IN SMA NEGERI 1 DEPOK
TO ENHANCE THE PUBLIC SPEAKING SKILL
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Maria Setyaningsih Nernere Student Number: 091214063
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
i
MATERIALS FOR AN ENGLISH CLUB
IN SMA NEGERI 1 DEPOK
TO ENHANCE THE PUBLIC SPEAKING SKILL
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Maria Setyaningsih Nernere
Student Number: 091214063
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA
iv
I dedicate this thesis to Bapa, Mama, Galuh, Vian, Putri
vii
Nernere, M.S. 2013. A Set of English Instructional Materials for the English Club in SMA Negeri 1 Depok to Enhance the Public Speaking Skill. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
SMA Negeri 1 Depok is one of the schools which has an English extracurricular namely English Club. It is programmed as an opportunity for students to compensate for their minimum speaking practice time. The English Club aims to enhance the students’ public speaking skill. Unfortunately, the materials of English Club are not designed based on the needs analysis. Therefore, in this research, the researcher designs a set of English instructional materials for the English Club in SMAN 1 Depok to enhance the public speaking skill.
There were two research problems in this research: 1) how is a set of English instructional material for the English Club in SMAN 1 Depok to enhance the public speaking skill designed? 2) what does the designed instructional materials for English Club in SMAN 1 Depok to enhance the public speaking skill look like? In order to answer the research problems, the researcher applied the adapted model of Educational Research and Development by Borg and Gall (1983) which consisted of five steps for the research and the adapted instructional design model by Jerrold E. Kemp (1977) which consisted of seven steps for the designing process. To gather the data needed in this research in the pre- design, the researcher distributed questionnaires to the participants, tutors and the coordinator of English Club. Then, in the post- design the researcher also distributed questionnaires to the lecturers of English Language Education Study Program from Sanata Dharma University and an English teacher who was the coordinator of English Club in SMAN 1 Depok to evaluate the designed materials.
In this research, the researcher also conducted interview to obtain the more complete data.
The research applied communicative language teaching as the approach used to design the materials. The designed materials consisted of six topics. They are: 1) Be an Effective Speaker, 2) Seize Their Attention, 3) Let’s Practice, 4) Let’s Write A Speech, 5) Let’s Prepare, 6) Let’s Perform. In each meeting, they were three main parts. They were: 1) pre- activity, 2) whilst activity and 3) post- activity. Based on the result of preliminary field testing, the designed materials are acceptable but they should be revised. The revised version of the designed materials is presented in appendix F.
viii
Nernere, M.S. 2013. A Set of English Instructional Materials for The English Club in SMA Negeri 1 Depok to Enhance The Public Speaking Skill. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
SMA Negeri 1 Depok adalah salah satu sekolah yang memiliki program ekstrakurikuler Bahasa Inggris yang bernama English Club. Program ini memberi kesempatan bagi siswa untuk mengatasi minimnya waktu untuk melatih keahlian berbicara. Dalam program ini, keahlian para siswa dalam berbicara di depan umum ditingkatkan. Sayangnya, materi English Club tidak didesain berdasarkan analisis kebutuhan. Oleh karena itu, dalam penelitian ini peneliti mendesain seperangkat materi Bahasa Inggris untuk English Club di SMAN 1 Depok demi meningkatkan keahlian berbicara di depan umum.
Dalam penelitian ini ada dua rumusan masalah, yaitu: 1) bagaimana seperangkat materi Bahasa Inggris untuk English Club di SMAN 1 Depok demi meningkatkan keahlian para siswa dalam berbicara di depan umum didesain, 2) seperti apa desain materi Bahasa Inggris untuk English Club di SMAN 1 Depok? Untuk menjawab rumusan masalah tersebut, peneliti mengaplikasikan model Educational Research and Development oleh Borg and Gall (1983) yang terdiri dari 5 langkah dan model Instructional Design oleh Jerrold E. Kemp (1977) yang terdiri dari 7 langkah untuk proses desain. Untuk mengumpulkan data yang dibutuhkan dalam penelitian sebelum mendesain materi, peneliti mendistribusi kuesioner bagi 96 peserta, 11 tutor dan seorang koordinator English Club. Kemudian setelah mendesain materi, peneliti mendistribusikan kuesioner untuk mengevaluasi materi kepada 2 dosen PBI Unversitas Sanata Dharma dan seorang guru Bahasa Inggris yang merupakan koordinator English Club. Dalam penelitian ini, peneliti mjuga melakukan interview untuk memperoleh data yang lebih lengkap.
Peneliti mengaplikasikan communicative language teaching sebagai dasar untuk mendesain materi. Materi yang didesain terdiri dari 6 topik. Topiknya adalah 1) Be an Effective Speaker, 2) Seize Their Attention, 3) Let’s Practice, 4) Let’s Write A Speech, 5) Let’s Prepare, dan 6) Let’s Perform. Setiap pertemuan terbagi dalam 3 bagian, yaitu: 1) kegiatan awal, 2) kegiatan inti dan 3) kegiatan akhir. Berdasarkan hasil dari tahap preliminary field testing, materi yang telah didesain dapat diterima sebagai bahan ajar, namun masih perlu direvisi. Materi yang telah direvisi dapat dilihat di lampiran F.
ix
First of all, I dedicate my greatest gratitude to my one and only Jesus for
His patience and great blessing. He always has His own way to motivate me. He
watches me find unpredictable problems and other difficulties on writing this
thesis then He lets me find a way. The path seems so far but He makes me feel
that there is a hope.
I would thank my sponsor, Agustinus Hardi Prasetyo, S.Pd., M.A., for
his guidance, advice and encouragement in his own style to support me in
finishing this thesis. I thank also Christina Lhaksmita Anandari, S.Pd., Ed.M.,
Patricia Angelina, M.Hum., Laurentia Sumarni, S.Pd., J. Sri Murwani, and
other lecturers who were willing to evaluate my design and share their knowledge
with me. I would also thank my advisor, C. Sih Prabandari, S.Pd., M.Hum.,
Caecilia Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd., Mbak Danik, Mbak Tari, and all of the
staff members of the English Language Education Study Program for all their
help.
My gratitude also goes to Priyanta Ari, S.Pd. and Ms. Agnes, the English
teachers in SMAN 1 Depok who are so kind. They guide me on gathering data and
give suggestion when I face problems. I also thank Ika as my partner in SMAN 1
Depok. The students in SMAN 1 Depok are also supportive. I am so blessed to
have them as the participants in my research.
