(A CLASSROOM ACTION RESEARCH OF THE FIFTH YEAR STUDENS OF SD NEGERI WONOKERTO BANCAK, IN THE
ACADEMIC YEAR OF 2009/2010)
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd)
in the English and Education Department
By:
SITIMUAWANAH NIM: 113060061
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT AND EDUCATION FACULTY STATE ISLAMIC STUDIES INSTITUTE (STAIN)
SALATIGA 2010
DECLARATION
In the name of Allah the most gracious the most merciful.
Hereby the writer fully declares that this thesis is made by the writer herself, and
it is not containing materials written or has been published by other “people” ideas
except the information from the reference.
The writer capable account this for thesis if in the future this thesis can be proved
of containing others idea or in fact the writer imitate the other thesis.
This declaration is made by the writer to be understood.
Salatiga, July 22nd, 2010
Researcher
SITIM UAW ANAH NIM 11306061
Hanung Triyoko, M.Hum, M.Ed
The Lecturer of Educational Faculty State Islamic Studies Institute of Salatiga ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR’S NOTE
Salatiga. July22nd, 2010
Case : Siti Muawanah’s Graduating Paper
Dear
The Head of State Islamic Studies Institute of Salatiga
Assalamualaikum, Wr. Wb.
After reading and correcting Siti Muawanah’s graduating paper entitled “The Use of Direct Method to Improve the Students’ Vocabulary Mastery (A Classroom Action
Research of the Fifth Year Student of SD Negeri Wonokerto Bancak, in The Academic Year of 2009/2010)”. I have decided and would like to propose that if it could
be accepted by educational faculty, I hope it would be examined as soon as possible.
Wassalamu’alaikum, Wr. Wb.
Consultant,
V /
NIP. 19730815 199903 1 003
This gradu atin g p a p er is w hole heartedfy d ed ica ted to:
1. M y B eloved fa th e r (N v r Q iglhim ) a n d m other (Sum am i) than
£
a d support, suggestion,tru st, fin an ce, encouragem ent You are the Best paren ts.
2. M y B eloved o ld Brothers: Jlsnau% a n d TCamdani, th an fo f o r yo u r support, fondness,
togetherness a n d love ''I love you so much
*
3. M y Best fr ie n d “rTri IQ ifoih” Thanfo f o r yo u r fondness, togetherness from en try here u n til
now , f o r accom panying me to fin ish m y gradu atin g paper a n d love"I love you so m uch’
4. M y sp ecia l someone
* .
M ...'
th an fo f o r yo u r love, sp irit, p a tien t, suggestion,togetherness.
5. M y frien d s in <PAI 06: Im ronah a n d I s ti Thanfo f o r yo u r togetherness, especially on the
m y sp ecia l m om ent in S T A IN
6. M y frien d s in S<D W onoforto: Q?afo<Bagus a n d <Bu T ri T h an foforyou rjofo, frien d ly, a n d
cooperation.
7. M y frien d s in TIBI 06 especially m y classm ate in TtBI C
8. The Big fa m ily af<PM II fom isariat J o fo Ting fo r S a la tig a
universe, because of Him, the writer could finish this graduating paper as one of
the requirement for Saijana Pendidikan in English Department of Education
faculty State Islamic Studies Institute (STAIN) Salatiga in 2010.
Secondly, peace and salutation always be given to Prophet Muhammad
SAW who has guided us from the darkness to the lightness.
However, this success would not be achieved without those supports,
guidance, advice, help and encouragement from individual and institution, and I
somehow realize that an appropriate moment for me to deepest gratitude for:
1. Dr. Imam Sutomo, M. Ag, the Head of State Islamic Studies Institute (STAIN)
Salatiga.
2. Suwardi, S.Pd, as a chief of Education Faculty.
3. Ruwandi, S. Pd. MA, as the previous chief of English Department.
4. Maslihatul Umami, S.Pd.i, MA as a chief of English Department.
5. Hanung Triyoko, M. Hum. M. Ed, as a consultant who has educated,
supported, directed and given the writer advice, suggestion, an
recommendation for this thesis from beginning until the end.
6. Dr. H. Sa’adi, M. Ag, as a consultant of academic.
7. All of the lecturers in English department
8. All of the staff who have helped the writer in processing of thesis
administration
Finally this graduating paper is expected to be able to provide useful
knowledge and information to the readers. And the writer is pleased to accept
more suggestion and contribution from the reader for the improvement of the
graduating paper.
Salatiga, July 22nd ,2010
Siti Mu ’awanah. 2010. the use o f direct method to improve the students ’
vocabularymastery(a classroom action research o f the fifrhyear studens o f SD Negeri wonokerto bancak, in the academic year o f2009/2010)
This study focuses on the use of direct method to improve the students’ vocabulary mastery. The objective are to find out the English’s taught at SD Negeri Wonokerto, to find out can the using of direct methods improve the students’ vocabulary mastery, to find out the teaching and learning situation when the teacher uses direct method, to find out best implement direct method to improve student’s vocabulary mastery, and to find out the strength and the weakness of implementing direct method in vocabulary mastery.
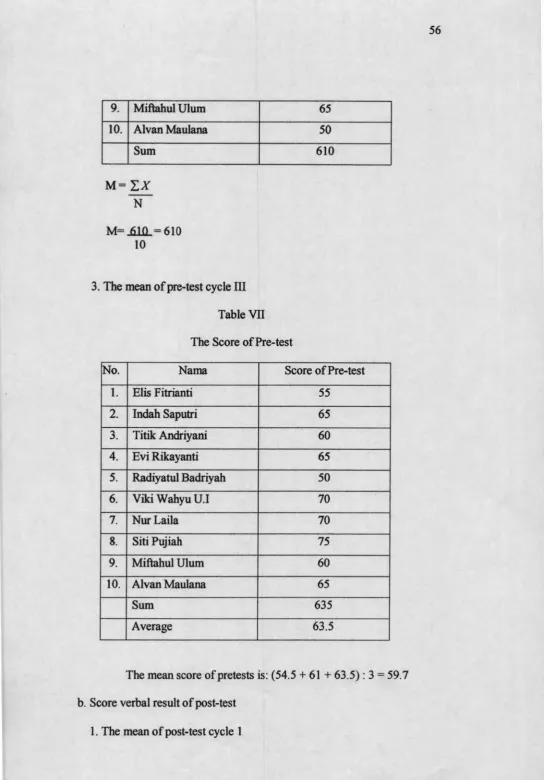
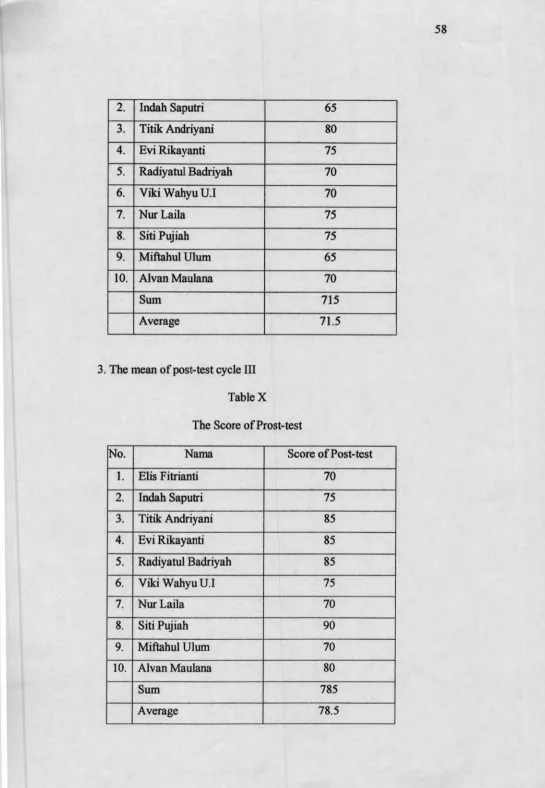
Based on conclusion cycle I, conclusion cycle II, and conclusion cycle III (P.61) shows that student activities at class indicate that students were motivated and interested in learning English lesson. The mean score of pretest 54.5 to 69 in post test cycle I, the mean score of pretest 61 to 71.5 in post test cycle II, and the mean score of pretest 63.5 to 78.5 in posttest cycle III. The result tells that direct method can improve students’ vocabulary mastery. From the score verbal cycle I show the mean of pretest is 54.5. The result of the action shows that using direct method can improve students’ vocabulary mastery. The implementation of direct method is reasonable because it can give the students a great motivation in learning vocabulary.
