CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The aim of the research is to improve students’ reading comprehension through semantic mapping technique. The result of the research implementation is presented in Chapter four which consists of two sections. The first section is the process of the research and the second one is the discussion.
a. Before Implementing the Action
There are two parts related to before implementing the action. Those were pre-interview and pre-questionnaire. The explanation was as follows: 1. The Result of Pre-Interview
Pre-interview was conducted on Monday, October 13th 2014 which was started at 07.00 a.m. and finished at 08.20 a.m. the writer asked the teacher some questions related with the condition of English teaching learning process before conducting the actions. The writer divided the interview three categories. Those were the general condition of the English teaching learning process especially when the teacher taught reading in the class, students’ participation and the students’ achievement in learning English.
answer was teacher used the classical model such as giving the students a text, asking them to read and then answering the question. Usually the text and the question had been written in the students’ handbook (LKS). In managing the class, the teacher said that she didn’t have special way, she just asked the students to keep silent when they made noise in the class. She couldn’t solve the class maximally moreover the class was so crowded. The last point of this category was the teacher seldom used media in teaching learning process. She thought she didn’t have enough time to prepare it.
Second category was the students’ participation in following reading class. When the writer asked the teacher about the students’ participation, she said that they had low spirit in joining the class, it could be seen when she asked some questions related to the lesson they just kept silent, because they couldn’t comprehend it well. They also had low motivation in reading and comprehending the content of the text, and they often couldn’t do the exercise by their selves even they couldn’t work together with their friends.
2. The Result of Pre-Observation
Pre-observation was conducted to observe the process of the English learning before doing the action. It was used to collect the data on how good the teachers’ performance and students’ activities and participation during the teaching learning process.
Pre-observation did on the VIIIB grade students of MTS Asy-Syafi’iyahKarangasemMargasariTegal. There were 27 students. It conducted on Monday, October 13th 2014. It started at 08.20 a.m. and finished 09.45 a.m.
The result of pre-observation could be seen at the following data. Table 4
Students’ Observation at Pre-Condition
Activity Percentage
Contributive Participation
Asking question 3.50 %
Answering question 21.20 %
Giving opinion 7.25 %
Initiative Participation
Initiating in doing task 55.48 %
Average 23.53 %
that the average score of students’ observations at pre-condition which only related 23.53 %.
3. The Result of Pre-questionnaire
The writer also gave them some questions through questionnaire to know the real condition that was happened during teaching and learning process. It conducted on Saturday, 16th October 2014. It was needed to know the students’ response about the action or teaching learning process given by the teacher. It also used to support the collecting data for determining the treatment in CAR. The result of pre-questionnaire was as follows.
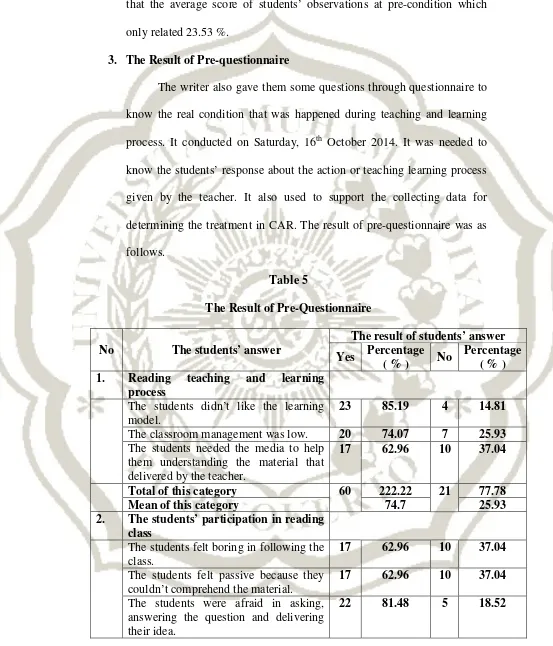
Table 5
The Result of Pre-Questionnaire
No The students’ answer
The result of students’ answer Yes Percentage
( % ) No
Percentage ( % ) 1. Reading teaching and learning
process
The students didn’t like the learning model.