I sincerely express my gratitude to my lovely parents, Papa Yus and
Mama Siwi, who always give their best love to me although I am the annoying
daughter. They are the best parents I have ever had in this life. I do feel blessed by
having Galuh, Vian, and Putri as my precious siblings who were annoying by
joking around about when I can finish my thesis. I also thank Ngare, Sawe, Pae,
Bue, Bibi, Om Dedy, Jo, and all of my family for their prayers and supports that
they give. I love them and I will always love them until the end of my life.
I would also thank my college friends who accompany my journey in PBI.
My special thanks go to Awang, Rini, Hehen, Rosi, all my caring friends in PBI,
x
give. I do also thank Gusti for his love, patience and support that he shares to me.
I thank the people around me for their suggestions, courage, and any help
to finish this undergraduate thesis and making it happen at last.
xi
Page
TITLE PAGE...i
APPROVAL PAGE...ii
DEDICATION PAGE...iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY...v
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI...vi
ABSTRACT...vii
F. Definition of the Terms...6
1. Instructional Material...6
2. Public Speaking...6
3. Speech...6
4. English Club...7
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE...8
A. Theoretical Description...8
1. Instructional Design...8
2. Educational Research and Development...12
xii
5. Speech...19
B. Theoretical Framework...21
1. Identifying Learner’s Characteristics and Needs...22
2. Formulating the goals, topics and general purposes...23
3. Formulating Learning Objectives...23
4. Listing Subject Content...23
5. Designing Learning Activities...24
6. Evaluating the Designed Materials...24
7. Revising the Designed Materials...24
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY...25
A. Research Method...25
B. Research Participants...28
C. Research Instruments...29
D. Data Gathering Technique...30
E. Data Analysis Technique...31
F. Research Procedures...32
CHAPTER IV RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION...36
A. The Steps of Designing Instructional Materials...36
1. Learner’s Characteristics...36
2. Goals, list topics, and the general purposes for teaching each topic...38
3. Subject Content...40
4. Learning Objectives...42
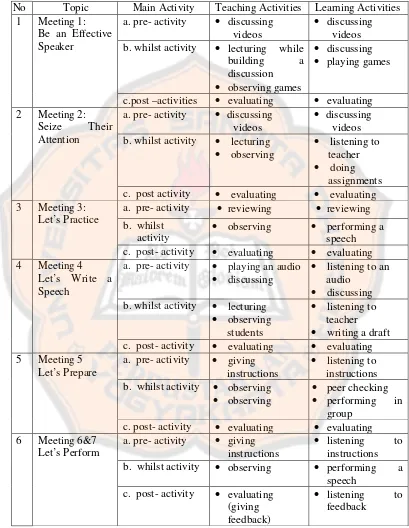
5. Learning Activities...43
6. Evaluation...46
7. Product Revision...51
B. Presentation of A Set Of English Instructional Materials...52
CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS...55
A. Conclusions...55
B. Recommendations...56
xiv
Table Page
Table 3.1 The Expected Data...31
Table 3.2 The Form of Evaluation Device...32
Table 4.1 The Learners’ Characteristics Summary...38
Table 4.2 List of The Topics...39
Table 4.3 List of Topics and Content...42
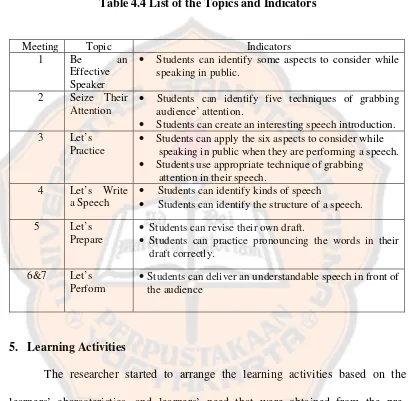
Table 4.4 List of Topics and Indicators...43
Table 4.5 The Description of Designed Materials...45
Table 4.6 The Description of Participants of Post- Design Survey...46
Table 4.7 The Result of Post- Design Survey...46
Table 4.8 The Strengths and Weaknesses of the Designed Materials...50
xv
Figure Page
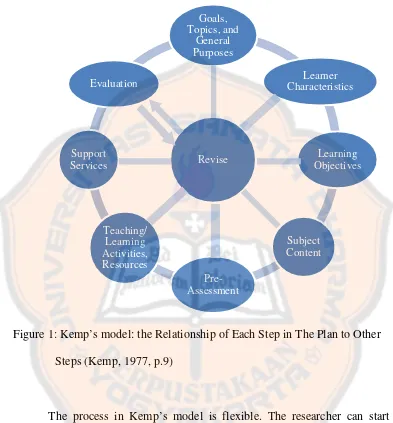
Figure 1: Kemp’s model: The Relationship of Each Step in The Plan to Other
Steps (Kemp, 1977, p.9)...10
Figure 2: Kemp’s model: The Combined R & D model and Kemp’s Model...27
xvi
Page
APPENDICES...60
Appendix A: Letter of Permission...61
Appendix B: Questionnaire and Interview Checklist for Research and Information Collecting and the results...63
Appendix C: Questionnaire of Preliminary Field Testing and the Result...71
Appendix D: Overview of the Designed Materials...74
Appendix E: Syllabus...77
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter consists of six major parts, namely the research background,
research problem, problem limitation, research objectives, research benefits, and
definition of terms.
A. Research Background
Based on TEFLIN (2013), the Minister of Kemendiknas decided to have
English as the local subject and/ or the extracurricular in schools (p.12). Some
schools in Yogyakarta put English as one of the extracurricular activities in school
to support their students in practicing English. One of those schools is SMAN 1
Depok, Sleman. This school facilitates the students with English Club. This
program is a place for students to practice their speaking skill to compensate for
minimum speaking practice time. Based on the statement of English Club’s
coordinator, the school expects that by facilitating the students to practice, their
ability to communicate in English orally will be developed, especially in public
speaking. Grice and Skinner (1995) say that studying public speaking helps
students to succeed in college, increases the students’ knowledge and builds the
students’ confidence (p.2). In this case, the school explicitly expects that through
English Club, there will be students who master debate, storytelling, and speech.
the debate, storytelling, and speech competitions which are held by the office of
education annually.
The English Club in SMAN 1 Depok is held from 6.30 to 7.30 a.m every
Saturday during one semester for the tenth grade students. In order to improve the
students’ public speaking skill and prepare them for debate, storytelling, and
debate competitions effectively in one semester, there should be good designed
materials and motivated students.
