DESIGNING A SET OF INTEGRATED ENGLISH
SUPPLEMENTARY SPEAKING MATERIALS
FOR SPEAKING IV SUBJECT IN
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
OF SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
A Thesis
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
A. Y. ADVENTA PRAMUSHANTI Student Number: 011214046
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM
DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
YOGYAKARTA
iv
Time grabs you by the wrist directs you where to go
So make the best at this test and don’t ask why
It’s not a question, but a lesson learned in time
(Time of Your Life,
a song by
Green Day)
Dedicated to:
vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
With the completion of this thesis, I would like to express my very first gratitude to Jesus Christ, for his abundant love and grace upon my life. I thank Him for His guidance and endless love that stand above all.
I am so much indebted to my major sponsor, Markus Budiraharjo, S.Pd., M.Ed. His guidance, encouragement and advice definitely contributed many to
the completion of my study. I thank him for being so inspiring. I would also express my sincere gratitude to my co-sponsor, Henny Herawati, S.Pd., M.Hum., for her support, advice, and time to read and revise my thesis.
My deepest gratitude goes to my parents, Bapak Teguh C. Dalyono and
Ibu Ceacilia Indah Retnowati, who always give love, encouragement and support. Their effort in raising and educating me made me who I am now. I cannot thank them enough for their love and patience. I also give my special gratitude to my beloved sister, A. M. Theoterra Yoshanti, for being my rock in my ups and downs. For me, she is the best sister one can ever have. I would like to thank my uncle, Y. Puryanto, SCY. His continuous prayer and love played a great role in my life.
vii
My next appreciation goes to Mbak Danik and Mbak Tari from the Secretariat and all library staffs for their encouragement and help.
I am very happy to give my endless thanks to my best friends, Widya, Tuty, Desi, Icha, Ella, Shinta, Diah, Sito, Adis, Niken, Naomi, Widi, Fajar, Leo, Bowo, Gelar, and Yos (`). Their love, encouragement, and companionship
color my days. I also thank Tuty for the grammar correction in my designed materials. My special thankfulness is given to Widya for being a truly friend. I thank her for the patience, support and advice especially in my hard days.
My special appreciation goes to my friends in Youth English Community, Mas Nunuk, Icha, Tunjung, Sisca, Endro, Retno, Mbak Retty,
Mbak Domi, Mas Ponky, Mas Silih and Mas Onggo for being a family. I really enjoyed the time when we worked and laughed. Thank for the coffee session and the wonderful times we’ve been through.
My thankfulness also flies to my friends in Teater Toedjoeh, Tika, Dika, Vita, Guntur, Rico, Adi, Otto and Wikan for helping me to find the meaning of life. I thank my dearest cousins, Tika ‘Cing’ and ‘Meme’ Dika for the laughter and the endless support. I would also thank Ceklex for all the gadget things and Maseko for creating beautiful layout in the designed materials.
Last but not least, with my grateful heart, I would like to express my special thankfulness to my only partner, Teddy Dwi Satrio Dumasthary for always being there. His love, patience, and support mean so much in my life. Thank you for being my other half.
viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE ………... PAGE OF APPROVAL ………. PAGE OF ACCEPTANCE ………... PAGE OF DEDICATION ………. STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ……….. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ………... TABLE OF CONTENTS ………... LIST OF FIGURES ………... LIST OF TABLES ……… ABSTRACT ………... ABSTRAK ………...
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION
A. BACKGROUND OF THE STUDY ………. B. PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION ………... C. PROBLEM LIMITATION ………... D. PROBLEM FORMULATION ……….. E. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY ……….. F. BENEFITS OF THE STUDY ………... G. DEFINITION OF TERMS ………...
ix
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
A. THEORETICAL DESCRIPTION ………... 1. Communicative Language Teaching ……….. a. Theory of Language and Language Learning ….……….. b. The Roles of Teachers and Students ………... c. The Roles of Instructional Materials ………... 2. Teaching Speaking ………... a. The Nature of Speaking ………... b. Principles for Designing Speaking Techniques ………... c. Type of Classroom Activity ………... 3. Public Speaking ……….. a. Preparing Speech ……….. b. Delivering Speech ….……… 4. Integrated Language Teaching ….………... a. Task-based Instruction ….………... b. Content-based Instruction ….……… 5. Instructional Material Design Models ……… a. Kemp’s Instructional Design Models ………... b. Yalden’s Instructional Design Models ….………... B. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ….………...
CHAPTER III: METHODOLOGY
A. RESEARCH METHODS ……….
1. Review of Related Literature ….………...
x
2. Survey Research ………... a. Pre-design Survey Research ………... b. Post-design Survey Research ….………... B. RESEARCH SETTING ….………... C. RESEARCH RESPONDENTS ……….... 1. Respondents of the Pre-design Survey Research ….………... 2. Respondents of the Post-design Survey Research ….…………... D. RESEARCH INSTRUMENT ………... 1. Questionnaire ….………... a. Questionnaire of the Pre-design Survey Research ….…………... b. Questionnaire of the Post-design Survey Research ….………….
2. Interview ….………
a. Interview of the Pre-design Survey Research ….……….. b. Interview of the Post-design Survey Research ….………
E. DATA GATHERING ………...
F. DATA ANALYSIS ….………..
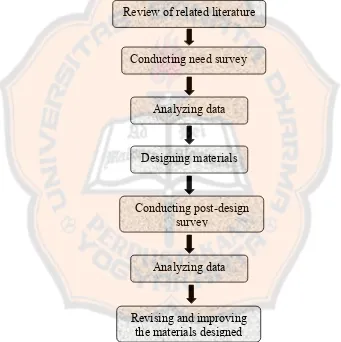
G. RESEARCH PROCEDURES ….………..
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
A. RESEARCH RESULTS ………... 1. The Results of Pre-Design Survey ….………. a. Conducting Need Survey ….………. 1) Result of the Questionnaire for Students ….………... 2) Result of Interview with Lecturers ……….
xi
b. Stating Competencies ….……….. c. Listing Subject Contents ….……….. d. Selecting Teaching/ Learning Activities ….………..
e. Evaluation ….………
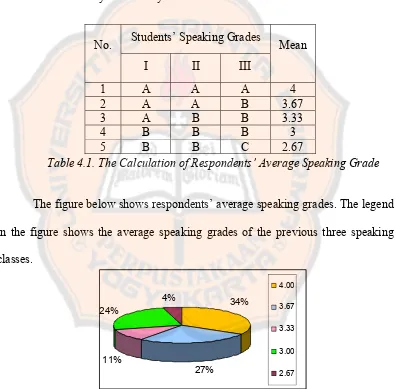
2. The Result of Post-Design Survey ….………. a. Description of the Respondents ….………... b. Data Presentation ….………. 1) Descriptive Statistics of the Respondents’ Opinions on the
Designed Materials ………. 2) Results of the Interview ….………. 3) Respondents’ Comments and Suggestions on the Designed
Materials ………. B. DISCUSSION ON THE DESIGNED MATERIALS ….……….. C. PRESENTATION OF THE DESIGNED MATERIALS ….………
CHAPTER V
A. CONCLUSIONS ….………..
B. SUGGESTIONS ….………..
BIBLIOGRAPHY ……….