TITLE... i
DECLARATION... ii
ATTENTIVE CONSELOR NOTES... iii
STATEMENT OF CERTIFICATION... iv
MOTTO... v
DEDICATION... vi
ACKNOWLEDGENMENT... vii
ABSTRACT... ix
TABLE OF CONTENT... x
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. The Background of the Study... 1
B. Statement of the Problem... 3
C. The Objectives of the Study... 3
D. The Significance of the Study... 3
E. Definition of Term... 5
F. Hypothesis... 7
G. Research Methodology... 7
H. The System of the Thesis Presentation... 12
C. The General Concept of Direct M ethod...27
CHAPTER HI RESEARCH REPORT A. General Situation of SD N Wonokerto... 34
B. The Situation of Educational Facilities and Tools.... 34
C. The Situation of The Teachers and Staffs... 36
D. The Situation of the Students... 37
E. Organization Structure... 38
CHAPTER IV ANALYSIS A. Field Note... 39
1. Cycle I ... 39
2. Cycle I I ... 47
3. Cycle H I... 50
B. Score Verbal of Students’ Vocabulary Mastery... 54
1. Score verbal result of pre-test... 54
2. Score verbal result of post-test...56
3. The result of difference score between pre-test and post-test... 59
C. Suggestion... 66
BIBLIOGRAPHY APPENDIX
A. The Background of the Study
Human beings need each other. To make a good communication,
let alone, as a social culture we need to communicate and language is a means
to communicate with other. Language is used by people to express and
receive some information, message, emotions and so on. There are many
kinds of languages used by people such as English, Dutch, India, French,
Spanish, Arab, Indonesia, etc. It depends on where the people live. English in
Indonesia is the foreign language.
Nowadays English becomes important. It is the key to international
currencies of technology, science, as well as commerce. As an international
language, English has gained its popularity all over the world including
Indonesia. In the past English was only taught in secondary schools. In
current years, however, the teaching of English is expanding into primary
or elementary school setting.
At present days, there are many elementary schools that teach English
not only as a local subject but also as compulsory subject. English has been
taught beginning from the first year to the sixth year. In junior high school,
English is taught as a compulsory subject and also as a basic knowledge to
master English in senior high school and higher education level (university).
Teaching English in Elementary school is different from teaching English in
higher level.
Teaching English in Elementary School is more focused on
vocabulary than on grammar. Reading and writing exercise are based on what
the students practice orally first. Pronunciation is also received special
attention. Vocabulary is central to language and of critical importance to
typical language learner. Without a sufficient vocabulary, one cannot
communicate effectively or express his ideas in both oral in written form.
Having a limited vocabulary is also a barrier that precludes learners from
learning a foreign language. (Fauziati,2002:155)
It is undeniable that most learners’ of vocabulary grows through
incidental learning such as through continuous exposure to
comprehensible language in reading, listening, speaking, and writing
exercises. Even though they are keen reader with different materials, take a
lot of benefits from direct vocabulary instruction. They can effectively
expand their vocabulary knowledge. Thus, meaningful and interesting
instruction should of course be organized to achieve successful learning.
Teaching vocabulary for elementary school needs an appropriate
method. The students must know not only the words but also the
pronunciation, the spelling, the shape and the meaning of the words.
Moreover in SD Negeri Wonokerto, in this school English teaching start
from fourth grade different with other Elementary which English teaching
start from first grade. Based on the explanation above, the writer wants to
conduct a classroom action research on teaching English using direct method
in an elementary school. She takes SD Negeri Wonokerto Bringin as the place
Students taught using direct method need to associate the meaning,
the spelling and the target language directly. To do this, the teacher
introduces new target language words or phrases by demonstrating their
meaning through the use of object, and picture; abstract vocabulary was
though by association of idea.(Richard and Rodgersl986: 10). Finally,
based on the whole explanation above the writer is interested in this study.
She is interested in observing “THE USE OF DIRECT METHOD TO IMPROVE THE STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY MASTERY (A Classroom Action Research Students of Fifth Grade SD Negeri Wonokerto Bancak in Academic Year 2009/2010)”as well as to train the student to spell the word correctly.
B. The Statement of the Problem
Based on the background of the study, this research is aimed at giving
answers on the following problems:
Can the use of direct method improve the students’ vocabulary mastery on
fifth grade of SD Negeri Wonokerto?
C. Objective of the study
The objectives of the study are:
To find out whether the use of direct methods can improve the students’
vocabulary mastery
D. Significance of the study
This study is expected to give practical and theoretical benefit.
a. For the writer
The findings of the research can be used as a starting point in
improving the writer’s teaching ability, especially teaching
vocabulary.
b. For the students
The findings of this research will enhance the students’
vocabulary.
c. For the English teacher
By teaching vocabulary using direct method, it will motivate
the students to be interested in learning English vocabulary.
And the finding of this research can be used as a consideration
in selecting the appropriate methods or techniques
implemented in English case especially in SD Negeri
Wonokerto.
d. For the other researches
The finding of this research can be used as one of the
references in conducting a research on English language
teaching, especially in the implementation of direct method.
e. For SD Negeri Wonokerto
The result of this research will improve the institution’s quality
especially in the English teaching learning process,
b. Theoretically
a. The result of the research paper can be used as input in English
teaching learning process especially for teaching vocabulary
using direct method.
b. The result of the research can be used as the reference for those
who want
to conduct a research in English teaching learning process.
c. The result of this study hopefully strengthens the knowledge of
the theory of direct method in vocabulary mastery.
E. Definition of Terms
1. Using
The base word of “using” is “use”. The definition of use is to put
into action or use, to control or direct the functioning of, informal, to
take advantage of unfairly, and to be depleted. (Roget’s II, 1980:1020)
2. Direct Method
The Direct Method is the learning of language in a relevant setting.
