THE EFFECT OF SYNTHESIZING STRATEGY
ON STUDENTS’
READING COMPREHENSION
IN RECOUNT TEXT
A THESIS
Submitted as the Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement
for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan
By:
YESSI VAN CARMELIA SIMBOLON
Registration Number: 2113121073
ENGLISH AND LITERATURE DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGES AND ARTS
ii
ABSTRACT
Simbolon, Yessi Van Carmelia. 2113121073. The Effect of Synthesizing Strategy on Students’ Reading Comprehension in Recount Text. A Thesis. Faculty of Languages and Arts, State University of Medan. 2016.
This study aims at investigating the effect of Synthesizing Strategy on students’ reading comprehension in recount text. This study was conducted by using experimental research design. The population of the study was the students of grade X of SMA Negeri 17 Medan in the academic year 2015/2016, which consisted of 10 parallel classes. Two classes were taken as the sample by applying clustering sampling and each groups consisted of 30 students. The sample was divided into two groups. The class X-4 was experimental group and class X-1 was control group. The Experimental group was taught by applying synthesizing strategy; otherwise the control group was thaught by using conventional strategy. The data of the study were obtained by objectives test. To determine the reliability of the test, KR-20 formula was used. The data calculation showed that the coefficient of reliability of the test was 0.84. It showed that the test was reliable and the reliability was very high. The data were analyzed by applying t-test formula. After the data were analyzed, the result of the study showed that t-observed (4.32) was higher than t-table (2.00) (t-t-observed > t-table) at the level of significance of α = 0.05 and at the degree of freedom (df) = 58. Therefore, the null hypothesis (Ho) is rejected and hypothesis alternative (Ha) is accepted. It means
that there is significant effect of synthesizing strategy on students’ reading
comprehension in recount text.
iii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Praise the Lord, the greatest and deepest countless thanks to most merciful, Jesus Christ for His amazing love, uncountable blessing and strength are given to the writer during her study and in completing this thesis. This thesis is people who give guidance, suggestions, advices, comments and moral supports. Therefore, the writer would like to express her thanks and sincere gratitude to:
Prof. Dr. Syawal Gultom, M.Pd., the Rector of State University of
Medan.
Dr. Isda Pramuniati, M.Hum., the Dean of Languages and Arts
Faculty.
Prof. Dr. Hj. Sumarsih, M.Pd., the Head of English Department
and also as her reviewer and examiner.
Dra. Meisuri, M.A., the Secretary of English Department and also
as her reviewer and examiner.
Nora Ronita Dewi, S.Pd., S.S., M.Hum., the Head of English
Education Study Program.
Prof. Dr. Berlin Sibarani, M.Pd., her Thesis Advisor, who has
guide, support, advises, and give his precious time in the process of completing this thesis.
Indra Hartoyo, S.Pd., M.Hum., her Academic Advisor and also as
her reviewer and examiner, who has supported her throughout the academic years and has given guidance, support, and comments.
All the Lecturers of English Department, who have taught,
guided, and advised her throughout the academic years.
Eis Sri Wahyuningsih, S.Pd., M.Pd., the administration staff of
English Department, for her attention, assistance, and information in completing this thesis.
Soagahon Simanungkalit, SH, the Headmaster of SMA Negeri 17
Medan, for his permission in allowing the writer to do the observation and to collect the data needed for the thesis.
Omega Simanjuntak, S.Pd., the English teacher of SMA Negeri 17
Medan, for the supports, guidance, suggestions, and motivations in the process of completing this thesis. And all the teachers and students at the school for the good cooperation.
Drs. Handipan Simbolon and Tumiar S. Situmeang, her beloved
parents, Riski Vanni Simbolon, Frans Doan Panjatio Simbolon,
Romual Panjohan Simbolon, her sister and brothers, for their
iv
that they have given to the writer during the study and in completing the thesis. This thesis is dedicated to you.
Julius Kwart Siboro S.E., her closest friend, for his pray, care and
love during the completing this thesis.
Fibie Liona, S.Pd., Irdawati, S,Pd., Dwi Suci, Era Enjelyna L,
Lestaria DS, S.Pd., Indah Pratama Prida, Intam Nilam Sari, Siti Khairin Nasroh S.Pd., Novia S.Pd., Sarah Marilyn Silaban, Tutwuri Situmeang, Dora Margaretha, Melitasari Purba,
Batsyeba Silaen, Nancy Panggabean, her beloved bestfriends,for
the courage, support, help and spirit during the completing of her thesis.
