DATA TIME SERIES
Time series merupakan data yang
diperoleh dan disusun berdasarkan
urutan waktu atau data yang
dikumpulkan dari waktu ke waktu.
Waktu yang digunakan dapat berupa
minggu, bulan, tahun dan sebagainya.
DATA TIME SERIES
• The rate variable is collected at equally spaced time periods, as is typical in most time series and forecasting applications.
• Many business applications of forecasting utilize daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, or annual data.
• The data may be:
• Instantaneous, such as the viscosity of a chemical product at the point in time where it is measured;
• It may be cumulative, such as the total sales of a product during the month; or
• It may be a statistic that in some way reflects the activity of the variable during the time
CONTOH 1
Harga saham AAPL: 5 tahun, direkam dalam data per minggu
CONTOH 2
KEGIATAN PERAMALAN (FORECASTING)
Merupakan bagian integral dari pengambilan keputusan. Mengurangi ketergantungan pada hal-hal yang belum
pasti (intuitif).
Ada saling ketergantungan antar divisi.
Contoh , kesalahan proyeksi penjualan akan mempengaruhi
ramalan anggaran, pengeluaran operasi, arus kas, persediaan, dst.
Dua hal utama dalam proses peramalan yang akurat dan bermanfaat:
Pengumpulan data yang relevan.
FIELD OF FORECASTING
The reason that forecasting is so important is that prediction of future events is a critical
input into many types of planning and decision-making processes, with application to areas
such as the following:
Operation Management: Business organizations routinely use forecasts of product sales or demand for services in order to schedule production, control inventories, manage the supply chain, determine staffing requirements, and plan capacity
Marketing: Forecasts of sales response to advertising expenditures, new promotions, or changes in pricing polices enable businesses to evaluate their
effectiveness, determine whether goals are being met, and make adjustments.
Finance and Risk Management: Investors in financial assets are interested in forecasting the returns from their investments. Financial risk management requires forecasts of the volatility of asset returns so that the risks
associated with investment portfolios can be evaluated Economics: Governments, fnancial institutions, and policy organizations require forecasts of major economic
variables, such as gross domestic product, population growth, unemployment, interest rates, inflation, job growth, production, and consumption
Industrial process control Demography
METODE PERAMALAN
Terdapat dua pendekatan peramalan :
Kualitatif
METODE PERAMALAN KUALITATIF
Metode ini digunakan ketika data historis langka atau bahkan tidak tersedia sama sekali;
Metode ini (biasanya) menggunakan opini dari para ahli untuk memprediksi kejadian secara subyektif;
Contoh: penjualan dari produk baru, lingkungan dan teknologi di masa mendatang.
Keuntungan: berguna ketika tidak ada data historis;
METODE PERAMALAN KUANTITATIF
Metode ini digunakan ketika tersedia data historis;
Metode ini mengkonstruksi model peramalan dari data yang tersedia atau teori peramalan;
Keuntungan: Obyektif
Metode peramalan causal
Meliputi faktor-faktor yang berhubungan dengan variabel yang diprediksi seperti analisis regresi. Mengasumsikan bahwa satu atau lebih faktor (variabel independen) memprediksi masa datang.
Metode Peramalan time series
merupakan metode kuantitatif untuk menganalisis data masa lampau yang telah dikumpulkan secara teratur dengan menggunakan teknik yang tepat.
Data historis digunakan untuk memprediksi masa datang
Hasilnya dapat dijadikan acuan untuk peramalan nilai di masa yang akan datang (Makridakis. S., 1999).
Input: variabel dependent dan independent Proses: hubungan sebab-akibat Output: model untuk meramalkan var dependen Input: data historis Proses: pembangki tan proses Output: model untuk meramalkan data masa datang
SYARAT-SYARAT PERAMALAN KUANTITATIF
1. Tersedia info pada waktu lalu
2. Info tersebut dapat dikuantitatifkan
3. Diasumsikan pola pada waktu-waktu lalu akan berlanjut di masa yang akan datang (assumption of constancy)
TIPE-TIPE METODE KUANTITATIF
1.
Naif/intuitif
2. Formal
•
Berdasarkan prinsip-prinsip statistik
t t t t t
y
y
y
y
y
1
1 Data mendatang = data sekarang + proporsi peningkatanKOMPONEN TIME SERIES
Trend
Seasonal
Cyclical
Random/ horisontalKOMPONEN/POLA DATA
Terdapat empat pola data yang lazim dalam peramalan:
1. Pola horisontal
2. Pola musiman
3. Pola siklis
HORISONTAL
MUSIMAN
Pola musiman: Terjadi bila mana nilai data dipengaruhi oleh faktor musiman (misalnya kuartal tahun tertentu, bulanan atau mingguan).
Menunjukkan puncak-puncak (peaks) dan lembah-lembah (valleys) yang berulang dalam interval yang konsisten.
SIKLIS
Pola siklis. Terjadi bila mana datanya dipengaruhi oleh fluktuasi ekonomi jangka panjang seperti yang berhubungan dengan siklus bisnis.
Pergerakan seperti gelombang yang lebih panjang daripada satu tahun. Belum tentu berulang pada interval waktu sama.
TREND
Pola trend. Terjadi bila mana ada kecenderungan kenaikan atau penurunan dalam data.
SIMPLE AVERAGE
•We will first investigate some averaging methods, such as the "simple"
average of all past data.
•Example. Seorang manager toko computer mempunyai data
penjualan notebook perbulan. Dia mempunyai data 12 bulan penjualan
sebagai berikut :
DATA
Bulan
Amount
Bulan
Amount
1
9
7
11
2
8
8
7
3
9
9
13
4
12
10
9
5
9
11
11
6
12
12
10
The computed mean or average of the data = 10. The manager decides to use this as the estimate for next demand. Is this a good or bad estimate?