This method has one basic rule and that is that no translation is
allowed. The meaning of the name "Direct Method" comes from the
fact that meaning is to be conveyed directly into the second language
through demonstration and visual aids, (http://www.saskschools.com,
Wednesday, 20 January: 12.30)
We can find the word of improve which has the meaning of
improve as to make better in quality or to make more
productive (Danbury, 2004:487)
In other words we can find the meaning of improve, some Theories
give the definitions about improves as the activities to raise on a the
productivity or value of land or property.
(http://www.thefreedictionary.com.saturday, 23 January: 11:55)
4. Students
On the teaching and learning process, there are some elements to
support the process of teaching and learning. The some elements of
this process for example teacher, students, material etc. The once of
crucial elements are students.
Student is a person attending an educational intuition, for example
high school or collage, one studying anything, one devoted to careful
and systematic study. (Grolier, 1974:972).
Inside of those definitions above, there are some definitions about
the word of students. Student can give the meaning of one who
enrolled or attends classes at a school, college, or university or a
learned person (especially in the humanities); some one who by long
study has gained mastery in one or more disciplines.
(http://www.theffeedictionary.com. Saturday 23 January 11:30)
Vocabulary is the stock of words used by a people, or a particular
uses or person, or a list of collection of the word of a language, book,
author, and branch of science or the like, in alphabetical order and
defined.
In other definition says that vocabulary is a collection of word
alphabetized a dictionary and the collection of word one know and
uses. (Http: //www.allwords.com, Saturday 23 January 11:40).
Grolier also says that vocabulary is a list of words and often
phrases, usually arranged alphabetically and defined or translated a
lexicon or glossary. All the word of language, the sum of word used
by, understood by, or at the command of a particular person, social
group, profession, trade or the like. (Grolier,1981:l 12).
F. Hypothesis
The researcher tries to determine the hypothesis of the research.
The hypothesis of this research is “there is an improvement toward
students’ vocabulary mastery”.
G. Methodology
1. The setting of the research
The research conducted at Elementary School for SD
Negeri Wonokerto on Jl. Sultan Agung No. 5 Bancak. The research
applied to the students of fifth grade. The students are from various
areas with various levels of economic families. Most of students have
under average ability. Those having above average ability have
sufficient vocabularies. The research conducted from April 2010 to
May 2010.
2. The Methodology of Research
The research method used in this study is action research.
There are some definitions of action research. The first deification is
given by kemmis that action research is from of collective self-
reflective inquiry undertaken by participant in social situation in order
to improve the rationally and justice of their own social or educational
practices, as well as understanding of this practices and the situation in
which these practices are carried out. (Wibawa, 2003:7)
The second definition action research is the research which
doing by the teachers on their class through self reflective inquiry with
the aim to make the better work so can improving the result of students
learning. (Aqib, 2009:3)
3. The Procedures of Research
This study used classroom action research, so in this case
the writer used some steps as kemmis stated. There are three cycles in
this action research in each cycle, the produces are as follows:
1. Planning
The activities the planning is:
a. Preparing materials, making lesson plan, and designing the
b. Preparing list of students’ name and scoring.
b. Teaching vocabulary by direct method.
c. Giving occasion to the students to ask any difficulties or
problem.
d. Asking the students some questions orally and students have
to answer orally about the theme.
e. Giving pretest.
process. He plans this observation fixable and writes something
that happened in the classroom.
The result of the observation is analyzed it is to
remember what happened that has been written in observation.
Reflection seeks to make sense of process, problems and real
issues in strategic action. It took account of the comprehend the
issues and circumstances in which they arose. Reflection has an
evaluative aspect, it asks the writer to weight the experience, to
judge whether effects were desirable, and suggest ways of
proceeding. The writer’s reflection is done by discussing with his
collaborator. Then the next cycle can decided or designed.
The procedures are briefly described in the following scheme:
Cycle I
Alternative of solving the problem
(plan of action) i = >
Problems C Action I
Reflection I
V4
*
*
7
Cycle II Action I has notgiven satisfactory
result
■
=»
Plan of action II 1----y Action II f l .Reflection II
<=>
Data Analysis | Observation IICycle III
V
Action I has not given satisfactory
result
i=^>
Plan of action III |---- Action IIIJJ
Reflection III Data Analysis ---- 1 Observation III
4. Technique of Collecting Data.
In this study, the write used written test, and observation in
collecting data. Written test (pretest and posttest) are used to know the
of the teaching and learning process when the method is applied. It is
very important in this case, not only to know their own feeling, but
also to know how they attitude in the classroom when the process of
teaching and learning.
5. Techniques of Data Analysis
After collecting the data, the next step of the study was
analyzing the data. The data were the result of pretest 1, 2, 3, and
posttest 1, 2, 3, there action. In analyzing the test scores of the written
test, a statistical technique used to find the mean score of the student.
The score technique is counting the percentage of the student who can
answer and cannot answer oral test in action 1, 2, 3, from the
observation sheets, the students’ behavior during the action is
analyzed.
H. The System of the Thesis Presentation
This thesis is divided into five chapters.
Chapter I is contains of introduction which covers the background
of the study; the theoretical framework, hypothesis, the methodology of
research, the procedures of research that there are 3 cycle which consist of
planning, action, observation and reflection, than technique of collecting
data and technique of data analysis.
In chapter II, the writer presents the review of related literature of
the study be describing theoretical foundation and research hypothesis,
the using of direct method in the process of teaching and learning, the
strengths and weaknesses of the using of direct method, and the teaching
of vocabulary through direct method.
In chapter III writer present about the brief report of research that
consist of general situation of SD N Wonokerto in academic year
2009/2010. The histories of the school, geographical placed the education
condition of teacher and students, the condition of the medium and the
infrastructure.
In chapter IV writer, present the data analysis of the data
interpretation that discusses the result of the test.
In chapter, V the writer ends the thesis by giving conclusion and
A. The General Concept of Classroom Action Research
Action research is classroom-based research conducted by teachers
in order to reflect upon and evolve their teaching. It is a systematic,
documented inquiry into one aspect of teaching and learning in a specific
classroom. The purpose of teacher research is to gain understanding of
teaching and learning within one’s classroom and to use that knowledge to
increase teaching efficacy/student learning.
(http://www.classroomaction.com. Monday, May 17: 10.15) Reflective
teachers do this every day, only not as carefully and systematically. With
training and support, you can learn how to systematize your inquiry from
informal reflection and teacher story sharing to formal research.
According to Elliot (in Hopkins, 1993: 45) action research might
be defined as the study of a social situation with a view to improve the
quality of action within it. In action research theories are not validated
independently and then applied to practice. They are validated through
practice.
Arikunto (2006: 3) divided three components in classroom action
research, there are:
a. Research
An activity to observe the object by use of ways and methodologies to
get the useful data or information to improve the quality of thing and
that is necessary for researcher.
b. Action
A motion of activity deliberated to action with certain purpose, in the
form of activity are cycle network for the student.
c. Classroom
A group of students, they get a lesson from a teacher in the same
time. She was conclude that classroom action research means
monitoring toward teaching learning process in the form of an action,
which is deliberated on action and occur in the class.
