described in their object.
Step II
I . Each student asked to think a:nd do the descriptive writing
exercises individually.
2. After 5 minute, the teacher asked to work the descriptive writing
exercises pair. And then they discuss their answer. In this session
the students was given for discussion I 0 minutes.
3. After that. The students share their answer with the whole class. Its
aim is to discuss their answer that they agreed in their partner.
During the some of groups present their answer; the other groups
can give their argument or opinion about the answer. In this point
the student have a long time to share their problem until they found
the correct answer.
Step HI
After applied step I and II then the students a:re given a test of
descriptive writing about animals by teacher and did this exercise
individually. It aims is to measure the students' understanding about
material that they were lea:rned. To finish the exercise, the students do it
without asking for help from their partner.
C. Hypothesis
According to the theory and the objective of the study. It can be formulated that:
H0 : There is no significance influence on students' achievement in
descriptive animal writing who taught by using TPS (Think Pair
Sha:re) technique.
Ha: There is significance influence on students' achievement in descriptive
animal writing who taught by using TPS (Think Pair Sha:re)
CHAPTER UI
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND FINDINGS
A.
Research Methodology
1. Objective of the Study
The objective of this study is to know the significance influence of TPS (Think Pair Share) technique on students' achievement in teaching descriptive writing of animal for the second year of SMPN 5 Bekasi. 2. Place and Location of Research
The research of this study was held at SMPN 5 Bekasi, where the writer conducted the research from July 14th to August 28111 2008. SMPN 5 is located at jln. raya Seroja Bekasi Utara and the phone number is (021. 8849355)/website. www. smpn5.kota-Bekasi.com. SMPN 5 Bekasi built in 1982. Previously, the name of SMPN 5 is SMPN 6. Then in 1996, the name is changed to SMPN 5. Since it built in 1982, there are five schools principal who led in.
1. 1986-1992 led in by Uci Sanusi. 2. 1992-1995 led in by Drs. Saju Juhana. 3. 1995-2000 led in by Drs. H. Zaenal Arifin. 4. 2000-2005 led in by Drs. H. mセRQQ。エ@ Sehabudin. 5. 2005- now led in by H. Saiful Bahri, M .. Pd
SMPN 5 has a large amount ofland it is about 6.583 M2• It also has
SMPN 5 has 71 teachers. such as 7 of nature education(IPA) teachers, 9 of mathematic teachers, 8 oflndonesian language teachers, 6 of English teachers, 5 of religion education teachers, 8 of social education (IPS) teachers, 2 of computer teachers, 5 of counseling teachers, 4 of sport and health teachers, and 9 is other teachers.
Now, the year of 2008-2009, SMPN 5 has 1137 students and 27 group of learning (Rombel). They are 371 students of VII class and the group ofleaming is 9. 397 students of VIII class and the group oflearning is 9. 369 students of XI class and the group oflearning is 9.
To support the teaching and learning process more effective, SMPN 5 has 29 classes. 456 tables. 1272 chairs. and 56 whiteboard. All of this learning equipment is well condition.
3. The Subject of Research
The subject of the research was the second year of students SMPN 5 Bekasi. It consists of two classes. They are VIII6 as called experiment and VIII7 as control class. The object of the research was teaching descriptive writing using TPS (Think Pair Share) technique and teaching descriptive writing without using TPS technique.
4. Population and Sample
In this research, the writer took the population from the second year of SMPN 5 Bekasi. The population is 9 classes. They are VIU1•2•3•4•5•6•7•8•9• The class of VIII1•2.3·4•9 called as superior classes and
VIII5•6•7•8 as regular classes. Each classes either superior or regular
24
5. Instrument of Research
The instrument of research used by the writer in data collecting is taken from the application test of descriptive writing about animal. The test consists of 24 items in testing of validity and reliability. The test of validity and reliability was tried out by students of VIII4 class.
