i
THE SEMANTIC ROLES ANALYSIS IN RECOUNT
TEXT
(A Study of the Sixth Semester Students of English
Education Department of IAIN Salatiga in the Academic
Year of 2015/2016)
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board Examiners as a Partial Fulfillment of the
Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd)
English Education Department of Teaching Training and
Education Faculty
State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
By
:
AANG HUNAIFY
113 12 016
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
v
Motto
“Man Jadda Wajada”
vi
DEDICATION
This graduating paper is dedicated to:
My God, Allah SWT who always beside me, listens to me, takes care of
me and gives me the best thing ever.
My beloved parents, my mother (Sofiyah) and my father (Ahmad
Zaenuri) who always pray, guide, motivate me to become a better
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Bismillaahirrahmaanirrahiim,
In the name of Allah, the most gracious and merciful, the kings of universe and space. Thanks to Allah because the writer could complete this research as one of the requirements to finished study in English Education Department of IAIN Salatiga.
This research would not have been completed without support, guidance, and help from individual and institution. Therefore, the writer would like to express special thanks to:
1. Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M.Pd as the Rector of IAIN Salatiga.
2. Suwardi, M.Pd., as the Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty.
3. Noor Malihah, Ph.D as the Head of English Education Department.
4. Faizal Risdianto, M.Hum as a counselor who has given the writer advice,
suggestion, and recommendation for this graduating paper from beginning
until the end. Thanks for your patience and care.
5. All lecturers in English Education Department of IAIN Salatiga. Thanks
for all guidance, knowledge, support, and etc.
6. My beloved mother and father. Thanks for everything (support and
praying) no one better than you.
7. My beloved sister (Neni Puji Astuty), my beloved brother (Imam Fauzi),
my little niece (Neima Rara Ghanis Putri) and my big family who fill my
viii
8. Special thanks to my candidate wife who always stands beside me and
takes the big part in supporting until finishing this research.
9. All of my friends TBI ’12 and CECs’ committee, thanks for the cheerful and your togetherness.
10. Everybody who has helped me in finishing this research. Thanks for all
supports, advice, suggestion and other helps that you all gives. The writer
hopes that this research will useful for everyone.
Salatiga, July 20th, 2016
ix ABSTRACT
Aang Hunaify. 2016. THE SEMANTIC ROLES ANALYSIS IN RECOUNT TEXT (A Study of the Sixth Semester Students of English Education Department of IAIN Salatiga in Academic Year of 2015/2016)
Counselor: Faizal Risdianto, S.S., M.Hum.
Keywords: semantic roles (agent, patient, instrument, time, location, recipient, goal, source, path, benefactive, content, experiencer), recount text.
This study mainly to describe the semantic roles in student’s recount text. The
objectives of the study namely: 1)to know the profile of students of the sixth semester of IAIN Salatiga in academic years 2015/2016 on their mastery semantic roles in writing recount text, 2) To identify the most dominant use semantic roles in writing recount text students of sixth semester of IAIN Salatiga in academic years 2015/2016. The writer uses a descriptive qualitative method to classy and
analyzes the semantic roles. The object of this study was 20 students’ recount text. To get the data used descriptive qualitative method. The findings of this research are following:
1. Agent in 156 data (33,92%), followed by location 123 data (26,73%), the time 59 data (12,83%), patient 50 data (10,83%), experiencer 43 data ( 9,35%), source 11 data (2,41%), instrument 9 data (1,96%), goal 5 data (1,09%), recipient 2 data (0,43%), benefactive 2 data (0,43%), path o data (0%) and the last content 0 data (0%). The data totals of semantic roles are 460 data.
x
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE ... i
DECLARATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR NOTES ... iii
PAGE OF CERTIFICATION ... iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENT ... vii
ABSTRACT ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... x
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Problem of the Study ... 3
C. Objectives of the study ... 4
D. Benefits of the Study ... 4
E. Definition of the Key Terms ... 5
F. Limitation of the Study ... 6
G. Review of Rrevious Research……….. 6
H. Graduating Paper Outline ... 7
CHAPTER II: THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK A. Semantic ... 9
B. Semantic Roles ... 9
C. Writing ………... 13
D. Recount Text ... 15
1. Definition of Recount Text ... 15
2. Types of Recount Text ... 16
3. Structute of Recount Text ... 18
xi
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Research of Method ... 21
B. Procedure of the Study ... 22
C. Object of the Study ... 23
D. Data source ... 23
1. Primary ... 24
2. Secondary ... 24
E. Method of Collecting Data ... 25
F. Technique of Data Analysis ... 25
CHAPTER IV: DATA ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION A. Identification ... 27
B. Classifying ... 49
C. Tabulating………. 50
D. Describing………. 50
CHAPTER V: CLOSURE A. Conclusion ... 53
B. Suggestion ... 53
REFERENCES
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Study
Language is used to convey the information, message, thought, opinion, and feeling. As Parker (1986:12) argues that what people have to do in communication is how they use language to communicate rather than the way of language is structured internally. However, language cannot be acquired spontaneously but it needs to be learned. English is one of the languages that people can learn it easily.
Nowadays, English as one of the international languages has become a very important thing in a communication. At the present day, we are entering the global information era where every nation in the world shares information to fulfill needs of knowledge. Regarding global information era, English is the essentially needed to be mastered by everyone because English is the first language that is considered important for the development of science, technology, art, culture and also a relationship with other countries. In English, there are four major skills in which need to be mastered, they are reading, writing, listening and speaking.