Action research deals with social practice. Education is a social
practice. In most cases, it involves the direct interaction of teacher and
groups of students. Classroom is complex arenas, secondary schools are
lives of intrigue and conspiracy. Trying to reach understanding of issues
concerned with teaching and learning, therefore, implies getting to grips
with a work range of human issues such as the attitude of students, the
politics within departments and the ethos an environment of the institution.
The aim of action research is to feed practical judgment in concrete
situation, and the validity of the theories or hypothesis it is not generate
depends so much on scientific test of truth as an their usefulness in helping
people to act more intelligently and skillfully. In resent years, action
and in service education, particularly within the field of self-evaluation
(Arikunto: 2006: 57).
1. The Characteristic of Classroom Action Research
Syamsuddin and Damaianti (2007: 197) outline the following
characteristics of classroom action research:
a. It examines problem which are deemed problematic by researcher
in teaching learning process.
b. The researcher can give treatment which planed action to solve the
problems and improve the quality, so the subject can get the
implication.
c. The steps of research in the form of cycle.
d. Such reflective thinking from researcher both after and before
research.
e. Contextual situational, which related to diagnosing and solving the
problem.
f. Classroom action research used collaborative approach.
g. Participatory, which each team member accompany in the research.
h. Self-evaluative, which the researcher evaluate by self continually
to improve the performance.
i. The procedure of research is on-the-spot which designed to handle
the real problem in that area.
j. The result applied immediately, long-range in perspective,
2. The Objective of Classroom Action Research
The objective of classroom action research is active of thing
and can be activity (Aqib, 2006: 27-29). That objects as follows:
a. Student
e. Element result of learning
Taken as target which must reach through learning, both
achievement level and formation.
f. Environmental
The student’s environmental in class, school, or in the home.
The move of activity which easy to arranged, engineered in the
form of action.
3. The steps of classroom action research
a. The first step is choosing a research question: it should be specific,
answerable, and lead to significant information on an aspect of
teaching or learning. Reflective teachers generally have questions
in their minds about what they observe in the classroom; this can
be a good place to start. If you don’t have a question in mind,
keeping a teaching journal of observations and questions can
provide potential questions. As you choose a question, be sure that
it is not too general or too big to be answered given your resources.
b. The second step is deciding what information you need in order to
answer your question and how it can be collected. Data can be
collected in a number of ways: by keeping a teacher journal of
observations, conducting student interviews, giving out
questionnaires, and testing. An instrument may already be
available to collect the information; for example, if you wish to
assess oral proficiency, the SOPI is a proven assessment tool.
However, you may need to develop your own instrument, for
example, a questionnaire specific to your classroom practices.
c. Third, the data must be analyzed. Organized narrative data is
perfectly valid in research. Basic statistical calculations are easily
investigating differences between male and female students, simple
statistical and narrative comparisons can be made.
d. The next step is to organize and write up the research and results.
This can be done informally, for your own information and perhaps
to share with colleagues, or more formally, to be shared and
disseminated to a wider audience in articles or presentations.
e. The final step is for the teacher to incorporate the results of the
research into classroom practice. Your research will give you a
basis for deciding to retain successful instructional practices,
modify those that are less successful, or introduce new practices to
address problem areas. (http://www.classroomaction.com.
Monday, May 17: 10.20)
B. The General Concept of Vocabulary
A vocabulary is defined as "all the words known and used by a
particular person. (Cambridge Advanced Learners Dictionary)
Vocabulary is basic to communication. If acquirers do not recognize the
meanings of the key words used by those who address them, they will be
unable to participate in the conversation. And if they wish to express
some idea or ask for information, they must be able to produce lexical
items to convey their meaning.
Vocabulary is also very important for the acquisition process. The
popular is belief is that one uses form and grammar to understand
carrier of meaning. Beginners often manage to communicate in English
by using the accumulative effect of individual word. (Scrivener, 1994:
73)
1. The status of vocabulary in the curriculum
The status of vocabulary has been considerably enhanced. This has
come partly as result of the development of communicative
approaches to language teaching, and partly through the stimulus of
comprehension based method such as the natural approach (Krashen
and Terrell, 1983: 11)
Rivers on the book “Language Teaching Methodology” has also
argued that the acquisition of an adequate vocabulary is essential for
successful second language use because, without an extensive
vocabulary, we will be unable to use the structures and functions we
may have learned for comprehensible communication. (Nunan, 1991:
117)
2. The role of vocabulary in the classroom: five initial conclusions:
a. Vocabulary is very important and needs to be dealt with
systematically in its own right
b. Our job does not finish as soon as a learner has first met some
new vocabulary
d. We need to distinguish between vocabulary for productive and
for receptive recognition and adapt our classroom work
appropriately
e. We need to deal not only with single word lexical items, but also
with longer, multi-word item. (Scrivener, 1994: 75)
3. Vocabulary growth
Initially, in the infancy phase, vocabulary growth requires no
effort. Infants hear words and mimic them, eventually associating
them with objects and actions. This is the listening vocabulary. The
speaking vocabulary follows, as a child's thoughts become more
reliant on its ability to express itself without gestures and mere
sounds. Once the reading and writing vocabularies are attained -
through questions and education - the anomalies and irregularities of
language can be discovered.
In first grade, an advantaged student (i.e. a literate student) knows
about twice as many words as a disadvantaged student. Generally,
this gap does not tighten. This translates into a wide range of
vocabulary size by age five or six, at which time an English-speaking
child will know about 2,500-5,000 words. An average student learns
some 3,000 words per year, or approximately eight words per day.
After leaving school, vocabulary growth reaches a plateau. People
may then expand their vocabularies by engaging in activities such as
reading, playing word games, and participating in vocabulary
programs.
4. Vocabulary in use
a. Core vocabulary
One way of looking at the status of words in lexical fields is
to consider whether some words are more core, or central to the
language, than other. The idea that there might be a core or basic
vocabulary of words at the heart of any language is quite an
appealing one to language educator. (McCarthy, 1990: 49)
Example of core words and how we might distinguish,
consider the set of words comprising the lexical field of ‘having a
weight above the norm’ we have in English fat, obese, overweight,
plump, podgy, stout, and several other words. We would probably
guess that fat was the most frequent. We can also say about fat that
is would normally be used to describe or define the other words,
bur not vice-versa. (Carrell, 1987: 81)
b. Procedural vocabulary
Identifying items in the lexicon that seem to carry a heavy
work-load ( e.g. the core vocabulary) must include a consideration
of how some words are characteristically used to talk about words,
communication. Widdowson (1983) describes this kind of
vocabulary as procedural. The key procedural or indexical words
such as contain, divided, affect, same, and so on enable me, a
complete newcomer to the field of endocrine system. (McCarthy,
1990: 50)
5. The stage of vocabulary
a. Classroom technique
Teacher can devise various activities relevant for promoting
vocabulary learning. Several sample activities presented here can
be integrated into second language instruction to promote
vocabulary learning and to support language skill development.
(Fauziati, 2002:159) That is, as follow:
• Semantic networks,
A semantic network consists of words which share
semantic features or semantic components. A componential
analysis can show what related and differentiates members of
a particular semantic network. This principle can be used to
teach vocabulary.