23 85.19 4 14.81
The classroom management was low. 20 74.07 7 25.93 The students needed the media to help
them understanding the material that delivered by the teacher.
17 62.96 10 37.04
Total of this category 60 222.22 21 77.78
Mean of this category 74.7 25.93
2. The students’ participation in reading class
The students felt boring in following the class.
17 62.96 10 37.04
The students felt passive because they couldn’t comprehend the material.
17 62.96 10 37.04
The students were afraid in asking, answering the question and delivering their idea.
No The students’ answer
The result of students’ answer Yes Percentage
( % ) No
Percentage ( % ) The students had low motivation in
reading and comprehending the text.
24 88.89 3 11.11
The students didn’t have self-confident and didn’t have good cooperation in doing teamwork.
20 74.07 7 25.93
Total of this category 100 370.36 35 129.64
Mean of this category 74.07 25.93
3. The students’ achievement in learning English
The monotone way in learning couldn’t rise the students’ achievement.
18 66.67 9 33.33
There were three categories to be interviewed by the writer. The first was reading teaching and learning process, second was the students’ participation in reading class, and the last was the students’ achievement in learning English.
b. After Implementing of the Action
The CAR was done in two cycles. Each cycle consisted of two actions. It needed 80 minutes (2 x 40’) for every action in teaching learning process. 1. The Report of Cycle 1
Cycle one consisted two actions and it had four phases in each action. Those were planning, acting, observing, and reflecting.
a. Planning The Action
The writer and the teacher made a plan for each action based on the existing problem found in the class. The problem was the students’ reading comprehension in reading class. The plans that the writer and the teacher assigned were; first, assigning semantic mapping technique as the students to improve students’ reading comprehension in a reading class. Second, dividing the class into five groups consisted of five or six students of each group. In this way, the writer and the teacher divided the groups randomly. Third, making lesson plan that was included the reading materials, and media. Fourth, preparing the observation sheet to observe the students’ and the teachers’ activities during teaching and learning process.
b. Implementing the Action of Cycle 1
learning process consisted of three main activities. Those were teaching, group discussion, and class discussion.
In teaching, the teacher presented the lesson plan that was prepared before. The teacher presented the lesson plan by using speech, discussion, and question and answer method. In group discussion, the students discussed the material given by the teacher. In class discussion, the teacher invited the students to discuss the result of teamwork.
2. The Implementation of 1st Action a. Opening
The first action in cycle 1 was held on Monday, November 3rd 2014. The lesson started at 07.00 a.m. until 08.20 a.m. The researcher and collaborator came to the class, greeted the students, and checked students’ attendance. Beginning the lesson, the students looked very fresh because it was the first lesson of that day. In this meeting there were 27 students in the classroom.
the story occur?, “ When does the story occur?, “Who is the main character?, etc.
The researcher recorded their responses on the whiteboard; listing them in the order they were given. When no further suggestions were raised, the researcher asked the students if they saw any ways to group their ideas.
b. Main activity
The researcher gave an explanation about the strategies to analyze the text. He gave a short explanation about the material of that day that was a narrative text. The text that would be discussed was “The Monkey and the Crocodile”.
Firstly, the researcher gave each student a copy of the text. The researcher asked the students to read the text silently.