2
However, in reality many students complained about difficulties in writing, includes writing recount text.
In this research, it will be observed about students’ ability in writing. There are some components that must be mastered by the students such as grammar, vocabulary, and punctuation. The writer found that students got difficulties in writing recount text because the sentence was not mastered well.
Nowadays, English teachers find out that most of the students still have poor writing skills. Realizing that language use is to communicate thoughts, ideas and feelings from a person to another, students should pay attention more on how it transforms the information and also in learning a foreign language as a second language. Students need to understand first the meaning of source of the language expression.
Semantics is the studies of language meaning. “There are disciplines which are concerned with the systematic study of ‘meaning’ in itself: psychology, philosophy, and linguistics. Their particular interests and approaches are different, yet each borrows from and works with them, Kreidler (1998:2)”. We wonder about the meaning of a new word. Sometimes we are not sure about the message we should get from something we read or hear, and we are concerned about getting our own messages across to others.
Instead of thinks of the word as “containers” of meaning, we can
3
If the situation is a simple event, as in the boy kicked the ball, then the verb describes an action (kick). The noun phrases in the sentence describe the roles of entities, such as people and things, involved in the action. We
can identify a small number of semantic roles (also called “thematic roles”)
Yule (2010:115).
Therefore the researcher look for and analysis the semantic roles in recount text. The research gave this research title as “THE SEMANTIC ROLES ANALYSIS IN RECOUNT TEXT (A Study of the Sixth
Semester Students of English Education Department of IAIN Salatiga
in the Academic Year of 2015/2016)”. B. Problem of the Study
Considering the background of study above, there is any problem but the researcher limit of the problem as follows:
1. What is the profile of students of the sixth semester of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2015/2016 on their mastery semantic roles (agent, patient, instrument, time, location, recipient, goal, source, path, benefactive,
content, experiencer) in writing recount text?
2. What is the most dominant use of semantic roles (agent, patient, instrument, time, location, recipient, goal, source, path, benefactive,
4 C. Objectives of the Study
Given the research questions, the research paper is aimed at the following matters:
1. To know the profile of students of the sixth semester of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2015/2016 on their mastery semantic roles (agent, patient, instrument, time, location, recipient, goal, source, path,
benefactive, content, experiencer) in writing recount text.
2. To identify the most dominant use semantic roles (agent, patient, instrument, time, location, recipient, goal, source, path, benefactive,
content, experiencer) in writing recount text students of the sixth semester of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2015/2016.
D. Benefits of the Study
The writer expects that the result of the study gives benefit in case of: 1. Theoretically
a. Giving some contributions to enlarging the knowledge about semantic roles, which is hoped that after analyzing and reading this research the reader will be more understand the semantic roles. b. The result of the research is expected to be able to encourage the next
5
2. Practically a. Students
The result of this research can be used addition information of semantic roles and recount text. Furthermore, students are motivated to master semantic roles and recount text so they can improve their writing skills.
b. For the english teacher
The result of the study will be useful for addition information in teaching writing concerning semantic roles and recount text. The writer also hopes the teachers teach writing skills not only use grammatical roles but also semantic roles. The teacher can improve the capability through many ways to develop the new method of language learning to upgrade the knowledge about semantic roles and recount text.
E. Definition of the Key Terms
1. Semantic Roles
6
2. Recount Text
Recount is the simple text type in the genre, formally recounts is sequential text that does title more than sequence series of events, Knapp (2005:223).
F. Limitation of the Study
This research specifically concerns on the semantic roles (agent, patient, instrument, time, location, recipient, goal, source, path,
benefactive, content, experiencer) and their writing skills in recount text in the Sixth Semester Students’ of English Education Department of IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of 2015/2016. The writer wants to limit this research in the analysis of semantic roles in recount text.
G. Previous Researches Review
To prove the originality of this study, however in collecting the data and writing the data, the writer wants to present the other thesis as comparison.
7
The second by Chandra Ayuningtyas in 2014, the student of Muhammadiyah University Surakarta entitle AN ANALYSIS OF SEMANTIC ROLES OF TITLE IN THE JAKARTA POST. From her research, she found there are twenty one patterns that are classified into three roles in the in the starting sentence (agent, theme, experience).
By considering those two previous researches, the researcher
conducts research entitled “The Semantic Roles Analysis in Recount Text”.
The researcher is more specific than previous researches. The researcher deliberately specifies the semantic roles and recount text. So the reader can know the profile of student semantic roles in recount text and to identify the most dominant use semantic roles in recount text.
H. Graduating Paper Outline
This research is divided into five chapters. Each chapter explains different matters in line with the topic that is discussed.
Chapter I is an introduction, consists of the background of the study, problems of the study, objectives of the study, benefits of the study, definition of key terms, limitation of the study and paper outline.
Chapter II is a theoretical framework, consists of semantic, semantic roles, writing and recount text.
8
Chapter IV is data analysis and discussion. It is the analysis to answer the problem of the research.