UK-KMK St. Martinus Unimed, OMK St. Michael Pangururan
and OMK St. Michael Durung, her lovely organization, for their
prayer, motivation, support, and spirit during completing this thesis.
Regular Dik A 2011, her friends, for their togetherness throughout
the four years. support and reminding everything in completing this thesis.
PPLT 2014 SMK Negeri 1 Laguboti, her friends, for the
togehterness and experiences shared.
Last but not least, the writer realizes that this thesis still has the paucity and mistakes, she conveniently to accept suggestions, comments, critics and advices for the better writing. She hopes that this thesis would be useful for those who read and feel interested in the field if this study.
Medan, April 2016 The Writer,
v
E. The Significance of the Study ... 6
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF LITERATURE ... 7
A. Theoretical Framework... 7
1. Reading Comprehension ... 7
a. The Concept of Reading Comprehension ... 7
b. The Factors Contribute of Reading Comprehension ... 8
c. Levels of Reading Comprehension ... 10
d. The Measurements of Reading Comprehension ... 11
2. Recount Text ... 14
a. The Grammatical Patterns of Recount Text ... 14
b. The Generic Structure of Recount Text ... 15
c. The Example of Recount Text ... 16
3. Synthesizing Strategy ... 17
a. The Nature of Synthesizing Strategy ... 17
b. The Procedure of Synthesizing Strategy ... 19
c. The Strengths and Weakness of Synthesizing Strategy ... 19
B. Relevant Studies ... 20
C. Conceptual Framework ... 21
vi
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 23
A. Research Design ... 23
B. Population and Sample ... 24
C. The Instruments for Collecting Data ... 24
1. Source of Data ... 24
a. Treatment in Experimental Group ... 26
b. Treatment in Control Group ... 27
4. Post-Test ... 27
1. Homogeneity of Variance ... 30
2. Normality of the Test ... 31
H. The Technique of Analyzing Data ... 32
I. Statistical Hypotheses ... 32
CHAPTER IV. DATA AND DATA ANALYSIS ... 33
A. Data Description ... 33
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 45
A. Conclusion ... 45
B. Suggestion ... 45
REFERENCES ... 47
vii
LIST OF TABLES
Pages
Table 1.1 Students’ Score of Reading Test ... 3
Table 3.1 Research Design ... 23
Table 3.2 Treatment for Experimental Group ... 26
Table 3.3 Conventional Teaching in Control Group ... 27
Table 3.4 Table of Specification ... 28
Table 4.1 Students’ Achievement Score in Pre-test and Post-test ... 34
Table 4.2 Test for Homogeneity of Variance ... 38
Table 4.3 Testing Normality ... 40
viii
LIST OF FIGURES
Pages
ix
LIST OF APPENDICES
Pages
Appendix A. Reading Comprehension Test ... 50
Appendix B. Answer Key of Reading Comprehension Test ... 55
Appendix C. The Scores of Pre-test and Post-test ... 56
Appendix D. The Calculation of Reliability ... 58
Appendix E. The Calculation of Reliability ... 59
Appendix F. The Calculation of t-Test ... 61
Appendix G. The Calculation of t-Test ... 63
Appendix H. Percentage Points of T Distribution ... 65
Appendix I. Test for Homogeneity of Variance of Pre-test in Experimental and Control Group ... 66
Appendix J. Test for Distribution of Frequency in Experimental Group ... 68
Appendix K. Test for Distribution of Frequency in Control Group ... 70
Appendix L. Testing Normality in Experimental Group ... 72
Appendix M. Testing Normality in Control Group ... 76
Appendix N. Table of Normality from 0 to Z ... 80
Appendix O. List of Testing Liliefors ... 81
Appendix P. F-Distribution (α = 0,05 in the Right Tail) ... 82
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. The Background of the Study
Reading means to understand and to get the information from written text. By reading, people can upgrade their knowledge. According to Grabe et al (2002:9) reading is the ability to draw meaning from the printed page and to interpret this information appropriately. Reading is one of communication skills that should be acquired by students. Students are expected to get knowledge and understand about the context that has been explained in the text. For it, students need reading activities because there is much information that must be shared as much as possible. Reading becomes an evolving interaction between the text and the background knowledge of the reader.