Unfortunately, the materials for this English Club have not been fixed yet
by the coordinator. Each semester, the coordinator only asks the tutors to create
the materials without any guidance as long as there are basic practices for debate,
storytelling and speech. Needs analysis was not conducted prior to the designing
process. The materials were designed only based on the coordinator’s expectation
without asking information about the students’ need first. Based on Kemp’s
instructional design’s model (Kemp, 1977), “in order to create materials, needs
analysis from some important parties such as students, teachers and other sponsors
are important to consider for creating the materials” (p.8). Since the fact says that
the materials have not been designed optimally, the researcher wants to design the
materials using the right steps. Later, the result of this research can be used
effectively to support the process of achieving English Club’s goal.
In order to enhance the students’ public speaking skill, the activities
designed in the materials will be based only on speech. The researcher limits the
activities because the materials to enhance the English public speaking skill
the principles of public speaking and speech, the student is expected to be a good
public speaker. Research shows that by taking a speech course, people can
improve their speech skills significantly. Moreover, Ross (1995) states that
testimonials by successful individuals have affirmed the value of speech training,
and research has indicated its usefulness to the people in better understanding
related to courses (p.4). By using speech as the context, the students, as educated
people, can learn how to manage their ideas and deliver them to the public. The
researcher will design the materials based on the needs analysis done to the
students, tutors and English Club’s coordinator. These materials will be useful for
the school since it is designed for the effectiveness of English Club itself. If the
material is well organized and the motivated students are guided through the right
method, the goal will be achieved.
B. Research Problem
This research is intended to answer the research problems which are stated
as follows:
1. How is a set of English instructional materials for the English Club in
SMAN 1 Depok to enhance public speaking designed?
2. What does a set of English instructional materials for the English Club in
C. Problem Limitation
The skill developed through this material is speaking, specifically in public
speaking. The English Club is held to develop the public speaking skill by using
storytelling, speech, and debate activities. In this case, the researcher will focus
only on designing English instructional materials by choosing speech as the
context for the activities. These materials are designed to guide the students to
perform a speech in public well. The researcher chooses to design the materials
for this program because it is closely related to students’ achievement in public
speaking. Since the time is limited, the researcher will design the materials
without implementing them.
D. Research Objectives
This research aims to:
1. design a set of English instructional materials for the English Club in SMAN 1
Depok
2. present the designed instructional speaking materials for the English Club in
SMAN 1 Depok
E. Research Benefits
This research will be useful for:
1. Students of SMAN 1 Depok
The researcher has done the observation on the activities of the English
Club by using the materials that they like and need. Then, they can be more
interested to join the activities designed for the English Club. Later on, they can
improve their public speaking skill significantly.
2. Tutors of the English Club in SMAN 1 Depok
The tutors can apply the suitable materials in the learning process so they
may find it easy to guide the students to achieve the expected goals.
3. SMAN 1 Depok
If the materials of English Club have been designed well based on the
needs analysis, the program of English Club can be done effectively. Then, the
students can improve their public speaking skill specifically skill needed to
deliver a speech. Later, there will be students of SMAN 1 Depok who master
public speaking skill born through this English Club. They can be the school’s
representatives who can join the speech competition.
4. PBI field and the readers
This research will help the PBI students and the readers to know the
suitable materials to improve the public speaking skill by applying speech
activities.
5. The future researchers
The future researchers can implement these designed materials in SMAN 1
Depok to measure the effectiveness of the materials. They also can apply these
F. Definition of Terms
There are several terms used in this research. In this research, the terms
are:
1. Instructional Material
In this research, the researcher will design a set of instructional materials.
According to Newby, Stepich, Lehman, and Russell (2000), “instructional
materials are the specific items used in a lesson and delivered through various
media (p.17)”. The media used for instructional materials are tutor’s printed book
and student’s handout compilation. In this research, the materials are designed for
the first seven meetings in English Club.
2. Public Speaking
Public speaking belongs to five levels of communication. Grice and
Skinner (1995) state that public speaking occurs when one person speaks face to
face with the audience, either large or small. Public speaking involves verbal,
vocal, and visual channels (p.10). In this research, public speaking is meant to
deliver a message, whether it is a story, speech or another message.
3. Speech
Based on Cambridge dictionary, speech is a formal talk given usually to a
large number of people on a special occasion. Due to Keppler and Gunther
(1994), speeches are sound waves that go out from the speakers across the room
and into the ears of the listeners. It is meant primarily to entertain, to inform, or to
defend (p.9). Grice and Skinner (1995) also say that commonly, speech has two
concludes that a speech is a form of communication in spoken language built by a
speaker to an audience for a purpose, whether to inform or to persuade.
4. English Club
English Club is one of the extracuricular activities. In SMAN 1 Depok, it is
held from 6.30- 7.30 a.m., before the learning activity starts. Every tenth grade
student has to join this activity. There are twelve classes in English Club and each
class consists of 16 students. This extracuricular aims to improve the students’
8
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter consists of two major parts. The first part will deal with the
theoretical description which covers main points, namely the instructional design,
educational research and development, communicative language teaching, public
speaking, and speech. Then, the second part will be about the theoretical
framework. The researcher will discuss the relation among the concepts stated
previously as the basis of designing the English instructional materials for English
Club in SMAN 1 Depok.
A. Theoretical Description
1. Instructional Design
There are some theories of instructional design that become the underlying
theories for many studies related to pedagogical design. In this research, the
researcher will adapt the instructional design proposed by Kemp.
“Instructional design is a process of systematic planning that establishes a way to
examine instructional problems and needs, set of procedure for solving them and
then evaluates the result (Kemp, 1977, p.7)”. The process is clearly stated and
arranged in order. Kemp’s model can be used at all education level from
elementary school up to college. Another benefit is that this model can be
implemented in the instructional unit for a single subject. It is suitable for this
(1977), the instructional design plan is designed to supply answers to three
questions. They are: “what must be learned (objectives); what procedures and
resources will work best to reach the desired learning levels (activities and
resources); how will we know when the required learning has taken place?
(evaluation)” (p.8).
The model proposed by Kemp consists of eight parts which are as follows:
a. Consider goals, and then list topics, stating the general purposes for teaching
each topic.
b. Enumerate the important characteristics of the learners for whom the
instruction is to be designed.
c. Specify learning objectives to be achieved in terms of measurable student
behavioral outcomes.
d. List the subject content that supports each objective.
e. Develop pre- assessments to determine the student’s background and present
level of knowledge about the topic.
f. Select teaching/ learning activities and instructional resources that will treat
the subject content so students will accomplish the objectives.
g. Coordinate such support services as budget, personnel, facilities, equipment,
and schedules to carry out the instructional plan.
h. Evaluate students’ learning in terms of their accomplishment of objectives,
with a view to revising and reevaluating any phases of the plan that needs
Here is the Kemp’s model:
Figure 1: Kemp’s model: the Relationship of Each Step in The Plan to Other
Steps (Kemp, 1977, p.9)
The process in Kemp’s model is flexible. The researcher can start the
process from whichever element ready to start with. The elements can be done in
different order, by not following the order stated on the figure above. The
researcher also can adapt the elements based on the researcher’s need and
situation. In this research, the researcher applied six steps adapted from eight
Kemp’s steps. They are as follows:
a. Enumerate the important characteristics of the learners for whom the
instruction is to be designed.