9 CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A.Semantic
“Semantic is the study of meaning in language, Hurford (2007:1)”. According to Yule (2010:112), “Semantic is the study of meaning words, phrases, and sentence in semantic analysis, there is always attempt to focus on what the words conventionally mean, rather than on what an individual speaker might want them to mean on a particular occasion”. This approach is concerned with objective or general meaning and avoids trying to account for the subject or local meaning. Doing semantics is attempting to spell out what it well knows when we behave as if we share knowledge of the meaning of a word, a phrase, or a sentence in the language.
Discussing writing in the study of semantic, there are important points of study in semantics that is also important in writing. Those points are the main item in the study. The point is a semantic role.
B. Semantic Roles
10
1. Agent
Agents are typically animated and normally instigate the actions they perform and do so willfully and intentionally actions reflected by the verb. Example:
The architect built a house.
The dog chased the rabbit. 2. Patient
The patient is something or someone that is affected or undergoes a change as a result of the action or is possessed or acquired.
Example:
The architect built a house.
The dogchased the rabbit.
3. Instrument
Something that an agent uses in order carries out an action. Example:
Ms. Smith hit the nail with the hammer.
The woman washes the clothes with the soap.
4. Time
The time when the action or state indicated by the verb takes place. Example:
The next lecture is on Friday.
11
5. Location
A place where an action happens, or where something in situated.
There are often different “types” of location (e.g. in a place – at a
place – near a place - around a place, etc). Example:
The swordsmen battle outside the castle gate.
I enjoyed Paris last night. 6. Recipient
Someone who comes into possession of something. Example:
The old man gave some food to the stray cat.
I threw the ball and Jasmine caught it. 7. Goal
A place that an action moves towards, or is directed towards (i.e. a target or destination).
Example:
The soldier aimed their rifles at the enemy.
We set out for the hills in a good humor. 8. Source
A place that an action starts from; or, the origin of a perception or experience.
Example:
12
They left the city at down. 9. Patch
Declare a track, trajectory, or a track that is reflected by the verbal. Example:
The dog ran through the garden.
The baby crawled across the room.
10.Benefactive
Someone who benefit from an action. Example:
Archibald bought his mother a bunch of flowers.
Sharon collected five hundred pounds for the famine relief fund.
11.Content
Reflected from the display of verbal meaning. Example:
Jesse knows that Chris lied.
Mona asked, “You met Mary Ann at supermarket”. 12.Experiencer
Someone who experiences some kind of perception (seeing, hearing, smelling) or mental experience (feeling, thinking, knowing, realising). Example:
13 C. Writing
1. Definition of Writing
Writing is one of four language skill should be mastered by every student. It is considerate as a difficult skill than others, according to Byrne (1997:1), writing is considered difficult in the mother tongue because of three factors; psychological, linguistic and cognitive because in writing skill people should pay attention to some aspects at the same time, such as content, text organization, purpose, vocabulary, appropriate diction, punctuation, and spelling.
Writing is kind of progressive activity. It means that when you start to write something then you start to think what you will say and write it down. And after finished your written, you read over the text that you have written and made some correcting and change if you found some mistake.
a) Types of Genre
There are fifteen types of genre text, Hartanto ( 2005:6) they are:
(1) Recount is a kind of genre used to retell events for the purpose of informing or entertaining.
(2) Narrative is a kind of genre used to amuse, to entertain and deal with actual or various experiences in different ways.
14
(4) Anecdote is a kind of genre used to share with others an account of an unusual or amusing incident.
(5) Spoof is a kind of genre used to retell an event with a humorous twist.
(6) Procedure is a kind of genre used to describe how something is accomplished through a sequence of actions or steps.
(7) Explanation is a kind of genre used to explain the process involved in the formation or working of natural or socio-cultural phenomena. (8) Report is a kind of genre used to describe the way think are, with
reference to arrange or natural, man-made and social phenomena in our environment.
(9) Analytical exposition is a kind of genre used to persuade the reader or listener to take action on some matter.
(10) Discussion is a kind of genre used to present (at least) two points of view about an issue.
(11) Description is a kind of genre used to describe a particular person, place or thing.
(12) Review is a kind of genre used to critique an art work or event for a public audience.
15
(14) Hortatory explosion is a kind of genre used to persuade the reader or listener that something should not be the case.
D. Recount Text
1. Definition of Recount Text
Recount is the simple text type in the genre, formally recounts is sequential text that does title more than sequence series of events, Knapp (2005:223). “Every story, no matter how simple, needs an orientation. Indeed it is impossible to tell a story unless we see that there are characters set up in particular time and place, although much post-modern narrative plays with this conversational, Knapp (2005:223)”.
According to Hyland (2009:5) quoted by Purniati (2014), recount is a text that tells about the past experience or event. According to Maulida (2013: Journal of English Language Teaching), “Recount text is the kinds of text retell the event which happened to the participant in the past”. Recount text begins by telling the reader who was involved, what happened, where this event took place and when it happened. The sequence of event is then described in some sort of order, for instance, a time order.
16
From the definition above, it can be concluded that a recount text is a written text, which is used to tell other people about their experience.
Allah decrees in holy Qur’an:
َكْيَلَع اَنْصَصَق ْنَم ْمُهْنِم َكِلْبَق ْنِم الًُسُر اَنْلَس ْرَأ ْدَقَل َو َكْيَلَع ْصُصْقَن ْمَل ْنَم ْمُهْنِم َو
“We have sent forth other apostles before you; of some, we have
Already told you the story, of others We have told you
nothing . . .”.