After the testing of validity and reliability was done, there are only 16 items left. The 16 items took as pre-post test. It used to know the gain score of students' achievement in 、・ウ」イゥーエゥカ\セ@ animal writing. The pre-post test will be done by students of VIII 6 as the experiment class and VIII 7 class as control class.
a. Validity
Test of validity has been done to measure the purpose of research. Its purpose is to measure how well it fulfills the function for which it is being used.
Validity has been defined as referring to the appropriateness, correctness, meaningfulness and usefulness of the specific inferences researchers make based on the data the research collect1• Scarvia B. Anderson on Suharsimi Arikunto' s
book said that "A test is a valid
if
measure what it purpose to1neasure "2.
In testing items of validity in this research, the writer used the formula of coefficient correlation of pearson's product moment3. The formula as follow:
1
• Jack. R Fraenkel and Norman E. Wallen," How To Design and Evaluate Research in
Education'", (New York: McGraw- Hill Companies Inc, 2003), P. 158
2 • Prof. Dr. Suharsimi Arikunto," Dasar-dasar Evaluasi Pendidikan", (Jakark1: 2008), P.
Rxy : Coefficient con-elation between X variable and Y variable.
X : Score of tried out items.
Y : Total of score for each student that was tried out. N : Number of tried out students
The conclusion of testing validity on 24 items which done by students of VIII 4 class showed that 8 items is invalid because score of T hitung is smaller than T tabel. Meanwhile 16
items is valid because the score of T1iitung is higher than Ttablc-The valid items are number 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 18, and 20. From 16 valid items; the writer takes the items as the instrument of research.
b. Reliability
Reliability refers to the consistency of score or answer from one administration to another. Reliability is defined as the extent to which the results can be considered consistent or reliable. Reliability refers to the consistency of the score obtained. It means that if it is used every time, it has the same results.
The formula to be used to find out reliability is K-R 20 formula ( Kuder Richarson 20). The formula is:
q : Proportion of students' wrong answer The interpretation of reliability coefficient is follow: 0.00-0.20 : Bad.
0.21-0.40 : Satisfacto1y. 0.41-0.70 : Good. 0. 71-1.00 : Excellent.
Negative : The entire item is not good (deleted).
26
According to the calculation of reliability score, the writer gets R II= 0. 753 I. It means that the test is reliable and it category is excellent.
c. Difficulty Power
The difficulty power show how easy or difficult the particular item proved in the test. The difficulty power of a test is indicated by the percentage of pupils who got the item right4.
The calculation is based on the upper and lower group only. Difficulty item may be necessary to motivate the good students and easy item will encourage and motivate the poor students.
The formula of difficulty power as follow:
P=!!__
JS
P : Difficulty power.
B : Number of students who give the conect answer. JS : Number of examinees.
The classification of difficulty power is: 0.00-0.15 : Very strong
d. Discrimination Index
The discrimination index of an item indicates the extent to
which the item discriminates between examinees, separating
good testees from the poor examinees. The discrimination
index refers to the degree of which it discriminate between
pupils with high and low achievement or the difference
between the number of pupils in the upper and lower groups
who got the item right5• To know the discrimination index of
the test, the writer used the formula as follow:
D= BA - Bii
=
p - pJ J A IJ
A B
JA : Number of upper group
Ja : Number oflower group
BA : Number of upper group who give the correct
answer
Ba : Number of lower group who give the wrong
answer
PA : Proportion of upper group who give the correct
answer.
Pa : Proportion of lower group who give the wrong
answer.
The classification of discrimination index score is:
0.00-0.20 0.21-0.40 0.41-0.70 0.71-1.00
Negative
: Poor.
: Satisfactory.
:Good.
: Excellent.
28
6. Technique of Data Collecting
To get the data for this skripsi, the writer used some techniques of
data collecting. They are:
1. Observation
Before doing the research, the writer first observed the
location where the research was cairied ont to ask penuission of
school principal to do research in that place and to know whether
the population and the object ofresearch is suitable or not.