In order to achieve the target of learning, the student should be considered as
an individual learner. Therefore, the students’ capabilities, need and interest
are important to be observed then used as consideration to plan the learning.
b. Consider goals, and then list topics, stating the general purposes for teaching
each topic.
The goals will be derived from the society, students and subject areas. When
the goal is identified, the researcher will list the major topics which will be the
scope of the course. The topics should be selected in detail (include the portion
and in what depth). Each topic should have general purposes using the clear
expression/ action verb.
c. Specify learning objectives to be achieved in terms of measurable student
behavioral outcomes.
The learning outcome consists of cognitive, psychomotor and affective. As the
result of instruction, those outcomes should be measurable.
d. List the subject content that supports each objective.
The subject content is related to the objectives and the learners’ need.
e. Select teaching/ learning activities and instructional resources that will treat
the subject content so students will accomplish the objectives.
The designer should select the suitable teaching/ learning method which will
be applied in class. The activities should be arranged then the students can
f. Evaluate students’ learning in terms of their accomplishment of objectives,
with a view to revising and reevaluating any phase of the plan that needs
improvement.
After the process of designing is finished, the result will be checked whether it
meet the objectives. Then, the designer will do the revision and reevaluation if
any to do the improvements.
2. Educational Research and Development
In order to produce a product which can meet its objectives, the researcher
needs to apply the theory of educational research and development. According to
Borg and Gall (1983), educational research and development (R & D) is a process
used to develop and validate educational products. R & D creates a design as a
solution to solve some practical problems in education.
The major steps in the R & D cycle in this research used to develop mini
courses are as follows (Borg& Gall, 1983, p.775) :
a. Research and information collecting
It includes review of literature, classroom observation, and preparation of
report of state of the art. In this step, the researcher collects the theories which
related to the research and other information needed.
b. Planning
In this step, the researcher focuses on defining skills, stating objectives
c. Develop preliminary form of product
It includes preparation of instructional materials, handbooks, and
evaluation devices.
d. Preliminary field testing
The researcher will conduct the survey using interview, observation and or
questionnaire from 1 to 3 schools, using 6 to 12 subjects. Then, the interview,
observational and questionnaire data would be collected and analyzed.
e. Main product revision
There will be revision of product as suggested by the preliminary field- test
results.
3. Public Speaking
The materials designed in this research are focused on enhancing the
students’ public speaking skill. According to Zarefsky (1996), “public speaking is
a communication process in which speakers and listeners jointly create meaning
and understanding (p.3)”. To get this successful communication, the students
should apply the principles of public speaking. Grice and Skinner (1995) say that
“the first principle is that the more effective you prepare, the better the speech you
will deliver and the more confident you will feel. The second principle is that
every public speech is a blend of content, organization, and delivery (p.16)”. It is
seen that preparation is the key to achieve the goal of communication that the
having well- arranged speech and rehearse to deliver a speech well. If they are
well- prepared, they will perform better.
In order to enhance the students’ speaking skill, the activities designed in
the materials should support the students. According to Harmer (2007), “good
speaking activities can and should be extremely engaging for the students
(p.123)”. If the teacher at class could provide the useful and interesting activity,
the students will get satisfaction from it. Then, they can show the good
performance. Davies (2000) suggests that script-based role play or simulations,
script-based conversations, and form-based interviews or surveys are the
examples of activities designed to encourage learners to communicate as naturally
as possible. By having practice on the usual things, students can be more fluent to
speak in class.
In a speaking class, the activities should be arranged properly. The concept of
learning is focused more on practice. It does not only concern on the language
construction. In assessing speaking, Klippel (2005) states some principles in
developing and selecting learning activities (p.83):
1. Target language is actually used as a means of communication.
The learning activities used in speaking class are reflected from the
spontaneous real communication. The tutor can guide the students to practice
on discussing trending topics or other real issues.
2. The existence of information gap and opinion gap which are considered as
To create communicative activities, it is good to involve the students in a
discussion where they can share their knowledge and inspire others with their
opinion.
3. Learning foreign language is not only a matter of memorizing a different set
of names for the things around us; it is also an educational experience.
In teaching speaking, the students do not only learn about the grammar and
other structural things but they can find new knowledge from some contexts
they have in the process of learning language.
4. Learning will be more effective if the learners are actively involved in the
process.
By taking active roles in the learning activities, the students can get a greater
chance to apply what they have learnt. In fact, something applicable is easier
to understand.
5. Learning becomes impossible even for the most extrovert person if the
atmosphere in the group is unsympathetic and the learner is afraid of being
ridiculed or mocked.
The first essential requirement for the use of learner- centered activities is a
relaxed and friendly atmosphere in the group. In order to achieve the goals of
the activities in speaking class, the preparation is not only on the activities.
The supporting class atmosphere should be considered also.
The activities in English Club will be considered success if good public
speakers could be born through. A good public speaker is the one who can deliver
Skinner (1995) say that “as a first-time public speaker, success may mean being
able to get up in front of the class, speak for at least the minimum time limit, and
have a decently organized speech on an appropriate topic (p.15)”.
