IMPROVING THE STUDENTS
’
SPEAKING ABILITY IN
EXPRESSING OPINION THROUGH PROBLEM BASED
LEARNING STRATEGY FOR THE ELEVENTH GRADE
STUDENTS OF MAN 2 SEMARANG IN THE ACADEMIC
2018/2019
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a partial fulfillment of the
requirement for
the Degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan
(S.Pd)
By:
MIR
’
ATUS SA
’
ADAH
113-14-031
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
ii
DECLARATION AND PERMISSION FOR PUBLICATION
The one who signed below:
Name : Mir’atus Sa’adah
Student ID Number : 113-14-031
Department : English Education Department
Faculty : Teacher Training and Education Faculty
Declares that this graduating paper was written by the researcher herself and the researcher didn’t copy from other researchers. Theories and citations were used based on the code ethics of writing graduating paper. I give permission to publish this graduating paper on IAIN Salatiga’s e-repository.
iii
Salatiga, September 14th 2018
Dr. H. Sa’adi, M. Ag
The Attentive Counselor’s note
Mir’atus Sa’adah
To the Dean of Teacher Training and
Education Faculty
Assalamu’alaikum, Wr. Wb.
After reading and correcting Dian Amalia’s graduating paper entitled
IMPROVING THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY IN EXPRESSING OPINION THROUGH PROBLEM BASED LEARNING STRATEGY FOR THE ELEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF MAN 2 SEMARANG IN THE ACADEMIC 2018/2019 I have decided and would like to propose that this paper can be accepted by the Teacher Training and Education Faculty. I hope this paper will be examined as soon as possible.
Wassalamu’alaikum, Wr. Wb.
Counselor
iv
A GRADUATING PAPER
IMPROVING THE STUDENTS’ SPEAKING ABILITY IN EXPRESSING OPINION THROUGH PROBLEM BASED LEARNING STRATEGY FOR THE ELEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF MAN 2 SEMARANG IN THE
ACADEMIC 2018/2019 WRITTEN BY:
Mir’atus Sa’adah
NIM. 113-14-031
Has been brought to the broad of examiners of English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty at the State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga of September28th, 2018, and hereby considered to have completed the requirements for the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd.) in English Second examiner : Sari Famularsih, M.A.
Salatiga, October 1, 2018 Dean of Teacher Training and Edycation Faculty of IAIN Salatiga
Suwardi, M.Pd.
NIP. 19670121 199903 1 002
MOTTO
MINISTRY OF RELIGIOUS AFFAIRS STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN) SALATIGA
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY Jalan Lingkar Selatan Km 02, Kel. Pulutan, Siderejo, Salatiga 50716, Telp(0298) 6031364 Website: http://www.tarbiyah.iainsalatiga.ac.id.E-mail:
v
“Inna ma’al’usri yusron”
(Verily, with every difficulty is relief)
vi
DEDICATION
This graduating paper is sincerely dedicated to:
1. My beloved father and mother (Bapak Sarju and Ibu Muslikhah) who always give me spirit and inspiration so that the writer can finish her study. Thanks a lot for your praying and guidance.
2. My beloved brothers and sisters (Mas Rohmad, Mbak Ifa, Dek Fina, Mas Rosid, Mbak Dewik) who always motivate and support the writer to do the best.
3. My lecturers in IAIN Salatiga, especially Mr. Sa’adi, M. Ag who guides the writer patiently.
4. My teacher in Al-Muntaha Islamic Boarding House (Nyai Hj. Zulaicho, A.H), thanks for your praying.
5. My beloved partner (Jo) who always motivate and support the writer to do the best.
6. All of TBI ’14, especially Anglila Wikasitakusumaning Ahayu.
7. All of Al-Muntaha Islamic Boarding House’s Students, especially (Jubet, Ecuk, Mbak Afi, Ryda, Hima, Okta).
vii
ACKNOWLEDGMENT Bismillahirrahmanirrahim,
Assalamu’alaikum Wr.Wb.
Alhamdulillahirobbil’alamin, all praises be to Allah SWT, the Most Gracious, and The Most Merciful who always bless and help the writer so the writer can finish the graduating paper. Bless and mercy are upon great the Prophet Muhammad SAW for his guidance that leads the writer to the truth.
However, this paper will not be finished without supports, advices, help and encouragement from several people and institution. Hence, the writer would like to express special thanks to:
1. Mr. Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M.Pd., the Rector of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) of Salatiga.
2. Mr. Suwardi, M.Pd, the Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty (IAIN) of Salatiga.
3. Mrs. Noor Malihah, Ph.D, the Head of English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty (IAIN) Salatiga.
4. My counselor Dr. H. Sa’adi, M.Ag. who gives great attention, suggestion and guidance for this graduating paper from chapter 1 until chapter 5. 5. All of lecturers and staffs of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) of
Salatiga
Salatiga, September 14th 2018
The writer
Mir’atus Sa’adah
viii ABSTRACT
Mir’atus Sa’adah. 2018. Improving the Students’ Speaking Ability in Expressing Opinion Through Problem Based Learning Strategy for the Eleventh Grade Students of MAN 2 Semarang in the Academic Year 2018/2019.
A Graduating Paper. English Education Department. Teacher Training and Education Faculty. State Institute for Islamic Studies Salatiga. Counselor:s Dr. H. Sa’adi, M. Ag.
This research focused in improving students’ speaking ability by applying Problem Based Learning (PBL) Strategy. The objectives of the study are to know and to find out the implementation of Problem Based Learning Strategy to improve students’ speaking ability and To know and to find out the result of improvement of speaking skills after using Problem Based Learning (PBL) strategy for the eleventh grade students of MAN 2 Semarang in the academic year 2018/2019. The methodology of research is classroom action research. Each cycle consists of planning, action, observation and reflection. From the result of this research shows an improvement of students’ speaking ability by using PBL strategy. It can be seen for the mean score of pre-test and test. In cycle I post-test higher than pre-post-test: 72.72 > 63.96. In cycle II: 84.06>77.13. It means that the implementation of PBL strategy is successful to improve students’ speaking ability.
ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS
DECLARATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE CONSELORS’ NOTE ... iii
STATEMENT OF CERTIFICATION ... iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... vii
ABSTRACT ... viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... ix
LIST OF APPENDIXES ... xi
CHAPTER I ... 1
INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of the Research ... 1
B. Research Questions ... 3
C. Objective of the Research ... 3
D. Significances of the research ... 4
E. Hypothesis and Success Indicator ... 5
F. Method of the Research ... 5
G. Graduating Paper Organization ... 10
CHAPTER II ... 11
A. Review of Previous Research... 11
B. Supporting Theories of Speaking ... 14
1. Speaking ... 14
a. Definition of speaking ... 14
b. Elements of speaking ... 15
c. Function of speaking ... 18
d. The classroom activities ... 19
2. Problem Based Learning ... 24
CHAPTER III ... 27
IMPLEMENTATION OF RESEARCH ... 27
x
B. Technique of data Collecting ... 27
C. Data Analysis ... 31
CHAPTER IV ... 33
A. Field Note ... 33
1. Description of Teaching and Learning Process in Cycle I ... 33
1) Planning ... 33
2) Action ... 34
3) Observation ... 34
4) Reflection ... 35
2. Description of Teaching Learning Process in Cycle II ... 35
1) Planning ... 35
2) Action ... 36
3) Observation ... 36
4) Reflection ... 36
B. Research Finding ... 37
xi
LIST OF APPENDIXES
A. Lesson Plan
B. Result of Students Activity C. Field Note
D. Note of Counselor
E. Official Statement from MAN 2 Semarang F. SKK
2 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Research
A language is a sign system of which the main function is communication among people. Speech is then the main instrument for human communication (Ferdinand dr Saussure 1959: 8-10). As an international language, English is very important and has many interrelationships with various aspects of life. In Indonesia, English is considered as the first foreign language from elementary school up to the university level.
English is the language of international politics, international business, international finance, of film, literature, research and technology (https://www.dur.ac.uk/englishlanguage.centre/expertenglish/ accessed on September 30th 20018). English is one of the international languages used by most of the world population, so each school has given English lesson, but this is not maximal because the condition of class does not support learning process, almost the class is messy class, students are not ready to learn and to understand the material. Ideal English classroom should be enjoyable and learning methods should be fun so students fell enjoy during teaching learning process.
3
is developed in child life, which is produced by listening skill, and at that period speaking skill is learned (Tarigan, 1990:3-4).
Based on the observation when the researcher taught in the classroom, there were many reasons that the students less in speaking. It may be caused by the students’ shy or lack of self -confidence to speak in English. So, their study have not been maximally. They did not use English in daily life although in giving gratitude and meeting. Sometimes the students were less concentration when they have learning in the classroom. They were sleepy, not to understand about the material but shy to ask to the teacher, and unfamiliar with using dictionary. They considered that study English is difficult and not their daily language, so their study about English being not interested.
From the reason, the researcher wants to improve the students’ interest in speaking ability by using Problem Based Learning Strategy. Teachers can use many strategies in language teaching, there are many kinds of strategy of language teaching, one of them is Problem Based Learning (PBL) Strategy. Problem Based Learning is one of the change from teaching paradigm to the learning paradigm (Barr and Tagg, 1995:271). This strategy can make the students active in the class and this strategy focused on the student centered.
4
to involve the emotional power to find a new knowledge and motivate them to be active in the class and improve their self-confidence on English language especially in speaking skill.
From explanation above, the researcher decides to conduct a research entitled “Improving the Students’ Speaking Ability in Expressing Opinion Through Problem Based Learning Strategy (A Classroom Action Research of the eleventh grade of MAN 2 Semarang in the Academic Year 2018/2019)”.
B. Research Questions
Based on the background of the study, there are some statements of the problem are as follows:
1. How is the implementation of PBL strategy improve students’ speaking ability in the eleventh grade of MAN 2 Semarang in the academic year 2018/2019?
2. How is the result of the implementation of PBL strategy improve students speaking ability in the eleventh grade of MAN 2 Semarang in the academic year 2018/2019?
C. Objective of the Research
According to the statement of the problem, the objectives of the study are as follows:
5
2. To know and to find out the result of improvement students’ speaking ability after using PBL strategy for the eleventh grade of MAN 2 Semarang in the academic year 2018/2019?
D. Significances of the Research
Through this classroom action research, the researcher hopes that it can give advantages for:
1. Theoretically, it is expected that the finding of this research can support and complete the previous theories related to improving students’ speaking ability through Problem Based Learning strategy. 2. In practice, the researcher expects that the finding of this research can
be useful for: a. The teachers
1) To improve the teacher’s ability to teach the students with a better strategy.
2) To increase the teacher’s professionalism in learning process. b. The Students
1) To make the students to active in the class. 2) To interest the students speaking up in the class. 3) To develop the students speaking ability.
4) To train the students confidence. c. The school
6
students’ involvement in teaching learning process. Besides, it creates good quality for students’ output.
E. Hypothesis and Success Indicator
By conducting this research, the researcher proposes a hypothesis: Using PBL Strategy in English subject can improve the students’ interest in speaking ability in expressing opinion for the eleventh grade of MAN 2 Semarang in the academic of year 2017/2018.
The success indicator of this research is taken from the passing grade (KKM) of English lesson in MAN 2 Semarang. The passing grade is 70 and the target of the passing grade is 85%.
F. Method of the Research
In this research, the researcher used Classroom Action Research (CAR). According to Suyadi (2015:18) informs that Classroom Action Research consists of three words, so there are three definitions, which can be explained:
1. Research is the activity of looking at an object by using a certain way to find accurate data.
2. Action is the activities that are intentional and planned with a specific purpose.
7
Based on three words; research, action and classroom, Classroom Action Research (CAR) means teaching and learning activities that are applied in the classroom with the aim of improving the teaching and
learning process.
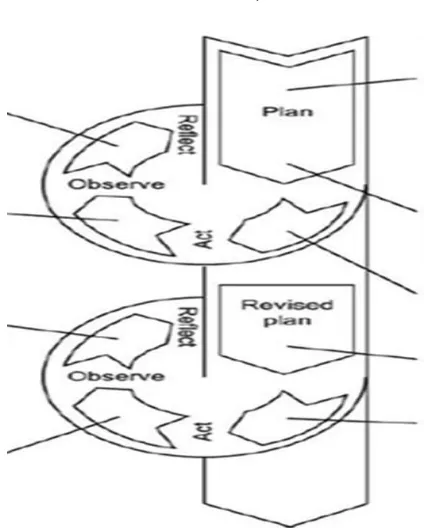
The models that usually applied in the action research is model by Kemmis & Mc Taggart. There are four steps in this model they are; planning, action observation and reflection. The whole actions above, which were applied in CAR as follows:
Figure 1.1 The Scheme Based on Kemmis and McTaggart (in McNiff, 2002: 58)
1. Planning
8
i) what kind of investigation is possible within the realities and constrain of your teaching situation; and ii) what potential improvements you think are possible.
2. Action
The plan is a carefully considered on which involves some deliberate interventions into your teaching situation that you put into action over an agreed period of time. The interventions are ‘critically informed’ as you question your assumptions about the current situation and plan new and alternative ways doing things.