After getting permission, then the 1.vriter continue with
giving a test to try out whether the test is valid and reliable or not.
The test of validity was done by students of VIII4 class.
Beside that the writer also observed about school facility
and some students activity to fulfill the data of research.
2. Teaching and learning Activity
The writer did the teaching ai1d learning process six times,
3 times in control class and 3 times in experiment class. Before the
writer did the teaching and learning activity for each class, the
wTiter did the pre-test.
3. Test
The writer gave the students posMest. The post-test was
given after the writer gave 3 times of the instruction about
descriptive of animal writing. The form of pre-test and post-test
items is similai-.
7. Technique of Analyzing the Data
Before analyzing the data, the writer arranged the data into
table of frequency distribution. It aims is to know whether the
score can be seen from higher score to lower score and whether the
score was normalized distribution or not.
[image:36.595.77.443.163.589.2]A. Normality and Homogeneity Testing
I. Normality Testing
The testing of normality was done to know the nonnality sample. The normality testing was done by using Chi Quadrate formula. 6 The formula is following:
(x' )=±(Jo-Je)2
;.1 fe
2. Homogeneity Testing
The testing of homogeneity both of experiment and control class was done to know the similarity between two populations which researched.
The testing of homogeneity was done by using Bartlet formula 7• The criterion of hypothesis is:
1. If FhiJung < Fiabcl, so the null hypothesis (H0 ) is accepted.
The population of two samples is homogeny.
2. If F11itung > Fiabcl, so the null hypothesis (H0 ) is rejected.
The population of two samples is not homogeny.
B. Test ofHyphotesis
To test of hypothesis, the data is analyzed by using test "t". The fonnula is:
S=
with;
n1
-l)S/ +(n
2-l)S,' }
30
Xi =average of experiment data X2 =average of control data
Ni =the number of experiment data
N1 =the number of control data
Si =mean of standard deviation of experiment data S2 =mean of standard deviation of control data T =calculation of' t" distribution
S =score of deviation
The calculation oft hitung is compared with t table by using the degree of significance 0.05.
It hypothesis criterion is:
If t hitung>t table, so the alternative hypothesis (Ha) is accepted.
If t hitung<t table , so the null hypothesis (H0 ) is rejected.
B. Research Finding
1. Data DescriptionAccording to the research methodology of this study, the writer collected the data by using pre-test and post-test. The pre-test and post-test took from the 88 students of second year of SMPN 5 Bekasi which consist of 44 students of control class and 44 students of experiment class.
Before the writer applies the TPS technique, the writer gives pre-test for the students in the control and experiment class. Its purpose is to know the students' knowledge about descriptive animal writing.
The following score of pre-test are:
Table 3.1
Data of Control Class (Pre-Test Scoire)
[image:38.595.55.442.107.537.2]' 4 35
--5 40
--6 40
7 40
0 8 40
9 45
10 45
11 50
' 12 50
13 50
14 55
15 55
16 55
17 55
18 55
19 55
20 55
21 55
22 55
23 55
24 55
-25 55
26 55
-27 55
28 55
29 60
no
l
2
3 4
5
-32
--33 60
34 60
35 60
36 60
37 60
38 60
39 60
40 '60
41 60
42 65
43 70
44 70
Pre-test score of control class got maximrnn score is 70 and minimum score is 30, average score is 53.04, median is 53.5, modus is 55.5 and standard deviation is 9.6. For the following description about pre-test score, see the table of frequency distribution below.