4. Communicative Language Teaching (CLT)
According to Richards and Rodgers (2001) CLT refers to various sets of
principles which reflects a communicative view of language and language
learning and which can be used to support a wide variety of classroom procedures
(p.172). CLT aims to foster and develop the learner’s communicative competence
(Hughes, 2002). In this communicative classroom, students ultimately have to use
the language, productively and receptively, in unrehearsed contexts.
a. Principles in Communicative Approach
These principles are as follows (Richard and Rodgers, 2001):
i. through using the language, the learners learn to communicate
In this approach, language learning means as learning to communicate in
which effective communication is sought. Furthermore, Hughes (2002) also
consider that communicative approach should places high value on language in
use. Then CLT links teaching methodologies to appropriate communicative tasks
(rather than seeing classroom tasks as a means of practicing a particular
grammatical feature) (p.24). The learners learn how to use the language. They do
not learn the language itself (the structure of it) explicitly. Organizational
language forms are not the central focus but rather aspects of language that enable
competence, grammar is not the main thing to concern about. Brown (2000)
confirms this idea by stating that classroom goals are focused on all of the
components of communicative competence and not restricted to grammatical or
linguistic competence (p.266). The more important thing is how the
communication works so the meaning can be delivered well.
ii. the goal of classroom activities is at authentic and meaningful communication
The activities held are to guide the learners to speak on specific things
which are around us. Brown (2000) also stated the same by stating that language
techniques are designed to engage learners in the pragmatic, authentic, functional
use of language for meaningful purposes.
iii. fluency is an important aspect of communication
Fluency and accuracy are seen as complementary principles underlying
communicative techniques. At times fluency may have to take on more
importance than accuracy in order to keep learners meaningfully engaged in
language use (Brown, 2000).
iv. the integration of different language skills is involved in the communication
To develop the learners’ speaking skills, the skills trained during the
activities are not only speaking, but also other skills. This is called integrated.
v. learning is a process of creative construction and involves trial and error
Hughes (2002) says “in CLT, the language is learnt, it is not an end in
itself but rather, it is a means to carry out communication. Error is considered as a
natural part of progression towards a greater understanding of the target language
b. Student’s Role
Hughes (2002) says that CLT places the learner at the centre of the
learning process and assess progress in relation to factors affecting the individual
(e.g level of motivation). It tends to favor inductive, student- centre routes to
understanding (rather than explicit, teacher- led explanation). The students should
take more active role on the activities so they can find the understanding by
themselves, not merely by teacher’s explanation.
c. Teacher’s Role
There are number of teachers’ role in this approach. Richards and Rodgers (2001)
classify those roles into three main categories. First, the teachers facilitate the
communication process among the learners, and between the learners and the
activities. Second, the teachers act as independent participants within the learning
teaching process. Finally, the teachers have a role as researcher and learner in
which they need to contribute knowledge, abilities and experiences.
There are three kinds of materials considered in CLT:
i. Text-based materials that based on the texts that help the teacher to initiate
conversation. The examples of these materials are visual cues, pictures, and
sentence fragments.
ii. Task-based materials
In order to support CLT classes, a variety of games, role play and task-
based communication activities have been prepared. These are usually in the
form of one- of- a- kind items: exercise handbooks, cue cards, pair
iii.Realia
Realia might be included as proponents of CLT. This might include
language based realia such as sign, magazines, newspaper, or visual sources
around which communicative activities can be built.
5. Speech
As stated in the research background, the researcher designs materials that
use speech as its focus. The students have been familiar with speech. As what
Rivers (1983) says that people are accustomed to speaking in which they can
deliver ideas to others. Through delivering a speech, man expresses his emotions,
communicates his intentions, reacts to other persons and situations, as well as
influences other human beings (p.162). Then, the researcher concludes that a
speech is a form of communication in spoken language which is made by a
speaker to an audience. It is a formal talk to communicate what the speaker
thought on certain topic to the audience for a certain purpose, whether to inform
or to persuade.
Students are expected to enhance their skill to communicate in public
through speech. Speech is a kind of activity to transmit a particular message to the
audience. To succeed in conveying the message, a speaker should have a good
preparation. A speaker must learn and apply the principles and strategies of
delivering a speech in public. According to Grice and Skinner (1995), the
body of speech, effective ideas’ development, effective conclusion, dynamic voice
and body to communicate his idea and correct word ideas correctly (pp. 16-22).
Grice and Skinner (1995) conclude that in the process of developing and
delivering a public speech, a speaker sharpens and uses eight categories of critical
thinking skills (p.25). The example is focusing skills as the speaker selects his
speech topic and narrows it to key points. A good speaker should be able to be
critical by developing his ideas and manage them into great speech. “Speech is not
spoken writing” (Bygate, 1987, p. 51). Since a speech is delivered not only to
individual people, a speaker should manage his own speech, not too long and
complicated as the writing has.
According to Miyata (1956), there are some techniques that should be
considered by a speaker. They are:
a. Developing rapport with an audience
A successful speaker needs to develop a rapport with an audience. He
needs them in his side to root him, support him, sympathize with him and believe
him. Eye contact and audience participation are the simplest and most effective
techniques used to establish audience rapport.
b. Using body language
As public speakers, students need to impart positive messages to their
audience. Through stance, gesture, and facial expression a speaker can add
c. Exploring voice
A speaker needs to be heard to get what he needs from his audience ─ a
reaction. He can whisper to make the audience nervous. He talks faster to let his
audience think. He snorts to make his audience smile. Voice is a tool for
manipulating the audience to where the speaker wants them.
d. Showing Composure
The speaker may be panicky, unsure, terrified, worried, excited, thrilled, or even
nauseous, but the audience must perceive composure. The first composure tactic
is gaining an understanding of their own bodies and how nervous energy affects
the performance. Second tactic is practice. The last one is to engage actively in the
exercise to relax.
B. Theoretical Framework
This part discusses the underlining theories to design the English speaking
instructional materials for SMAN 1 Depok. In the process of designing, the
researcher implements the cycles of Educational Research and Development (R &
D) to obtain the goal of this research. Unfortunately the steps in R & D are still
general. Therefore, the researcher applies the specific steps from adapted Kemp’s
model. This model is used because of its flexibility so that the steps can be
simplified based on the situation and any revisions also can be done in any steps.
In this research, the researcher does not implement all steps of Kemp’s model.
The researcher omits the pre-assessment and support services. In the process of
theories. Other theories are also used, as stated in the theoretical descriptions.
They are communicative language teaching, public speaking, and speech. Those
theories are under the umbrella of R & D, since R & D is the main framework of
this research.
Since the learners of English Club want to have more practices to enhance
their speaking ability, the researcher decides to apply theory of communicative
language teaching as an approach used to create and select the learning activities
in English Club’s class. The principles of Communicative Language Teaching
(CLT) are appropriate to be applied in order to enhance students’ speaking ability.
The CLT’s principles, characteristics and kinds of material will be used as the
consideration during the process of designing materials to create the
communicative atmosphere.
The theory of speaking and speech will guide the researcher to create
materials which focus only on improving and developing students’ speaking skill.
Besides, since the aim of English Club is focused to prepare the students for
storytelling, speech and debate competition so the theories of those aspects are
really needed.