According to Westwood (2001:10) a reader must be able to identify words rapidly, know the meaning of almost all of the words, and be able to combine the sequential units of meaning into a coherent message. It means that reading activity is not only known about how to read and to spell the word well, but also how to receive the information and to interpret the information appropriately.
2
comprehension because it involves the competence to find some information in reading text. M. Glenberg (2011) stated that comprehension is related to action: Understanding a situation or a text means that the understanding can be used to guide effective action, and that this definition holds whether one is understanding situations, dialogue, or text. Additional comprehension skills that must be taught
and practiced include assessing and connecting with students’ background
knowledge, pre teaching of new vocabulary, clarification of key concepts, linking to prior knowledge and personal relevance, instruction in strategies, teacher-guided and student-centered discussions about the content, previewing, predicting, summarizing, selecting main ideas, self-monitoring, and teacher feedback for understanding (Snow, Burns, & Griffi n, 1998) in Willis (2008:128).
Some teacher usually orients to the students’ textbook in teaching
reading. Teacher just follows the material of the textbook by reading the text, translating in to Indonesian and then answers the question related. These activities do not give any influence for improving students’ ability in reading comprehension because it cannot give contribution to the students reading comprehension. It makes the students only be passive in the teaching learning process.
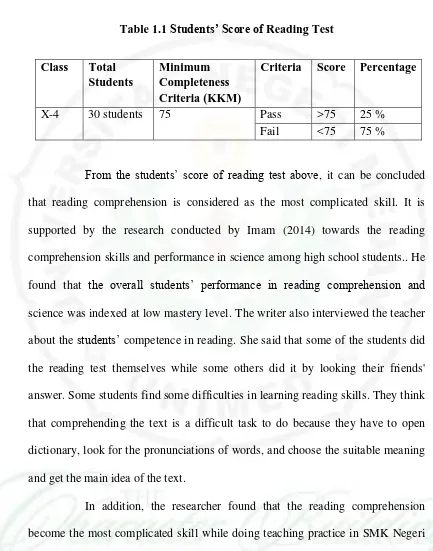
3
Table 1.1 Students’ Score of Reading Test
Class Total comprehension skills and performance in science among high school students.. He found that the overall students’ performance in reading comprehension and science was indexed at low mastery level. The writer also interviewed the teacher about the students’ competence in reading. She said that some of the students did the reading test themselves while some others did it by looking their friends' answer. Some students find some difficulties in learning reading skills. They think that comprehending the text is a difficult task to do because they have to open dictionary, look for the pronunciations of words, and choose the suitable meaning and get the main idea of the text.
4
students become lazy to think because they just do the usual instruction without getting the sense of comprehending the text.
A strategy in teaching learning process especially in reading comprehension is important to make the teaching learning process effective and interesting. The students will feel enjoy in reading subject. There are some strategies in teaching reading comprehension. The teacher must be able to make
variations, and choose the suitable strategy in order to attract students’ interest in
reading. For this purpose, the writer proposes a strategy named synthesizing strategy. According to Duffy (2009:178) synthesizing is creative. That is, readers must create a single understanding from a variety of sources.
5
Thus, in order to make students read easily, the writer is very
interested in conducting a study on students’ comprehension in reading recount
text by applying synthesizing strategy.
B. The Problem of the Study
Based on the background of the study, the research problem of this study was formulated as the following: “Is there any significant effect of synthesizing strategy on students’ reading comprehension in recount text?”
C. The Objective of the Study
Related to the problem of the study, the objective of this study was to
identify the significant effect of applying Synthesizing Strategy on students’
reading comprehension in recount text.
D. The Scope of the Study
This study was focused on using Synthesizing Strategy on Students’
6
E. The Significance of the Study
The findings of the study were expected to have both theoretical and practical significances.
1. Theoretically
a. It was useful for the reader, to add reference or to give alternative way in teaching and learning reading
b. It was providing some information for those who were interested in conducting the further research, especially in reading comprehension.
2. Practically
a. It was useful for students by teacher’s help to develop their reading skills in learning English
45
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
A. Conclusion
Based on the data analysis, it is concluded that applying synthesizing strategy significantly affects the students’ reading comprehension in reading
recount text. It is seen from the data which had obtained in the post-test of experimental group were: the total score was 2235 and the mean score was 74.5, while the data in control group were: the total score was 2005 and the mean score was 66.83. Therefore, alternative hypothesis (Ha) is accepted and null hypothesis (Ho) is rejected. This is supported by the data analysis results in which the t-observed 4.32 is higher than the t-table (2.00) at the significant level of 0.05.