Table 3.2
Data of Frequency Distribution of Control Class (P:re-Test Score)
median Raw score Cumulative
interval f frequency
30-36 6 33 29.5-36.5 13.64%
--··
37-43 8 40 36.5-43.5 18.18%
44-50 10 47 43.5-50.5 22.73%
51-57 8 54 50.5-57.5 18.18%
.. MMMセMMMMM
- - 11.36%
58-64 5 61 57.5-64.S
[image:40.595.41.445.97.699.2]'!1'111111111
4 2ッNAbMMNeゥゥelセZlャZ[[eャNNNNNNe[[[AS⦅NNNe[ゥASNNNMe[ャZZZZ]]Z[[j@
29.5·36.5 36.5-43.5 43.5-50.5 50.5·57.5 57.5-64.5 64.5-71.5
From the schematic above, it can be seen that the greatest number
of score is 43.5-50.5 (22.73%). According to the calculation of pre-test
score, it was known that mean score is 53.04. It is not standard score
because the students do the pre-test before the teacher gives them the
subject matter about descriptive writing about animal. They do the test
based on their knowledge that they have been had.
After the students got the pre-test, then they taught the descriptive
writing about animal by the teacher through tradition.al method, after that
the writer gives them post-test. In post-test, they got the maximum score is
80 and minimum score is 30. The average score is 63.90, the median score
is 60.83, the modus score is 61.5 and standard deviation is 10.27. For the
[image:41.595.178.310.604.706.2]clear description, see the following table below.
Table 3.3
Data of Control Class (Post-Test Score) Subject Post-test score
1 45
MMMセM
2 65
3 70
34
6 50
7 75
8 65
-9 65
10 60
11 70
--·-12 75
13 70
14 65
15 75
16 75
17 70
18 75
19 65
20 70
21 75
-22 65
23 65
24 70
25 55
26 65
27 65
28 65
29 80
30 75
31 65
35 75
36 55
37 75
38 65
39 75
-40 50
-41 55
·
-42 55
·
-43 75
44 55
-Table 3.4
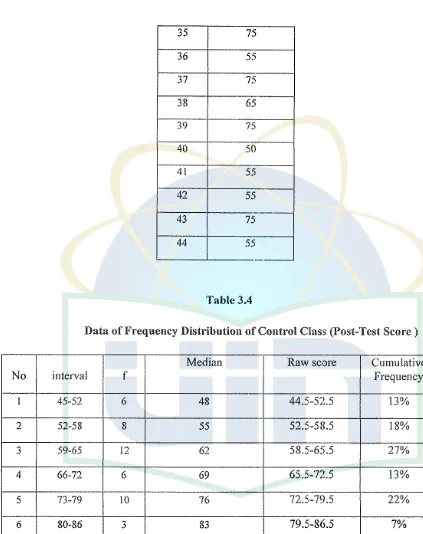
Data of Frequency Distribution of Control Class (Post-Test Score)
Median Raw score Cumulative
No interval f Frequency
1 45-52 6 48 44.5-52.5 13%
2 52-58 8 55 52.5-58.5 18%
3 59-65 12 62 58.5-65.5 27%
4 66-72 6 69 65.5-72.5 13%
5 73-79 10 76 72.5-79.5 22%
6 80-86 3 83 79.5-86.5 7%
[image:43.595.33.456.92.626.2]36
lo
Raw LimitI
15
..
M
セ@
f--
-r
Mセ@ セ@
セ@ セ@
1-1-I- f-1- 1-1- I - .... 1-1- I-·
セ@
セ@
_
...
1-1- QMセ@
1-1-セ@ Mセ@ Mセ@ QMセ@ Mセ@
El
I- f-1-,_ 1-1- 1-1- 1-1-
,__
' -L
0
44.s.s2.s s2.s-sa.s sa.5-65.s as.ri.-12.s 12.s..19.s 79.5-86.5
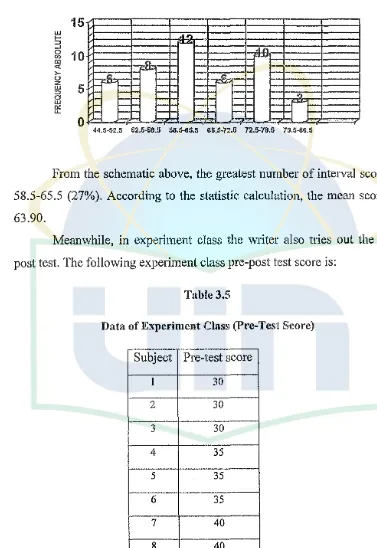
From the schematic above, the greatest number of interval score is 58.5-65.5 (27%). According to the statistic calculation, the mean score is 63.90.