These are the steps of designing instructional materials that used by the
researcher:
1. Identifying Learner's Characteristics and Needs
In this step, the researcher applied Research and Information Collecting of R
& D model to identify the learner’s characteristics and needs. In this step, the
researcher distributed different questionnaires to the tenth grade students who
had joined English Club and all the tutors of English Club. After that, the
researcher also interviewed the coordinator of English Club to get the data
about the learner’s characteristics and English Club.
2. Formulating the goals, topics and general purposes
This step was under the umbrella of Planning from R & D model. From the
interview done with the coordinator of English Club, the goal of English Club
and the students’ need was simply concluded. By considering those data and
doing library study, the researcher formulated the goals, decided the topics
and formulated the general purposes as the planning step before designing
materials.
3. Formulating Learning Objectives
In this step, the researcher applied planning from R & D model as the
umbrella of formulating learning objectives from Kemp’s model. The
researcher formulated the learning objectives for each meeting using the
appropriate action verbs.
4. Listing Subject Content
This Kemp’s step was under the umbrella of developing preliminary form of
product from R&D model. In this step, the researcher chose the appropriate
subject content and listed them. This subject content should be suitable with
5. Designing Learning Activities
This step was under the umbrella of Developing Preliminary Form from R &
D model. Supported by some theories provided in chapter II, the researcher
chose the suitable learning activities and arranged them in order to achieve the
objectives for each meeting.
6. Evaluating the Designed Materials
This step was under the umbrella of Preliminary Field Testing from R & D
model. After designing the materials, the designed materials were evaluated
by the experts to measure whether the materials were suitable with the
objectives. The evaluation was done through filling out the questionnaire of
preliminary field testing.
7. Revising the Designed Materials
This was the last step of Kemp’s model which was under the umbrella of
Main Product Revision from R & D model. In this step, based on the
feedback from the experts, the researcher revised the designed materials. This
step aimed to improve the quality of materials so it could be used as the
25
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
The purpose of this chapter is to present the method used to answer the
research questions stated in the chapter I. This chapter is presented in six parts,
namely the research method, research participants, research instrument, data
gathering technique, data analysis technique, and research procedure.
A. Research Method
There were two research problems stated in Chapter I. Firstly, the research
was aimed to find out how a set of English instructional materials for the English
Club in SMAN 1 Depok is designed. Then, the second aim of this research was to
present a set of English instructional materials for the English Club in SMAN 1
Depok. To answer these problems, the researcher applied the educational
Research and Development (R & D). Borg and Gall (1983) state that R & D is a
process used to develop and validate educational products (p.772). The steps of
this process were usually referred to the R & D cycle. Adapted from Borg and
Gall (1983), the cycle in this research would consist of (775):
1. Research and information collecting
In this step, the researcher would identify learner's characteristics and
needs which was the step of Kemp’s model. In this step, library study and needs
analysis were conducted. Library study was done to find out the supporting
information about the learners’ characteristics (achievement, motivation, and
enthusiasm, and difficulty on learning speaking) and needs. The instruments of
needs analysis were questionnaire and interview. There were different
questionnaires distributed to students and tutors. After obtaining data through
questionnaires, the researcher interviewed the coordinator of English Club to find
out the learner’s characteristics and the school’s expectation of English Club and
how to achieve them.
2. Planning
In this step, the researcher applied the Kemp’s step of formulating the
goals, topics and general purposes and formulating learning objectives. After
getting the data needed, the researcher would define the skill, formulate the goals,
topics and general purposes of the designed materials. Then, the objectives for
each topic were formulated. This was the planning step before designing the
whole materials.
3. Developing preliminary form of product
In this step, the researcher listed appropriate subject content and designing
the suitable learning activities in order to achieve the objectives. This was the step
where the whole aspects were developed into an educational product. This step
also included the process of making tutor’s handbook and evaluation devices.
4. Preliminary field testing
This step implemented the step of evaluating the designed materials from
Kemp’s model. In this step, the research distributed questionnaire to the English
questionnaire would be the consideration for the researcher to create the better
product. The comments and suggestion from the experts were really needed. To
obtain the clearer explanation, the research may conduct an interview.
5. Main product revision
As the last step of Kemp’s model, in this step, the researcher would do the
revision of product as suggested by the preliminary field- test result to produce the
better design.
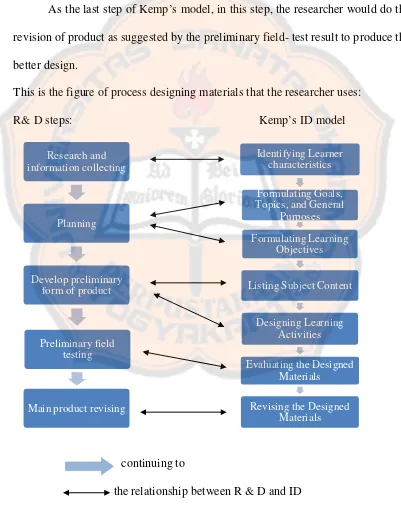
This is the figure of process designing materials that the researcher uses:
R& D steps: Kemp’s ID model
continuing to
the relationship between R & D and ID
Figure 2: Kemp’s model: the Combined R & D model and Kemp’s Model
B. Research Participants
1. Participants in Research and Information Collecting
Before designing the material, the researcher would collect the information
about learner’s characteristics (achievement, motivation, and enthusiasm, and
difficulty on learning speaking) and needs. The target population was the
participants of English Club. They were tenth grade students who belonged to six
classes. Fraenkel and Wallen (2009) say that as simple random sampling is more
effective with larger numbers of individuals, cluster random sampling is more
effective with larger numbers of clusters (p.95). Then, the researcher decided to
apply cluster sampling. There were three classes chosen as the sample. They were
classes XB, XD, and XF. Each class consisted of 32 students. These three classes
were chosen because the researcher had taught them so she had already known the
students’ characteristics. This information supported the researcher to do the
research. Then, in order to collect the information about the students’
characteristics and the method used in class, the researcher would distribute the
questionnaires to all eleven tutors. After that, the researcher would interview the
coordinator of English Club to find out the school’s expectation about the English
Club.
2. Participants in Preliminary Field Testing
The designed material would be evaluated by an English teacher of SMAN
1 Depok who is the coordinator of English Club and lecturers of ELESP Sanata
to get the feedback from the experts. The result from the questionnaires would be
used by the researcher to evaluate and revise the designed material.
C. Research Instruments
1. Instrument in Research and Information Collecting
In the stage of data collection, the researcher used different questionnaires
which were distributed to the students and tutors. The questionnaires would be
used to collect the data of learner’s characteristics (achievement, motivation, and
enthusiasm, and difficulty on learning speaking), learner’s needs and all about
English Club. The questionnaires were written in Bahasa so the respondents could
feel easy to state their opinion. Questionnaire distributed to students consisted of
13 close- ended questions and three open- ended questions. Then, the
questionnaires for tutors consisted of four open- ended questions.