3. Observation
This phase involves you in observing systematically the effects of the action and documenting the context, action and opinion of those involved. It is a data collection phase where you use ‘open-eyed’ and
‘open-minded’ tools to collect information about what is happening.
4. Reflection
9 G. The subject of the research
The subject of this research is the second year students of MAN 2 Semarang XI MIA 2 in the academic year 2018/2019.
Table 1.1 List of Students’ Name of XI MIA 2 class of MAN 2 Semarang
No Student’s Name Sex
1. AUA Female
2. AC Female
3. BS Female
4. DF Female
5. DW Female
6. ES Female
7. EPH Female
8. FA Female
10
17. MR Male
18. M Male
19. RA Female 20. ODY Female 21. PSN Female 22. PNA Female 23. RAPS Female 24. SR Female 25. SRN Female 26. SS Female
27. SM Male
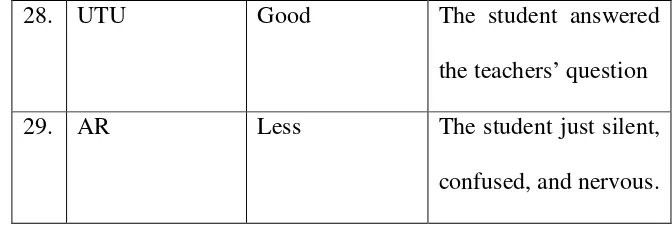
28. UTU Female
29. AR Female
H. Graduating Paper Organization
This graduating paper has five chapters. Each chapter has different elements as follows:
11
12 CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Review of Previous Research
In this research paper, the researcher takes five previous researches comparison. The first is Khikmah’s paper (2011). In her paper about The Use of Student Team Achievement Divisions (STAD) Method and Authentic Material toward Speaking Skill. This research was conducted at
MA Mir‟atul Muslimien. Eighteen students of the second grade students of MA Mir‟atul Muslimien 2015 were instructed through STAD strategy
and authentic material to improve their speaking skill. This research used classroom action research (CAR). In cycle I, there are 72.23% students passed the standardized score (KKM). It means the target of this research has not achieved yet because the target for students passing KKM is 75%. However, in cycle II, there are 77.78%students passing the KKM. This mean this research has been completed and shows that STAD can improve
the students‟ speaking skill. The result of the research, the researcher
13
The second is Fadilah’s paper (2011). In her paper talk about the use Problem Solving Activitiesto teach students’ speaking skill. The research used quantitative method with one group pretest-posttest design. The instrument of this research was the t-test. The population of this research 20 of class control and experiment group speaking 1 of IAIN Salatiga. The sample was entire population. The data of this research were collected by using the pretest and posttest to the students’ sample. The results of the data analysis showed that: the mean of control group was 1.04 and the experiment group was 2.56 and observed was 1.81. The t-critical value with degree of freedom (df) = 19 and significance level at 0.05 was 0.90. Based on the analysis above the alternative hypothesis of this research was accepted, because the observed was bigger than t-critical value (1.81 > 0.90). It could also be concluded that teaching speaking skill using problem-solving activities improved the students’ speaking skills.
14
the students’ self-efficacy where in the 1st cycle, it is 61%, in the 2nd cycle, it is 43%. The study results show that the implementation of Problem Based Learning (PBL) model can improve the students’ problem solving skill and self-efficacy.
The fourth is Fahma’s paper (2016). In her thesis talked about the implementation of problem based learning model in improving learning achievement on accounting subject students. This research was classroom action research that consisted of two cycles. Each cycle consisted of four stages: planning, action, observation, and reflection. The subjects of this research were the students of XI AK3 class of SMK Negeri 4 Klaten. The data analysis technique used in this research was descriptive comparative analysis. It was to compare the initial condition before action implementation with the results of the research in Cycle 1 and 2. The results of the research show that: (1) Problem-Based Learning (PBL) model can improve the students’ accounting learning achievement that was proven that: (a) the improvement of the students’ learning achievement that the percentage before the action implementation was only 58.82% was improved to 100% after the action implementation, (b) the students were able to solve problems by having group discussions, (2) improving the students’ accounting learning achievement using Problem-Based Learning (PBL) model was conducted by having group discussions.
15
Lingkung registered in 2012/2013. The data of the study were collected trough tested. The findings of the study showed that experimental group taught by the problem based learning have better ability than control group which is taught by the conventional method. So, it can conclude that the used of problem based learning in teaching descriptive text can improve students’ speaking ability in expressing description people, things, and places.
To differentiate with those papers, this research is focused on the students’ interest in speaking ability and analyze the ability of the second year students of MAN 2 Semarang in speaking ability in the academic year 2018/2019. The researcher chooses the strategy of PBL and the purpose is to improve the students’ speaking ability.
B. Supporting Theories of Speaking 1. Speaking
a. Definition of Speaking
Bailey (2005: 2), “Speaking consists of producing systematic verbal utterance to convey meaning. Speaking is an interactive process of constructing meaning that involves producing, receiving and processing information. It is often spontaneous, open-ended and evolving.
16
Therefore, the researcher concludes that speaking is ability to produce the language and share their ideas.
b. Elements of Speaking
In accordance to Harmer, (2007: 269-271), The ability to speak fluently presupposes not only knowledge of language features, but also the ability to process information and language
‘on the spot’.
a. Language features Among the elements necessary for spoken production (as opposed to the production of practice examples in language drills, for example) are the following:
a) Connected speech
Effective speakers of English need to be able not only to product the individual phonemes of English (as in saying I would have gone) but also to use fluent ‘connected speech’ (as in I’d’ve gone). In connected speech sounds are modified (assimilation), omitted (elision), added (linking
r), or weakened (through contraction and stress patterning). b) Expressive device
17
the extra expression of emotion and intensity. Student should be able to deploy at least some of such suprasegmental features and devices in the same way if they are to be fully effective communicators.
c) Lexis and grammar
Spontaneous speech is marked by the use of a number of common lexical phrases, especially in the performance of certain language function. Teacher should therefore supply a variety of phrases for different functions such as agreeing or disagreeing, expressing, surprise, shock, or approval. Where students are involved in specific speaking contexts such as a job interview, we can prime them, in the same way, with certain useful phrases which they can produce at various stages of an interaction.
d) Negotiation language
Effective speaking benefits from the negotiation language we use to seek clarification and to show the structure of what we are saying. We often need to ‘ask for clarification’ when we are listening to someone else talk.
b. Mental/social processing
18
above, success is also dependent upon the rapid processing ability that talking necessitates.
a) Language processing
Effective speakers need to be able to process language their own heads and put it into coherent order so that it comes out in forms that are not only comprehensible, but also convey the meanings that are intended. Language processing involves the retrieval of words and phrases from memory and their assembly into syntactically and propositionally appropriate sequences. One of the main reasons for including speaking activities in language lessons is to help students develop habits of rapid language processing in English.