(QS.Al.Mu’min: 78)
From the verse above, we know that Allah told stories of prophets before he knows rightness with ration truths. From the verse, we can also conclude that we can tell personal experience through an article which can remind us past experience although glad or sorrowful. We can get good value to be better in the future by past experience.
2. Type of Recount Text
Sue Stubs (2009:8) describe that types of recount text are: a) A factual recount
17
b) Literary or imaginative recount
Literary recount entertains the reader by recreating the
events of an imaginary world as though they are real “A day in my
life as a family pet”. For example; emotive language, specific
detail, and the first person narration are used to give the writing impact and appeal.
c) A procedural recount
A procedural recount in records the steps taken in completing a task or procedure. The use of technical terms, an accurate time sequence, and first person narration (I or we) give credibility to the information provided. Examples included a flow chart of the actions required for making bread, a storyboard of a videotaped script or advertisement, the steps taken to solve a mathematical problem.
d) A biographical recount
A biographical recount told the story of person’s life using a third person narrator (he, she, and they). In the case, of an autobiography, first person narrator (I, we) is used. It is usually factually accurate and records specific names, times, places, and events. A purely factual, informative biography, however, would lack the appeal provided by personal responses and memorable
anecdotes. There is often an evaluation of subject’s achievement in
18 3. Generic Structure of Recount Text
Sue Stubs (2009:8) describe that a recount has three parts; there are orientation, events, and reorientation:
a) Orientation
The orientation provides all the necessary background information to enable the audience to make sense of the test. The ensure that the orientation is detailed and thorough, use the 5 x w formula (who, what, when, where, why). The writer or speaker to give information about what happened, who or what was involved. When and where the events occurred and why. An awareness of audience and purpose will assist the author in selecting the amount of detail needed.
b) Events
Event should be selected carefully to add to the audience’s
understanding of the topic. Student should be prepared to discard events and details that are unimportant or uninteresting. c) Reorientation
This final section concluded the recount by summarizing
outcomes or results, evaluation the topic’s importance or
19 4. Language Feature of Recount Text
Language feature of recount text explained by Sue Stubs (2009:8), there are as follows:
a) Simple past tense is used in recount.
b) Subject-specific terms (larvae, topography) are used to record facts and events accurately. They also add authenticity and credibility to the tone of the writing.
c) Specific descriptive words (adjectives) help the audience visualize or imagine events.
d) A range of conjunction (because, although, while) is used to link clauses within sentences.
e) Time connectives (firstly, next, finally) are used to link separated events or paragraphs into a cohesive whole text.
f) Passive voice is used, particularly in factual recounts, to give objective to the text.
g) Adverbs (yesterday, outside) and adverbial phrases. h) Specific participant (nouns and pronoun).
i) Pronouns are used to provide cohesion by tracking participants through the text
j) A range of sentence type (simple, compound and complex) is used to add variety and interest.
20 CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This research method of study was described in six points, they were type research of method, procedure of the study, object of the study, data source, method of data collecting, and technique of data analysis. The explanation of each point is discussed further in detail explanation.
A. Research of Method
The semantic roles analysis which is applied by the students in the writing recount text, the writer used descriptive qualitative research method. Moloeng (2002:3) state qualitative research method is defined as a research procedure which produces descriptive data in the form of words written or spoken of the person. In line with the statement, Moelong (2002:3) define that qualitative research method is a specific tradition in social science, which fundamentally relies on the observation of humans in its own region and relate to the person in a language and terminologies.
21 B. Procedure of the Study
Isaac and Michael (1984:46) state that the purpose of descriptive research is to describe systematically the facts and characteristic of a given population or area interest, factually and accurately. Descriptive research is used in the literal sense of describing situation or events. Dealing with it, the writer defined the procedure of the study based on that theory. The procedure of descriptive research as follows:
1. To define the objectives in clear. 2. To design the approach.
3. To collect the data, 4. To analyze the data,
5. To draw the conclusion, and 6. To report the result.
22 C. Object of the Study
The object of the study was semantic roles (agent, patient, instrument, time, location, recipient, goal, source, path, benefactive, content, experiencer) in recount text. “Sample is defined as a part or a representative of the population that is investigated, Arikunto (2002: 109)”. He added that if the participants of the research are more than one hundred, the researcher could take sample 10-15 % of the population. Samples are 20 students of Sixth Semester of English Department Students of IAIN Salatiga. From these samples, hopefully, could give some data or information that supports the study. Semantic roles became the important part of the paragraph. Knowing in semantic roles could help in clearly understanding the paragraph.
D. Data Source
23
In order to analyze semantic roles found in the student’s recount
text, the writer used the data sources both from primary and secondary data describe as follows:
1. Primary
Regarding Arikunto (2010:22) “primary data source is data
in the verbal from or word that spoken, gesture or attitude done by the trustworthy subject, in another word this is research
subject related to researched variable”. In this research, the
primary data source took from the student’s recount text from
the sixth semester students of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga in the academic year of 2015/2016.
