THE IMPLEMENTATION OF “MAKE A MATCH” MODEL
TO IMPROVE WRITING SKILLS FOR THE ELEVENTH
GRADE OF MAN 2 SEMARANG IN THE ACADEMIC YEAR
Submitted to the Board requirements for
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
i
MPLEMENTATION OF “MAKE A MATCH” MODEL
TO IMPROVE WRITING SKILLS FOR THE ELEVENTH
GRADE OF MAN 2 SEMARANG IN THE ACADEMIC YEAR
OF 2018/2019
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd.)
By:
Nur Kayati
NIM.11314020
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
SALATIGA
2018
MPLEMENTATION OF “MAKE A MATCH” MODEL
TO IMPROVE WRITING SKILLS FOR THE ELEVENTH
GRADE OF MAN 2 SEMARANG IN THE ACADEMIC YEAR
of Examiners as a partial fulfillment of the Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd.)
v
MOTTO
Man Jadda Wa Jada
“Where there is a will there is a way”
ْۗﻢِﮭِﺴُﻔْﻧَﺎِﺑﺎَﻣا ْوُﺮِّﯿَﻐُﯿﯨﱣﺘَﺤٍﻣ ْﻮَﻘِﺑﺎَﻣُﺮِّﯿَﻐُﯾ َﻼَﮭﱣﻠﻟﺎﱠﻧِا
Verily never will Allah change the condition of
people until they change it themselves.
(Ar-Ra’d:11)
Life is not about finding yourself. Life is about
creating yourself.
vi
DEDICATION
This graduating paper is dedicated to:
1. My beloved parents (Mr. Raban (alm) and Mrs. Kusnah) who always
support me materially and morally. Thank you for your endless love and
prayer, thank you for raising me up to more than I can be.
2. My beloved sisters, Siti Harmini and Munawaroh, my beloved brothers in
law, Jumarno and Slamet Widodo, and my beloved nephew, Syarif
Maulana. Thank you for always cherish of me.
3. My beloved second parents of Dar Al Yatama Orphanage, Mr. Sigit
Riwiyanto and Mrs. Mustaghfirotun Idriss. Thank you for taking care of
me since I was in senior high school until I finished my study in
university.
4. My beloved best friends, Tasfiatun Niswati, Sinta Dewi P, Anglila W, who
always be there supporting, listening, and amusing me.
5. My beloved sisters from another mother and father, Rina Anggaini, Umi
Nashikhatuzzulfah, Tiyas Utami, Dwi Sri Utami, Umi Mahfudhoh, April
Liyani, Bayu Alfin Maulana who always reminds me to take care of
everything and give me strength.
6. My big family of LKSA Dar Al Yatama. Thank you for being the part of
my wonderful journey.
7. My best partners of graduating paper in Mrs. Setia Rini’s group that
vii
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Assalamu’alaikumWr. Wb.
Alhamdulillahirabbil’alamin, all praises be to Allah SWT the Most
Gracious and Most Merciful who always blesses and helps the researcher, so the
researcher can finish this graduating paper as one of the requirements for Sarjana
Pendidikan (S.Pd.) in English Education Department of Teacher training and
Education Faculty of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga.
Peace and salutation may always be given to Prophet Muhammad SAW.
who has guided as from the darkness to the brightness. However, this graduating
paper will not be finished without support, advices, help, and encouragement from
several people and institution. Hence, the researcher would like to express special
gratitude to:
1. Dr. H. Rahmat Hariyadi, M.Pd. as the Rector of State Institute for Islamic
Studies (IAIN) Salatiga.
2. Suwardi, M.Pd. as the Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of
State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga.
3. Noor Malihah, Ph.D. as the Head of English Education Department of
State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga.
4. Dr. Setia Rini, M. Pd as the counselor, who gives great attention,
suggestion and guidance for this graduating paper from chapter I until
ix ABSTACT
Kayati, Nur. 2018. The Implementation of “Make A Match Model” to Improve Writing Skills for the Eleventh Grade of MAN 2 Semarang in the
Academic Year of 2018/2019. A Graduating Paper, English Education
Department, Teacher Training and Education Faculty, State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga. Counselor: Dr. Setia Rini, M.Pd.
The objectives of the study are: To find out the implementation and to know the result of the implementation of “Make A Match” model to improve writing skills for the eleventh grade of MAN 2 Semarang in the academic year of 2018/2019. The numbers of subject of the research are 29 students of XI MIA 1 class of MAN 2 Semarang.
The methodology of this research was classroom action research. The research consisted of two cycles and each cycle consisted of four steps, they were; planning, acting, observing, and reflecting. The data collected were qualitative but also supported by quantitative data. The qualitative data were gained through observation and documentation. The data were in the form field notes, observation checklist and photographs. Meanwhile, the quantitative data was collected from the test. The researcher used SPSS 18.00 for analyzing the test.
The writer finds that there is a significant improvement on students’ writing skills after treatment by using “make a match” model in cycle I and cycle II. The result of pre-test cycle I is 0 % of the students who reach the passing grade. The total presentation of the students who cannot reach the passing grade in the post-test cycle 1 is 51.72 %. T-test cycle I was 13.7 while T-table is 2.048 for df 28 and the significance 5%. The sig 2 (tailed) value is 0,000 and T-test is 13.7, thus the sig 2 (tailed) value <0.05 and T-test is bigger than T-table. Thus, Ha is accepted. Meanwhile, in the pre-test cycle II, there are students who can pass the passing grade, and the presentation is 72.41 %. Meanwhile, there are three students by the presentation 10.34 % who cannot reach the passing grade in the post-test cycle II. T-test in the cycle II is 4.93 while T-table shows 2.048 for df 28 and the significance 5 %. The sig 2 (tailed) value < 0.05 and T-test is bigger than T-table. Thus, Ha is accepted. The target presentation of the passing grade has been achieved.