b) Interacting with others
Most speaking involves interaction with one or more participants. This means that effective speaking is also involves a good deal of listening, and understanding of how the other participants are feeling, and a knowledge of how linguistically to take turns or allow others to do so.
c) (On-the-spot) information processing
19
tell us the moment we get it. The longer it takes for ‘the penny to drop’ the less effective we are as instant communicators. However, it should be remembered that this instant response is very culture-specific, and is not prized by speakers in many other language communities.
c. Function of Speaking
According to Richards (2008: 21) the functions of speaking are; talk as interaction, talk as transaction, talk as performance. They are as follows:
a) Talk as interaction
Talk as interaction refers to what we normally mean by
“conversation” and describes interaction that serves a
primally social function. When people meet, they exchange
greetings, engage in small talk, recount recent experiences,
and so on, because they wish to be friendly and to establish a
comfortable zone of interaction with others. The focus is
more on the speakers and how they wish to present
themselves to each other than on the message.
b) Talk as transaction
20
than the participants and how they interact social with each other. In such transaction,
talk is associated with other activities. For example, students may be engaged in hands-on activities (e.g., in a science lesson) to explore concepts associated with floating and sinking. In this type of spoken language students and teachers usually focus on meaning or on talking their way to understanding. (Richard 2008:24) in (Jones 1996:14).
Examples of talk as transaction are:
1. Classroom group discussion and problem-solving
activities
2. A class activity during which students design a poster
3. Discussion needed computer repairs with technician
4. Making a telephone call to obtain flight information
5. Asking someone for directions on the street
6. Buying something in a shop
7. Ordering food from a menu in restaurant.
c) Speaking as performance
This refers to public talk, that is, talk that transmits information before an audience, such as classroom presentations, public announcements, and speeches.
d. The classroom activities
Harmer (2001: 348-352) observes that there are seven classroom speaking activities, such as:
21
Playing script and acting out the dialogues are two kinds of the acting scripts that should be considered by the teacher in the teaching and learning process. In the playing script, it is important for the student to teach it as real acting. The role of the teacher in this activity is as theatre directors, drawing attention to appropriate stress, intonation, and speed. This means that the lines they speak will have real meaning. By giving students practice in these things before they give their final performances, the teacher ensures that acting put is both a learning and language producing activity. In acting the dialogue, the students will be very helped if they are given time to rehearse their dialogues before the performance. The students will gain much more from the whole experience in the process.
b) Communication Games
Games are designed to provoke communication between students. The games are made based on the principle of the information gap so that one student has to talk to a partner in order to solve a puzzle, draw a picture, put a thing in the right order, or find similarities and differences between pictures. Television and radio games, imported into the classroom, often provide good fluency activities.
22
One of the reason that the discussions fail (when they do) is that students are reluctant to give an opinion in front of the whole class, particularly if they cannot think of anything to say and are not, anyway, confident of the language they might use to say it. Many students feel extremely exposed in discussion situation.
Discussion is probably the most commonly used activity in the oral ability class. Here, the students are allowed to express their real opinions. Discussion range is divided into several stages frim highly formal, whole-group staged events to informal small-group interaction. Harmer (2001:272).
d) Prepared talks
A popular kind of activity is the prepared talk were a student makes a presentation as a topic of their own choice. Such talks are not designed for informal spontaneous conversation, because they are prepared, they are more
‘writing-like’ than this. However, if possible, students should
speak from notes rather than from a script.
23
e) Questionnaires
Questionnaires are useful because, by being pre-planned, they ensure that both questioner and respondent have something to say to each other. Students can designed questionnaires on any topic that is appropriate. As they do so the teacher can act as a resource, helping them in the design process. The results obtained from questionnaires can than form the basis for written work, discussion, and prepared talks.
f) Simulation and role-play
Role-play are effective when they are open-ended, so that different people have different views of what the outcome should be, and a consensus has to be reached.
According to Ken Jones (1982: 4-7) in Harmer (2001: 274) have the following the characteristics:
1. Reality of function
The students must not think of themselves as students, but as real participants in the situations.
2. A simulated environment
The teacher says that the classroom is an airport check-in area for example.
24
Students must see how the activity is constructed and they must be given the necessary information to carry out the simulation effectively.
g) The roles of the teacher
As with any other types of classroom procedure, teachers need to play a number of different roles during the speaking activity described above. However, three have particular relevance if we are trying to get students to speak fluently:
1. Prompter
Students sometimes get lost, cannot think of what to say next, or in struggle out of such situations on their own, and indeed sometimes this may be the best option. However, we may be able to help them and the activity to progress by offering discrete suggestions. If this can be done supportively-without disrupting the discussion, or forcing students out of role it will stop the sense of frustration that some students feel when they come to a
‘dead end’ of language or ideas.
2. Participant
25
to participate in discussions or role-play themselves. That way they can prompt covertly, introduce new information to help the activity along, ensure continuing student engagement, and generally maintain a creative atmosphere.
3. Feedback provider
The vexed question of when and how to give feedback in speaking activities is answered by considering carefully the effect of possible different approaches.
2. Problem Based Learning Strategy
Problem-based learning is an approach to learning that has been constructed from a perspective that considers a whole range of theories. (Maggi, 2004:34).
According to Karen (2013:623) Problem based learning is an active and engaging pedagogy to use for teaching information literacy concepts and ability at both the undergraduate and graduate level.
https://www.google.co.id/search?q=karen+E.+downing+2013&oq=ka
ren+E.+downing+2013&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8 accessed July 11 2018.
26
a. Students are presented with a problem (case, research paper). Students working in permanent groups organize their ideas and previous knowledge related to the problem and attempt to define the broad nature of the problem.
b. Throughout discussion, students pose questions called “learning issues” that delineate aspects of the problem that they do not understand. These learning issues are recorder by the group and help generate and focus discussion. Students are continually encouraged to define what they know and more importantly what they don’t know.
c. Students rank, in order of importance, the learning issues generated the session. They decide which questions will be followed up by the whole group and which issues can be assigned to individuals, who later teach the rest of the group. Students and instructor also discuss what resources will be needed to research the learning issues and where they could be found.