APPENDICES
APPENDIX A: Letter of Permission ………... APPENDIX B: Questionnaires ………
xii
APPENDIX C: The Raw Data of the Post Design Survey ……….. APPENDIX D: General Description, Syllabus and Lesson Plan of the
Designed Materials ………... APPENDIX E: Presentation on the Designed Materials ………....
112
xiii
LIST OF FIGURES
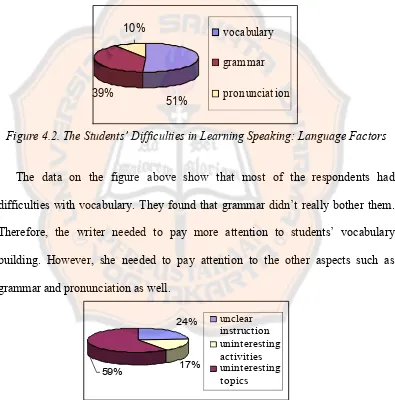
Figure 2.1. Kemp’s Instructional Design Model ..……….. Figure 2.2. Yalden’s Instructional Design Model ..……… Figure 2.3. The Writer’s Model in Designing the Instructional Design ……. Figure 3.1. The Research Procedure ..………... Figure 4.1. The Respondents’ Average Speaking Grade ..……….. Figure 4.2. The Students’ Difficulties in Learning Speaking: Language
Factors ..……… Figure 4.2. The Students’ Difficulties in Learning Speaking: Instructional
Factors ..……… Figure 4.4. The Communication Skills Needed ..………... Figure 4.5. The Topic Selection ...………..
page 33 34 38 52 56
58
xiv
LIST OF TABLES
Table 3.1. The table of the description of the respondents of questionnaire in post-design survey research ..………... Table 3.2. The table of description of the respondents of the interview in the post-design survey research ..………... Table 3.3. The respondent’s opinion on the designed materials ..……... Table 4.1. The Calculation of Respondents’ Average Speaking Grade ….. Table 4.2. The Respondents’ Opinion of the Speaking Class ..…………... Table 4.3. The Results of Interview with Lecturers ..………... Table 4.4. The Competencies and Indicators ..……… Table 4.5. The Description of the Respondents of the Questionnaire in
Post-design Survey ..………... Table 4.6. The Description of the Respondents of the Interview in
Post-design Survey ..………... Table 4.7. The Descriptive Statistics of Respondents’ Opinion on the
Materials Development ..………... Table 4.8. The Descriptive Statistics of Respondents’ Opinion on the
Impact of the Designed Materials to Students’ Learning Process ……... Table 4.9. The Results of the Interview ..……… Table 4.10. Presentation of the Final Version of the Designed Materials ..
page
46
46 50 56 59 63 66
75
76
77
xv ABSTRACT
Pramushanti, A.Y. Adventa. 2007. Designing a Set of Integrated English Supplementary Speaking Materials for Speaking IV Subject in English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program. Sanata Dharma University.
One of the most fundamental skills required these days is the ability to communicate orally particularly using English language. A speaking class which generally employs segregated language instruction methods and put a heavy focus on linguistic functions is considered to be insufficient in developing students’ knowledge as it puts little emphasis on authentic communication. The integrated language instruction offers a real-life integration of language skills which is believed to provide students with meaningful learning experiences.
This study was intended to design a set of integrated English supplementary speaking materials for Speaking IV subject in the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. There were two problems formulated in this study. The first problem concerned with how a set of supplementary integrated English instructional speaking materials for speaking IV subject on English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University was designed. The second one dealt with what the designed supplementary integrated English instructional speaking materials would look like.
In order to answer the two problems formulated previously, the writer employed the survey research which was divided to pre-design survey research and post-design survey research. To answer the first problem, the writer modified two instructional design models, which were Kemp’s and Yalden’s instructional design models. The writer applied five steps which were adapted from those two instructional design models. The steps were (1) conducting needs survey, (2) stating competencies, (3) listing subject content, (4) selecting teaching/ learning activities and resources (5) evaluation. Related to the second problem, the writer presented the final version of the designed materials which had been revised and improved based on the respondents’ comments and suggestions.
The final version of the designed materials consisted of ten units. Each unit consisted of two parts, namely the multimedia materials and the classroom materials. The multimedia materials consist of two sections namely reading section and listening section. The classroom materials covered activities used in the classroom which consists of speaking and writing activity.
xvi
ABSTRAK
Pramushanti, A.Y. Adventa. 2007. Designing a Set of Integrated English Supplementary Speaking Materials for Speaking IV Subject in English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris. Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Salah satu ketrampilan dasar yang dibutuhkan pada masa sekarang adalah kemampuan komunikasi lisan khususnya menggunakan bahasa Inggris. Sebuah kelas berbicara yang umumnya memiliki instruksi pengajaran yang tersegregasi dan menekankan pada fungsi-fungsi linguistik dianggap tidak memadai dalam mengembangkan pengetahuan siswa dikarenakan terbatasnya penekanan pada komunikasi otentik. Instruksi pengajaran yang terintegrasi menawarkan sebuah integrasi ketrampilan-ketrampilan bahasa yang otentik.
Studi ini bertujuan untuk menyusun seperangkat materi berbicara tambahan bahasa Inggris yang terintegrasi bagi mata kuliah Speaking IV di Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris Universitas Sanata Dharma. Ada dua permasalahan yang dirumuskan dalam studi ini. Masalah pertama berhubungan dengan bagaimana seperangkat materi berbicara tambahan bahasa Inggris yang terintegrasi bagi mata kuliah Speaking IV di Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris Universitas Sanata Dharma disusun. Masalah kedua berkaitan dengan bentuk dari seperangkat materi berbicara tambahan bahasa Inggris yang terintegrasi.