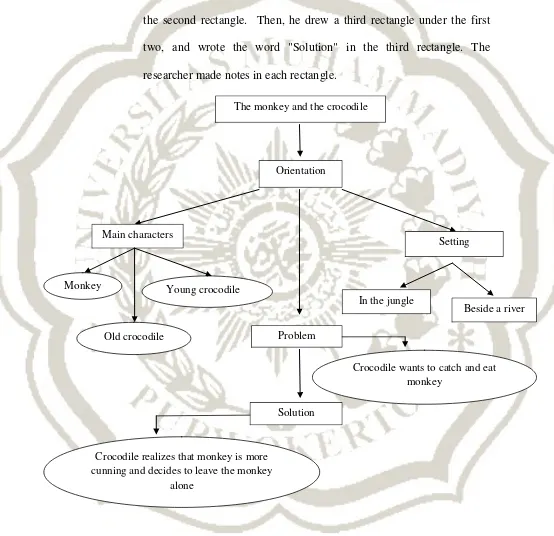
Thirdly, the researcher drew a rectangle on the whiteboard. The researcher wrote the word "Orientation" in the rectangle. He drew another rectangle under the first one, and wrote the word "Problem" in the second rectangle. Then, he drew a third rectangle under the first two, and wrote the word "Solution" in the third rectangle. The researcher made notes in each rectangle.
Q
Figure 5: Story map “The monkey and the crocodile” The monkey and the crocodile
Orientation
Main characters
Setting
In the jungle
Beside a river
Monkey Young crocodile
Old crocodile Problem
Crocodile wants to catch and eat monkey
Solution
Crocodile realizes that monkey is more cunning and decides to leave the monkey
Finally, after the students had finished “personalizing” the reading map, they were given the opportunity to offer new information for supplementing the whiteboard version of the map. The researcher recorded the new information. As he had expected, because of the differences among students’ experiences and interpretations of what was important in the reading, there were some disagreements about the final shape the map should take. This part of the activity is the most valuable because it produces an interaction among students. c. Closing activity
Before closing the lesson, the researcher evaluated the students’ reading comprehension. It was done by giving the tasks based on the text given before. During the activities, the researcher monitored the class in finding the equivalents of the unfamiliar words and in discussing the text. Due to the limitation of time, the researcher asked the students to continue their work at home.
3. The Implementation of 2nd Action a. Opening
gave the clues about the topic that will be given by asking “Do you know the story of “The legend of Toba Lake”?” “Where does the story occur? Etc.
b. Main activity
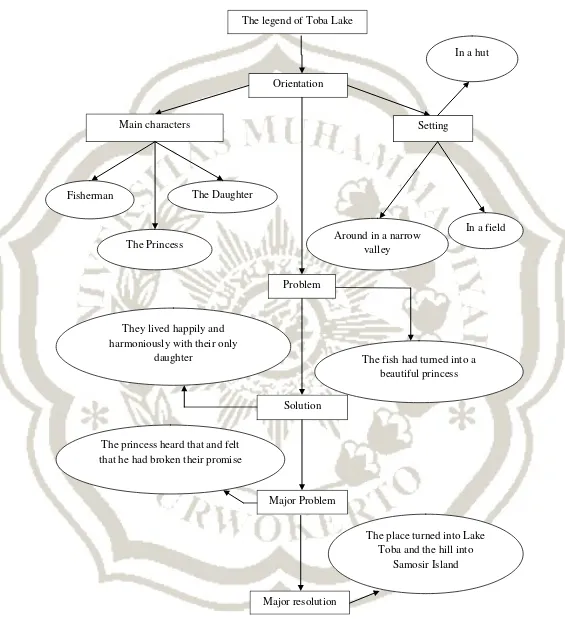
The researcher selected the topic of narrative text from the Developing Competence in English book, entitled “The Legend of Toba Lake”. The researcher asked the students to read the text silently. Then, he asked them to construct a semantic map. In the beginning, some of the students could not make the concept well. The researcher guided the students how to construct the map. The researcher constructed a map through nodes and lines bond through establishing relationships between the words/phrases taken from the text. Then, the researcher clarified the way the words/phrases are constructed in a map, and taught them how to read the map well. The students paid attention enthusiastically.
Figure 6: Story map “The legend of Toba Lake” The legend of Toba Lake
Orientation
Main characters Setting
Around in a narrow valley
In a field In a hut
Fisherman
The Princess
The Daughter
Problem
The fish had turned into a beautiful princess
Solution They lived happily and
harmoniously with their only daughter
Major Problem
Major resolution The princess heard that and felt
that he had broken their promise
The place turned into Lake Toba and the hill into
c. Closing activity
Before ending the class, the researcher evaluated students’ comprehension by giving tasks which should be done by using semantic mapping strategy.