x
TABLE OF CONTENT
TITLE ... i
DECLARATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR’S NOTE ... iii
STATEMENT OF SERTIFICATION ... iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNWLEDGEMENT ... vii
ABSTRACT ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... x
LIST OF FIGURE AND TABLES... xiii
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Research ... 1
B. Statement of the Research Question... 5
C. Objectives of the Research ... 5
D. Significance of the Research... 6
E. Hypothesis and Success Indicator ... 7
F. Research Methodology ... 8
xi
2. Subject of the Research ... 10
3. Steps of the Research ... 12
4. Techniques of Data Collection and Research Instrument ... 14
5. Data Analysis ... 18
G. Graduating Paper Outline ... 20
CHAPTER II: THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK A. Supporting Theories ... 22
1. Writing Texts ... 22
2. Make A Match Model ... 53
B. Review of Previous Study ... 55
CHAPTER III: IMPLEMENTATION OF RESEARCH A. The Procedure of the Research ... 59
1. Cycle I ... 59
2. Cycle II ... 62
B. The Minimal Standard of Successful ... 65
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION A. Research Findings ... 66
1. Cycle I ... 66
2. Cycle II ... 81
B. Discussion ... 96
xii
A. Conclusion ... 100
B. Suggestions ... 102
BIBLIOGRAPHY
xiii
LIST OF FIGURE AND TABLE
Figure 1.1 The Scheme based on Kemmis and McTaggart ... 10
Figure 2.1 The Scheme based on Harmer ... 26
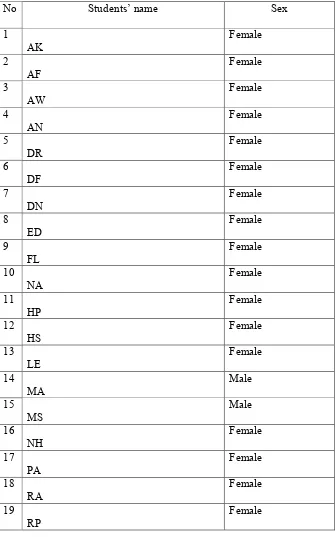
Table 1.1 List of the Students’ Name of XI MIA 1 Class of MAN 2 Semarang 11 Table 1.2 Research Schedule ... 12
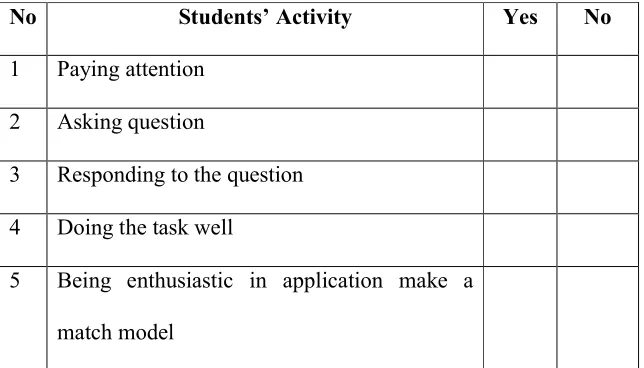
Table 1.3 Students’ Observation Checklist ... 16
Table 1.4 Teachers’ Observation Checklist ... 16
Table 2.1 Scoring Rubric according to The Jacob ... 31
Table 4.1 Form the Result of Students’ Observation Checklist Cycle I ... 76
Table 4.2 Form of Result Teachers’ Observation Checklist Cycle I ... 76
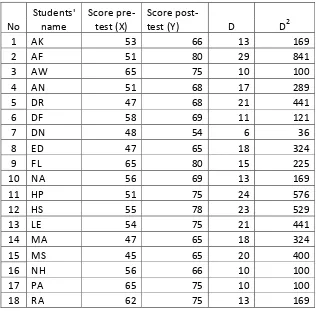
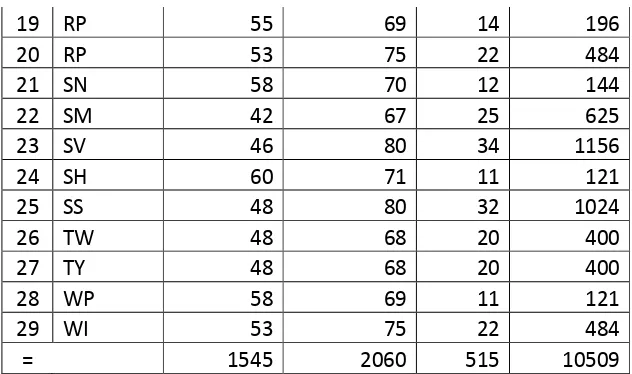
Table 4.3 The Students’ Score Pre-Test and Pos-Test Cycle I ... 77
Table 4.4 Count of Passing Grade of the Pre-Test and Post-Test in the cycle I 78 Table 4.5 Descriptive Statistic Cycle I ... 79
Table 4.6 Paired Samples Test Cycle I ... 80
Table 4.7 Form the Result of Students’ Observation Checklist Cycle II ... 90
Table 4.8 Form of Result Teachers’ Observation Checklist Cycle II ... 90
xiv
Table 4.10 Count of Passing Grade of the Pre-Test and Post-Test in the cycle II 93
Table 4.11 Descriptive Statistic Cycle II ... 93
Table 4.12 Paired Samples Test Cycle II ... 94
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
In this chapter, the researcher presents the background of the study,
statement of the problems questions, objective of the study, significance of the
study, review of previous study, hypothesis and success indicator, research
methodology, and graduating paper outline
A. Background of the Research
English is the important subject of the teaching-learning process in the
school. English is starting from kindergarten up to the university. English is
not a mother language or English is a foreign language in Indonesia and it is
taught formally at the school, thus is not easy learned it for Indonesian’s
student. However, English must be learned, since English is the International
language that connects Indonesia with the other country. It helps students get
information and knowledge in more than one aspect.
There are four basic skills should be mastered by the students, they are
reading, speaking, writing, and the last is listening. Rini (2009:3) states that,
“They are used to encourage the students to develop their competence….” It
means that four skills of English increasing students ability in many aspects.
If students only master one of them, the students get difficulties to understand
what they learn. For example, when students write a sentence, they should
2
structure of the sentence. Then, if they have written a sentence correctly, thus
they will be able to speak correctly also.
In this research, the researcher will focus on writing aspect. According
to Nur R, (2009:1), “…proficiency in English, particularly writing skill, is
generally assumed to be the most essential for a successful study.” It means
that writing is the aspect that is needed by the students because it is one of
particular importance in English.
Harmer (2001:79) said that, “The visual demonstration of language
construction is invaluable for both our understanding of how it all fits
together and as an aid to committing the new language to memory. Students
often find it useful to write sentence using new language shortly after they
have studied it.” It means that writing can reinforce the student memories.
Nur R (2009:2) also states about the importance of writing, “Writing skill
covers the mastery of language, mechanical skills, treatment of content,
stylistic skills, and evaluative skills.”
The main key of writing a text is the students have to master the
vocabulary and also the tenses. Thus, the students can arrange the vocabulary
and tenses to be a correct sentence. Moreover when make a good text needs
coherence and cohesive.
As interviews that hold on Wednesday, 3rd May 2018 with Mrs.
Noviati Jamila, she is English teacher in MAN 2 Semarang. There were many
problems that obstruct in teaching-learning process. The researcher asked
3
the teaching learning process, the teacher said that the situations of the
students depend on their class. There are active classes and also passive
classes. The class area also influence the students comprehension.