MSE
•We shall compute the "mean squared error":
•The "error" = true amount spent minus the estimated amount. •The "error squared" is the error above, squared.
•The "SSE" is the sum of the squared errors. •The "MSE" is the mean of the squared errors.
KOMPUTASI
Bulan $ Error Error Squared
1 9 -1 1 2 8 -2 4 3 9 -1 1 4 12 2 4 5 9 -1 1 6 12 2 4 7 11 1 1 8 7 -3 9 9 13 3 9 10 9 -1 1 11 11 1 1 12 10 0 0
MSE TERBAIK
So how good was the estimator for the next demand ? Let us compare the estimate (10) with the following estimates: 7, 9, and 12.
Performing the same calculations we arrive at:
Estimator 7 9 10 12 SSE 144 48 36 84 MSE 12 4 3 7
BUKTI ANALISIS
Dapat dibuktikan secara matematis bahwa estimator yang
meminimalkan MSE pada himpunan data random adalah mean.
2 1Minimum MSE
0
n i id
Y
a
da
DATA WITH TREND
Selanjutnya kita lihat data timeseries yang mengandung trend.
Next we will examine the mean to see how well it predicts net income over time for data having a trend. The next table gives the income before taxes of a PC
KOMPUTASI DATA
Year $ (millions) Mean Error Squared Error 1985 46.163 48.776 -2.613 6.828 1986 46.998 48.776 -1.778 3.161 1987 47.816 48.776 -0.960 0.922 1988 48.311 48.776 -0.465 0.216 1989 48.758 48.776 -0.018 0.000 1990 49.164 48.776 0.388 0.151 1991 49.548 48.776 0.772 0.596 1992 48.915 48.776 1.139 1.297 1993 50.315 48.776 1.539 2.369 1994 50.768 48.776 1.992 3.968
BUKTI EMPIRIS
The question arises: can we use the mean to forecast income if we suspect a trend ? A look at the graph below shows clearly that we should not do this.
Kasus di atas dapat diselesaikan antara lain dengan menggunakan
regresi trend atau metode perataan yang lain seperti MA ganda,
Metode Eksponensial Smoothing Linear Holt atau Brown.
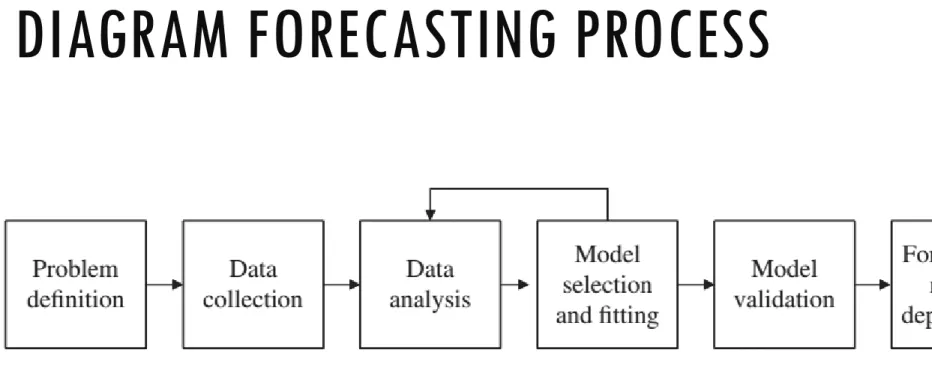
Problem definition:
• Understanding of how forecast will be used by customer
• The desired form of the forecast (e.g., are monthly forecasts required)
Data collection:
• Obtaining the relevant history for the variable(s) that are to be forecast, including historical information
• The key here is “relevant”; not all historical data are useful for the current problem
Data analysis:
• Selection of the
forecasting model to be used
• Time series plots of the data should be constructed and visually inspected for recognizable patterns, such as trends and seasonal or other cyclical
components
Model selection and fitting:
• Consists of choosing one or more forecasting models and fitting the model to the data
• By fitting, we mean estimating
the unknown model parameters (OLS, optimization method)
Model validation:
• An evaluation of the forecasting model to determine how it is likely to perform in the intended application
• A widely used method for
validating: data splitting, where the data are divided into two segments—a fitting segment and a forecasting segment
Forecasting model deployment:
• Involves getting the model and the
resulting forecasts in use by the customer
Monitoring forecasting model performance:
• Should be an ongoing
activity after the model has been deployed to ensure that it is still performing satisfactorily
DATA FOR FORECASTING
EXTRACT
Data extraction refers to obtaining data
from internal sources and from external
sources
Such as third party vendors or government
entities and financial service organizations
TRANSFORMATION
transformation stage involves
applying rules to prevent
duplication of records and dealing
with problems such as missing
information.
Sometimes we refer to the
transformation activities as data
cleaning
Data cleaning is the process of examining data to detect potential errors, missing data, outliers or unusual values, or other inconsistencies and then correcting the errors or problems that are found.
LOAD
Finally, the data are loaded into the data warehouse where
they are available for modeling and analysis.
IMPUTATION
Data imputation is the process of correcting
missing data or replacing outliers with an
estimation process.
Imputation replaces missing or erroneous values with a “likely” value based on other available information
Mean value imputation consists of
replacing a missing value with
the sample average calculated from the non-missing observations.
If the data does not have any specific trend or
seasonal pattern
However, one must be careful if there are trends or seasonal patterns
IMPUTATION
Stochastic mean value imputation:
Consider the time series 𝑦
1, 𝑦
2, … , 𝑦
𝑇and suppose that one observation
𝑦
𝑗is missing. We can impute the missing value as
where k would be based on the seasonal variability in the data. It is usually chosen as some multiple of the smallest seasonal cycle in the data, example: 12 for monthly data.