Untuk menjawab kedua permasalahan diatas, penulis menggunakan survei riset yang terbagi menjadi survei sebelum penyusunan materi dan survei setelah penyusunan materi. Untuk menjawab rumusan permasalahan pertama, penulis menggabungkan dua model materi pengajaran dari Kemp dan Yalden. Penulis menerapkan lima langkah yang diadaptasi dari kedua model tersebut. Langkah-langkah tersebut adalah (1) melakukan survei kebutuhan, (2) menyebutkan tujuan pembelajaran, (3) mendaftar isi materi, (4) menyeleksi aktivitas belajar mengajar dan sumber-sumber belajar, dan (5) melakukan evaluasi. Sehubungan dengan permasalahan kedua, penulis menyajikan rancangan akhir materi yang telah direvisi dan dikembangkan berdasarkan komentar-komentar dan umpan balik dari responden.
Rancangan akhir materi terdiri dari sepuluh unit. Setiap unit terdiri dari dua bagian, yaitu materi multimedia dan materi kelas. Materi multimedia terbagi menjadi dua bagian, yaitu membaca dan mendengarkan. Materi kelas meliputi aktifitas-aktifitas yang digunakan dalam proses pembelajaran di kelas yang terdiri dari aktifitas berbicara dan menulis.
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents some important points to initiate a discussion of the main problem of this study. They include the background of the study, the problem identification, the problem limitation, the problem formulation, the objectives of the study, the benefits of the study, and the definition of terms.
A. Background of the Study
Today, as the world is becoming more globalised, the needs, demands, and aspiration of the society let a new trend taking place. Zarefsky explained that today’s society undergoes a shift in economy, from “dominance in economy to dominance by information” (Zarefsky, 1996: 5). In Grice and Skinner, Hasling (1990) also pointed out that in a civilized culture, to defend our lives, the verbal ability is the one which we rely more than our physical strength, properties, and principles. Clearly, good communication skills, including oral communication (both interpersonal and public), listening, and written communication, play a critical role in this era. People are facing greater competitive pressures in many aspects of life, such as in school, communities, or workplaces. Therefore, only those who are well-prepared and multi-skilled will be able to survive.
in this global era. In Indonesia, mastering English is no longer a luxury, yet it is a must, a minimum requirement for people who wish to stand out.
According to Lazaraton (2001), for most people, knowing a certain language means being able to speak that language. Even speaking is viewed as the most demanding, most language learners also feel it to be the most difficult skill to master. This is even felt by those who specially learn this language in their education, such as students of English Letters or English Language Education Study Program. While there are classes which are specially designed to promote student’s oral skill, they still find difficulties to organize their ideas and express them orally, especially when they face real situation such as to speak in public or interact with others outside the class.
the learning of speaking. It potentially limits students’ chance to speak and distract students’ attention to the speaking process.
The description above provides an overview on the instruction and materials given in a speaking class. We may conclude that a speaking class commonly tends to have segregated-fashion teaching and focus on linguistic functions. Oxford (2001) pointed out that learning the language in a segregated fashion, meaning to say to put a heavy focus on one specific skill and eliminate other skills may be considered as less meaningful to the learning process. She also stated that learning language skills in a segregated fashion which was believed to maximize the learning would not ensure adequate preparation for later success in the use of the language in everyday life. It is contrary to the integrated way that people use language in normal communication.
was caused by a heavy focus on learning about and analyzing the language itself with little emphasis on authentic communication.
From the discussion above we may conclude that not only that it is found to be less meaningful, a speaking class which has segregated-fashion teaching and focuses on functional linguistic is also found to be less relevant and efficient. Thus, integrating the speaking skills to other skills such as listening, reading, and writing will surely promote the meaningfulness of learning. Integrating all four skills together with characteristics of the teacher, the learner, the setting, and the relevant languages is known as integrated-skills approach (Oxford: 2001). The integrated-skill approach exposes English language learners to authentic language and challenges them to interact naturally in the language. It is authentic because it reflects how we really use the language.
Based on the explanation above, the innovation of using integrated-skills approach and content-based instruction with interesting authentic materials will give significant contribution on student’s competence in English. The advantages gained of using integrated skills approach and authentic materials considered being able to promote English proficiency of students of English Language Education Department of Sanata Dharma University. This study was intended to design supplementary materials for students of English Language Education Department of Sanata Dharma University based on integrated skills approach. The materials designed in this study are particularly for the speaking IV subject on English Education Department.
B. Problem Identification
One of the most fundamental skills required these days is the ability to communicate orally (both interpersonally and publicly), particularly using English language. Even speaking is viewed as the most demanding, most language learners also feel it to be the most difficult skill to master. This is even felt by those who specially learn this language in their education, such as students of English Letters or English Language Education Study Program. Even they perform well in the speaking class, sometimes they still have difficulties when they face real communication such as to speak in public or interact with others outside the class especially native speakers.
function, is considered to be insufficient in promoting student’s oral competence. Oxford (2001) stated that incapability of using language in a real life was caused by a heavy focus on learning about and analyzing the language itself with little emphasis put on authentic communication. Instruction which employs the use of authentic communication will surely be meaningful for learners and lead them to communicate effectively.
The description given previously becomes the main reason for the writer to design a set of English speaking materials which is able to give meaningful learning to language learners. The instructional speaking materials will be designed in an integrated fashion. Here, the speaking skill is integrated with other skills such as listening, reading, and writing. The materials given is not only restricted to communicative expressions, it also pays attention to vocabulary and pronunciation. The materials designed also make use the principles of content-based language instruction since it has advantages such as such as providing a wider knowledge and develop thinking skills that surely promote meaningful learning.
The ability to express ideas in front of audiences surely will be a valuable asset, especially in an increasingly competitive working world.
The increasing role of public speaking urges a need to set a good basis in learning public speaking skill. Designing a set of integrated English instructional materials for speaking IV subject is believed to be able to promote student’s oral competency in accordance to the goal of this subject. The integrated materials will cover multi skills which link topics, communicative functions, pronunciation, vocabulary, and also the four language skills, such as listening, speaking, reading, and writing. The writer will use both written and audio sources in the designed materials. Such sources set a good preparation on students before they express their ideas orally, moreover the ability of expressing response and interpretation on information on the message conveyed in the source is expected to provide a meaningful learning to students as well as set a good basis for the mastery of public speaking skill.
C. Problem Limitation
The problems to be discussed in this study are limited on designing a set of supplementary integrated English instructional speaking materials for speaking IV subject on English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. This study is not intended to be an experimental project.
D. Problem Formulation
1. How is a set of supplementary integrated English instructional speaking materials for speaking IV subject on English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University designed?
2. What will be a set of supplementary integrated English instructional speaking materials for speaking IV subject on English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University look like?
E. Objectives of the Study
Based on the problems that have been formulated above, this study is undertaken to:
1. design a set of supplementary integrated English instructional speaking materials for speaking IV subject on English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University.
2. present the designed set of supplementary integrated English instructional speaking materials for speaking IV subject on English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University.