The second question is about problem in the class. The teacher said
that the students usually had difficulties in writing. The teacher answered that
in particular writing subjects, the lack of vocabulary, the students faced many
difficulties in proposing their idea to be an appropriate text, and less
enthusiastic in the lesson became the problem in the class too.
The third question is about the Standardized of Minimum Score
(KKM) of English subject and the Curriculum that is used in MAN 2
Semarang. The teacher said that Standardized of Minimum Score (KKM) in
MAN 2 Semarang is 70, and MAN 2 Semarang uses Curriculum 2013
Revision.
The fourth question is about the method that is used in writing. The
teacher said that for now she follows the instruction in the book. The last
question is about make a match model. The teacher said that she never uses
make a match model.
The conclusion from that interview in term of students’ difficulties in
writing was the eleventh grade of MAN 2 Semarang, they had problems such
us; lack of vocabulary, the students faced many difficulties in proposing their
idea to be an appropriate text, and less enthusiastic in the lesson became the
4
in writing activities. Thus, the students are more enthusiasts in writing
activity.
Nowadays, teachers can use many ways in the teaching-learning
process, for example is game, thus the teaching learning-process is not
monotonous and the students are not getting bored. Varieties method or
model is needed to make the teaching-learning process more interesting.
Sutarmiyati (2016:3212) states that variety learning model will increase the
student’s enthusiast.
There are many of games that can be applied; one of them is “make a
match” model. Make a match model is the game of teaching-learning that
developed by Curran (Huda, 2016:135). It is part of cooperative learning, that
emphasize grouping and pair discussing. In this model, the teacher should
prepare some cards that consist of topics. According Arifah &
Kusumarasdyati (2013:02), teachers can motivate and encourage their
students to be more interested and enthusiastic in learning English by using
make a match model. Hopefully, by using the game, the teaching-learning
process will be more interesting, make the student comfortable, enthusiastic
with the material and improving the students ability in writing. Through make
a match model, the students can propose their idea since the cards in make a
match model only show the clue of text or the main idea and the students
have to develop the cards.
According to whole explanation, the researcher is interested in doing
5
MODEL TO IMPROVE WRITING SKILLS FOR THE ELEVENTH GRADE OF MAN 2 SEMARANG IN THE ACADEMIC YEAR OF 2018/2019
B. Statement of the Research Questions
Based on the background of the study, the researcher decides the problems of the research are:
1. How is the implementation of “Make A Match” model to improve writing
skills for the eleventh grade of MAN 2 Semarang in the academic year of
2018/2019?
2. How far is the improvement of student’s writing skills by implementing
“Make A Match” model for the eleventh grade of MAN 2 Semarang in the
academic year of 2018/2019?
C. Objective of the Research
The objectives of the study are to answer the question above. In this
research, the researcher has some purposes according to the statement of the
problems.
1. To find out the implementation of “Make A Match” model to improve
writing skills for the eleventh grade of MAN 2 Semarang in the academic
6
2. To know the improvement of student’s writing skills by implementing
“Make A Match” model for the eleventh grade of MAN 2 Semarang in the
academic year of 2018/2019.
D. Significance of the Research
The researcher hopes that this research gives advantages, contribution
and also useful for the students, the teacher, the school, the reader and the
writer especially about the implementation of “make a match” model to
improve writing skills for the eleventh grade of MAN 2 Semarang in the
academic year of 2018/2019 as the statement below:
1. For the students
The advantages of this research, it can support the students achieve
in writing skills. It can increase students’ motivation in English.
Teaching-learning process using “make a match” model can make students become
active and enthusiast in writing skills. It can help students feel fun and
receive much knowledge easily.
2. For the teacher
The advantages of this research, it can support English teachers to
use this model in teaching writing. They can apply new model in
teaching-learning process in order to make the students more enthusiast in their
7 3. For the school
The advantages of this research, it can develop the curriculum of
the English teaching-learning process. It can develop the accreditation
score of the school. When the students feel comfort with the
teaching-learning process, then they understand with the material and the final result
the students can get more score in their exam.
4. For the researcher
The advantages of this research is the researcher can understand
more about the implementation of make a match model to improve
students in writing skills and can know deeply how to make students
interested with the teaching-learning process.
E. Hypothesis and Success Indicator
Hypothesis is temporary for the problems of research to reasonable
show with the grouping of data (Arikunto, 1998:7). According Hopkins
(1980:15), “Hypothesis provides a very important element of the scientific
approach by giving something for collected data and results to support or not
support”. It means that hypothesis is used to measuring for the researcher.
Hypothesis of this research is if use make a match model can achieve the
students in writing skills.
The success indicator of this research is taken from the students’ Basic
Competence shown in Lesson Plan (RPP). The students’ success and failure
8
of the passing grade (KKM). The passing grade of English lesson in MAN 2
Semarang is 70. The teacher and the researcher expect that there are at least
85% of the students who pass the passing grade.
F. Research Methodology 1) Research Design
This research was CAR (Classroom Action Research). Action
research tried to take a study since it explored whether something could
be done in a better way or not. This type of research was done for the
purposes to improve local classroom practices. Action research provides
a chance for teachers to reflect on their own practices (Cresswell,
2005:550). The researcher took two cycles in this action research. In this
research, every cycle consisted of two meetings. After the first cycle was
done, the second cycle followed the first cycle and hope it could improve
the activities of the first cycle. The designs of activities that were done by
researcher according to Kemmis and Mc Taggart, 1988:14 in (Hopkins,
1993:47) are as follows:
a. Planning
In this stage, the researcher needed to prepare instrument which
was support in learning process, they were:
1) Formulated the purpose of learning, prepared the material, made
9
2) Prepared sheets for classroom observation. Prepared camera to
take photos the situation of the class.
3) Prepared pre test and post test to measure students’ achievement
in writing texts.
b. Action
In this action, the researcher implemented the action research
and did some actions, they were:
(1) Gave the pre test.
(2) Thought writing texts in class by using make a match model.
(3) Gave occasion to the students to ask any difficulties or problems.
(4) Gave the post test
c. Observation
Observation is one of the instruments to know the students
feeling, thinking and anything they do in the learning process. The
researcher observed the action of the students in learning process by
field note which was helped by partner researcher. In this researcher,
the researcher also gave the students pre test and post test that both of
them analyzed by the researcher.
d. Reflection
Based on the result of the observation, the researcher made
evaluation to the students during teaching learning process. It was
10
first cycle. The researcher did better in the next cycle like the first
cycle.