Carter (1998: 215) on Endang fauziati book, gives example
of word sets and grids provided by Rudska et.al. as follow:
1. Show the way in which the semantic components of the
2. Make a scale which marks degrees of intensity attaching to
items
3. Show the way in which such exercises can be carried out
collaboratively, there are often extremely revealing of
learners’ lexical knowledge.
• Memorization,
Memory is also very important in the development of a
second language, and it is vocabulary which requires more
generous treatment for memorization compared with other
aspects of second language development.
• Context
It is undeniable that developing vocabulary can be managed
through inferring word meaning from its context is quite
possible. He assembles the steps as follows (Nation in Carter
1998:210-211);
1. Look at the unknown word and decide its part of speech
2. Look at the clause or sentence containing the unknown
5. Check if your guess is correct
• The word wall approach
The word wall technique is developed by Green (1993). It is
originally designed to challenge and motivate first language
students in elementary and secondary classrooms to develop
vocabulary learning and to internalize new vocabulary,
b. Presenting vocabulary
To present vocabulary the teacher has decided to teach a
related set of words, for example, items of clothing: shirt, trousers,
jacket, sock, dress, jeans. The teacher has a number of options
available. First, there is the question of how many words to
present. This will depend on the following factors:
• The level of the learners
• The learners’ likely familiarity with the words
• The difficulty of the item
• Their “teach ability’, whether, for example, the can be easily
explained or demonstrated.
• Whether items are being learned for production (in speaking
and writing) or for recognition only (as in listening and
reading). (Thombury, 2002: 75-76)
Furthermore, the number of new words presented should not
decided on the number of items to teach, there is then the choice of
the sequence of presentation, either:
• Meaning first, then form, or
• Form first, then meaning
In the first option the teacher could, for example, hold up a
picture of a shirt (the meaning), and then say It ’s shirt (the form).
In ‘form first’ presentation she could say shirt a number of times,
have the students repeat the word, and only then point to the
picture.
The next set of choices relates to the means of presentation -
whether to present the meaning through: translation, real things,
pictures, actions/ gestures, definition, or situation. And whether to
present the word in its: spoken form, or written form. (Thombury,
2002: 77)
c. Vocabulary tests
The purpose of vocabulary tests is to measure the
comprehension and production of words used in speaking or
writing. Four general kinds of vocabulary tests are presented:
1. Limited respond, is for beginners. These tests items require
either a simple physical action like pointing at something or a
2. Multiple-choice complete, is a tests in which a sentence with a
missing word is presented; students choose one of four
vocabulary items given to complete the sentence.
3. Multiple-choice paraphrase, is a tests in which a sentence with
one words underlined is given. Students choose which of four
words is the closest in meaning to the underlined item.
4. Simple completion (words), has students write in the missing
part of words that appear in sentences. (Madsen, 1983: 12)
C. The General Concept of Direct Method
The reaction to grammar-based approaches and the subsequent call
to use more traditional ways of learning other languages came from
diverse sources and in different ways with various labels. The approaches
have been called natural, psychological, phonetic, new, reform, direct,
analytic, imitative, and so forth. What they have in common is that they
refer to traditional ways of learning based on the use of language in
communicative situations usually without recourse to native language.
(Cole, 1931:55)
The first trend to establish itself with a name was the natural
method. The report of the Committee of twelve in 1901 originated by
the Modem Language Association describes it as follow:
In its extreme form the method consisted of a series of monologues
by the teacher interspersed with exchanges of question and answer
gesticulation, by attentive listening, and by dint of much repetition
the learner came to associate certain acts and objects with certain
combinations of the sounds and finally reached the point of
reproducing the foreign words of phrase. The study grammar was
reserved for a still later period.
The so-called psychological method was similar. Its basic
characteristic was that the instructor attempted to make association of
ideas either with each other or with something concrete. Frequently
used were objects, diagrams, charts and pantomime was a frequent
device.
The series method advocated by Francois Gouin was perhaps the
best known technique used by the psychological methodologists. The
technique is simple: it consists of relating activities in a series relating
to a specific activity.
The phonetic method belongs also in this group because of its
insistence on oral expression. The students were drilled first in the
discrimination and production of the sounds of the new language using
short idiomatic phrases and making liberal use of phonetic symbols.
The direct method was also very popular in certain circle in the
United Stated at the beginning of the 20th century. It is, with minor
modification, the method preferred by academies and specialized
schools whose sole purpose is to train persons in skills in another
The Direct Method is the learning of language in a relevant setting.
This method has one basic rule and that is that no translation is allowed.
The meaning of the name "Direct Method" comes from the fact that
meaning is to be conveyed directly into the second language through
demonstration and visual aids. (http://www.saskschools.com,
Wednesday, 20 January: 12.30)
1. The principles of the Direct Method are as follows:
Classroom was conducted exclusively in the target language;
Only everyday vocabulary and sentences were taught;
Oral communication skills were build up in a carefully graded
progression organized around question and answer exchanges
between teachers and students in small, intensive class;
Grammar was taught inductively;
New teaching points were introduced orally;
Concrete vocabulary was taught through demonstration, objects,
and pictures, whereas abstract vocabulary was taught by
association of ideas;
Both speech and listening comprehension were taught; and
Correct pronunciation and grammar were emphasizes. (Richards
and Rodgers, 1993: 9 -10)
The main purpose of direct method is mastery of foreign language
(Subyako-Nababan, 1993: 16) Using on this method like native speaker. To reach
this purpose, learners had had given exercises to understand words and
sentences with meaning although demonstration, shows, actions, also
mime. (E.g. This is a ..., I’ am writing, He’s smiling)
2. Strategies using direct method (http://www.saskschools.ca/,
Wednesday, 20 January: 12.35):
a. Question & Answer: The teacher asks questions of any nature and
the students answer. In preparation for this activity the teacher
models, extensively, the use of complete answers to questions.
Objective: Experiment with words and sentence patterns to create
interest and variety.
b. Dictation: The teacher chooses a grade appropriate passage from a
book and reads the text aloud three times. The first time the passage
is read the students only listen. The second time the passage is read
it is read phrase by phrase, with the teacher pausing long enough for
students to write down what they have heard. The third time the text
is read, it is read at normal speed and the students check their work.
Objective: Listen attentively, courteously, and purposefully to a
range of texts from a variety of cultural traditions for pleasure and
c. Reading Aloud: Students take turns reading sections of a passage,
play, or dialog out loud. At the end of each student's turn the teacher
uses gestures, pictures, examples, or role play to help the students
make meaning of the text.
Objective: Orally and silently read a range of contemporary and
classical grade appropriate texts for enjoyment and information.
c. Getting Students to Self-Correct: The teacher when provided with
the opportunity should have the students self-correct by offering
them a choice between what they said and the proper pronunciation.
For example if the student says, "I have Cree apples," the teacher
should say, "Do you have Cree apples or three apples?"
Objective: Reflect on speaking behaviors and strategies.
d. Map Drawing: Students are provided with a blank map of Canada.
The teacher gives specific instructions to the students.