F. Benefits of The Study
This study is expected to be beneficial for the following people: 1. The lecturers
materials to the lectures of English Education Study Program especially those who teach speaking IV subject. The materials are expected to be able to promote meaningful learning.
2. The students
The materials designed may give different atmosphere to the learning process of students of English Language Education Study Program, especially those who are involved in speaking IV subject. The integrated materials are expected to foster their English interactive communication competence and to help learners to develop all language skills as well as their thinking and collaborative skill.
G. Definition of Terms
In order to avoid misinterpretation, there are several terms used in this study that need to be operationally defined.
1. Design
2. Supplementary
Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary of Current English defines supplementary as additional or extra. In this study, supplementary means additional.
3. Instructional material
According to Leslie J. Briggs (1984), instructional materials refer to the entire process of the analysis of learning needs and goals and the development of a delivery system to meet the needs; including the development of instructional and the activities and the tryout and revision of all instruction and learner assessment activities. Dick and Reiser (1989) stated that instructional materials refer to materials planned or designed for the use of teachers. In this study, instructional materials means set of activities and materials designed based a previous analysis on learners’ needs.
4. Speaking
According to Widdowson (1979) speaking refers to a kind of active and productive interaction that makes use of aural mediums such are lips and tongue, and the other oral activities. In speaking activity, face to face interaction is emphasized including dialogue, cooperative learning, discussion, or other forms of verbal exchange as an act of communication. In this study, speaking refers to a process of oral communication.
5. Integrated materials
speaking, reading and writing. In this study, integrated materials refer to a set of instructional materials that cover multi skills, including communicative functions and vocabulary and also the four language skills. These materials are employed by teachers as a mean to help the learners develop all four English skills, to obtain learners’ desired performance and to foster English interactive communication competence.
6. Speaking IV subject
12 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter presents detailed discussion about some theories underlying the study. This chapter is divided into two sections, namely: Theoretical Description and Theoretical Framework. In the first section, the writer will describe some theories which serve as a foundation for this study. The theoretical framework summarizes the writer’s framework and the steps in designing the instructional materials for Speaking IV subject.
B. Theoretical Description
This section deals with the discussion of theory of communicative language teaching, theory of teaching speaking for English as a second language, theory of public speaking, theory of integrated language teaching, and theory of instructional materials design model according to Kemp and Yalden.
1. Communicative Language Teaching
Today, Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) is being the most widely used approach in language teaching. It has influenced many other language teaching approaches and methods. Richard and Rodgers (1986) define communicative language teaching as:
CLT is a product of educators and linguists who had grown dissatisfied with the audiolingual and grammar-translation methods of foreign language instruction. They observed that students could produce sentence accurately in a lesson, but could not use it in the real communication outside the classroom. As Hymes (1971), as cited in Larsen-Freeman (2000), said that being able to communicate required more than linguistic competence; it required communicative competence. This perspective became the basis of the goal of Communicative Language teaching, which is communicative competence. a. Theory of Language and Language Learning
Communicative Language Teaching viewed language as communication. Larsen-Freeman said that beside the linguistic competence (the knowledge of forms and their meaning) language learners also need knowledge of functions language is used for. Thus, learner needs knowledge of forms and meaning, and functions of a certain language. Therefore, CLT considers developing communicative competence as the goal of language teaching. Richard and Rodgers (1986) stated 4 characteristics of this communicative view of language:
1. Language is a system for the expression of meaning.
2. The primary function of language is for interaction and communication.
3. The structure of language reflects its functional and communicative uses.
4. The primary units of language are not merely its grammatical and structural features, but categories of functional and communicative meaning as exemplified in discourse (161).
communicative principle, task principle, and meaningfulness principle. Communicative principle believes that activities which involve real communication will promote learning. The task principle is when language is used for carrying out meaningful tasks in the teaching-learning activities, it will promote learning. In the meaningfulness principle, language that is meaningful to the learner supports the learning process.
b. The Roles of Teachers and Students
In Communicative Language Teaching teachers and students have different roles form those found in more traditional language classroom. Breen and Candlin (1980) in Richard and Rodgers (1986) see students as negotiator between the self, the learning process, and the object of learning. Larsen-Freeman (2000) considers students as communicators. They are actively engaged in negotiating meaning even they have lack competence in the target language. Students are more responsible managers of their own learning.
c. The Roles of Instructional Materials
Richard and Rodgers (2001) state that the primary role of materials in Communicative Language Teaching is promoting communicative language use. There are three kinds of materials used, which are text-based materials, task-based materials, and realia. Text-based materials used consist of a theme, a task analysis for thematic development, a practice situation description, a stimulus presentation, comprehension questions, and paraphrase exercises. The second type materials, task-based materials, consist of sets of tasks need to be completed by students, such as a variety of games, role plays, simulations, and other task-based communication activities. The last material is realia. This material is also known as authentic or from-life materials. They include language-based realia, such as signs, magazines, advertisements, and newspapers, or graphic and visual sources around which communicative activities can be built, such as maps, pictures, symbols, graphs, and charts.
The principle of Communicative Language Teaching, which is communicative competence, becomes the basic principle in designing the integrated English supplementary speaking materials. The principle was applied in the As the principle of being able to communicate required more than linguistic competence; it required communicative competence. This perspective became the basis of the goal of
2. Teaching Speaking
skills, which are listening, reading, speaking and writing. However, it is also been considered one of the most complex skills of the teaching-learning process. a. The Nature of Speaking
Levelt (1989) proposed that speech production involves four major processes, which are conceptualization, formulation, articulation, and self-monitoring. Conceptualization is concerned with planning the message content. Speaker checks everything that occurs in the interaction to ensure that the communication goes to plan. After conceptualization, speaker is being a formulator. The formulator finds the words and phrases to express meaning, sequencing them, and putting in appropriate grammatical markers. The third process, articulation, involves the motor control of articulator organs, such as lips, tongue, teeth, mouth cavity, and breath. The last stage, self monitoring, is concerned with language users being able to identify and self-correct mistakes. All this happen very fast and, to be successful, depends on automation (Bygate, 1987 as reviewed by Carter and Nunan, 2001).
In order to speak in another language, possessing language competence is not sufficient; one should have communicative competence. Nunan (1991) stated that communicative competence includes linguistic competence, sociolinguistic and conversational skills that enable the speaker to know how to say what to whom, and when.
b. Principles for Designing Speaking Techniques
Brown (2001) stated that there are several principles of designing speaking techniques:
a. Use techniques that cover learner needs
Use techniques that cover learner needs, from language-based focus on accuracy to message-based focus on interaction, meaning, and fluency. When doing a task such as game, discussions, and role play, make sure that the tasks include techniques designed to help learners to perceive and use the building blocks of language.
b. Provide intrinsically motivating techniques
c. Encourage the use of authentic language in meaningful contexts.