Four activities in each cycle can be described as follows:
Figure 1.1 The Scheme based on Kemmis and McTaggart 1988:14 (in Hopkins, 1993:48)
2) Subject of the Research
The object of this research was the eleventh grade of MIA 1 in
11
12
3) Steps of the Research
In conducting the research, the researcher carried out the steps
which summarize in the following research schedule. This research was
done on July 2018 until August 2018. The table of research schedule was
written below:
staff of MAN 2 Semarang
Office staff
MAN 2
Semarang
13
Meet the English teacher to
do a consultation about the
lesson plan
Doing action in the class
(cycle I)
Doing action in the class
(cycle I)
Treatment
In the classroom
of eleventh MIA
14
(07.00-08.30)
8 August, 6th
2018
Doing action in the class
(cycle I)
Doing action in the class
(cycle II)
Doing action in the class
(cycle II)
Doing action in the class
(cycle II)
4) Techniques of Data Collection and Research Instrument
The researcher presented the act of collecting data are as follows:
a) Interview
According to Schostak (2006: 54) in Alshenqeeti (2014:40)
15
that have get information deeply about a certain topic or subject.
Aditya (2013:16) stated that interview is meeting between partners for
exchange information through question and answer, thus could be
interpret the meaning of topic or phenomenon. Nazir (1988:235) said
that interview process interaction between interviewer and respondent
use guide interview. The researcher used this interview to get data for
the background of the research. And the result of the interview
explained in the background of the research.
b) Observation
According to Spradley (1980) in Creswell (2002:212),
observation is one of the collecting data form that often used and the
researcher able to get different part in the process. Creswell
(2002:213) also assumed that observation is the process of collecting
the information by observing people and places in the research’s
place. Observation was a crucial role in the classroom research. In
addition, the researcher observed the learning process. In this research,
the researcher took observations in two cycles; cycle I and cycle II.
The researcher used the observation checklist to make it more
systematic. It consisted of students’ and teachers’ observation
checklist. The students’ and teachers’ observation checklist was
16
Table 1.3 Students’ Observation Checklist
No Students’ Activity Yes No
1 Paying attention
2 Asking question
3 Responding to the question
4 Doing the task well
5 Being enthusiastic in application make a
match model
Table 1.4 Teacher’s Observation Checklist
No Teacher’s activities Yes No
1 Greeting students before the lesson begins
2 Praying before the lesson begins
3 Checking students attendant
4 Reminding previous materials
5 Preparing and giving of the material
6 Giving opportunity for asking questions
7 Giving explanation of the materials
8 Guiding the students activity
9 Giving feedback after the lesson
17 c) Test
According to Brown (2000:384), test is the way to measure the
student’s knowledge and some procedures that consist of instrument
that needs activity on the part of tester. To get the data, the researcher
gave to the students the test that consists of pre-test and post-test. The
function of pretest was to know how far the students’ improvement in
writing skills before applying “make a match” model. The function of
post-test is to know the students’ improvement in writing skills after
applying “make a match” model. The researcher used essay for
pre-test and post-pre-test. In the pre-pre-test and post-pre-test (see in appendix),
explain the detail clues. The researcher gave 45 minutes to do the pre
test and 45 minutes for post test.
d) Documentation
According to Arikunto (2010:201), the word documentation is
from document that has meaning written object. The researcher
investigates the written object as books, magazine, document,
regulation, field note and the others (Arikunto, 2010:201). The
researcher needed some documentations and data to know about the
school situation of this study. In this research, the researcher chose to
using photos and field note as the documentation of the research (see
18 5) Data Analysis
After collecting the data, the next steps of study is analyzing the
data. Kothari (2014:130) said that there is several kind of analysis the
data including descriptive analysis and statistical analysis.
a) Descriptive analysis
Kothari (2014:130) argues that descriptive analysis is the explanation or sharing about one variable in research deeply. According to Sugiyono (2014:14), the descriptive analysis is about the research’s interpretation about the data that found in the
field. The researcher used the observation sheet and field note. b) Statistical analysis
Kothari (2014:131) states that statistical analysis or inferential
analysis is about significance of the test to examine the hypotheses
until find conclusions. Lodico, Spaulding & Voegtle (2006:243) stated
that the researcher should be able to make summarize in form of
statistical analysis to make sense the data. In this research, statistical
technique was used to know the extent to using make a match model
toward the students’ improvement in writing skills from the result of
pre-test and post-test.
(1) Score of Students’ Test
The researcher measured the students’ improvement in
writing skills by scoring the students’ test. According to Kherudin
19
performance in test and can evaluate the student’s performance in
test. The researcher uses scoring rubric (it can be seen in table
2.1) for evaluate the student’s test. The students’ score test was
from the result of pre-test and post-test.
(2) Calculate the Result of the Test
After scoring the students’ test, the researcher calculated
the data uses the t-test to determine there was a significant
difference in cycle I and cycle II. The researcher uses Statistical
Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) application for analysis the
data. Arkkelin (2014:2) argues that SPSS is used to understanding
and interpreting the research’s data. The researcher used SPSS
Base that gives the range of data entry, statistical, or informing
capabilities.
The steps for analyzing by using SPSS as follow:
(a) Open SPSS
(b) Click Data View, insert the data. In Variable view, in the
column of name, change the name of VAR00001 into pre test
and change the name of VAR00002 into post test. Then
change the number of decimals from 2 into 0.
(c) Click Data View, then click Analyze, choose Descriptive
Statics and click Descriptive. Move the pre test and post test
into variable (s). Then click Ok. Copy the result of
20
(d) Click Analyze, choose Compare Means, and then click
Paired-Sample T Test. Then copy the result into word.
G. Graduating Paper Outline
This study is organizes into five chapters as follows:
Chapter 1 is tells about introduction presenting the background of the
research, statement of the research questions, objective of the research,
significances of the research, hypothesis and success indicator, research
methodology and graduating paper outline.
Chapter II is describes about theoretical framework that related of the
literature and the review of previous research. Theoretical framework consists
of underlying the writing of the study; they are the definition of writing,
definition of text, teaching writing, writing process, classroom technique in
writing, the writing assessment scoring rubric, genres of writing, definition of
make a match model, the steps of make a match model, and the last is the
advantages and disadvantages of using make a match model.
Chapter III is the implementation of the research. This chapter consists
of procedure of the research.
Chapter IV presents about Research Finding and Discussion. This
chapter consist the result of the implementation make a match model to
improve writing text for the first grade of MAN 2 Semarang in the academic
21
Chapter V, as the last chapter in this study contains the conclusion
and suggestion of the research based on the analysis in chapter four.
Bibliography
22 CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
In this chapter consists of supporting theories and the review of previous
research. Supporting theories describe some information related to writing text
and make a match model.