2. Secondary
According to Arikunto (2010:22) “the secondary data
source is data acquired from graphic (table, note, SMS, book, etc), photo, movies, video recorder, things, etc to enrich
primary data”. The writer used several references to support the
24 E. Method of Collecting Data
In this study, the writer used documentation as the method of collecting data. Arikunto (2010:274) defines “a documentation method is finding data that related by using book, transcript, newspaper, magazine, ancient inscription, notes of a meeting, agenda, etc. compared to another method this method is rather not difficult”. Documentation method is observed not living but inanimate object. The writer held the document by
collecting the data source, they were the student’s recount text of the sixth semester students of State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga in the academic year of 2015/2016. There are 20 recount texts
F. Technique of Data Analysis
The writer concerned on the semantic roles analysis in recount text. Krippendorff, (2004:25) :
1. Identification
Identification was conducted to determine the semantic roles (agent, patient, instrument, time, location, recipient, goal, source, path, benefactive, content, experiencer) used in the student’s recount text. By these step, the writer could determine the semantic roles type which was applied by the students.
2. Classifying/Unitizing
25
content, experiencer) provided the student’s recount text. Moreover,
the writer could determine the most dominant use of semantic roles
(agent, patient, instrument, time, location, recipient, goal, source, path,
benefactive, content, experiencer) which were applied by students. 3. Tabulating
Once the date was grouped, the writer created a table in the form of a diagram where it clarified the ration between the number of semantic roles (agent, patient, instrument, time, location, recipient, goal, source, path, benefactive, content, experiencer).
4. Describing
After the third step, the writer conducted the last step, which is the description of the result of the data analysis. In this, the writer described the data presented.
26 CHAPTER IV
DATA ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter is the main part of the whole graduating paper. The writer wants to analyze and discuss the semantic roles analysis in recount text. The complete discussions will describe below:
A. Identification
Based on the 20 data of the student’s recount text of IAIN Salatiga,
the writer presents, and analyzes those data to answer the problems of the statement in chapter I. Those are presented in table 4.1.
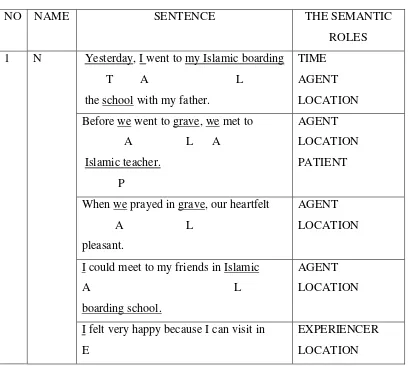
Table 4.1 Distribution of Student’s Recount Text
NO NAME SENTENCE THE SEMANTIC
When we prayed in grave, our heartfelt A L
pleasant.
AGENT LOCATION
27
Islamic teacher’s grave and I could meet L
First, we made a visit to some beach at A Second, we went to Baron Beach and
A L there we take a lunch. A
AGENT LOCATION
I also played an ATV to around the beach. A P L
AGENT PATIENT LOCATION last we went to Parangtritis Beach till take
A L spending my holiday last semester. P T
28
I only stayed at home, because I did have A L A
any event to be followed.
AGENT LOCATION
After I woke up on sunday morning, I A T A turned up my laptop and watched the film. P P
AGENT TIME PATIENT
I watched the film for 2 hours. A P T
Library to brows something interesting.
AGENT In library, I opened my laptop and
T A P
29
4. M On monday, my family and I went to Elo T A L River in purpose to have a vocation.
TIME
It came formerly from my family’s idea to A
have a break from crowded days on working days.
AGENT
Firstly the reason why we choose Elo A P River because it was well-known with rafting.
AGENT PATIENT
Many people were interested in rafting in A
spared time in this location. S
AGENT SOURCE
And in brief, we were amazed and E
interested all single things inside of it.
EXPERIENCER
We did rafting while enjoying a screamed A
when the boats were stocked among river stares.
30
I decided to continue my study at A S
I tried to apply in many universities. A L
AGENT LOCATION First, I applied at Yogyakarta.
A L I followed the test step by step.
A
AGENT
I spent 3 days in Yogyakarta. A T L
AGENT TIME LOCATION When the result was announced, I could
A not get my name on the list. P
AGENT PATIENT
I felt so shock because I realized that I E E E failed in the test.
EXPERIENCER
After that, I decided to didn’t continue to A
study. S
31
In the other hand, my brother asked to A
applied in another university. L
AGENT LOCATION
So I applied in Semarang. A L
Finally, I applied in STAIN Salatiga and A L
accepted in STAIN Salatiga. L
AGENT LOCATION
6 WFS Yesterday, I visited Yogyakarta. T A L
TIME AGENT LOCATION There are so many places that amazed me
E in Yogyakarta.
P
EXPERIENCER LOCATION
I went to Taman Sari and Malioboro. A L
AGENT LOCATION Me and my family very happy visiting
E Yogyakarta. L
EXPERIENCER LOCATION
I bought some souvenir from Malioboro, A P L such as a t-shirt, ring and shoes.
AGENT PATIENT LOCATION Yogyakarta is the beautiful area, has so
L
32
many beautiful place and politeness people.
I also went to Kraton Yogyakarta and A L
Alun-Alun Kidul that has mitos if we across but we two bringin in the center of alun-alun kidul, everything that we want
My friend and I went to Malang. A L I had many impressive experiences during
B
the vocation.
BENEFACTIVE
The first day, we visited Jatim Park Zoo T A L
We saw many animals in the Jatim Park E P L
The second day, we enjoyed the day on T E
TIME
33
CubaRondo waterfall and we played so L A
much water and selfi together. P
LOCATION AGENT PATIENT
They were so tame but sometimes they A A could be naught.