Learners need to be introduced to real interaction pattern, such as the basic interactional pattern as follow: initiate, respond, and follow up. That pattern could be introduced through the use of dialogue to be read or listening activity before a spoken task. One should be remembered is to keep the models meaningful. d. Provide appropriate feedback and correction
Learners may get feedback not only from the teacher; in ESL situation they may get such feedback “out there” beyond the classroom. Yet, teacher still needs to give corrective feedback that are appropriate for the moment.
e. Capitalize on the natural link between speaking and listening
Many interactive techniques that involve speaking will also of course include listening. Teacher can get benefits by integrating these two skills since they can reinforce one another. Skills in producing language are often initiated through comprehension.
f. Give students opportunity to initiate oral communication
Part of oral communication competence is the ability to initiate conversation, to nominate topics, to ask questions, to control conversations, and to change the subject.
g. Encourage the development of speaking strategies
purpose, so teacher may give a chance to practice such strategies as asking for clarification (What?), using fillers (Uh, I mean, Well), or using conversation maintenance cues (Uh, huh, Right, Yeah, Okay, Hm).
In summary, the design of a set of speaking instructional materials should consider the use of techniques that cover the spectrum of learners’ needs, from language based focus on accuracy to massage-based focus on interaction, meaning, and fluency. The technique should be intrinsically motivating. It also should encourage the use of authentic language in meaningful context as well as the development of speaking techniques. Integrating the natural link between speaking and listening since these two skills is beneficial. The technique should give opportunities to students to initiate oral communication. And, finally make sure that the technique provide appropriate channel for feedback and correction. c. Type of Classroom Activity
According to Ur (1996), there are four items defining a successful speaking activity:
the opportunity for learners to talk most of the time instead of a class centered on the teacher; the whole students’ participation; high motivation due to the topic of discussion chosen by the teacher, and finally the acceptable level of language accuracy among the whole group (120).
David Nunan (2003) suggested sort of speaking activities as follows: a. Information Gap
b. Jigsaw Activity
This is a bidirectional or multidirectional information gap. Each person in a pair or group has the same information the other persons need. For example, one learner describes his family to another, while his partner draws a family tree diagram and labels it with name and information about the speaker’s family. c. Role Plays
In this activity, students are given particular roles in the target language. For example, one student plays a hotel receptionist handling complaint from his guest. The other plays the role of a hotel guest complaining the late wake-up call. Role plays give learners practice speaking the target language before they must do so in a real environment.
d. Simulation
Simulation is more elaborate than role-plays. In a simulation, props and documents provide somewhat realistic environment or language practice. For instance, in a language lesson about the grocery store, students bring in “products” (biscuits, fruits, vegetables, coffee) to be sold and even play money for making their purchases.
e. Contact Assignment
When we talk to someone, we usually do so for transferring information (transactional speech) and also social purpose (interactional speech); thus, speaking activities inside the classroom need to embody both interactional and transactional purposes.
3. Public Speaking
As a form of public communication, public speaking has always been considered important in societies. Mastering public speaking skill brings advantages to those who posses it, such as promoting individual achievement in school, work, and life in general. Grice and Skinner (1994) divide the advantages of studying public speaking skill into three levels: personal, professional, and public. On the personal level, it helps someone to promote academic achievement. As an active form of learning, it increases knowledge and also builds one’s confident and self-esteem. Furthermore, skills learned in studying public speaking can be used in other courses or study. Mastering public speaking skill also increases one’s chance to get desired job and advancing in it. Finally, public speaking binds people into groups and propels social movement and social change.
a. Preparing Speech
central idea. However, he also stated some steps of preparing the speech which are elaborated as follows:
a. Selecting a topic
For some people, finding a topic may lead to a trouble. Whereas topics can be found anywhere, it can be based on someone’s personal interests and hobbies, academic major or interests, or even people that interest him/ her. Problems that are in the news or situation of the speaker’s environment are also sources of topics.
Speaker may start by listing a speech topic followed by collecting interesting information from magazines, newspapers, and other mass media. This step is followed by formulating title. Topics and title might be worded identically. The title of speech is important for several reasons. Good title helps speakers to consolidate their thoughts and purpose. It should also fit the audiences and occasions.
b. Stating the purpose and central idea
themselves or even help them escape from reality; he is speaking to entertain. This speech contains jokes, stories, and varieties of humors.
After deciding the general purpose and choosing a topic, the purpose is limited to one specific aspect of the topic. The specific purpose aims to describe precisely what it is that you want your audience to understand, believe, feel, or what you are going to say. When preparing or outlining the speech, always start with a precise statement of the specific purpose.
The specific purpose is followed by central idea which is a mini-outline of what is going to be said. It may be in the form of a summary of the main thoughts, the thesis and claim the speaker made, or the action or belief the speaker wishes the audiences to adopt.
c. Gathering materials
Major ways and aspects of gathering speech materials are conversation and interview, library study, and note-taking.
d. Forms of support
b. Delivering Speech
Speech delivery is an important element of public speaking. Grice and Skinner (1994) define speech delivery as the manner in which a speaker presents his/ her speech through voice qualities, bodily actions, and language. For some listeners, strong delivery is able to cover up the weak content. It can also support important and well-organized ideas; in the contrary, poor delivery can diminish the impact of those same ideas. Effective delivery doesn’t only help the speaker, it also help the listener to get the key points of a speech. Speech is best delivered in a natural, comfortable, and spontaneous look; above all, it is best when the listener is not aware of it at all. Let the audiences notice the hard work of creating a best delivery is momentarily distracting them for what the speaker is saying.
There are three elements of effective delivery: voice (vocal delivery), body (physical delivery) and language. This section focus on vocal and physical delivery which will be discussed as follows:
1) Vocal Delivery
important to make emphasis both on something that has just said and something that is going to say. It also enables the speaker to mark transitions.
The volume, or the loudness or softness of a speaker’s voice, is an important element. The volume used in delivering speech depends on the setting in which the speech is delivered and also the facility provided, such as the use of microphone. Zarefski (1995) states that vary the volume at a certain key points are a good idea as well as regulate the general volume of an entire speech. It can be used either to understate ideas or to over-claim them. As well as volume, speaker has to pay attention to pitch, the placement of voice in the musical scale which are ranging from high to low. Using a monotone, in which the entirely speech is delivered at the same level undoubtedly cause boredom. To sustain audiences’ interest, mark transitions, and add emphasis to parts of the speech, a speaker should vary the pitch.