4. Observing the Action
The writer did observation during the implementation of teaching learning process to improve students’ reading comprehension using semantic mapping. The observation of cycle 1 was conducted on each action. In this matter, the writer did observation toward implementation of the action using checklist.
a. The 1st Action
The writer observed the individual students’ activity in class both individual and group activity.
1) The Result of Individual Students’ Activity
The observation was done on Monday, November 3rd 2014. It started at 10.40 a.m. and finished at 12.00 p.m. the writer did observation to the students during the teaching and learning process. Observation of the action 1 gave the result of the data as follows:
Table 6
Individual Students’ Activity Action 1 Cycle 1
Activity Percentage
Contributive Participation
Asking question 11.11 %
Answering question 33.33 %
Giving opinion 37.04 %
InitiativeParticipation Initiating in doing task 92.59 %
In the first action, it could be seen that 11.11 % or three students were able to ask question. Based on the observation, they were shy in asking question even sometime they asked using Indonesian language. While 9 students or 33.33 % were able to answer the question. In giving opinion, 10 students or 37.04 % could give their opinion. The last category, it was great since even if in asking question, answering question and giving opinion they were low, but in doing the task they had good initiated, it reached 92.59 % and the average percentage of students’ activity was 43.52 %.
b. The 2nd Action
The writer observed the individual students’ activity and students’ group activity in the class.
1) The Result of Individual Students’ Activity
The observation was carried out on Saturday, November 8th 2014. It started at 10.00 a.m. and finished at 11.20 a.m. the writer did the observation during the teaching learning process.
Observation of the action 2 gave the result of the data as follows:
Table 7
Individual Students’ Activity Action 2 Cycle 1
Activity Percentage
Contributive Participation
Asking question 14.81 % Answering question 33.33 % Giving opinion 40.74 % Initiative
Participation
Initiating in doing task 100 %
In the second action it had little improvement. Students who asking the question were 14.81 %, they answered the question till 33.33 %, giving their opinion 40.74 % and 100 % students had good initiated in doing the task given by the teacher. 2) The Result of Students’ Group Activity
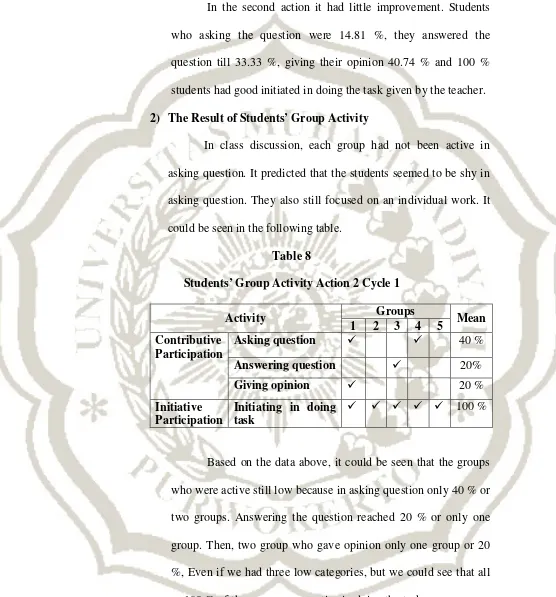
In class discussion, each group had not been active in asking question. It predicted that the students seemed to be shy in asking question. They also still focused on an individual work. It could be seen in the following table.