Meanwhile, in experiment class the writer also tries out the pre-post test. The following experiment class pre-pre-post test score is:
Table 3.5
Data of Expetiment Class (Pre-Test Score)
Subject Pre-test score
I 30
2 30
3 30
4 35
5 35
6 35
7 40
8 40
9 40
[image:44.595.65.442.146.694.2]13 40
' 14 40
15 45
16 45
17 45
18 45
19 50
20 50
-21 50
22 50
' 23 50
24 50
-25 55
26 55
27 55
28 55
29 55
30 55
31 55
32 60
33 60
34 60
-35 60
36 60
37 65
38 6 5
no I
2
3
4
5
6
38
42 70
43 70
44 70
--From the table of pre-test score above, it was known that the maximum score is 70 and the minimum score is 30. Meanwhile, the mean score is 50.02, the median score is 44.5, the modus score is 47 and standard deviation is 11.43.
[image:46.595.35.443.204.623.2]The description about experiment class pre-test score. See the figure of table of frequency distribution below.
Table 3.6
Data of Frequency Distribution of Experim1mt Class
(Pre-Test Score)
median Raw score Cumulative
interval f Frequency
30-36 4 33 29.5-36.5 9%
37-43 4 40 36.5-43.5 9%
-44-50 5 47 43.5-50.5 11.5%
51-57 15 54 50.5-57.5 34%
58-64 13 61 57.5-64.5 29.5%
65-71 3 68 64.5-71.5 7%
w
15
,_
セ@
セ@ 101:;
z
w
fii
"'
セ@
5
0
セ@
-
-
I -:J
29.5.3&.5 36.5-43,5
·---
iMセ@iMセ@
L⦅セ@
...
セ@i]セ@
I -·-
L⦅セ@iMセ@l;;I
'- -
>--·-
' セLLL@c,,-43.6-50.5 00.&.57.6 64,5-71.6
joRawlimit
I
From the schematic above, it can be seen that the score 50.5-57.5 is the greatest score which got by students. The percentage of score is 34%. The mean score is 50.02. According to the greatest and mean score, it can be concluded that the students' score of pre-test is not minimum standard of English lesson score.
Afterwards, to make students' improvement on their achievement or score in descriptive animal writing, the writer gives them the instruction through TPS technique. the purpose is to make students easier to understand their instruction and they cru1 increase their achievement in descriptive animal writing.
After the students gave the instruction by using TPS technique, then the students gave the post-test. In the post-test, it was known that the maximum score is 95 and the minimum score is 6:5. Meanwhile, the mean score is 81.09, median score is 82.5, modus score is 81.78 and standard deviation is 8.23. The description about post-test, see the table below.
Table 3.7
Data of Experiment Class (Post-Test Score) Subject Post-test score
---I 80
[image:47.595.74.442.133.572.2]40
5 85
6 80
7 90
8 80
9 65
JO 80
11 65
12 65
13 70
14 80
15 95
16 80
17 80
18 80
19 80
-20 75
-21 75
22 60
23 90
24 75
25 85
26 90
27 80
28 80
29 65
30 90
34 85
35 75
36 65
37 95
38 75
39 70
40 85
41 75
42 90
43 80
44 80
Table 3.8
Data of Frequency Distribution of Experiment Class (Post-Test Score)
median Raw score Cumulative
no interval f Frequency
I 65-69 5 67 64.5··69.5 11.36%
2 70-74 5 72 69.5··74.5 11.36%
3 75-79 6 77 74.5··79.5 13.64%
4 80-84 15 82 79.5··84.5 34.09%
-5 85-89 5 87 84.5··89.5 11.36%
6 90-94 6 92 89.5··94.5 13.64%
7 95-99 2 97 94.5··99.5 4.55%
[image:49.595.36.440.105.667.2]w
16 14 12
§
10 0"'
OJ
"'
セ@ill
5
セ@ u.. 8 6 4 2 0 .セ@
セ@
-II
iセ@
セセ@
t=:-セセ@
=i::
.