AGENT
We could make a close interaction with A
them, after that we went back home A L During my vocation in Yogyakarta I got
L B many experiences.
LOCATION BENEFACTIVE
34
INSTRUMENT When arrived in Prambanan.
L
LOCATION
We walk around the temple. A L
AGENT LOCATION Prambanan Temple looked very beautiful
L
and we enjoyed the scenery around the E
temple.
LOCATION EXPERIENCER
After visiting, we went to the hotel to the A L
We went to the restaurant near the hotel to A L
have a dinner.
AGENT LOCATION
After finishing dinner, we went to the A
the hotel took a rest. L
AGENT LOCATION
In the following day, we decided to visit T A
It took about 2 hours to get there. T
TIME
We arrived in the Parangtritis Beach at A L
35
04.00 pm. T
We were amazed at the beauty of E
Parangtritis scenery.
EXPERIENCE
We decided to watch beautiful sunset A S
there.
AGENT SOURCE
We were very happy and enjoyed it so E
much.
EXPERIENCER
9. SNN In the senior high school exactly two classes, I went to Jakarta-Bandung.
A L
AGENT LOCATION
With all students of grade two, we tour A
there and also some teachers to the company.
AGENT
As holiday we need about four days A T
AGENT TIME Many place on the Jakarta, such as TMII,
L L
Very tired after that, but I feel satisfied E
because it was the first experienced went
36
to Jakarta and Bandung. L
And after that, I went to Jakarta again last A L T
I was alone, but in Jakarta, there was my E L Very bored in the bus because nothing
L
was accompany just hand phone made me E
We were there for three days. A T
AGENT TIME The first day, we visited Tanjung Benoa
T A L beach.
TIME AGENT LOCATION We played water sports at there.
A P
37
We went to Penyu Island to see unique A L
an animal such as big turtles, snake and sea birds.
AGENT LOCATION
We felt enjoyed and happy. E
EXPERIENCER
The second day, we visited Kuta Beach in T A L
We saw the lovely sunrise there. E P
EXPERIENCER PATIENT Then, we enjoyed a beautiful wave and
A smooth sand.
EXPERIENCER
The last day, we spent our time on Tanah T A P L Tanah Lot was a nice place.
L
LOCATION
We saw so many tourists there. E P
We went back home and bring so many A L
38
unforgettable memories of Bali. P It took about 4 hours to get Pacitan.
T L At 2 a.m. our first destination was Soge
T S Beach.
TIME SOURCE
We decided to sleep in the car while A S L We came in and enjoyed our time there.
E
EXPERIENCER
We played the sand and made a big sand A P P castle.
39
We also took a lot of pictures. A P
AGENT PATIENT After that, we went to Tabuhan Cave.
A L
AGENT LOCATION We enjoyed it so much and felt very
E
There are Mountain Semeru, apple of L L garden many places.
LOCATION
I’m walking around in there and I’m A E
something to bring on goes home. P L
TIME AGENT LOCATION
In there we start from Batu and finish in A L
Lamongan. L
AGENT LOCATION
Ha ha lamongan so foody city. L
LOCATION
I love Lamongan any place and watching E L
store on the road, like a Malioboro L
40 Yogya was hot and crowded.
L
LOCATION
First, we went to Taman Pintar. A L
Many interesting spots, but I could not E
enjoy that one because I had to check them.
EXPERIENCER
Then we went to Gembira Loka. A L
AGENT LOCATION I rode the visitor train to surrounding the
A P 200.
AGENT PATIENT
41 We played football in the coastline.
A P L
AGENT PATIENT LOCATION After that, we built a castle from sand.
A P I
AGENT PATIENT INSTRUMENT In the night, we made bonfire together.
T A P
TIME AGENT PATIENT We roasted fishes and squints then we ate
A P A them.
AGENT PATIENT
42
At the morning, we went home. T A L
TIME AGENT LOCATION It was a moment I never forgot.
E
EXPERIENCER
15. WL A week ago I spent my holiday to visited T A P
Gedong Songo temple in Bandungan. L L
TIME AGENT PATIENT LOCATION I went there with my friends by car.
A I
AGENT
INSTRUMENT Bayu one of my friend drove the car.
A P
AGENT PATIENT He drove very fast like a racer.
A We started to walk from the first until
A S L
apparently, that is the smell of belerang.
EXPERIENCER
43
After we satisfied with that view of that E
temple, we walked from the higher A temple until lower temple. L
EXPERIENCER AGENT
LOCATION
In the first temple, tina helped me to by a L A P After friend took a picture again for the
A P
the memory of our holiday at our vacation.
AGENT PATIENT
After that, we went home to rest our A L
I got the birthday present. R
RECEPIENT
I got a flower, a cake, it was shocked R
when I saw my parents there. E P
RECEPIENT EXPERIENCER PATIENT
They had made me felt happy. A E
AGENT
44 We left our dormitory at 8 am and arrived
A L T
After arriving in Elo River, the guide T A prepared for us some floats, helmets oars and one raft.
LOCATION AGENT
Guides gave us instruction before going A
to the river. L
AGENT LOCATION
A few minutes after that we were ready to T A
We went down to the river with two A L
guides who accompany us.
AGENT LOCATION
We enjoyed our experience and saw E
beautiful view.