2) Physical Delivery
The body gives the speaker valuable set of visual resources, just as the voice does by giving verbal and auditory resources. The body is used to enhance the message of the speech. According to Grice and Skinner (1994), there are six elements of physical delivery, namely: appearance, posture, facial expression, eye contact, movement, and gestures. Speakers need to pay attention to their appearance which is the physical features, including dress and grooming. Appearance is important; it determines audience’s first impression. There are some considerations in selecting the proper attire, such as the occasion when delivering speech, the audiences, the topic carried out, and the image that the speaker wish to create.
The next point to be concerned is posture, which is the position of a speaker’s body while delivering a speech. Speech delivery must be free of annoying mannerism such as shifting weight back and front or tapping one foot on the floor. There are two things must be avoided: rigidity and sloppiness.
4. Integrated Language Teaching
meaning to say that one skill or component is taught with the absence of another skills or components.
There are reasons that underlie the question why courses are not integrated in the first place, such as the notion of logicality it is easier to teach one skill separately from the other (skills) and the administrative considerations. According to Mohan (1986) as cited by Oxford (2001), in the segregated-skill approach, which is also known as language-based approach, the key of successful learning is seen from the mastery of discrete language skill. For that reason, in the segregated-skill classes, the instruction presented is frequently in terms of skill-linked learning strategies, such as reading strategies, speaking strategies, listening strategies, and writing strategies.
Oxford (2001) states that such approach would not ensure adequate preparation for later success in the language use. It is contrary to the integrated way that people use language in normal communication. According to Brown (2001), in daily life, language is used in a communicative and interactive framework. In the real world of language use, most of our natural performance involves not only the integration of one or more skills, but also connection between the way we think and feel and act.
approach. The language arts –listening, speaking, reading, and writing- are interrelated and interdependent processes. The language process can be learned more effectively in connection with each other, rather than in isolation, because they support each other. Brown (2001) stated that this model provides real-life integration of language skills, gets students to perceive the relationship among several skills, and provides teacher with a great deal of flexibility in creating interesting and motivating lesson.
McCloskey describes the term integrated in four ways:
(1) Language is taught with integration of listening, speaking, reading, and writing in conjunction with our rich multicultural literary erutage; (2) language instruction is integrated into content area instruction; (3) Students from various language and cultural background are integrated in the classroom and work collaboratively; (4) Student’s home experiences and native culture experiences are integrated into school experiences in the new culture (1992: 2).
The integrated language instruction benefits students as well as teacher in some ways. It exposes students to the authentic use of language and challenges them to interact naturally in the target language. They are given opportunities to learn through language by applying their knowledge of applying their knowledge of language to their speaking, listening, reading, and writing experiences. Here, the learning of real content is promoted, not just the dissection of language form. It also motivates students, both internally and externally.
through language, while the second type stresses doing tasks that require communicative language use. The explanation of those two types is elaborately as follow:
a. Task-based Instruction
In task-based instruction, students participate in communicative tasks in English. According to Brown (2001) task-based curriculum specifies what a learner needs to do with the English language in terms of target tasks and organizes a series of pedagogical tasks intended to reach those goals. Target task is target which students must accomplish beyond the classroom, while pedagogical task which form the nucleus of classroom activities. Those targets are different with function of language. They are more related to classroom instruction. Basic pair work and group work are often used to increase student’s interaction and collaboration. The goals of a course with task-based instruction center on learner’s pragmatic language competence.
b. Content-based Instruction
1) Theme-based language instruction
In such instruction, the language class is structured around topic or themes. The course might be organized around several unrelated topics or, it might involve organizing curriculum for an entire course around one major topic. The primary purpose of theme-based instruction is to help student develop L2 competence within specific content areas. The evaluation in this model focuses on language skills and functions.
2) Sheltered content instruction
The second type of instruction, sheltered content, consists of content course taught in the second language by a content area specialist. This course assumes an institutional framework such as high school, community college, or university. Its primary purpose is to help students to master content material, while the focus of evaluation is on the content mastery.
3) Adjunct language instruction
In this model, students at the same time are enrolled in two link courses: a language course and a content course. The idea is that the two courses share the content base and complement each other in terms of mutually coordinated assignments. The purposes of the course is not only helping students to master the content material, but also introducing students to L2 academic discourse and develop transferable academic skills. The evaluation is done to both the content mastery and the language aspect.
language development and academic achievement while providing students with worthwhile and interesting subject matter. It also enhances both language and concept development and promotes positive attitudes. The models also provide students with opportunities to learn conversation and conversation skills which may not be practiced as effectively in the more traditional literature-based curriculum. (Giauque, 1987 as reviewed by Brinton et. al, 1989).
Peachey (2002) states that by taking information from different sources, re-evaluating and restructuring that information can help students to develop very valuable thinking skills that can then be transferred to other subjects. The inclusion of a group work element within the framework given above can also help students to develop their collaborative skills, which can have great social value.
5. Instructional Material Design Models
There are two models that will be presented in this section. The first model is Kemp’s model and the second one is Yalden’s. Those two models will be combined and used as the basis in developing the instructional materials.
a. Kemp’s Instructional Design Models
levels. The last question is about how to notice that the required learning has taken place.
Kemp’s instructional design plan consists of eight parts:
1. Considering goals, and then listing topics, stating the general purposes for teaching each topic.
2. Enumerating the important characteristics of the learners for whom the instruction is to be designed.
3. Specifying the learning objectives to be achieved in terms of measurable students behavioral outcomes.
4. Listing the subject content that supports each objective.
5. Developing pre-assessments to determine the student’s background and present level of knowledge about the topic.
6. Selecting teaching/learning activities and instructional resources that will treat the subject content so students will accomplish the objectives.
7. Coordinating such support services as budget, personnel, facilities, equipment, and schedules to carry out the instructional plan.