Objectives: Listen purposefully to determine the main ideas and
important details; use language appropriate to audience, purpose,
and situation.
To have a clearer picture of how Direct Method is implemented in
the classroom, the following are the techniques outlined by Intosh
1. Lessons begin with a brief anecdote or dialogue in the target
language, and in modem conversational style.
2. The material is first presented orally with actions or pictures.
3. The mother tongue is never used
4. The preferred type of exercise is a series of questions in the
target language based on the anecdote or dialogue, and answered
in the target language.
5. Verbs are used first and systematically conjugated much later.
6. Advanced students read literature for comprehension and
pleasure.
7. The culture associated with the target language is also taught
inductively.
3. Subyako-Nababan (1993: 16) explains the strengths and weakness of
direct method:
a. The strengths of direct method:
1. Learners always give attention
2. Learners know much of words
4. Learners get much try on the conversation, especially topics
which have teaching in the classroom.
b. The weakness of direct method:
1. This method has principles, probably can used by private schools
which have few the lessons. But, this method can’t used by state
schools which have more he lessons
2. This method require teacher which can speak fluently like native
A. General Situation of SD N Wonokerto
SDN Wonokerto is one of elementary schools in Wonokerto
village, Bancak sub district, Semarang regency, other Islamic elementary
school there. The location is very strategies. It is located in front of local
district administer Wonokerto. Exactly the location of this school is in
Sultan Agung street number 5 Wonokerto.
Most of people there have a job as farmer. Many people have
knowledge more about Islamic religion can be said as religious people.
Because of that the parents more give motivation to their children to teach
religion education than common education. There are two of Islamic
elementary school (MI) and one of State Elementary school. Thought of
people like that, they more interest education in MI, because besides get
science of religion, but also get science of common. So that way SD N
Wonokerto have 92 students while MI almost 200 students.
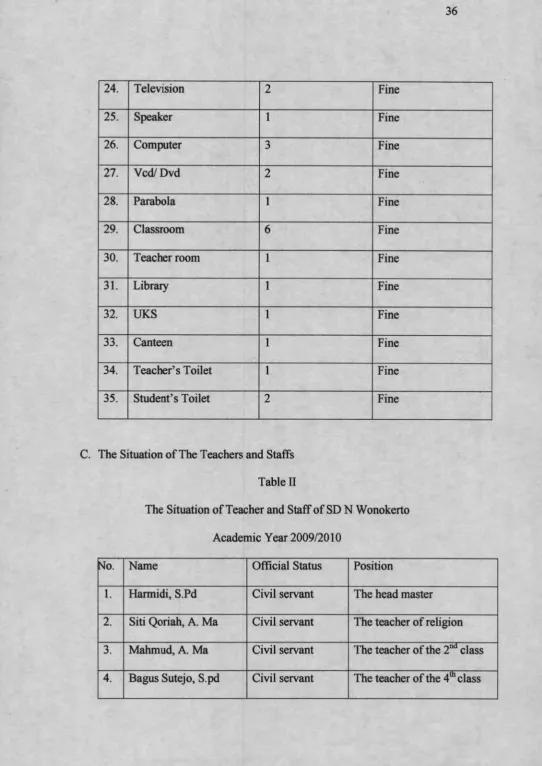
B. The Situation of Educational Facilities and Tools
Table I
Educational Facilities and Tools in SD N Wonokerto
Academic Year 2009/2010
0. Facilities Total Condition
1. Typewriter 1 Fine
2. Black board 7 Fine
3. Absence board 6 Fine
4. Map 4 Fine
5. Globe 1 Fine
6. Cupboard 8 Fine
7. Chair 60 Fine
8. Table 58 Fine
9. Desk 25 Fine
10. Tend 2 Fine
11. O’clock 4 Fine
12. Tool clean 18 Fine
13. Stove 1 Fine
14. Weight 1 Fine
15. Common Book 112 Fine
16. Social Book 99 Fine
17. Indonesian Book 99 Fine
18. Mathematic Book 99 Fine
19. Physics Book 103 Fine
20. Musical Instrument 1 Fine
21. Tool Volley 1 Fine
22. Tool Table tennis 2 Fine
24. Television 2 Fine
25. Speaker 1 Fine
26. Computer 3 Fine
27. Vcd/Dvd 2 Fine
28. Parabola 1 Fine
29. Classroom 6 Fine
30. Teacher room 1 Fine
31. Library 1 Fine
32. UKS 1 Fine
33. Canteen 1 Fine
34. Teacher’s Toilet 1 Fine
35. Student’s Toilet 2 Fine
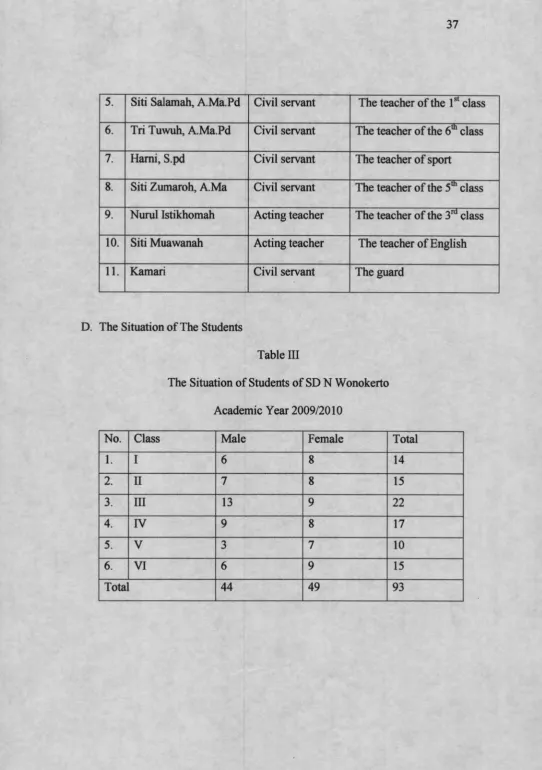
C. The Situation of The Teachers and Staffs
Table II
The Situation of Teacher and Staff of SD N Wonokerto
Academic Year 2009/2010
No. Name Official Status Position
1. Harmidi, S.Pd Civil servant The head master
2. Siti Qoriah, A. Ma Civil servant The teacher of religion
3. Mahmud, A. Ma Civil servant The teacher of the 2nd class
5. Siti Salamah, A.Ma.Pd Civil servant The teacher of the 1st class
6. Tri Tuwuh, A.Ma.Pd Civil servant The teacher of the 6to class
7. Hami, S.pd Civil servant The teacher of sport
8. Siti Zumaroh, A.Ma Civil servant The teacher of the 5th class
9. Nurul Istikhomah Acting teacher The teacher of the 3m class
10. Siti Muawanah Acting teacher The teacher of English
11. Kamari Civil servant The guard
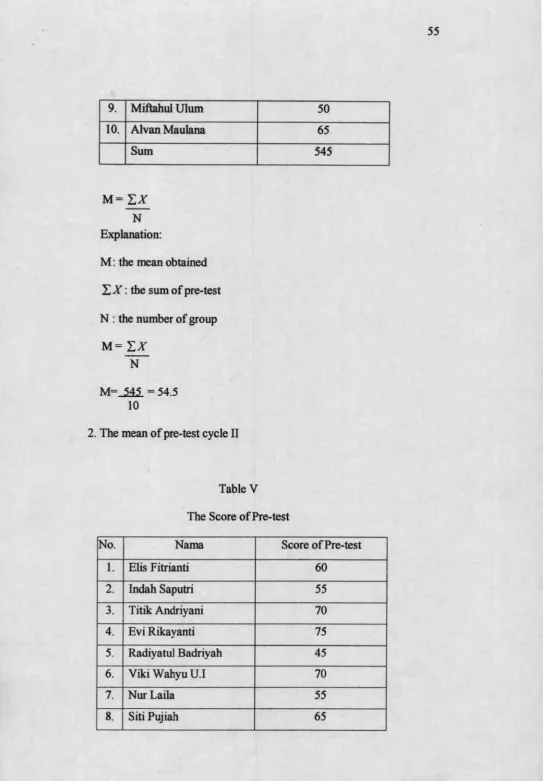
D. The Situation of The Students
Table HI
The Situation of Students of SD N Wonokerto
Academic Year 2009/2010
No. Class Male Female Total
1. I 6 8 14
2. II 7 8 15
3. III 13 9 22
4. IV 9 8 17
5. V 3 7 10
6. VI 6 9 15
E. Organization Structure
Organization Structure of SD N Wonokerto
OF THE FIFRH YEAR STUDENS OF SD N Wonokerto KEC. B ANCAK
b. List of students’ name
c. Teaching aids (e.g. picture, flash card, real thing, real thing model, tape
recorder )