A.Supporting Theories 1. Writing Texts
a. Definition of Writing
Robert (1964:143) states that, “Writing is a partial representation
of units of language expression.” It is mean that writing is one of those
four language skills, which is used as one medium to communicate with
others, in academic field, as well as in daily life. According Ghaith
(2002) in text Nur R (2008:2), “Writing is about more than making our
thoughts and ideas visible and concrete.”
b. Definition of Text
Text is the variety type of communication expression such as
written, spoken, picture, or symbol, that all of them are used to
delivering the information (Pardiyono, 2016:2-3).
1) Written Text
Written text can be found in the variety of printed media and
23
notebooks, magazines, novels, newspapers and the others that load a
text are including in written text.
2) Spoken Text
Spoken text is the text that can be found as spoken. For
example, when we speak with others, reigning over to others, give
instruction to others and so on, it can be conclude as spoken text.
Spoken text is the type of spoken communication expression.
3) Picture
Advertisements use pictures or images to deliver the message
or information to others. It is conclude as picture text.
4) Symbol
There is often found the variety of symbol that has different
purposes. For example the symbol of don not smoke in this area,
toilet for men, toilet for woman, restaurant, parking area, and others.
All of them are include as types of text because are form to deliver
the information.
c. Teaching Writing
Writing is an important part that must be mastered by the
students. So that, from earlier enter the school, the students are able to
learn writing. Harmer (2001:79) state that, the reasons for teaching to
the students of English as a foreign language include reinforcement,
language development, learning style and, most importantly, writing as
24 1) Reinforcement
Some students obtain languages in a purely oral/aural way,
but by seeing the language written down get the benefit greatly. The
visual demonstration of language construction is important for both
the understanding of how it all fits together and as a support to
committing the new language to memory.
2) Language Development
The mental activities that have to go through in order to
fabricate written texts are all part of the ongoing learning experience.
3) Learning style
Some student mostly study language quickly by looking and
listening. For many learners, procedure language is the slow way.
Writing is appropriate for such learners. It can also be quite
reflective activity instead face-to-face communication.
d. Writing Process
According to Harmer (2004:4) the process of writing has four
elements. It can be explain as follow:
1) Planning
Before starting to write, the writers try to plan and establish
the planning to write by making detail notes. Some people write few
words is enough, even though others may do all their planning in
25
When planning, writers have to think about three main issues
(Harmer, 2004: 4-5):
a) They have to consider the purposes of their writing since it
influences the type of text that produce, the language that they are
used and the information they choose to include.
b) The experienced writers think about the audience that they are
writing, since that influence the shape of the writing, the language
choosing, for example, it is formal or informal in tone.
c) Thirdly, writers have to consider the structure content of that
piece, how best way to sequence the fact, ideas, or arguments
which they have decided to include.
2) Drafting
It can refer to the first version of a piece of writing as a draft.
The word “go” at the text is often make assumption that it can be
amended later. As the writing process continuous into editing, a
number of drafts maybe produced on the way to the final version
(Harmer, 2004:5).
3) Editing (reflecting and revising)
After the writer have produced a draft later they read through
what they have written to see where it works and where it does not.
Perhaps that they are written is ambiguous or confusing. Then, they
may move the paragraphs or write a new introduction. They may use
26
Reflecting and revising are often helped by editors who
comment and make suggestions. Another reader’s reaction can help
the author to make appropriate revisions (Harmer, 2004:5).
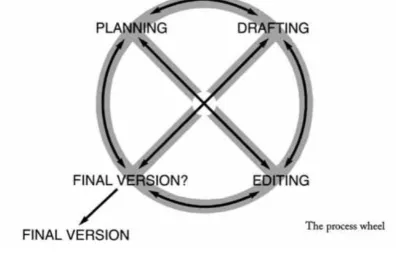
4) Final Version
Once writers have edited their draft, make a change that is
necessary, and produce their final version. This is different from
both the original plan and the first draft, since things have changed in
the editing process. It can decide to present these stages in following
way: “planning- drafting- editing- final draft” (Harmer, 2004:5).
It needs to represent these aspects of the writing process in a
different way. Therefore, the writer can take the way from any
direction in this process wheel below (Harmer, 2004:6).
Figure 2.1 The Scheme based on Harmer (2004: 6)
Sometimes the first three stages of the process can take
almost no time at all and it can plan, (re-)draft, and (re-)edit very
quickly in their heads as their write. Even though, it approaches the
27
written, and revise it before sending it off. It is just that at certain
times do this more carefully than at others (Harmer, 2004:6).
Spears & David (2008:5) stated that, “It is useful to think of
journey toward a finished paper as having three stages: prewriting,
writing, revising.” It means that according to them, there are three steps
in processing writing. They providing a steps-by-step discussion of the
way one students and they explain in through of Hernandez’s
assignment. The steps can explain as follow:
1) Prewriting
In prewriting process, Hernandez needed to prepare in several
way (Spears & David, 2008: 6-12):
a) Understand the writing Task
First of all, Hernandez read the assignment carefully and
then asked for clarification. She was not sure whether the paper
requirements would allow her to observe only students from her
own classes or whether she needed to observe widely. She should
focus on students behavior in own college classes.
b) Use brainstorming strategies to find and narrow the topic
Hernandez used various strategies to explore this subject:
(1) Free writing
After returning from an exam where she saw students
using cell phones to cheat, Hernandez sat her computer and let
28 (2) Listing
Hernandez made list of the various forms of cheating
she had observed.
(3) Clustering
Using her list and her notes from rewriting, Hernandez
made clusters of her ideas.
(4) Reading
Hernandez sought out and read several articles she
found on the collage library’s online database to help her think
about the effects of cheating on both students and instructors.
(5) Talking
Talking with others can help a writer formulate ideas.
c) Consider the audience
Instead, Hernandez was writing for large audience, she
also pays attention with: the reader’s knowledge about the
subject, the reader’s values, the reader’s interests, and the
reader’s diversity.
2) Writing
a) Writing the thesis statement
The thesis is the heart of the essay. Without a clear,
well-thought-out thesis, it is hart to rescue an essay no matter how
many hours put into it. The thesis has three functions:
29
(2) It indicates what the writer’s approach to that subject will be.
(3) It helps the writers to organize the supporting ideas.
b) Planning the structure
(1) Introduction
The opening should draw the reader into the world into
the paper be showing about what are going to discuss. The
thesis should be clearly stated in the introduction, which does
not have to be only one paragraph. For a complicated subject,
the introduction might stretch over two or three paragraph.
(2) Body
The content of the body should be arranged as outline
as a method of organizing the information.
(3) Conclusion
(a) Sum up the examples, details, and reasons offered in the
body to support the thesis.
(b) Present a solution to the problem posed.