Table 8
Students’ Group Activity Action 2 Cycle 1
Activity Groups Mean
1 2 3 4 5 Contributive
Participation
Asking question 40 %
Answering question 20%
Giving opinion 20 %
c. Evaluating
After did the action in cycle 1, the writer evaluated the improvement of the students’ reading comprehension by giving a test. The first test was pre-test in the beginning of the research before the action, and post-test in the end of cycle one. Then, the writer tried to calculate the improvement of pre-test and post-test in cycle 1 by using the formula as follow:
P1 = y1 – y x 100 % Y
Where P1 : Percentage of Students’ Improvement Y1 : Post – test Cycle 1
Y : Pre – test
The improvement in cycle 1 was as follow: Pre – test
(Y)
Post – test Cycle 1
(Y1) Improvement
5.65 6.60 16.81 %
d. Reflecting
The result of test showed that the improvement only reached 16.81 %, so it had not fulfilled the indicator of success that was 30 %. The result of students’ observation in getting the data of students’ ability in cycle 1 was as follows; the students’ ability in making semantic mapping was still low, it happened because they had less of vocabulary so they couldn’t create their idea to make a good semantic mapping.
Where P2 : Percentage of Students’ Improvement Y2 : Post-test Cycle 2
Y : Pre-test
The improvement in cycle 2 was as follow: Pre–test
(Y)
Post–test Cycle 2
(Y2) Improvement
5.65 8.25 30.16 %
The improvement in cycle 1 and cycle 2 as follow:
Post–test Cycle 1 Post–test Cycle 2 Improvement
6.60 8.25 30.16
5. The Implementation of Cycle 2
The cycle consisted of two actions which consisted of four phases. Those were planning, acting, observing, and reflecting.
a. Planning the Action
improvement. In solving the problem of cycle 1, the researcher and the teacher re-planned the action in cycle 2. The plan that the researcher and the teacher made were as follows;
First, the researcher applied to use semantic mapping as a technique and solutions to improve the students’ reading comprehension. The researcher and the teacher arranged the action that would be done in two actions. Second, the writer divided the class into some groups so that the students would not bore. Third, the writer prepared or made lesson plan that was agreed by the teacher. Fourth, the teacher and the writer prepared the media to support the teaching and learning process. Fifth, preparing the observation sheets to observe the teachers’, the individual students’ and the students’ group activity in teaching learning process.
b. Implementing the Action of Cycle 2
There were two actions in cycle 2. The teacher and the researcher collaborated in conducting the planned action.
6. The Implementation of 1st Action a. Opening
been introduced in the previous meeting. After that, he conducted brainstorming activities to activate the students’ prior knowledge about the topic of the lesson. He showed them a picture of a Prambanan temple, gave them some questions related to the topic such as: “Have you ever seen the temple?” and “Which temples have you visited?”, and introduced the topic to be discussed in the meeting, which was “Prambanan Temple”. To expand the brainstorming activities, he also asked the students to mention the things that they usually find at a temple and the activities that people do at the temple.
Afterwards, the researcher asked the students to classify the information about the temple and recorded the information in the form of a semantic map. Then, the researcher divided the class into groups. b. Main activity
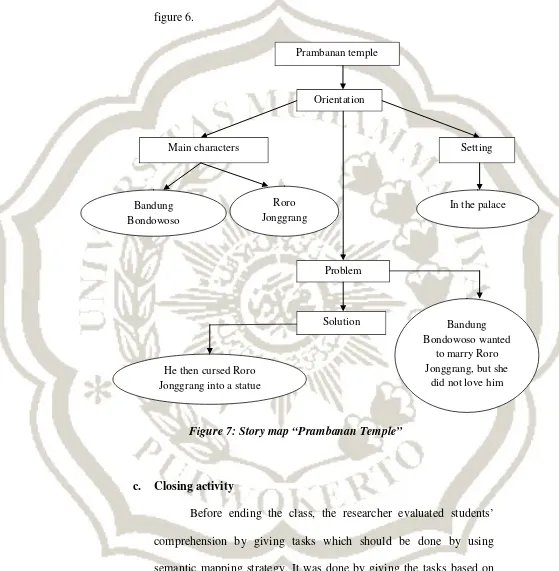
complete. The semantic map made by the students in presented in figure 6.