EXPERIENCER
Maybe for about a quarter our, suddenly the guide pushed me into the river A P L
45
I was shocked, but I was not afraid E E
becauseI can swim. E
EXPERIENCER
It was so fantastic when I swam in the E
Willy-nilly I force myself to swim. A P We made decision to take a rest and we
A S A
46
I spent one day in Semarang just window A T L
shopping in Paragon Mall. L
AGENT TIME LOCATION
I did not buy anything because it is so A
expensive.
AGENT
I saw a handsome boy in there, he is E P
Chinese so he has slanting of eyes.
EXPERIENCER PATIENT
After in Paragon, I went to Johar Market. L A L
AGENT LOCATION In Johar market, I bought bandeng presto
L A P
because as the one of special in Semarang. L
LOCATION AGENT PATIENT
After went to mall and market just L
window shopping I went to Simpang Lima. A L
AGENT LOCATION
In Simpang Lima, I took a picture with L A P
mysister.
LOCATION AGENT PATIENT Simpang Lima closes with Lawang Sewu
47
One day in Semarang I just did window T L A
shopping and took picture. P
TIME LOCATION AGENT PATIENT I did not shop clothes or something
A P
else because any goal went to Semarang L just refreshing without spent a lot much G
In the first week, however, I just stayed at T A
home and had my brain related from the L
contra lined study.
TIME AGENT LOCATION
For this reason, I decided to go my A
friend’s house to visit a waterfall. S L
AGENT SOURCE LOCATION
It was located in Klaten, 2 hours from my L T
house.
LOCATION TIME
My friend and I enjoyed the relaxing E
nuance and fresh air in the Sumunding L
48
Place.
In the following week, I had myself being A
spoiled with the picture view in the Andong Mountain.
Hopefully, I would be able to spend my A
upcoming holiday with more pleasurable G First, we visited Parangtritis beach.
A L
AGENT LOCATION We felt the wind blew across to us.
E Second, we visited Gembira Loka Zoo.
A L
AGENT LOCATION We saw many kinds of animals there such
E P
49
as monkeys, tigers, crocodiles, snakes, etc.
We looked around in the Zoo, and also A L
took pictures of those animals. P
As soon as we finished our lunch, we A A
50 B. Classifying
From the table 4.1, the writer found that there type reference and inference which are applied by the students in making the recount text. From the explanation, the writer makes a table and figure to show the comparison among them, so they are easily identified.
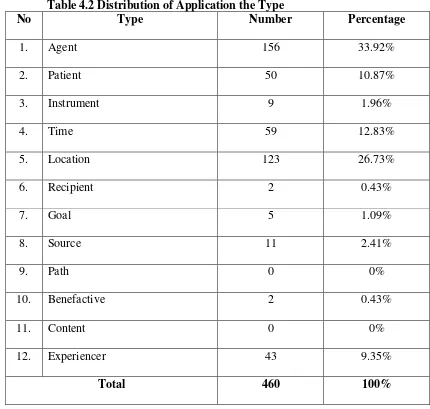
Table 4.2 Distribution of Application the Type
No Type Number Percentage
1. Agent 156 33.92%
2. Patient 50 10.87%
3. Instrument 9 1.96%
4. Time 59 12.83%
5. Location 123 26.73%
6. Recipient 2 0.43%
7. Goal 5 1.09%
8. Source 11 2.41%
9. Path 0 0%
10. Benefactive 2 0.43%
11. Content 0 0%
12. Experiencer 43 9.35%
51 C. Tabulating
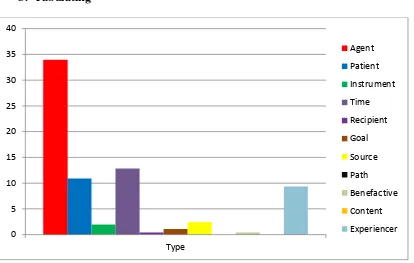
Figure 4.1 Distribution of Application the Type
D. Describing
From the table 4.2 and figure 4.1, it can be concluded that
1. The profile of students their mastery semantic roles in recount text is agent in 156 data (33,92%). Followed by location 123 semantic roles are 460 data.
2. The most dominant use semantic roles (agent, patient, instrument, time, location, recipient, goal, source, path,
52 CHAPTER V
CLOSURE
After conducting, presenting the data, analyzing the data and discussing the result, in this chapter the researcher would like to present the conclusion and suggestion of this research.
A. Conclusion
After the analyzing of the student’s recount text in the previous
chapter, the writer makes conclusion as follows:
1. 33, 92% students used agent, while 26, 73% students used location, 12, 83% students used patient, 9, 35% students used experiencer, 2, 41% students used source, 1, 96% students used instrument, 1, 09% students used goal, 0, 43% students used recipient, 0, 43% students used benefactive, 0% students used path and content. The data totals of semantic roles are 460 data.
2. Agent was frequently used by the students 156 data (33, 92%). Furthermore, it was the most dominant used by students’ recount text.
B. Suggestion
Based on the conclusion above, the writer proposes the suggestion to those might be benefited to the result of this research.
1. For the readers
The researcher hopes that this research could be improving the
reader’s knowledge about semantic roles in writing especially to make a
53
about semantic roles. It is also hoped after reading this research the readers would understand if sometimes people have implied intention in their text, so the reader can communicate well with the others trough their written text.