(c) Leave the reader with something challenging to think
about.
(d) Indicates future possibilities related to the topic.
(e) Ask a thought-provoking question.
3) Revision
Hernandez in Spears & David (2008:12) kept in mind three
30
a) Identify any large changes, such as additions to content.
b) Identify any stylistic changes, such as the need to revise unclear
sentence structure or overuse of a descriptive word.
c) Identify any grammatical, spelling, or typographical errors.
e. Classroom Technique in Writing
Through Fauziati (2005:151), since writing as a process, it must
apply in the classroom practice; certain characteristic should be well
recognized. Some of the characteristic are as follows:
1) Instruction should be focused on the writing process. This means that
students can starting up into the process and the teacher should
prepare to help the students’ writing process with suggestion, and
correction to help the students overcome difficulties encountered in
each of the stage.
2) The writing task should encourage students to write a variety of
modes besides expository writing. This is based on the
understanding that people do use different modes f writing, and they
do need different process
3) Conferencing is an important part of the classroom activity. It
happens between teacher and students as well as between students.
4) The main role of teacher is as a facilitator. The teacher no longer
focuses just on error in the product, but is free to respond to a
31
understanding and giving nice responses to what the students’
writing.
5) The students would work and help each other, rather that work alone
or just with the teacher, the classroom would be arranged in the
manner of workshop, where students can work in pair, or groups.
6) A bond which ties all members of the class into one community,
whose member feels responsible for each other’s growth, can be
created in such classroom.
f. The Writing Assessment Scoring Rubric
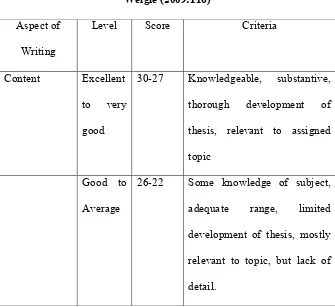
The Jacobs et al. (1981) in Weigle (2009:116)
Table. 2.1 Scoring Rubric according to The Jacobs et al. (1981) in Weigle (2009:116)
Aspect of
Writing
Level Score Criteria
Content Excellent
to very
good
30-27 Knowledgeable, substantive,
thorough development of
thesis, relevant to assigned
topic
Good to
Average
26-22 Some knowledge of subject,
adequate range, limited
development of thesis, mostly
relevant to topic, but lack of
32 Fair to
poor
21-17 Limited knowledge of subject,
little substance, inadequate
development of topic.
Very
poor
16-13 Does not show knowledge of
subject, not substantive, not
pertinent, not enough to
Evaluate.
Organization Excellent
to very
good
20-18 Fluent expression, ideas
clearly stated/supported,
succinct, well-organized,
logical sequencing, cohesive
Good to
average
17-14 Somewhat choppy, loosely
organized but main ideas stand
out, limited support, logical
but incomplete sequencing.
Fair to
poor
13-10 Ideas confused or disconnected
lack of logical sequencing and
development.
20-18 Sophisticated range, effective
33
good word form mastery,
appropriate register.
Good to
Average
17-14 Adequate range, occasional
errors of words/idiom form,
choice, usage, but meaning not
obscured.
Fair to
poor
13-10 Limited range, frequent errors
of words/idiom form
choices/usage, meaning
confused or obscured.
Very
poor
9-7 Essentially translation, little
knowledge of English
vocabulary, idioms, word
form, not enough to evaluate
Language use Excellent
to very
good
25-22 Effective complex
construction, few error of
agreement, tense, number,
word order/function. Articles,
pronouns, prepositions, but
meaning seldom obscured.
Good to
average
21-18 Effective but simple
construction, minor problem in
34
errors of agreement, tense,
number, word order/function,
articles, pronoun, preposition,
but meaning seldom obscured.
Fair to
poor
17-11 Major patterns is
simple/complex construction,
mechanics, frequent error of
negation, agreement, tense,
number, word order/function,
articles, pronoun, preposition
and/or fragments, run on,
deletions.
Very
poor
10-5 Virtually no mastery of
sentence construction rules,
35
paragraphing but meaning not
obscured.
Fair to
poor
3 Occasional errors of spelling,
punctuation, capitalization,
paragraphing, poor hand
writing, meaning confused or
obscured.
purposes. He explains the various text or genre of text as follow:
1) Descriptive
a) Definition of Descriptive Texts
According to Pardiyono (2016:19), descriptive text is kind
of text is made for giving information to the reader about the
visual image or mental of the object; about “what an object is
36
word portraits. Such paragraphs attempt to give the reader a clear
picture of objects, places, animals, or person.”
b) Purposes of Descriptive Texts
This text has aims to describe what an object is like
(Pardiyono, 2016:8).
c) Generic Structure of Descriptive Text
Pardiyono (2016:16) divide the generic structure of
descriptive text into two parts:
(1) Identification
The content of this component is about the main topic
of the text that would be described in the next paragraph.
Pardiyono (2016:203) also said that the information that is
delivered in the text is about the reality or fact in this era.
(2) Description
The explanation of what in object is like appropriate
with the main topic.
d) Language Feature of Descriptive Text
(1) Using present tense
For example: provides, asks, etc.
(2) Using simple sentence that have one predicate
37
(3) Using relation verb (is/are, have/has)
For example: It is very wet during the rainy season.
(Pardiyono, 2016:204-210)
e) Example of Descriptive Text
The small brown book, a collection of poems, looked
every bit of its fifteen years. The front cover had been torn off and
repaired with brown adhesive tape. The inside front cover listed
faded names of students who had previously used the book. The
lower right-hand corners of the first seventy-five pages were
ragged, giving the impression that an over-enthusiastic student
had decided to eat the book. Other pages revealed careful pen and
pencil marks. Still others revealed water and food stains made by
careless students. The brown and yellowing book was well used
(Bossone, 1977:134).
2) Procedure
a) Definition of Procedure
According to Pardiyono (2016:39), procedure text is kind
of text that arrange to give information to the reader about how
the jobs are doing to be finished.
b) Purposes of Procedure
The text has aims to tell the procedures, to tell the steps
38 c) Generic Structure of Procedure
Pardiyono (2016:16) divide the generic structure of
procedure text into two parts:
(1) Identification/The Aim
Including the topic of the activity or the job that be
done.
(2) Steps
The explanation about the consecutively step of the
activity or job.
d) Language Feature of Procedure
(1) Action Verbs As Imperatives
Cut, grasp, connect, secure, remove, align, etc.
(2) A Range of Adverbials
(a) Time (when?): first, second, third, next, finally, lastly, etc.
(b) Manner (how?): carefully, very slowly, finely, firmly with
one hand, etc.