I
a
Raw LimitI
42 :
-__
,_
-·-1-セe@
-·-1-=I::セ@
a
セ@
=
セ@セL@
.
.
From the schematic above, it can be seen that the interval score 79.5-84.5 is the greatest score which got by the students. According to the statistic calculation, the average score of post-test is 81.09. So it can be concluded that there is an improvement on students' score before the application of TPS technique and after the application of TPS technique.
[image:50.595.74.438.126.522.2]The improvement of students' score either in control or experiment class can be seen based on the table below.
Table 3.9
The improvement of students' achievement in descriptive animal writing in control class (without using TPS technique) and experiment class {using TPS technique)
Control Experiment
No. Data
Pre-test Post-test Pre-tiest Post-test
I. N 44 44 44 44
2. Mean 53.04 63.90 50.02 81.09
100
80
60
40
20
0
experiment control
Ill! Pre-test D Post-test
Schematically, it can be seen that the mean score of experiment class is higher than the mean score of control class. The mean score of control class pre-test is 53.04 and post-tests score is 63.90. Meanwhile, in experiment class, the mean score of pre-test is 50.02 and post-test score is 81.09. From the data above, it can be concluded that there is an improvement on students' achievement in learning descriptive animal writing either in control or experiment class but the improvement of experiment class is higher than the control class.
2. Data Analysis
After the writer collected the data of rese:arch, so the writer analyzed it. To analysis the data, the writ1er uses some formula statistically.
A). The Normality and Homogeneity Testin1g.
I. Normality Testing
no interval
1 30-36
2 37-43
I
3 44-50
' 4 51-57
5 58-64
6 65-71
no interval
The criterion of nonnality testing is:
If the
x
2i.uw•g<x
21abd, the data is normalized distribution. [image:52.595.5.471.189.649.2]If the X2 hUang > X21abd, the data is tll).J1011Tialized distribution.
Table 3.10
Data of Normality Testing of Control Class !.fre-Tcst)
Class
z-interval mean s score o-z fe fo f-fe (f-fe)2
29,5 53,04 9,6 -2.45 0.4929 1.5664 4 2,4336 5,92240896
36.5 53,04 9,6 -1.72 0.4573 5.2096 4 -1,2096 1,46313216
-·-43,5 53,04 9,6 -0.99 0.3389 10.3972 5 -5,3972 29,1297678
50,5 53,04 9,6 -0.26 0.1026 12.3ll2 15 2,6888 7,22964544
57,5 53,04 9,6 0.46 0.1772 9.0552 13 3,9448 15,561447
64,5 53,04 9,6 l.19 0.383 3.9424 3 -0,9424 0,88811776
-71,5 53,04 9,6 1.92 0.4726
44
Chi Quadrate
3.780905
0.280853
---
2.8016940.587241
1.718509
0.225273
9.394475
Based on the table above. It was known that the total of
x'
hUang, ondb= k-1=6- l = 5 and a= 0.05 known that X21abd
=•
11.070, so, X2Mamg(9.394475) < x'1ahet (11.070), it concluded that the sample is normalized distribution.