After distributing the questionnaires, the researcher also did the interview
with the coordinator of English Club to find out the specific aims of the English
Club program, the method used and the learner’s characteristics. The interview
consisted of six main questions. By having interview, the researcher could dig
more information, as what Borg and Gall (2007) state that using interview helped
researcher to follow up a respondent’s answer to obtain more information and
clarify vague statement (p.228). Questionnaire and interview were used in this
research because according to Borg and Gall (2007), questionnaire and interview
were used extensively in educational research to collect the data about phenomena
the like (p.228). They also could be used to collect data about observable
phenomena more conveniently than by direct observation.
2. Instrument in Preliminary Field Testing
This research would use questionnaire to get the comments and
suggestions about the materials which had been designed. The questionnaire
consisted of 13 close- ended questions and two open- ended questions. The data
collected would be used to evaluate the designed material. According to Borg and
Gall (1983), questionnaires are appropriate to use in the preliminary field test.
Then, to obtain the clearer data, the researcher also conducted interview with the
evaluators (p.781).
D. Data Gathering Technique
In this research, the data used was collected from the questionnaires and
interview. First, in research and information collecting, the researcher conducted
library study which led to any information related to designing English speaking
instructional materials for high school. The researcher distributed questionnaires
to tenth grade students (XB, XD, and XF) and the tutors of English Club. The
researcher also conducted interview with the coordinator of English Club to
collect information about the aim and all about English Club.
To gather data on preliminary field testing, the researcher distributed
questionnaires to English teacher of SMAN 1 Depok and lecturers of ELESP
Sanata Dharma University as the experts. The data gathered would be used to
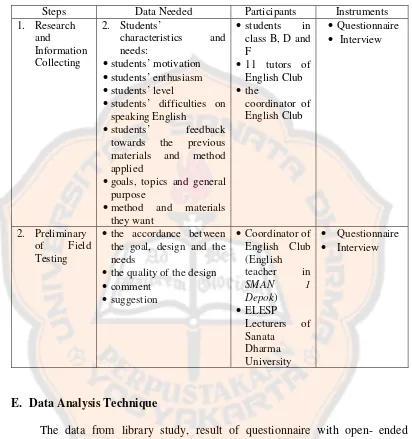
Table 3.1 The Expected Data
Steps Data Needed Participants Instruments
1. Research
•students’ difficulties on speaking English
•students’ feedback
towards the previous materials and method applied
•goals, topics and general purpose
•method and materials
they want
•the accordance between
the goal, design and the needs
•the quality of the design
•comment
E. Data Analysis Technique
The data from library study, result of questionnaire with open- ended
questions and interview would be analyzed in the form of description. Then the
data from questionnaire with close- ended questions would be analyzed in the
form of percentage. In analyzing the close- ended questions in the questionnaire
for students, the researcher would observe how many students agree about the
In the questionnaire for preliminary field testing, the estimation of the
participants’ opinion on the designed material used four points of agreements
namely:
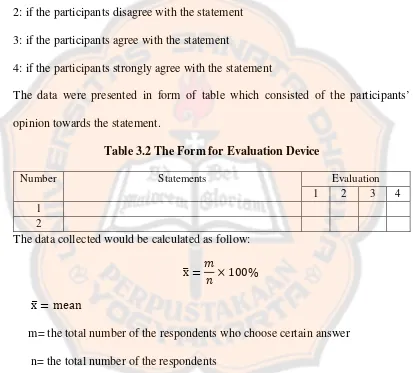
1: if the participants strongly disagree with the statement
2: if the participants disagree with the statement
3: if the participants agree with the statement
4: if the participants strongly agree with the statement
The data were presented in form of table which consisted of the participants’
opinion towards the statement.
Table 3.2 The Form for Evaluation Device
Number Statements Evaluation
1 2 3 4
1 2
The data collected would be calculated as follow:
x�=𝑚𝑚
𝑛𝑛 × 100%
x�= mean
m= the total number of the respondents who choose certain answer
n= the total number of the respondents
The comment and suggestion from the experts would be used as a guide to revise
and make the better material.
F. Research Procedure
The research procedures conducted were based on the integration of R &
was the main framework for this research and the researcher would implement
Kemp’s model as the specific steps to follow. There were 5 steps of research
procedures in this research. The steps were discussed as follows:
1. Research and Information Collecting
a. Identifying research problem
The researcher analyzed the educational problem in her surroundings. Finally,
she found it in her PPL’s school. Then she started to identify the research
problem.
b. Making proposal
After identifying the research problem, the researcher made the proposal and
proposed it to SMAN 1 Depok where the English Club held.
c. Asking for a letter of research permission
First, she asked for a letter to conduct a research from the chairperson of PBI.
Since the researcher needed the data from the students and coordinator of
English Club in SMAN 1 Depok, she should ask permission letter from the
Local Department who was responsible for the research permission in Sleman
and. Then she gave the permission letter to the headmaster of SMAN 1 Depok.
d. Collecting new knowledge and information related to the research
The researcher did the library study to find any information related to
designing English instructional materials to enhance public speaking. She
looked for the supporting theories from books and related information on the
e. Conducting survey
After having the review of literature, the researcher did survey by distributing
the questionnaires to three classes as the representative of tenth grade students
who were the members of English Club. The researcher also distributed
questionnaire to the tutors of English Club. The coordinator of English Club
would be interviewed also to find the school’s expectation from the
implementation of English Club in school.
f. Analyzing Needs Analysis Data
Based on needs analysis data, the researcher started to analyze them as the
basis before designing the instructional materials.
2. Planning
Based on the data of students’ wants and needs and school’s expectation,
the researcher formulated the goals of designed materials. Certainly, the focus of
the program would be on enhancing public speaking ability.
3. Development of Preliminary of Product
In this step, the researcher designed the material based on the data gathered
before. The students’ handout for the first seven meetings and tutor’s handbook
were created. Then, the evaluation devices were also prepared.
4. Preliminary Field Testing
The researcher distributed questionnaires of preliminary field testing to the
English teachers of SMAN 1 Depok and lecturers of ELESP Sanata Dharma
5. Main Product Revision
The evaluation from English teachers of SMAN 1 Depok and lecturers of
ELESP Sanata Dharma University as the experts were used as guidance to revise
36
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents the discussion and the finding of the research. It
focuses on finding the most appropriate design using speech activities for English
Club in SMAN 1 Depok. This chapter answers two questions stated in the research
problems. The first part is the discussion of the steps of designing instructional
materials. The second part presents the findings of the research that focuses on the
presentation of English instructional material to enhance public speaking skill
through using speech as the context for English Club in SMAN 1 Depok.