(c) Place (where?): in a moderate oven, through the tunnel,
onto the bread board, etc.
(d) Reason (why?): to form a soft batter, so that the filling does
39 e) Example of Procedure
Drinking a glass of lemon tea is always ice in the morning.
Everyone can make it. Here is how to make a glass of nice the
lemon tea. All you need are hot water, sugar, tea, and lemon.
First, take a glass and pour hot water in it. Then, put in some
sugar and some tea. Tea bag is recommended. Stir the sugar for a
moment. And then squeeze a lemon, and take its juice. Add the
lemon juice into the glass and stir them using a tea spoon for
seconds. The lemon tea is ready to drink. It is nice and healthy
(Pardiyono, 2016:41-42).
3) Recount
a) Definition of Recount
Pardiyono (2016:61) states that recount text is kind of text
that often are used in the communication context, whether spoken
or written.
b) Purposes of Recount
The text has aims to tell the past event or the past activity
(Pardiyono, 2016:5).
c) Generic Structure of Recount
Pardiyono (2016:13) divided the generic structure of
40 (1) Orientation
The content of orientation is the topic or event that will be
reported including what the event, who, doing what, where, and
when.
(2) Sequence of events or activities
The explanation of consecutively the variety of event; what
the writer doing or what the happen.
d) Generic Feature of Recount
(1) Adverbs of Time
For example: first, then, next, afterwards, at the end of the
summer, etc.
(2) Past Tense Action Verbs
For example: drove, began, brought, carried, saw, etc.
(3) Person and Place Describing Words
For example: small, huge, interesting, new, rustic, fun-filled,
etc (Fortune & Tedick, 2003).
e) Example of Recount
One day, a few of my friends and I went on a picnic. We
visited Prambanan temple. We had a good time and all of us were
very happy. It is a beautiful temple in central Java. It is located in
Klaten, about 30 kilometers south of Solo. To get to this place is
41
there…..It was a nice day and we were all happy. We planned to
go back to that place the other time (Pardiyono. 2016:63-64).
4) Narrative
a) Definition of Narrative
Pardiyono (2016:79) states that narrative text is kind of
text that consist of life story of someone in the past, whether it is
factual or not. According to Richard (1977:173), “narrative
paragraphs tell a story or an incident.”
b) Purposes of Narrative
The text has aims to narrate of story of a problematic event
in order to arouse readers’ emotion, to make them to think, to get
a lesson of moral value (Pardiyono, 2016:7).
c) Generic Structure of Narrative
Pardiyono (2016:15) divide the generic structure of
narrative text into four parts:
(1) Orientation
It is containing of the topic or character in the story; what
or who, what happen, where, and when.
(2) Complication
It is consist of the explanation of the story in harmony,
42 (3) Resolution
It is containing of activity that will be done to overcome
the problems.
(4) Coda
It is consist of the closing of the story, and tells about the
moral value of the story.
d) Language Feature of Narrative
(1) Adverbs of Time (sometimes non-specific)
For example: one day, once upon a time, later, afterwards, in
the end, etc.
(2) Past Tense Action Verbs
For example: fought, chased, marched, jumped, slammed, etc.
(3) Person and Place Describing Words
For example: small, hidden, handsome, beautiful, mysterious,
etc.
(4) Dialogue or “Saying” Verbs
For example: said, screamed, replied, insisted, remarked, etc.
(Fortune & Tedick, 2003)
e) Example of Narrative
After Odysseus escaped from the Cyclops, he and his crew
came to the island ruled by Aeolus, god of the winds. Odysseus
was a guest of Aeolus for one month. As Odysseus prepared to
43
sight of home, the weary Odysseus fell asleep. His men, thinking
that the leather bag contained gifts, opened it. Out rushed the
winds that blew them back to Aeolus’s island (Bossone,
1977:138).
5) Information Report
a) Definition of Information Report
Information report is kind of text that is made to give
information to the readers consist of knowledge surrounding us
about nature phenomenon, social, politic, scientific knowledge
building on the reality (Pardiyono, 2016:107).
b) Purposes of Information Report
This text has aims to define, to describe, to give example,
to classify, to tell more about an object, phenomenon, event etc.,
in order to transfer knowledge, etc. (Pardiyono, 2016:10).
c) Generic Structure of Information Report
Pardiyono (2016:17) divide the generic structure of
information report text into two parts:
(1) General statement of a phenomenon
It is containing of to topic that will be explained detail
and scientific.
(2) Description (defining, classifying, etc.)
It is consist about the explanation including definition,
44
d) Language Feature of Information Report
(1) Infrequent Use of Adverbs of Time
(2) Relational (or linking) Verbs
For example: to be, to have (Frogs are amphibians. Frogs have
webbed feet.)
(3) Terms and Taxonomies
(a) Technical Terms: Tadpoles, transparent lenses, webbed
feet, etc.
(b) Taxonomies: Conductor, strings, woodwind, brass,
percussion.
(4) Nominal Groups with Adjectives/Adjective Phrases
For example: Those young, fresh water tadpoles navigate with
their long tails.
(5) Purposeful Use of Personal Pronouns ( I, we, you, he, she, it,
they)
(a) Inclusion (close reader-writer relationship): You can see
that frogs have eyes that stick out so they can see well.
(b) Exclusion (distant reader-writer relationship): Frogs have
protruding eyes, which allow for excellent vision.
(6) Nominalization (verb as a noun)
For example: When we run, we can sprint, hurdle or we
45
involves either sprinting, hurdling or distance running (Fortune
& Tedick, 2003).
(7) Example of Information Report
People are familiar with food allergies. It is said that
food allergies or food intolerances affect nearly everyone. It is
an unpleasant reaction in the body as the result of food
consumption. People often have an unpleasant reaction to
something they eat if they have a food allergy. Some others say
that they have to modify the family diet because one of the
family members is suspected of having a food allergy. In
children, it is found that only about three percent have
clinically proven to have got allergic reaction to foods. While
in adults, the prevalence of food allergy drops to about one
percent of the total population (Pardiyono, 2016:109-110).
6) Explanation
a) Definition of Explanation
According to Pardiyono (2016:131), explanation text is
kind of text that is made to give information to the readers about
the process as a background of the phenomenon formation.
b) Purposes of Explanation
This text has aims to explain how a phenomenon or an
event forms or occurs, to explain the process of a formation or an
46
c) Generic Structure of Explanation
Pardiyono (2016:16) divide the generic structure of
explanation text into two parts:
(1) General statement about an event or a phenomenon
It will tell about the topic of natural phenomenon.