d. Sheet for classroom observation
1. Curriculum/Core Content Observed
Evidence/Comments
A. Current unit of study is aligned to standards for age group.
B. Interventions are focused on student need and documented
2. Assessment
A. Teacher utilizes appropriate questioning skills
C. Assessment involves critical thinking
3. Instruction
A. Research based practices used to engage all students
B. Instruction reviews prior knowledge
C. Class objectives/essential questions are used
D. Instruction addresses varied learning styles
E. Lesson uses manipulatives/technology
F. Students can articulate goals for learning
4. Culture
A. Teacher has high expectations for all students
B. Teacher has a good rapport with students
C. Teacher manages classroom behavior effectively
D. Students are engaged in classroom activity
5. Leadership
A. Classroom routines are consistently practiced
6. Organization
A. Teacher uses varied grouping strategies.
B. Materials organized and easily accessible by students
C. Transitions are performed without disruption
7. Planning
Student Work Displayed □ Teacher Demonstration □
Technology Available □ Appropriate Resources □
Cooperative Group Activity □
e. Tests (pretest and posttest)
The models of pretest and posttest in cycle I is almost same consist of
two exercises that is, exercise one the students complete the sentences with
look at the picture and answer the question, and exercise two there are two
columns consist of English language and Indonesian language. The students
match the columns with the correct translation. But in the posttest is more
difficult than pretest. The students are let independent to answer the
question and match of time from number to sentences, even there is short
story to understand of the students.
2. The implementation of the action
On Wednesday, the seventh of April 2010 the teacher and the writer
entered her English class. Then she introduced the mode of presentation in
studying vocabulary. The steps are as follow. Use English language to teach,
rarely to use Indonesian language, explain clearly but not give meaning
directly, the students let to think or look for that meaning with picture, mime,
real thing. Before the lesson, she gave pretest to the class for about 30 minutes.
time and daily activities. I have o’clock on the blackboard, the way to write and
read o’clock is minute first then hour (the teacher wrote on black board: hour
past/to minute). For example: (the teacher turned hand of o’clock to some of
number) it is ten past five. “ How to use to?” one of students questioned. “Past
use if long hand of o’clock show between twelve and six, and to use between
six and twelve (teacher while o’clock), but we write minus to hour so not
appropriate writing of numeral of time. For example: 02.50, it is ten to three.
May not, it is two past fiftieth.
The teacher : “Do you understand?”
The students : “No, sulit bu (difficult mom).”
The teacher : “Ini tidak sulit, munkin kalian belum terbiasa, (this is not
difficult, may be you yet usual) mana yang sulit?” (where is the
difficult)
The students : “Itu kok bisa jadi tiga bu? (students showed one of example).”
The teacher
(why it can become three, moml)
: “this mean is sepuluh menit lagi jam tiga bias juga jam tiga
kurang sepuluh menit.” (this mean is ten to three)
The students : “Jadi to itu artinya kurang bu?” (so, to have mean kurang)
The teacher : “No, to have mean ke, but appropriated with the contexs, here
can mean menuju, so can translate sepuluh menit lagi menuju
jam tiga. Do you understand?”
you silent and I will give question about time, if you can answer
you can go out, but if can’t answer still stay here.
All of students silent and waited the question from teacher. Then
teacher gave question to the students one by one. “Evi 03.15?” It is three past
quarter, Evi answered.” No. It is a quarter past three, Evi answered again.”
Good, please go out. Then Siti 01.50? Siti answered: It is one past fiftieth. No,
other. “Saya bu,” (Vikki rises his hand). Ok. It is ten to one. “Still wrong,
teacher said.” That activity has finished after almost of students got the
question. Just some of students haven’t question, because time to break had
arrived.
On Wednesday, the fourteenth of April 2010, she entered the English
class. This is the situation.
The teacher : “Good morning, students?”
The students : “Good morning, mom.”
The teacher : “How are you today?’
The students : “I’m fine thank you and you?”
The teacher : “I’m fine too, thank you. What time is it?”
Siti : “Jam setengah sepuluh.” {half past nine)
The teacher : “In English, please!”
Siti : “mmm... a half past nine.”
The teacher : “Good.” Bagaimana yang lain masih ingat pelajaran kemaren
lesson, how the way to write and read time in English?)
The students : “Menit dulu past atau to jam.” (Minute first past or to hour)
The teacher : “Very good. Now, we will study about daily activity, what
mean of daily activity, Titik?”
Titik : “Tidak tahu bu, activity itu aktifitas kalau daily tidak tahu.” (/
don ’t know, activity is aktifitas if daily, 1 don ’t know)
The teacher : “Maksudnya aktivitas sehari-hari.” (the mean is daily activity)
The teacher started to explain about daily activity. She used pictures which
there are meaning of word in English each picture to explain. After then, the
teacher gave picture to each student.
The teacher : “Sudah bawa gambar semua? Sekarang kalian berkelompok,
setiap kelompok minimal tiga orang, buat minimal tiga kalimat
sesuai gambar yang kalian bawa dilengkapi waktu! For example:
it is takes a bath (teacher showed one of picture, the sentence is I
take a bath at 06.00. Subjectnya boleh siapa saja” (have you
bring picture? Now, make a group, each group consist o f
minimal three people, make minimal three sentences as that
picture complete with time)
Alvan : “Boleh buka kamus bu?” (May I open the dictionary)
The teacher : “Yes. Nanti presentasi dan setiap siswa harus membaca (Your
write will be presented and each student must read the sentence)
The students wrote the sentence, they are busy open dictionary. Sometimes
The students : “Yes. No.” (Some of students say “Yes” and others say “No”)
The teacher : “Five minute again.”