2. For the other researcher
The researcher hopes that this research could be one of the references in studying about semantic roles in paragraph especially in recount text and hope that in the future there will be other researchers who will conduct the same topic to complete this research although in a different field.
3. For the learning process
54
REFERENCES
Arikunto, Suharsimi. (1990).Manajemen Penelitian.Jakarta: Rineka Cipta. Arikunto, Suharsimi. (2002).Prosedur Penelitian. Jakarta:PT. Bina Aksara. Arikunto, Ssuharsimi. (2010).Prosedur Penelitian Satuan Pendidikan Practik.
Jakarta:PT. Bina Aksara.
Byne,d. (1997).Teaching Writing Skills (Longman Handbooks for Language Teacher).
New York: Longman Group UK Limited.
Fitri, Maulida Vany.(2013). Using A Shared Writing Strategy in Teaching A Recount Text to Junior High School Students. Jounal of English Language Teaching
(online)Vol.1 No.2 Serie.
http://ejournal.unp.ac.id/index.php/jelt/article/view/1959, retrieved on may 2016).
Hartanto, Rudi. (2005).Genres of Text.Semarang: UNNES.
Hurford, James, R. (2007). Semantics A Coursebook. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Isaac and Michael. (1984).Handbook and Research and Evaluation. London: Edits Publisher.
Knapp.P. and Watkins. M. (2005). Genre, Text, Grammar. Australia: University of New Sourth Wales Press Ltd.
Kreidler,Charles. (1998).Introducing English Semantics. London: Routledge 11 New Fetter lane.
Krippendorff, K. (2004). Content Analysis: An Introduction to Its Methodology.USA: Sage Publication, inc.
55
Parker. (1986). Principle of Language Learning. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Priyana, Joko. (2008). Interlanguage: English for Senior High School Students X.
Jakarta: Pusat Pembukuan Depatmen Pendidikan Nasional.
Purniati, (2014). Improving Students’ Reading Comprehension in Recount Text
Through Two Stay Two Stay Technique.Salatiga: English department of educational faculty IAIN Salatiga
Spratt,M. (2005). ET. Al. TKT Teaching Knowledge Test Course. UK: Cambridge University Press.
Stubbs, Sue. (2000). Targeting Text. Australia: Blake education.
Van Valin, Robert, D. (2004). An Introduction to Syntax. UK: Cambridge University Press.
Yule,George. (2010). The Study of Language. New York: Cambridge University Press.
57
58
Nama : Aang Hunaify Fakultas : Tarbiyah dan Ilmu Keguruan
NIM :11312016 Jurusan: Tadris Bahasa Inggris
No. Nama Kegiatan Pelaksanaan Keterangan Nilai
1. Orientasi Pengenalan Akademik dan Kemahasiswaan (OPAK)
05-07 September 2012
Peserta 3
2. Orientasi Pengenalan Akademik dan
3. Orientasi Dasar Keislaman
(ODK)
10 September 2012
Peserta 2 4. Seminar “Enterpreneurship
dan Perkoperasian” 11 September 2012
Peserta 2 5. Achievement Motivation
Training (AMT)
12 September 2012
Peserta 2 6. Library User Education 13 September
2012
pembasmi galau” 06 Oktober 2012 Peserta 2
9. English Friendship Camp
“EFC and social work in merbabu foothill 2012”
19 Oktober 2012 Peserta 2
10. Penerimaan Anggota
Baru JQH
12. Seminar Nasional“How to
develop the best
generation”
01 juni 2013 Panitia 8
13. Seminar Nasional
“Mengawal pengendalian
BBM bersubsidi, kebijakan BLSM yang tepat sasaran serta pengendalian inflasi dalam negeri sebagai dampak kenaikan harga
BBM bersubsidi ”
08 juli 2013 Peserta 8
14. Workshop ESQ
“membangun generasi 15-16 November 2013
59
mahasiswa terbaik”
15. Seminar Nasional “Guru
kreatif dalam implementasi
kurikulim 2013”
18. English Friendship Camp
“CEC is the Best Way for
Festival 2014” 14 November 2014
Panitia 3 21. Scholarship Forum 15 November
2014
Panitia 3 22. CEC Festival 2014 20-22 November
2014
community 2015; prospects and challenges for Islamic
dalam mendukung program pemerintah melalui focusing on Classroom Management: How to
untuk membentuk karakter
bangsa yang bermartabat”
60
31. Scholarship Guideline Seminar
28 Desember 2015
Peserta 2
Jumlah 117
Salatiga, 18 Juli 2016 Mengetahui,
Wakil Dekan Bidang
Kemahasiswaan dan Kerjasama
Achmad Maimun, M.Ag. NIP. 19700510 199803 1 003
CURRICULUM VITAE
Name : Aang Hunaify
Place/Date of Birth : Kab. Semarang, 20 Agustus 1991
Address : Dsn. Doplang1, Rt 06 Rw 04, Ds. Pakis, Kecamatan Bringin, Kabupaten semarang, Jawa Tengah Email Address : [email protected]
61
Educational Background : 1. SD N Pakis (1998-2003) 2. SMP N 2 Bringin (2003-2006) 3. SMK N 2 Salatiga (2006-2009) Experiences :
1. Member of Showbiz Division at CEC (2012-2013) 2. Member of Religion Division at CEC (2013-2014) 3. Chief of CEC (2014-2015)