Figure 7: Story map “Prambanan Temple”
c. Closing activity
Before ending the class, the researcher evaluated students’ comprehension by giving tasks which should be done by using semantic mapping strategy. It was done by giving the tasks based on the text given before. During the activities, the researcher monitored
Prambanan temple
Orientation
Problem
Solution Main characters
Bandung Bondowoso
Roro Jonggrang
Setting
In the palace
Bandung Bondowoso wanted
to marry Roro Jonggrang, but she
did not love him He then cursed Roro
the class, in finding the equivalents of the unfamiliar words and in discussing the text. Due to the limitation of the time, the researcher asked the students to continue their work at home.
7. The Implementation of 2nd Action a. Opening
The second meeting was held on Saturday, November 15th 2014. The lesson started at 10.40 a.m. until 12.00 p.m.The researcher told the students that he would use the technique that had been introduced in the previous meeting. Seeing that the students were ready with the lesson, the researcher began to carry out brainstorming activities. The topic that would be discussed was “The Boys and the Frogs”. The researcher asked the students to tell everything they knew about the topic. Since the students knew about the topic already, they automatically gave the information and classified them into some clusters.
b. Main activity
information they obtained from the text. While the students were busy with the assignment, the researcher and the observer monitored the class.
Then, the researcher asked the students to report their work. He asked one of the groups to draw the semantic map on the board. Some students expressed their opinion spontaneously when they found their friends made mistakes or when the information was incomplete.
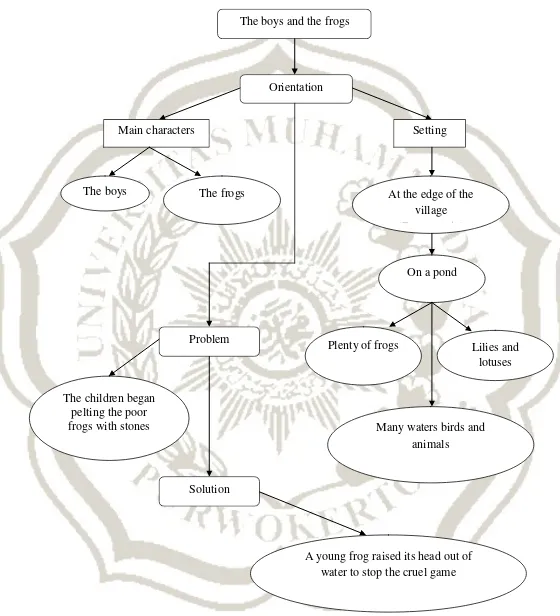
Figure 8: Story map “The boys and the frogs” The boys and the frogs
Orientation
Main characters
The boys The frogs
Problem
Solution The children began
pelting the poor frogs with stones
Setting
At the edge of the village
(B i )
On a pond
Plenty of frogs Lilies and lotuses
Many waters birds and animals
c. Closing activity
Before ending the class, the researcher evaluated students’ comprehension by giving tasks which should be done by using semantic mapping strategy. It was done by giving the tasks based on the text given before. During the activities, the researcher monitored the class, in finding the equivalents of the unfamiliar words and in discussing the text. Due to the limitation of the time, the researcher asked the students to continue their work at home.
8. Observing
The researcher did observation during the implementation of the teaching and learning process to improve students’ reading comprehension using semantic mapping. The observation of cycle 2 was conducted in each action. In this matter, the researcher did the observation toward implementation of the action using checklists.
Based on the observation that had been conducted by the researcher during the teaching and learning process, it showed that there was a better improvement in cycle 2.
a. The 1st Action
The researcher observed the individual students’ activity and students’ group activity in the class during the learning process. 1) The Result of Individual Students’ Activity
did observation to the students during teaching and learning process. It showed a better improvement in cycle 2.