A. The Steps of Designing Instructional Materials
The researcher used some related theories as the basis in the process of
designing. The researcher applied the theories of Educational Research and
Development (R & D) proposed by Borg and Gall (1983), and combined with the
steps of Kemp’s model (1977). The adapted R & D was the main framework for
this research, and then the adapted Kemp’s model was used as the specific steps
followed in this research. These steps were, as follows:
1. Learner’s Characteristics
In order to know the learners’ characteristics, the researcher distributed
questionnaires to students of XB, XD, and XF, also tutors of English Club in
SMAN 1 Depok. The researcher also collected the information about the students
The learners were tenth grade students of SMAN 1 Depok. The
coordinator of English Club confirmed that the participants belong to students
who have good marks in English subject. He stated that the students could be
considered as intermediate- level students. Based on the academic report, it could
be seen that they already have good basic in English subject. The tutors also
confirmed that most of the students were having good understanding in English.
They already had the confidence of speaking in public. They found difficulties on
delivering the ideas. When they performed a speech, some of them just spoke out
what they had memorized without paying attention whether their audiences
understand the speech.
Based on the analysis of the questionnaires distributed to the students and
tutors, the participants of English Club were generally motivated to practice their
speaking skills during the English Club. They felt interested to learn about speech
as new experience for them to enhance their public speaking skill. Commonly,
they just practiced about daily conversation. Based on the questionnaires
distributed to tutors, the tutors also agreed that most of the students were highly
motivated to join the activities during English Club, although few students were
not interested to speak in public since they lacked confident. Still, all students
were discipline to join the activities in English Club. They liked to join activities
done in partner and group. They needed to have individual exercises to train their
own public speaking skill.
Eventhough the students had good understanding on grammar, they often
the tutor’s opinion, it was seen that they still did not have good vocabulary
mastery and they had problems in memorizing.
Here is the figure of the learner’s characteristics description.
Table 4.1 The Learners’ Characteristics Summary
Learning Motivation
• Most students were motivated to learn public speaking by joining English Club.
• Still, few students were not interested in speaking.
Enthusiasm • The students were highly motivated to join the activities in
English Club.
• They liked the activities done in group or partner. English speaking
ability
• The students were considered in the level of pre- intermediate to intermediate-level students.
• The students had good marks in English subject (based on their academic report)
• Some students lacked confident
• The students often make mistakes on grammar and
pronunciation
• The students didn’t have good vocabulary mastery
• Some students had problem in memorizing.
2. Goals, list of topics, and the general purposes for teaching each topic
Based on the result of interviewing the coordinator of English Club, it was
clearly known that the program of English Club was held to facilitate the students
for practicing their English speaking skill, especially in public speaking skill. The
school had a specific goal to prepare their students for joining storytelling, speech
and debate competition held by office of Education in Yogyakarta.
The students also had their own expectation. In the questionnaires, there
were three open- questions used to know what the students expected from
speaking class in English Club (the materials and methods implemented in the
English Club’s meeting). In conclusion, the result of questionnaire shows that the
They like to learn new issues and practices with friends. Realizing the importance
of public speaking, they gave positive responses toward using speech as the
context to help students to enhance their public speaking skill.
Based on those facts, the students’ and the school’s needs were clearly
seen. To get the general purpose, those needs were combined each other. While
the learners’ needs emphasized practice of their speaking skill, the school’s needs
emphasized the improvement of public speaking skill, especially on storytelling,
speech and debate. In this chance, the researcher focused only on speech.
Therefore, the purpose of the design is to enhance public speaking skill of English
Club’s students in SMAN 1 Depok. Later on, students can practice speaking to
improve their public speaking through practicing speech. The researcher proposes
six main topics to reach that goal. These six topics are arranged based on the
theories of public speaking and speech.
Table 4.2 The List of Topics
Topics Meeting 1:
Be an Effective Speaker Meeting 3:
Seize Their Attention Meeting 2:
Let’s Practice Meeting 4
3. Subject Content
As previously mentioned in the Chapter II, the students should master the
basic techniques to improve their public speaking skill. Since the activities
designed on the materials would be conveyed through speech activities, the
researcher used theory of public speaking and speech as the main framework of
the learning activities. The researcher chooses some basic techniques to master
public speaking such as knowing some basic aspects to be an effective speaker,
technique of how to grab the audience’s attention, how to be good in
remembering, and information about kinds of speech and the structure of speech.
Each topic takes one meeting of English Club which lasts for 60 minutes. Further
description is presented in the following explanation.
The first meeting is about learning basic aspects concerned to be an
effective speaker. This is an introduction for students to learn about speech. This
introduction facilitates the students and their tutors to have the same perspective
about speech and the aspects concerned to be an effective speaker. As previously
mentioned in Chapter II, preparation is the key for a success speech. The
preparation will be easier through understanding the principles of public speaking.
First, the more effective that a speaker prepares, the better the speech he will
deliver and the more confident he will feel. There are some aspects considered to
be an effective speaker. Those aspects are message, accuracy, self- control, body
language, voice, and audience. In order to provide the real context of learning,
The second meeting will be about how to get audience’s attention. As a
speaker, the first objective is to secure the audience’s attention. Getting audience’s
attention is an important step that should be accomplished by the speaker in the
introduction of the speech. The strategy of grabbing audience’s attention will be
discussed. Then, the students will practice to write a speech’s introduction by
implementing the techniques of grabber that they have learnt before.
In the third meeting, the students practice what have been learnt in the
previous meetings. The students are performing the speech they have. By
performing individually, the students can know how good they apply six basic
aspects to be an effective speaker. The tutor and other students will give
evaluation on the students’ performances. The evaluation will be about message,
accuracy, self- control, body language, voice and how to deal with audience.
As stated in the second principle of public speaking, every public speech is
a blend of content, organization, and delivery (Grice & Skinner, 1995). It means
that a speaker should pay attention to how to create the content, how the structure
of speech will be and how he delivers his speech. If he can master it, he will
perform better. This is why the researcher allocates the fourth meeting for
students to know more about the content. In this meeting, the kinds of speech,
how they arrange the organization of the speech and how they connect the ideas in
speech will be elaborated. These aspects will be used by the students to prepare
their own speech by creating a speech form articles provided by the tutor. Then,
they will guide to list each point stated for the content to help them mastering