27
28 CHAPTER III
IMPLEMENTATION OF RESEARCH
A. The Procedures of the Research
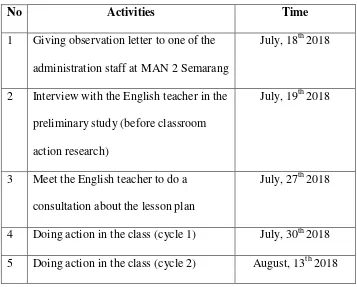
In conducting the research, the researcher carries out the steps which summarized in the following research schedule. The research schedule is shown below:
Table 1.2 Research Schedule
No Activities Time
1 Giving observation letter to one of the administration staff at MAN 2 Semarang
July, 18th 2018
2 Interview with the English teacher in the preliminary study (before classroom action research)
July, 19th 2018
3 Meet the English teacher to do a consultation about the lesson plan
July, 27th 2018
4 Doing action in the class (cycle 1) July, 30th 2018 5 Doing action in the class (cycle 2) August, 13th 2018
B. Technique of Data Collecting
29
1. Observation
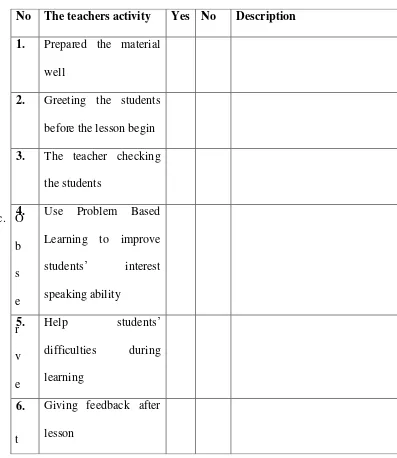
According to Kothari (2004: 96), observation is the most commonly used to observe the students’ activities in teaching and learning process. In conducting action research, the researcher observes the learning process. The learning process is taught by the teacher, while the researcher only observes the teaching learning process. The observation consists of two cycles. There are the cycle I, and cycle II. The researcher uses observation checklist in order to make more systematic and field notes to get more detail information in teaching and learning process. The observation sheet consists of students’ observation checklist, teachers’ observation checklist and the use of Problem based Learning. The table below show the table of observation sheet as follows:
a. The students activity
Table 1.3 Form the Result of Students’ observation Checklist cycle I
3. Responding the question 4. Accomplish task
30
eachers activity
Table 1.4 Form the Result of Teacher’s observation Checklist cycle I
he use of Problem based Learning Strategy Activity
Table 1.5 form the result of using Problem Based Learning Strategy Checklist Cycle I before the lesson begin
31
1. The teacher and the students have internet and access.
2. The students can follow Problem Based Learning instructions.
3. The teacher does teaching and learning process by Problem Based learning Strategy.
2. Test
According to Arikunto (2010:193), test is the series of the questions or exercises and other tools that use to survey the skill, knowledge intelligence, or the talent by individuals or group. The researcher uses pre-test and post-test.
a. Pre-test
In this research the pre-test will be given in the first time. Pre-test is given to the students before the teacher using her media in the teaching-learning process. The objective is to know about the students’ speaking skill before treatment.
32
Post-test will be given in the last sessions after the media will be applied. The goal of the post-test is to know the improvements of speaking skill after the students got a treatment. 3. Documentation
According to Arikunto (2010:274), documentation is an activity to look for variable like notes, transcribes, books, newspaper, etc. Documentation is done to get important data for the research. In this research, the researcher uses, field notes, photos and records in doing pre-test and post-test as the documentation of the research.
C. Data Analysis
In analyzing data, the researcher uses mixed methods to analyze the data (Creswell, 2012:16).
1. Qualitative Data
In analyzing qualitative data collected based on words from a small member of individual, thus the participants’ views are obtained and analyzed the data for description (Creswell, 2012:16). In this research, the data of observation checklist is analyzed by qualitative. 2. Quantitative Data
In the other hand, quantitative technique data analysis is used to process the data. The quantitative data is processed by the teacher and the researcher to get the score of the students. The maximum score is 100. The process measurement based on:
33
There are five components in scoring speaking; they are pronunciation, intonation, fluency, grammar, and vocabulary. The researcher uses an analytical scoring rubric to analyze the data related to the students speaking test.
b. Calculate the result of the test
34 CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDING
A. Field Note
In this implementation, the researcher arranged two cycles. In each cycle, the steps are planning, acting, observing, and reflecting.
1. Description of Teaching and Learning Process in Cycle I
The researcher used Problem Based Learning (PBL) strategy to teaching Expressing Opinion, which it can improve students’ speaking ability. The steps of cycle 1 was conducted on Monday, July 30th 2018 at 10.15 a.m. and Monday, August 06th 2018 at 10.15 a.m. The procedure as below:
a. Planning
The activities are:
1) Preparing materials, making lesson plan, and design the step in doing the action.
2) Preparing list of students’ name and scoring.
3) Preparing teaching aids (hand out about the material expressing opinion, pictures).
4) Preparing sheets for student’s and teacher’s observation sheets. 5) Preparing test for pre-test and post-test (to know whether
35 b. Action
The activities are:
1) The researcher introduce herself
2) The researcher informed her purpose in doing the research 3) The researcher invited the teacher to teach students
4) The teacher gave a pre-test to know the students’ achievement before the applying PBL strategy.
5) Giving the materials and explain the expression of asking and giving opinion, language feature of expression.
6) Giving the example of the topic asking and giving opinion. 7) The teacher divided class to be five groups to discussed about
the topic.
8) The teacher applied PBL strategy to teach the students and observe learning activity.
9) Giving chance for the students to present their work in front of the class.
10)The teacher gave occasion to the students to ask any difficulties or problems.
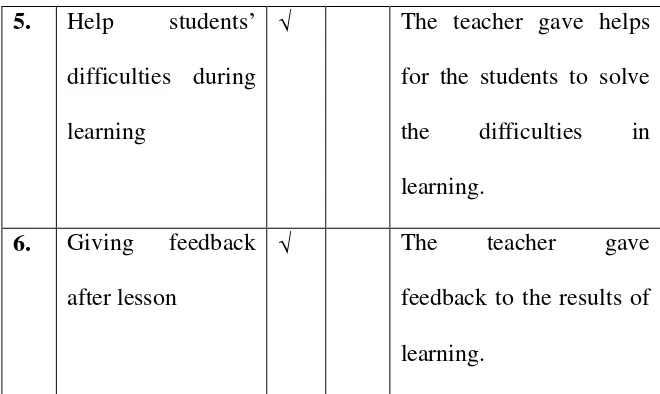
11)Giving feedback.
12)The teacher gave a post-test
c. Observation
36
2) Observing the students’ attention and all the activities in the learning process.
3) Observing the teacher’s activities.
d. Reflection
1) Analyzing the data of this cycle.
2) The teacher and the researcher will discuss the result of the cycle.
3) Make a conclusion of the cycle I.