(2) Explanation of the process of formation or occurrence
It is consist of explanation about the process that the
cause of phenomenon done.
d) Language Feature of Explanation
(1) Relational (or linking) Verbs
For example: to be, to have (In the combustion of food, oxygen
(O2) is used and carbon dioxide (CO2) is given off.
(2) Technical Terms and Taxonomies
(a) Technical Terms: Metabolism, thermal stress, digestion,
oxygen consumption, basal metabolic rate, etc.
(b) Taxonomies: Human biological system. For example
circulatory, skeletal, digestive, muscular, etc.
(3) Nominal Groups with Adjectives/Adjective Phrases
For example: The ideal standard metabolic rate of an animal is
established by determining its metabolism under the least
47
(4) Absence of Personal Pronouns
(I, we, you, he, she, it, they) Exclusion (distant
reader-writer relationship): Nominalization (verb as noun)
For example: when we run, we can sprint, handle or we
can run over longer distance. The sentence become:
Running involves either sprinting, hurdling or distance running
(Fortune & Tedick, 2003).
e) Example of Explanation
Photosynthesis is a process in which green plants use
energy from the sun to transform water, carbon dioxide, and
minerals into oxygen and organic compounds. Photosynthesis
happens when water is absorbed by the roots of green plants and
then it is carried to the leaves by the xylem, and carbon dioxide is
obtained from air that enters the leaves through the stomata and
diffuses to the cells containing chlorophyll. The green pigment
chlorophyll is converting the active energy of light into a latent
form that can be stored and used when it is needed (Pardiyono,
2016:137).
7) Analytical Exposition
a) Definition of Analytical Exposition
Exposition is kind of text that is made to give information
to the readers about opinions or arguments that we made as a
48
b) Purposes of Analytical Exposition
This text has aims to expose arguments or opinions in
response to a problem or event in order to judge or to persuade
(Pardiyono, 2016:11).
c) Generic Structure of Analytical Exposition
Pardiyono (2016:17) divided the generic structure of
descriptive text into three parts:
(1) General statement containing a thesis
It is consist of the declaration about something that will
be argued.
(2) Description of arguments
It consists of arguments with the data, general realities,
or the other arguments.
(3) Reiteration
It is containing about arguments that justifying the
declaration.
d) Language Feature of Analytical Exposition
(1) Using simple present tense
For example: A school examination is important because it
forces the students to learn more.
(2) Using adjective clause
49 (3) Using adverbial clause
For example: When the examination time has come, most
students are worried
(4) Using connectives
For example: They can communicate and make many business
contacts with different people.
(Pardiyono, 2016:241-245)
e) Example of Analytical Exposition
I think one of the most useful things in the world for
human beings is TV. Indeed, it is the most wonderful thing that
man has ever invented. There are many advantages that people
can take from having TVs. TVs not only entertain people but also
teach them many important things. Through this wonderful
invention, people can learn about different parts of the world
which may be located thousands miles away. Motions pictures
which are taken from many different parts of the world have been
made to entertain as well as teach people. Some films are
purposely designed to entertain people as well as to teach them.
Even, some programs on TV now have been made to teach pupils
50 8) Discussion
a) Definition of Discussion
Discussion text is kind of text that is made to analyze a
problem from two different sides: from positive side and negative
side. It is made to give conception a problem (Pardiyono,
2016:177).
b) Purposes of Discussion
This text has aims to discuss an issue in two points of
view, to show the strength and the weakness, to describe the
positive points and negative points (Pardiyono, 2016:12).
c) Generic Structure of Discussion
Pardiyono (2016:18) divided the generic structure of
discussion text into four parts:
(1) General statement about an issue
It consist of one declaration about something or social
issue that must be discussed, because that declaration have
positive sight and negative sight.
(2) Arguments for
It is containing the positive sight or the advantages
about the issue.
(3) Arguments against
It is containing the negative sight or the disadvantages
51 (4) Recommendation
It is consist about the suggestion about what should we
do to receive to the issue.
d) Language Feature of Discussion
(1) Modals (to position a reader in a certain way)
(a) Certainty: must, will, should, etc.
e.g., We must conserve our forests.
(b) Less Certainty: Might, may, could, etc.
e.g., We might have solar powered cars in the future.
(2) Nominalization (to create authority and de-personalize text)
(3) Connectives (as signposts for reader)
(a) Clarifying: to put it another way, in particular, to illustrate,
etc.
(b) Showing Cause/Effect: is caused by, so that, etc.
(c) Indicating Time: initially, soon, until, before, etc.
(d) Sequencing Ideas: first, second, next, in summary, etc.
(e) Adding Information: additionally, furthermore, etc.
(f) Condition/Concession: if…the, even though, etc.
(4) Conjunctions (to link clauses within sentences)
(a) Clarifying: for instance, in other words, that is, namely, etc.
(b) Showing Cause/Effect: consequently, accordingly
52
(d) Sequencing Ideas: first, second, finally, in the first place,
etc.
(e) Adding Information: and, most convincing, likewise,
moreover, furthermore, etc.
(f) Condition/Concession: when…then, although, but,
however, otherwise, nevertheless, despite this, etc.
(Fortune & Tedick, 2003)
e) Example of Discussion
One of the most wonderful gadgets in the market today is a
mobile phone. It is small but has wonderful uses. Nowadays, a
mobile phone is not anymore to be considered as something
‘special’. Mobile phones have become such daily needs. People
cannot live without mobile phones in their hands. Wherever they
go and whatever they do, mobile phones are always with them.
Using a mobile phone, people cannot only communicate with
other people, but also enjoy music, make photos, have some
chats, etc. Mobile phones are always very helpful to people. On
the other hand, mobile phones have also created many problems
to people. One of them is that people sometimes make some
uncontrolled calls that cost a lot….Therefore; it always suggested
using the mobile phones properly in order that they can take the
53 2. Make A Match Model
a) Definition of Make A Match
According Rahmawati & Aryanti (2016:305), make a match is
learning technique using card. The division of the group “make a
match” model and there are two groups of problem and holding group
answer. Cullan (1994) in Huda (2014:251) states that “Make a Match”
model is one of the important model in teaching-learning process.
Arifah & Kusumarasdyati (2013:2), make a match is one of the
techniques which is introduced in cooperative learning. Make a match
technique is a kind of technique that leads the students to find their
partner. In this technique, the students are divided into two groups, “A”
group and “B” groups. Each of the students of the group gets one card.
b)The Steps of Make A Match Model
According to Huda (2014:251-252), teacher should make
preparation when using make match model. The preparation can explain
as follow:
(1) Make questions appropriate with the material that will be delivered,
then write them into question cards.
(2) Make the answers key from that questions and write them into
answered cards also. It is better that the question cards and
answered card has different color.
(3) Make a rule; the students have high score will get gift and the low