The relationship of each element is illustrated in the diagram as follows:
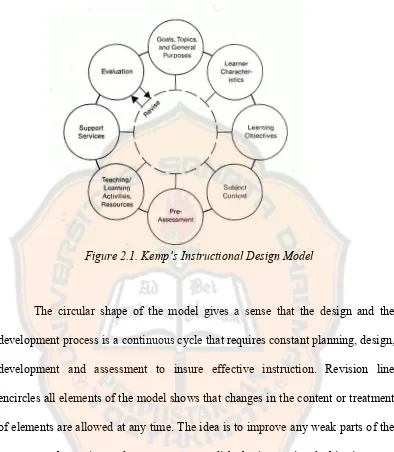
Figure 2.1. Kemp’s Instructional Design Model
The circular shape of the model gives a sense that the design and the development process is a continuous cycle that requires constant planning, design, development and assessment to insure effective instruction. Revision line encircles all elements of the model shows that changes in the content or treatment of elements are allowed at any time. The idea is to improve any weak parts of the program to better insure learners to accomplish the instructional objectives at a satisfactory level. Yet, Soekamto (1993) proposes weakness of this model which is there is no explanation about what should be done in the steps which related with the decision of learning-teaching activities and instructional resources. b. Yalden’s Instructional Design Models
Need n of classroom procedures communication. The syllabus is designed to describe classroom experiences which more closely approximate an environment of real languages use. The stages in the language program development are illustrated as follow:
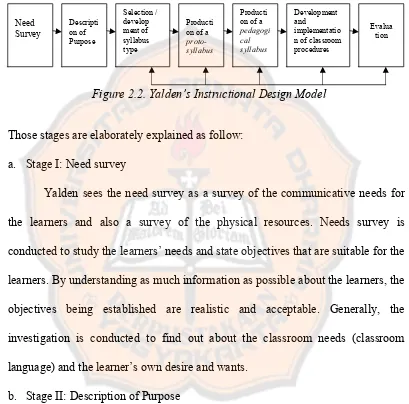
Figure 2.2. Yalden’s Instructional Design Model
Those stages are elaborately explained as follow: a. Stage I: Need survey
Yalden sees the need survey as a survey of the communicative needs for the learners and also a survey of the physical resources. Needs survey is conducted to study the learners’ needs and state objectives that are suitable for the learners. By understanding as much information as possible about the learners, the objectives being established are realistic and acceptable. Generally, the investigation is conducted to find out about the classroom needs (classroom language) and the learner’s own desire and wants.
b. Stage II: Description of Purpose
teaching/learning activities. It is necessary to select certain aspects of the target language which will be given special prominence in the preparation of the syllabus.
c. Stage III: Choice of a syllabus type
The choice of a syllabus type is done when the general category of a language program has been decided. According to Yalden, a syllabus is an instrument by which the teacher can achieve a degree of fit among the needs, the aims of the learners, and the classroom activities. She employs a proposed range of syllabus from a structural syllabus to completely learner-centered one in which there would be no prospective or input syllabus at all, but only one which would grow out of situation as the course progressed.
d. Stage IV: Production of proto-syllabus
At this stage, the designer will turn to the description of the content that the syllabus will have, that is, the preparation of syllabus specification. This includes the description of language and language use to be covered in the program. The data gathered in the previous stages has considerable contribution to the determination of the syllabus content.
e. Stage V: Production of pedagogical syllabus
The second one is the development of testing sequence and decisions on testing instruments.
f. Stage VI: Development and implementation of classroom procedures
This stage mainly concerns on the development of classroom procedures such as selection of exercise type and teaching techniques, preparation of lesson plans, and preparation on weekly schedule. In order to have good competence in developing materials and teaching techniques, language teachers are also needed to equip themselves with briefing or workshop on principles, desired outcome, and exploitation or creation of teaching materials.
g. Stage VII: Evaluation
The final stage in developing a language program is evaluation. The evaluation is done not only to the students but also to the teaching as well as the overall design of the course. The evaluation enables the designer to revise the type and content of the syllabus.
h. Stage VIII: Recycling Stage
The line and arrows underneath the five latest stages show that there is a recycling stage in which the fit between the goal set and the final performance of the learner is determined. If here are discrepancies, revision and adjustment can be made anywhere in the system based on the feedback provided to the syllabus designer.
C. Theoretical Framework
Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. In order to design the materials, the writer makes use the theories on Communicative Language Approach, Teaching Speaking Skill, Integrated Language Instruction, and Instructional Design Model from Kemp and Yalden. Those theories give a significant contribution to the process of designing the materials.
Speaking is considered one of the most complex skills of the teaching-learning process. No wonder that language learners sometimes still found difficulties in speaking English in their everyday life even they had outrageous performance in their speaking class. This phenomenon invites the writer to look in depth about the teaching of the speaking skill. Despite teachers have made use the principle of Communicative Language Approach, which is developing communicative competence as the goal of language teaching by giving students real and meaningful tasks, there is still emphasis on linguistic functions of language. The teaching of speaking which is segregated form other skills, such as listening, reading, and writing, and also the instruction being carried out which tends to be task-based considered to be insufficient in developing students’ knowledge.
materials. The content-based instruction is chosen because it has some advantages for students such as developing a wider knowledge, developing student’s thinking skill, and certainly, creating such an interesting and motivating atmosphere since English is used as a means to and end.
The writer also used the principle of Communicative Language Teaching, which is communicative competence. The principle was applied in the steps undertaken by the writer in designing the integrated speaking materials, especially in stating competencies, listing subject contents, and selecting teaching/learning activities.
In order to design a set of integrated speaking materials, the writer creates her own model adopted from Kemp and Yalden. Those models basically have similar steps in designing a material; moreover, they are flexible since there are chance to do revision in the process of designing the materials. The writer finds that the model is suitable with the steps used by the writer. The writer will initiate the design by need survey taken from Yalden and then followed by other steps combined from those two models. The steps in designing the instructional materials are as follow:
Figure 2.3. The Writer’s Model in Designing the Instructional Design
Evaluation
Selecting Teaching/Learning
Activities
Lis ting S ubject Content
Stating Competencies Conducting
Needs Survey
As the model shows us, the entire steps in designing the instructional materials are encircled by two lines. The outer line represents that all the five elements included in the designing process are a unity. The second line encircles all elements of the model is the revision line. It shows that revision can be done in any steps of the development of the instructional design. The idea is to improve any weak parts of the program to better insure learners to accomplish the instructional objectives at a satisfactory level. The description of each step of the model above following the ideal sequence is as follow:
1. Conducting Need Survey (adopted from Yalden)
This step is adopted from the first stage of Yalden’s instructional design model. The need survey is conducted in order to get information on the nature of Speaking IV subject, and also on learner’s characteristics such as needs, wants, interests, and their opinion on the existing speaking class. The information is collected by distributing questionnaires to semester IV students of English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University, and also to lecturers of Speaking IV subject in the same setting. Based on the information gathered in the need survey, the writer analyzing student’s characteristic which serve as a basis in stating the objective of the material, as well as the subject content.
2. Stating Competencies (adopted from Yalden)
i.e. the competency that has to be mastered by the students as a result of learning a certain subject, the writer refers to the goal and topics for Speaking IV subject which are stated in Panduan Akademik Program Studi Pedidikan Bahasa Inggris Univeritas Sanata Dharma (2002) and also the existing syllabus of the Speaking IV subject.
3. Listing Subject Content (adopted from Kemp)
The third step is adopted from the fourth stage of Kemp’s model, i.e. Subject Content. This step includes selection and organization of the specific knowledge and also skills that meet the competencies and student’s characteristics. The selection of subject content is based on the data gathered in the need survey. In the need survey, students are given chance to select topic and communication function that they interested most. The writer uses 8 mostly chosen topics in the designed materials.