Observation of the action 1 resulted as follows: Table 9
Individual Students’ Activity Action 1 Cycle 2
Activity Percentage
Contributive Participation
Asking question 51.85 % Answering question 55.55 % Giving opinion 44.44 % Initiative
Participation
Initiating in doing task 100 %
Average 62.96 %
Based on the data above, it could be seen that the students who asked question were 51.85 % or 14 students from 27 students. The students who answered the question were 55.55 % or 15 students. Then, 44.44 % or 12 students were giving their opinion and all of the students were enthusiastic in doing the task. From the data, it could be seen that the students were confident, they were not shy anymore in asking and answering the question, giving their opinion and doing the task. As the result they were active in the class even if it had not maximal yet.
b. The 2nd Action
1) The Result of Individual Students’ Activity
The observation was conducted on Saturday, November 15th 2014. It started at 10.40 a.m. and finished at 12.00 p.m. the researcher did the observation to the students during teaching and learning process.
Observation of the action 2 resulted as follows: Table 10
Individual Students’ Activity Action 2 Cycle 2
Activity Percentage
Contributive Participation
Asking question 77.78 % Answering question 85.19 %
Giving opinion 77.78 %
Initiative Participation
Initiating in doing task 100 %
Average 67.69 %
According to the observation resulted above. It could be seen that the students’ resulted of action 2 had improved. The students who asked the question showed 77.78 % or 21 students. In answering the question showed 85.19 % or 23 students. On the other hand, the students who did the exercises were 100 % or it means that all of the students doing the exercises. In this result, most of the students had been active and involved in learning process.
2) The Result of Students group Activity
second action in cycle 2 was done on Saturday, November 15th 2014. It started at 10.40 a.m. and finished at 12.00 p.m. it could be seen in the table below.
Table 11
Result of Students’ Group Activity in Action 2 Cycle 2
Activity Groups Mean
1 2 3 4 5 Contributive
Participation
Asking question 60 %
Answering question 40%
Giving opinion 60 %
Initiative Participation
Initiating in doing task 100 %
From the data above, it could be concluded that the groups who were active in asking the question began to improve became 60 %. In answering question got improvement became 40 %. The groups who gave opinion became 60 %. Then the groups who did exercises became 100 %.
c. Evaluating
After did the action in cycle 2, the writer evaluated the improvement of the students’ reading comprehension by giving a text. She gave them post-test in the end of cycle 2. Then, the writer tried to calculate the improvement of pre-test cycle 1 and post-test cycle 2, then the writer also calculated the improvement from post-test cycle 1 and post-test cycle 2 by using the formula as follows:
P2 = y2 – y x 100 % y
They also still confuse how to make semantic mapping when they had read the text. It also because of the teacher never used the technique before, so she didn’t apply it maximally. But, even if the students’ reading comprehension using semantic mapping in cycle 1 still low, they could show us their improvement between action 1 and action 2. Although, the increasing number of students’ activity not significant enough. It had not reached the criteria of the success of the action that already determined by the teacher and researcher.
d. Reflecting
The researcher and the collaborator teacher discussed toward the conclusion of implementing semantic mapping in the action. It was conducted on Saturday, November 15th 2014 at 12.30 p.m. the teacher and the researcher felt satisfied because their effort to improve the students’ reading comprehension using semantic mapping had been reached.
The first improvement could be seen from the test that given by the writer. In cycle 1 the improvement of the students’ reading comprehension from pre-test to post-test reached 16.81 %. Then, in cycle 2 it raised up to 30.16 %.
The students’ activity in cycle 2 also showed an improvement from action 1 to action 2. The average in cycle 2 was 74.07 %. The students who asked question improve 25.93 %. The students who answered question raised 29.64 %. The students who gave opinion improved 33.34 %. While, the students in doing exercises were stable and reached 100 %.
From the test, the observation and reflection in this cycle, the researcher found an improvement of the students’ reading comprehension using semantic mapping. The teacher and the researcher felt satisfied and decided to stop the research in CAR based on the consideration from the result of the research.