B. Suggestions
This study showed that reading comprehension by using Synthesizing strategy could improve students’ reading comprehension in recount text. In relation above, some suggestions are offered as the following:
1. Synthesizing strategy is significantly effective, it is suggested that the teacher should apply this strategy in teaching process in order to improve students’ reading comprehension in in recount text.
46
47
REFERENCES
Arikunto, S. 2010. Prosedur Penelitian: Suatu Pendekatan Ptraktik: Edisi Revisi VI. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta
Ary, et al. 2010. Introduction to Research in Education in Eight Edition. Belmont: Wadsworth Cengage Learning
Brown, Douglas H. 2004. Language Assessment: A Principle Teaching in Classroom. New York: Pearson Education Inc
Cain, Kate & Oakhil, Jane. 2006. Assessment matters: Issues in the measurement of reading comprehension. British Journal of Educational Psychology Vol. 76
Caldwell, Joanne Schudt. 2008. Reading Assessment: A Primer for Teachers and Coaches Second Edition. London: The Guilford Press
Cummins, Sunday. 2011. Teaching for Synthesis of Informational Texts with Read-Alouds. International Reading Association. Volume 64(6) pp.394-405 Dirgeyasa, I Wy. 2014. College Academic Writing: A genre based perspective.
Medan: Unimed Press
Dougherty Stahl, Katherine A. 2009. Synthesized Comprehension Instruction in Primary Classrooms: A Story of Successes and Challenges', Reading & Writing Quarterly, 25: 4, 334 — 355
Duffy, Gerald G. 2009. Explaining Reading: A Resource for Teaching Concepts, Skills, and Strategies. New York: The Guildford Press
. 2002. Teaching and Researching Reading. Harlow: Pearson Journal Of Educators And Education, Vol. 29, 81–94
48
Knapp, et al. 2005. Genre, Text and Grammar. Teaching And Assessing Writing.
Australia. University of New South Wales Press
Lems, et al. 2010. Teaching Reading to English Language Learner. New York: Guilford Press
M. Glenberg, Arthur. 2011. How Reading Comprehension is embodied and why that Matters. International Electric Journal of Elementary Education. Vol. 4(1), 5-18
Michael, John. 2013. The Reading Comprehension Level of Intermediate Pupils Across Content Areas: Towards a Proposed Reading Enhancement Program.
Graduate Research Journal.Vol. 6, 1-2
Miller, Debbie. 2002. Reading with Meaning: Teaching Comprehension in the Primary Grades. Portland: Stenhouse Publishers
Moreillon, Judi. 2007. Collaborative Strategies for Teaching Reading Comprehension. Chicago: American Library Association
Oktadela, Resy. 2014. Improving Students’ Reading Comprehension of Academic Texts by Using Synthesizing Strategy at Semester IV/B of the English Department of FKIP UIR Pekanbaru. Journal English Language Teaching (ELT) Volume 2(1)
Pardiyono. 2007. Pasti Bisa Teaching Genre-Based Writing. Yogyakarta: Andi Offset
Paris, Scott G. 2005. Children's Reading Comprehension and Assessment. London: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, publishers
Scull, Janet. 2010. Embedding Comprehension within Reading Acquisition Processes. Australian Journal of Language and Literacy. Vol. 33, No. 2, pp. 87-107
Snow, Catherine E. 2002. Reading for Understanding Toward an R&D Program in Reading Comprehension. Arlington: Rand Education
Sudjana, Nana. 2005. Metode Statistika. Bandung. Tarsito
49
Westwood, Peter. 2001. Reading and Learning Difficulties: Approaches to Teaching and Assessment. Victoria: Acer Press
. 2008. What Teachers Need to Know about Reading and Writing Difficulties. Victoria: Acer Press
Willis, Judi. 2008. Teaching Brain to Read: Strategies for Improving Fluency, Vocabulary, and Comprehension. Virginia: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development
Zhao, Ruilan and Alan Hirvela. 2015. Undergraduate ESL students’ engagement in academic reading and writing in learning to write a synthesis paper.