Tablc3.H
Data of Normality Testing of Control Class .illost-Test)
Class
z
interval mean s score o-z
:1:1:
Chi
3 59-65
4 66-72
5 73-79
6 80-86
no interval
I 30-36
2 37-43
3 44-50
4 51-57
5 58-64
6 65-71
57.5 63,9 10,27 -0.62 0.2324 9.6976 12 2,3024 5,30104576 0.546635
63.5 63,9 10,27 -0.03 0.012 9.5656 6 -3,5656 12,7135034 1.329086
69.5 63,9 10,27 0.54 0.2054 7.1808 10 2,8192 7,94788864 1.106825
75.5 63,9 10,27 1.12 0.3686 3.8632 2 -!,8632 3,47151424 0.898611
81.5 63,9 10,27 1.71 0.4564 5.494828
From the table above, it was known that the total of
;r'
Mtung, on db= k-1
= 6 - I
= 5 and
CL= 0.05 known that ;r21abel= I 1-070,
;r2Mtung=
5.494828, so
;r
21""'"" (5.494828) < ;r21abd (I 1.070), it can be concluded [image:53.595.2.473.112.643.2]that the sample was normalized distribution.
Table 3.12
Data of Normality Testing of Experiment Class (Pre-Test)
Class z- Chi
interval mean s score o-z fe fo f-fe (f-fe)2 Quadrate
29,5 50 11,43 -2.45 0.4929 1.5664 4 2,3788 5,65868944 3.780905
36,5 50 11,43 -1.72 0.4573 5.2096 4 0,7268 0,52823824 0.280853
43,5 50 11,43 -0.99 0.3389 10.3972 5 1,2132 1,47185424 2.801694
50,5 50 11,43 -0.26 0.1026 12.3112 15 -3,3608 l l,2949766 0.587241
57,5 50 11,43 0.46 0.1772 9.0552 13 -1,4108 1,99035664 1.718509
64,5 so 11,43 1.19 0.383 3.9424 3 4,162 17,322244 0.225273
- ·
71,5 50 11,43 1.92 0.4726 9.394475
According to the table above, it was known the total of
;r
2,,'"'"•, on
uo interval
1 65-69
2 70-74
3 75-79
4 80-84
5 85-89
6 90-94
7 95-99
46
Table3.B
Data of Normality Testing of Experiment Clasi.JPost-Test)
Class
z
Chiinterval mean s score 0-z fe fo Qセヲ・@ (f-fe)2 Quadrate
64.5 81,09 8,23 -2.01 0.4778 2.5784 5 2,4216 5,86414656 2.274335
69.5 81,09 8,23 -1.4 0.4192 5.7684 5 -0,7684 0,59043856 0.102357
74.5 81,09 8,23 -0.8 0.2881 9.3632 6 -3,3632 I l,31l1142 1.208039
79.5 81,09 8,23 -0.19 0.0753 10.3136 15 4,6864 21,962345 2.129455
84.5 81,09 8,23 0.41 0.1591 3.228 5 -3,228 10,419984 1.266405
89.5 81,09 8,23 1.02 0.3461 4.4572 6 1,5428 2,38023184 0.53402
94.5 81,09 8,23 1.62 0.4474 1.7468 2 2 4 2.289902
99.5 81,09 8,23 2.23 0.4871 9.804514
Based on the table above, it was known the total of
x
2 """"g , on db= k-1 = 7- 1 = 6 and a = 0.05 known that X2tabd = 12.592, x'ltittmg =
9.804514 so,
x
2,,,,,,,,g
(9.804514)<x
2'"'" (12.592) it can be concluded thatthe sample was normalized distribution.
2. Homogeneity Testing
The testing of homogeneity both of experiment and control
class was done to know the similarity between two populations
which researched.
The testing of homogeneii:1 was done by using Bartlet
formula. The criterion of hypothesis is:
2. If F1iitung > Ftnbcl , so the null hypothesis (l-10 ) is
rejeeted. The population of two samples is not
homogeny.
For experiment class, it was known that ,:i;2
1;,,,,,g
(2.99)s
z
21ahd(3.841) so