Then, the teacher waited for about five minute. She walked around chair and
table in the class while looked student’s writing. After she looked that all of the
student have finished, she asked one of group to present their writing. And
group one come forward to present.
The teacher : “Silent please, listen your friends!”
Evi : “I wake up at half past five. And she wake up at six o’clock.”
Titik : “I go to school at a quarter to six.”
The teacher : “Really Titik, kamu berangkat sekolah jam 05.45.” (really
Titik, you go to school at a quarter to six)
Titik : “Salah-salah, I go to school at a quarter to seven.” (No, I go to
school at a quarter to seven)
Badri ah : “I sleep at nine o’clock.
The teacher : “Let’s give applause! Then next group.”
The other group came forward to present until the last group. Then the teacher
gave explain about adding s/es to the verb with subject she, he, it. After that the
teacher gave post test to the student for about 30 minute.
3. Observation
In this first meeting teacher and writer (collaborator) observed teaching
learning process. By monitoring the student activity in this action we can see
that the planning is visible. Curriculum/core content appropriate current unit of
questioning skills, assessment is related to instruction too, but assessment yet
involves critical thinking. The instruction reviews prior knowledge that is the
teacher given pretest. But the student looked still confuse when they are answer
pre test. They are busy to question to their friends and teacher. They need a
long time to answer that question.
When the lesson began, students looked lazy and give up because they
think this lesson is very difficult. Then teacher demonstration on the classroom
activity, the teacher used o’clock to explain. The teacher used appropriate
resource to teach. The students began attention teacher’s explain. Research
based practices used to engage all students and class objectives/essential
questions are used. Some of students understand, and other not yet. Most of
them are confuse use to, to showed time. But, when teacher more give explain
again, the students looked understand. A good point is, when the teacher was
closed the meeting, she gave question to each students to reflection their
knowledge after study, classroom routines are consistently practiced.
4. Reflection
After analyzing the result of action in cycle I, the teacher can conclude
that the teacher should give brief explanations because there are some of
students confused and did not understand. She can repeat explain until the
students can understand. She must give support to the students who though this
theme is very difficult. Using media like o’clock is important to add knowledge
of the students can be answered the question by teacher when they are given
question orally before they go out of class. And some of students did their test
correctly. The problem in this cycle is some students difficult to calculate
minute and remember that minute on using to to say time, they didn’t
understand picture which given by teacher, so they didn’t know the meaning. It
is very important to continue to the next cycle to motivate them to master then-
vocabulary and give more exercise. The second cycle is carried out as follow
up of the first cycle. The teacher used the same method but different theme.
B. Cycle 2
Based on the result of cycle 1, it is necessary for the teacher to continue the
next cycle.
1. Planning
The activities are preparing:
a. Material, making lesson-plan, and designing the steps in doing the action
b. List of students’ name
c. Teaching aids (e.g. picture, flash card, real thing, real thing model, tape
recorder)
d. Sheet for classroom observation
1. Assessment Observed
Evidence/Comments A. Assessment involves critical thinking
B. Lesson uses manipulatives/technology
C. Students can articulate goals for learning
3. Culture
A. Teacher has high expectations for all students
B. Teacher has a good rapport with students
C. Teacher manages classroom behavior effectively
D. Students are engaged in classroom activity
4. Organization
A. Teacher uses varied grouping strategies.
B. Materials organized and easily accessible by students
C. Transitions are performed without disruption
Classroom Activities
Student Work Displayed □ Cooperative Group Activity □
Technology Available □
e. Some exercise from action 1 in cycle 1 (The pictures about theme in cycle I
that is take a nap a, breakfast, lunch and other)
f. Some difficult words from action 1 in cycle 1 (breakfast, lunch, take a nap,
g. Tests (pretest and posttest)
The models of pretest and posttest in cycle II is same but level of the
question is different consist of two exercises that is, exercise one the
students match the pictures with choose the words correctly, and exercise
two the form of the question is multiple choice there are ten question and
there are four answer to choose the correct answer. The writer makes the
same model of pretest and posttest in cycle II because the writer wants to
know improve of her teaching.
2. The implementation of the action
On Wednesday, the twenty firth of April 2010 the teacher (the writer)
entered her English class. She repeated gave question about time like the
teaching learning process in action 1 cycle. In action 1 cycle 1 the student are
still confuse to use to, in this time about that. The teacher has given that
question to students who have yet to understand about that. Besides, there were
some students didn’t understand the picture so they don’t know that meaning,
suck as breakfast, lunch, take a nap, arrive, in this case the teacher explained
again with the time and the student’s activity was made example. When the
students can be responded explain from the teacher and can be found the
meaning of that words, she asked their students to write that words and the
meaning on the book.
After she finished some problems in action 1 cycle 1, she began action
2. She introduced the mode of presentation in studying vocabulary, the steps
lesson he gave pre test to them. The theme on the cycle 2 is about part o f body.
The situation was as follow:
Students, now stand up. This is head, ear, aye, nose, mouth, hand, and
leg (the teacher while show the meaning with raise part of body). Now repeat
after me while raise your hand head they said head, ear they said ear, nose,
mouth, hand, leg. Once again, head, ear, aye, nose, mouth, hand, leg. They said
head, ear, aye, nose, mouth, hand, leg. Now let’s play game to remember that
words. If I raise part of body, you must be said what is it, understand? They
said yes (together). Then the teacher raise her part of body as she want. The
students said words as teacher’s hand which showed part of body.
She continued explain part of head, and part which has yet to explain
before. Now pay attention the picture in the black board. She explained all
picture, this is hair, cheek, chin, and neck (she showing the picture part of
head). Then this is shoulder, chest, elbow, stomach, finger, knee, and foot (the
teacher showed other part of the picture).After finished she ask to the students
to write it. Any question students? They said ulangi bu, belum mudeng. one
more mom, we have yet to understand). Then the teacher repeated her
explanation again. After she finished, she said because time is up, we will
continue next meeting, see you next time. The answered see you.
The next day on Wednesday, the twenty eighth April 2010, the teacher
(the writer) entered her English class. She said the students as follow:
The teacher : “Good morning students?”
The students : “I’m fine thank you.”
The teacher : “Who is absent today?”
The students : ‘Tidak ada bu.” (no one mom)
The teacher : “Now we will continue the last theme, do you remember it,
what is it?”
The students : “Part of body: head, leg, hand, ear, aye, cheek.” (they said
different words each other, even there are students are silent)
The teacher : “Now, each of you said three words part of body while raise
the part of your body, start from Ela!”
Ela : “Eye, nose, leg.” (She raised her body correctly)
The teacher : “Ok. Next Ulum.”
Ulum : “Hair, head, hand.”
The teacher asked each student. There are three students which just can be
answered one or two words. After this activity the teacher continued the lesson
that is body activity or the function of body.
The teacher : “What the function of eye?”
The students : “Untuk melihat, (to see)
The next, teacher ask the student to mention the function of body with real of
instruction teacher. When she said leg she walked, she said hand she write
some thing until the students can answered correctly. Then the teacher wrote
the words which mention of students with the Function. She asked the students