There were some reasons why the researcher and the teacher stopped the research. First, there was no improvement of the students’ reading comprehension using semantic mapping. Second, the indicator success of this research was reached. It was based on the post result which showed more than 30 % improvement.
C. Discussion of the Data after Implementing the Actions
In this part, the discussion will describe the improvement of students’ reading comprehension using semantic mapping and the result of students’ observation and interview.
1. The Improvement of Students Reading Comprehension Using Semantic Mapping
Table 12
Improvement of Students’ Reading Comprehension
Students’ Reading Comprehension
Improvement
Cycle 1 Cycle 2
16.81 % 30.16 %
Based on the data above, it could be seen that students’ reading comprehension related to the implementation of semantic mapping improved from cycle 1 to cycle 2. It happened because students were ready and confident in joining the reading class.
2. The Result of Students’ Activity Using Observation
The indicator success of students’ reading comprehension also could be seen from the improvement of students’ activity from the observation. In cycle 1 the improvement reached 45.37 %, and in cycle 2 the improvement raised up to 74.07 %.
3. The Result of Interview
4. The Result of Pre – Questionnaire
The successful of using semantic mapping in reading class also could be seen from the questionnaire that written from the students. The result of pre and post-questionnaire were as follows:
Table 13
The Result of Pre – Questionnaire
NO Pertanyaan Jawaban
A. Proses PembelajaranBahasaInggris Y (%) T (%)
1. Model pembelajaranmembosankan,
kurangmenarikdantidakmendorongandauntukberpartisipa sisecaraaktif di kelas.
82,28 17,72
2. Pengelolaankelasoleh guru
dirasabelumcukupefektifdalammembantumenciptakansu asanabelajarbahasa inggris yang nyamanuntukanda.
78,06 21,94
3. Kurangadanya media
pembantupengajaranbahasainggriskhususnya reading oleh guru.
60,53 39,47
B. KeaktifanSiswa
4. Andakurangbersemangatuntukmengikutipelajaranbahasai nggris yang guru berikan.
60,53 39,47 5. Andakurangaktifdalam proses pembelajaranbahasa
inggris karenatidakmenguasaimateri.
9. Model pembelajaran yang
Table 14
The Result of Post – Questionnaire
NO Pertanyaan Jawaban
A. Proses PembelajaranBahasaInggris Y (%) T (%)
1. Apakah modelpembelajaranyang dilakukan oleh guru sudah
tidak membosankan dan menarik sehingga
mendorongandauntuk lebih aktif di kelas?
100 -
2. Apakah pengelolaankelasoleh guru dengan semantic mapping dirasasudahcukupefektifdalammembantumenciptakansuasana belajarbahasainggris yang nyamankhususnya reading untukanda?
100 -
3. Apakah guru sudah menggunakan media
pembantu(contoh:gambar) dalam pengajaranbahasainggriskhususnya reading oleh guru?
74,07 25,93
B. KeaktifanSiswa
4. Apakah anda merasa senang dan lebih
bersemangatuntukmengikutipengajaran reading dengan
menggunakan semantic mapping?
92,59 7,41
5. Apakah anda merasa lebih aktif dan lebih mudah dalam memahami materi yang diberikan dengan menggunakan semantic mapping?
70,37 29,63
6. Apakah anda lebih merasa percaya diri dalam bertanya, menjawab pertanyaan, dan mengajukan pendapat?
66,67 33,33
7. Apakah anda lebih merasa termotivasi untuk membaca dan memahami isi bacaan?
74,07 25,93
8. Apakah anda sudah dapatbekerjasecaramandirimaupun secara kelompokselama proses belajarbahasainggris?
96,30 3,70
C. PrestasiBelajarBahasaInggrisSiswa
9. Apakah pengajaran reading dengan semantic mapping dapat meningkatkan prestasi belajar anda?
92,59 7,41
10. Apakah pengajaran reading dengan semantic mapping sudah cukup efektif dalam membantu kesulitan belajar bahasa inggris anda selama ini?
55,56 44,44
TOTAL 822.22 177.78