2. Description of Teaching and Learning Process in Cycle II
The second cycle will be done based on the result of reflection from the first cycle. If the result from observation shows that the quality of the students was still low, it is needed another action in order to make enhancement of the quality for the next cycle. The topic is same with cycle I. The steps of cycle 2 was conducted on Monday, August 13th 2018 at 10.15 a.m. and Monday, August 20th 2018 at 10.15 a.m.The procedures are as follow:
a. Planning
a. Making lesson plan for cycle II as teaching guidance in the learning process.
b. Preparing material.
37 b. Action
1. Giving expressing opinion pre-test.
2. The teacher asked the students about their problems on the previous lesson.
3. Giving feedback.
4. The teacher re-explained about the material using PBL Strategy.
5. The teacher divided class to be five groups to discussed about the topic.
6. Giving chance for the students to present their work in front of the class.
7. Giving post-test.
8. Ask the students to make a dialogue using asking and giving opinion expression with their partner.
9. Giving motivation for students.
c. Observation
a. Observing the learning process concentrate on the students’ interest in teaching speaking.
b. Observing the students’ attention and all the activities in the learning process.
c. Observing the teacher’s activities.
d. Reflection
38
b. The teacher and the researcher will discuss the result of the cycle.
c. The researcher and the teacher make a conclusion after comparing the students’ score between cycle I and cycle II to find out how far the enhancement of students’ speaking ability.
d. The standardized score KKM (Kriteria Ketuntasan Minimum) in MAN 2 Semarang 70. Based on this rule, the mean score post-test must pass the KKM.
B. Research Finding
The research consists of two cycles, each cycle consists of planning, implementation of action, observation, and reflection. The whole steps of this research would be explained in the description below:
1. Cycle I a. Planning
In this step, the researcher prepared:
1) Lesson plan, in order to control the teaching learning process, the researcher used the lesson plan as guidance for the teacher’s activities in the class.
2) Materials, in the first cycle the researcher used topic about “Social Media”. She looking for the material in the internet.
39
4) Test (pre-test and post-test), pre-test is a test that is given to the students before the teaching learning process. Meanwhile, post-test is a test that is given to the students after learning process was conducted. The test is the teacher asked to the students to make simple text about expressing opinion.
b. Acting
The researcher conducted in two days. The action of the cycle I consist of two parts. The pre-test and treatment were conducted in day 1 and treatment and post-test were conducted in day 2. The first part of cycle 1 was conducted on Monday, July 30th 2018 at 10.15 a.m. The teacher and the researcher entered the class, and the teacher greeted the students in the class by saying “Assalamualaikum wr wb”. All the students answered the greeting of the teacher. The teacher asked one of the students (Yanis) to lead the pray by saying
“Bismillahirohmanirrohim” then followed by all students. Then, the
40
allowed the students to open dictionary and internet. When the students were doing the pre-test, the teacher walked around the class to check the students while doing the test. Most of students were nervous and confuse to tell their opinion. 2 boys (Muhammad Rifqi and Mursadi) asked about how to give the response of expressing opinion. The teacher answered “Expressing Opinion had two response there are agree and disagree, you have to explain your reasons”. There was one boy, (Muhammad Yanis Zainudin) lookedbored, he still did not do the test. He was enjoyed with his Smartphone. Most of the students accessed the internet, especially Google Translate to get the answers. In doing the pre-test, the teacher called the students’ name one by one.
After have finished the pre-test, she began the teaching learning process. The teacher told to the students about the topic is expressing opinion. She gave the examples of expressing opinion. After students read the hand out, the teacher asked them any difficult words or not. Then, one student (Rita Anisa) raised her hand to ask question. She asked “Miss, what is the meaning of convinced?”. “Yakin”the teacher answer. “Any other questions?” asked the teacher. The students just silent. After she answer the question from the student, she asked the students to present the result of their discussion in front of class. The time was up, the teacher closed the meeting.
41
“Assalamualaikum wr wb”. All the students answered the greeting of
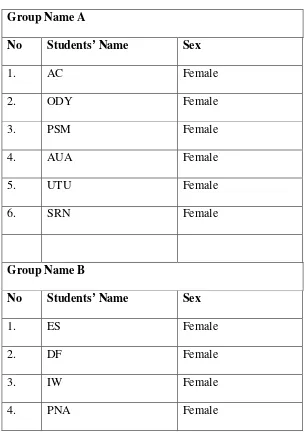
the teacher. The teacher asked one of the students (Yanis) to lead the pray by saying “Bismillahirohmanirrohim” then followed by all students. The teacher opened the meeting and checked the students’ attendance list and no one absent. The next activity in the class, the teacher used Problem Based Learning Strategy, the students divided to be 5 groups consist of 5-6 member. This group divided by rank order and mixed between male and female. For the teams’ data are follows:
Table 1.6 Students’ team Formation Group Name A
No Students’ Name Sex
1. AC Female
2. ODY Female
3. PSM Female
4. AUA Female
5. UTU Female
6. SRN Female
Group Name B
No Students’ Name Sex
1. ES Female
2. DF Female
42
5. SS Female
6. RAPS Female
Group Name C
No Students’ Name Sex
1. AR Female
2. FA Female
3. FH Female
4. MR Male
5. M Male
6. NA Female
Group Name D
No Students’ Name Sex
1. DW Female
2. EPH Female 3. FNZ Female 4. MDS Female
5. MYZ Male
6. SM Male
Group Name E
43
1. BS Female
2. HH Female
3. HCAM Female
4. HK Female
5. PNA Female
The teacher gave explanation and asked them to do the task for the group. The teacher gave the different topic in each group. She gave 15 minutes to discussed their topic and 30 minutes to speak up in front of the class. When the students were doing the task, the teacher walked around the class to check the students while doing the task and also allowed the students to open dictionary and internet. “Please opened your dictionary and look for the supporting sentences in the internet.
44
After the teacher applies Problem Based Learning Strategy, the teacher gave a post-test to the students in 45 minutes. The teacher asked the students to join with their friend and make a simple dialogue about expressing opinion, then they speak up in front of the class. After having post-test, and their speaking performance have been being recorded, then the teacher closed the class.
c. Observation
The researcher observed students and teacher activity by using the observation checklist in the learning process. This observation checklist was purposed to know how far the situation and enthusiasm of the students’ and teachers’ activity during teaching and learning process. The purpose of this activity was to evaluate the teaching and learning process, collected the data and monitored the class.
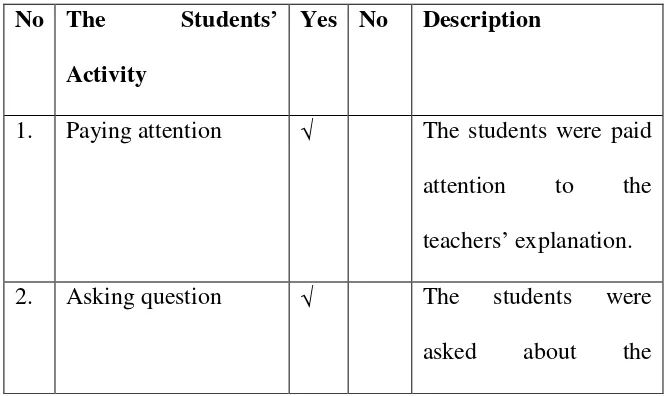
1) The students activity
Table 3.1 form the result of students activity checklist
No The Students’ Activity
Yes No Description
1. Paying attention The students were paid attention to the teachers’ explanation. 2. Asking question The students were
45
difficult of words. 3. Responding the
question
The students were
answered the teachers’ question
2) The Result of Students Observation Checklist cycle I
46
4. DF Less The student just silent, confused, and nervous. 5. DW Good The student answered
the teachers’ question 6. ES Good The student answered
the teachers’ question 7. EPH Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 8. FA Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 9. FNZ Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 10. FHR Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 11. HH Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 12. HCAM Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 13. HK Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 14. IW Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 15. MDS Less The student just silent,
47
16. MYZ Less The student just silent, confused, and nervous. 17. MR Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 18. M Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 19. RA Good The student answered
the teachers’ question 20. ODY Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 21. PSN Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 22. PNA Good The student answered
the teachers’ question 23. RAPS Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 24. SR Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 25. SRN Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 26. SS Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 27. SM Less The student just silent,
48
Table 3.3 Form the Result of Teacher’s observation Checklist cycle I
49
feedback to the results of learning.
4) Observe the use of Problem based Learning Strategy activity
Table 3.4 form the result of using Problem Based Learning Strategy Checklist Cycle I
No Criteria Yes No Description
1. The teacher and the students have internet and access.
The teacher and the students
had internet access. WiFi could be reach in XI MIA 2 class.
2. The students can follow Problem Based Learning instructions.
The students can follow
Problem Based Learning instructions.
50
Strategy.
The researcher got the data from the test of the cycle I and analyzed the data of pre-test and post-test based on rubric speaking assessment. There are five aspects in scoring such as; pronunciation, intonation, fluency, grammar and vocabulary.
The researcher analyzed the data of pre-test and post-test. The calculation and result of both tests are presented below:
1) Score of Cycle I
a) The Result of Pre-test and Pos-test Cycle I
Table 3.5 The result of Pre-test and Post-test cycle I
No Student’s Name Pre-test (X)
Post-test (Y)
1. AUA 65 73
2. AC 50 59
3. BS 58 60
4. DF 63 70
5. DW 78 80
6. ES 74 84
7. EPH 58 76
8. FA 61 78
51
10. FHR 60 69
11. HH 60 70
12. HCAM 69 75
13. HK 66 65
14. IW 58 75
15. MDS 64 79 16. MYZ 62 72
17. MR 65 75
18. M 60 78
19. RA 70 87 20. ODY 59 68 21. PSN 65 70 22. PNA 70 75 23. RAPS 69 76
24. SR 68 74
25. SRN 67 77 26. SS 69 70 27. SM 54 60 28. UTU 70 72
29. AR 68 70
52
Table 3.6 The result of difference score between Pre-test and Post-Pre-test cycle I
53
From the table above, it showed the students’ score in the pre-test and post-test of the cycle I, thus the researcher could calculate the number of students who reached the passing grade as written below:
54
>70 2 6.89% 18 62.06% Total 29 100% 29 100%
From the table above it can be seen that the mean of pre-test in cycle I 63.96 is with standard deviation 6.2649. While mean post-test in cycle I is 72.72 with standard deviation 6.5132. The quantity (N) of the students is 29 students.
(1) The passing grade of the cycle I
Cycle I also has shown that the students can improve their English score in speaking skill. It is shown by the mean of post-test 72.72, it is better than the mean of pre-post-test 63.96. The researcher also calculates the passing grade is 70.
(2) Significant
a) Descriptive statistic cycle I
55
To know there was a significant improvement in speaking skill, the researcher analyzed the result of pre-test and post-test by using SPSS 22.
b) Paired Simple Test Cycle I
Table 3.8 Paired Samples Test
From the table above can be seen that:
a. T-test cycle I is 8.388
b. T-table (=0,05) from the quantity (N) 29 is 2.048 c. T-test > T-table = 8.388> 2.048
56
t-table was 2.048 for df 28 and the significance 5%. From the explanation above, it can be seen that the sig.2 (tailed) value was 0.000 and t-test was 8.388, thus the sig. 2 (tailed) value < 0.05 and T-test was bigger than T-table. It means that Ha was accepted.
d. Reflecting
After analyzing the result of cycle I, the researcher and the teacher should give brief explanation because some students confused and did not understand. It spent much time, students active in learning. But the were interested at the early cycle. They were not ready yet, when the teacher came and started the lesson.
The KKM of English lesson was 70 but the student’s scores of the pre-test show that there are only 6.89% of the students who get score higher than KKM. In the post-test, the student’s scores show that there are 62.06% of the students who get score higher than KKM. It means that although there is an improvement, the researcher and the teacher have to conduct the next cycle because there must be at least 85% of the students who get score higher than KKM.
57 2. Cycle 2
Based on the result of the cycle I, it is necessary for the researcher to continue to the next cycle:
a. Planning
1) Lesson plan as a guide for teacher, so teaching and learning process can be controlled.
2) Material
In the second cycle the researcher used topics about “Full Day School, Giving Gadget to Child, Physical Punishment in The School, Alcohol, and Smoking in a Public”.
3) Teaching aid
The researcher prepared some instrument of teaching aids. They are board marker, sheet of paper, handout for students, and picture.
4) Test (pre-test and post-test), pre-test is a test that is given to the students before the teaching learning process. Meanwhile, post-test is a test that is given to the students after learning process was conducted. The test is the teacher asked to the students to make simple text about expressing opinion.
b. Acting
58
some photos and videos in doing pre-test and post-test for documentation. The teacher and the researcher entered the class, and the teacher greeted the students in the class by saying “Assalamualaikum wr wb”. All the students answered the greeting of the teacher. The teacher asked one of the students (Yanis) to lead the pray by saying
“Bismillahirohmanirrohim” then followed by all students. After that,
the teacher opened the meeting and checked the students’ attendance list. After checked students’ attendance list, the teacher told that they would have a pre-test in 45 minutes, she added that the pre-test almost same with the first pre-test. The pre-test was; the students must give their opinion based on the picture about “Full Day School”. Then, the teacher gave pre-test sheet for the students. The teacher gave 10 minutes for preparing their answer, and 35 minutes for practice one by one. While the students were doing the pre-test, the teacher walked around the class and made sure that all the students did the test well. Most of students doing the test. Then the teacher asked the students to do the test by themselves, and allowed the students to open dictionary and internet.
After the pre-test have done, the teacher reminded the material about expressing opinion. Three students (Mursadi, Yanis, and Mella) still confused and most of the students have understand with the material.
“Any question so far?” asked the teacher. The students just silent.
59
confused the different between agree and disagree.”The student asked. Then, the teacher repeated the material.
The time was up, and the teacher closed the class.
On Monday 20th August, 2018 at 10.15 a.m. The teacher and the researcher entered the class, and the teacher greeted the students in the class by saying “Assalamualaikum wr wb”. All the students answered the greeting of the teacher. The teacher asked one of the students (Yanis) to lead the pray by saying “Bismillahirohmanirrohim” then followed by all students. After that, the teacher opened the meeting and checked the students’ attendance list and no one absent. The next activity in the class, the teacher used Problem Based Learning Strategy in 45 minutes and 45 minutes to post-test. The students divided to be 5 groups consist of 5-6 member. This group divided by rank order and mixed between male and female. For the teams’ data are follows:
Table 6.1 Form Students’ team Formation Group Name A
No Students’ Name Sex
1. AC Female
2. PNA Female
3. PSM Female
4. AUA Female
5. UTU Female
60 Group Name B
No Students’ Name Sex
1. ODY Female
2. DF Female
3. IW Female
4. MDS Female
5. SS Female
6. RAPS Female
Group Name C
No Students’ Name Sex
1. ES Female
2. FA Female
3. FH Female
4. MR Male
5. M Male
6. NA Female
Group Name D
No Students’ Name Sex
1. DW Female
61
3. FNZ Female
4. PNA Female
5. MYZ Male
6. SM Male
Group Name E
No Students’ Name Sex
1. BS Female
2. HH Female
3. HCAM Female
4. HK Female
5. SRN Female
The teacher made the activities in the class like English Debate. The teacher gave explanation and asked them to do the task for the group. The teacher gave the different topic in each group. She gave 15 minutes to discussed their topic and 30 minutes to speak up in front of the class. When the students were doing the task, the teacher walked around the class to check the students while doing the task and also allowed the students to open dictionary and internet. “Please opened your dictionary and look for the supporting sentences in the internet”.
62
member discussed with their group. One student (Heppy) asked to the teacher “Miss, how about this sentence? Is it correct?” The teacher answered “Yes, it is correct. Keep doing the test well.” After that, the teacher asked the group to explain about their topic in front of the class and giving opinion about agree or disagree in their topic. Another group have attention and giving a response. Every group has a chance to speak up in front of the class and deliver their opinion about their topic.
After the teacher applied Problem Based Learning Strategy, the teacher gave a post-test to the students in 45 minutes. The teacher asked the students to join with their friend and make a simple dialogue about expressing opinion and response, then they speak up in front of the class. After having post-test, and their speaking performance have been being recorded, then the teacher closed the class.
c. Observation
In the cycle 2, the researcher made two observational checklist for the teacher and the students. The explanation of the result of the teacher’s observational checklist as follows:
1) The students’ activity
Table 3.9 Table the Students activity No The Students’
Activity
Yes No Description
63
answered the teachers’ question
2) The Result of Students’ Observation Checklist cycle II
64
the teachers’ question. 3. BS Good The student answered
the teachers’ question. 4. DF Good The student answered
the teachers’ question. 5. DW Good The student answered
the teachers’ question. 6. ES Good The student answered
the teachers’ question 7. EPH Good The student answered
the teachers’ question. 8. FA Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 9. FNZ Good The student answered
the teachers’ question. 10. FHR Good The student answered
the teachers’ question. 11. HH Good The student answered
the teachers’ question. 12. HCAM Good The student answered
the teachers’ question. 13. HK Good The student answered
65
the teachers’ question. 15. MDS Good The student answered
the teachers’ question. 16. MYZ Good The student answered
the teachers’ question. 17. MR Good The student answered
the teachers’ question. 18. M Less The student just silent,
confused, and nervous. 19. RA Good The student answered
the teachers’ question 20. ODY Good The student answered
the teachers’ question. 21. PSN Good The student answered
the teachers’ question. 22. PNA Good The student answered
the teachers’ question 23. RAPS Less The student answered
the teachers’ question. 24. SR Good The student answered
the teachers’ question. 25. SRN Good The student answered
66
67
students students’ attendance.
4. Use Problem
Problem Based Learning to improve students’ interest in speaking ability
feedback to the results of learning.
4) Observe the use of Problem based Learning Strategy Activity
Table 3.12 form the result of using Problem Based Learning Strategy Checklist Cycle II
No Criteria Yes No Description
1.
The teacher and the students have internet and access.
The teacher and the students
had internet access. WiFi could be reach in XI MIA 2 class.
68
Problem Based Learning instructions.
Problem Based Learning instructions.
3. The teacher does teaching and learning process by Problem assessment (see appendix 4). There are five aspects in scoring such as; pronunciation, intonation, fluency, grammar and vocabulary.
The researcher analyzed the data of pre-test and post-test. The calculation and result of both tests are presented below:
1) Score of Cycle II
a) The Result of Pre-test and Pos-test Cycle II
Table 3.13 The result of Pre-test and Post-test cycle II
69
4. DF 77 85
5. DW 88 94
6. ES 89 94
7. EPH 85 88
8. FA 78 80
9. FNZ 76 84
10. FHR 75 85
11. HH 75 89
12. HCAM 78 80
13. HK 76 90
14. IW 75 89
15. MDS 87 94
16. MYZ 79 85
17. MR 70 78
18. M 60 70
19. RA 68 75
70
21. PSN 78 79
22. PNA 80 85
23. RAPS 76 80
24. SR 83 89
25. SRN 70 87
26. SS 70 85
27. SM 78 81
28. UTU 76 80
29. AR 77 87
b) The Result of Difference Score Between Pre-test and Post-test Cycle I
Table 3.14 The result of difference score between Pre-test and Post-test cycle II
No Students’ Name Pre-test (X)
Post-test (Y)
D D2C
1. AUA 78 80 2 4
71
3. BS 86 90 14 196
4. DF 77 85 8 64
5. DW 88 94 6 36
6. ES 89 94 5 25
7. EPH 85 88 3 9
8. FA 78 80 2 4
9. FNZ 76 84 8 64
10. FHR 75 85 10 100
11. HH 75 89 14 196
12. HCAM 78 80 2 4
13. HK 76 90 26 676
14. IW 75 89 24 576
15. MDS 87 94 7 49
16. MYZ 79 85 6 36
17. MR 70 78 8 64