4. Selecting Teaching / Learning Activities and Resources (adopted from Kemp and Yalden)
This step is adopted from Kemp’s Teaching/Learning Activities and Resources in Yalden’s Pedagogical Syllabus. After listing the subject content, the writer compiles materials from many sources or by adapting them and making some adjustments. In this study, the writer uses the Integrated Language Instruction as the instruction to teach speaking. Thus, not only the materials include the other skills, such as listening, reading, and writing, it also include the language elements, such as vocabulary and pronunciation. Yet, the emphasis is on the speaking process.
42 CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY
This chapter discusses the research methodology used to answer the problem presented in Chapter I. There are seven sections discussed in this chapter. They are research methods, research setting, research respondents, research instrument, data gathering, data analysis, and research procedures.
A. Research Methods
This part gives further discussion on the method used to answer the problem formulation sated in chapter 1. The problems concerned with how a set of integrated English supplementary materials for speaking IV subject in English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University is designed and what the designed materials look like. In order to solve the two problems mentioned above, two research methods were employed in this study. They were review of related literature and survey study. Both of them are categorized into descriptive study. According to Sprinthall, Schmutee, and Sirois (1991), descriptive study has description as its primary purpose. The following is the elaboration of these two methods:
1. Review of Related Literature
English language teaching, theory of instructional design, and theory of teaching speaking skill.
2. Survey Research
The survey study was conducted to gather data from the appropriate and qualified respondents. The survey was done by distributing questionnaires and interviewing. In this study, the survey research was conducted twice. They were pre-design survey research and post-design survey research.
a. Pre-design survey research
The pre-design survey research was conducted before designing the materials. This survey was conducted as a part of need analysis to gain information on the learning needs of students of Speaking IV subject. The survey was conducted by giving questionnaire to students of Speaking IV subject and conducting interview to the lecturers of the subject. The writer used the result of this research as an input in designing integrated English supplementary materials for the related subject.
b. Post-design survey research
They were also asked to give suggestions and recommendations on the designed materials.
The second category of respondents was students of English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University University. The interview was conducted in order to obtain appropriate comments and suggestion to the multimedia materials. Their suggestions were used to revise and improve the designed materials.
B. Research Setting
The research was conducted at English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. Since Speaking IV is a compulsory subject in English Language Education Study Program, all the survey and respondents in this study were undertaken in this setting. Thus, the result of the research would be relevant to this study. The pre-design survey research was conducted on May 2006, at the second semester of the year 2005/2006. While the post-design survey research was conducted on the first semester of the year 2006/2007.
C. Research Respondents
The respondents of the research were divided into two groups. They were the respondents of pre-design survey research and respondents of the post-design survey research.
1. Respondents of the Pre-design Survey Research
Education Study Program in Sanata Dharma University. Considering on limitations of manpower, ability, chance, and economical factors, the writer had 45 students as the respondents of this first survey. They were asked to fill in questionnaire which aimed to investigate student’s learning needs. Random sampling was applied in conducting this research since it is a fair technique in which each member of the population has the equal chance to be chosen as sample. The following table represents the description of the respondents of the pre-design survey research.
The second group was the lecturer of Speaking IV subject. At the time the pre-design survey research was conducted there were 3 (three) lecturers teaching the subject. All of them became the respondents of this first survey. They were interviewed in order to gain information on the nature of the course, the existing materials and teaching technique, and also the difficulties had been faced by the students and lecturers.
2. Respondents of the Post-design Survey Research
Table 3.1. The table of the description of the respondents of questionnaire in post-design survey research
The second category of respondents was students of English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. The description of which is shown as follows:
Table3.2. The table of description of the respondents of the interview in the post-design survey research
D. Research Instruments
The instruments used in this research were questionnaire sheet and interview questions.
1. Questionnaire
In order to gather the data for the need survey the writer used questionnaire. Questionnaires are used to obtain information concerning facts, belief, feelings, intentions, etc (Ary, Jacobs, and Razavieh, 1990).
a. Questionnaire of the Pre-design Survey Research
In the pre-design survey research, the designer combined two form of questionnaire, which is closed (or restricted) and open (or unrestricted). In the
Education Background Experience in Teaching Speaking
(in years) Respondent
S1 S2 S3 < 5 5-10 >10 PBI
Lecturers English Instructors
Group of Respondents Semester
Students of English Language Education
closed questionnaire, the respondents chose answer from the suggested responses which aimed to investigate their learning needs, such as their opinion on the existing Speaking IV course, the learning strategies, and the selection of topics. b. Questionnaire of the Post-design Survey Research
After the designer completed the material design, the second questionnaire was distributed to the lecturers of English Language Education Study Program and other English instructors who had experience in teaching Speaking subject. The questionnaire aimed to get their opinion and suggestions on the designed materials. The result of this questionnaire served as the basis of material’s evaluation and revision.
2. Interview
An interview is conducted to obtain information by actually talking to the subjects (Selinger and Shahomy, 1996). We can say in other words that an interview has to be done by face to face to the respondents in an oral form. For getting the more complete and credible data related to the problem of the study, this interview was conducted.
a. Interview of the Pre-design Survey Research
An interview was conducted in the pre-design survey research. The designer interviewed 3 (three) lecturers who were teaching Speaking IV subject. The interview aimed to gain information on the goals of the course, the nature of the course and the students as well as the difficulties had been faced by both students and lecturers, and also lecturer’s suggestion for the designer.
b. Interview of the Post-design Survey Research
multimedia materials was taken place before conducting the interview in order to give clear description of the designed materials, so that the responses from the respondents were able to achieve.
E. Data Gathering
F. Data Analysis
Data analysis is the result of systematically search and arrangement on the materials accumulated by researcher such as interview transcript, field notes, and other materials in order to increase their own understanding of them and enable them to present what they have discovered to others (Bogdan and Biklen, 1982). The data analysis was conducted twice, the first one was conducted after the designer did the needs survey and the second data analysis was conducted after the designer conducting post-design survey research.
There were two types of data taken from the survey research. The first one was data from the pre-design survey which was gathered by distributing questionnaire to the students of speaking IV subject and interviewing lecturers of the subject. The analysis on this data served as a basic consideration in designing the instructional materials. The second data was gathered in the post-design survey research by distributing questionnaire to the lecturers of English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University and other English instructors who had experience in teaching Speaking subject and students of the same setting in order to gain their opinion and suggestion on the designed materials. The data was used to do the evaluation and revision on the design materials.
The opinion of the respondents of the post-design survey research was in the form of four points of agreement as stated below: